Environmental Drivers of Pesticide Toxicity: Temperature and pH Shift Azoxystrobin’s Effects on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Substance
2.2. Test Organisms
2.3. Fish Embryo Test
2.4. Hsp70 Determination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Survival Rate
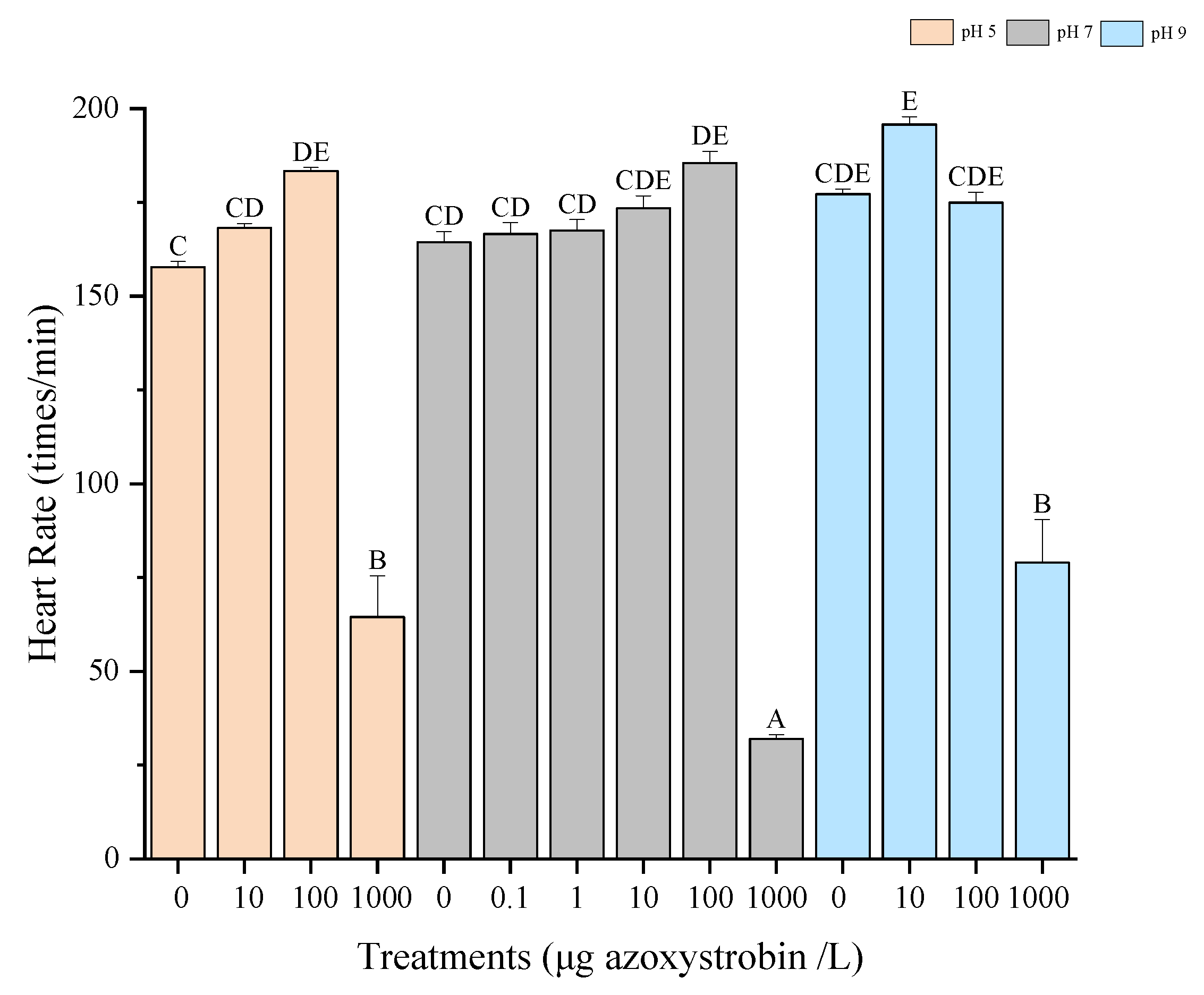
3.2. Heart Rates
3.3. Hatching Rates
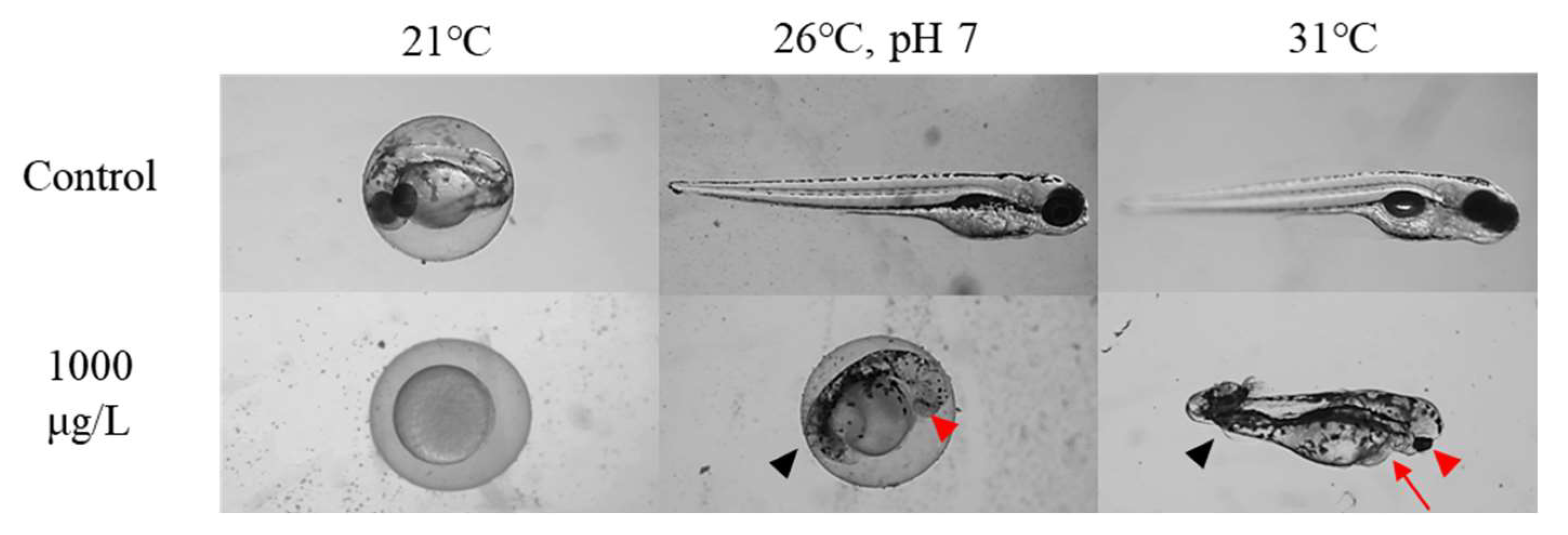
3.4. Malformation
3.5. Hsp70
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohr, S.; Antony, M.; Contardo-Jara, V.; Scholz, U.; Bader, S.; Polleichtner, C.; Arts, G. Evaluating Herbicidal Risks of the Fungicide Tebuconazole: Differential Sensitivity of Dicot and Monocot Macrophytes in Freshwater Mesocosms. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2025, 37, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Reproductive toxicity of azoxystrobin to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador, P.; Vega, C.; Navarro Pacheco, N.I.; Moratalla-López, J.; Palacios, J.; Crettaz Minaglia, M.C.; López, I.; Díaz, M.; Rico, A. Effects of the Fungicide Azoxystrobin in Two Habitats Representative of Mediterranean Coastal Wetlands: A Mesocosm Experiment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 267, 106828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenzen, N.; Lentzen-Godding, A.; Probst, M.; Schulz, H.; Schulz, R.; Liess, M. A Comparison of Predicted and Measured Levels of Runoff-Related Pesticide Concentrations in Small Lowland Streams on a Landscape Level. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, E.T.; Lopes, I.; Pardal, M.Â. Occurrence, fate and effects of azoxystrobin in aquatic ecosystems: A review. Environ. Internat. 2013, 53, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, J.; Pérez Coll, C.S.; Rojas, D.E.; Cristos, D.; Aronzon, C.M. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Complex Environmental Matrices from the Lower Paraná River Basin. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, C.; Duan, M.; Cao, N.; Jin, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Pang, S. Environmental Levels of Azoxystrobin Disturb Male Zebrafish Behavior: Possible Roles of Oxidative Stress, Cholinergic System, and Dopaminergic System. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 269, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, A.M. Development, Validation and Application of a Method Based on DI-SPME and GC–MS for Determination of Pesticides of Different Chemical Groups in Surface and Groundwater Samples. Microchem. J. 2010, 96, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.F.; Kjær, J.; Olsen, P.; Rosenbom, A.E. Leaching of Azoxystrobin and Its Degradation Product R234886 from Danish Agricultural Field Sites. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.W.; Clough, J.M.; Godwin, J.R.; Hall, A.A.; Hamer, M.; Parr-Dobrzanski, B. The Strobilurin Fungicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Willis, A.; Satbhai, K.; Ramalingam, L.; Schmitt, C.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Crago, J. Developmental toxicity in embryo-larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to strobilurin fungicides (azoxystrobin and pyraclostrobin). Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Chai, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. Toxicity of three strobilurins (kresoxim-methyl, pyraclostrobin, and trifloxystrobin) on Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 36, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yan, B.; Martyniuk, C.J. A comprehensive review of strobilurin fungicide toxicity in aquatic species: Emphasis on mode of action from the zebrafish model. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Li, H.; Zhao, F.; Wu, P.; Qian, L.; Huang, L.; Pang, S.