Featured Application
This study reveals the potential of microwave-assisted processing as a promising pre-treatment strategy to enhance the nutritional profile and technological value of acorn flour in baked goods. The results may be applied in the development of value-added bakery products with improved antioxidant properties and cleaner-label formulations, contributing to the differentiation of functional ingredients in the food industry.
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of microwave treatment on the physical properties and bioactive compound content of acorn flour and its subsequent effects on the quality of muffins. Acorn flour, both dry and hydrated (flour-to-water mixture = 1:1, w/v), was subjected to microwave processing at varying power levels (925, 1295, and 1850 W) and exposure times (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 3.0 min). The treated flour was incorporated into composite wheat–acorn muffins, which were analyzed for key physical attributes, including volume, porosity, crumb firmness, and color. In addition, the chemical composition of the muffins was assessed, with a particular focus on antioxidant activity and the content of bioactive compounds such as total free phenolics, flavonoids, and tannins. The results indicated that microwave treatment significantly influenced the antioxidant potential and technological properties of acorn flour-based muffins. Microwave treatment at 925 W for 3 min or 1295 W for 1.5 min under moist conditions resulted in muffins with enhanced antioxidant capacity (e.g., an increase in total free phenolics by up to 61.4% and flavonoids by up to 135.9%, and a reduction in tannin content by up to 38.2%), as well as improved volume and sensory acceptance. However, high-power treatment (1850 W) negatively affected muffin volume, porosity, and firmness. These findings emphasize the effectiveness of controlled microwave processing in improving both the nutritional and technological qualities of bakery products enriched with acorn flour.
1. Introduction
According to statistical data, the global population is steadily increasing. In 2024, it reached 8.16 billion, and projections indicate that it may rise to 10.18 billion by 2100 [1,2]. When considered in the context of the ongoing climate crisis—which negatively impacts primary food production and poses a significant threat to global food security [3]—it becomes evident that substantial changes to the current global food system are necessary [4,5]. The use of unconventional food sources has been identified as one potential approach to addressing food security challenges [6].
Oak fruits (Quercus spp.) represent an example of such unconventional food sources. They are rich in starch and also contain considerable amounts of dietary fiber, minerals, and bioactive compounds [7,8,9,10]. Historical and archaeological studies suggest that acorns were consumed from prehistoric times through the 19th and 20th centuries, typically prepared using relatively simple methods adapted to specific cultural and regional contexts [11,12,13]. Despite their historical significance, acorns are rarely used in the modern food industry [9]. However, increasing interest in functional foods—defined as foods that provide additional health benefits beyond their basic nutritional value—and the revival of traditional processing methods have renewed attention to acorns as a potentially valuable dietary component [13].
One of the primary factors limiting the consumption of acorns is their high content of tannins—phenolic compounds responsible for their characteristic astringent and bitter taste. These compounds are natural plant defense compounds that deter herbivores and inhibit premature seed germination [14,15]. Tannins remain controversial among plant bioactive compounds due to their antinutritional effects and potential health risks when consumed in excessive amounts [15,16]. Nevertheless, growing evidence supports their preventive and therapeutic roles in human health [14,17,18,19].
Due to their high tannin content, raw acorns are generally unsuitable for direct consumption. However, several traditional methods have been developed to reduce their bitterness. These include prolonged soaking in water, which facilitates tannin leaching, and fermentation processes that promote tannin degradation [12]. Thermal treatments such as roasting, boiling, and drying also contribute to the reduction in tannins but may simultaneously affect the nutritional profile of acorn-based products, including acorn flour [20,21,22].
Recent studies have focused on the application of modern processing techniques, such as microwave treatment, in the production of various flours to improve their properties, e.g., whole wheat flour [23], rice flour [24], chickpea flour [25], flaxseed flour [26], and pumpkin flour [27]. Unlike conventional heating methods, microwave heating is volumetric in nature—heat is generated internally throughout the material rather than transferred from an external surface [28,29]. This process influences the structure and chemical composition of food through several mechanisms, including protein denaturation, structural modification of polysaccharides (affecting digestibility), thermal degradation or release of phenolic compounds, alterations in starch and fiber structures, and a reduction in enzymatic activity, which may slow undesirable reactions such as lipid hydrolysis [29,30,31].
The scientific literature reports various effects of microwave processing on tannin content in plant-based raw materials. For example, El-Geddawy et al. [32] found that microwave heating for 1–2 min at 9295 MHz reduced tannin content in oilseeds (peanut, sesame, soybean, safflower, and sunflower) by 8.8% to 24.4%, depending on the material and processing duration. Bhat et al. [25] observed a reduction in tannin content ranging from 4.0% to 38.9% in chickpea flour (sattu) treated with microwave power from 450 to 900 W for 5–30 min, accompanied by an increase in total phenolic content from 72.1 to 239.1%. Waseem et al. [33] reported an 84% reduction in tannin content in potato flour subjected to microwave processing at 1.1 kW for 2 min. Similarly, Javed et al. [34] demonstrated that microwave pre-treatment of soybean seeds (0.9 kW, 1.5 min) prior to flour production led to an 88% reduction in tannin content. In this case, total phenolic content decreased (from 368 to 330 mg GAE (gallic acid equivalent)/100 g), while total flavonoid content remained relatively stable (90 to 88 mg GAE/100 g). In contrast, Hassan et al. [35] found that microwave treatment of sorghum seeds (400 and 700 W for 15 and 30 s) had no statistically significant effect on tannin, phenolic, or flavonoid content. However, to date, no studies have specifically investigated the impact of microwave treatment on tannin content in acorns or acorn flour.
Although the degradation of tannins is a desirable outcome of microwave treatment of acorn flour, its impact on other bioactive phenolic compounds must also be considered. Microwave processing can both enhance and degrade phenolic compounds, depending on the processing parameters and the physicochemical properties of the raw material. Alterations in the phenolic profile have been documented; selected phenolic acids, flavonoids, and flavanols may be either released or degraded depending on the power and duration of heating. Compounds such as quercetin and myricetin, which are sensitive to high temperatures, may degrade under microwave exposure, whereas others such as gallic acid may be liberated from hydrolyzable tannins [28,29,36]. Therefore, optimizing microwave treatment conditions is critical to achieving the desired reduction in antinutritional factors while preserving or enhancing beneficial bioactive compounds.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of microwave treatment on the physical properties and bioactive compound content of acorn flour. Acorn flour was subjected to microwave heating at varying power levels and durations. The treated flour was then incorporated into wheat–acorn muffins, which were analyzed for their organoleptic (color, aroma, taste, and texture) and physical properties (volume, porosity, crumb firmness, and color). A key aspect of this study involved analyzing how microwave treatment influenced the chemical composition of the muffins, specifically focusing on the concentrations of free phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and tannins, along with their associated antioxidant activity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Commercially available acorn flour (Dary Natury, Koryciny, Poland) was used as the primary experimental material in this study. The flour was subjected to microwave treatment and subsequently incorporated into wheat–acorn muffins as a functional enrichment ingredient. In addition to acorn flour, the muffin formulation consisted of refined wheat flour (Polskie Młyny, Warsaw, Poland), water, sugar (Polski Cukier, Toruń, Poland), whole hen eggs (Eko-Kluczek, Łomża, Poland), rapeseed oil (Bunge Polska Sp. z o.o., Kruszwica, Poland), baking powder (Delecta, Włocławek, Poland), vanilla sugar (Delecta, Włocławek, Poland), and salt (Cenos, Września, Poland).
2.2. Acorn Flour Microwaving
Acorn flour was subjected to both dry and wet microwave treatments. For the dry treatment, 40 g of flour was placed in 10-centimeter-diameter glass Petri dishes. For the wet treatment, 50 g of flour was mixed with 50 mL of water (1:1 w/v ratio) and transferred to sealable, glass, microwave-safe containers measuring 8.5 × 8.5 × 5 cm. Microwave processing was performed at power levels of 925 W (for durations ranging from 1.0 to 3.0 min), 1295 W (for durations ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 min), and 1850 W (for 0.5 and 1.0 min). The specific power levels and exposure times were selected based on preliminary tests, in which acorn flour was subjected to microwave heating at power levels ranging from 400 to 1850 W and for durations between 0.5 and 10 min. Samples for the main experiment were chosen based on the sensory evaluation of the treated flour, with particular attention given to color and odor.
