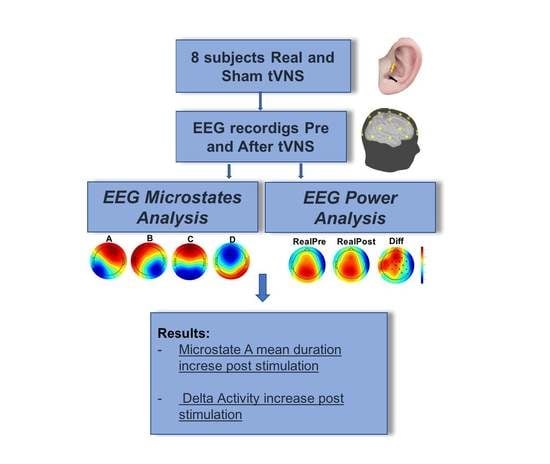
Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates and Delta Activity in Healthy Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. tVNS Procedure
2.4. Safety Evaluation
2.5. EEG Recordings
2.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.6.1. EEG Data Analysis
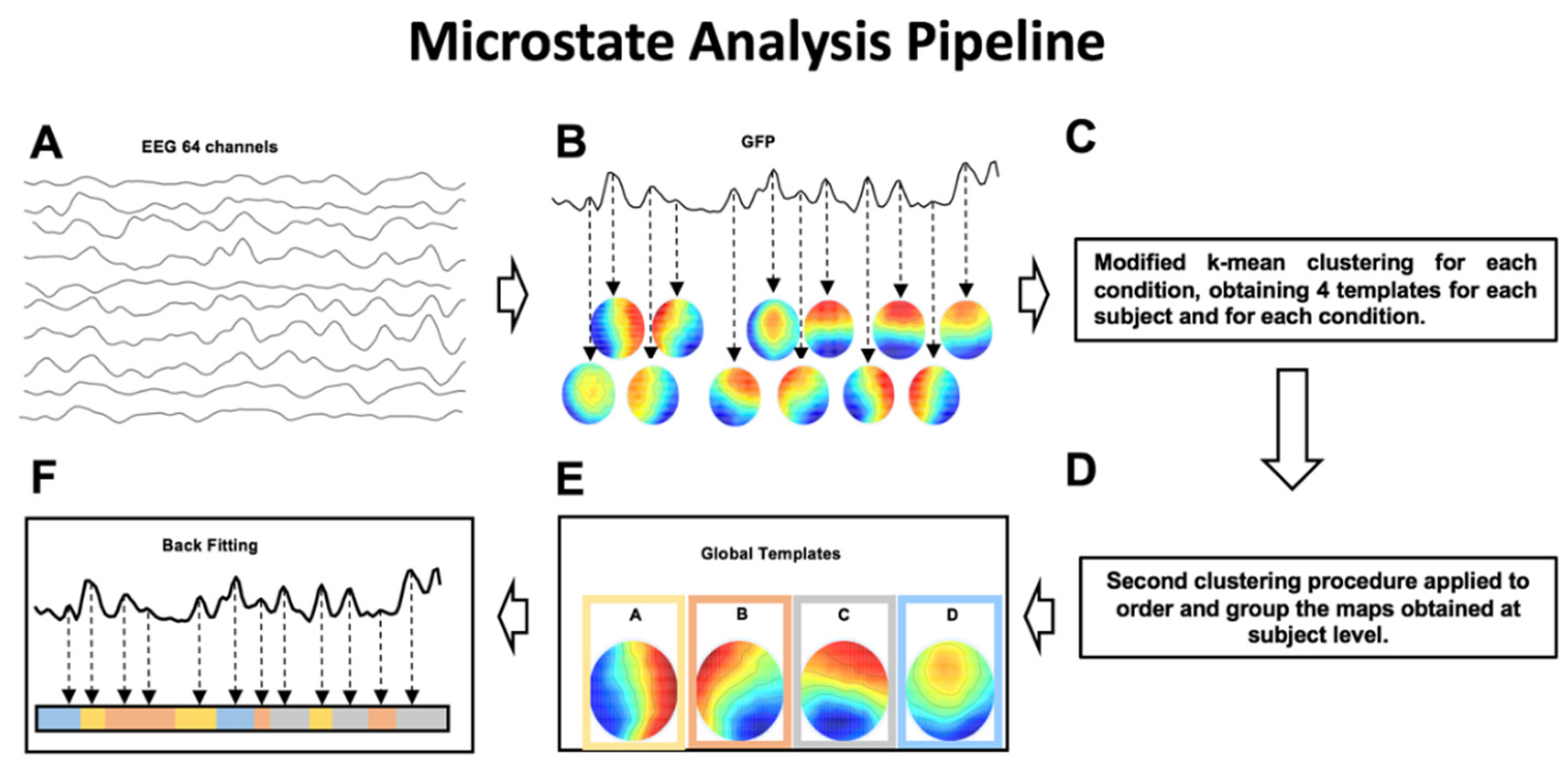
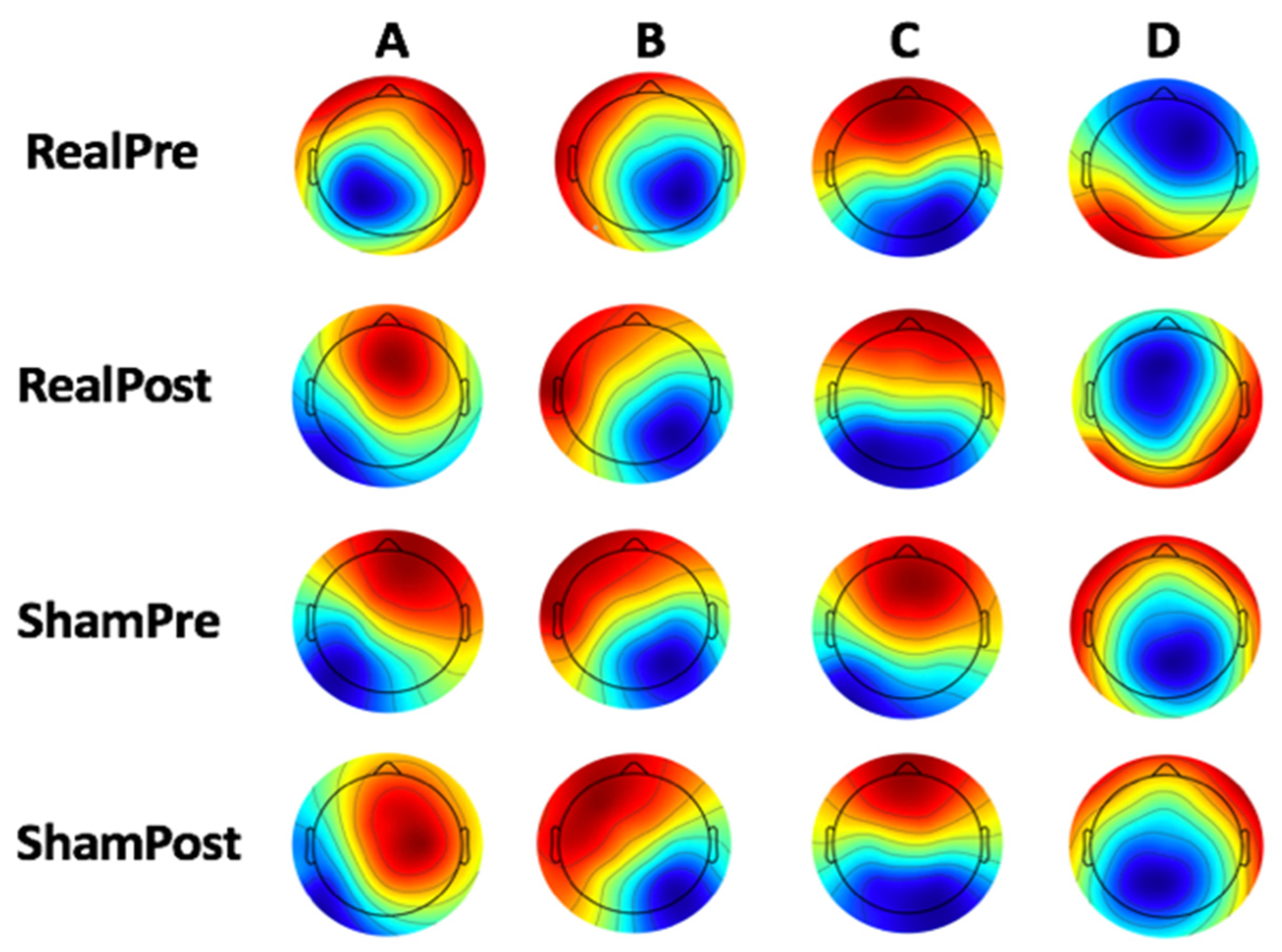
2.6.2. Microstates Analysis
- mean microstate duration (ms)—the average duration of each global microstate was calculated as the average time interval during which this microstate remained stable whenever it appeared [14];
- mean microstate occurrence (Hz)—the frequency with which each global microstate occurred, calculated as the average number of times per second that this microstate became dominant during the EEG time course; the microstate occurrence provides an indication of the tendency of the underlying neural generators to be activated and become dominant;
- mean microstate coverage (%)—for each global microstate, this metric was calculated as the fraction of the total recording time during which this microstate was dominant [14];
- global explained variance (GEV)—percent variance explained by each of the maps per experimental session (i.e., Real vs. Sham; at GFP peaks only).
