The Use of NaOH Solutions for Fouling Control in a Membrane Bioreactor: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
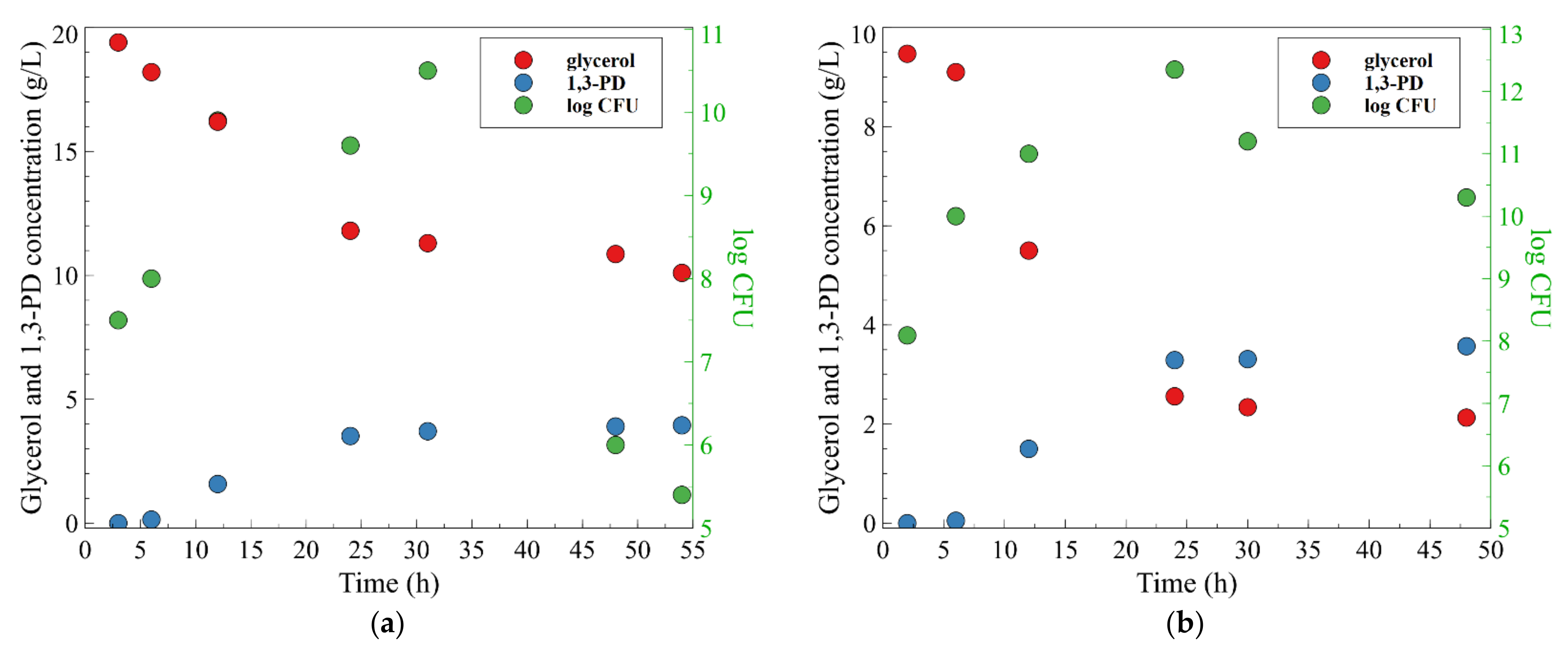
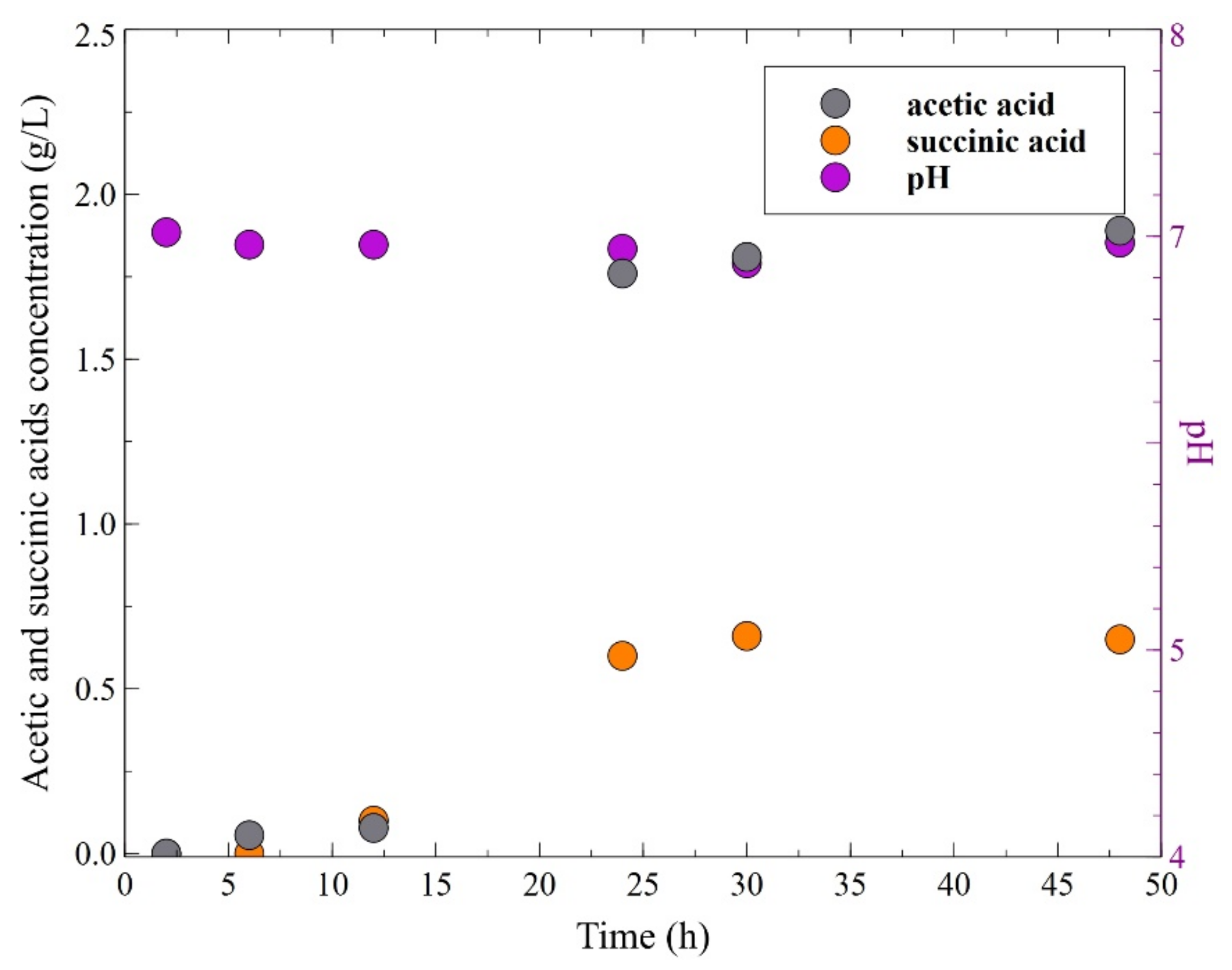
3.1. 1,3-Propanediol Formation
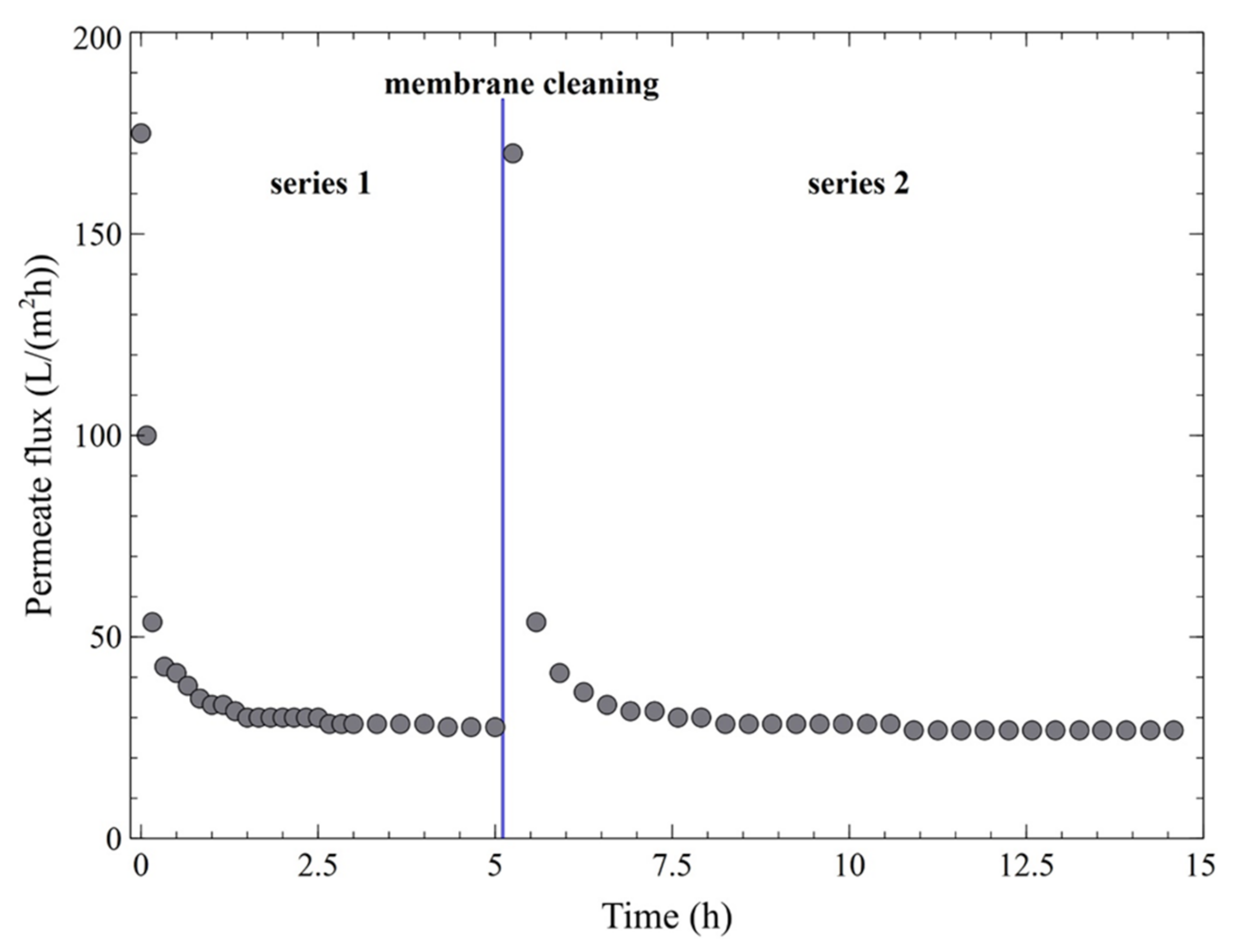
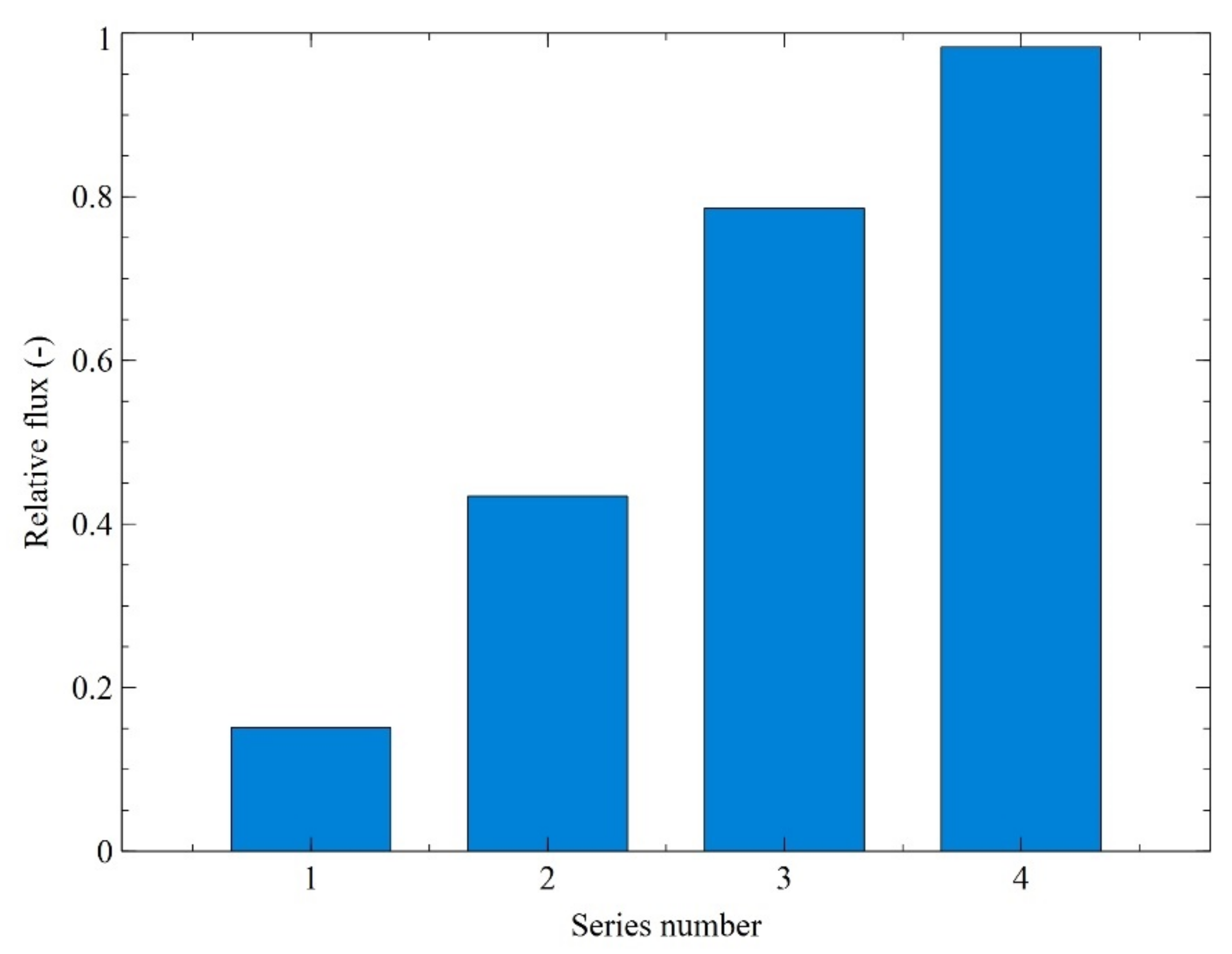
3.2. Ultrafiltration Performance
3.3. Design and Maintenance of MBR Facility: Technological Conception
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Bioconversion Process | Membrane Characteristic | Membrane Cleaning Agents | Ref. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Product | Carbon Source | Microorganism | Buffer | Module Configuration | Membrane Type | Material | Pore Diameter (µm) or Cut-Off (kDa) | Length (m) | Surface Area (m2) | ||
| lactic acid | glucose | Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | NH4OH | external | hollow fiber | PS 1 | 300 kDa | n/a | 0.2500 | n/a | [15] |
| lactic acid | glucose | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Ca(OH)2 | external | NI | organic | 1 kDa | n/a | 16.0000 | n/a | [16] |
| lactic acid | glucose | Bacillus coagulans | NaOH | external | hollow fiber | ceramic | 0.04 µm | n/a | 0.0330 | n/a | [17] |
| lactic acid | glucose | Bacillus coagulans | n/a | external | hollow fiber | ceramic | 0.04 µm | 0.190 | 0.0330 | alkaline solution (1% Asiral, Asiral Industrie-Reiniger GmbH, Neustadt, Germany) | [18] |
| lactic acid | lactose, glucose and galactose | Lactobacillus bulgaricus | NH4OH | external | hollow fiber | PS 1 | 30 kDa | 0.268 | 0.0350 | n/a | [19] |
| lactic acid | glucose | Bacillus coagulans | n/a | external | tubular | ceramic | 0.05 µm, 100 kDa and 20 kDa | n/a | 0.0040 | n/a | [20] |
| lactic acid | lactose | Lactococcus lactis | NH4OH | submerged | hollow fiber | PVDF 2 | 0.04 µm | n/a | 0.0200 | - | [21] |
| lactic acid | glucose, fructose and sucrose | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | NaOH | external | hollow fiber | PES 3 | 20 kDa | n/a | 0.1800 | 250 ppm NaOCl (backwashing) | [22] |
| biohydrogen | glucose | Clostridium beijerinckii, Clostridium pasteurianum and Enterobacter sp. | NaOH | submerged | hollow fiber | PTFE 4 | 0.10 µm | n/a | 0.1950 | n/a | [23] |
| biohydrogen | glucose | Clostridium, Enterobacter and Ethanoligenens | NaOH | submerged | hollow fiber | PTFE 4 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | [24] |
| biohydrogen | glucose | n/a | NaOH | submerged | submerged tubular | PVDF 2 | 250 kDa | n/a | 0.0400 | NaOH (pH = 12) and HNO3 (pH = 2) | [25] |
| biohydrogen | n/a | Clostridium thermopalmarium and Clostridium butyricum | HCl and NaOH | submerged | fiber | n/a | 0.05 µm | 0.490 | n/a | n/a | [26] |
| biohydrogen | glucose | n/a | n/a | submerged | hollow fiber | PVDF 2 | 0.04 µm | 0.215 | 0.1000 | not performed | [27] |
| biogas | n/a | n/a | n/a | external | tubular | ceramic | 150 kDa | 0.300 | 0.1000 | 2% NaOH and 1% HNO3 | [28] |
| biogas | n/a | n/a | n/a | submerged | hollow fiber | n/a | 0.03 µm | 0.250 | 0.5000 | 14% w/v (200 ppm) NaOCl, 1 g/L NaOCl and 1 g/L C6H8O7 | [29] |
| biogas | n/a | n/a | NaHCO3 | submerged | hollow fiber | n/a | 0.04 µm | n/a | 0.0470 | 2 g/L citric acid and NaOCl solution containing 2 g/L effective chlorine | [30] |
| fructose and gluconic acid | sucrose | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | acetate buffer | n/a | n/a | n/a | 100 kDa | n/a | n/a | n/a | [31] |
| fructose and gluconic acid | sucrose and glucose | Aspergillus niger | acid/acetate buffer | submerged | n/a | regenerated cellulose | 100 kDa | n/a | n/a | n/a | [32] |