2.3. Wheat–Acorn Muffins Preparation
The ratio of acorn flour to wheat flour in the muffin formulation was 50:50 (w/w), based on the dry matter content of each flour type. The proportion of acorn flour used in muffin preparation was determined based on preliminary trials, in which the acorn flour content ranged from 10% to 70%. Based on the evaluation of its impact on the baking quality, a 50% substitution was found to provide a satisfactory enhancement of antioxidant properties without significantly compromising the physical or sensory attributes of the final product.
The amount of water added was established experimentally, taking into account the moisture content of the acorn flour. It was assumed that optimal muffin volume and texture could be achieved by adding 1.2 g of water per 1 g of dry matter in the acorn flour. The proportions of the remaining ingredients were kept constant across all formulations: sugar (50 g), whole hen eggs (30 g), rapeseed oil (40 mL), baking powder (4 g), vanilla sugar (4 g), and salt (0.5 g).
All muffin variants were prepared using the same standardized procedure. First, the dry ingredients were mixed. The eggs were whipped with sugar using a stand mixer equipped with a whisk attachment (JAZ S.R.O., Nové Mesto nad Váhom, Slovakia) for 5 min until a light and fluffy consistency was achieved. Rapeseed oil was then gradually added in a thin stream while mixing continuously. Subsequently, water and the dry ingredient mixture were incorporated, and the dough was mixed until homogeneous. The mixture was portioned into silicone muffin molds at 30 g per portion. Baking was conducted at 180 °C for 25 min in a modular Quail Mini Piccolo 4 bakery and confectionery oven (Wachtel, Hilden, Germany). In total, sixteen experimental muffin variants were prepared using acorn flour subjected to microwave treatment under various conditions, along with one control sample containing untreated acorn flour.
For sample identification, we used the following abbreviations and codes: AF—acorn flour; 0—control samples; W—wet microwave treatment; 925, 1295, 1850—microwave power (in watts); 0.5…3.0—microwave processing time (in minutes).
2.4. Determination of Water Content in Acorn Flour
The water content in acorn flour was determined according to AOAC Method 925.10 [37]. A 2 g sample of flour was weighed into a weighing vessel and placed in a Binder FD 115 air-drying oven (Binder GmbH, Tuttlingen, Germany) at 130 °C for 1 h. Drying was repeated until a constant flour mass was achieved.
2.5. Assessment of Flour and Muffin Color Parameters
The color assessment of flour and baked products was conducted using a Hunter ColorFlex EZ spectrophotocolorimeter (HunterLab, Reston, VA, USA). Color measurements were recorded in the CIE L*a*b* color space, where L* represents lightness (ranging from 0 = darkest to 100 = lightest); a* represents the green–red axis (negative values = green, positive values = red); b* represents the blue–yellow axis (negative values = blue, positive values = yellow). In the case of muffins, color was measured separately for the crust and the crumb.
2.6. Measurement of Muffin Crumb Firmness
Crumb firmness was assessed using a TA.HDplus texture analyzer (Stable Micro Systems Ltd., Godalming, UK) in accordance with AACC Standard Method 74-09 [38]. Cubes measuring 25 × 25 × 25 mm were cut from the center of each muffin and subjected to a compression test using a P/36R cylindrical probe. The probe operated at a test speed of 1.7 mm/s and applied a compressive force until the sample was deformed to 25% of its original height. Crumb firmness was expressed as the maximum force (N) required to achieve this level of compression.
2.7. Determination of Muffin Volume
The muffin volume was measured instrumentally using a TexVol BVM 6630 device (Perten Instruments, Hägersten, Sweden). The volume of whole muffins was determined by placing them on a rotating support inside the device. Measurements were performed using laser topography technology where a laser sensor, mounted on a movable arm scanning in a semicircular motion, recorded the muffin dimensions.
2.8. Determination of Muffin Crumb Porosity
The porosity of muffin crumbs was assessed using the Jacobi method, as described in Marciniak-Lukasiak et al. [39]. Cubes with a side length of 3 cm were cut from the center of the muffins. These crumb cubes were then broken down into smaller pieces and compressed by hand until compact, air-free crumb balls were obtained. A 100 cm3 graduated cylinder was filled with 30 cm3 of oil. The crumb balls were then immersed in the oil, and their volume was determined based on the difference in oil levels before and after immersion. Crumb porosity was mathematically calculated as the percentage of pores in the crumb structure using the following formula:
where:
- Vp—volume of the porous crumb (cm3);
- Vnp—volume of the compressed (non-porous) crumb (cm3).
2.9. Organoleptic Evaluation of Muffins
The organoleptic evaluation of the muffins was carried out following the method described by Zdybel et al. [40], with minor modifications. The assessment was conducted in a sensory analysis laboratory under controlled environmental conditions: natural lighting, an ambient temperature of 22 °C, and a relative humidity of 65%. A panel of 20 trained evaluators, aged between 20 and 45 years, participated in this study. A key inclusion criterion for panelists was a non-smoking status.
The baked goods were assessed using a 5-point hedonic scale, where 5 = “I like it very much” and 1 = “I dislike it very much”. The following quality parameters of muffins were evaluated: color, aroma, taste, and texture. Based on these parameters, overall acceptance was determined using the following coefficients: color = 0.2, aroma = 0.3, taste = 0.3, and texture = 0.2.
2.10. Extraction of Antioxidant Compounds
The extraction of antioxidant compounds, primarily free phenolic compounds, from flour and product samples was performed according to the method described by Konopka et al. [41], with modifications. A 100 mg (±0.01 g) sample was extracted three times with 1.0 mL of 80% methanol. The mixture was shaken at 1400 rpm for 10 min at 30 °C using a Thermomixer (Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany) and subsequently centrifuged at 25,000× g in an Eppendorf 5417R centrifuge (Eppendorf AG) for 10 min. The combined supernatants were evaporated to dryness at 45 °C using a Büchi R-210 rotary evaporator (BÜCHI Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland) under reduced pressure. The resulting dry extract was reconstituted in 5 mL of methanol.
2.11. Determination of Total Free Phenolic Content
The total content of free phenolic compounds was determined according to the method described by Konopka et al. [41]. The reaction mixture was prepared by combining 0.5 mL of the methanolic extract solution (prepared as described in Section 2.10), 0.5 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent diluted with deionized water (1:2, v/v), 3.5 mL of 14% sodium carbonate solution, and deionized water to a final volume of 10 mL. The mixture was stirred and then left to stand in the dark for 60 min. After incubation, the solution was centrifuged, and absorbance was measured at 720 nm against a reagent blank (prepared using methanol instead of the extract solution) using a multifunctional microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega v. 1.30, BMG LABTECH, Offenburg, Germany). The total free phenolic content was calculated from a calibration curve constructed using gallic acid and expressed as mg per 100 g of dry matter (mg/100 g d.m.). All analyses were conducted in triplicate.
2.12. Determination of Total Free Flavonoids
The total free flavonoid content was determined spectrophotometrically according to Makhlouf et al. [42] with modifications. A total of 100 μL of the extract (prepared as described in Section 2.10) was mixed with 400 μL of deionized water and 30 μL of a 5% NaNO2 solution. The samples were allowed to stand for 6 min, after which 30 μL of a 10% AlCl3 solution was added and left for an additional 6 min. Then, 400 μL of 2 M NaOH solution was added to the mixture, and distilled water (40 μL) was added to a final volume of 1 mL. The samples were incubated at room temperature for 15 min, and the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 510 nm against the reagent blank using a multifunctional microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega). The total flavonoid content in muffins was calculated from a calibration curve prepared with catechin and expressed in mg/100 g of dry matter (mg/100 g d.m.).
2.13. Determination of Tannin Content
Tannin content in the samples was determined using the conventional HCl–vanillin colorimetric assay, as described by Herald et al. [43], with modifications. For sample preparation, approximately 0.2 g of flour or muffin was extracted with 8 mL of 1% hydrochloric acid (HCl) in methanol for 20 min in a water bath at 30 °C. The resulting extracts were centrifuged at 12,333× g in an Eppendorf 5810R centrifuge (Eppendorf AG) for 10 min, and the supernatant was collected for analysis.
