An Elliptic Blending Turbulence Model-Based Scale-Adaptive Simulation Model Applied to Fluid Flows Separated from Curved Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Formulation and Implementation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. 3D Asymmetric Diffuser Flow
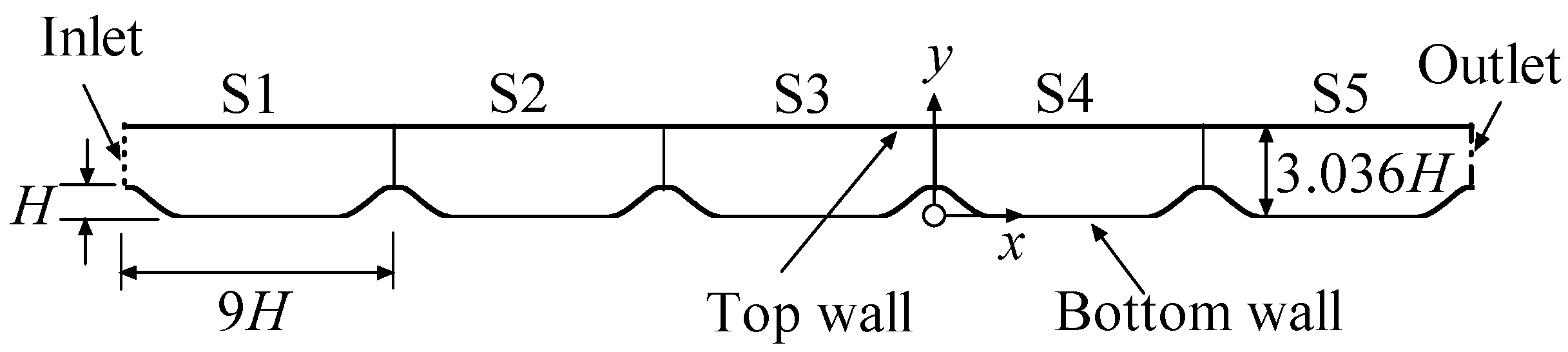
3.2. 2D Periodic Hills Flow
3.3. 2D U-Turn Duct Flow
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argyropoulos, C.D.; Markatos, N.C. Recent advances on the numerical modelling of turbulent flows. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 693–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, P.A. Some Recent Developments in Turbulence Closure Modeling. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2018, 50, 77–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, J.; von Terzi, D. Hybrid LES/RANS methods for the simulation of turbulent flows. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2008, 44, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. A review of hybrid RANS-LES methods for turbulent flows: Concepts and applications. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2020, 114, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R.; Egorov, Y. The scale-adaptive simulation method for unsteady turbulent flow predictions. Part 1: Theory and model description. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2010, 85, 113–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Krajnović, S. Validation of a novel very large eddy simulation method for simulation of turbulent separated flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2013, 73, 436–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, P.A. Near-wall turbulence closure modelling without damping functions. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 1991, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, F.; Laurence, D. A robust k-ε-v2/k elliptic blending turbulence model applied to near-wall, separated and buoyant flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 33, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, R. Recent progress in the development of the Elliptic Blending Reynolds-stress model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2015, 51, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z.W.; Liu, Y. Development of a k-ω-φ-α turbulence model based on elliptic blending and applications for near-wall and separated flows. J. Turbul. 2017, 18, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Liu, Y. An improved k-ω-φ-α turbulence model applied to near-wall, separated and impinging jet flows and heat transfer. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Durbin, P.A.; Medic, G. Development of an elliptic blending lag k−ω model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 76, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Agarwal, R.K. Development and Validation of an Elliptic Blending Lag SST k−ω Turbulence Model. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2020 FORUM, Virtual Event, 15–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. A shear stress transport incorporated elliptic blending turbulence model applied to near-wall, separated and impinging jet flows and heat transfer. Comput. Math. Appl. 2020, 79, 3257–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbein, B.; Maduta, R.; Jakirlić, S.; Tropea, C. A Scale-Resolving Elliptic-Relaxation-Based Eddy-Viscosity Model: Development and Validation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjalić, K.; Popovac, M.; Hadžiabdić, M. A robust near-wall elliptic-relaxation eddy-viscosity turbulence model for CFD. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2004, 25, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.; Ferreira, J.C.; Esch, T.; Konno, B. The SST turbulence model with improved wall treatment for heat transfer predictions in gas turbines. In Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress, Tokyo, Japan, 2–7 