2.6.3. Power Spectral Density Analysis
2.6.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Safety Measures and Tolerability
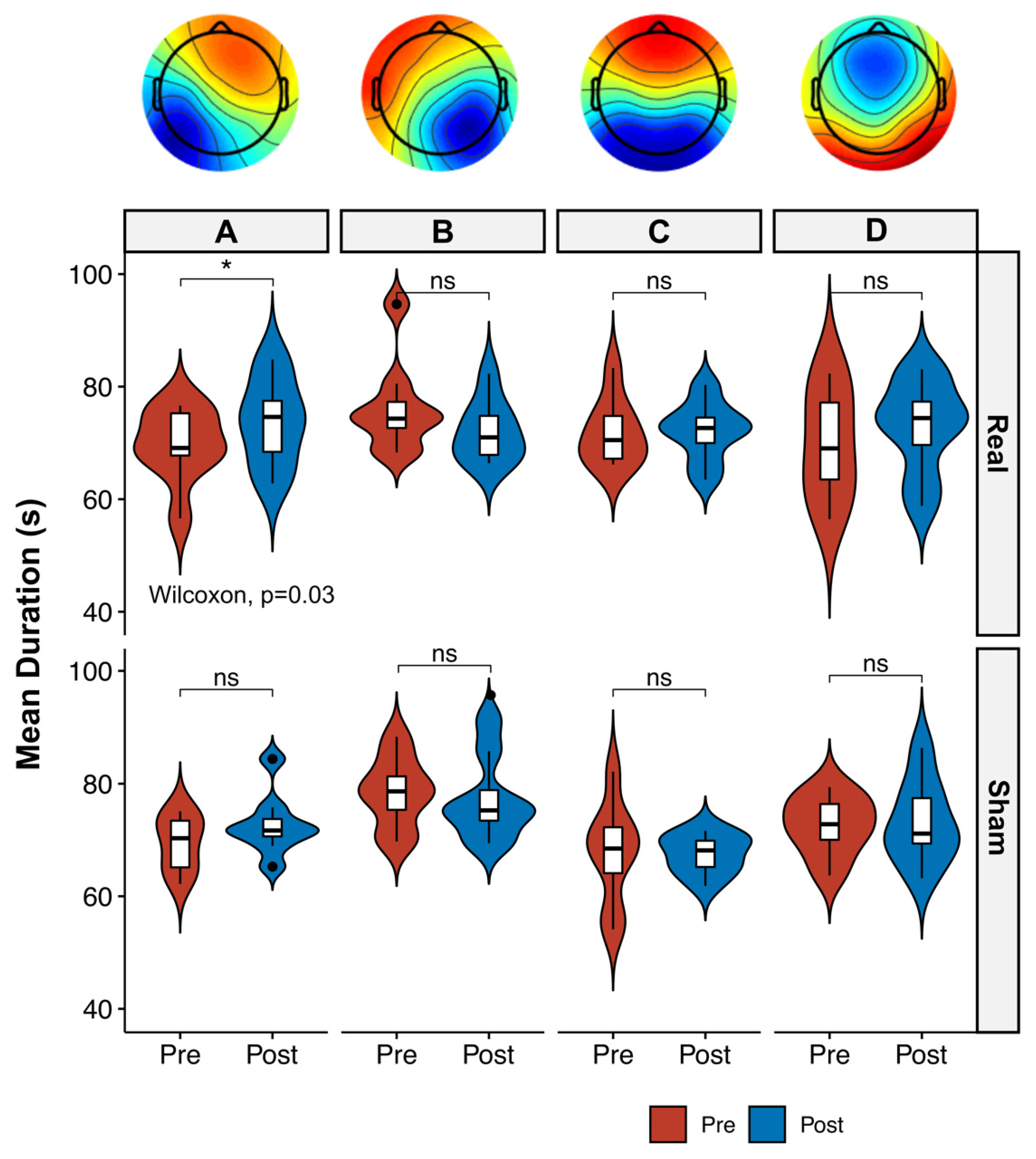
3.2. Microstate Analysis
3.3. Power Spectrum
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstate Metrics
4.2. Power Spectrum Activity
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Menachem, E. Vagus-nerve stimulation for the treatment of epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, S.; Bajbouj, M. Efficacy of vagus nerve stimulation in the treatment of depression. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenza, G.; Tombini, M.; Lanzone, J.; Ricci, L.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Casciato, S.; Morano, A.; Giallonardo, A.T.; Di Bonaventura, C.; Beghi, E. Antidepressant effect of vagal nerve stimulation in epilepsy patients: A systematic review. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, D.A.; Brown, V.J. Vagal nerve stimulation: A review of its applications and potential mechanisms that mediate its clinical effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, S.C. Vagus nerve stimulation: Mood and cognitive effects. Epilepsy Behav. 2004, 5, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borckardt, J.J.; Anderson, B.; Andrew Kozel, F.; Nahas, Z.; Richard Smith, A.; Jackson Thomas, K.; Kose, S.; George, M.S. Acute and long-term VNS effects on pain perception in a case of treatment-resistant depression. Neurocase 2006, 12, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventureyra, E.C.G. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation for partial onset seizure therapy. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2000, 16, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, T.; Kiess, O.; Hösl, K.; Terekhin, P.; Kornhuber, J.; Forster, C. CNS BOLD fMRI effects of sham-controlled transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in the left outer auditory canal—A pilot study. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Oliviero, A.; Pilato, F.; Saturno, E.; Dileone, M.; Meglio, M.; Colicchio, G.; Barba, C.; Papacci, F.; Tonali, P.A. Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on cortical excitability in epileptic patients. Neurology 2004, 62, 2310–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.M.; D’Agostini, M.; Verkuil, B.; Van Diest, I. Moving beyond belief: A narrative review of potential biomarkers for transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, H.M.; Bauer, S. Lessons learned from transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS). Epilepsy Res. 2019, 153, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, G.; Mecarelli, O.; Pulitano, P.; Tombini, M.; Ricci, L.; Lanzone, J.; Brienza, M.; Davassi, C.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Assenza, G. Eslicarbazepine Acetate Modulates EEG Activity and Connectivity in Focal Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanna, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Michel, C.M.; Farzan, F. Microstates in resting-state EEG: Current status and future directions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, D.; Ozaki, H.; Pal, I. EEG alpha map series: Brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 67, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.M.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Topographic ERP analyses: A step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr. 2008, 20, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.J.; Keel, J.C.; Greenberg, B.D.; Adams, L.F.; Schmidt, P.J.; Rubinow, D.A.; Wassermann, E.M. Menstrual cycle effects on cortical excitability. Neurology 1999, 53, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, F.; Assenza, G.; Di Pino, G.; Musumeci, G.; Ranieri, F.; Florio, L.; Barbato, C.; Di Lazzaro, V. The effect of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on cortical excitability. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallgatter, A.J.; Neuhauser, B.; Herrmann, M.J.; Ehlis, A.-C.; Wagener, A.; Scheuerpflug, P.; Reiners, K.; Riederer, P. Far field potentials from the brain stem after transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. J. Neural Transm. 2003, 110, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeroff, C.B.; Mayberg, H.S.; Krahl, S.E.; McNamara, J.; Frazer, A.; Henry, T.R.; George, M.S.; Charney, D.S.; Brannan, S.K. VNS therapy in treatment-resistant depression: Clinical evidence and putative neurobiological mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Baker, W.; Hiraki, T.; Greenberg, J.H. The effect of right vagus nerve stimulation on focal cerebral ischemia: An experimental study in the rat. Brain Stimul. 2012, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polak, T.; Markulin, F.; Ehlis, A.-C.; Langer, J.B.M.; Ringel, T.M.; Fallgatter, A.J. Far field potentials from brain stem after transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation: Optimization of stimulation and recording parameters. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Croce, P.; Zappasodi, F.; Marzetti, L.; Merla, A.; Pizzella, V.; Chiarelli, A.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for feature-less automatic classification of Independent Components in multi-channel electrophysiological brain recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, P.; Quercia, A.; Costa, S.; Zappasodi, F. EEG microstates associated with intra-and inter-subject alpha variability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koenig, T.; Lehmann, D.; Merlo, M.C.G.; Kochi, K.; Hell, D.; Koukkou, M. A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1999, 249, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custo, A.; Van De Ville, D.; Wells, W.M.; Tomescu, M.I.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Electroencephalographic resting-state networks: Source localization of microstates. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage-Castellanos, A.; Martínez-Montes, E.; Hernández-Cabrera, J.A.; Galán, L. False discovery rate and permutation test: An evaluation in ERP data analysis. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, J.; Van De Ville, D.; Michel, C.M. BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.; Milz, P.; Kochi, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Nishida, K.; Isotani, T.; Kinoshita, T. The resting microstate networks (RMN): Cortical distributions, dynamics, and frequency specific information flow. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1949. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. Neuroimage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappasodi, F.; Perrucci, M.G.; Saggino, A.; Croce, P.; Mercuri, P.; Romanelli, R.; Colom, R.; Ebisch, S.J.H. EEG microstates distinguish between cognitive components of fluid reasoning. Neuroimage 2019, 189, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschwind, M.; Hardmeier, M.; Van De Ville, D.; Tomescu, M.I.; Penner, I.-K.; Naegelin, Y.; Fuhr, P.; Michel, C.M.; Seeck, M. Fluctuations of spontaneous EEG topographies predict disease state in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomescu, M.I.; Rihs, T.A.; Roinishvili, M.; Karahanoglu, F.I.; Schneider, M.; Menghetti, S.; Van De Ville, D.; Brand, A.; Chkonia, E.; Eliez, S. Schizophrenia patients and 22q11. 