For the assay, a 1 mL aliquot of extract was transferred into two separate test tubes designated as the sample and the sample control. Both tubes were pre-incubated at 30 °C for approximately 5 min in a water bath. A freshly prepared working vanillin reagent—composed of equal volumes of 1% vanillin and 8% HCl solutions—was added in a volume of 5.0 mL to the sample tube at precise 1-minute intervals. In parallel, 5.0 mL of 4% HCl was added to the sample control. All tubes were then incubated at 30 °C for exactly 20 min. After incubation, the absorbance was measured at 500 nm using a multifunctional microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega), with methanol serving as the reference blank. Final absorbance values were obtained by subtracting the absorbance of the control from that of the corresponding sample. Tannin concentration was quantified based on a standard calibration curve prepared with catechin solutions ranging from 0 to 1 µg/mL and expressed as catechin equivalents (CE) per 100 g of dry matter (mg CE/100 g d.m.).
2.14. Determination of Antioxidant Capacity
Antioxidant capacity was determined spectrophotometrically, following the method reported by Skrajda-Brdak et al. [44]. The previously prepared extract of free phenolic compounds was used for the analysis. A volume of 50 μL of the extract was placed into a well of a clear 96-well microplate, followed by the addition of 250 μL of a methanolic solution of DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; 0.2 mM). The mixture was shaken and incubated in the dark at room temperature for 30 min. Absorbance was then measured at 517 nm against a methanol blank using a multifunctional microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega). Antioxidant capacity was calculated based on a calibration curve corresponding to the percentage reduction in DPPH radicals by various concentrations of Trolox in methanol and expressed as millimoles of Trolox equivalent per 100 g of dry matter (mM TE/100 g d.m.).
2.15. Statistical Analysis
The obtained results were subjected to statistical analysis using the Statistica 13.3 PL software package (StatSoft, Kraków, Poland). The normality of the data distribution was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, while the homogeneity of variances was verified using Levene’s test. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was performed at a significance level of p ≤ 0.05 to determine statistically significant differences between the flours and product samples—with respect to the analyzed parameters. Finally, the results were subjected to cluster analysis (CA) in order to observe the differences and similarities of the muffin samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Microwave Treatment on Moisture Content and Color Characteristics of Acorn Flour
Acorn flour was subjected to microwave treatment using two approaches: dry and wet systems. The results demonstrated that microwave processing significantly affected the moisture content of the acorn flour samples (Figure 1).
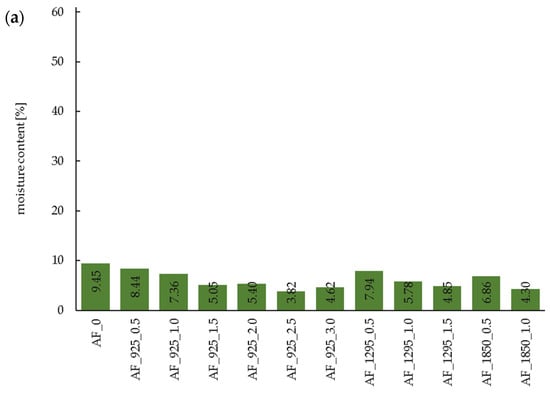
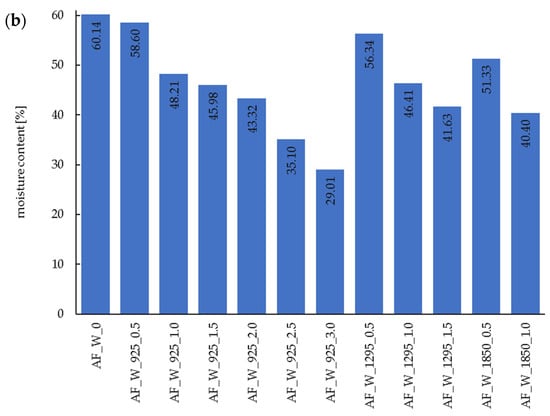
Figure 1.
Moisture content of acorn flour after dry (a) and wet (b) microwave treatment. AF—acorn flour; 0—control samples; W—wet microwave treatment; 925, 1295, 1850—microwave power (in watts); 0.5…3.0—duration time (in minutes).
Regardless of the treatment system (dry or wet microwave application), both the power level and duration of microwave exposure influenced the efficiency of water removal. Higher microwave power resulted in lower residual moisture content in the samples at a given processing time. For acorn flour subjected to dry microwave treatment for 1.0 min, the moisture content decreased to 5.43%, 3.69%, and 1.51% at 925 W, 1295 W, and 1850 W, respectively. These values correspond to moisture reductions of 46.9%, 63.9%, and 85.5% relative to the untreated control sample (AF_0). In the case of wet microwave treatment under the same processing time (1.0 min), the moisture content was 48.21%, 46.41%, and 40.40% at 925 W, 1295 W, and 1850 W, respectively, representing reductions of 19.8%, 22.8%, and 32.8% compared to the wet control sample (AF_W_0). With respect to processing time, longer exposure consistently leads to lower moisture content. Notably, the rate of moisture reduction in wet-treated samples was slower than in dry-treated ones. This phenomenon may be attributed to the substantially higher initial water content in the wet samples, which, while efficiently absorbing microwave energy, may also have limited penetration depth and energy distribution [45].
Microwave treatment also affected the external appearance of acorn flour, particularly its color, as reflected in changes to the L*, a*, and b* color parameters (Table 1). The most pronounced change was observed in lightness (L*), with flour samples exhibiting progressive darkening in response to microwave exposure. This was evidenced by a decrease in L* values, which intensified with increasing microwave power and processing time. Among the dry microwave-treated samples, the lowest L* value (54.11) was recorded in the sample treated at 925 W for 3.0 min, representing an 11.3% reduction compared to the untreated control. For samples processed for the same duration (1.0 min) but at different power levels, lightness decreased with increasing power, yielding L* values of 58.94, 57.75, and 56.13 for 925 W, 1295 W, and 1850 W, respectively. Wet microwave-treated samples demonstrated substantially lower lightness values than their dry-treated counterparts, with differences reaching up to 51% under identical power and time conditions. A stronger correlation was observed between processing time and lightness reduction in wet-treated samples. This intensified effect may be attributed to the facilitation of Maillard reactions under high-moisture conditions [46,47]. Similar flour darkening following microwave treatment has also been reported by Wani et al. [48] in studies on chestnut flour.

Table 1.
Color properties of microwave-treated acorn flour.
The a* and b* color parameters of acorn flour were also dependent on the microwave treatment (Table 1). In dry microwave-treated samples, a* values increased with processing time, indicating an intensification of the red color component. The highest a* value was observed in the sample treated at 925 W for 3.0 min, representing a 22.6% increase compared to the untreated control. For the b* parameter, statistically significant differences were noted relative to the control sample, reflecting an enhancement in the yellow color parameter. However, variations in the microwave power and processing time did not result in statistically significant differences among the treated samples. In the case of wet microwave-treated flour, a* values were generally higher than in the control; however, the changes were inconsistent across treatments, preventing the identification of a clear trend. Conversely, the b* values decreased significantly, with the lowest value recorded in the sample treated at 925 W for 3.0 min—representing a 27.5% reduction compared to the control. According to Rao et al. [49], such color changes during microwave processing may be attributed to the degradation of flavanol-containing pigments.
3.2. Effect of Microwave Treatment on Antioxidant Properties of Acorn Flour
The application of microwave treatment as a pre-treatment for acorn flour affected both the phenolic compound profile and antioxidant capacity (Table 2). In general, total free phenolic (TFP) and flavonoid contents increased, whereas the tannin content decreased. The magnitude of these changes was dependent on the duration and power level of the microwave treatment.

Table 2.
Total free phenolics (TFPs), flavonoids, and tannins contents and antioxidant capacity of microwave-treated acorn flour.
The total free phenolic (TFP) content in the acorn flour analyzed in this study (2243.50 mg GAE/100 g d.m. in the control sample) was more than twice as high as the value reported for laboratory-produced acorn flour by Levent and Aktaş [50] (992.03 mg GAE/100 g d.m.). A substantially lower TFP content (49.8 mg GAE/100 g d.m.) was reported by Mousavi et al. [51] for commercially available acorn flour in Iran. Beltrão Martins et al. [52], in their analysis of acorn flour available in Portugal, found a phenolic content approximately 25.2% lower (1679 mg GAE/100 g d.m.) compared to the present study.
When comparing the phenolic compound content across different acorn flours, it is essential to consider that the raw material originates from various oak species, which may account for differences in chemical composition [8,53,54,55]. Moreover, production processes such as debittering and thermal treatments may differ significantly between manufacturers and can substantially affect the final phenolic content of the flour [56].
