Feasibility and Potential Clinical Ramifications of Using Bacteriophage Therapy for S. aureus Necrotizing Fasciitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. S. aureus NF Clinical Isolates
2.2. Bacteriophage Activity Againts S. aureus NF Clinical Isolates
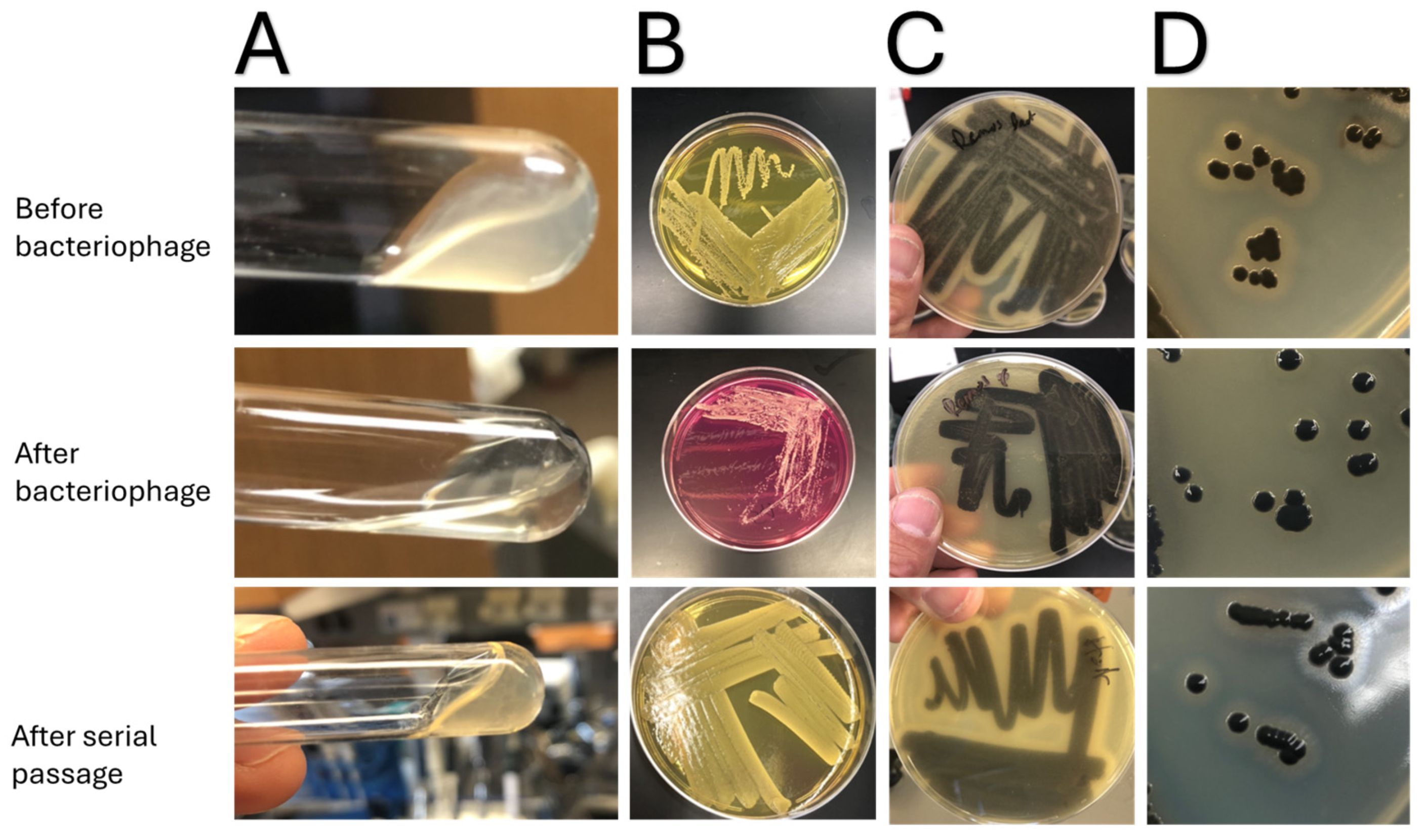
2.3. Phenotypic Enzyme Variation Before and After Bacteriophage Therapy
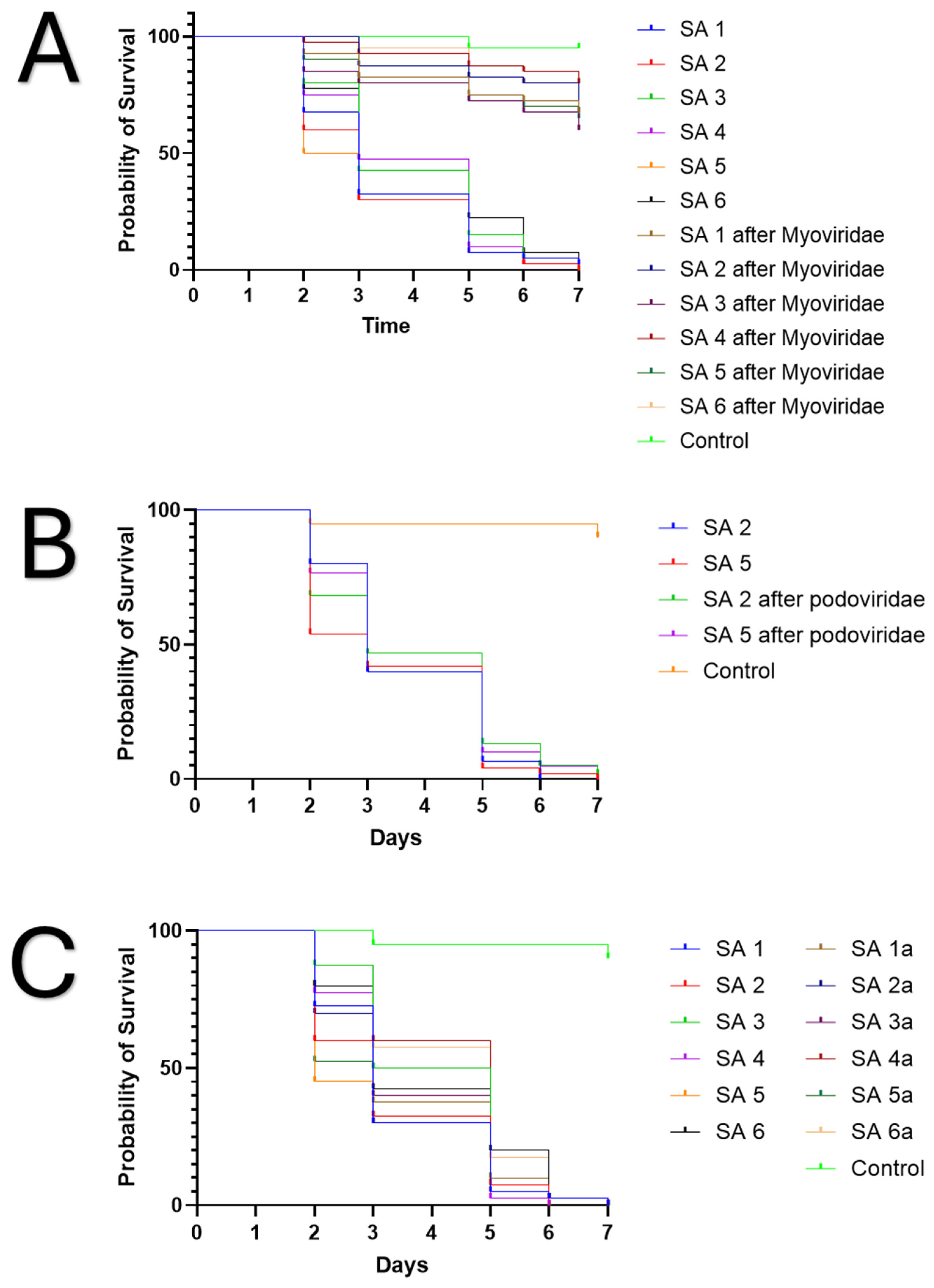
2.4. Changes in Global Virulence Seen with Caenorhabditis Elegans Assay
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonne, S.L.; Kadri, S.S. Evaluation and Management of Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Allaw, F.; Wehbe, S.; Kanj, S.S. Necrotizing fasciitis: An update on epidemiology, diagnostic methods, and treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 37, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvanendran, R.; Huey, J.C.; Pasupathy, S. Necrotizing fasciitis. Can. Fam. Physician 2009, 55, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koch, C.; Hecker, A.; Grau, V.; Padberg, W.; Wolff, M.; Henrich, M. Intravenous immunoglobulin in necrotizing fasciitis—A case report and review of recent literature. Ann. Med. Surg. 2015, 4, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, J.; Kao, L.S.; Keeley, J.A.; Grigorian, A.; Neville, A.; de Virgilio, C. Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2024, 159, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Kang, E.; Wu, Y.C.; Huang, C.U.; Lin, X.Y.; Tsai, F.C.; Tsai, C.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, F.Y.; et al. Is Prompt Hyperbaric Oxygen Adjunctive Therapy Able to Reduce Mortality and Amputation in Management of Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection? Surg. Infect. 