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Qiu, L. Parental exposure to azoxystrobin causes developmental effects and disrupts gene expression in F1 embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, H.-R.; Gräff, T.; Schweizer, M.; Blumhardt, J.; Burkhardt, J.; Ehmann, L.; Hebel, J.; Heid, C.; Kundy, L.; Kuttler, J.; et al. LogD-based modelling and ΔlogD as a proxy for pH-dependent action of ionizable chemicals reveal the relevance of both neutral and ionic species for fish embryotoxicity and possess great potential for practical application in the regulation of chemicals. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, A.; Von Der Ohe, P.C.; Köhler, H.-R.; Sellier, O.; Junghans, M. Aquatic thresholds for ionisable substances, such as diclofenac, should consider pH-specific differences in uptake and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heugens, E.H.W.; Hendriks, A.J.; Dekker, T.; Straalen, N.M.V.; Admiraal, W. A Review of the Effects of Multiple Stressors on Aquatic Organisms and Analysis of Uncertainty Factors for Use in Risk Assessment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2001, 31, 247–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterauer, R. Temperature-dependent effects of the pesticides thiacloprid and diazinon on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 86, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Gong, Z.; Kelly, B.C. Assessing pH-dependent toxicity of fluoxetine in embryonic zebrafish using mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2731–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, L.; Teixidó, E.; Keddi, I.; Escher, B.I.; Klüver, N. pH-Dependent Uptake and Sublethal Effects of Antihistamines in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Chemi. 2019, 38, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, T.S.; Henriques, J.F.; Almeida, A.R.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Scholz, S.; Domingues, I. Zebrafish embryo tolerance to environmental stress factors—Concentration–dose response analysis of oxygen limitation, pH, and UV-light irradiation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, R. DarT: The embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio-a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 2002, 19, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer, M.; Von Der Ohe, P.C.; Gräff, T.; Kühnen, U.; Hebel, J.; Heid, C.; Kundy, L.; Kuttler, J.; Moroff, F.-M.; Schlösinger, A.-F.; et al. Heart rate as an early warning parameter and proxy for subsequent mortality in Danio rerio embryos exposed to ionisable substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Köhler, H.-R.; Triebskorn, R. Proteotoxicity and Apical Toxicity of Nicosulfuron to Danio rerio Embryos: A Comprehensive Assessment at Different Temperatures and pH. Pollutants 2024, 4, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ho, N.Y.; Alshut, R.; Legradi, J.; Weiss, C.; Reischl, M.; Mikut, R.; Liebel, U.; Müller, F.; Strähle, U. Zebrafish embryos as models for embryotoxic and teratological effects of chemicals. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Lian, D.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; You, J. The feasibility of the zebrafish embryo as a promising alternative for acute toxicity test using various fish species: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-236-fish-embryo-acutetoxicity-fet-test_9789264203709-en (accessed on 26 July 2013).