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mathey, F.; Cokljat, D.; Bertoglio, J.P.; Sergent, E. Specification of LES inlet boundary conditions using vortex method. In Proceedings of the 4th Internal Symposium, Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer, Antalya, Turkey, 12–17 October 2003; pp. 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Cherry, E.M.; Elkins, C.J.; Eaton, J.K. Geometric sensitivity of three-dimensional separated flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, E.M.; Elkins, C.J.; Eaton, J.K. Pressure measurements in a three-dimensional separated diffuser. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2009, 30, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, J.; Schlatter, P.; Fischer, P.F.; Henningson, D.S. Direct numerical simulation of separated flow in a three-dimensional diffuser. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 650, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, F.; Revell, A.; Craft, T. Application of recently developed elliptic blending based models to separated flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 35, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Improved two equation k-ω turbulence models for aerodynamic flows. In NASA Technical Memorandum; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Speziale, C.G.; Sarkar, S.; Gatski, T.B. Modelling the pressure–strain correlation of turbulence: An invariant dynamical systems approach. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 227, 245–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, R.; Hanjalić, K. Elliptic blending model: A new near-wall Reynolds-stress turbulence closure. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, T.; Abe, K.-I. An investigation of LES and Hybrid LES/RANS models for predicting 3-D diffuser flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2009, 31, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakirlić, S.; Maduta, R. Extending the bounds of ‘steady’ RANS closures: Toward an instability-sensitive Reynolds stress model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2015, 51, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, L.; Leschziner, M. Large eddy simulation of separated flow in a streamwise periodic channel constriction. In 2nd Internatioanl Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena: Stockholm, Sweden, 2001. In Proceedings of the 2nd Internatioanl Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena, Stockholm, Sweden, 27–29 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich, J.; Mellen, C.P.; Rodi, W.; Temmerman, L.; Leschziner, M.A. Highly resolved large-eddy simulation of separated flow in a channel with streamwise periodic constrictions. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 526, 19–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, M.; Peller, N.; Rapp, C.; Manhart, M. Flow over periodic hills–Numerical and experimental study in a wide range of Reynolds numbers. Comput. Fluids 2009, 38, 433–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Leschziner, M.; Abe, K.; Temmerman, L. Investigation of Anisotropy-Resolving Turbulence Models by Reference to Highly-Resolved LES Data for Separated Flow. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2002, 69, 161–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, F.-S.; Kalitzin, G. Computations of transonic flow with the v2–f turbulence model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2001, 22, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arolla, S.K.; Durbin, P.A. Modeling rotation and curvature effects within scalar eddy viscosity model framework. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2013, 39, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Qiu, B.; Guo, Q.; Zhuqing, L. Review on the sensitization of turbulence models to rotation/curvature and the application to rotating machinery. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 341, 46–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, D.; Seegmiller, H.; McConnaughey, P. Comparison of experiment with calculations using curvature-corrected zero and two equation turbulence models for a two-dimensional U-duct. In Proceedings of the 21st Fluid Dynamics, Plasma Dynamics and Lasers Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–20 June 1990; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 1990. AIAA 90–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, W.D.; Walters, D.K.; Leylek, J.H. A simple and robust linear eddy-viscosity formulation for curved and rotating flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2009, 19, 745–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, P.E.; Menter, F.R. Sensitization of the SST Turbulence Model to Rotation and Curvature by Applying the Spalart-Shur Correction Term. J. Turbomach. 2009, 131, 041010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, T.P.; Walters, D.K. A Three-Equation Variant of the SST k-ω Model Sensitized to Rotation and Curvature Effects. J. Fluids Eng. 2011, 133, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

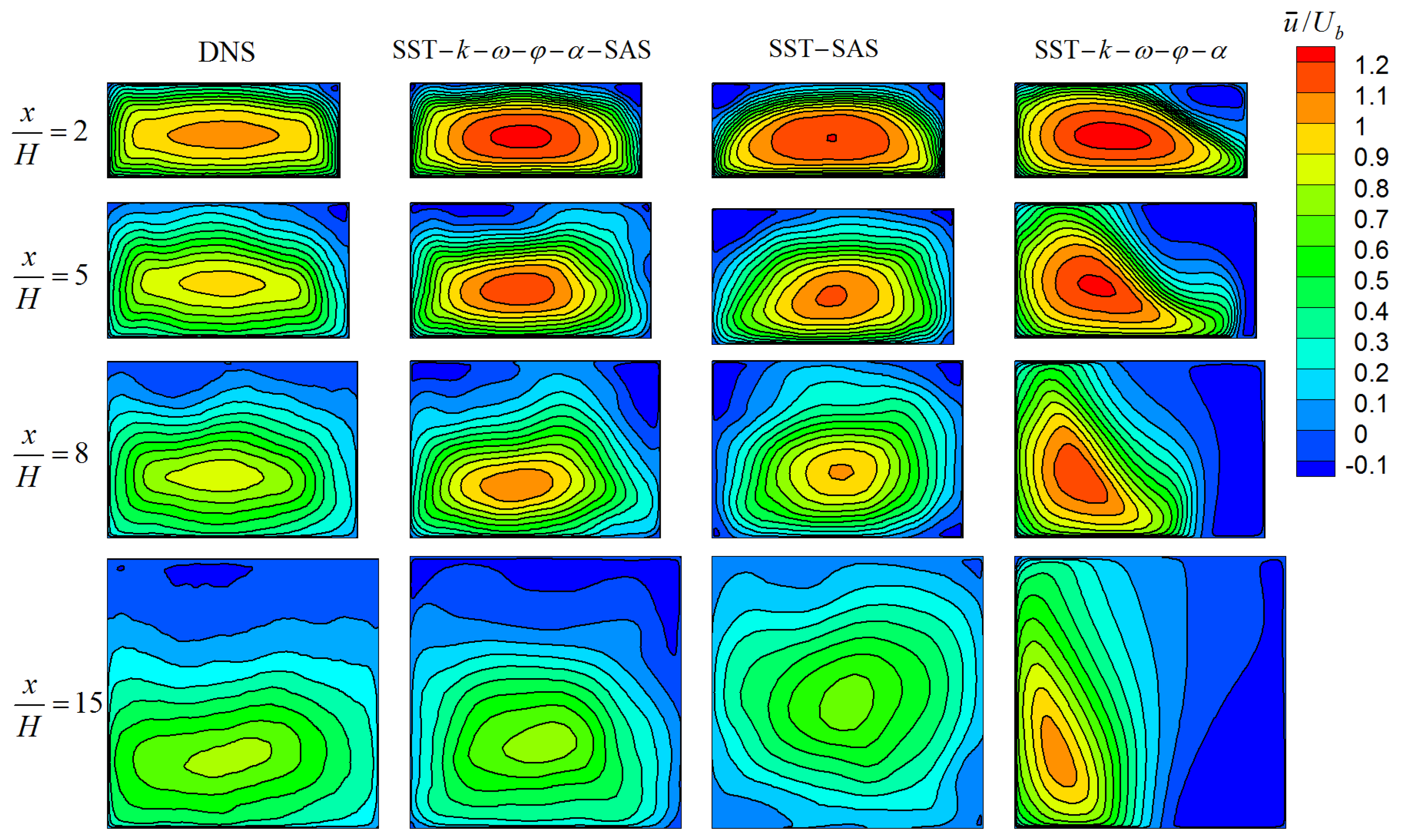
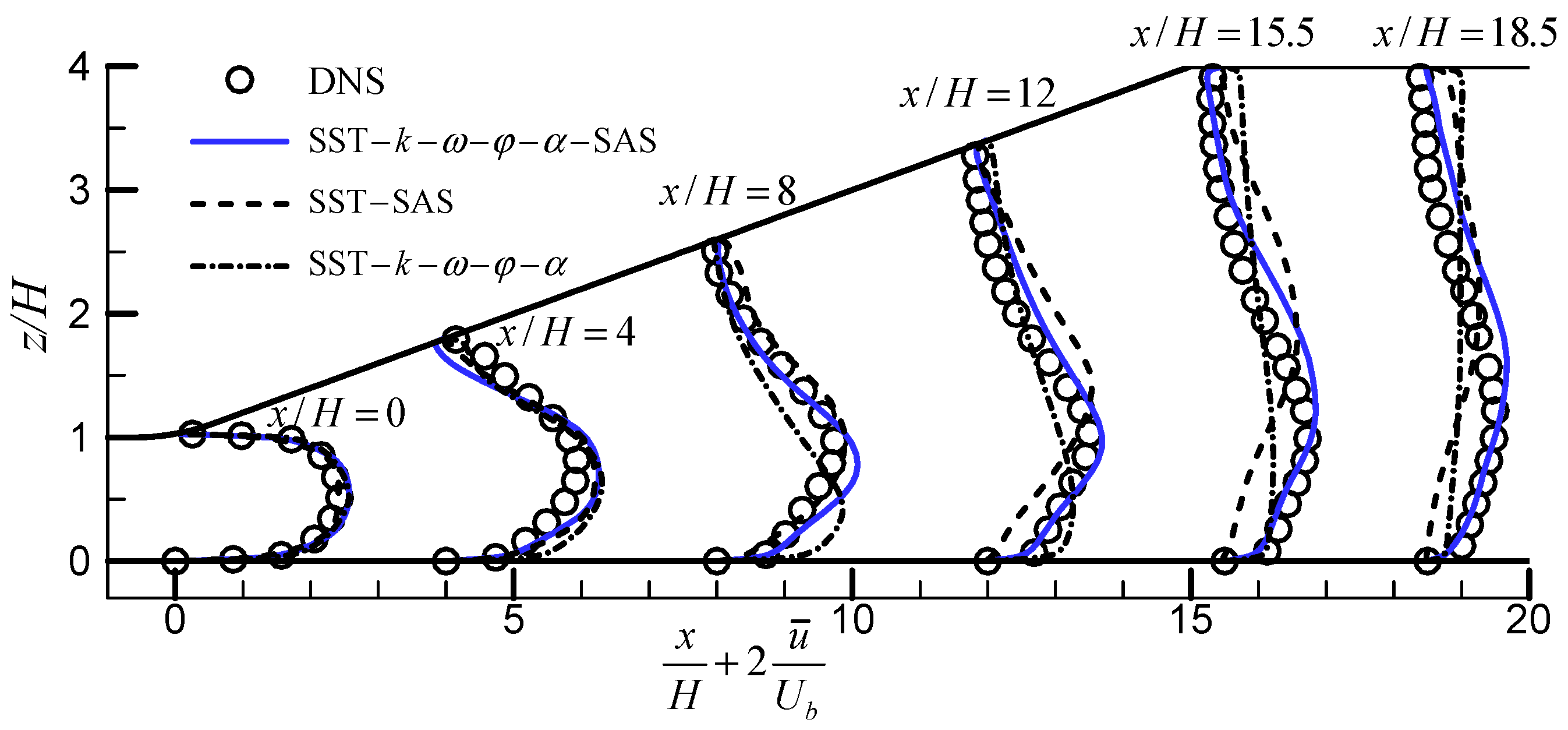
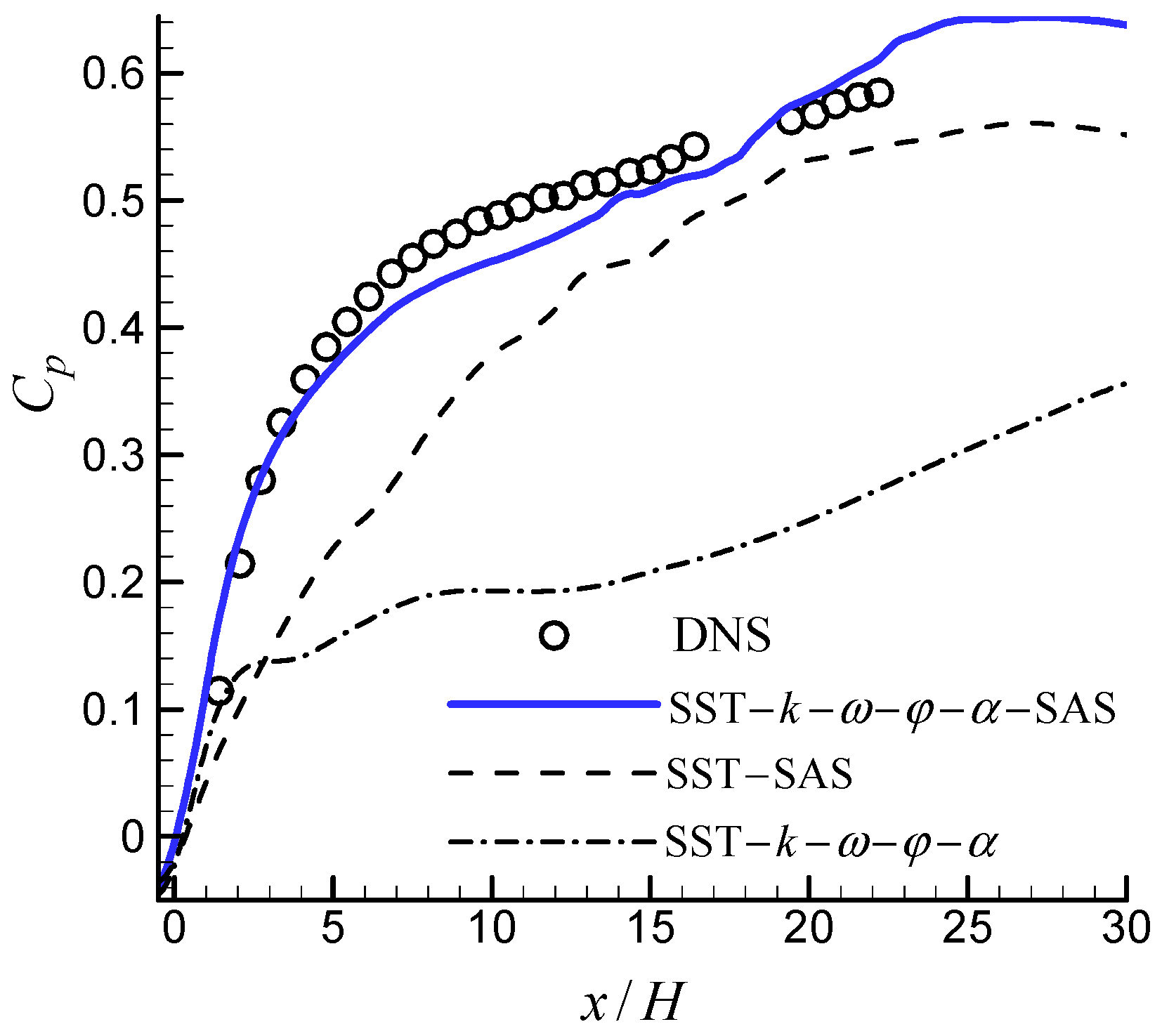

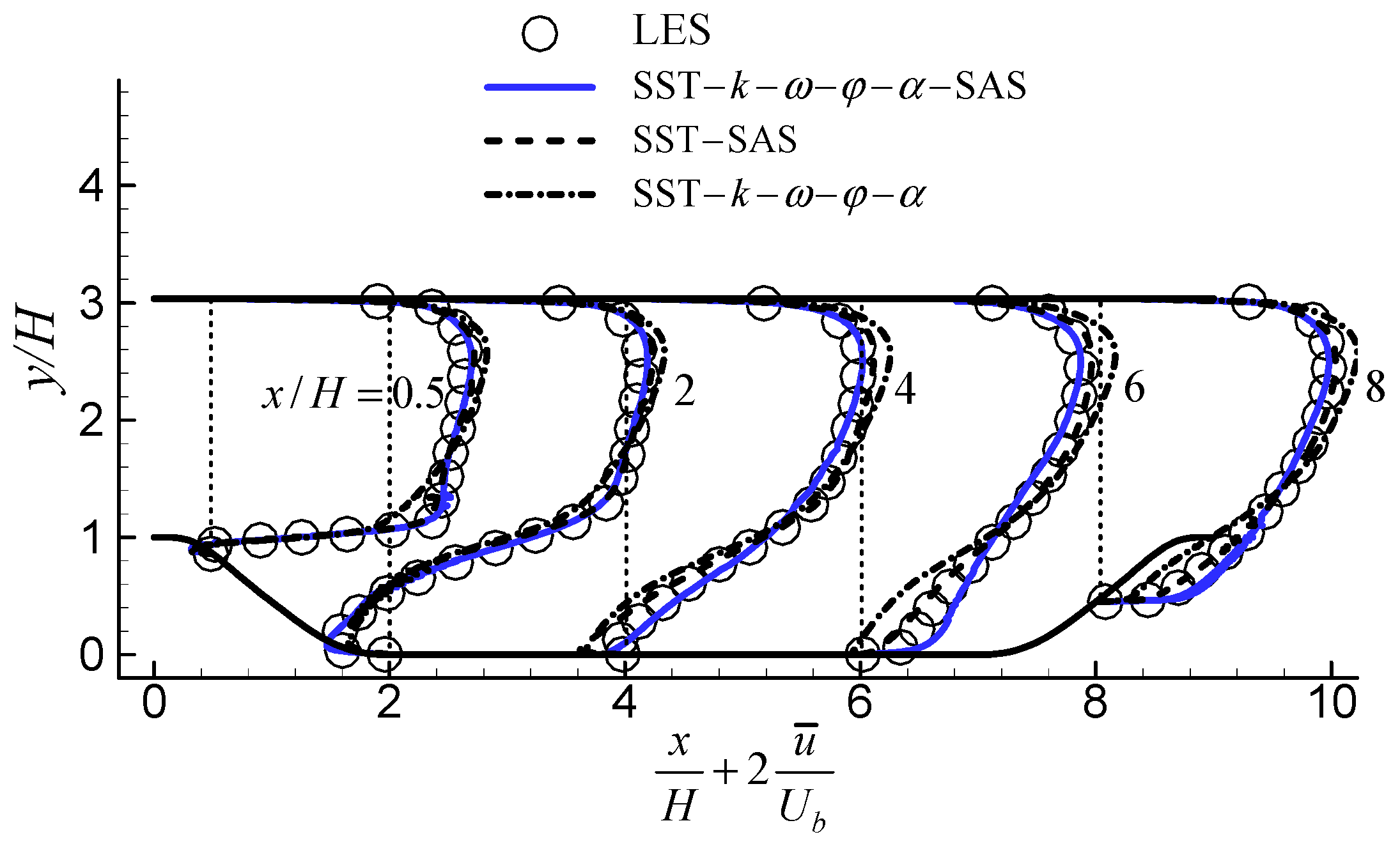
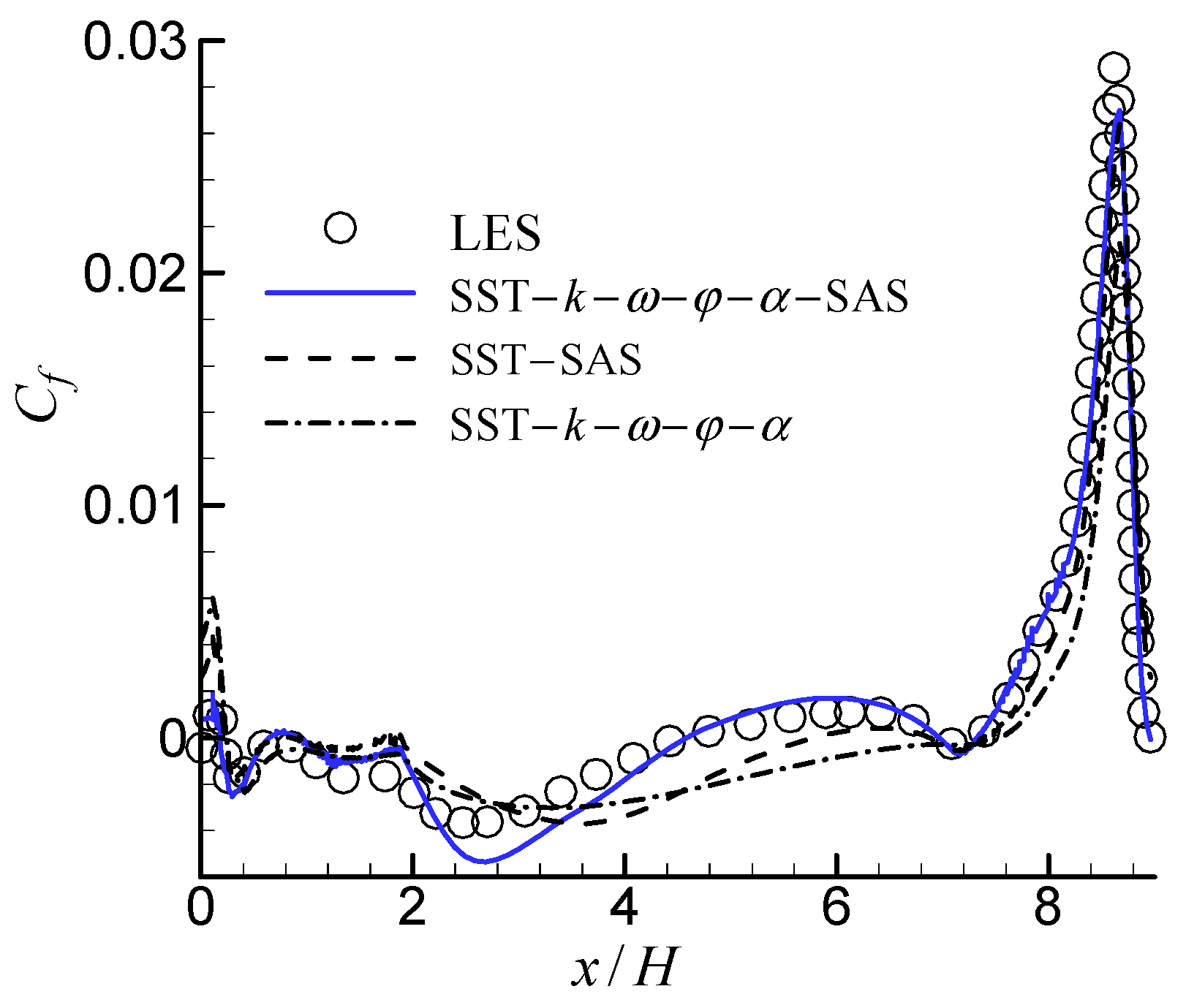
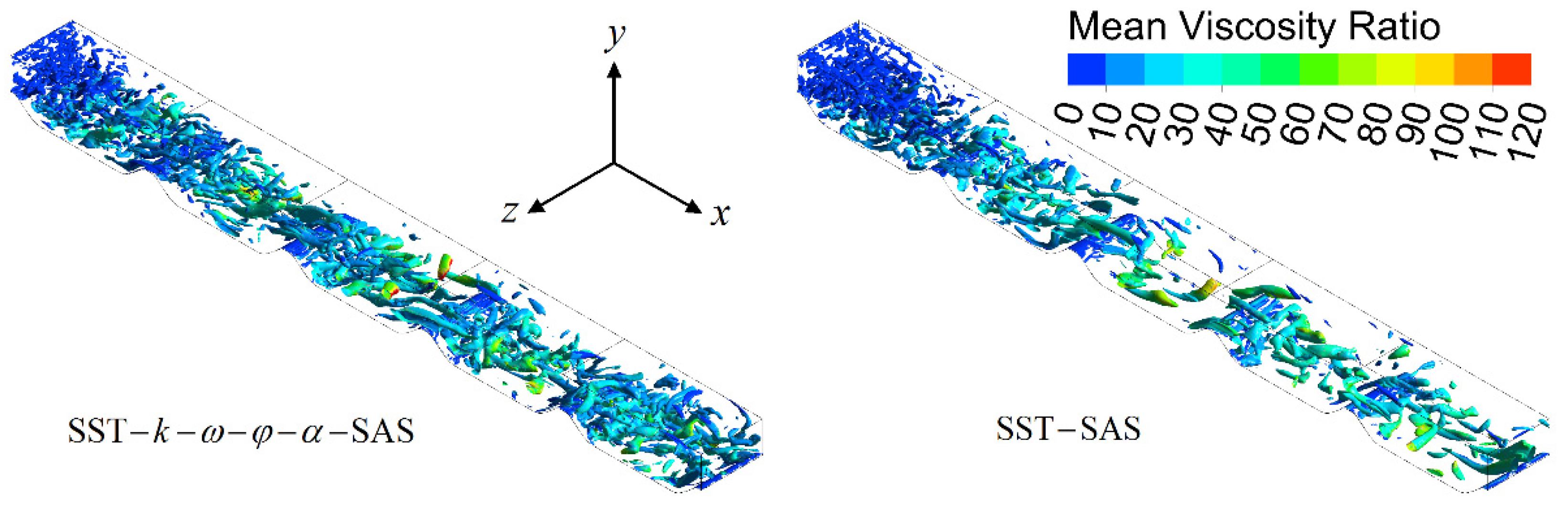
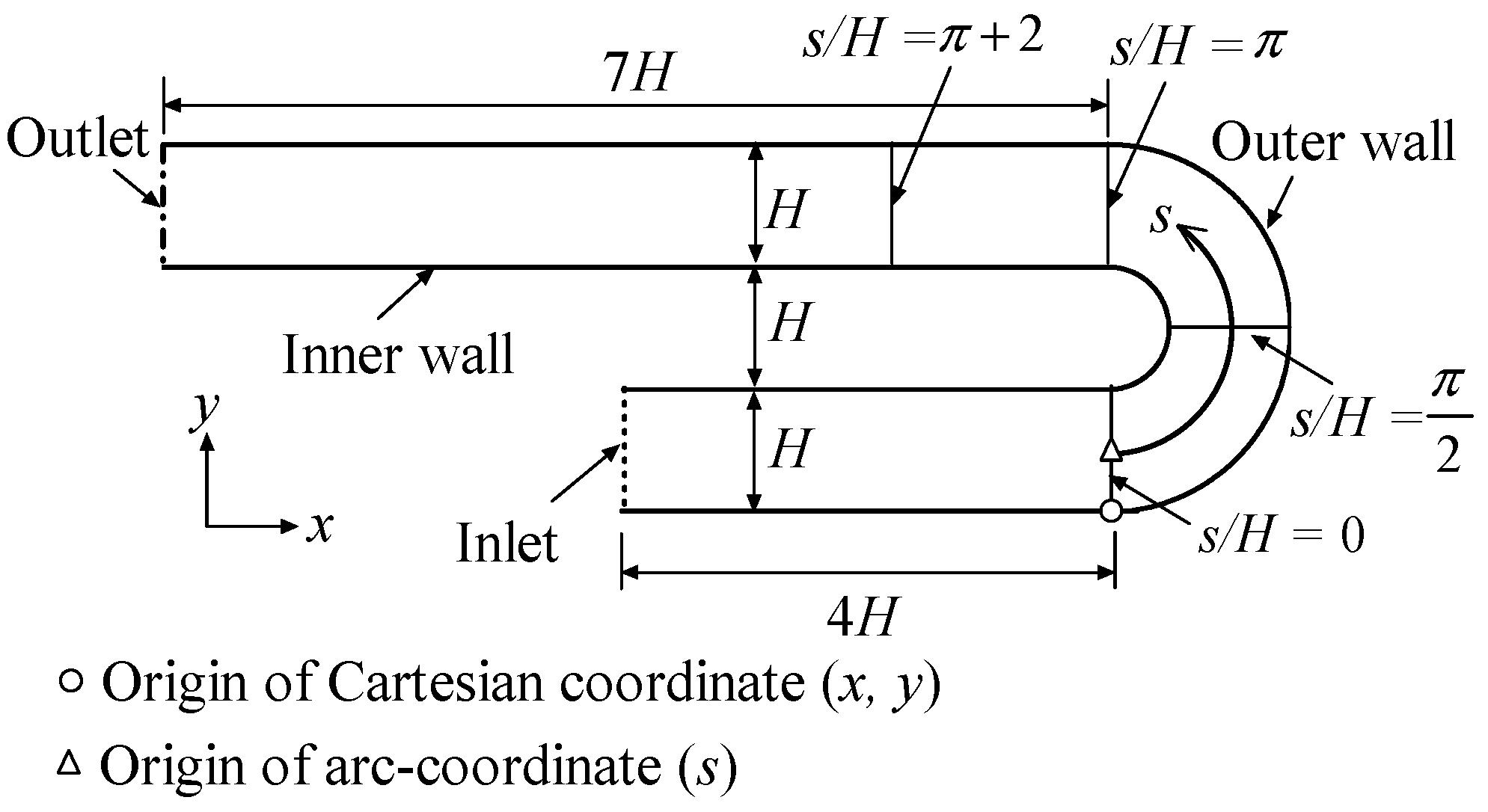