2024, 25, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doub, J.B.; Shishido, A.; Srikumaran, U.; Haskoor, J.; Tran-Nguyen, P.; Lee, M.; Würstle, S.; Lee, A.; Kortright, K.; Chan, B.K. Salphage: Salvage bacteriophage therapy for a recalcitrant Klebsiella pneumoniae prosthetic shoulder infection—A case report. Acta Orthop. 2022, 93, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doub, J.B. Bacteriophage therapy: Are we running before we have learned to walk? Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.B.; Troemel, E.R. Microbial pathogenesis and host defense in the nematode C. elegans. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 23, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaladevi, A.; Balamurugan, K. Response of Caenorhabditis elegans during Klebsiella pneumoniae pathogenesis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, G.A.; Lodise, T.P.; Tamma, P.D.; Knisely, J.M.; Alexander, J.; Aslam, S.; Barton, K.D.; Bizzell, E.; Totten, K.M.C.; Campbell, J.L.; et al. Antibacterial Resistance Leadership Group. Considerations for the Use of Phage Therapy in Clinical Practice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0207121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doub, J.B.; Urish, K.; Lee, M.; Fackler, J. Impact of Bacterial Phenotypic Variation with Bacteriophage therapy: A Pilot Study with Prosthetic Joint Infection Isolates. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 119, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, A.G.; Lindsay, J.A.; Read, T.D. Determinants of Phage Host Range in Staphylococcus Species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00209-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Azam, A.H.; Tanji, Y. Peculiarities of Staphylococcus aureus phages and their possible application in