Organic Solvent Nanofiltration of Water-in-Oil Pickering Emulsions—What Influences Permeability?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Particle type;
- Particle mass fraction;
- Dispersed phase fraction;
- Presence of catalyst and reaction (by-)products;
- Shear rate/crossflow velocity;
- Organic solvent type.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of w/o Pickering Emulsions
| Component | CAS-Nr. | Purity | ρ (20 °C) | η (20 °C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [−] | [%] | [g mol−1] | [kg m−3] | [mPa s] | |
| 1-dodecene | 112-41-4 | for synthesis | 168.32 | 758.4 | 1.25 |
| dodecane | 112-40-3 | >99.0 | 170.33 | 749.5 | 1.44 |
| decene | 872-05-9 | >97.0 | 140.27 | 740.8 | 0.71 |
| octene | 111-66-0 | >99.0 | 112.21 | 714.9 | 0.29 |
| heptane | 142-82-5 | >99.2 | 100.20 | 680.0 | 0.36 |
| Short Name | Particle Type | Access to Particles | Particle Shape | Size | Hydrophobicity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H15 | HDK®H15 | commercial | fractal-like | 50–150 nm | 50% | [20] |
| H20 | HDK®H20 | 50% | [21] | |||
| H30 | HDK®H30 | 50% | [22] | |||
| H2000 | HDK®H2000 | 25% | [23] | |||
| 50− | 50 C18n− | in-house | spherical | 50 nm | 113° | [18] |
| 50+ | 50 C18n+ | 50 nm | 107° | |||
| 100+ | 100 C18n+ | 100 nm | 105° |
2.2. Drop Size Distribution
2.3. Rheological Behavior
2.4. Permeation of Pure Solvents and Filtration of w/o Pickering Emulsions
