Salvia miltiorrhiza Alleviates Memory Deficit Induced by Ischemic Brain Injury in a Transient MCAO Mouse Model by Inhibiting Ferroptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal
2.2. Induction of tMCAO in Mice
2.3. Experimental Groups and Drug Treatment
2.4. Neurological Deficit Scoring (mNSS) and Survival Rate
2.5. Quantification of Infarction Size
2.6. Neuroimaging
2.7. Behavior Test
2.7.1. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
2.7.2. Passive Avoidance Test (PAT)
2.8. Tissue Processing and Molecular Works
2.8.1. Tissue Preparation
2.8.2. Western Blot (WB)
2.8.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.8.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8.5. Nissl Staining
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
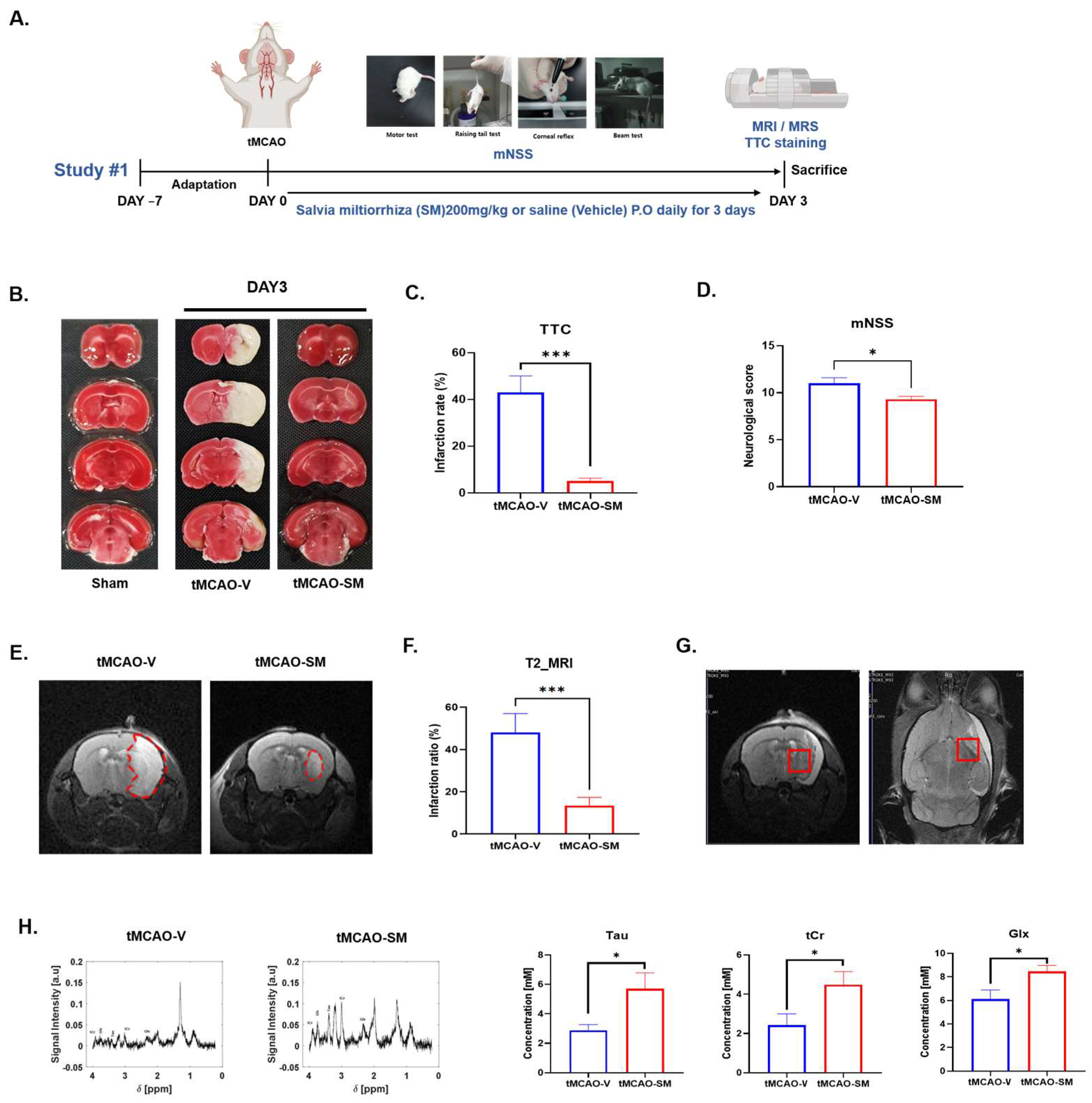
3.1. SM Administration Reduced Cerebral I/R Injury and Recovered Metabolites in tMCAO Mouse Brain
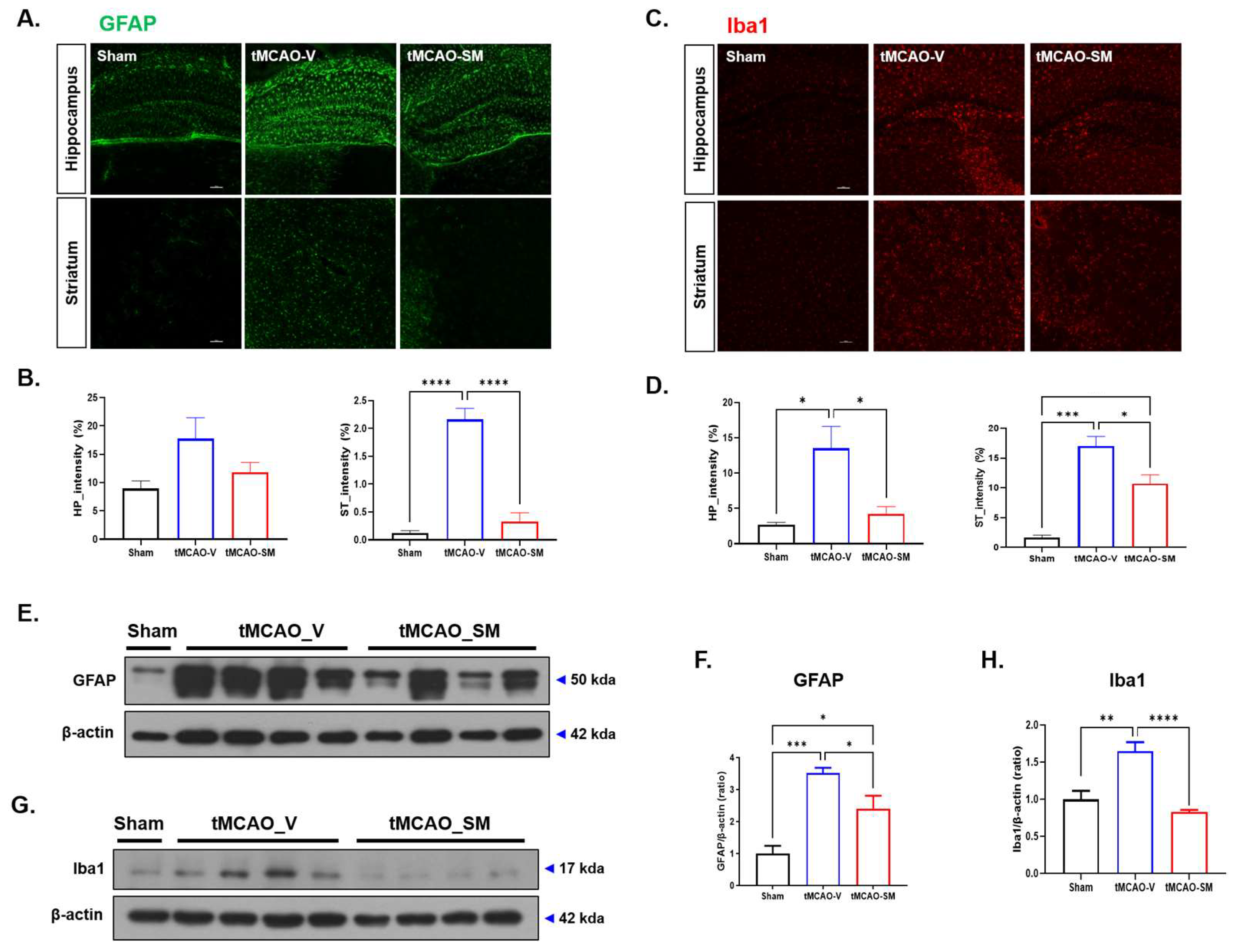
3.2. SM Administration Reduced Gliosis in tMCAO Mouse Brain
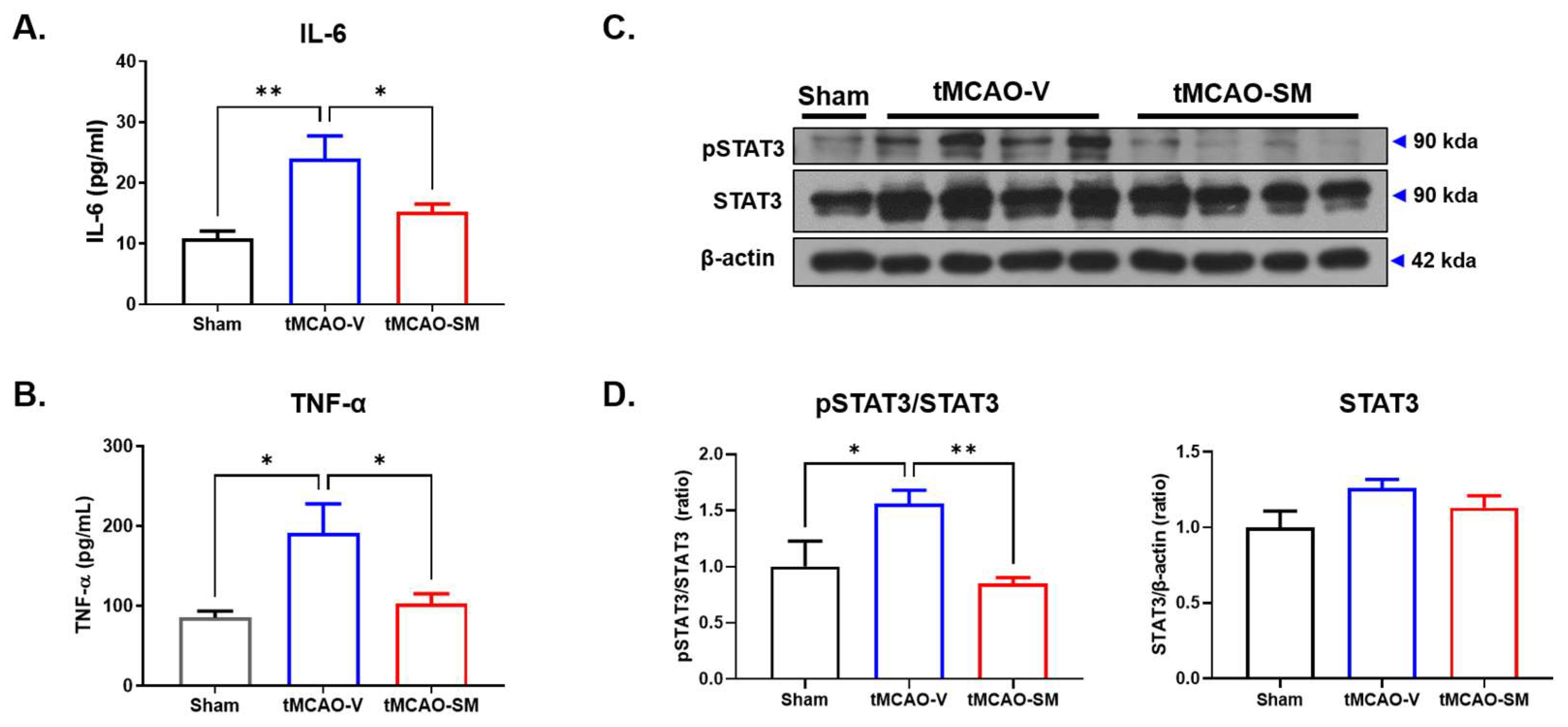
3.3. SM Administration Attenuated Inflammation in tMCAO Mouse Brain
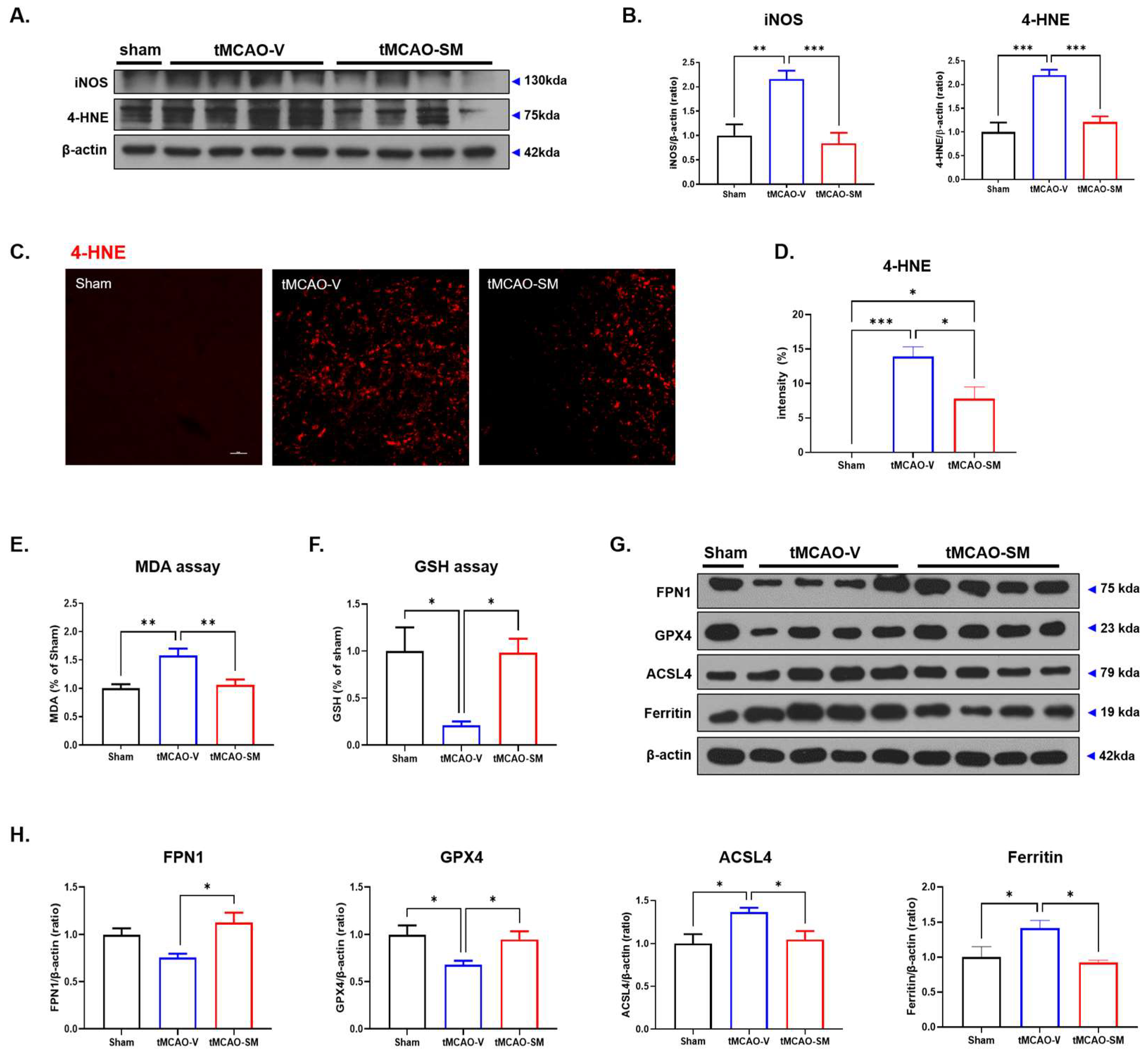
3.4. SM Administration Attenuated Oxidative Stress and Reduced Ferroptosis in tMCAO Mouse Brain
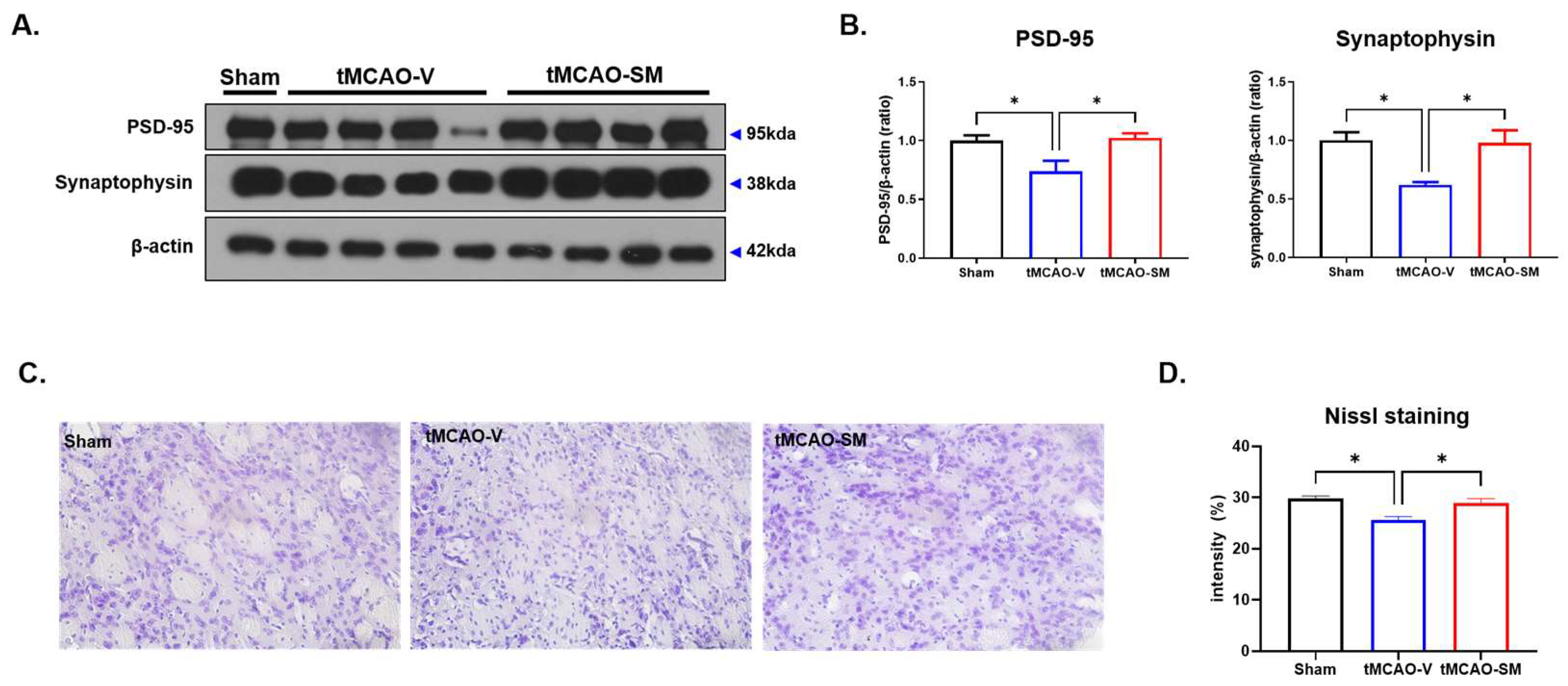
3.5. SM Administration Induced Synaptic Stability and Reduced Neuronal Loss in tMCAO Mouse Brain
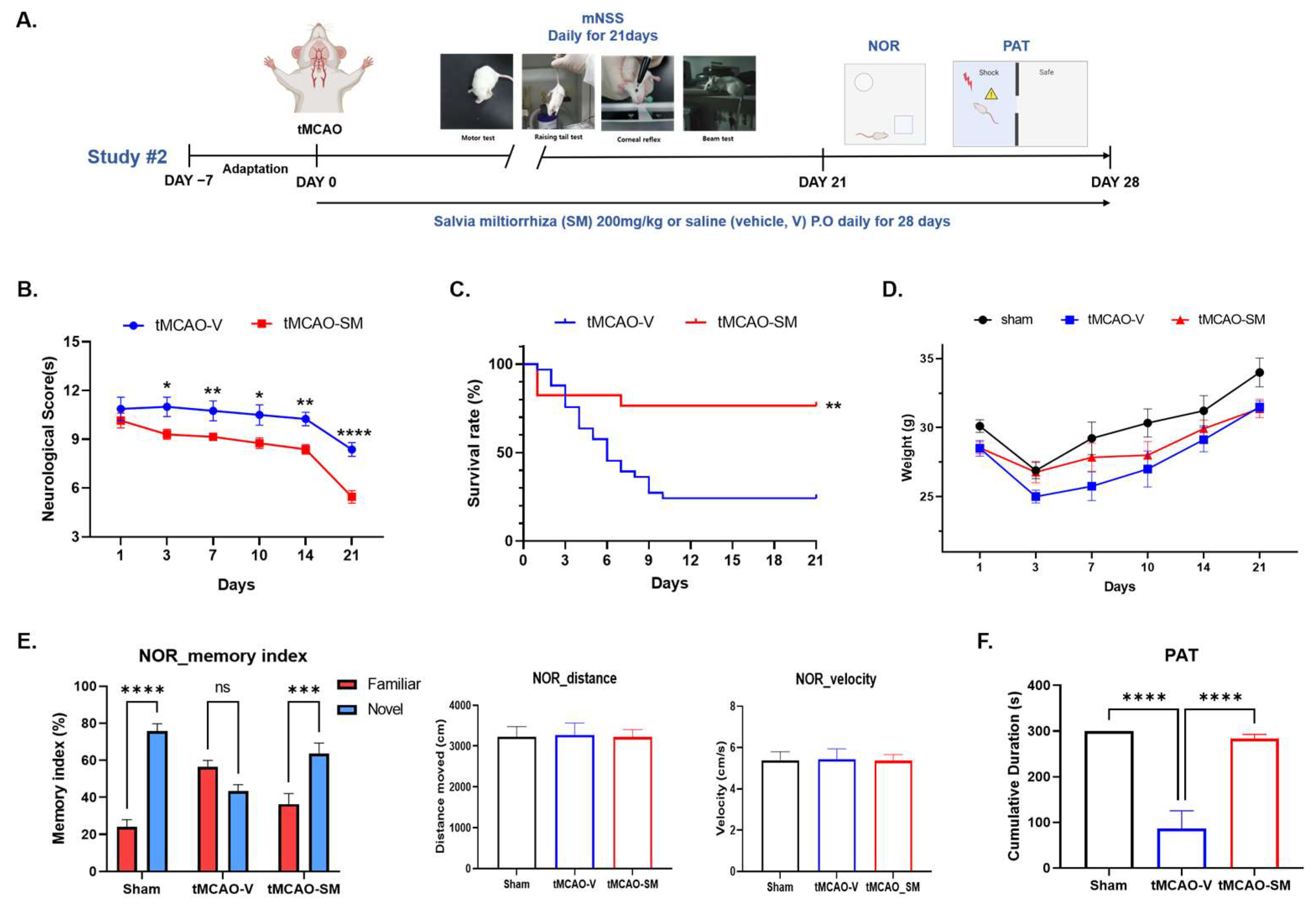
3.6. Repeated SM Administration Showed Long-Term Neuroprotective Effects against Brain Injures Following tMCAO
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, B.C.V.; De Silva, D.A.; Macleod, M.R.; Coutts, S.B.; Schwamm, L.H.; Davis, S.M.; Donnan, G.A. Ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpich, F.; Rincon, F. Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.W.; Crawford, J.D.; Desmond, D.W.; Godefroy, O.; Jokinen, H.; Mahinrad, S.; Bae, H.J.; Lim, J.S.; Kohler, S.; Douven, E.; et al. Profile of and risk factors for poststroke cognitive impairment in diverse ethnoregional groups. Neurology 2019, 93, e2257–e2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqueveque, P.; Ortega, P.; Pino, E.; Saavedra, F.; Germany, E.; Gómez, B. After Stroke Movement Impairments: A Review of Current Technologies for Rehabilitation. In Physical Disabilities—Therapeutic Implications; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, A.; Lenahan, C.; Chen, S. Ferroptosis: An emerging therapeutic target in stroke. J. Neurochem. 2022, 160, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Tai, B.; Li, W.; Li, T. Ferroptosis and Its Multifaceted Roles in Cerebral Stroke. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 615372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.X.; Li, C.; Yan, X.L.; Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.N. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Ferroptosis/Oxytosis in Ischemic Stroke: Possible Targets and Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6643382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.L.; Ding, S.Y.; Du, X.Z.; Wang, J.H.; Li, X.L. Ferroptosis-A Novel Mechanism With Multifaceted Actions on Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 881809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, Q.; Shu, Q. Targeting Ferroptosis as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhao, H.; Ren, K.; Feng, Q.; Xu, Y. New insights in ferroptosis: Potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1020918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalkovicova, M.; Danielisova, V. Neuroprotection and antioxidants. Neural. Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, S.; Ge, A.; Xu, H.; Zeng, J.; Ge, J. The mechanism of ferroptosis regulating oxidative stress in ischemic stroke and the regulation mechanism of natural pharmacological active components. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, L.; He, W.; Zhang, W. