Advances and Applications of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
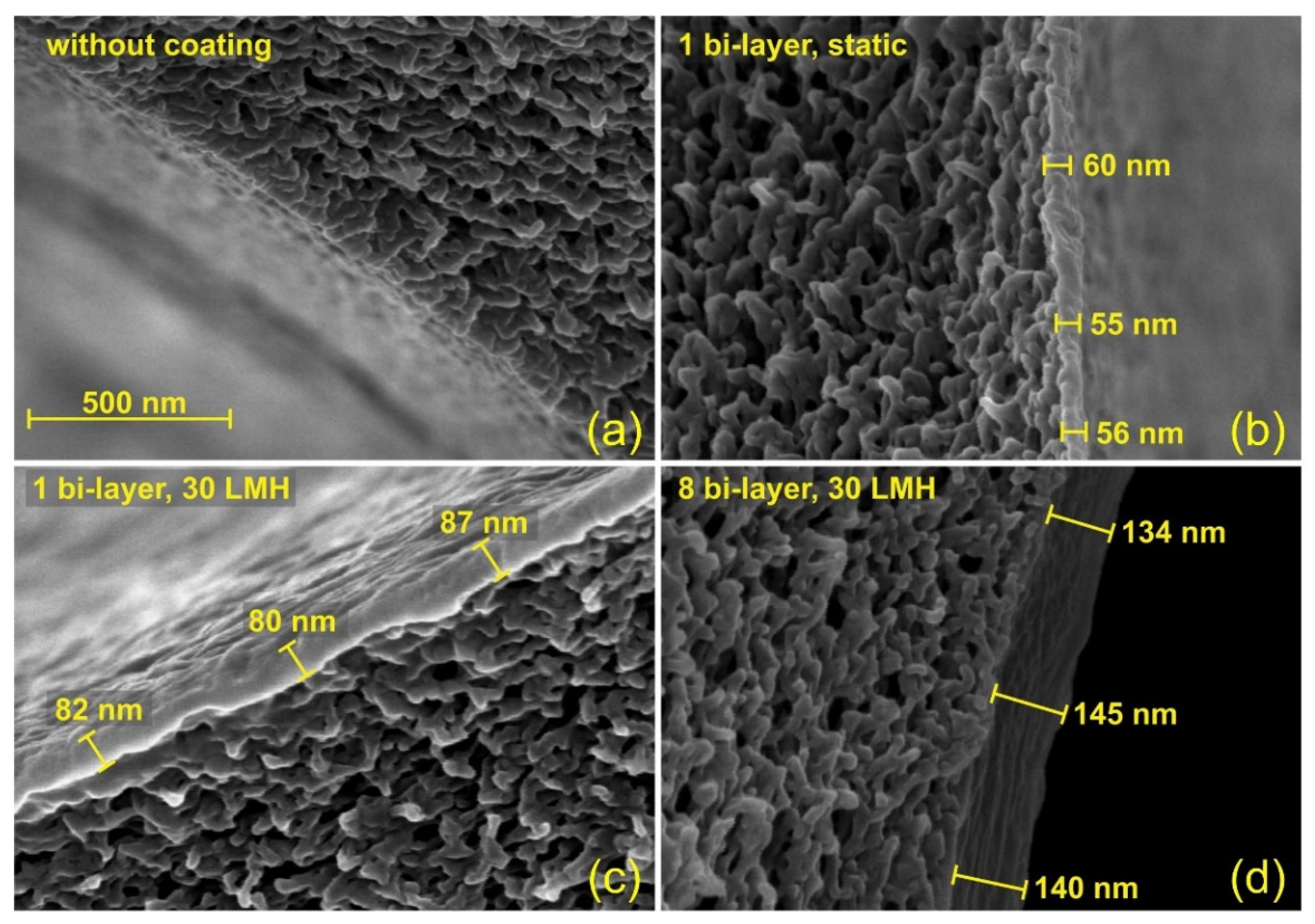
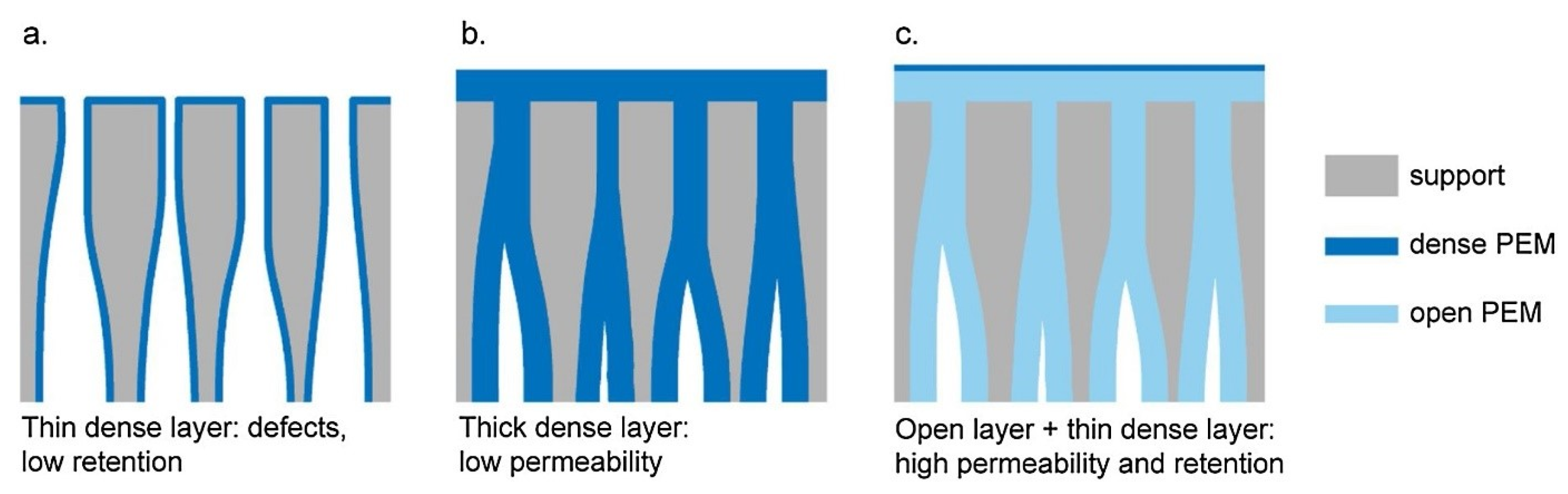
2. Preparation Methods
3. Applications
3.1. Freshwater Treatment
3.1.1. Natural Organic Matter Removal
3.1.2. Water Softening
3.2. Municipal Wastewater Treatment
3.2.1. Organic Micropollutant Removal
3.2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance
3.2.3. Micro- and Nanoplastics Removal
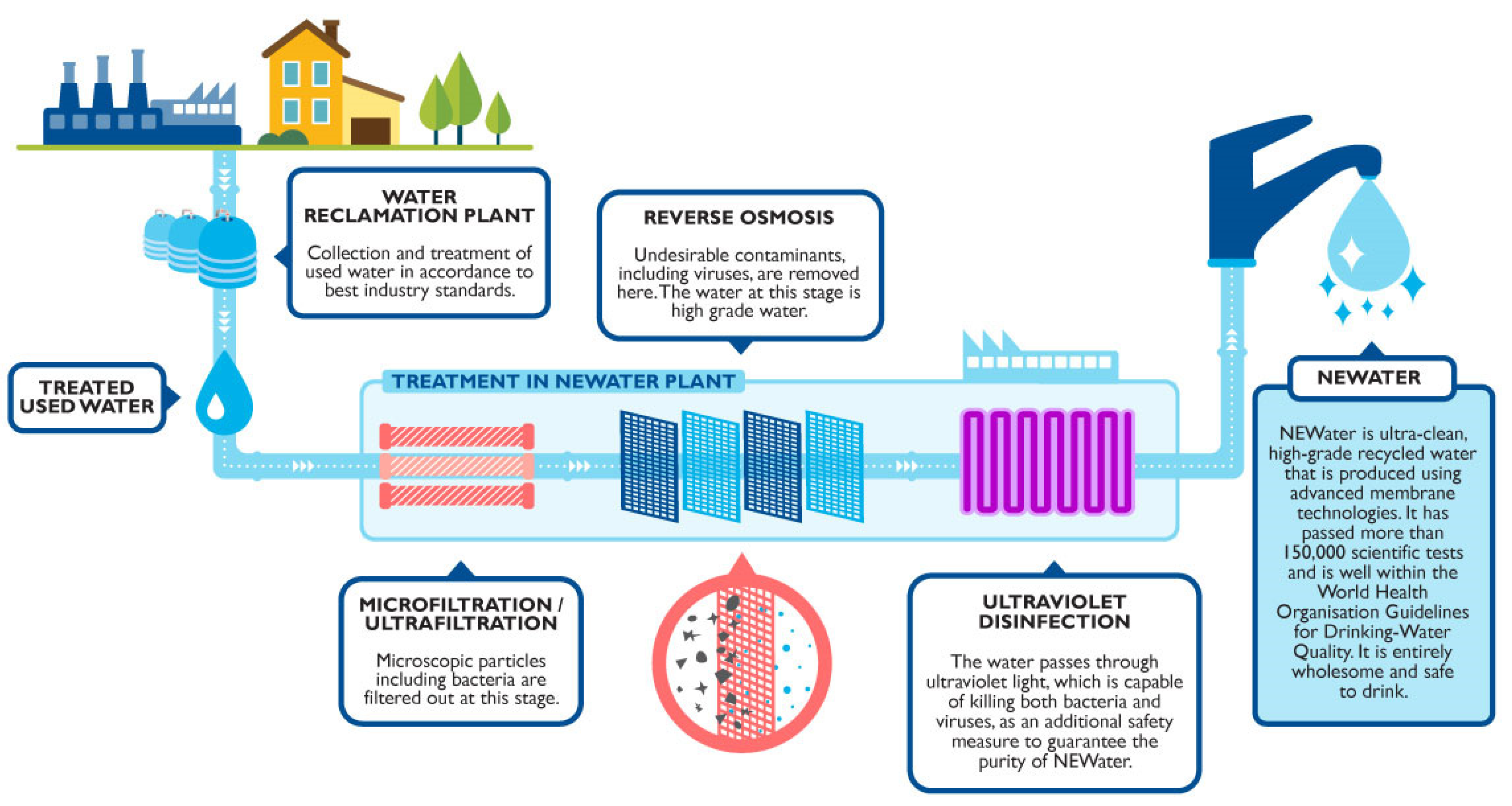
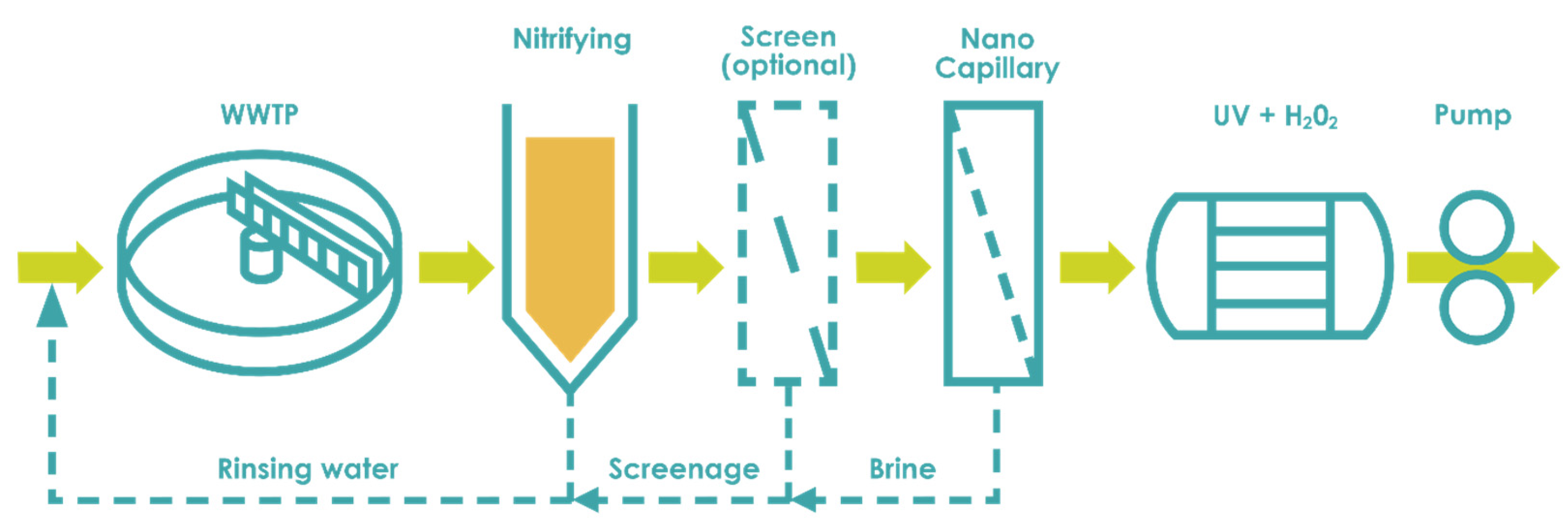
3.2.4. Wastewater Reuse
3.3. Industrial Wastewater Treatment
3.3.1. Heavy Metal Removal
3.3.2. Sulfate Removal
3.3.3. Organics Removal
Textile Industry
Oil and Gas Industry
Other
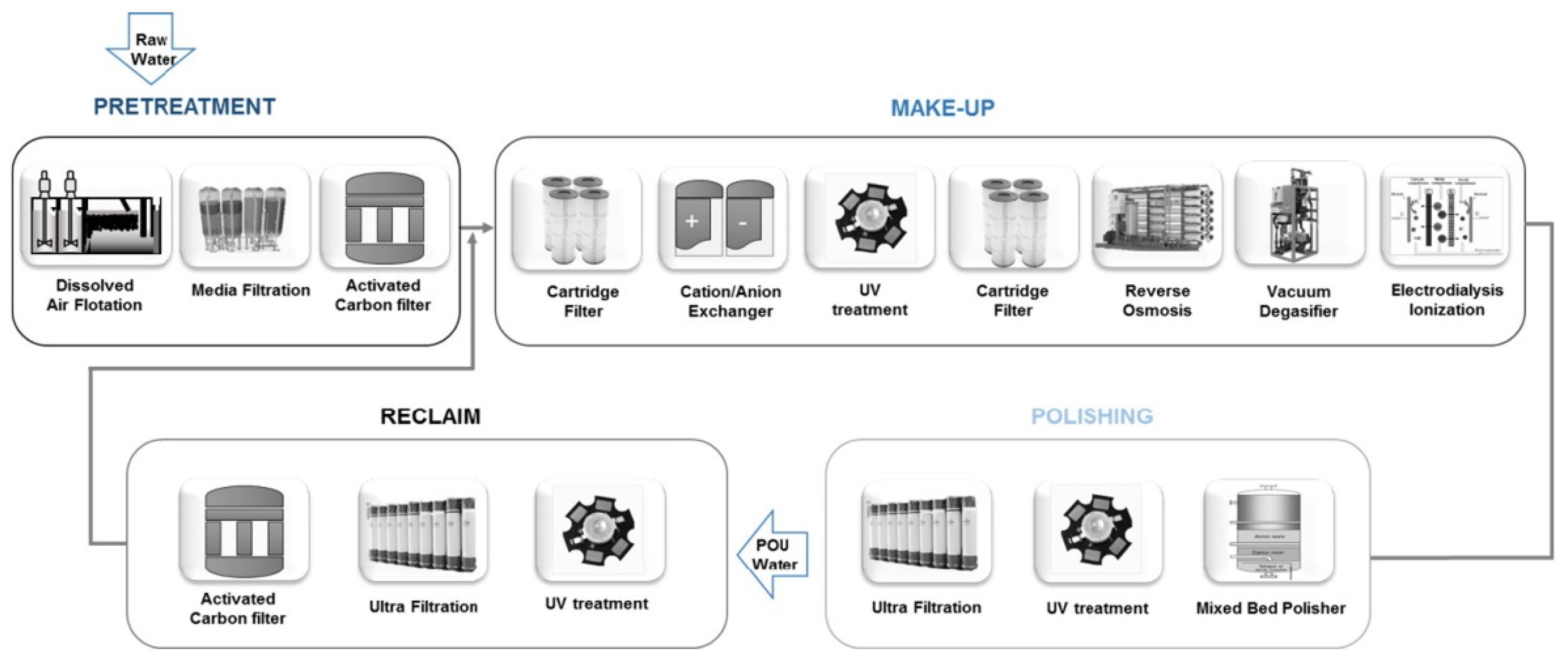
3.4. Ultrapure Water Production
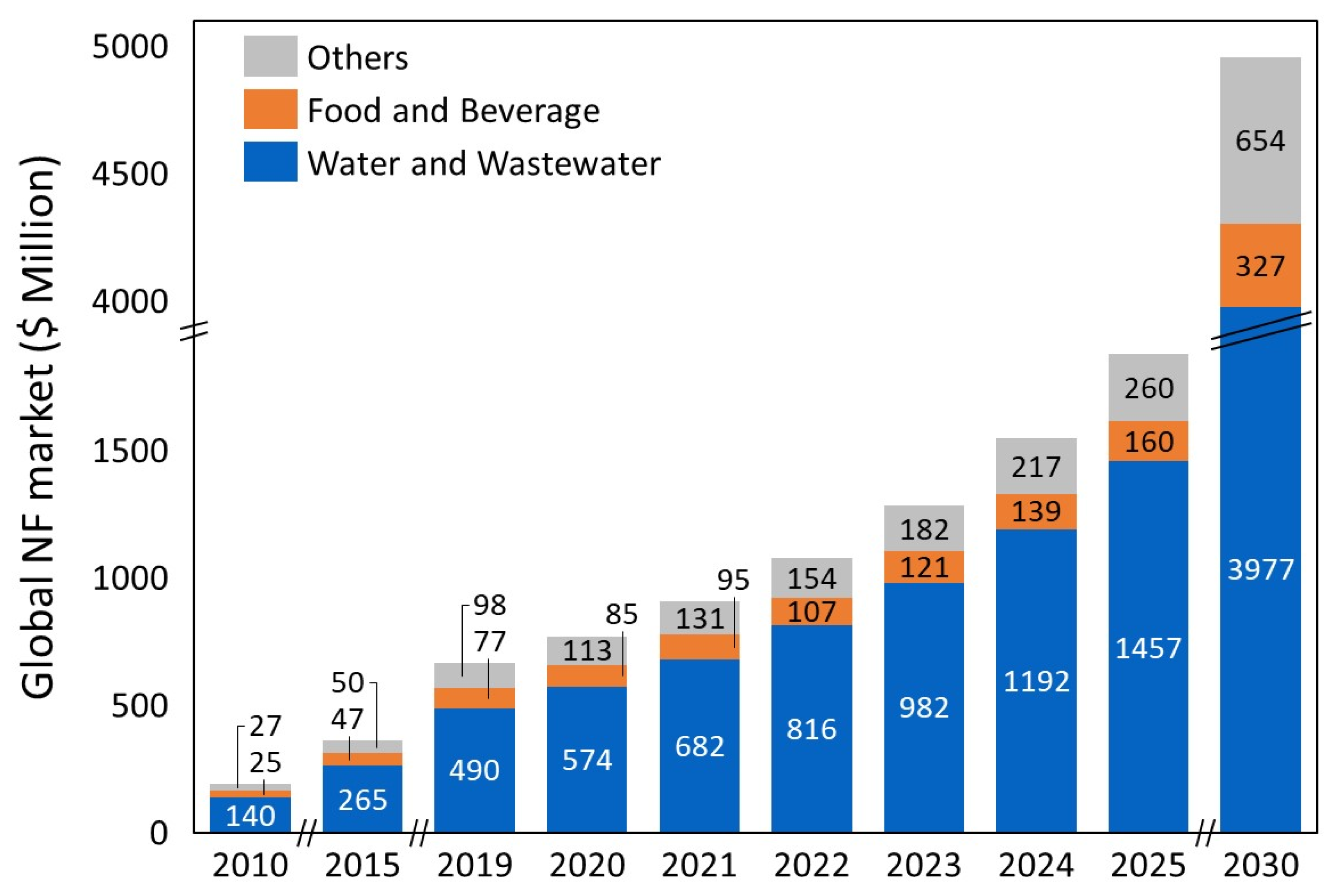
3.5. Food and Beverage Industry
3.5.1. Dairy Industry
3.5.2. Sugar Industry
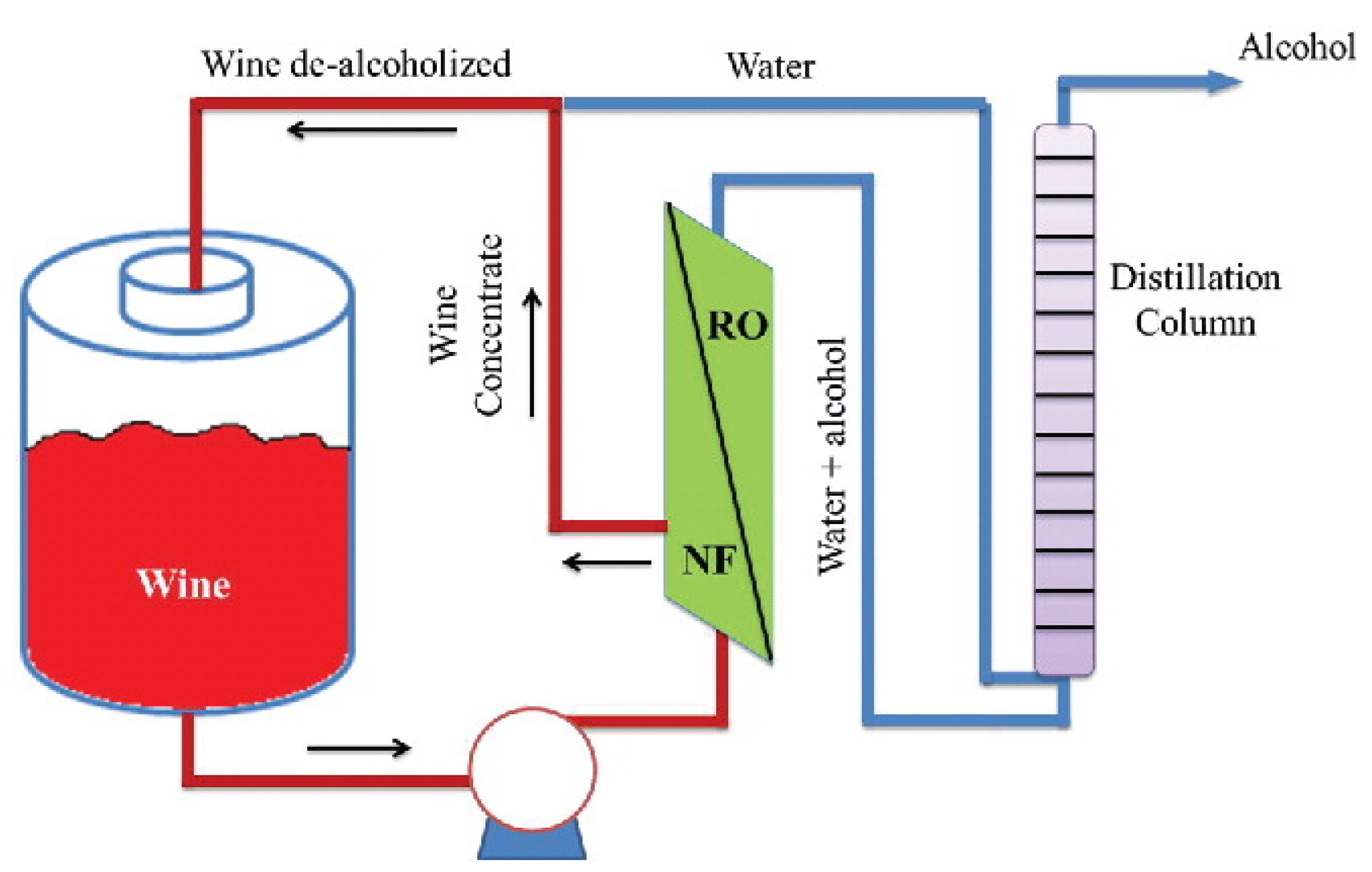
3.5.3. Beverage Industry
3.5.4. Other
3.6. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
3.6.1. Caustic and Acid Recovery
Cleaning Solutions
Other Applications
3.6.2. Metal Recovery
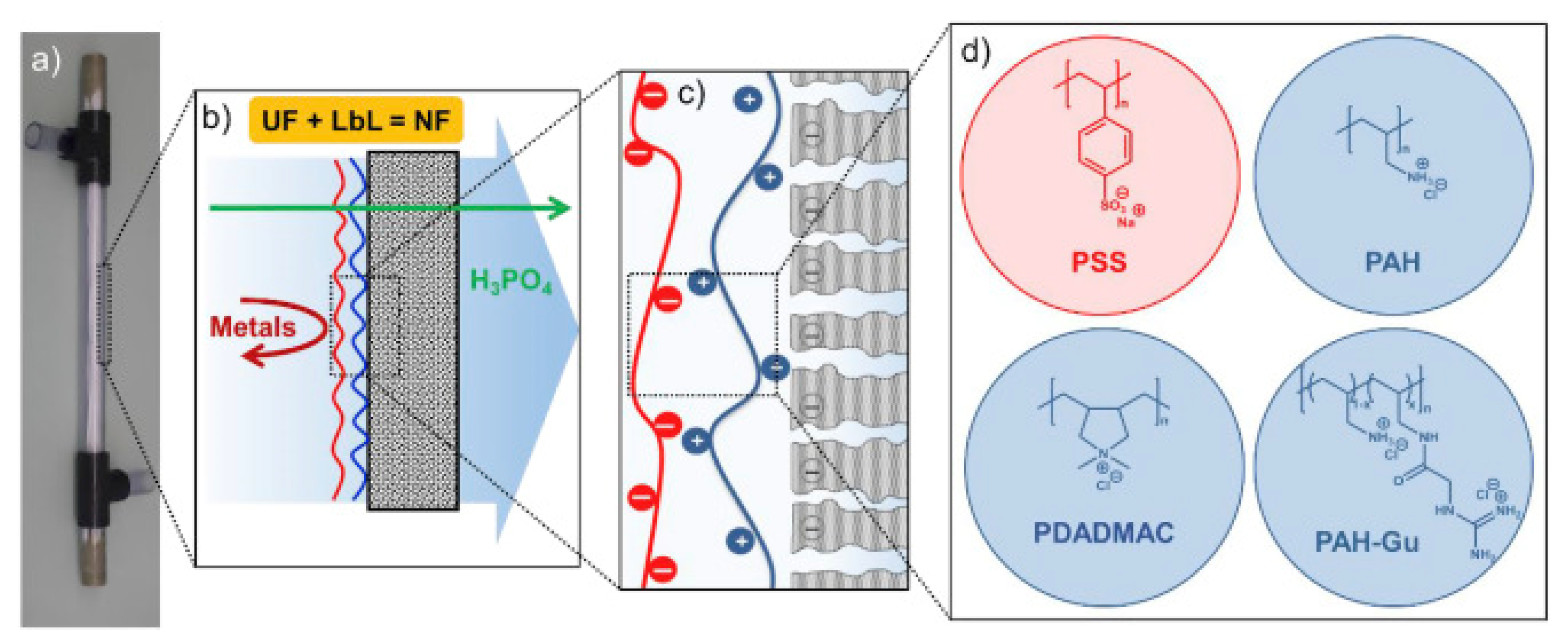
3.6.3. Phosphorus Recovery
3.6.4. Organic Solvent Nanofiltration
3.7. Biorefinery
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, R.W. Reverse Osmosis. In Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 207–251. ISBN 9781118359686. [Google Scholar]
- Labban, O.; Liu, C.; Chong, T.H.; Lienhard V, J.H. Fundamentals of low-pressure nanofiltration: Membrane characterization, modeling, and understanding the multi-ionic interactions in water softening. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 521, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P. Nanofiltration extends the range of membrane filtration. Environ. Prog. 1988, 7, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, M.A.; de Vos, W.M.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; de Grooth, J. Bridging the gap between lab-scale and commercial dimensions of hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 624, 119100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.; Bruening, M.L.; Zholkovskiy, E. Modelling nanofiltration of electrolyte solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 268, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, J.M.M.; Boom, J.P.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Strathmann, H. Retention measurements of nanofiltration membranes with electrolyte solutions. J. Memb. Sci. 1998, 145, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, O.; Chong, T.H.; Lienhard, J.H. Design and Modeling of Novel Low-Pressure Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber Modules for Water Softening and Desalination Pretreatment. Desalination 2018, 439, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Walters, M.; Ainscough, T.J.; Williams, P.M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes and processes: A review of research trends over the past decade. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearns, C. Global Membrane Filtration Market; BCC Publishing VMR2507A; BCC Research LLC: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Kang, G.; Yu, H.; Jin, Y.; Cao, Y. From reverse osmosis to nanofiltration: Precise control of the pore size and charge of polyamide membranes via interfacial polymerization. Desalination 2019, 466, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barassi, G.; Borrmann, T. N-chlorination and Orton Rearrangement of Aromatic Polyamides, Revisited. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jung, S.; Sohn, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Biocide application for controlling biofouling of SWRO membranes—An overview. Desalination 2009, 238, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Koops, G.H.; Mulder, M.H.V.; van den Boomgaard, T.; Smolders, C.A. Wet spinning of integrally skinned hollow fiber membranes by a modified dual-bath coagulation method using a triple orifice spinneret. J. Memb. Sci. 1994, 94, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allegrezza, A.E.; Charpentier, J.M.; Davis, R.B.; Coplan, M.J. Hollow Fiber Reverse Osmosis Membranes. AIChE Symp. Ser. 1977, 73, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Li, K. From Polymeric Precursors to Hollow Fiber Carbon and Ceramic Membranes. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2008, 13, 81–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; Liu, B.; Yu, H.; Du, X.; Li, G.; Snyder, S.A. Hydraulic backwashing for low-pressure membranes in drinking water treatment: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 540, 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; van Dijk, J.C. Air sparging in capillary nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 284, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Grooth, J.; Haakmeester, B.; Wever, C.; Potreck, J.; de Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Long term physical and chemical stability of polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 489, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futselaar, H.; Schonewille, H.; van der Meer, W. Direct capillary nanofiltration for surface water. Desalination 2003, 157, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keucken, A.; Wang, Y.; Tng, K.H.; Leslie, G.L.; Persson, K.M.; Köhler, S.J.; Spanjer, T. Evaluation of novel hollow fibre membranes for NOM removal by advanced membrane autopsy. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Dual layer composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for low-pressure water softening. Polymer 2014, 55, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidén, A.; Lavonen, E.; Persson, K.M.; Larson, M. Integrity breaches in a hollow fiber nanofilter—Effects on natural organic matter and virus-like particle removal. Water Res. 2016, 105, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentair X-flow X-Flow HFW1000. Available online: https://xflow.pentair.com/en/products/hfw1000 (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- NX Filtration Direct Nanofiltration Membranes. Available online: https://nxfiltration.com/technology/ (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- Ochemate NÜF N80. Available online: http://www.ochemate.com/productDisplay.aspx?id=93 (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- De.mem Ltd. De.mem IPO Prospectus. Available online: https://demembranes.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/De.mem-Replacement-Prospectus.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- 3E Memtech Pte Ltd. 3E Products. Available online: https://www.3ememtech.com/products (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- Urper, G.M.; Sengur-Tasdemir, R.; Turken, T.; Ates Genceli, E.; Tarabara, V.V.; Koyuncu, I. Hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes: A comparative review of interfacial polymerization and phase inversion fabrication methods. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2120–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, C.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of non-solvent additives on the morphology and separation performance of poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMIA) hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2015, 365, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Wessling, M. Preparation of porous hollow fiber membranes with a triple-orifice spinneret. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroko, I.; Makowski, M.; Spill, F.; Livingston, A. The effect of membrane formation parameters on performance of polyimide membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). Part B: Analysis of evaporation step and the role of a co-solvent. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 381, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutczak, S.M.; Tanardi, C.R.; Kopeć, K.K.; Wessling, M.; Stamatialis, D. “Chemistry in a spinneret” to fabricate hollow fibers for organic solvent filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifakhr, M.; de Grooth, J.; Trzaskus, K.; Roesink, H.D.W.; Kemperman, A.J.B. Single-step synthesis of a polyelectrolyte complex hollow-fiber membrane for forward osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 264, 118430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkame, T.; Shibuya, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Shintani, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Yoshioka, T. Thin-film composite hollow-fiber nanofiltration membranes prepared from benzonitrile containing disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) random copolymers coated onto polyphenylene oxide support membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 631, 119336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H. Preparation and characterization of negatively charged hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane by plasma-induced graft polymerization. Desalination 2012, 286, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wei, J.; Wang, X. Nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes with high charge density prepared by simultaneous electron beam radiation-induced graft polymerization for removal of Cr(VI). Desalination 2014, 346, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Ahmadiannamini, P.; Hoogenboom, R.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Layer-by-layer preparation of polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for separation. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1817–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, D.; Kamp, J.; Erik Wong, J.; Wessling, M. Precise tuning of salt retention of backwashable polyelectrolyte multilayer hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 499, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Melia, C.R. Chapter 18: Fundamentals of particle stability. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 10, pp. 317–362. [Google Scholar]
- Keucken, A.; Liu, X.; Lian, B.; Wang, Y.; Persson, K.M.; Leslie, G. Simulation of NOM removal by capillary NF: A numerical method for full-scale plant design. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 555, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Barbeau, B.; Bérubé, P. Nanofiltration and tight ultrafiltration membranes for natural organic matter removal–Contribution of fouling and concentration polarization to filtration resistance. Membranes 2017, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Fatah, M.A. Nanofiltration systems and applications in wastewater treatment: Review article. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jährig, J.; Vredenbregt, L.; Wicke, D.; Miehe, U.; Sperlich, A. Capillary nanofiltration under anoxic conditions as post-treatment after bank filtration. Water 2018, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, S.J.; Lavonen, E.; Keucken, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Spanjer, T.; Persson, K. Upgrading coagulation with hollow-fibre nanofiltration for improved organic matter removal during surface water treatment. Water Res. 2016, 89, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keucken, A.; Wang, Y.; Tng, K.; Leslie, G.; Spanjer, T.; Köhler, S. Optimizing Hollow Fibre Nanofiltration for Organic Matter Rich Lake Water. Water 2016, 8, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidén, A.; Persson, K.M. Comparison between ultrafiltration and nanofiltration hollow-fiber membranes for removal of natural organic matter: A pilot study. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-AQUA 2016, 65, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentair—Operating Experience with Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration for Potable Water Production|X-Flow. Available online: https://xflow.pentair.com/en/case-studies/taswater (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Water Wastewater Asia. From Peat Water to Drinking Water: Development of Drinking Water Supply for Dumai City; Water Wastewater Asia: Singapore, 2021; pp. 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, R. Strategic Assessment of Drinking Water Production Systems Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Perspective A Case Study of Norrvatten Future Drinking Water Production Alternatives; KTH Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Dorji, P.; Shon, H.K.; Hong, S. Applications of capacitive deionization: Desalination, softening, selective removal, and energy efficiency. Desalination 2019, 449, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M. Membrane separation techniques—Removal of inorganic and organic admixtures and impurities from water environment—Review. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2019, 45, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.I.; Bergwerff, L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Picioreanu, C. A two-dimensional mechanistic model for scaling in spiral wound membrane systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 241, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Interfacially polymerized composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for low-pressure water softening. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 430, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Mixed polyamide-based composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes with improved low-pressure water softening capability. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 468, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Crosslinked layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte nanofiltration hollow fiber membrane for low-pressure water softening with the presence of SO42- in feed water. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 486, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengur-Tasdemir, R.; Urper-Bayram, G.M.; Turken, T.; Ates-Genceli, E.; Tarabara, V.V.; Koyuncu, I. Hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes for surface water treatment: Performance evaluation at the pilot scale. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, S.M.K.; Saroj, D.P. 14-Membrane technologies for municipal wastewater treatment. In Advances in Membrane Technologies for Water Treatment; Basile, A., Cassano, A., Rastogi, N.K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 443–463. ISBN 978-1-78242-121-4. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Hao Ngo, H.; Duc Nghiem, L.; Hai, I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aemig, Q.; Hélias, A.; Patureau, D. Impact assessment of a large panel of organic and inorganic micropollutants released by wastewater treatment plants at the scale of France. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grooth, J.; Reurink, D.M.; Ploegmakers, J.; De Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Charged Micropollutant Removal With Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes Based On Polycation/Polyzwitterion/Polyanion Multilayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17009–17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Abtahi, S.M.; Akkilic, N.; Roesink, H.D.W.; de Vos, W.M. Weak polyelectrolyte multilayers as tunable separation layers for micro-pollutant removal by hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 537, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi, S.M.; Ilyas, S.; Joannis Cassan, C.; Albasi, C.; de Vos, W.M. Micropollutants removal from secondary-treated municipal wastewater using weak polyelectrolyte multilayer based nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 548, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abtahi, S.M.; Marbelia, L.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Ahmadiannamini, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Albasi, C.; de Vos, W.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Micropollutant rejection of annealed polyelectrolyte multilayer based nanofiltration membranes for treatment of conventionally-treated municipal wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; de Grooth, J.; Nijmeijer, K.; De Vos, W.M. Multifunctional polyelectrolyte multilayers as nanofiltration membranes and as sacrificial layers for easy membrane cleaning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 446, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Brinke, E.; Reurink, D.M.; Achterhuis, I.; de Grooth, J.; de Vos, W.M. Asymmetric polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes with ultrathin separation layers for highly efficient micropollutant removal. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Brinke, E.; Achterhuis, I.; Reurink, D.M.; De Grooth, J.; De Vos, W.M. Multiple Approaches to the Buildup of Asymmetric Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Membranes for Efficient Water Purification. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater 2020, 2020, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Goh, K.; Chong, T.H.; Wang, R. Layer-by-layer assembly based low pressure biocatalytic nanofiltration membranes for micropollutants removal. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 615, 118514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolong, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, M.R.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Tabe-Mohammadi, A. Negatively charged polyethersulfone hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of bisphenol A from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, R.X.; Wang, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Wang, X.L. Fabrication of a thin film nanocomposite hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for wastewater treatment. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 488, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, V.; McCleaf, P.; Lindegren, K.; Ahrens, L. Efficient removal of per- And polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water treatment: Nanofiltration combined with active carbon or anion exchange. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Sha, S.; Luo, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang Jackie, X. Treatment train approaches for the remediation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, Á.; Gorri, D.; Urtiaga, A. Efficient treatment of perfluorohexanoic acid by nanofiltration followed by electrochemical degradation of the NF concentrate. Water Res. 2017, 112, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, T.; Hu, G.; Ma, J.; Song, R.; Li, J. Efficient removal of perfluorooctane sulphonate by nanofiltration: Insights into the effect and mechanism of coexisting inorganic ions and humic acid. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 610, 118176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, C.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Fabrication of novel poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for effective removal of trace amount perfluorooctane sulfonate from water. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 477, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Feys, E.; Anglès d’Auriac, M.; Wennberg, A.C.; Umar, M.; Schwermer, C.U.; Uhl, W. Combined membrane filtration and 265 nm UV irradiation for effective removal of cell free antibiotic resistance genes from feed water and concentrate. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 598, 117676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, C.X.; Hübner, U.; Fajnorova, S.; Schwartz, T.; Drewes, J.E. Antibiotic microbial resistance (AMR) removal efficiencies by conventional and advanced wastewater treatment processes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Kong, X.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Liu, D. High removal efficiency of antibiotic resistance genes in swine wastewater via nanofiltration and reverse osmosis processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipko, K.; Reif, D.; Wögerbauer, M.; Hufnagl, P.; Krampe, J.; Kreuzinger, N. Removal of extracellular free DNA and antibiotic resistance genes from water and wastewater by membranes ranging from microfiltration to reverse osmosis. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóvão, M.B.; Tela, S.; Silva, A.F.; Oliveira, M.; Bento-Silva, A.; Bronze, M.R.; Crespo, M.T.B.; Crespo, J.G.; Nunes, M.; Pereira, V.J. Occurrence of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes and viral genomes in wastewater effluents and their treatment by a pilot scale nanofiltration unit. Membranes 2021, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Toxic effects of microplastic on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: Interactions between microplastic and algae. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; An, Y.J. Effects of micro- and nanoplastics on aquatic ecosystems: Current research trends and perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Pérez-Pomeda, I.; Sanchís, J.; Rossini, C.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Cytotoxic effects of commonly used nanomaterials and microplastics on cerebral and epithelial human cells. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poerio, T.; Piacentini, E.; Mazzei, R. Membrane processes for microplastic removal. Molecules 2019, 24, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malankowska, M.; Echaide-Gorriz, C.; Coronas, J. Microplastics in marine environment: A review on sources, classification, and potential remediation by membrane technology. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzaskus, K.; Elshof, M.; Kemperman, A.; Nijmeijer, K. Understanding the role of nanoparticle size and polydispersity in fouling development during dead-end microfiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 516, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PUB. Singapore’s National Water Agency PUB NEWater. Available online: https://www.pub.gov.sg/watersupply/fournationaltaps/newater (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Energy and Resources Factory. Water Factory—The New Source; Energy and Resources Factory: Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology: Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. ISBN 978-3-7643-8340-4. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry; Division of Toxicology and Human Health Sciences ATSDR’s Substance Priority List. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/index.html (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Granger, M.; Marnane, I.; Alvarez, D. Industrial Waste Water Treatment—Pressures on Environment; European Environment Agency: København, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Daman Parihar, R.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Preet, G.; Sidhu, S.; Shreeya Bali, A.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kumar Thukral, A.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Cassano, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Mozumder, M.S.I.; Uddin, M.T.; Islam, M.A.; Drioli, E. Influence of operating parameters on the arsenic removal by nanofiltration. Water Res. 2010, 44, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qdais, H.A.; Moussa, H. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by membrane processes: A comparative study. Desalination 2004, 164, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, M.; Guha, B.K. Effect of pH on rejection of hexavalent chromium by nanofiltration. Desalination 2008, 219, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. A study on acid reclamation and copper recovery using low pressure nanofiltration membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cséfalvay, E.; Pauer, V.; Mizsey, P. Recovery of copper from process waters by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. Desalination 2009, 240, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, C.V.; Mikulášek, P. Influence of operating variables on the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by nanofiltration. Desalination 2014, 343, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, Z.V.P.; Chaudhari, L.B. Application of nanofiltration for the rejection of nickel ions from aqueous solutions and estimation of membrane transport parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuhorka, J.; Wallace, E.; Mikulášek, P. Removal of micropollutants from water by commercially available nanofiltration membranes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, N.; Yusof, N.; Lau, W.J.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F. Recent trends of heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by membrane technologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Sun, S.P.; Zhu, W.P.; Chung, T.S. Chelating polymer modified P84 nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for high efficient heavy metal removal. Water Res. 2014, 63, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.S. Design of nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes made from functionalized bore fluids containing polyethyleneimine (PEI) for heavy metal removal. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 603, 118022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.P.; Sun, S.P.; Gao, J.; Fu, F.J.; Chung, T.S. Dual-layer polybenzimidazole/polyethersulfone (PBI/PES) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metals removal from wastewater. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 456, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.P.; Gao, J.; Sun, S.P.; Zhang, S.; Chung, T.S. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimer (PAMAM) grafted on thin film composite (TFC) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metal removal. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 487, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Chung, T.S. Layer-by-layer construction of graphene oxide (GO) framework composite membranes for highly efficient heavy metal removal. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 515, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Kong, X.; Wang, S.; Xiang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Removal of heavy metals from electroplating wastewater by thin-film composite nanofiltration hollow-fiber membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 17583–17590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Qin, S.; Liu, T.; Jivkov, A. Experimental and numerical study of the effects of solution concentration and temperature on concrete under external sulfate attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 139, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breysse, D. Deterioration processes in reinforced concrete: An overview. In Non-Destructive Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete Structures: Deterioration Processes and Standard Test Methods; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 28–56. ISBN 9781845695606. [Google Scholar]
- Ikumi, T.; Segura, I. Numerical assessment of external sulfate attack in concrete structures. A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 121, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozen Sulfaat—Kenniscentrum InfoMil. Available online: https://www.infomil.nl/onderwerpen/lucht-water/handboek-water/wetgeving/algemene-regels-lozingsroute-schema/zorgplicht/lozen-sulfaat/ (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Pino, L.; Vargas, C.; Schwarz, A.; Borquez, R. Influence of operating conditions on the removal of metals and sulfate from copper acid mine drainage by nanofiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Reig, M.; Gibert, O.; Valderrama, C.; Cortina, J.L. Evaluation of NF membranes as treatment technology of acid mine drainage: Metals and sulfate removal. Desalination 2018, 440, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, T.J.K.; Modise, S.J.; Krieg, H.M.; Keizer, K. The removal of acid sulphate pollution by nanofiltration. Desalination 2001, 140, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lee, J.; Gwak, G.; Chung, C.M.; Choi, J.W.; Cho, K.; Hong, S.W. Sequential combination of nanofiltration and ettringite precipitation for managing sulfate-rich brines. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Water Resources and Water Supply Hamburg University of Technology Treatment of Groundwater with Increased Sulfate Concentration. Available online: https://www.tuhh.de/alt/wwv/dvgw-tuhh/dvgw-research-centre-tuhh/suleman.html (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- DVGW Deutscher Verein des Gas- und Wasserfaches e.V. SULEMAN. Available online: https://www.dvgw.de/themen/forschung-und-innovation/forschungsprojekte/dvgw-forschungsprojekt-suleman (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Mergel, D.; Ernst, S.; Jacki, E.; Claasen, L.M.; Stumme, J.; Wendler, B. Sulfathaltige Grundwässer durch Nanofiltration Nutzbar Machen-Aerobe und Anaerobe Verfahrensvarianten; Energie-Wasser-Praxis: Bonn, Germany, 2021; pp. 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dsikowitzky, L.; Schwarzbauer, J. Industrial organic contaminants: Identification, toxicity and fate in the environment. Environ. Chem Lett 2014, 12, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, S.; Shuai, S.; Zhou, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Color removal and COD reduction of biologically treated textile effluent through submerged filtration using hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2013, 314, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Khulbe, K.; Matsuura, T. Thin Film Composite and/or Thin Film Nanocomposite Hollow Fiber Membrane for Water Treatment, Pervaporation, and Gas/Vapor Separation. Polymers 2018, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.Y.; Bian, L.X.; Yuan, H.G.; Pang, B.; Lin, Y.K.; Tong, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Wang, X.L. Fabrication of a high-flux thin film composite hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for wastewater treatment. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 478, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; De, S. Treatment of textile plant effluent by hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane and multi-component steady state modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Li, F.Y.; Sun, S.P.; Zhao, B.W.; Liang, C.Z.; Chung, T.S. Nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for textile wastewater treatment: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 114, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Polymeric nanofiltration membranes for textile dye wastewater treatment: Preparation, performance evaluation, transport modelling, and fouling control—A review. Desalination 2009, 245, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.A.; Lin, M.Q.; Shen, L.Z.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, J.Y. Levels, composition profiles and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sludge from ten textile dyeing plants. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.P.; Hatton, T.A.; Chan, S.Y.; Chung, T.S. Novel thin-film composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes with double repulsion for effective removal of emerging organic matters from water. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Cheng, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Quan, S.; Ma, J.; Zhao, S.Z.; Wang, K.Y. Newly developed nanofiltration (NF) composite membranes by interfacial polymerization for Safranin O and Aniline blue removal. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 430, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Xiao, C.; An, S.; Zhao, J.; Hao, J.; Chen, K. Preparation of high-flux PSF/GO loose nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes with dense-loose structure for treating textile wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, K.; Zhou, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ling, H. Green preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride loose nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes with multilayer structure for treating textile wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. Annual Energy Outlook 2021 Narrative; EIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Igunnu, E.T.; Chen, G.Z. Produced water treatment technologies. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2014, 9, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, S.; Micó, M.M.; Arnaldos, M.; Medina, F.; Contreras, S. State of the art of produced water treatment. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 186–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanudjaja, H.J.; Hejase, C.A.; Tarabara, V.V.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Membrane-based separation for oily wastewater: A practical perspective. Water Res. 2019, 156, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Khajeh, A.; Mesbah, M. Membrane filtration of wastewater from gas and oil production. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 367–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Drewes, J.E. Viability of nanofiltration and ultra-low pressure reverse osmosis membranes for multi-beneficial use of methane produced water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Produced water treatment by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 322, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, S.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N.; Abdullah, P.; Jaafar, O. Comparative study of NF and RO membranes in the treatment of produced water-Part I: Assessing water quality. Desalination 2013, 315, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, S.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N.; Abdullah, P.; Jaafar, O. Comparative study of NF and RO membranes in the treatment of produced water II: Toxicity removal efficiency. Desalination 2013, 315, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Graf von der Schulenburg, D.A.; Kruithof, J.C.; Johns, M.L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Biofouling of spiral-wound nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: A feed spacer problem. Water Res. 2009, 43, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virga, E.; de Grooth, J.; Žvab, K.; de Vos, W.M. Stable Polyelectrolyte Multilayer-Based Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes for Produced Water Treatment. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2230–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, H.H.; Seo, G.T.; Jeong, D.W. Advanced oxidation processes and nanofiltration to reduce the color and chemical oxygen demand of waste soy sauce. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verified Market Research Global Ultrapure Water Market Size and Growth Forecast 2025. Available online: https://www.bccresearch.com/partners/verified-market-research/global-ultrapure-water-market.html (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Lee, H.; Jin, Y.; Hong, S. Recent transitions in ultrapure water (UPW) technology: Rising role of reverse osmosis (RO). Desalination 2016, 399, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Production of high-purity water by membrane processes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 3, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Long, T. A critical review on challenges and trend of ultrapure water production process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.W.; Teow, Y.H.; Ho, K.C.; Rosnan, N.A. Chapter 5—Recent Developments in Nanofiltration for Food Applications. In Nanomaterials for Food Applications; López Rubio, A., Fabra Rovira, M.J., Martínez Sanz, M., Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 101–120. ISBN 978-0-12-814130-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, K.; Dave, H.K.; Patel, T.M. Revisiting the recent applications of nanofiltration in food processing industries: Progress and prognosis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; Arqués, J.L.; Rodríguez, R.; Nuñez, M.; Medina, M.; Talarico, T.L.; Casas, I.A.; Chung, T.C.; Dobrogosz, W.J.; Axelsson, L.; et al. Membrane Applications for Lactose Recovering. In Lactose and Lactose Derivatives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; Volume 32, pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.; Sarkar, S.; Sarkar, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, C. Recovery of whey proteins and lactose from dairy waste: A step towards green waste management. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 101, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, T.; Shimada, M.; Ushida, Y.; Seki, N.; Watai, N.; Ohnishi, M.; Tamura, Y.; Ito, A. Demineralisation of whey by a combination of nanofiltration and anion-exchange treatment: A preliminary study. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2015, 68, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelon, M.; Manera, A.P.; Carvalho, A.L.; Maugeri Filho, F. Concentration and purification of galacto-oligosaccharides using nanofiltration membranes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, F. Current and future applications for nanofiltration technology in the food processing. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkova, A.; Bubník, Z.; Kadlec, P.; Pridal, J. Potentials of separation membranes in the sugar industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 26, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyura, J.; Šereš, Z.; Eszterle, M. Influence of operating parameters on separation of green syrup colored matter from sugar beet by ultra-and nanofiltration. J. Food Eng. 2005, 66, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, F.; Razavi, S.M.A.; Elahi, M. Purifying anion exchange resin regeneration effluent using polyamide nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2011, 278, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruksasri, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Haltrich, D.; Novalin, S. Fractionation of a galacto-oligosaccharides solution at low and high temperature using nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Jiang, Z. Composite polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for oligosaccharides nanofiltration separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmali, M.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Tang, J.; Cong, H. Sugar fractionation using surface-modified nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massot, A.; Mietton-Peuchot, M.; Peuchot, C.; Milisic, V. Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis in winemaking. Desalination 2008, 231, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.; Mendes, A. Dealcoholizing wine by membrane separation processes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2011, 12, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rayess, Y.; Mietton-Peuchot, M. Membrane Technologies in Wine Industry: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, C.M.; Palacio, L.; Prádanos, P.; Hernández, A.; González-Huerta, C.; Pérez-Magariño, S. Comparative study of red grape must nanofiltration: Laboratory and pilot plant scales. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warczok, J.; Ferrando, M.; López, F.; Güell, C. Concentration of apple and pear juices by nanofiltration at low pressures. J. Food Eng. 2004, 63, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conidi, C.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Cassano, A. Membrane-based operations in the fruit juice processing industry: A review. Beverages 2020, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arend, G.D.; Adorno, W.T.; Rezzadori, K.; Di Luccio, M.; Chaves, V.C.; Reginatto, F.H.; Petrus, J.C.C. Concentration of phenolic compounds from strawberry (Fragaria X ananassa Duch) juice by nanofiltration membrane. J. Food Eng. 2017, 201, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conidi, C.; Cassano, A.; Caiazzo, F.; Drioli, E. Separation and purification of phenolic compounds from pomegranate juice by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes. J. Food Eng. 2017, 195, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Ng, H.T.; Chung, T.S. A Conceptual Demonstration of Decaffeination via Nanofiltration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7737–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, S.; Prudêncio, E.S.; Nunes, G.L.; Guizoni, K.; Fogaça, L.A.; Petrus, J.C.C. Antioxidant properties of tofu whey concentrate by freeze concentration and nanofiltration processes. J. Food Eng. 2015, 160, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Zhou, R.; Qin, X. Recovery and purification of potato proteins from potato starch wastewater by hollow fiber separation membrane integrated process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, M.; Bye, K.P. Advances in organic solvent nanofiltration rely on physical chemistry and polymer chemistry. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalska, I. Membrane technology for the recovery of contaminated single-phase acidic detergents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 124, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novalic, S.; Dabrowski, A.; Kulbe, K.D. Nanofiltration of caustic and acidic cleaning solutions with high COD part 1. Recycling of sodium hydroxide. J. Food Eng. 1998, 38, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawson, A.J. Regeneration of cleaning and processing solutions using membrane technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.; Crespo, J.G.; Santos, M.A.; Velizarov, S. Oil refinery hazardous effluents minimization by membrane filtration: An on-site pilot plant study. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novalic, S.; Dabrowski, A.; Kulbe, K.D. Nanofiltration of caustic and acidic cleaning solutions with high COD part 2. Recycling of HNO3. J. Food Eng. 1998, 38, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.; Riera, F.A.; Álvarez, R.; Álvarez, S. Nanofiltration regeneration of contaminated single-phase detergents used in the dairy industry. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkell, A.; Krawczyk, H.; Thuvander, J.; Jönsson, A.S. Evaluation of membrane performance and cost estimates during recovery of sodium hydroxide in a hemicellulose extraction process by nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bóna, Á.; Bakonyi, P.; Galambos, I.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Separation of Volatile Fatty Acids from Model Anaerobic Effluents Using Various Membrane Technologies. Membranes 2020, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Ye, Y.; Razmjou, A.; Chen, V. High-Value Organic Acid Recovery from First-Generation Bioethanol Dunder Using Nanofiltration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 11940–11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Scott, J.; Sharma, B.K.; Rajagopalan, N. Advanced treatment of hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater with nanofiltration to recover carboxylic acids. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Zheng, J.; Bargeman, G.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Benes, N.E. PH stable thin film composite polyamine nanofiltration membranes by interfacial polymerisation. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 478, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshof, M.G.; de Vos, W.M.; de Grooth, J.; Benes, N.E. On the long-term pH stability of polyelectrolyte multilayer nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 615, 118532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrobas, D.L.P.; Hund, K.L.; Mccormick, M.S.; Ningthoujam, J.; Drexhage, J.R. The Growing Role of Minerals and Metals for a Low Carbon Future; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watari, T.; Nansai, K.; Nakajima, K. Review of critical metal dynamics to 2050 for 48 elements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshkaki, A.; Graedel, T.E.; Ciacci, L.; Reck, B.K. Resource Demand Scenarios for the Major Metals. Environ. Sci. Technol 2018, 52, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Geng, C.; Guo, H.; Du, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ji, S. Synthesis of positively charged polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for removal of divalent metal ions. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, P.K.; Chung, K.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Srivastava, R.R. Advance review on the exploitation of the prominent energy-storage element Lithium. Part II: From sea water and spent lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Miner. Eng. 2017, 110, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemabad, M.; Verliefde, A.; Cornelissen, E.R.; D’Haese, A. Crown ether containing polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for lithium recovery. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 595, 117432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; He, B.; Cui, Z. Preparation and characterization of positively charged polyamide composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membrane for lithium and magnesium separation. Desalination 2015, 369, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Xu, Z.L.; Ding, H.; Tang, Y.J. Positively charged capillary nanofiltration membrane with high rejection for Mg2+ and Ca2+ and good separation for Mg2+ and Li2+. Desalination 2017, 420, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.; Tam, J.; Yang, M.; Azimi, G. Technospheric Mining of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): Process Optimization, Kinetic Investigation, and Microwave Pretreatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remmen, K.; Schäfer, R.; Hedwig, S.; Wintgens, T.; Wessling, M.; Lenz, M. Layer-by-layer membrane modification allows scandium recovery by nanofiltration. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.C.; Peter, J.; Oenema, O. Science of the Total Environment Phosphorus flows and balances of the European Union Member States. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1078–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Köser, J.; Wessling, M.; Wintgens, T. Phosphorus recovery in an acidic environment using layer-by-layer modified membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 582, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Köser, J.; Wessling, M.; Wintgens, T. Assessment of Layer-By-Layer Modified Nanofiltration Membrane Stability in Phosphoric Acid. Membranes 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paltrinieri, L.; Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Chu, L.; Köser, J.; Wintgens, T.; Wessling, M.; de Smet, L.C.P.M.; Sudhölter, E.J.R. Improved phosphoric acid recovery from sewage sludge ash using layer-by-layer modified membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 587, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Chung, T.S. Polyelectrolyte functionalized lamellar graphene oxide membranes on polypropylene support for organic solvent nanofiltration. Carbon N. Y. 2017, 122, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutczak, S.M.; Luiten-Olieman, M.W.J.; Zwijnenberg, H.J.; Bolhuis-Versteeg, L.A.M.; Winnubst, L.; Hempenius, M.A.; Benes, N.E.; Wessling, M.; Stamatialis, D. Composite capillary membrane for solvent resistant nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 372, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Japip, S.; Lai, J.; Chung, T. Revitalize integrally skinned hollow fiber membranes with spatially impregnated 3D-macrocycles for organic solvent nanofiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.S.; Chong, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, W.; Bae, T.H.; Wang, R. Thin-film composite hollow fibre membrane for low pressure organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 597, 117760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Tian, L.; Su, B. Fabrication of polyimide-based hollow fiber membrane by synergetic covalent-crosslinking strategy for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Xu, S.; Tian, L.; Su, B.; Han, L.; Mandal, B. Fundamental understanding on the preparation conditions of high-performance polyimide-based hollow fiber membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, H.M.M.; Wang, K.Y.; Hua, D.; Japip, S.; Chung, T.S. From ultrafiltration to nanofiltration: Hydrazine cross-linked polyacrylonitrile hollow fiber membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 542, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi Tashvigh, A.; Chung, T.S. Robust polybenzimidazole (PBI) hollow fiber membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 572, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Shi, G.M.; Wang, K.Y.; Lai, J.Y.; Chung, T.S. Employing a green cross-linking method to fabricate polybenzimidazole (PBI) hollow fiber membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.P.; Chan, S.Y.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Chung, T.S. Facile Synthesis of Dual-Layer Organic Solvent Nanofiltration (OSN) Hollow Fiber Membranes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3019–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, X.X.; Sairam, M.; Steinke, J.H.G.; Livingston, A.G.; Bismarck, A.; Li, K. Polyaniline hollow fibres for organic solvent nanofiltration. Chem. Commun. 