2.4.1. Pre-Treatment of the Membrane
2.4.2. Pressure Stepping Experiments
2.4.3. Long-Term Filtration Experiments
2.4.4. Concentration Experiments
3. Results
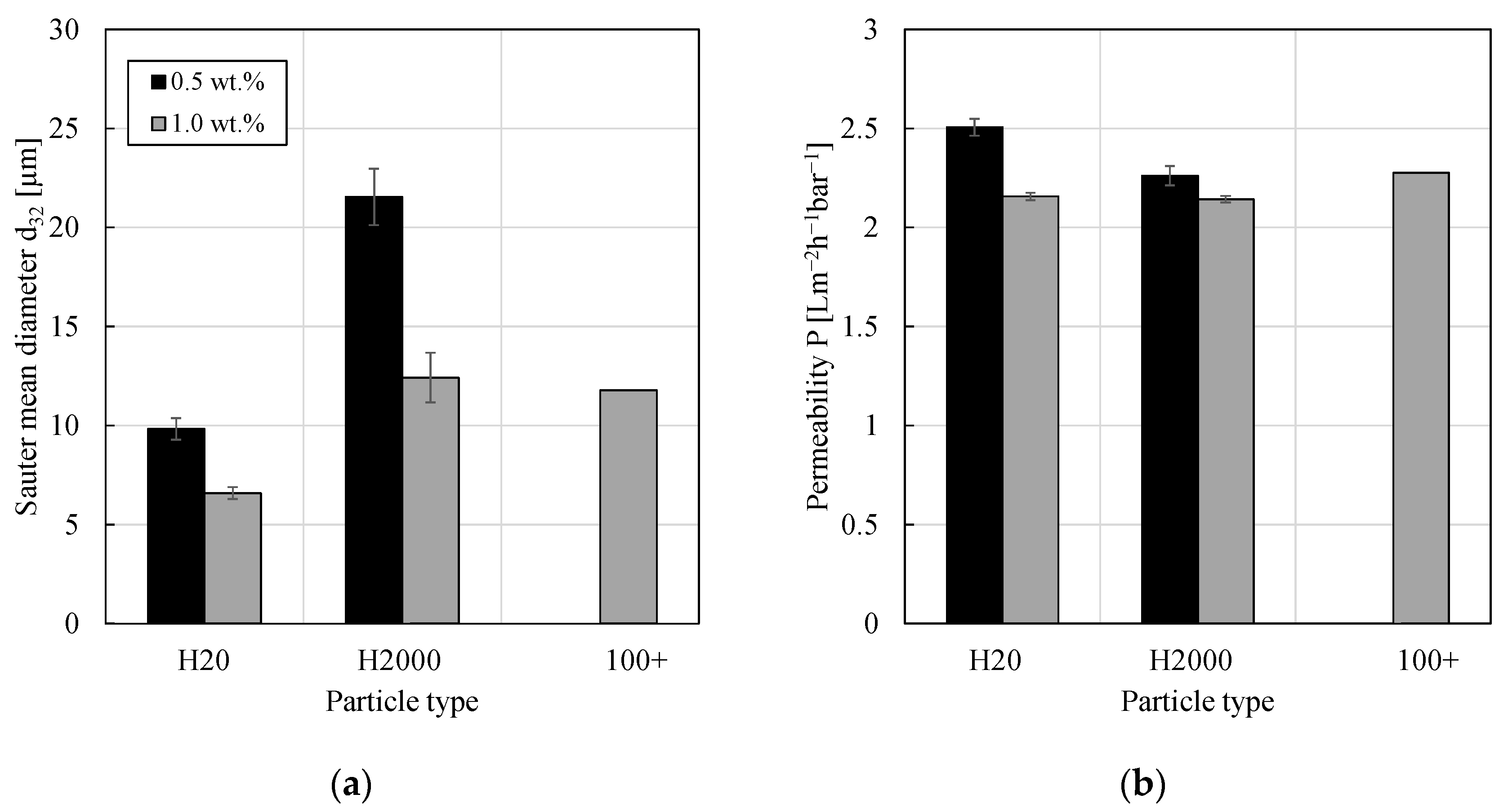
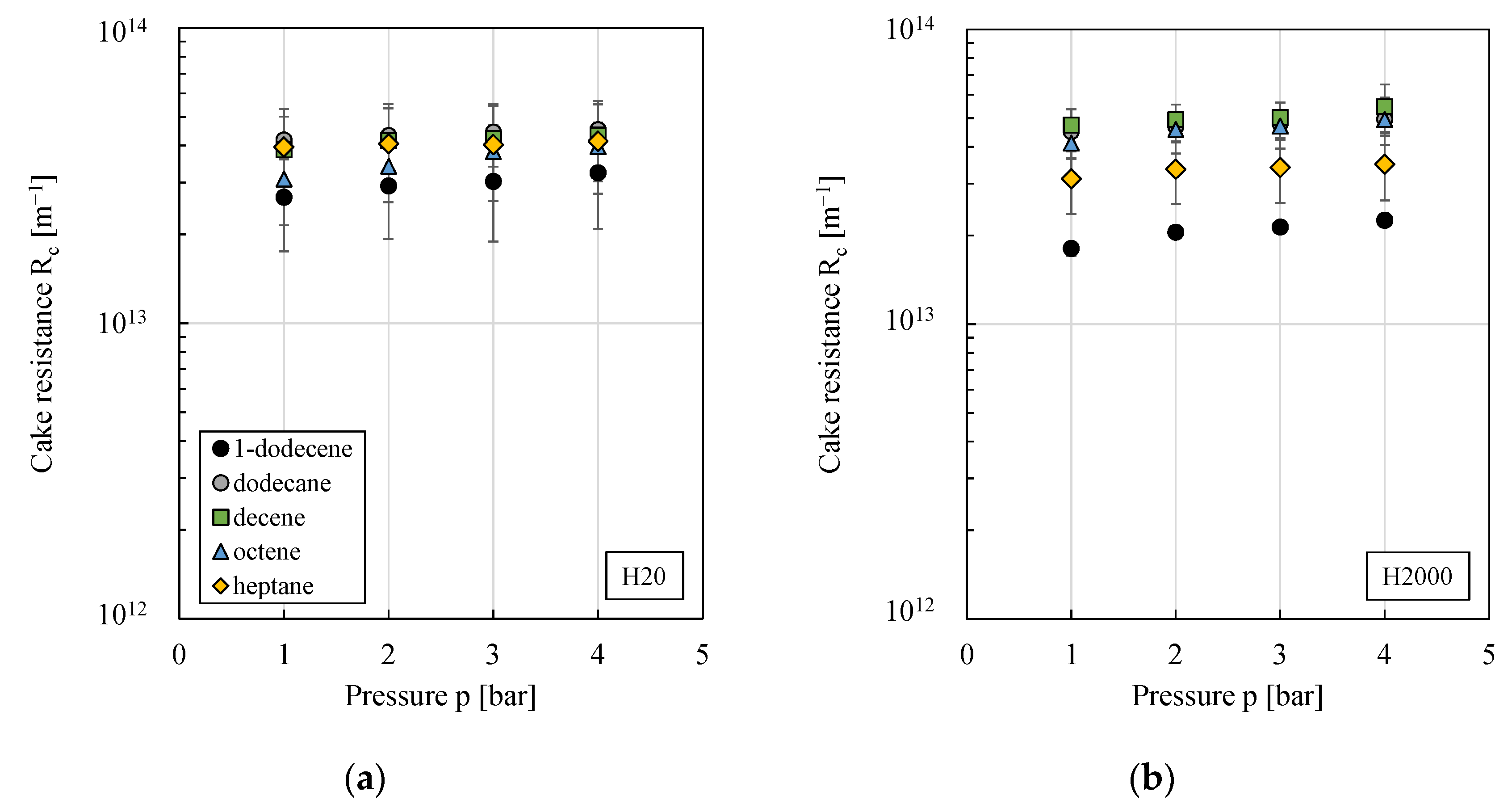
3.1. Impact of Particle Type
3.2. Impact of Particle Concentration
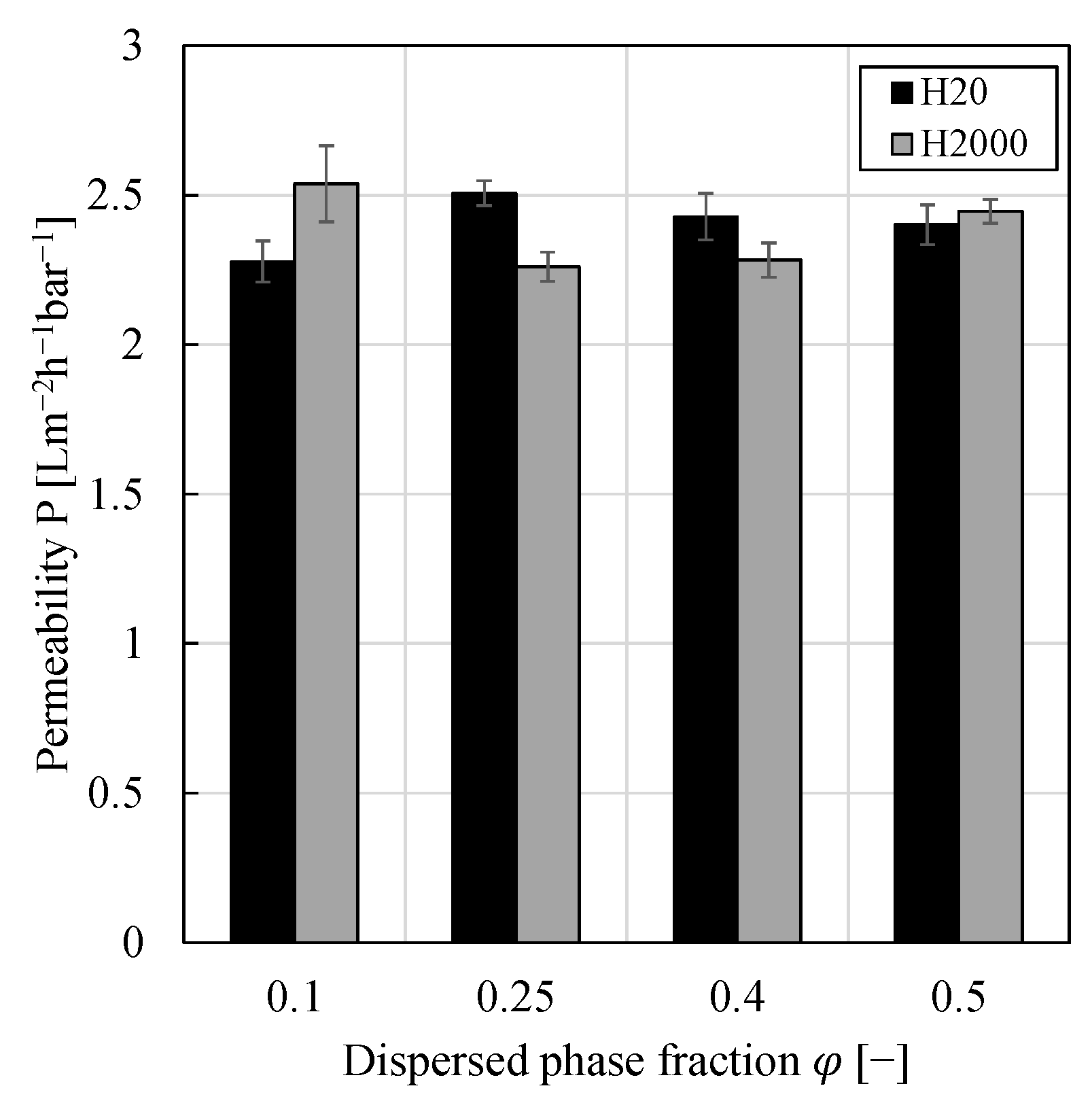
3.3. Impact of Dispersed Phase Fraction
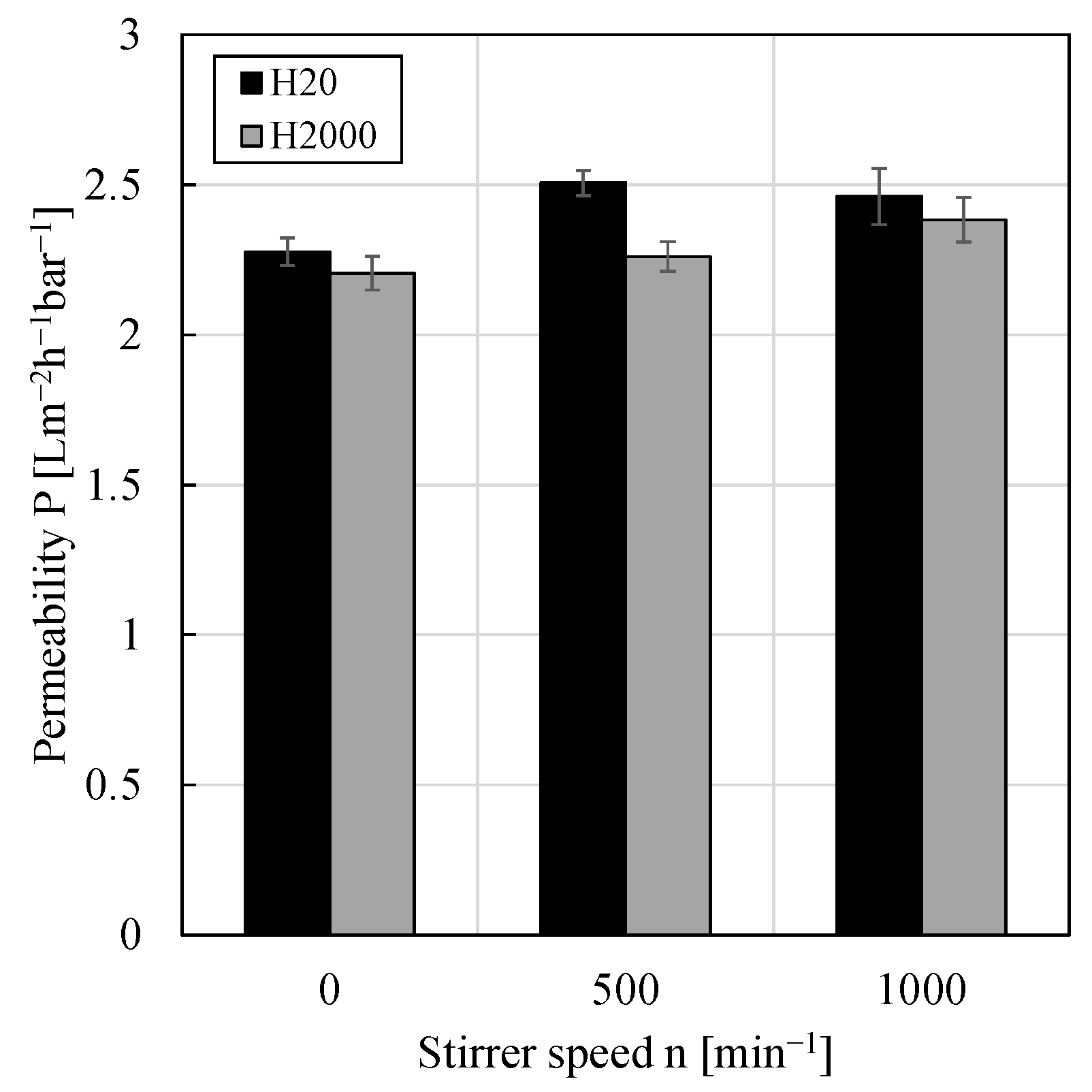
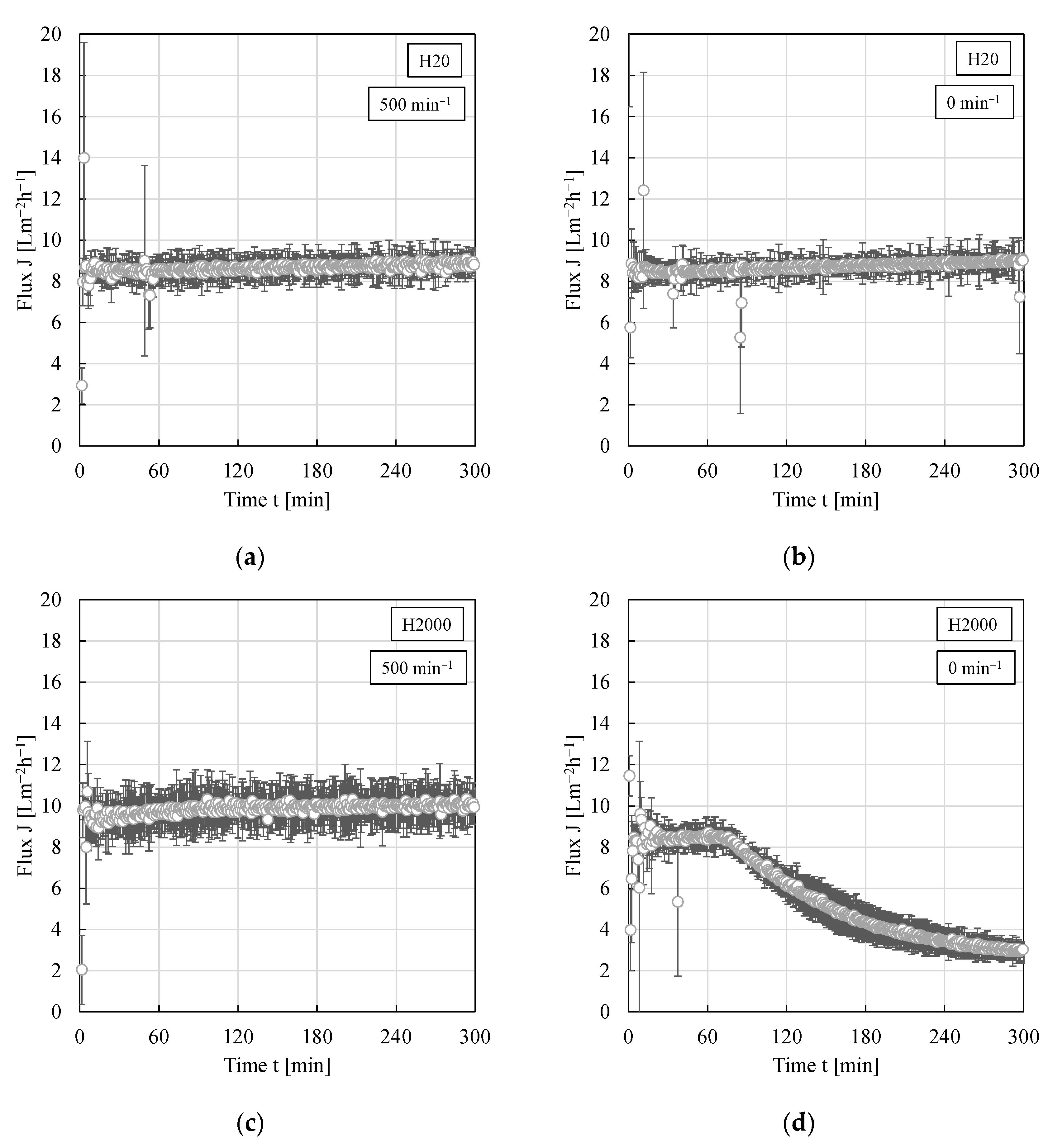
3.4. Impact of Shear Rate/Crossflow Velocity
3.5. Impact of Organic Solvent Type
3.5.1. Pure Organic Solvent Flux
3.5.2. Filtration of w/o PEs Using Different Organic Solvents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pickering, S.U. CXCVI.-Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binks, B.P. Particles as surfactants—Similarities and differences. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bai, S.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M.B.; Wang, D. Nanoparticle cages for enzyme catalysis in organic media. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5694–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Xin, H.; Yang, H. Pickering emulsion as an efficient platform for enzymatic reactions without stirring. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6838–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyse, A.; Plikat, C.