Enhancing the Detection and Identification Sensitivity of Organophosphorus Pesticide-Related Phenols via Derivatization and LC-ESI-MS/MS: A Straightforward Approach to Identify the Specific Pesticide Involved in Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Synthesis of N-(2-(Bromomethyl)benzyl)-N,N-diethylethanaminium Bromide (CAX-B) Reagent
2.2.2. Derivatization Procedure
2.2.3. Spiking of Environmental Matrix Extracts
2.3. Instrumentation
2.3.1. LC-ESI-MS/MS (MRM)
LC-ESI-MS/MS (MRM) Analysis of the Phenols Prior to Derivatization
LC-ESI-MS/MS (MRM) Analysis of CAX-Phenol Derivatives
2.3.2. LC-ESI-HRMS/MS (Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry)
2.4. Comparison of the Sensitivity of the Phenols Before and After Derivatization with CAX-B
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Derivatization Strategy and Optimization of the Derivatization Reaction Between Phenols and CAX-B
3.2. High-Resolution MS/MS (Orbitrap) and MRM Analysis (QTRAP) of Targeted Phenols
3.3. High-Resolution MS/MS (Orbitrap) and MRM Analysis (QTRAP) of Targeted Phenols and Structural Insights Gained After Derivatization
3.4. Method Evaluation
3.5. Application in Real-World Matrices
3.6. Sensitivity Enhancement After Derivatization with CAX-B Using a QqQ Instrument
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USEPA. The Environmental Fate and Effect Division (EFED) Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) Chapter for Dicrotophos; Office of Pesticide Programs Special Docket for Pesticide Reregistration Risk Assessments, USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- USEPA. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED). DCPA; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- USEPA. The Environmental Fate and Effect Division (EFED) Environmental Risk Assessment for Profenofos; Office of Pesticide Programs Special Docket for Pesticide Reregistration Risk Assessments, USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Reemtsma, T.; Lingott, J.; Roegler, S. Determination of 14 monoalkyl phosphates, dialkyl phosphates and dialkyl thiophosphates by LC-MS/MS in human urinary samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, G.; Dar, M.A.; Nimesh, S.; López-Chuken, U.J.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F. Microbial degradation of organophosphate pesticides: A review. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Sancho, J.V.; Pozo, O.J. An estimation of the exposure to organophosphorus pesticides through the simultaneous determination of their main metabolites in urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 808, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.K.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, V.P. Bacterial degradation of nitrophenols and their derivatives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Jain, A.; Singh, V.K.; Verma, K.K. Solid-phase extraction combined with headspace single-drop microextraction of chlorophenols as their methyl ethers and analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Talanta 2011, 83, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcudia-León, M.C.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Determination of phenols in waters by stir membrane liquid–liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2176–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, W.W.; Chen, B.; Wu, M.; Li, S.G. Determination of 13 phenolic compounds in rice wine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, D.; Barceló, D. Comparative study of on-line solid phase extraction followed by UV and electrochemical detection in liquid chromatography for the determination of priority phenols in river water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 311, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Lu, Y.; He, Q.; Mmereki, D.; Zhou, G.; Chen, J.; Tang, X. Determination of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol, phoxim and chlorpyrifos-methyl in water samples using a new pretreatment method coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 4204–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.; Hartmann, F.; Herrmann, H. Analysis of nitrophenols in cloud water with a miniaturized light-phase rotary perforator and HPLC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jáuregui, O.; Moyano, E.; Galceran, M.T. Liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry for chlorinated phenolic compounds: Application to the analysis of polluted soils. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 823, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, D.; Barceló, D. Off-line and on-line solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography for the determination of priority phenols in natural waters. Chromatographia 1995, 40, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappiello, A.; Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Berloni, A.; Bruner, F. New approach for the analysis of acidic pesticides in water by LC/MS with a particle beam interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Simultaneous determination of nine phenolic compounds in imitation wild Dendrobium officinale samples