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of the AKT/GSK3beta signaling pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 193, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahonar, A.; Saadatnia, M.; Khorvash, F.; Maracy, M.; Khosravi, A. Carotenoids as Potential Antioxidant Agents in Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, R.; Ord, E.N.; Work, L.M. Oxidative Stress and the Use of Antioxidants in Stroke. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 472–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; He, L.F.; Li, Y.J.; Shen, Y.; Chao, R.B.; Du, J.R. Cardioprotective effect of water and ethanol extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza in an experimental model of myocardial infarction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Ming, Q.L.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L.P. Salvia miltiorrhiza: Traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, J.; Hao, S.; Ming, A.; Wang, X.; Su, F.; Zhang, Z. Salvianolic acid B attenuates apoptosis and inflammation via SIRT1 activation in experimental stroke rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 115, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Lin, S.G.; Zhou, Z.W.; Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Duan, W.; Yu, X.Q.; Wen, J.Y.; Chowbay, B.; Li, C.G.; et al. Tanshinone IIB, a primary active constituent from Salvia miltiorrhza, exhibits neuro-protective activity in experimentally stroked rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 417, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Hsieh, C.L. Pharmacological effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) on cerebral infarction. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meim, X.-D.; Cao, Y.F.; Che, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Shang, Z.P.; Zhao, W.J.; Qiao, Y.J.; Zhang, J.Y. Danshen: A phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U.; Iadecola, C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, R.; Li, B.; Gu, L.Y.; Gou, H. An in vivo and in vitro study: High-dosage Danshen injection induces peripheral vascular endothelial cells injury. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sanberg, P.R.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, M.; Willing, A.E.; Sanchez-Ramos, J.; Chopp, M. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 2682–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, J.; Nauerth, A.; Friedburg, H. RARE imaging: A fast imaging method for clinical MR. Magn. Reson. Med. 1986, 3, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottomley, P.A. Spatial localization in NMR spectroscopy in vivo. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1987, 508, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, I.; Starcuk, Z.; Choi, I.Y.; Gruetter, R. In vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy of rat brain at 1 ms echo time. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. A constrained regularization method for inverting data represented by linear algebraic or integral equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lim, D.K.; Suh, Y.H.; Chang, K.A. Long-Term Treatment of Cuban Policosanol Attenuates Abnormal Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response via Amyloid Plaques Reduction in 5xFAD Mice. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Zoppo, G.; Ginis, I.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Iadecola, C.; Wang, X.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Inflammation and stroke: Putative role for cytokines, adhesion molecules and iNOS in brain response to ischemia. Brain Pathol. 2000, 10, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lu, J.; Shao, A.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, J. Glial Cells: Role of the Immune Response in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; di Sciacca, R.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G. Inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3574–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Qiu, S. Interleukins and Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 828447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bi, R.; Sun, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, B.; Jin, H. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Acute Ischemic Stroke-Related Thrombosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 8418820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.O.; de Freitas, F.A.; Sampaio-Silva, J.; Rokita-Rosa, L.; Barros, P.L.; Levy, D.; Bydlowski, S.P. Ferroptosis Mechanisms Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Wong, H.Y.; Chai, Y.Y.; Shi, C.W.; Amino, N.; Kikuchi, S.; Huang, S.H. Lipid peroxidation dysregulation in ischemic stroke: Plasma 4-HNE as a potential biomarker? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, L.S.; Demir, S.; Rota, S.; Koseoglu, M. Increased serum malondialdehyde levels in chronic stage of ischemic stroke. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2006, 208, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Identification of ACSL4 as a biomarker and contributor of ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, P.; Levi, S. Ferritin, iron homeostasis, and oxidative damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Z.Q.; Yu, H.Y.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Cui, Y.R.; Feng, J.C.; Feng, J. Emerging Role of Ferroptosis in the Pathogenesis of Ischemic Stroke: A New Therapeutic Target? ASN Neuro 2021, 13, 17590914211037505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, A.; Dirnagl, U.; Urra, X.; Planas, A.M. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: Targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.H. Natural medicine in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Challenges and prospective. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 216, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yin, G.; Hu, Y.; Shi, S.; Jiang, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Tang, C.; Lyu, H. Coicis semen protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting angiogenesis via the TGFbeta/ALK1/Smad1/5 signaling pathway. Aging 2020, 13, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Talei, S.; Hassanzadeh, N.; Mokhtari, T.; Akbari, M.; Malek, F.; Jameie, S.B.; Sadeghi, Y.; Hassanzadeh, G. The Neuroprotective Effects of Flaxseed Oil Supplementation on Functional Motor Recovery in a Model of Ischemic Brain Stroke: Upregulation of BDNF and GDNF. Acta Med. Iran. 2017, 55, 785–792. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalakshmi, B.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lee, S.-D.; Maurya, N.; Kiefer, R.; Bharath Kumar, V. Review of Danshen: From its metabolism to possible mechanisms of its biological activities. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 85, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, K.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Yague, E.; Hu, Y. Exploration of the Mechanism of Salvianolic Acid for Injection Against Ischemic Stroke: A Research Based on Computational Prediction and Experimental Validation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 894427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Tanshinone IIA Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Microglial Activation and Polarization via NF-kappaB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 641848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, W. Cryptotanshinone possesses therapeutic effects on ischaemic stroke through regulating STAT5 in a rat model. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, I.B.; Anderson, M.A.; Song, B.; Levine, J.; Fernandez, A.; Gray-Thompson, Z.; Ao, Y.; Sofroniew, M.V. Glial scar borders are formed by newly proliferated, elongated astrocytes that interact to corral inflammatory and fibrotic cells via STAT3-dependent mechanisms after spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 12870–12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, H.; Li, Y.; Mamtilahun, M.; Liu, C.; Shi, R.; Lee, J.H.; Tian, H.; et al. Stroke subtype-dependent synapse elimination by reactive gliosis in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulke, E.; Gelderblom, M.; Magnus, T. Danger signals in stroke and their role on microglia activation after ischemia. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418774254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, B.; Schnell, A.; Liu, K.J. Normobaric hyperoxia delays and attenuates early nitric oxide production in focal cerebral ischemic rats. Brain Res. 2010, 1352, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shi, W.; Li, J.; Duan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, L.; Luo, Y. Chrysophanol attenuates nitrosative/oxidative stress injury in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 138, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, M.; Fan, L.; Lou, Z. Serum 4-hydroxynonenal associates with the recurrence of patients with primary cerebral infarction. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 998512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, L.; Martin, M.M.; Abreu-Gonzalez, P.; Ramos, L.; Argueso, M.; Sole-Violan, J.; Riano-Ruiz, M.; Jimenez, A. Serum malondialdehyde levels in patients with malignant middle cerebral artery infarction are associated with mortality. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Ogawa, N.; Asanuma, M.; Ota, Z.; Mori, A. Regional differences in late-onset iron deposition, ferritin, transferrin, astrocyte proliferation, and microglial activation after transient forebrain ischemia in rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1995, 15, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Comish, P.B.; Tang, D.; Kang, R. Characteristics and Biomarkers of Ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 637162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Zhang, J.J. The Emerging Roles of Ferroptosis in Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, G.; Sun, C.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Z. ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 93, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaris, D.; Barbouti, A.; Pantopoulos, K. Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: An intimate relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Yan, C.Z.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.S.; Chang, S.Y.; Yu, P.; Wu, W.S.; Zhao, C.Y.; Chang, Y.Z.; Duan, X.L. Hepcidin is involved in iron regulation in the ischemic brain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. Post-stroke cognitive impairment: Epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, B.; O’Neill, B.; Evans, J.J.; Coen, R.F.; Lawlor, B.A. A review of screening tests for cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.D.; Pang, P.; Zhou, X.T.; Hu, F.; Xiong, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, D.; Hu, Y.Z.; et al. Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1548–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, G.; Kim, J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, D.; Baek, H.-M.; Chang, K.-A. Salvia miltiorrhiza Alleviates Memory Deficit Induced by Ischemic Brain Injury in a Transient MCAO Mouse Model by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040785
Ko G, Kim J, Jeon Y-J, Lee D, Baek H-M, Chang K-A. Salvia miltiorrhiza Alleviates Memory Deficit Induced by Ischemic Brain Injury in a Transient MCAO Mouse Model by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(4):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040785
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Geon, Jinho Kim, Yeong-Jae Jeon, Donghun Lee, Hyeon-Man Baek, and Keun-A Chang. 2023. "Salvia miltiorrhiza Alleviates Memory Deficit Induced by Ischemic Brain Injury in a Transient MCAO Mouse Model by Inhibiting Ferroptosis" Antioxidants 12, no. 4: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040785
APA StyleKo, G., Kim, J., Jeon, Y.-J., Lee, D., Baek, H.-M., & Chang, K.-A. (2023). Salvia miltiorrhiza Alleviates Memory Deficit Induced by Ischemic Brain Injury in a Transient MCAO Mouse Model by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Antioxidants, 12(4), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040785