| fructose and gluconic acid | sucrose and glucose | Aspergillus niger | acetate buffer | submerged | n/a | regenerated cellulose | 100 kDa | n/a | n/a | n/a | [33] |
| propionic acid | glycerol | Propionibacterium thoenii | NaOH | external | n/a | mineral | 500 kDa | n/a | 0.0150 | n/a | [34] |
| propionic acid | lactose | Propionibacterium acidici-propionici, Propionibacterium thoenii, Propionibacterium jensenii, Propionibacterium freudenreichii, Lactococcus lactis | NaOH | external | n/a | n/a | 300 kDa | n/a | 1.670 and 34.200 | n/a | [35] |
| propionic acid | glucose | Propionibacterium acidi-propionici | NH4OH | n/a | tubular | ceramic | NI | 0.640 | 0.1000 | n/a | [36] |
| ethanol | sucrose | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | NaOH | external | tubular | PES 3 | 0.02 µm | n/a | 0.1000 | 500 mg/L H2O2 and NaOCl solution containing 100 mg/L active chlorine | [37] |
| ethanol | saccharose | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | NaOH | external | tubular | PPP 5 | 25 kDa | n/a | 0.0250 | n/a | [38] |
| succinic acid | glucose | Actinobacillus succinogenes | NaOH | external | n/a | ceramic | 300 kDa | n/a | 0.1600 | n/a | [39] |
| succinic acid | glucose | Actinobacillus succinogenes and Mannheimia succiniciproducens | n/a | external | hollow-fiber | n/a | 300 K | n/a | 0.1000 | n/a | [40] |
| butyric acid | glucose | Clostridium tyrobutyricum | n/a | external | n/a | PS 1 | 100 kDa | n/a | n/a | 10 g/L NaOH and 10 g/L NaOCl | [41] |
| 1,3-PDO | glycerol | Citrobacter freundii | NaOH | external | tubular | ceramic | 8 kDa | n/a | 0.0038 | 1% NaOH | [42] |
References
- Roccaro, P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A. Membrane bioreactors for wastewater reclamation: Cost analysis. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Do, K.-U.; Chu, X.-Q. Performances of membrane bioreactor technology for treating domestic wastewater operated at different sludge retention time. In Development in Wastewater Treatment Research and Processes; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Vural, C.; Topbaş, T.; Dağlıoğlu, S.T.; Dağlı, Ö.; Oral, R.; Kabay, N.; Özdemir, G. Assessment of microbial and ecotoxicological qualities of industrial wastewater treated with membrane bioreactor (MBR) process for agricultural irrigation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevri, A.; Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C. Anaerobic MBR technology for treating municipal wastewater at ambient temperatures. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Caccamo, F.M.; Argiolas, S.; Bellazzi, S.; Baldi, M.; Bertanza, G. Strong minimization of biological sludge production and enhancement of phosphorus bioavailability with a thermophilic biological fluidized bed reactor. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomnonkhaow, U.; Uwineza, C.; Mahboubi, A.; Wainaina, S.; Reungsang, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Membrane bioreactor-assisted volatile fatty acids production and in situ recovery from cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BCC Research. Membrane Bioreactors: Global Markets. 2019. Available online: https://www.bccresearch.com/market-research/membrane-and-separation-technology/membrane-bioreactors.html (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Sohn, W.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Deng, L.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, X. A review on membrane fouling control in anaerobic membrane bioreactors by adding performance enhancers. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K. A systematic review of moving bed biofilm reactor, membrane bioreactor, and moving bed membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Comparison of research trends, removal mechanisms, and performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyunlu, B.; Daly, S.; Casey, E. Membrane bioreactors for the production of value-added products: Recent developments, challenges and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Khan, M.A.; Ngo, H.H.; Johir, M.A.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Ni, B. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors—An introduction. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Belafi-Bako, K.; Bakonyi, P. Integration of membranes and bioreactors. In Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Jacob-Lopes, E., Queiroz Zepka, L., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Iorhemen, O.; Hamza, R.; Tay, J. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Membrane fouling. Membranes 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.; Yue, X.; Shi, X.; Ng, K.K.; Ng, H.Y. Membrane fouling between a membrane bioreactor and a moving bed membrane bioreactor: Effects of solids retention time. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.; Beloded, A.; Derunets, A.; Grosheva, V.; Vakar, L.; Kozlovskiy, R.; Shvets, V. Biosynthesis of lactic acid in a membrane bioreactor for cleaner technology of polylactide production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wei, M.; Yu, L. Enhancement of pilot scale production of L(+)-lactic acid by fermentation coupled with separation using membrane bioreactor. Process. Biochem. 2012, 47, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Czermak, P. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for continuous lactic acid fermentation. Membranes 2017, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Quitmann, H.; Czermak, P. Lactic acid production in a membrane bioreactor system with thermophilic Bacillus Coagulans: Online monitoring and process control using an optical sensor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejayadi, S.; Cheryan, M. Lactic acid from cheese whey permeate. Productivity and economics of a continuous membrane bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 43, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Aden, M.; Czermak, P. Intensification of a fermentation process for producing lactic acid in a ceramic membrane combined bioreactor system. In Proceedings of the FILTECH Conference, Wiesbaden, Germany, 22–24 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ramchandran, L.; Sanciolo, P.; Vasiljevic, T.; Broome, M.; Powell, I.; Duke, M. Improving cell yield and lactic acid production of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris by a novel submerged membrane fermentation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403–404, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, H.; Cai, D.; Wang, B.; Qin, P.; Wang, Z.; Tan, T. Improvement of L-lactic acid productivity from sweet sorghum juice by repeated batch fermentation coupled with membrane separation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaudie, M.; Dumas, C.; Vuilleumier, S.; Ernst, B. Biohydrogen production in a continuous liquid/gas hollow fiber membrane bioreactor: Efficient retention of hydrogen producing bacteria via granule and biofilm formation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaudie, M.; Clion, V.; Dumas, C.; Vuilleumier, S.; Ernst, B. Intensification and optimization of continuous hydrogen production by dark fermentation in a new design liquid/gas hollow fiber membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrón, G.; Muñoz-Páez, K.M.; Hernández-Mendoza, C.E. Biohydrogen production using a granular sludge membrane bioreactor. Fuel 2019, 241, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akca, M.S.; Bostancı, O.; Aydin, A.K.; Koyuncu, I.; Altinbas, M. BioH2 production from food waste by anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 27941–27955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.M.; Taheri, E.; Fatehizadeh, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for the production of BioH2: Electron flow, fouling modeling and kinetic study. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, M.; Bernat, K.; Mikucka, W. Membrane bioreactor technology: The effect of membrane filtration on biogas potential of the excess sludge. Membranes 2020, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglia, A.; Akyol, Ç.; Frison, N.; Katsou, E.; Eusebi, A.L.; Fatone, F. Long-term operation of a pilot-scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) treating high salinity low loaded municipal wastewater in real environment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chang, S.; Guo, Q.; Hong, Y.; Wu, P. Brewery wastewater treatment using an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.D.; Tomotani, E.J.; Vitolo, M. Invertase, glucose oxidase and catalase for converting sucrose to fructose and gluconic acid through batch and membrane-continuous reactors. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neves, L.C.M.D.; Vitolo, M. Continuous production of gluconic acid and fructose using membrane bioreactor. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitolo, M. Membrane reactor applied to enzyme conversion of sucrose and glucose. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 9, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyaval, P.; Corre, C.; Madec, M.-N. Propionic acid production in a membrane bioreactor. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1994, 16, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomban, A.; Roger, L.; Boyaval, P. Production of propionic acid from whey permeate by sequential fermentation, ultrafiltration, and cell recycling. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1993, 42, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, J.P.S.G.; Moura, M.J.; Carrondo, M.J.T. Some engineering parameters for propionic acid fermentation coupled with ultrafiltration. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1990, 24–25, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylitervo, P.; Franzén, C.; Taherzadeh, M. Continuous ethanol production with a membrane bioreactor at high acetic acid concentrations. Membranes 2014, 4, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzoch, K.; Rychtera, M.; Markvichov, N.S.; Pospíchalová, V.; Basařová, G.; Manakov, M.N. Application of a membrane recycle bioreactor for continuous ethanol production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 34, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yin, J.; Xing, J.; Wan, Y. Effectively converting carbon dioxide into succinic acid under mild pressure with Actinobacillus succinogenes by an integrated fermentation and membrane separation process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.I. Continuous production of succinic acid using an external membrane cell recycle system. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; McGraw, A.; Lorenz, N.; Beitle, R.R.; Clausen, E.C.; Hestekin, J.A. Continuous fermentation of Clostridium tyrobutyricum with partial cell recycle as a long-term strategy for butyric acid production. Energies 2012, 5, 2835–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waszak, M.; Gryta, M. The ultrafiltration ceramic membrane used for broth separation in membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 305, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Wei, Y.