In both wet and dry microwave-treated acorn flour, changes in total free phenolic (TFP) and flavonoid contents were observed, with microwave exposure time playing a pivotal role in the extent of these changes. TFP and flavonoid levels increased with treatment duration up to 1.5 min at 925 W and up to 1.0 min at 1295 W, followed by a decline with further exposure. Notably, despite the reduction in TFP content at extended processing times, all treated samples still exhibited higher levels than the untreated control. The highest TFP content was recorded in the sample treated for 1.5 min at 925 W, showing a 24.4% increase compared to the control, and in the sample treated for 1.0 min at 1295 W, with a 21.8% increase.
The existing literature supports the role of microwave treatment in enhancing the antioxidant potential of food products, primarily through the release of bound phenolic compounds into their free forms [57]. Alkaltham et al. [58] demonstrated that microwave treatment (900 W, 5–10 min) increased both free and bound phenolic and flavonoid contents in Leptadenia pyrotechnica stems. However, prolonged exposure and elevated temperatures led to a subsequent decline in these compounds, which is consistent with the findings of the present study. Similar patterns were reported by Sun et al. [59] for whole wheat flour and Singh et al. [57] for Kodo millet flour. According to Sun et al. [59], the observed increase in phenolic content may be attributed to microwave-induced structural modifications at the cellular level, facilitating the release of phenolics from cell walls and promoting the dissociation of protein–phenolic complexes. The subsequent decrease in content with extended exposure is likely due to the thermal degradation of phenolic compounds, which are known to be heat-sensitive [57].
The high tannin content in acorn flour represents a significant antinutritional factor [60,61]. Microwave treatment is one of the methods employed to reduce tannin content in food materials [62,63]. The present study demonstrated that both the duration and power of microwave treatment significantly impacted tannin reduction. Specifically, the greatest decrease in tannin content in dry microwave-treated samples was observed in the sample treated at 1850 W for 1 min (a 36.9% reduction) and in the sample treated at 925 W for 3 min (a 31.9% reduction). In contrast, the reduction in tannin content in wet microwave-treated samples was lower, with a maximum decrease of 28.6% observed in the sample treated at 1850 W for 1 min. These results align with those reported by Sheikh et al. [62], who found a reduction in tannin content with increasing microwave treatment duration in plum kernels. Similarly, Singh et al. [64] confirmed the effect of microwave heating on tannin reduction in various grains, including pearl millet (45.5%), finger millet (45.2%), and sorghum (77.5%) following microwave treatment at 900 W for 40–100 s. Javed et al. [34] also reported an 88% reduction in tannin content in soybean flour after exposure to 0.9 kW microwaves for 1.5 min. According to Waseem et al. [33], the reduction in tannin content during microwave treatment may result from the heat generated within the product due to increased molecular motion, which can disrupt hydrogen bonds.
The observed changes in antioxidant capacity were directly related to variations in the content of antioxidant compounds, exhibiting trends similar to those observed for total free phenolics and flavonoids. The highest antioxidant capacity was recorded in the dry microwave-treated sample for 2.0 min at 925 W (a 32.3% increase) and in the wet microwave-treated sample for 1.0 min at 925 W (a 19.9% increase). In general, wet microwave-treated samples exhibited lower antioxidant capacity compared to their dry counterparts. According to Singh et al. [57], the antioxidant capacity may be influenced not only by phenolic compounds and flavonoids but also by compounds formed during browning reactions, such as melanoidins. Sheikh et al. [62] further suggest that the increase in antioxidant capacity may be attributed to the breakdown of cellular structures, which enhances the release of pigments and phenolic compounds into the matrix.
3.3. Effect of Microwave-Treated Acorn Flour Addition on Technological Properties of Muffins
Microwave treatment of acorn flour significantly influenced the technological quality characteristics of wheat–acorn muffins (Table 3). The volume and crumb structure of the muffins varied according to the power and duration of microwave exposure: Short microwave treatments resulted in increased muffin volume and crumb porosity while maintaining lower firmness; however, with extended treatment times, these parameters deteriorated. Moreover, higher microwave power levels further exacerbated the decline in these quality attributes.

Table 3.
Technological properties of wheat–acorn muffins in relation to microwave treatment of acorn flour.
The volume of muffins containing dry microwave-treated flour was influenced by both the duration and power of microwave treatment. Higher volumes were observed in samples baked with flour subjected to shorter processing times and lower microwave power. The highest volumes were recorded for the sample with flour microwaved for 1.0 min at 925 W (82.64 cm3) and for 0.5 min at 1295 W (79.19 cm3). Prolonging the treatment time and increasing the power resulted in a reduction in muffin volume. Notably, only the sample treated for 3.0 min at 925 W exhibited a statistically significant decrease in volume compared to the control sample (a 5.8% reduction). The remaining samples either showed no statistically significant difference or demonstrated a higher volume than the control.
The volume of muffins containing wet microwave-treated flour was lower than that of muffins with dry microwave-treated flour, although it was either not statistically significantly different from or higher than the control. The only sample with wet microwave-treated flour that exhibited a volume lower than the control was the sample treated for 1.0 min at 1850 W (65.33 cm3, an 8.4% reduction). As observed in the dry microwave-treated flour samples, longer processing times and higher microwave power resulted in a decrease in muffin volume.
The porosity of muffins containing both dry and wet microwave-treated flour followed trends similar to those observed for volume. Longer processing times and higher microwave power resulted in reduced porosity, indicating a more compact crumb structure. When comparing samples treated at the same microwave power and duration, muffins containing wet microwave-treated flour exhibited lower porosity than those containing dry microwave-treated flour. Changes in porosity were also evident in the cross-sections of the muffins (Figure 2). In addition to porosity, which is expressed as the proportion of empty spaces within the crumb structure, the size and distribution of pores also changed. In muffins with dry microwave-treated acorn flour, larger and irregularly distributed pores appeared in the crumb structure compared to the control sample, leading to the formation of empty spaces. The effect of wet microwave-treated acorn flour on the structure and porosity of the crumb was more dependent on the microwave power used, detailed as follows: At 925 W, muffins exhibited uniform porosity. Higher microwave power led to uneven porosity in the crumb, which decreased further as the power and time increased. Samples with wet microwave-treated flour at 1850 W were characterized by a moist, compact crumb.


Figure 2.
External appearance and cross-section of wheat–acorn muffins with dry and wet microwave-treated acorn flour. AF—acorn flour; 0—control samples; W—wet microwave treatment; 925, 1295, 1850—microwave power (in watts); 0.5…3.0—microwave processing time (in minutes).
Microwave treatment of acorn flour significantly influenced the firmness of the muffin crumb. Muffins containing flour treated with lower microwave power levels and/or shorter durations exhibited lower crumb firmness compared to the control. This reduction in firmness can be attributed to the higher porosity of the crumb, which, despite its increased volume, remains delicate and prone to deformation. In contrast, muffins made with flour subjected to higher microwave power and longer durations had a denser structure and increased firmness, requiring greater force for compression.
The crumb firmness values of muffins with dry microwave-treated flour were lower than those of the control sample, with reductions of up to 34.8% (for the sample AF_925_1.0). However, samples with flour treated for the longest durations at 925 W and 1850 W deviated from this trend, exhibiting firmness values that were 72.5% and 30.2% higher than the control, respectively. For these samples, longer microwave exposure resulted in higher compression forces. Conversely, for samples treated at 1295 W, increasing microwave treatment time led to a decrease in compression force, although these differences were not statistically significant (α = 0.05).
For muffins with wet microwave-treated flour, crumb firmness increased with longer microwave exposure, regardless of the power level used. Firmness values for these samples were lower than those of the control for flour treated at 925 W (from 1.0 to 3.0 min) and at 1295 W (up to 1.0 min). However, samples treated at 1295 W for 1.5 min and at 1850 W exhibited higher compression force values, with the highest value recorded for the sample treated at 1850 W for 1.0 min, showing a 173% increase in force compared to the control.
In the study by Ha et al. [65] on the effect of a microwaved corn starch–pea protein composite on muffin quality and physical properties, muffins containing the composite microwaved at 700 W exhibited a lower rise (center height), lower specific volume, and lower hardness. These changes were dependent on the number of microwave cycles (20 s microwave, 40 s rest)—the more cycles applied, the more pronounced the observed changes. Similarly, Soleimanifard et al. [66] assessed the impact of microwave baking at different power levels (150–600 W) on cupcake quality. They found that higher microwave power during baking resulted in increased cupcake height, porosity, and hardness while reducing density. The findings of the present study align with these observations, where higher microwave power and longer exposure time resulted in more pronounced changes in technological properties.