2 deletion syndrome adolescents at risk express the same deviant patterns of resting state EEG microstates: A candidate endophenotype of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. Cogn. 2015, 2, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüders, H.O.; Najm, I.; Nair, D.; Widdess-Walsh, P.; Bingman, W. The epileptogenic zone: General principles. Epileptic Disord. 2006, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Assenza, G.; Pellegrino, G.; Tombini, M.; Di Pino, G.; Di Lazzaro, V. Wakefulness delta waves increase after cortical plasticity induction. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenza, G.; Capone, F.; di Biase, L.; Ferreri, F.; Florio, L.; Guerra, A.; Marano, M.; Paolucci, M.; Ranieri, F.; Salomone, G. Oscillatory activities in neurological disorders of elderly: Biomarkers to target for neuromodulation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, F.; Miccininilli, S.; Pellegrino, G.; Zollo, L.; Guglielmelli, E.; Sterzi, S.; Di Lazzaro, V. Combining Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Upper-Limb Robotic Rehabilitation in Chronic Stroke Patients. Brain Stimul. Basic Transl. Clin. Res. Neuromodul. 2019, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercia, A.; Zappasodi, F.; Committeri, G.; Ferrara, M. Local use-dependent sleep in wakefulness links performance errors to learning. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gloor, P.; Ball, G.; Schaul, N. Brain lesions that produce delta waves in the EEG. Neurology 1977, 27, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariai, H.; Matsuzaki, N.; Juhász, C.; Nagasawa, T.; Sood, S.; Chugani, H.T.; Asano, E. Ictal high-frequency oscillations at 80–200 Hz coupled with delta phase in epileptic spasms. Epilepsia 2011, 52, e130–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steriade, M. Coherent oscillations and short-term plasticity in corticothalamic networks. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursin, R. Serotonin and sleep. Sleep Med. Rev. 2002, 6, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nitz, D.; Siegel, J. GABA release in the dorsal raphe nucleus: Role in the control of REM sleep. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1997, 273, R451–R455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wostyn, S.; Staljanssens, W.; De Taeye, L.; Strobbe, G.; Gadeyne, S.; Van Roost, D.; Raedt, R.; Vonck, K.; van Mierlo, P. EEG derived brain activity reflects treatment response from vagus nerve stimulation in patients with epilepsy. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2017, 27, 1650048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricci, L.; Croce, P.; Lanzone, J.; Boscarino, M.; Zappasodi, F.; Tombini, M.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Assenza, G. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates and Delta Activity in Healthy Subjects. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100668
Ricci L, Croce P, Lanzone J, Boscarino M, Zappasodi F, Tombini M, Di Lazzaro V, Assenza G. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates and Delta Activity in Healthy Subjects. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100668
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicci, Lorenzo, Pierpaolo Croce, Jacopo Lanzone, Marilisa Boscarino, Filippo Zappasodi, Mario Tombini, Vincenzo Di Lazzaro, and Giovanni Assenza. 2020. "Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates and Delta Activity in Healthy Subjects" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100668
APA StyleRicci, L., Croce, P., Lanzone, J., Boscarino, M., Zappasodi, F., Tombini, M., Di Lazzaro, V., & Assenza, G. (2020). Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates and Delta Activity in Healthy Subjects. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100668