A Comparative and Sex-Specific Study of Bio-Electrical Impedance Analysis and Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Whole-Body and Segmental Body Composition in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
2.5. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
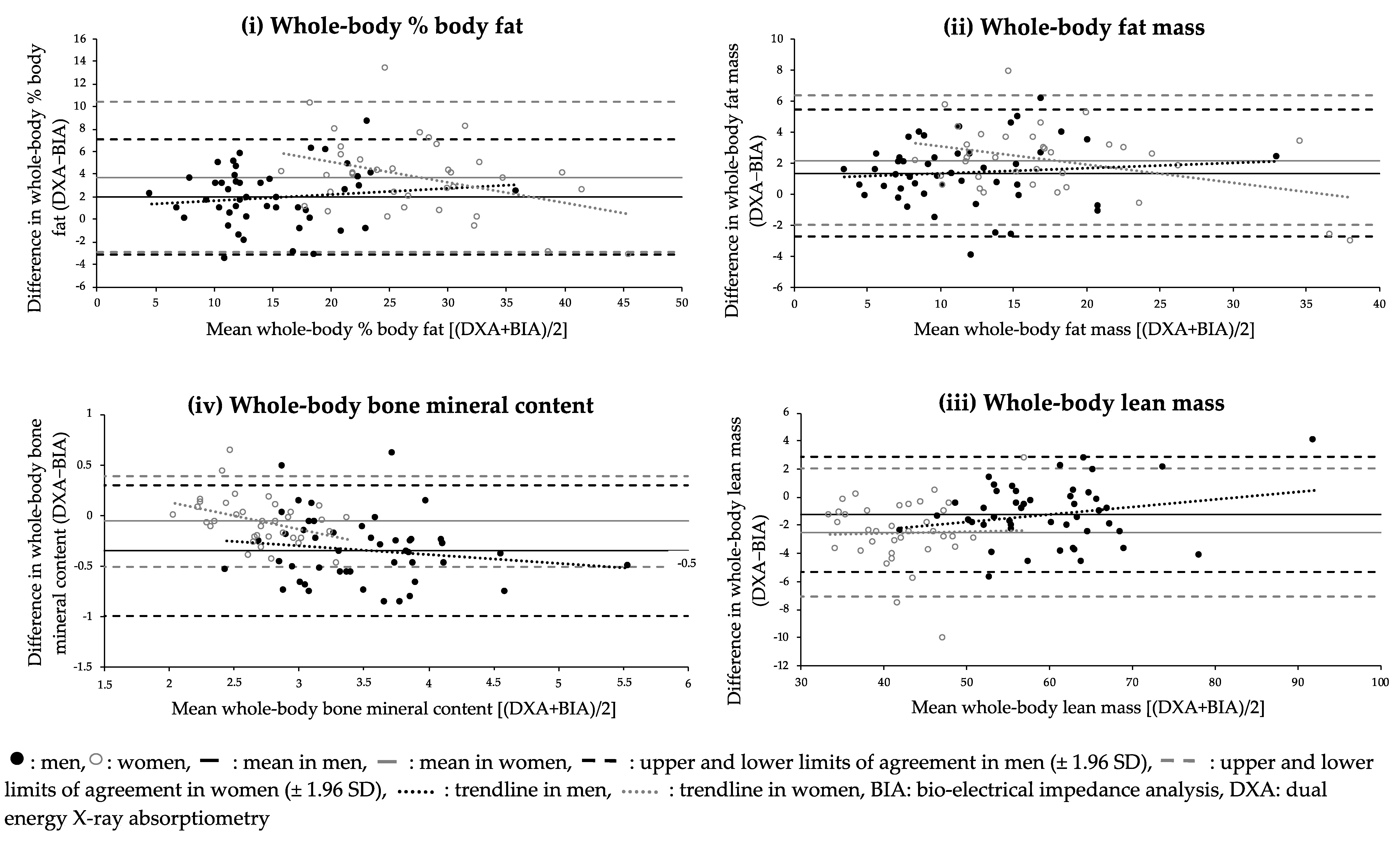
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deliens, T.; Deforche, B.; Chapelle, L.; Clarys, P. Changes in weight and body composition across five years at university: A prospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Bolonchuk, W.W.; Hall, C.B.; Siders, W.A. Validation of tetrapolar bioelectrical impedance method to assess human body composition. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 60, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heydenreich, J.; Kayser, B.; Schutz, Y.; Melzer, K. Total energy expenditure, energy intake, and body composition in endurance athletes across the training season: A systematic review. Sports Med. Open 2017, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bishop, C.; Turner, A.; Read, P. Effects of inter-limb asymmetries on physical and sports performance: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogowski, I.; Creveaux, T.; Genevois, C.; Klouche, S.; Rahme, M.; Hardy, P. Upper limb joint muscle/tendon injury and anthropometric adaptations in French competitive tennis players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2016, 16, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gomez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis--part I: Review of principles and methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InBody. Inbody S10. Available online: https://uk.inbody.com/products/inbody-s10/ (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- D’Hondt, J.; Chapelle, L.; Van Droogenbroeck, L.; Aerenhouts, D.; Clarys, P.; D’Hondt, E. Bioelectrical impedance analysis as a means of quantifying upper and lower limb asymmetry in youth elite tennis players: An explorative study. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021; 1–12, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; Mazzilli, M.; Gobbo, L.A.; Coratella, G. Assessment of body composition in athletes: A narrative review of available methods with special reference to quantitative and qualitative bioimpedance analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielemann, R.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Orlandi, S.P.; Xavier, M.O.; Bergmann, R.B.; Assuncao, M.C.; Grupo de Estudos em Composição Corporal e Nutrição. Estimation of body fat in adults using a portable a-mode ultrasound. Nutrition 2016, 32, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobelli, A.; Formica, C.; Wang, Z.; Heymsfield, S.B. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry body composition model: Review of physical concepts. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, E941–E951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toombs, R.J.; Ducher, G.; Shepherd, J.A.; De Souza, M.J. The impact of recent technological advances on the trueness and precision of DXA to assess body composition. Obesity 2012, 20, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swissray. Norland Elite. Available online: http://www.swissray.com/SRI/product.php?action=view&cid=16&pid=20 (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Nana, A.; Slater, G.J.; Stewart, A.D.; Burke, L.M. Methodology review: Using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for the assessment of body composition in athletes and active people. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, K.; Kwok, A.; Evans, A.; Mata, F.; Verdejo-Garcia, A.; Hart, K.; Ward, L.C.; Truby, H. Comparison of a bioelectrical impedance device against the reference method dual energy x-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry for the evaluation of body composition in adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esco, M.R.; Snarr, R.L.; Leatherwood, M.D.; Chamberlain, N.A.; Redding, M.L.; Flatt, A.A.; Moon, J.R.; Williford, H.N. Comparison of total and segmental body composition using DXA and multifrequency bioimpedance in collegiate female athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.J.; Erceg, D.N.; Schroeder, E.T. Utility of multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance compared to deuterium dilution for assessment of total body water. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 72, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Bruyere, O.; Geerinck, A.; Hajaoui, M.; Scafoglieri, A.; Perkisas, S.; Bautmans, I.; Gielen, E.; Reginster, J.Y.; Buckinx, F.; et al. Equation models developed with bioelectric impedance analysis tools to assess muscle mass: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 35, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriano, J.M.; Ioannidou, E.; Wang, J.; Thornton, J.C.; Horlick, M.N.; Gallagher, D.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Pierson, R.N. Pencil-beam vs fan-beam dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry comparisons across four systems: Body composition and bone mineral. J. Clin. Densitom. 2004, 7, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, T.S.; Carter, L.; Marfell-Jones, M. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment: International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Glasgow, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mukaka, M.M. A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, B.S. Agreement between single-frequency bioimpedance analysis and dual energy x-ray absorptiometry varies based on sex and segmental mass. Nutr. Res. 2018, 54, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLester, C.N.; Nickerson, B.S.; Kliszczewicz, B.M.; McLester, J.R. Reliability and agreement of various InBody body composition analyzers as compared to dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in healthy men and women. J. Clin. Densitom. 2020, 23, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Nickerson, B.S.; Wilborn, C.D.; Urbina, S.L.; Hayward, S.B.; Krieger, J.; Aragon, A.A.; Tinsley, G.M. Comparison of multifrequency bioelectrical impedance vs. dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry for assessing body composition changes after participation in a 10-Week resistance training program. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanama, K.; Putadechakun, S.; Srisuwarn, P.; Vallibhakara, S.A.; Chattranukulchai Shantavasinkul, P.; Sritara, C.; Kantachuvesiri, S.; Komindr, S. Evaluation of body composition in hemodialysis Thai patients: Comparison between two models of bioelectrical impedance analyzer and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. J. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 2018, 4537623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shafer, K.J.; Siders, W.A.; Johnson, L.K.; Lukaski, H.C. Validity of segmental multiple-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis to estimate body composition of adults across a range of body mass indexes. Nutrition 2009, 25, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingo, B.C.; Barry, V.G.; Ellis, A.C.; Gower, B.A. Comparison of segmental body composition estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 28, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.R. Body composition in athletes and sports nutrition: An examination of the bioimpedance analysis technique. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67 (Suppl. 1), S54–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deurenberg, P.; Yap, M.; van Staveren, W.A. Body mass index and percent body fat: A meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1998, 22, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Men (n = 47) Mean ± SD | Women (n = 36) Mean ± SD | Independent Sample t-Test p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 22.2 ± 1.2 | 21.2 ± 1.8 | 0.005 * |
| Height (cm) | 180.8 ± 7.8 | 166.3 ± 7.1 | <0.001 * |
| Weight (kg) | 75.1 ± 11.4 | 62.2 ± 10.7 | <0.001 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.9 ± 2.5 | 22.5 ± 3.7 | 0.554 |
| Male Participants | Mean ± SD | Mean Difference | p-Value | F-Value | Effect Size (np2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fat (%)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 14.0 ± 5.7 | 2.0 | <0.001 * | 26.039 | 0.361 |
| DXA | 16.0 ± 6.0 | ||||
| Fat mass (kg)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 10.8 ± 5.5 | 1.4 | <0.001 * | 21.202 | 0.315 |