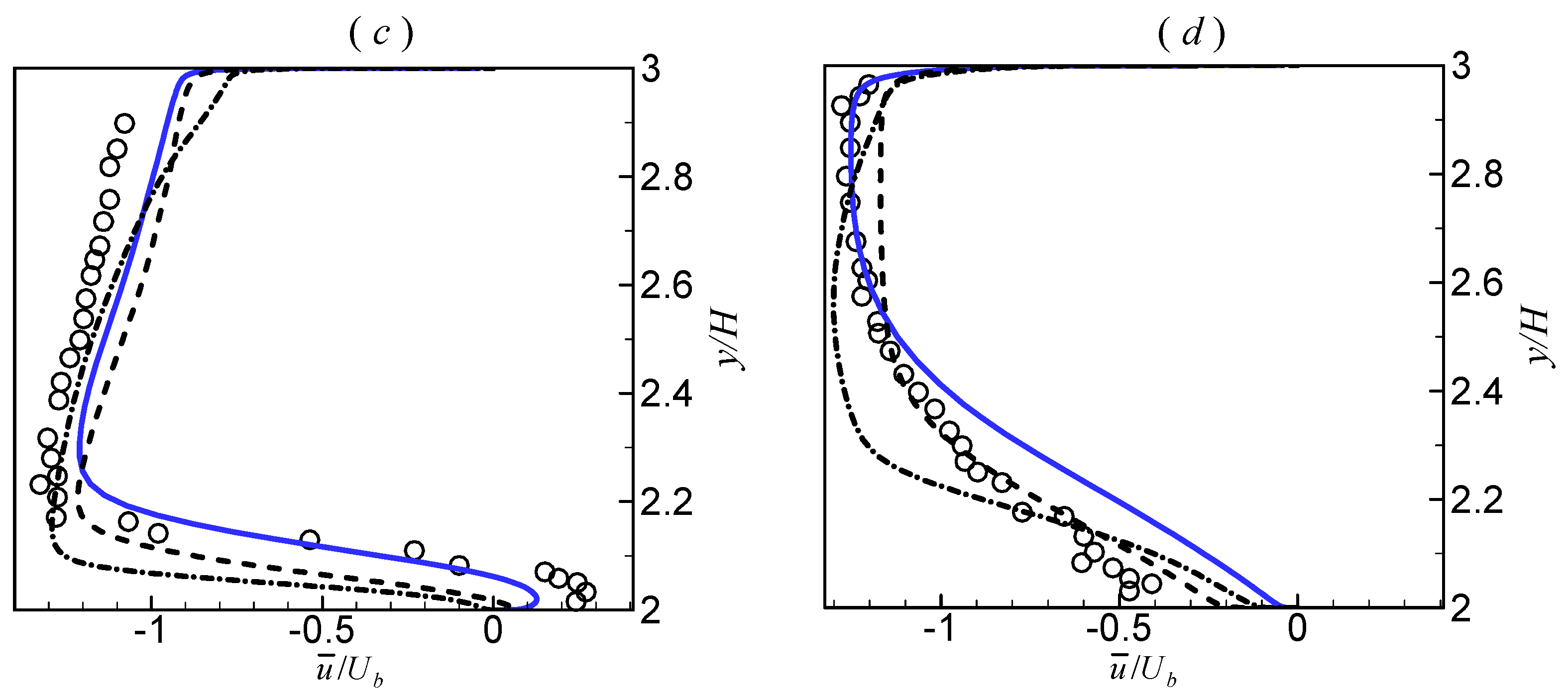
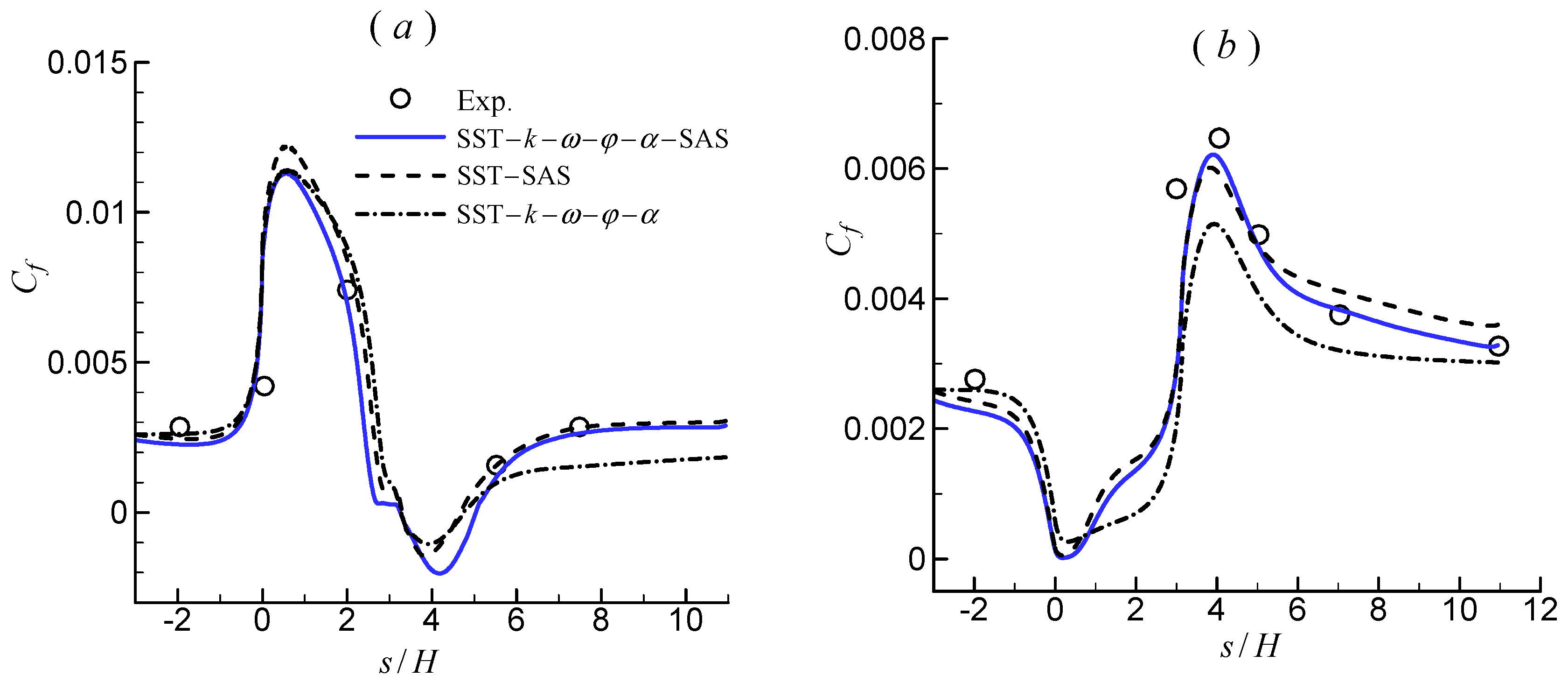
| Model | Sep. | Reatt. | Len. |
|---|---|---|---|
| LES | 0.22H | 4.72H | 4.50H |
| SST–k–ω–φ–α–SAS | 0.18H | 4.62H | 4.44H |
| SST–SAS | 0.22H | 5.79H | 5.57H |
| SST–k–ω–φ–α | 0.24H | 7.54H | 7.30H |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Yang, L. An Elliptic Blending Turbulence Model-Based Scale-Adaptive Simulation Model Applied to Fluid Flows Separated from Curved Surfaces. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042058
Yang X, Yang L. An Elliptic Blending Turbulence Model-Based Scale-Adaptive Simulation Model Applied to Fluid Flows Separated from Curved Surfaces. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(4):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042058
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xianglong, and Lei Yang. 2022. "An Elliptic Blending Turbulence Model-Based Scale-Adaptive Simulation Model Applied to Fluid Flows Separated from Curved Surfaces" Applied Sciences 12, no. 4: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042058
APA StyleYang, X., & Yang, L. (2022). An Elliptic Blending Turbulence Model-Based Scale-Adaptive Simulation Model Applied to Fluid Flows Separated from Curved Surfaces. Applied Sciences, 12(4), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042058