phage therapy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4279–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totten, K.M.C.; Patel, R. Phage Activity against Planktonic and Biofilm Staphylococcus aureus Periprosthetic Joint Infection Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0187921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egido, J.E.; Costa, A.R.; Aparicio-Maldonado, C.; Haas, P.J.; Brouns, S.J.J. Mechanisms and clinical importance of bacteriophage resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuab048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleriot, I.; Pacios, O.; Blasco, L.; Fernández-García, L.; López, M.; Ortiz-Cartagena, C.; Barrio-Pujante, A.; García-Contreras, R.; Pirnay, J.P.; Wood, T.K. Improving phage therapy by evasion of phage resistance mechanisms. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2024, 6, dlae017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignoli, T.; Douglas, E.; Duggan, S.; Fagunloye, O.G.; Adhikari, R.; Aman, M.J.; Massey, R.C. Wall Teichoic Acids Facilitate the Release of Toxins from the Surface of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wanner, S.; Schade, J.; Keinhörster, D.; Weller, N.; George, S.E.; Kull, L.; Bauer, J.; Grau, T.; Winstel, V.; Stoy, H.; et al. Wall teichoic acids mediate increased virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, K.; Chaurasiya, A.; Banerjee, T.; Singh, R.; Yadav, G.; Kumar, A. Comparative study of phenotypic and genotypic expression of virulence factors in colonizing and pathogenic carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB). BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gálvez-Silva, M.; Varas, M.A.; Allende, M.L.; Chávez, F.P.; Marcoleta, A.E. Zebrafish Larvae Microinjection and Automated Fluorescence Microscopy for Studying Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection and the Host Immune Response. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2852, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