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Ji, X.-J. Reprogramming the metabolism of Klebsiella pneumoniae for efficient 1,3-propanediol production. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 236, 116539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zabed, H.M.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X. Notable improvement of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and 1,3-propanediol coproduction using modular coculture engineering and pathway rebalancing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4625–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Paul, C. Advances in research on production of 1,3-PD by immobilized technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 714, 022009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-L.; Liu, F.-Y.; Yang, W.; Li, C.-L.; Zhu, B.-W.; Zhu, X.-H. Production of 1,3-propanediol and lactic acid from crude glycerol by a microbial consortium from intertidal sludge. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drożdżyńska, A.; Leja, K.; Czaczyk, K. Biotechnological production of 1,3-propanediol from crude glycerol. BioTechnologia 2011, 1, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fokum, E.; Zabed, H.M.; Ravikumar, Y.; Elshobary, M.E.; Chandankere, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yun, J.; Qi, X. Co-fermentation of glycerol and sugars by Clostridium beijerinckii: Enhancing the biosynthesis of 1,3-propanediol. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celińska, E.; Drożdżyńska, A.; Jankowska, M.; Białas, W.; Czaczyk, K.; Grajek, W. Genetic engineering to improve 1,3-propanediol production in an isolated Citrobacter freundii strain. Process. Biochem. 2015, 50, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Fan, Y. State-of-the-art developments in fabricating ceramic membranes with low energy consumption. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 14966–14987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugham, T.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Gopal, S.; Nambikkattu, J.; K, R.; Aboulella, A.M.; Ranil Wickramasinghe, S.; Banat, F. Recent developments in porous ceramic membranes for wastewater treatment and desalination: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.B.; Hai, F.I.; Jegatheesan, V.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D.; Yamamoto, K. Applications of membrane bioreactors in biotechnology processes. In Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-)Membranes; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 223–257. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Novel membranes and membrane materials. In Membrane-Based Salinity Gradient Processes for Water Treatment and Power Generation; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 201–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gruskevica, K.; Mezule, L. Cleaning methods for ceramic ultrafiltration membranes affected by organic fouling. Membranes 2021, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.; Yang, P.; Lee, P.-H.; Kim, J. Novel staged anaerobic fluidized bed ceramic membrane bioreactor: Energy reduction, fouling control and microbial characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 553, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Quek, P.J.; Wang, Z.; Ng, H.Y. Alkali-assisted membrane cleaning for fouling control of anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 240, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beqqour, D.; Achiou, B.; Bouazizi, A.; Ouaddari, H.; Elomari, H.; Ouammou, M.; Bennazha, J.; Alami Younssi, S. Enhancement of microfiltration performances of pozzolan membrane by incorporation of micronized phosphate and its application for industrial wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.M.; Roshni, M.; Vasanth, D. Treatment of aqueous bacterial solution using ceramic membrane prepared from cheaper clays: A detailed investigation of fouling and cleaning. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 29, 100797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. Ceramic membrane technology for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review of performance, full-scale applications, membrane fouling and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Application of ultrafiltration ceramic membrane for separation of oily wastewater generated by maritime transportation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 261, 118259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Comparison of polypropylene and ceramic microfiltration membranes applied for separation of 1,3-PD fermentation broths and Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast suspensions. Membranes 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bao, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, K.; Zhou, M.; He, L.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Chai, Z.; Song, Y. Mesoporous polymer-derived ceramic membranes for water purification via a self-sacrificed template. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11100–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruah, G.L.; Nayak, A.; Belfort, G. Scale-up from laboratory microfiltration to a ceramic pilot plant: Design and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 274, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubadillah, S.K.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Rahman, M.A.; Harun, Z.; Jaafar, J.; Nomura, M. Fabrications and applications of low cost ceramic membrane from kaolin: A comprehensive review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4538–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.K.; Kashif, A.; Rout, P.R.; Aslam, M.; Fuwad, A.; Choi, Y.; Banu J, R.; Park, J.H.; Kumar, G. A brief review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors emphasizing recent advancements, fouling issues and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Shi, Y.; Jegatheesan, V.; Haq, I.U. A review on the mechanism, impacts and control methods of membrane fouling in MBR system. Membranes 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinardell, S.; Astals, S.; Peces, M.; Cardete, M.A.; Fernández, I.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J. Advances in anaerobic membrane bioreactor technology for municipal wastewater treatment: A 2020 updated review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 130, 109936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vela, R.J. A review of the factors affecting the performance of anaerobic membrane bioreactor and strategies to control membrane fouling. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 607–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, I.; Sinha, A. A review on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors: Control and mitigation. In Environmental Contaminants; Gupta, T., Agarwal, A.K., Agarwal, R.A., Labhsetwar, N.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 281–315. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Ren, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yao, P. A review of the current in-situ fouling control strategies in MBR: Biological versus physicochemical. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D. New configurations and techniques for controlling membrane bioreactor (MBR) fouling. OALib 2020, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, H.S.; Turan, N.B.; Engin, G.O. Fouling control in MBR in a sustainable perspective. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 21–57. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, K.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Current state and challenges of full-scale membrane bioreactor applications: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zondervan, E.; Roffel, B. Evaluation of different cleaning agents used for cleaning ultra filtration membranes fouled by surface water. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Oh, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shin, H.-S.; Chae, S.-R. Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review. Water Res. 2017, 114, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Padmasiri, S.I.; Fitch, M.; Norddahl, B.; Raskin, L.; Morgenroth, E. Influence of cleaning frequency and membrane history on fouling in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Desalination 2007, 207, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, S.; Wan, Y. How do chemical cleaning agents act on polyamide nanofiltration membrane and fouling layer? Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 17653–17670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Lovitt, R.W. Fouling strategies and the cleaning system of NF membranes and factors affecting cleaning efficiency. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, N.; Judd, S. Chemical cleaning of potable water membranes: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gul, A.; Hruza, J.; Yalcinkaya, F. Fouling and chemical cleaning of microfiltration membranes: A mini-review. Polymers 2021, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Wei, C.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. Outlining the roles of membrane–foulant and foulant–foulant interactions in organic fouling during microfiltration and ultrafiltration: A mini-review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Chen, J.; Xue, W.; Huang, X. Chemical cleaning of nanofiltration membrane filtrating the effluent from a membrane bioreactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhangelsky, E.; Kuzmenko, D.; Gitis, N.V.; Vinogradov, M.; Kuiry, S.; Gitis, V. Hypochlorite cleaning causes degradation of polymer membranes. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 28, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Clarification of 1,3-propanediol fermentation broths by using a ceramic fine UF membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. The application of ultrafiltration for separation of glycerol solution fermented by bacteria. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gryta, M.; Tomczak, W. Microfiltration of post-fermentation broth with backflushing membrane cleaning. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Cross-flow microfiltration of glycerol fermentation broths with Citrobacter freundii. Membranes 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbirato, F.; Himmi, E.H.; Conte, T.; Bories, A. 1,3-propanediol production by fermentation: An interesting way to valorize glycerin from the ester and ethanol industries. Ind. Crop. Prod. 1998, 7, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drożdżyńska, A.; Pawlicka, J.; Kubiak, P.; Kośmider, A.; Pranke, D.; Olejnik-Schmidt, A.; Czaczyk, K. Conversion of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol by Citrobacter freundii and Hafnia alvei—Newly isolated strains from the Enterobacteriaceae. New Biotechnol. 