The use of acorn flour in bakery and pastry products is valuable due to its bioactive components; however, it presents challenges in terms of its impact on technological properties and physical characteristics. Acorn flour is a gluten-free raw material with relatively high fat and fiber content [52,67], which negatively affects the quality of baked goods, including their volume and textural properties [60,68,69,70,71]. The firmness of acorn muffins, as reported by Masmoudi et al. [71], was 8.8% lower than that of wheat muffins, while their height decreased by 26.1%. Similarly, in the study by Molavi et al. [60], an increase in the hardness of sponge cakes was observed with increasing proportions of acorn flour. Given the negative effect of acorn flour on the quality characteristics of products, various processing methods—including microwave treatment—are being explored to mitigate these changes.
Changes in the technological properties of muffins baked with microwave-treated acorn flour may be attributed to alterations in starch during the microwave treatment process. As reported by Lewicka et al. [72], microwave treatment modifies the gelatinization mechanism and affects the rheological properties of starch. This process is a critical functional aspect of starch, playing a significant role in food processing technology. In studies by Calix-Rivera et al. [73], the impact of microwave treatment on tef flour was evaluated, focusing on parameters such as amylose content, damaged starch, and pasting properties. The authors demonstrated that microwave treatment reduced the content of damaged starch while increasing the amylose content. These changes in the chemical composition and structural modifications of starch resulted in increased water absorption and solubility indexes. Additionally, pasting properties were altered, with an increase in pasting temperature and a decrease in viscosity. Importantly, the moisture content of the flour influenced the extent of these changes, with higher moisture content leading to more pronounced effects during microwave treatment.
The studies by Náthia-Neves et al. [74] also indicated the influence of microwave treatment on functional properties, particularly hydration properties and protein recovery, with reductions observed in albumins, globulins, and prolamins. Uthumporn et al. [75] examined the effects of microwave treatment on corn and rice flour properties, reporting an increase in amylose content and gelatinization temperature alongside a decrease in swelling power and solubility. Villanueva et al. [76], in their assessment of the effect of microwave treatment on rice flour, identified not only the changes already observed by other authors [64,65] but also modifications in the morphological structure of the flour particles and the ratio of crystalline-to-amorphous regions.
The effect of microwave heating on the functional properties of flour, including pasting properties (primarily a significant reduction in viscosity), was also observed in chestnut flour in the studies by Wani et al. [48]. However, no studies are currently available that directly address the behavior and changes in acorn starch during microwave treatment, which represents a potential area for future research.
3.4. Effect of Microwave-Treated Acorn Flour Addition on Color Parameters of Muffins
The incorporation of microwave-treated acorn flour into wheat–acorn muffins significantly influenced the color of the baked goods (Table 4, Figure 2). These color changes were observed in both the crust and the crumb of the muffins and were dependent on the microwave power and the duration of exposure to the flour.

Table 4.
Color properties of wheat–acorn muffins in relation to microwave treatment of acorn flour.
The crust lightness of muffins baked with dry microwave-treated acorn flour was generally lower than that of the control sample. The highest crust lightness was observed in the sample with dry microwave-treated flour subjected to 1.0 min at 925 W (L* = 36.32), which was the only sample to exhibit an 11.5% increase in lightness compared to the control. In the other samples with dry microwave-treated flour, crust lightness either did not differ significantly or was lower than that of the control sample. Changes in crust lightness were primarily influenced by the duration of microwave treatment: the longer the flour was treated, the lower the crust lightness of the resulting muffins. Microwave power had a lesser effect on crust color changes; statistically significant differences were observed only at 925 W, which produced muffins with the lightest crust. Dry microwave-treated flour also affected other crust color parameters, specifically a* and b*. The values of these parameters decreased as a function of both time (a* parameter) and time and power (b* parameter).
The crust lightness of muffins baked with wet microwave-treated flour was lower than that of muffins baked with dry microwave-treated flour. An increase in treatment time and power resulted in a decrease in the L parameter, though these changes were less pronounced than those in muffins with dry microwave-treated flour. The lowest L* values were recorded for samples microwaved at 1295 W, with a reduction of up to 22.5% compared to the control sample. The values of the a* and b* parameters were lower than those of the control sample but the changes were irregular, with no clear relationship between treatment time and power.
The color changes resulting from microwave-treated acorn flour also influenced the crumb color of muffins (Table 4). The lightness (L* parameter) of the crumb in muffins with dry microwave-treated flour depended on treatment time and power. For shorter treatment times, regardless of power, the differences were not statistically significant. However, with prolonged microwave treatment, the crumb became darker. The darkest crumb was observed in the sample containing flour microwaved at 1295 W for 1.5 min, with a 46.3% reduction in the L* value compared to the control sample. The values of the a* and b* parameters also changed, though these changes were less pronounced than those observed for crumb lightness. The proportions of red (a* value) and yellow (b* value) hues remained statistically unchanged, except in samples subjected to the longest microwave treatment times.
The crumb color of muffins with wet microwave-treated flour was darker than both the control sample and muffins with dry microwave-treated flour. The most pronounced decrease in lightness was observed in the sample treated for 3.0 min at 925 W, with a 26.5% reduction in the L* parameter value compared to the control sample. Increasing treatment time further reduced crumb lightness. The changes in the a* parameter among samples treated for the same time but at different power levels were not statistically significant. However, treatment time resulted in statistically significant differences in the a* parameter only at the highest power of 1850 W. The b* parameter exhibited greater variation, decreasing with increasing microwave power and prolonged processing time.
Acorn flour is a raw material that significantly influences the color of products made with it, even in its raw form, due to its natural color. In the study by Kim et al. [77], the addition of acorn jelly and acorn extract affected the color of wheat muffins, resulting in darker baked goods. Hoeche et al. [78] conducted baking tests using wheat muffins with a 50% addition of acorn flour, which were subsequently subjected to sensory evaluation. The results revealed differences in color between the control and the enriched samples. Amina and Djamel [79] investigated the effect of processing acorn flour through fermentation and the germination of acorns and its impact on the functional properties of the flour and cookies made from it, including color. The authors found that while the inclusion of acorn flour reduced the lightness of the sample (lower L* values), the use of fermentation did not have a significant effect on the color when compared to the sample with unfermented flour.
3.5. Effect of Microwave-Treated Acorn Flour Addition on Antioxidant Properties of Muffins
The incorporation of microwave-treated acorn flour into wheat–acorn muffins influenced the content of free phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and tannins, as well as the antioxidant capacity (Table 5). These changes were dependent on the duration and power of microwave treatment, following a linear trend: longer microwave treatment durations and higher power levels resulted in increased content of phenolic compounds and flavonoids, as well as enhanced antioxidant capacity, while the tannin content decreased.

Table 5.
Total free phenolics (TFPs), flavonoids, and tannins contents and antioxidant capacity of wheat–acorn muffins in relation to microwave treatment of acorn flour.
The incorporation of acorn flour, even in its raw form, results in an increase in the antioxidant content of the final product, owing to the naturally high levels of antioxidants present in acorns and their derived products. Purabdolah et al. [80] observed an over seven-fold increase in the total free phenolic compound content in wheat bread enriched with acorn flour. Similarly, Mousavi et al. [51] reported an eighteen-fold increase in phenolic compound content in Iranian toasted wheat bread containing 30% acorn flour compared to the control sample. Skendi et al. [81] found that the total free phenolic compound content was 1.5 times higher in gluten-free bread with 25% acorn flour than in the control sample. Beltrão Martins et al. [82] documented a 2-fold increase in total phenolic compound content, a 7-fold increase in ortho-diphenols, and approximately a 1.5-fold increase in flavonoid content in gluten-free bread with 35% acorn flour compared to control samples. However, available studies on the use of acorn flour in cake and muffin production [60,71,77,78] do not provide information regarding the phenolic compound content or antioxidant properties of the resulting products.
The content of phenolic compounds and flavonoids in muffins baked with the addition of microwaved acorn flour was significantly lower than in the flour itself. As acorn flour was one of the recipe ingredients, it contributed to a substantial reduction in the concentration of antioxidant compounds in the final product. Furthermore, the impact of high temperatures during baking must be considered as these can lead to the degradation of phenolic compounds and flavonoids, which are known for their low thermal stability [44,83].