2008, 47, 6324–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, A.; Peeva, L.; Han, S.; Nair, D.; Luthra, S.S.; White, L.S.; Freitas Dos Santos, L.M. Membrane separation in green chemical processing: Solvent nanofiltration in liquid phase organic synthesis reactions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 984, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadiannamini, P.; Li, X.; Goyens, W.; Joseph, N.; Meesschaert, B.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Multilayered polyelectrolyte complex based solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes prepared from weak polyacids. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Joseph, N.; Szymczyk, A.; Volodin, A.; Nijmeijer, K.; de Vos, W.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Weak polyelectrolyte multilayers as tunable membranes for solvent resistant nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 514, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Goyens, W.; Ahmadiannamini, P.; Vanderlinden, W.; De Feyter, S.; Vankelecom, I. Morphology and performance of solvent-resistant nanofiltration membranes based on multilayered polyelectrolytes: Study of preparation conditions. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 358, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, N.; An, Q.F.; Guo, H. Counterion exchanged hydrophobic polyelectrolyte multilayer membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 620, 118827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadiannamini, P.; Li, X.; Goyens, W.; Meesschaert, B.; Vanderlinden, W.; De Feyter, S.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Influence of polyanion type and cationic counter ion on the SRNF performance of polyelectrolyte membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 403–404, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G.; Pongpairoj, P.; Field, R. Microfiltration of algae (Chlorella sorokiniana): Critical flux, fouling and transmission. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 387–388, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, R.; Kuritz, T.; Powell, L.; Adcock, D. Membrane-based energy efficient dewatering of microalgae in biofuels production and recovery of value added co-products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5599–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baerdemaeker, T.; Lemmens, B.; Dotremont, C.; Fret, J.; Roef, L.; Goiris, K.; Diels, L. Benchmark study on algae harvesting with backwashable submerged flat panel membranes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monte, J.; Sá, M.; Galinha, C.F.; Costa, L.; Hoekstra, H.; Brazinha, C.; Crespo, J.G. Harvesting of Dunaliella salina by membrane filtration at pilot scale. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Vandamme, D.; Foubert, I.; Muylaert, K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Harvesting microalgal biomass using submerged microfiltration membranes. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avram, A.M.; Ahmadiannamini, P.; Vu, A.; Qian, X.; Sengupta, A.; Ranil Wickramasinghe, S. Polyelectrolyte multilayer modified nanofiltration membranes for the recovery of ionic liquid from dilute aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 2017, 134, 45349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinwurm, F.; Drljo, A.; Friedl, A. Lignin concentration by nanofiltration and precipitation in a lignocellulose biorefinery. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 45, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.D.; Pinto, P.C.R.; Rodrigues, A.E. Lignin valorization: Concentration of model phenolic compounds by nanofiltration. U. Porto J. Eng. 2017, 3, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, R.; Götzinger, G.; Sixta, H.; Friedl, A.; Harasek, M. Evaluation of alkali resistant nanofiltration membranes for the separation of hemicellulose from concentrated alkaline process liquors. Desalination 2006, 192, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, N.K.; Law, J.Y.; Chai, P.V.; Rohani, R.; Mohammad, A.W. Recovery of organic acids from fermentation broth using nanofiltration technologies: A review. J. Phys. Sci. 2017, 28, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sosa, P.A.; Roca, C.; Velizarov, S. Membrane assisted recovery and purification of bio-based succinic acid for improved process sustainability. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 501, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.I.; Alvarez, S.; Riera, F.A.; Álvarez, R. Lactic acid recovery from whey ultrafiltrate fermentation broths and artificial solutions by nanofiltration. Desalination 2008, 228, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpuch, C.; Galier, S.; Kanchanatawee, S.; Balmann, H.R. de Nanofiltration as a purification step in production process of organic acids: Selectivity improvement by addition of an inorganic salt. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
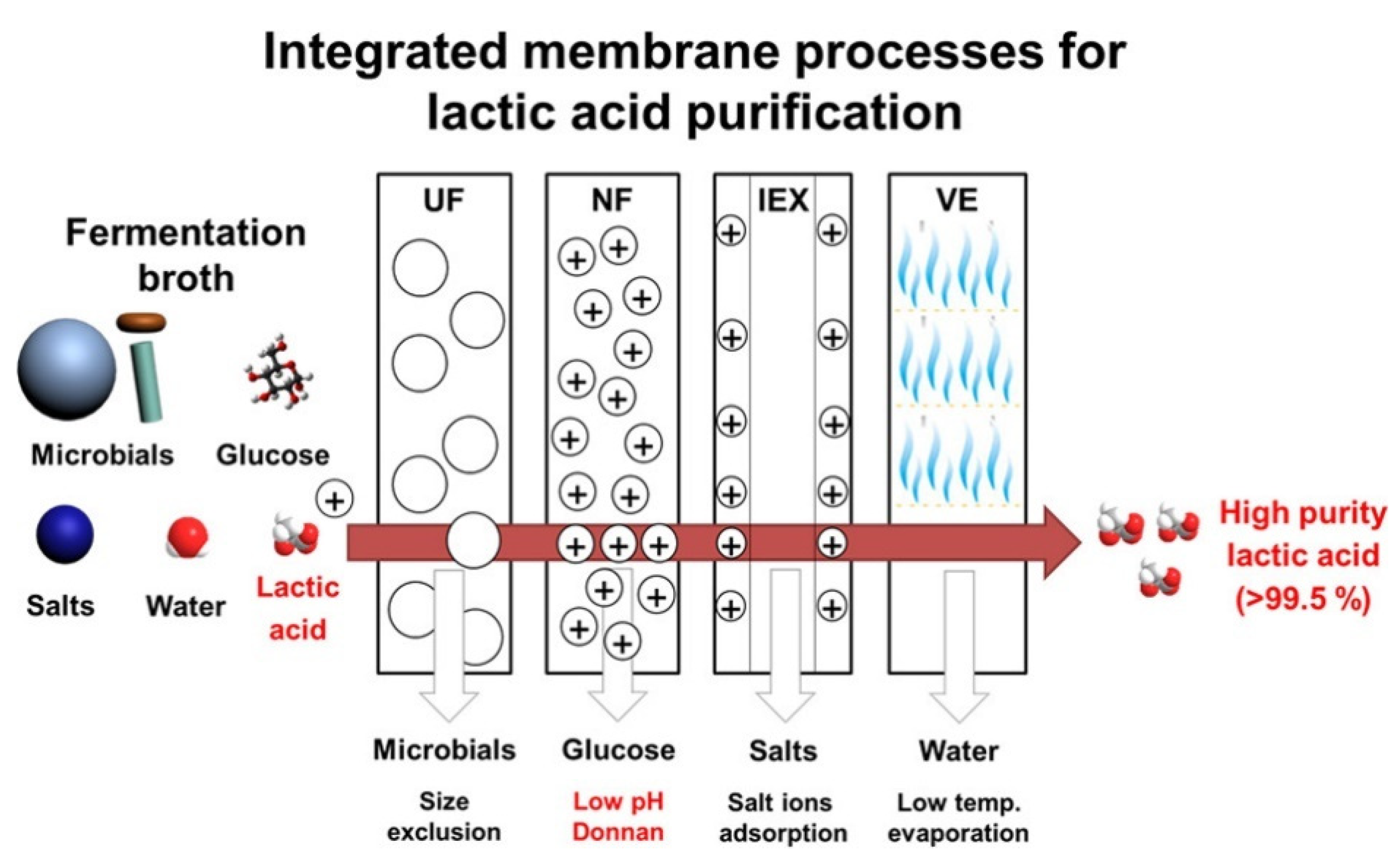
- Lee, H.D.; Lee, M.Y.; Hwang, Y.S.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, H.B. Separation and Purification of Lactic Acid from Fermentation Broth Using Membrane-Integrated Separation Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8301–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Company | Location | Product Name | MWCO (Da) | Operating Mode | Material Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3E Memtech Pte Ltd. | Singapore | 3E-NF20A 3E-NF40A 3E-NF60 3E-NF80A 3E-NF90A | n.a. | Inside-out | PES/PVDF + proprietary NF coating |
| De.mem Limited | Australia/ Singapore | De.mem NF | >200 | Outside-in | PEI based TFC |
| NX Filtration | The Netherlands | dNF80 dNF40 | 800 400 | Inside-out | PES-PEM |
| Pentair X-Flow | The Netherlands | HFW1000 | 1000 | Inside-out | PES-PEM |
| Ochemate | China | NÜF N80 | 200–500 | Outside-in | Polyamide based TFC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sewerin, T.; Elshof, M.G.; Matencio, S.; Boerrigter, M.; Yu, J.; de Grooth, J. Advances and Applications of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110890
Sewerin T, Elshof MG, Matencio S, Boerrigter M, Yu J, de Grooth J. Advances and Applications of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110890
Chicago/Turabian StyleSewerin, Tim, Maria G. Elshof, Sonia Matencio, Marcel Boerrigter, Jimmy Yu, and Joris de Grooth. 2021. "Advances and Applications of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review" Membranes 11, no. 11: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110890
APA StyleSewerin, T., Elshof, M. G., Matencio, S., Boerrigter, M., Yu, J., & de Grooth, J. (2021). Advances and Applications of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review. Membranes, 11(11), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110890