2014, 31, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsoviti, M.; Paramithiotis, S.; Drosinos, E.H.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Nychas, G.-J.E.; Zeng, A.-P.; Papanikolaou, S. Screening of bacterial strains capable of converting biodiesel-derived raw glycerol into 1,3-propanediol, 2,3-butanediol and ethanol. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Saab, V.; Matos, P.; Ribeiro, C.M.; Coelho, M.A. Evaluation of 1,3-propanediol production from glycerine by Clostridium butyricum NCIMB 8082. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 38, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Grzechulska-Damszel, J.; Bastrzyk, J.; Waszak, M. The study of glycerol-based fermentation and broth downstream by nanofiltration. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2014, 16, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homann, T.; Tag, C.; Biebl, H.; Deckwer, W.-D.; Schink, B. Fermentation of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella and Citrobacter strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1990, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelis, L.D. Ceramic membrane filtration of organic compounds: Effect of concentration, PH, and mixtures interactions on fouling. Sep. Purification Technol. 2013, 118, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, A.; Cambiella, Á.; Benito, J.M.; Pazos, C.; Coca, J. Ultrafiltration of oil-in-water emulsions with ceramic membranes: Influence of PH and crossflow velocity. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ahmad, R.; Kim, J. Alginate to simulate biofouling in submerged fluidized ceramic membrane reactor: Effect of solution PH and ionic strength. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





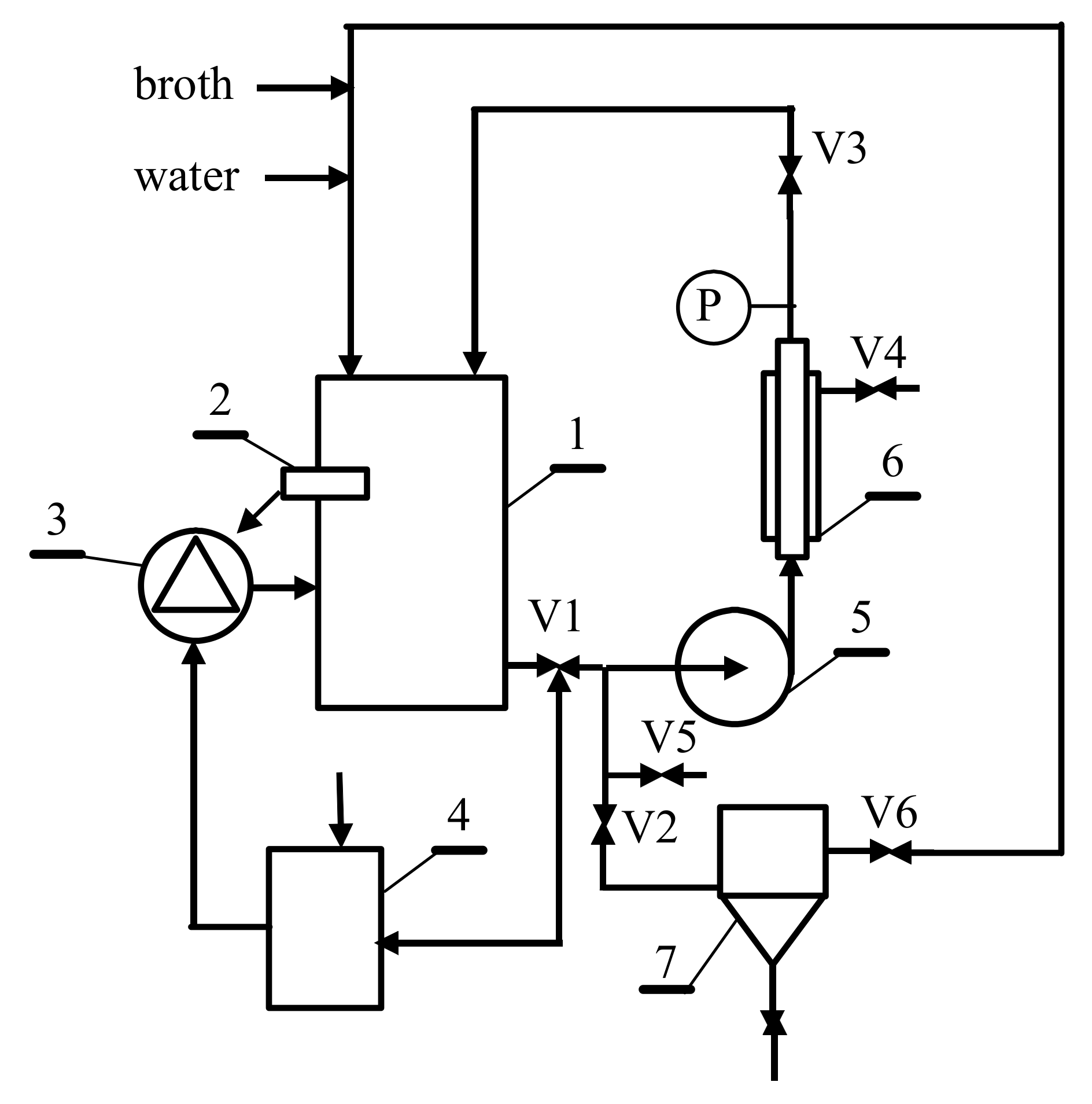
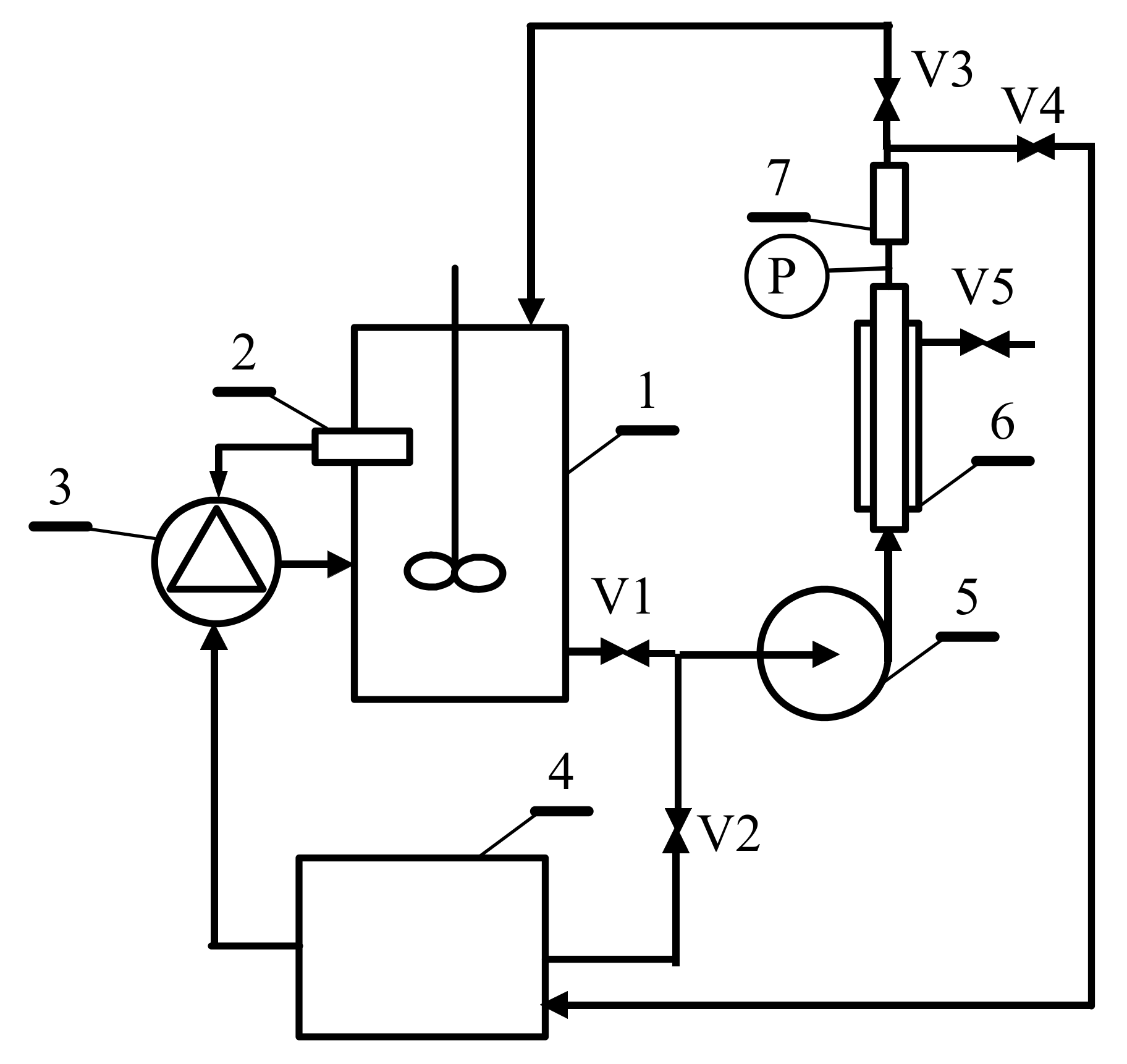
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Number of channels | (-) | 1 |
| Cutoff | (kDa) | 8 |
| External diameter | (mm) | 10 |
| Channel diameter | (mm) | 6 |
| Length | (mm) | 220 |
| Area | (m2) | 3.8 × 10–3 |
| Support material | (-) | TiO2 |
| Membrane material | (-) | ZrO2 |
| Step | Q (dm3/h) | TMP (MPa) | T (K) | t (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distilled water rinsing | 350 | 0 | 303 | 5 |
| 1% NaOH cleaning | 5 | |||
| Distilled water rinsing | 5 | |||
| 1% NaOH cleaning | 10 | |||
| Distilled water rinsing | 5 |
| Broth pH | Log CFU/mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Start | t = 30 min | t = 60 min | |
| 7.0 | 12.62 | 12.64 | 12.65 |
| 8.5 | 12.61 | 12.64 | 11.83 |
| 9.4 | 12.63 | 11.72 | 10.55 |
| 10.0 | 12.60 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczak, W.; Grubecki, I.; Gryta, M. The Use of NaOH Solutions for Fouling Control in a Membrane Bioreactor: A Feasibility Study. Membranes 2021, 11, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110887
Tomczak W, Grubecki I, Gryta M. The Use of NaOH Solutions for Fouling Control in a Membrane Bioreactor: A Feasibility Study. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110887
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczak, Wirginia, Ireneusz Grubecki, and Marek Gryta. 2021. "The Use of NaOH Solutions for Fouling Control in a Membrane Bioreactor: A Feasibility Study" Membranes 11, no. 11: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110887
APA StyleTomczak, W., Grubecki, I., & Gryta, M. (2021). The Use of NaOH Solutions for Fouling Control in a Membrane Bioreactor: A Feasibility Study. Membranes, 11(11), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110887