Microwave treatment of acorn flour influences the enhancement in antioxidant properties and the reduction in antinutritional compounds in muffins (Table 5). This effect results from the changes occurring in the flour during microwave processing, as outlined in Table 2. Notably, in muffins—unlike in flour—the content of free phenolic compounds and flavonoids increased linearly, with no decrease in the concentration of these compounds even with prolonged microwave treatment. In addition to the microwave processing of the flour used in the formulation, the baking process itself may also affect the phenolic compound content in muffins. Abdel-Aal and Rabalski [84] demonstrated that during the preparation and baking of muffins made from blends of hairless canary seed, wheat, and corn, the content of bound phenolic acids decreased while the content of unbound phenolic acids increased. As sugar is incorporated into the muffin batter, the increase in antioxidant properties may result not only from the release of phenolic compounds from their bound form but also from the Maillard reaction. This reaction, occurring under high temperatures during baking, leads to the formation of compounds with strong antioxidant properties, such as melanoidins [85,86].
3.6. Effect of Microwave-Treated Acorn Flour Addition on Organoleptic Characteristics of Muffins
Changes in the technological quality and physical properties of wheat–acorn muffins, resulting from the microwave processing of the acorn flour, influenced the organoleptic evaluation of the baked goods (Table 6). Statistically significant differences were predominantly observed at the longest processing times and/or the highest microwave power levels. For muffins made with dry microwave-treated acorn flour, increases in color and taste scores were recorded for samples processed at 925 W for 3.0 min (by 12.5% and 24%, respectively) and at 1850 W for 1.0 min (by 10.9% and 18.9%, respectively). However, these samples simultaneously received statistically significantly lower scores for texture. In muffins prepared with wet microwave-treated acorn flour, the effects of microwave treatment on scores followed a similar pattern to those observed for dry-treated flour. Longer microwave durations at 925 W and 1850 W significantly improved aroma and taste scores compared to the control sample. Nevertheless, extended microwave processing led to lower texture scores.

Table 6.
Organoleptic properties of wheat–acorn muffins in relation to microwave treatment of acorn flour.
The overall acceptance of the wheat–acorn muffins indicated that the microwave treatment of acorn flour prior to incorporation into the muffins enhanced product acceptability. Specifically, dry microwave treatment of acorn flour improved muffin acceptance, particularly for samples prepared with flour treated at 925 W and those subjected to the longest processing time. For muffins containing wet microwave-treated acorn flour, the highest acceptance was noted in samples with flour treated at the lowest power level.
3.7. Multivariate Analysis of Wheat–Acorn Muffins Quality
The results of the physical, chemical, and organoleptic characteristics of the wheat–acorn muffins were subjected to multivariate analysis by cluster analysis (CA). The hierarchical cluster analysis was performed by applying the Ward method and Euclidean distance. Figure 3 shows the dendrogram obtained for muffins with dry and wet microwave-treated acorn flour.
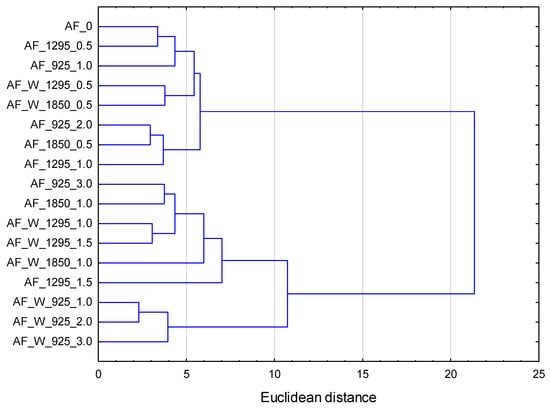
Figure 3.
Dendrogram for wheat–acorn muffins with dry and wet microwave-treated acorn flour. AF—acorn flour; 0—control samples; W—wet microwave treatment; 925, 1295, 1850—microwave power (in watts); 0.5…3.0—microwave processing time (in minutes).
It was observed that, for a Euclidean distance of less than 10, three distinct clusters could be identified. Cluster 1 was characterized by muffins made with wet microwave-treated acorn flour, particularly those processed at lower microwave power and for shorter durations. These samples exhibited more favorable organoleptic properties, including higher scores for color, aroma, and taste, as well as better overall acceptance. Technologically, they were distinguished by greater volume and crumb porosity, alongside relatively lower crumb firmness. Their color was lighter and more uniform, with higher lightness (L* parameter) values and well-balanced red and yellow hues. Chemically, muffins in this cluster showed elevated levels of phenolic compounds and flavonoids, reduced tannin content, and improved antioxidant capacity. Cluster 2 included samples with dry microwave-treated flour, mostly processed at moderate microwave power and shorter durations. These muffins showed intermediate characteristics between the other two clusters. Their sensory and technological properties were balanced, with moderate volume, acceptable porosity, and firmness. The color parameters and bioactive compound content were also within a moderate range, indicating that these treatments preserved quality without producing extreme changes. In contrast, Cluster 3 comprises muffins made with acorn flour subjected to more intense conditions—either higher power, longer microwave duration, or both. These samples generally scored lower in organoleptic evaluation, particularly in texture and overall acceptance. Technological traits such as crumb firmness were elevated, and both muffin volume and porosity were reduced, indicating a denser and less-desirable crumb structure. The color was notably darker, with significantly lower lightness values. Moreover, these muffins showed reduced levels of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity, while the tannin content was comparatively higher, likely due to less effective degradation under the harsher processing conditions.
In summary, the clustering results emphasize the influence of microwave treatment parameters on muffin quality. Milder treatments, especially under moist conditions, tend to preserve or enhance desirable characteristics, whereas high-power or prolonged treatments may have detrimental effects on product quality.
4. Conclusions
The study conducted demonstrates that microwave treatment plays a crucial role in modifying the properties of acorn flour, directly influencing the antioxidant capacity and overall quality of muffins. The application of microwave heating enhances the content of free phenolic compounds and flavonoids while reducing tannin levels, leading to an improved antioxidant potential in the final product. These changes in antioxidant properties and overall quality were dependent on microwave power and exposure time.
Muffins prepared with wet microwave-treated flour at lower power and shorter durations demonstrated the most desirable characteristics, including improved sensory acceptance, optimal texture, lighter crumb and crust color, and enhanced antioxidant properties. In contrast, muffins made with flour subjected to high microwave power or prolonged exposure were associated with diminished quality attributes, such as increased firmness, reduced volume and porosity, and lower consumer acceptability. These findings suggest that moderate microwave processing, particularly under moist conditions, can be an effective method for enhancing both the functional and technological performance of acorn flour in bakery applications while minimizing negative effects on product quality.