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M.; Drews, A. Continuous two-phase biocatalysis using water-in-oil Pickering emulsions in a membrane reactor: Evaluation of different nanoparticles. Catal. Today 2019, 331, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.M.B.; Binks, B.P. Catalysis in Pickering emulsions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10221–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera-Titus, M.; Leclercq, L.; Clacens, J.-M.; De Campo, F.; Nardello-Rataj, V. Pickering interfacial catalysis for biphasic systems: From emulsion design to green reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2006–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Quinlan, P.J.; Tam, K.C. Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3512–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.; Cui, Z.; Xia, W.; Binks, B.P.; Yang, H. Biphasic biocatalysis using a CO2-switchable Pickering emulsion. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4062–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skale, T.; Stehl, D.; Hohl, L.; Kraume, M.; von Klitzing, R.; Drews, A. Tuning Pickering emulsions for optimal reaction and filtration conditions. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2016, 88, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skale, T.; Hohl, L.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. Feasibility of w/o Pickering emulsion ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyse, A.; Plikat, C.; Grün, M.; Delaval, S.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M.; Drews, A. Impact of enzyme properties on drop size distribution and filtration of water-in-oil Pickering emulsions for application in continuous biocatalysis. Process. Biochem. 2018, 72, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempin, M.V.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. W/O Pickering emulsion preparation using a batch rotor-stator mixer—Influence on rheology, drop size distribution and filtration behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 573, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempin, M.V.; Stock, S.; von Klitzing, R.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. Influence of particle type and concentration on the ultrafiltration behavior of nanoparticle stabilized Pickering emulsions and suspensions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempin, M.V.; Schroeder, H.; Hohl, L.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. Modeling of water-in-oil Pickering emulsion nanofiltration—Influence of temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehl, D.; Hohl, L.; Schmidt, M.; Hübner, J.; Lehmann, M.; Kraume, M.; Schomäcker, R.; von Klitzing, R. Characteristics of stable Pickering emulsions under process conditions. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2016, 88, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempin, M.V.; Drews, A. What Governs Pickering Emulsion Properties During Preparation via Batch Rotor-Stator Homogenizers? Chem. Ing. Tech. 2021, 93, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Schlander, A.; Kempin, M.; Geisler, R.; Stehl, D.; Spanheimer, K.; Hondow, N.; Micklethwaite, S.; Weber, A.; Schomäcker, R.; et al. The quantitative impact of fluid vs.solid interfaces on the catalytic performance of Pickering emulsions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 2355–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem Database. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Wacker Chemie AG. Technical Data Sheet HDK®H15; Wacker Chemie AG: Munich, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wacker Chemie AG. Technical Data Sheet HDK®H20; Wacker Chemie AG: Munich, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wacker Chemie AG. Technical Data Sheet HDK®H30; Wacker Chemie AG: Munich, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wacker Chemie AG. Technical Data Sheet HDK®H2000; Wacker Chemie AG: Munich, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Binks, B.P.; Lumsdon, S.O. Catastrophic phase inversion of water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by hydrophobic silica. Langmuir 2000, 16, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaß, S. Experimental Analysis, Modeling and Simulation of Drop Breakage in Agitated Turbulent Liquid/Liquid-Dispersions. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hohl, L.; Röhl, S.; Stehl, D.; von Klitzing, R.; Kraume, M. Influence of nanoparticles and drop size distributions on the rheology of w/o Pickering emulsions. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2016, 88, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BORSIG Membrane Technology GmbH. Liquid Separation. Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. Membrane Data Sheet oNF-3; Borsig: Gladbeck, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, T.; Bai, R.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, Y. Enzyme-loaded mesoporous silica particles with tuning wettability as a Pickering catalyst for enhancing biocatalysis. Catalysts 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binks, B.P.; Philip, J.; Rodrigues, J.A. Inversion of silica-stabilized emulsions induced by particle concentration. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frelichowska, J.; Bolzinger, M.A.; Chevalier, Y. Effects of solid particle content on properties of o/w Pickering emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzold, M.; Röhl, S.; Hohl, L.; Stehl, D.; Lehmann, M.; von Klitzing, R.; Kraume, M. Mass Transfer and Drop Size Distributions in Reactive Nanoparticle-Stabilized Multiphase Systems. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2017, 89, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Lumsdon, S.O. Effects of oil type and aqueous phase composition on oil-water mixtures containing particles of intermediate hydrophobicity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2959–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, F.; Sun, X.; Li, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Xing, F.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Factors that affect Pickering emulsions stabilized by graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4843–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manga, M.S.; York, D.W. Production of concentrated Pickering emulsions with narrow size distributions using stirred cell membrane emulsification. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9050–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, X.; Perez Gonzalez, A.J.; Huang, Q. Kafirin nanoparticles-stabilized Pickering emulsions: Microstructure and rheological behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedel, D.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. Modelling and prediction of organic solvent flux and retention of surfactants by organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harogoppad, S.B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Diffusion and sorption of organic liquids through polymer membranes. 5. Neoprene, styrene-butadiene-rubber, ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer, and natural rubber versus hydrocarbons (C8–C16). Macromolecules 1991, 24, 2598–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



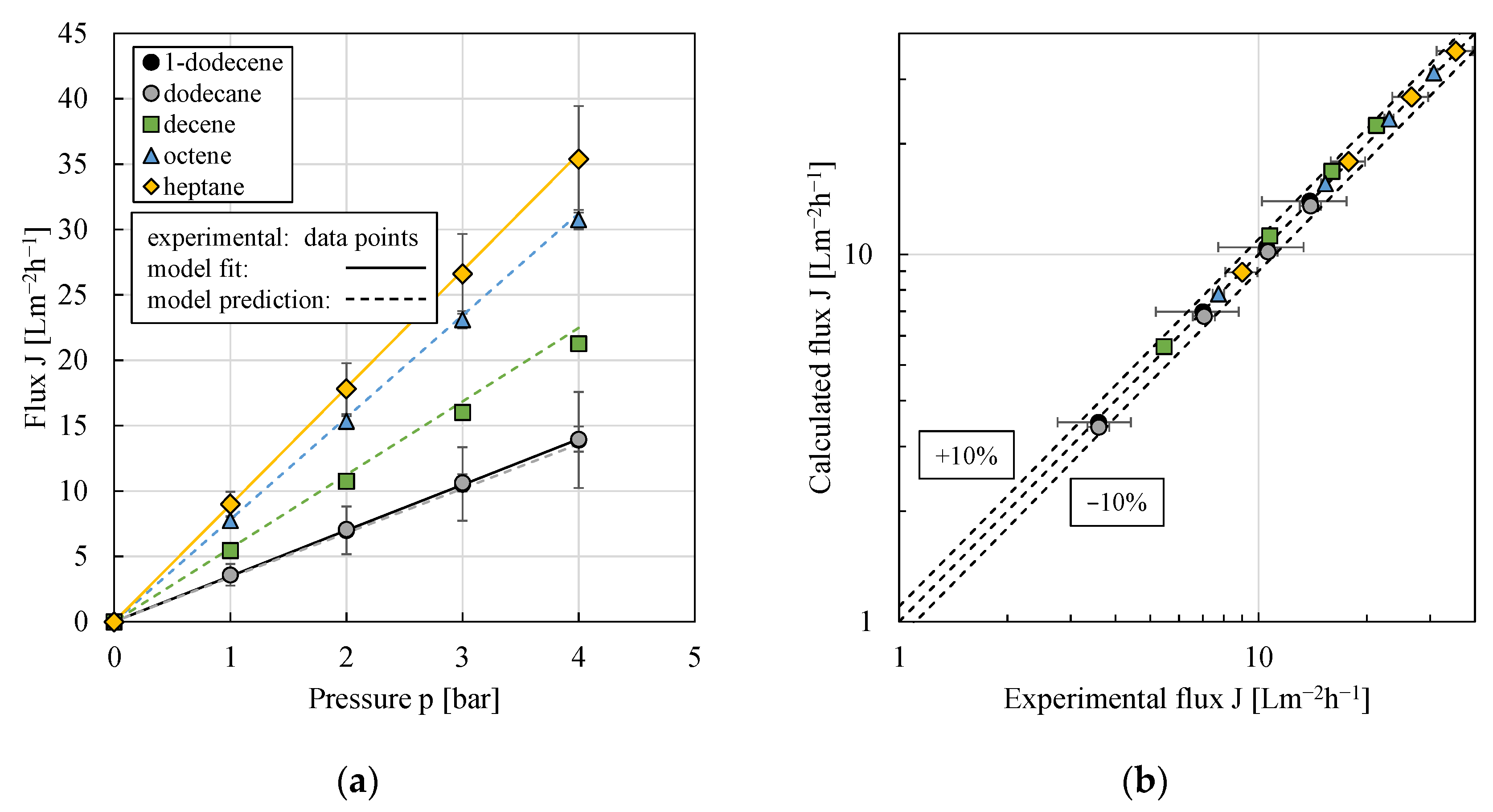


| Organic Solvent | mi | cim |
|---|---|---|
| [g] | [mol m−3] | |
| 1-dodecene | 1.58 ± 0.03 | 3214.8 |
| dodecane | 1.57 ± 0.03 | 3148.3 |
| decene | 1.51 ± 0.02 | 3746.5 |
| octene | 1.36 ± 0.03 | 4429.5 |
| heptane | 1.20 ± 0.03 | 4613.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kempin, M.V.; Drews, A. Organic Solvent Nanofiltration of Water-in-Oil Pickering Emulsions—What Influences Permeability? Membranes 2021, 11, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110864
Kempin MV, Drews A. Organic Solvent Nanofiltration of Water-in-Oil Pickering Emulsions—What Influences Permeability? Membranes. 2021; 11(11):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110864
Chicago/Turabian StyleKempin, Maresa Vivien, and Anja Drews. 2021. "Organic Solvent Nanofiltration of Water-in-Oil Pickering Emulsions—What Influences Permeability?" Membranes 11, no. 11: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110864
APA StyleKempin, M. V., & Drews, A. (2021). Organic Solvent Nanofiltration of Water-in-Oil Pickering Emulsions—What Influences Permeability? Membranes, 11(11), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110864