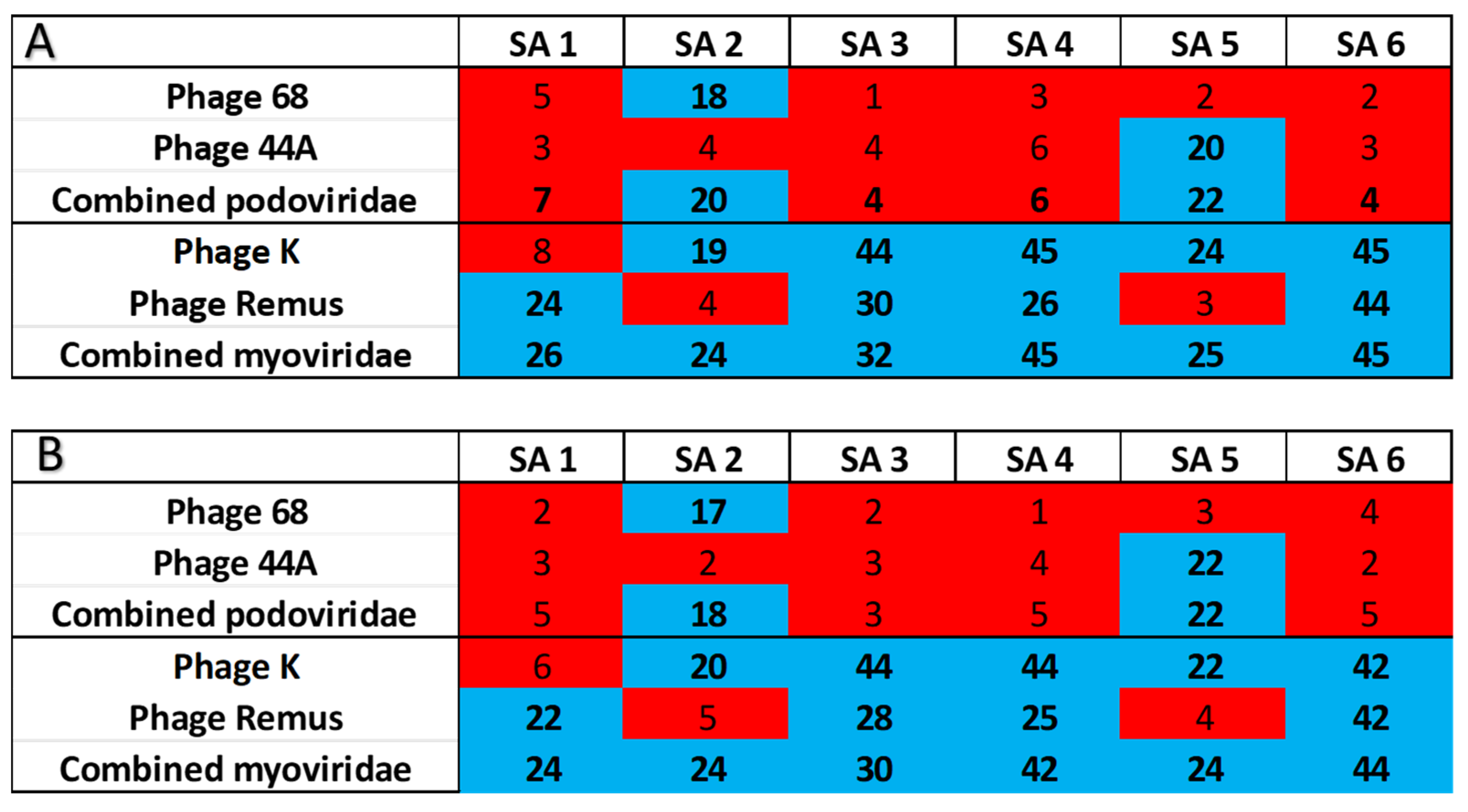
| Podoviridae (P68, 44A) | Myoviridae (K, Remus) | |
|---|---|---|
| Combined coverage | 2/6 (33.3%) | 6/6 (100%) |
| Single phage | 1/6 (16.7%) 1 | 5/6 (83.3%) 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doub, J.B.; Dunbar, D.; Jain, S.; Manchester, M.; Berle, L.; Madhiwala, J.; Anderson, B.; Malick, R.; Jacobs, M.; Urish, K.L. Feasibility and Potential Clinical Ramifications of Using Bacteriophage Therapy for S. aureus Necrotizing Fasciitis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165609
Doub JB, Dunbar D, Jain S, Manchester M, Berle L, Madhiwala J, Anderson B, Malick R, Jacobs M, Urish KL. Feasibility and Potential Clinical Ramifications of Using Bacteriophage Therapy for S. aureus Necrotizing Fasciitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165609
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoub, James B., Dakarai Dunbar, Sara Jain, Maggie Manchester, Lila Berle, Janvi Madhiwala, Bradley Anderson, Riva Malick, Max Jacobs, and Kenneth L. Urish. 2025. "Feasibility and Potential Clinical Ramifications of Using Bacteriophage Therapy for S. aureus Necrotizing Fasciitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165609
APA StyleDoub, J. B., Dunbar, D., Jain, S., Manchester, M., Berle, L., Madhiwala, J., Anderson, B., Malick, R., Jacobs, M., & Urish, K. L. (2025). Feasibility and Potential Clinical Ramifications of Using Bacteriophage Therapy for S. aureus Necrotizing Fasciitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165609