Overall, the results underscore the potential of microwave processing as a valuable technique for improving the nutritional quality of acorn flour-based products. Future research should focus on optimizing microwave treatment parameters to maximize antioxidant retention while further evaluating sensory and textural attributes to ensure consumer acceptance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.S. and M.T.; methodology, E.S. and M.T.; validation, E.S.; formal analysis, E.S.; investigation, E.S.; resources, E.S. and M.T.; data curation, E.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S. and M.T.; writing—review and editing, E.S. and M.T.; visualization, E.S. and M.T.; supervision, M.T.; project administration, E.S.; funding acquisition, E.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland (project number 2021/41/N/NZ9/02668).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Norrman, K.-E. World Population Growth: A Once and Future Global Concern. World 2023, 4, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worldometer. World Population by Year. Updated 2023. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/world-population-by-year/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Jovović, Z.; Velimirović, A.; Yaman, N. Climate and Crop Production Crisis. In Agriculture and Water Management Under Climate Change; Çetin, Ö., Ed.; Springer Briefs in Earth System Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Bayer, P.E.; Edwards, D. Climate Change and the Need for Agricultural Adaptation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 56, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencák, T.; Dordevic, D.; Tremlová, B. Utilization of Oak (Genus) Tree Parts in Food Industry: A review. MASO Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariutti, L.R.B.; Rebelo, K.S.; Bisconsin-Junior, A.; de Morais, J.S.; Magnani, M.; Maldonade, I.R.; Madeira, N.R.; Tiengo, A.; Maróstica, M.R., Jr.; Cazarin, C.B.B. The Use of Alternative Food Sources to Improve Health and Guarantee Access and Food Intake. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaticci, L.; Santanatoglia, A.; Vittadini, E.; Beghelli, D.; La Terza, A.; Zengin, G.; Caprioli, G. Quantification of Bioactive Compounds by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and Evaluation of Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Acorn Flour Extracts. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, R.; Abderrabba, M.; Mejri, J. Comparative Chemical Composition of Two Quercus Species Seeds Growing in Tunisia. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinha, A.F.; Barreira, J.C.; Costa, A.S.; Oliveira, M.B.P. A New Age for Quercus spp. fruits: Review on Nutritional and Phytochemical Composition and Related Biological Activities of Acorns. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 947–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinha, A.F.; Barreira, J.C.; Ferreira, I.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P. Therapeutic, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Acorns (Quercus nuts): A review. In Bioactive Compounds in Underutilized Fruits and Nuts; Murthy, H., Bapat, V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, L.G.; Bernardino, R.; Bernardino, S.; Afonso, C. Acorns: From an Ancient Food to a Modern Sustainable Resource. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, D.M.; Bondioli, C.; Hamzeh Hosseini, S.; Miara, M.D.; Musarella, C.M.; Mohammadi, D.; Manduzai, A.K.; Issa, K.D.; Sulaiman, N.; Khatib, C.; et al. Food security beyond cereals: A Cross-Geographical Comparative Study on Acorn Bread Heritage in the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Foods 2022, 11, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Welp, M.; Zdruli, P. Provisioning Ecosystem Services Related with Oak (Quercus) Systems: A Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Islam, M.N.; Faruk, M.O.; Ashaduzzaman, M.; Dungani, R. Review on Tannins: Extraction Processes, Applications and Possibilities. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 135, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Sharma, V.; Thakur, A. An overview of anti-nutritional factors in food. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, J.; Tanwar, B.; Goyal, A.; Sharma, R.; Gat, J.; Kumar, A. Health Effects, Sources, Utilization and Safety of Tannins: A Critical Review. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, N.; Shah, M.A.; Rasul, A.; Chauhdary, Z.; Saleem, U.; Khan, H.; Ahmed, N.; Uddin, M.S.; Mathew, B.; Behl, T.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Ellagic Acid in Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on Underlying Molecular Mechanisms of Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeriglio, A.; Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; Trombetta, D. Proanthocyanidins and Hydrolysable Tannins: Occurrence, Dietary Intake and Pharmacological Effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1244–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwole, O.; Fernando, W.B.; Lumanlan, J.; Ademuyiwa, O.; Jayasena, V. Role of Phenolic Acid, Tannins, Stilbenes, Lignans and Flavonoids in Human Health—A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 6326–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amina, M.; Djamel, F.; Djamel, H. Influence of Fermentation and Germination Treatments on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Acorn Flour. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 24, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, P.R.; Leitão, A.E.; Beirão-da-Costa, M.L. Effect of drying temperatures on chemical and morphological properties of acorn flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, P.R.; Beirão-da-Costa, M.L. Effect of Drying Temperatures on Starch-Related Functional and Thermal Properties of Acorn Flours. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Yan, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhai, L. Microwave and Steam Processing: A Novel Approach to Modifying the Characteristics of Reconstituted Whole Wheat Flour and Dough. Molecules 2025, 30, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yunos, N.S.H.; Hafid, H.S.; Omar, F.N.; Mohammed, M.A.P.; Wakisaka, M.; Mustapha, N.A.; Baharuddin, A.S. Microwave-Assisted Treatment for the Improvement of Rice Flour Properties and Rice Flour Bread Quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 9157–9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Qureshi, I.; Jan, K.; Habib, M.; Maurya, V.K.; Shakya, A.; Bashir, K. Physicochemical, Thermal and Sensory Properties of Microwave-Treated Chickpea Flour (Sattu). J. Culin. Sci. Technol. 2024, 18, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, B.; Kaur, A. Microwave Processing Effects on Physico-Chemical, Functional Properties, Phenolic Profile, and Maillard Products of Flaxseed Flour and Flaxseed Press Cake Flour. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 218, 118900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, D.W.; Admassu, S. Pumpkin Flour Qualities as Affected by Ultrasound and Microwave Pre-Drying Treatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 2409–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhag, R.; Dhiman, A.; Deswal, G.; Thakur, D.; Sharanagat, V.S.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, V. Microwave processing: A way to reduce the anti-nutritional factors (ANFs) in food grains. LWT 2021, 150, 111960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Ci, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Microwave Technology: A Novel Approach to the Transformation of Natural Metabolites. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, P.; Kulawik, P.; Zając, M.; Migdał, W. Microwave Applications in the Food Industry: An Overview of Recent Developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7989–8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlu, N.; Pandiselvam, R.; Saka, I.; Kamiloglu, A.; Sahni, P.; Kothakota, A. Impact of Different Microwave Treatments on Food Texture. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 709–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Geddawy, M.A.U.; Sorour, M.A.; Abou-El-Hawa, S.H.; Taha, E.M.M. Effect of Domestic Processing and Microwave Heating on Phenolic Compounds and Tannins in Some Oil Seeds. SVU-Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 1, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Akhtar, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ismail, T.; Lazarte, C.E.; Hussain, M.; Manzoor, M.F. Effect of Microwave Heat Processing on Nutritional Indices, Antinutrients, and Sensory Attributes of Potato Powder-Supplemented Flatbread. J. Food Qual. 2022, 1, 2103884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Waseem, M.; Mehmood, T.; Hussain, A.; Adil, M.; Abdi, G. Effect of Microwave Heat Processing on Nutritional, Antioxidant, Antinutrient, and Sensory Indices of Soy Flour Enriched Functional Noodles. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, T.; Imran, M.; Xu, C.; Khan, M.K. Microwave Processing Impact on the Phytochemicals of Sorghum Seeds as Food Ingredient. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e13924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kanchan, S. A review on the impact of microwave processing on physicochemical properties of different cereal grains and flours. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 3, 45–83. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC 925.10; Moisture in Flour. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019.