| DXA | 12.2 ± 5.6 | ||||
| Lean mass (kg)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 60.6 ± 8.4 | 1.2 | <0.001 * | 15.485 | 0.252 |
| DXA | 59.4 ± 8.9 | ||||
| Bone mineral content (kg)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 0.4 | <0.001 * | 52.655 | 0.534 |
| DXA | 3.3 ± 0.6 | ||||
| Fat mass (kg)—Right arm | |||||
| BIA | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.180 | 1.853 | 0.039 |
| DXA | 0.7 ± 0.4 | ||||
| Fat mass (kg)—Right leg | |||||
| BIA | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 1.1 | <0.001 * | 17.270 | 0.273 |
| DXA | 3.0 ± 1.5 | ||||
| Lean mass (kg)—Right arm | |||||
| BIA | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 0.3 | <0.001 * | 51.171 | 0.527 |
| DXA | 3.3 ± 0.6 | ||||
| Lean mass (kg)—Right leg | |||||
| BIA | 10.5 ± 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.847 | 0.380 | 0.001 |
| DXA | 10.5 ± 1.9 | ||||
| Female Participants | Mean ± SD | Mean Difference | p-Value | F-Value | Effect Size (np2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fat (%)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 25.5 ± 7.8 | 3.7 | <0.001 * | 43.808 | 0.556 |
| DXA | 29.2 ± 6.6 | ||||
| Fat mass (kg)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 16.4 ± 7.7 | 2.2 | <0.001 * | 38.616 | 0.525 |
| DXA | 18.6 ± 6.9 | ||||
| Lean mass (kg)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 43.5 ± 5.5 | 2.5 | <0.001 * | 42.316 | 0.547 |
| DXA | 41.0 ± 5.5 | ||||
| Bone mineral content (kg)—Whole-body | |||||
| BIA | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.137 | 2.311 | 0.062 |
| DXA | 2.7 ± 0.3 | ||||
| Fat mass (kg)—Right arm | |||||
| BIA | 0.9 ± 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.233 | 1.475 | 0.400 |
| DXA | 1.1 ± 0.6 | ||||
| Fat mass (kg)—Right leg | |||||
| BIA | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 3.3 | <0.001 * | 65.491 | 0.658 |
| DXA | 5.7 ± 2.7 | ||||
| Lean mass (kg)—Right arm | |||||
| BIA | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 0.4 | <0.001 * | 78.658 | 0.692 |
| DXA | 1.8 ± 0.3 | ||||
| Lean mass (kg)—Right leg | |||||
| BIA | 7.5 ± 1.1 | 0.9 | <0.001 * | 22.644 | 0.438 |
| DXA | 6.6 ± 1.3 | ||||
| Men (n = 47) | Women (n = 36) | Fisher r- to z-Transformation p-Value (Z-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body fat (%)—Whole-body | 0.90 *,e | 0.90 *,e | 1.00 (0.00) |
| Fat mass (kg)—Whole-body | 0.93 *,e | 0.96 *,e | 0.21 (−1.25) |
| Lean mass (kg)—Whole-body | 0.97 *,e | 0.91 *,e | 0.01 (2.45) * |
| Bone mineral content (kg)—Whole-body | 0.85 *,d | 0.81 *,d | 0.58 (0.56) |
| Fat mass (kg)—Right arm | −0.018 a | 0.26 a | 0.22 (−1.23) |
| Fat mass (kg)—Right leg | −0.029 a | 0.43 *,b | 0.03 (−2.12) * |
| Lean mass (kg)—Right arm | 0.87 *,d | 0.61 *,c | 0.01 (2.71) * |
| Lean mass (kg)—Right leg | 0.80 *,d | 0.65 *,c | 0.16 (1.40) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Hondt, J.; Waterplas, J.; Chapelle, L.; Clarys, P.; D’Hondt, E. A Comparative and Sex-Specific Study of Bio-Electrical Impedance Analysis and Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Whole-Body and Segmental Body Composition in Healthy Young Adults. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157686
D’Hondt J, Waterplas J, Chapelle L, Clarys P, D’Hondt E. A Comparative and Sex-Specific Study of Bio-Electrical Impedance Analysis and Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Whole-Body and Segmental Body Composition in Healthy Young Adults. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157686
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Hondt, Joachim, Jana Waterplas, Laurent Chapelle, Peter Clarys, and Eva D’Hondt. 2022. "A Comparative and Sex-Specific Study of Bio-Electrical Impedance Analysis and Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Whole-Body and Segmental Body Composition in Healthy Young Adults" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157686
APA StyleD’Hondt, J., Waterplas, J., Chapelle, L., Clarys, P., & D’Hondt, E. (2022). A Comparative and Sex-Specific Study of Bio-Electrical Impedance Analysis and Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Whole-Body and Segmental Body Composition in Healthy Young Adults. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157686