- Vincze, K.; Graf, K.; Scheil, V.; Köhler, H.-R.; Triebskorn, R. Embryotoxic and proteotoxic effects of water and sediment from the Neckar River (Southern Germany) to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Mao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H. Effects of two strobilurins (azoxystrobin and picoxystrobin) on embryonic development and enzyme activities in juveniles and adult fish livers of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 207, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Lv, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q. Mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and transcriptomic alterations induced by four strobilurins in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sheedy, C.; Nilsson, D.; Goss, G.G. Evaluation of Interactive Effects of UV Light and Nano Encapsulation on the Toxicity of Azoxystrobin on Zebrafish. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Wu, P.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Qian, L.; Pang, S.; Qiu, L. Short-term developmental effects and potential mechanisms of azoxystrobin in larval and adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 198, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, C.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Gong, Y.-X.; Wang, G.-X. Toxic effects of three strobilurins (trifloxystrobin, azoxystrobin and kresoxim-methyl) on mRNA expression and antioxidant enzymes in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) juveniles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompermaier, A.; Kirsten, K.; Soares, S.M.; Fortuna, M.; Kalichak, F.; Idalencio, R.; Koakoski, G.; Barreto, R.E.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Waterborne agrichemicals compromise the anti-predatory behavior of zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38559–38567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könemann, S.; Meyer, S.; Betz, A.; Županič, A.; Vom Berg, C. Sub-Lethal Peak Exposure to Insecticides Triggers Olfaction-Mediated Avoidance in Zebrafish Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11835–11847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerheide, S.D.; Morimoto, R.I. Heat Shock Response Modulators as Therapeutic Tools for Diseases of Protein Conformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33097–33100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, J.; Welsh, J.P.; Manthiram, K.; Swartz, J.R. Comparing the functional properties of the Hsp70 chaperones, DnaK and BiP. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 149, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sharma, A.; Mishra, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Chowdhuri, D.K. Heat Shock Proteins in Toxicology: How Close and How Far? Life Sci. 2010, 86, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckwert, H.; Alberti, G.; Kohler, H.-R. The induction of stress proteins (hsp) in Oniscus asellus (Isopoda) as a molecular marker of multiple heavy metal exposure: I. Principles and toxicological assessment. Ecotoxicology 1997, 6, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominassi, L.; Ressel, K.N.; Brooking, A.A.; Marbacher, P.; Ransdell-Green, E.C.; O’Brien, K.M. Metabolic rate increases with acclimation temperature and is associated with mitochondrial function in some tissues of threespine stickleback. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb244659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voituron, Y.; Roussel, D.; Teulier, L.; Vagner, M.; Ternon, Q.; Romestaing, C.; Dubillot, E.; Lefrancois, C. Warm Acclimation Increases Mitochondrial Efficiency in Fish: A Compensatory Mechanism to Reduce the Demand for Oxygen. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2022, 95, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Omar, A.A.; Khalil, R.H.; Selema, T.A.M.A.; Elsamanooudy, S.I.; El-Saftawy, H.A.M.; Sabry, E.A.; Fawzy, R.M.; Abdel-Razek, N. Influences of thermal stress on the growth biometrics, stress indicators, oxidative stress biomarkers, and histopathological alterations in European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax, juveniles. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, L.; Teixido, E.; Seiwert, B.; Escher, B.I.; Klüver, N. Influence of pH on the uptake and toxicity of β-blockers in embryos of zebrafish, Danio rerio. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 201, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, M.; Brilisauer, K.; Triebskorn, R.; Forchhammer, K.; Köhler, H.-R. How glyphosate and its associated acidity affect early development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PeerJ 2019, 7, e7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasseur, M.V.; Buchner, D.; Mack, L.; Hartmann, S.; Beketov, M.A. Multiple Stressor Effects of Insecticide Exposure and Increased Fine Sediment Deposition on the Gene Expression Profiles of Two Freshwater Invertebrate Species. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of Multiple Environmental Stressors on Zoobenthos Communities in Shallow Lakes: Evidence from a Mesocosm Experiment. Animals 2023, 13, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, O.; Stalder, T.; Cournoyer, B.; Fornelos, N.; Altaner, C.; Derome, N.; Forney, L.J.; Daguenet, T.; Risso, C.; Nicolas, P.; et al. Impacts of Multiple Anthropogenic Stressors on the Transcriptional Response of Gammarus fossarum in a Mesocosm Field Experiment. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Arle, J.; Jahnig, S.C.; Schäfer, R.B. The Hierarchy of Multiple Stressors’ Effects on Benthic Invertebrates: A Case Study from the Rivers Erft and Niers, Germany. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.S.; Schertzinger, G.; Eberhardt, J.; Bittner, M.; Sures, B. Parasites and Pollutants: Effects of Multiple Stressors on Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrot, V.; Ashauer, R.; Charles, S.; Galic, N.; Gergs, A.; Nyman, A.M.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Vandenbrouck, T.; Zimmer, E.I.; Jager, T. Environmental Risk Assessment of Time-Variable Toxicant Exposure with Toxicokinetic–Toxicodynamic Modeling Calibrated and Validated on the Reproduction of Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Endpoints | 12 hpf | 24 hpf | 48 hpf | 60 hpf | 72 hpf | 96 hpf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival rate | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Developmental delays 1 | ☑ | |||||
| Heart rates | ☑ | |||||
| Hatching success | ☑ | ☑ | ||||
| Malformations 2 | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Köhler, H.-R.; Triebskorn, R. Environmental Drivers of Pesticide Toxicity: Temperature and pH Shift Azoxystrobin’s Effects on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Development. Environments 2025, 12, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090334
Li Z, Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R. Environmental Drivers of Pesticide Toxicity: Temperature and pH Shift Azoxystrobin’s Effects on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Development. Environments. 2025; 12(9):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090334
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zequn, Heinz-R. Köhler, and Rita Triebskorn. 2025. "Environmental Drivers of Pesticide Toxicity: Temperature and pH Shift Azoxystrobin’s Effects on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Development" Environments 12, no. 9: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090334
APA StyleLi, Z., Köhler, H.-R., & Triebskorn, R. (2025). Environmental Drivers of Pesticide Toxicity: Temperature and pH Shift Azoxystrobin’s Effects on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Development. Environments, 12(9), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12090334