- American Association of Cereal Chemists International (AACCI). Method 74-09.01: Bread Firmness by Universal Testing Machine. In Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak-Lukasiak, K.; Lesniewska, P.; Zielińska, D.; Sowinski, M.; Zbikowska, K.; Lukasiak, P.; Zbikowska, A. The Influence of Chestnut Flour on the Quality of Gluten-Free Bread. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdybel, B.; Różyło, R.; Sagan, A. Use of a waste product from the pressing of chia seed oil in wheat and gluten-free bread processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, I.; Tańska, M.; Faron, A.; Czaplicki, S. Release of Free Ferulic Acid and Changes in Antioxidant Properties during the Wheat and Rye Bread Making Process. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, F.; Squeo, G.; Barkat, M.; Pasqualone, A.; Caponio, F. Comparative Study of Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Properties of Quercus: Flour and Oil. N. Afr. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 3, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herald, T.J.; Gadgil, P.; Perumal, R.; Bean, S.R.; Wilson, J.D. High-Throughput Micro-Plate HCl–Vanillin Assay for Screening Tannin Content in Sorghum Grain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2133–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrajda-Brdak, M.; Konopka, I.; Tańska, M.; Czaplicki, S. Changes in the Content of Free Phenolic Acids and Antioxidative Capacity of Wholemeal Bread in Relation to Cereal Species and Fermentation Type. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Mahanti, N.K.; Thakur, M.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Microwave Heating: Alternative Thermal Process Technology for Food Application. In Emerging Thermal and Nonthermal Technologies in Food Processing, 1st ed.; Srivastav, P.P., Verma, D.K., Patel, A.R., Al-Hilphy, A.R., Eds.; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 25–67. [Google Scholar]
- Michalak, J.; Czarnowska-Kujawska, M.; Klepacka, J.; Gujska, E. Effect of Microwave Heating on the Acrylamide Formation in Foods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, F.I.; Chinnan, M.S.; Ebenso, E.E.; Edem, C.A.; Iwegbue, C.M.A. Colour Change: An Indicator of the Extent of Maillard Browning Reaction in Food System. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 9325–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Hamid, H.; Hamdani, A.M.; Gani, A.; Ashwar, B.A. Physico-Chemical, Rheological and Antioxidant Properties of Sweet Chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) as Affected by Pan and Microwave Roasting. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.V.; Akhil, K.G.; Sunil, C.K.; Venkatachalapathy, N.; Jaganmohan, R. Effect of Microwave Treatment on Physical and Functional Properties of Foxtail Millet Flour. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2021, 9, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levent, A.; Aktaş, K. Nutritional Composition and Staling Properties of Gluten-Free Bread-Added Fermented Acorn Flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, B.; Ghaderi, S.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Pourmahmoudi, A. Effect of Varying Levels of Acorn Flour on Antioxidant, Staling and Sensory Properties of Iranian Toast. Int. J. Food Stud. 2021, 10, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrão Martins, R.; Gouvinhas, I.; Nunes, M.C.; Ferreira, L.M.; Peres, J.A.; Raymundo, A.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Acorn Flour from Holm Oak (Quercus rotundifolia): Assessment of Nutritional, Phenolic, and Technological Profile. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakuri, F.; Eghlima, G.; Behboudi, H.; Babashpour-Asl, M. Phytochemical Variation, Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Wild Populations of Iranian Oak. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, M.; Damiri, F.; Rezzak, Y.; Berrada, M.; Bouyazza, L. Chemical Composition, Nutritional, and Antioxidant Activity of Two Quercus Species Acorns Growing in Morocco. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2024, 13, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizemmour, Z.; Mechmeche, M.; Messadi, N.; Hamdi, M.; Kachouri, F. Evaluation of the Physicochemical, Nutritional, and Antioxidant Activities of Acorn from Quercus spp.: A Comparative Study Between Algerian and Tunisian Varieties. Chem. Afr. 2024, 7, 4273–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oracz, J.; Żyżelewicz, D.; Pacholczyk-Sienicka, B. UHPLC-DAD-ESI-HRMS/MS Profile of Phenolic Compounds in Northern Red Oak (Quercus rubra L., syn. Q. borealis F. Michx) Seeds and Its Transformation during Thermal Processing. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Kurichh, R.; Bist, Y.; Kheto, A.; Kumar, Y.; Sharma, R.; Shikha, D.; Saxena, D.C. Effect of Microwave Roasting on the Physicochemical, Functional, Rheological, and Antioxidant Properties of Kodo Millet Flour. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2024, 2024, 6861190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaltham, M.S.; Hayat, K.; Salamatullah, A.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Hassan, A.B. Effect of Microwave and Conventional Heat Treatment on Total Phenolic Compounds, HPLC Phenolic Profile, and Antioxidant Activity of Leptadenia pyrotechnica (Forssk.) Decne Stem. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ji, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, H. Effect of Low Temperature Microwave Treatment on Lipid Stability and Antioxidant Capacity of Whole Wheat Flour. LWT 2023, 182, 114854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H.; Keramat, J.; Raisee, B. Evaluation of the Cake Quality Made from Acorn–Wheat Flour Blends as a Functional Food. J. Food Biosci. Technol. 2015, 5, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Papoti, W.T.; Kizaki, N.; Skaltsi, A.; Karayannakidis, P.D.; Papageorgiou, M. The Phytochemical Rich Potential of Acorn (Quercus aegilops) Products and By-Products. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, M.A.; Saini, C.S.; Sharma, H.K. Antioxidant Potential, Anti-Nutritional Factors, Volatile Compounds and Phenolic Composition of Microwave Heat-Treated Plum (Prunus domestica L.) Kernels: An Analytical Approach. Br. Food J. 2022, 124, 3236–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozolina, K.; Sarenkova, I.; Muizniece-Brasava, S. The Anti-Nutritional Factors of Legumes and Their Treatment Possibilities: A Review. Res. Rural Dev. 2023, 38, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gupta, S.; Kaur, R.; Gupta, H.R. Process Optimization for Anti-Nutrient Minimization of Millets. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2017, 36, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ha, M.; Firdhausa, A.S.; Chung, H.-J. Microwave Treatment Modifies the Physicochemical Properties of Starch-Protein Composite for Improved Gluten-Free Muffin Quality. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5141558 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Soleimanifard, S.; Shahedi, M.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Askari, G.R. Investigating Textural and Physical Properties of Microwave-Baked Cupcake. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.; Costa, E.M.; Borges, A.; Carvalho, A.P.; Monteiro, M.J.; Pintado, M.M.E. Nutritional Characterization of Acorn Flour (a Traditional Component of the Mediterranean Gastronomical Folklore). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2016, 10, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrušková, M.; Švec, I.; Kadlčíková, I. Effect of Chestnut and Acorn Flour on Wheat/Wheat-Barley Flour Properties and Bread Quality. Int. J. Food Stud. 2019, 8, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, R.B.; Jianu, C.; Velciov, A.B.; Poiană, M.A.; Negrea, M.; Cocan, I.; Riviș, A.; Hădărugă, N.; Stoin, D. Quality Parameters assessment of cakes produced from acorn-rice flour mixtures. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2023, 29, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-I.; Joo, J.-I.; Kim, J.-M. Changes in the Quality of Bread Added with Acorn Flour during Storage Periods. J. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life 2017, 27, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, M.; Besbes, S.; Bouaziz, A.; Khlifi, M.; Yahyaoui, D.; Attia, H. Optimization of Acorn (Quercus suber L.) Muffin Formulations: Effect of Using Hydrocolloids by a Mixture Design Approach. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicka, K.; Siemion, P.; Kurcok, P. Chemical Modifications of Starch: Microwave Effect. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 867697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calix-Rivera, C.S.; Villanueva, M.; Náthia-Neves, G.; Ronda, F. Changes on Techno-Functional, Thermal, Rheological, and Microstructural Properties of Tef Flours Induced by Microwave Radiation—Development of New Improved Gluten-Free Ingredients. Foods 2023, 12, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Náthia-Neves, G.; Calix-Rivera, C.S.; Villanueva, M.; Ronda, F. Microwave Radiation Induces Modifications in the Protein Fractions of Tef Flours and Modulates Their Derived Techno-Functional Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthumporn, U.; Nadiah, N.I.; Koh, W.Y.; Zaibunnisa, A.H.; Azwan, L. Effect of Microwave Heating on Corn Flour and Rice Flour in Water Suspension. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, M.; Harasym, J.; Munoz, J.M.; Ronda, F. Microwave Absorption Capacity of Rice Flour. Impact of the Radiation on Rice Flour Microstructure, Thermal and Viscometric Properties. J. Food Eng. 2018, 224, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, W.K.; Choi, C.S.; Cho, S.M. Quality Characteristics of Muffins with Added Acorn Jelly Powder and Acorn Ethanol Extract Powder. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 41, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeche, U.; Kelly, A.; Coci, F. Acorn: Staple food from the past or novel food for the future?—An Investigation into the Desirability and Acceptability of Acorn Flour Products. Dublin Gastronomy Symposium, Dublin, Ireland, 3–4 June 2014. Available online: https://arrow.tudublin.ie/dgs/2014/june314/1/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Amina, M.; Djamel, F. Effect of Fermentation and Germination Treatments on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Enriched Biscuits with Acorn Flour. Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 19, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Purabdolah, H.; Sadeghi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Kasheninejad, M.; Tabarestani, H.S.; Mohamadzadeh, J. Techno-Functional Properties of the Selected Antifungal Predominant LAB Isolated from Fermented Acorn (Quercus persica). Food Meas. 2020, 14, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendi, A.; Mouselemidou, P.; Papageorgiou, M.; Papastergiadis, E. Effect of Acorn Meal-Water Combinations on Technological Properties and Fine Structure of Gluten-Free Bread. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrão Martins, R.; Gouvinhas, I.; Nunes, M.C.; Alcides Peres, J.; Raymundo, A.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Acorn Flour as a Source of Bioactive Compounds in Gluten-Free Bread. Molecules 2020, 25, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaban, H.; Ioannou, I.; Chebil, L.; Slimane, M.; Gerardin, C.; Paris, C.; Charbonnel, C.; Chekir, L.; Ghoul, M. Effect of Heat Processing on Thermal Stability and Antioxidant Activity of Six Flavonoids. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Rabalski, I. Changes in Phenolic Acids and Antioxidant Properties during Baking of Bread and Muffin Made from Blends of Hairless Canary Seed, Wheat, and Corn. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfeo, V.; Bravi, E.; Ceccaroni, D.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.; Marconi, O. Effect of Baking Time and Temperature on Nutrients and Phenolic Compounds Content of Fresh Sprouts Breadlike Product. Foods 2020, 9, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, Y. Bread Characteristics and Antioxidant Activities of Maillard Reaction Products of White Pan Bread Containing Various Sugars. LWT 2018, 95, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).