using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3117–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraji, M.; Bakhshi, M. Determination of phenols in water samples by single-drop microextraction followed by in-syringe derivatization and gas chromatography–mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1098, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Sánchez, J.A.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Romero-González, R.; Barco-Bonilla, N.; Martínez-Vidal, J.L.; Garrido-Frenich, A. Simultaneous analysis of chlorophenols, alkylphenols, nitrophenols and cresols in wastewater effluents, using solid phase extraction and further determination by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2011, 85, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhi, H.R.; Esrafili, A.; Farahani, H.; Gholami, M.; Baneshi, M.M. Simultaneous derivatization and extraction of nitrophenols in soil and rain samples using modified hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9055–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, T.; Balogh, C.; Serfőző, Z.; Molnár-Perl, I. Analysis of phenolic compounds in the dissolved and suspended phases of Lake Balaton water by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11966–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Sánchez, J.A.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido-Frenich, A.; Martínez Vidal, J.L. Application of a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe-based method for the simultaneous extraction of chlorophenols, alkylphenols, nitrophenols and cresols in agricultural soils, analyzed by using gas chromatography–triple quadrupole-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5724–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Brunete, C.; Miguel, E.; Tadeo, J.L. Determination of tetrabromobisphenol-A, tetrachlorobisphenol-A and bisphenol-A in soil by ultrasonic assisted extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5497–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. SW-846 Test Method 8041A: Phenols by Gas Chromatography; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 1–28.
- Tchieno, F.M.M.; Tonle, I.K. p-Nitrophenol determination and remediation: An overview. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 37, 20170019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolli, W.G.; Lanças, F.M.; Dos Santos Neto, Á.J.; Silveira, H.C.S. Determination of pesticide residues in urine by chromatography-mass spectrometry: Methods and applications. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1336014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamin, T.S.; Madmon, M.; Hindi, A.; Shifrovich, A.; Prihed, H.; Blanca, M.; Weissberg, A. Enhanced LC-ESI-MS/MS sensitivity by cationic derivatization of organophosphorus acids. Molecules 2023, 28, 6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernica, M.; Poloucká, P.; Seifertová, M.; Šimek, Z. Determination of alkylphenols in water samples using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry after pre-column derivatization with dansyl chloride. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1417, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Giese, R.W. Cationic xylene tag for increasing sensitivity in mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madmon, M.; Shifrovich, A.; Tamar, S.Y.; Weissberg, A. Simple and fast determination of free cyanide in drinking water by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry following “in vial” derivatization. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 463, 116553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihed, H.; Shifrovitch, A.; Yamin, T.S.; Madmon, M.; Belay, C.; Blanca, M.; Weissberg, A. Rapid and simple identification of trace amounts of sodium azide in beverages and bodily fluids followed by derivatization and liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissberg, A.; Dagan, S. Interpretation of ESI(+)-MS-MS Spectra—Towards the Identification of “Unknowns”. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 299, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
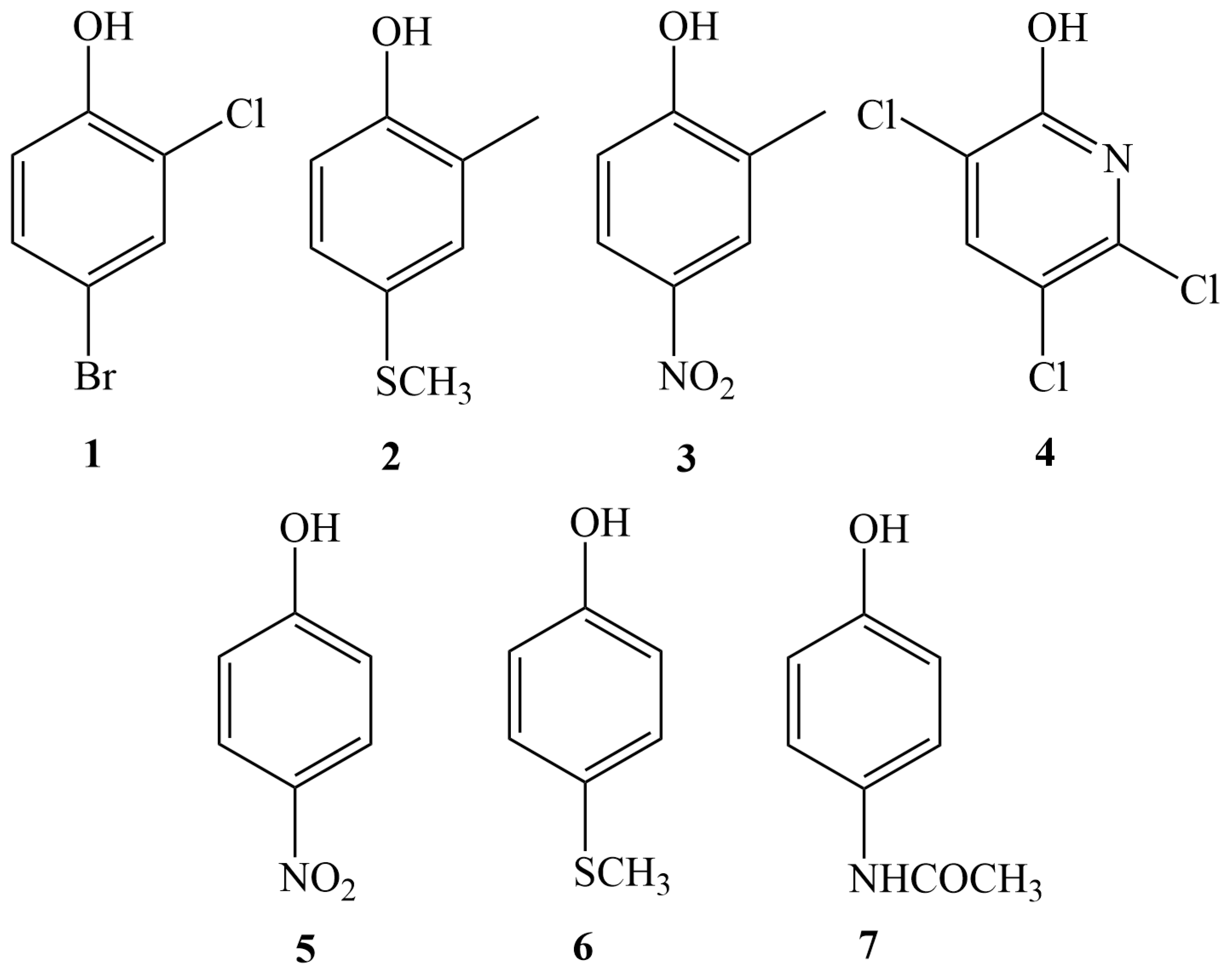
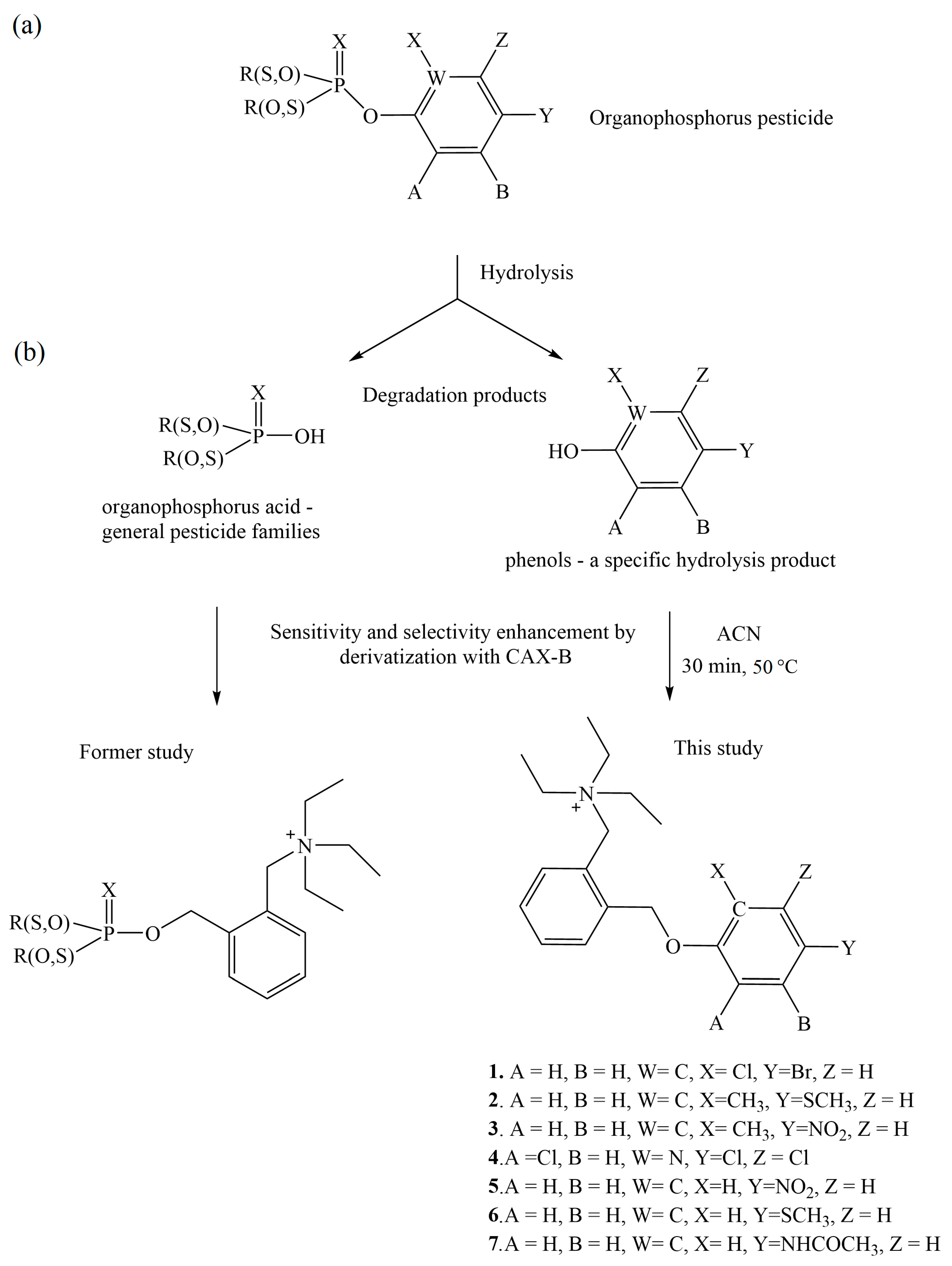
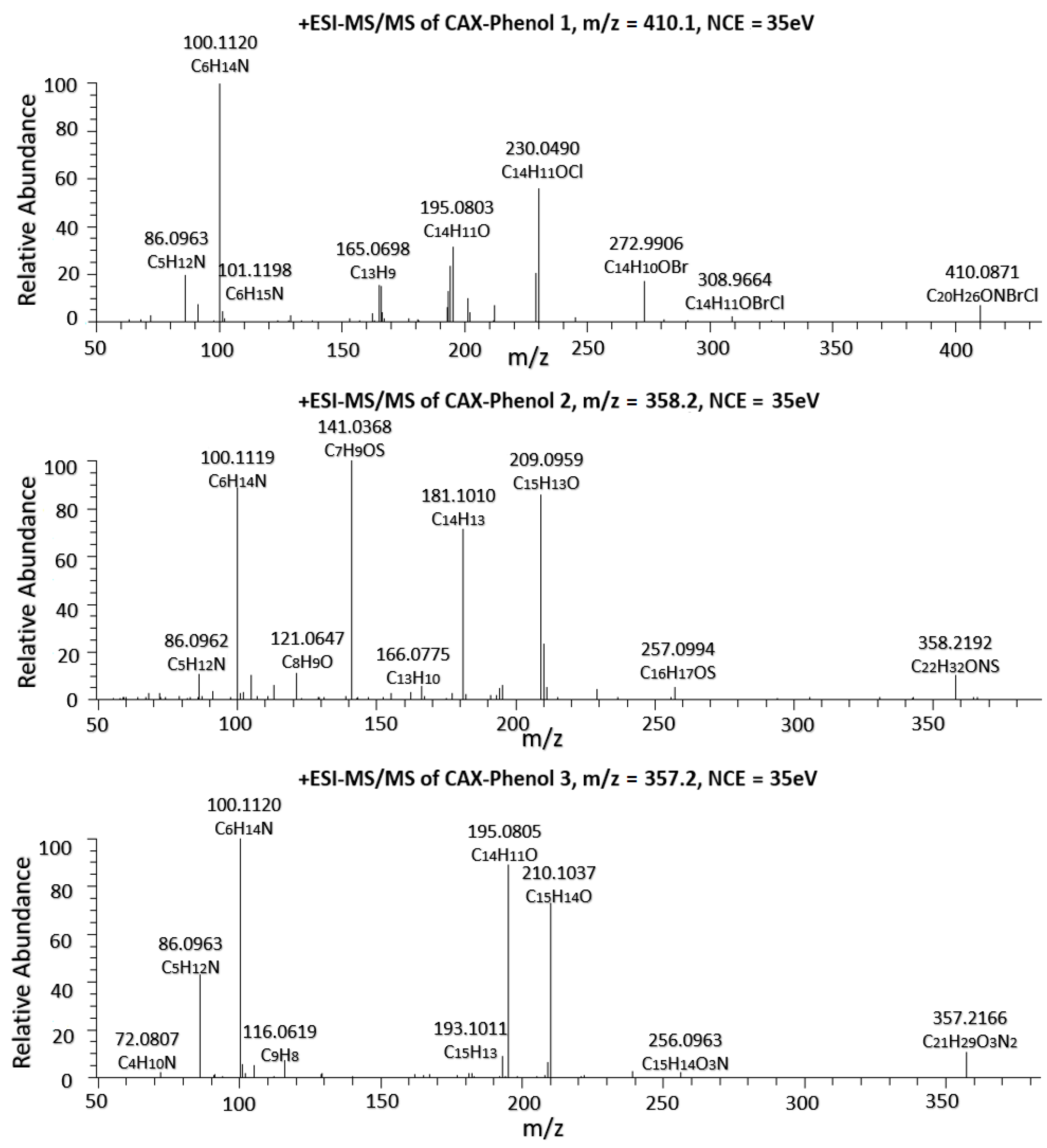
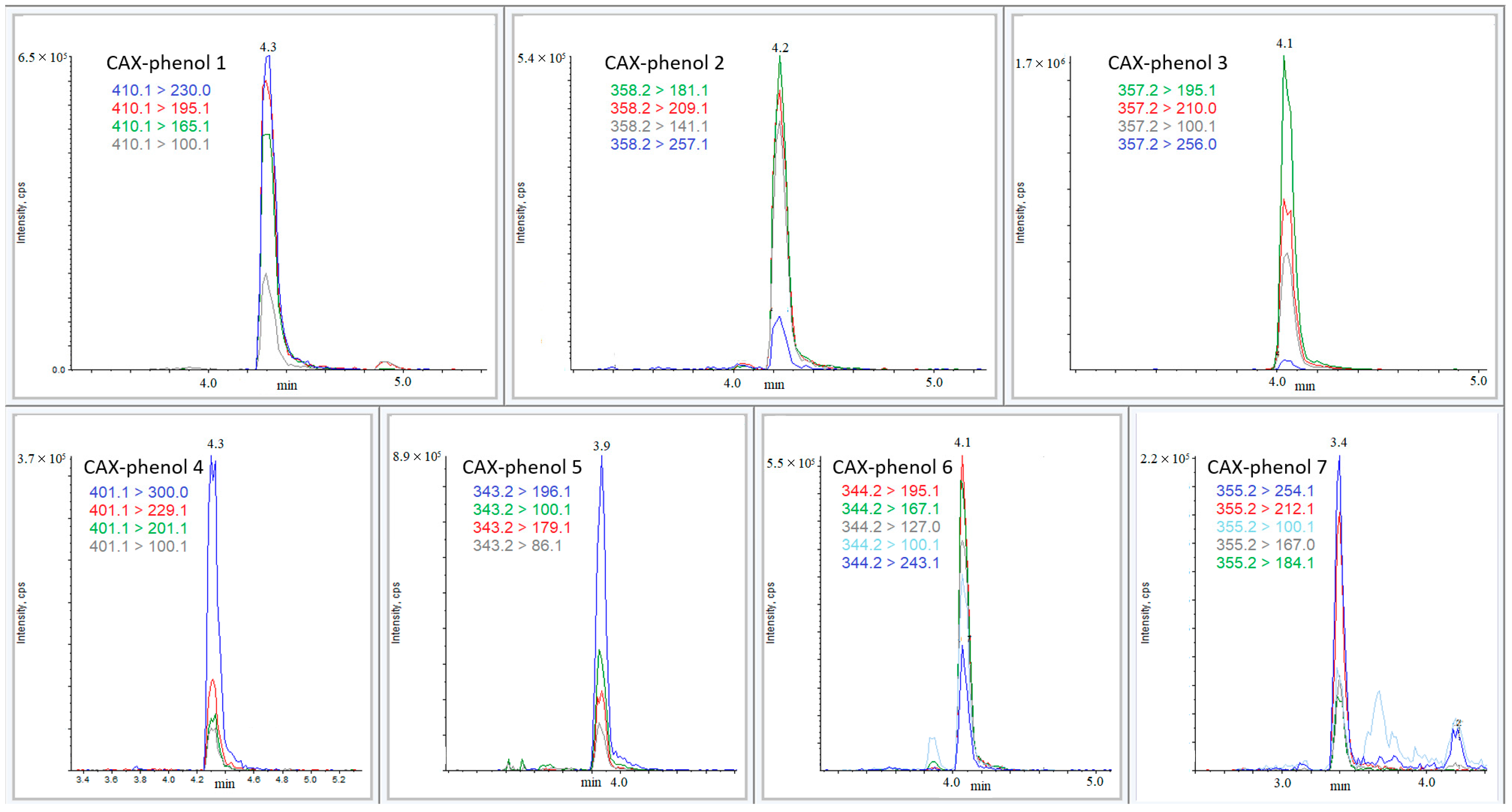

| Phenol | Formula | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion | Declustering Potential (V) | Collision Energy (eV) | Intensity Ratio | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C6H3BrClO− | (−)204.9 | 168.9 78.9 | 50 | 20 30 | 1.0 17.6 | 7.0 |
| 2 | C8H9OS− | (−)153.0 | 138.0 | 30 | 20 | - | 6.4 |
| 3 | C7H6NO3− | (−)152.0 | 122.0 106.0 93.0 | 30 | 25 30 40 | 32 2.3 1.0 | 6.2 |
| 4 | C5HCl3NO− | (−)195.9 | 159.9 | 50 | 20 | - | 7.4 |
| 5 | C6H4NO3− | (−)138.0 | 108.0 92.0 | 40 | 25 30 | 10.0 1.0 | 5.5 |
| 6 | C7H7OS− | (−)139.0 | 124.0 | 40 | 15 | - | 6.0 |
| 7 | C8H10NO2+ | (+)152.1 | 134.1 110.1 | 40 | 20 20 | 1.0 30.6 | 3.6 |
| CAX-Phenol | Formula | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion | Declustering Potential (V) | Collision Energy (eV) | Intensity Ratio | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
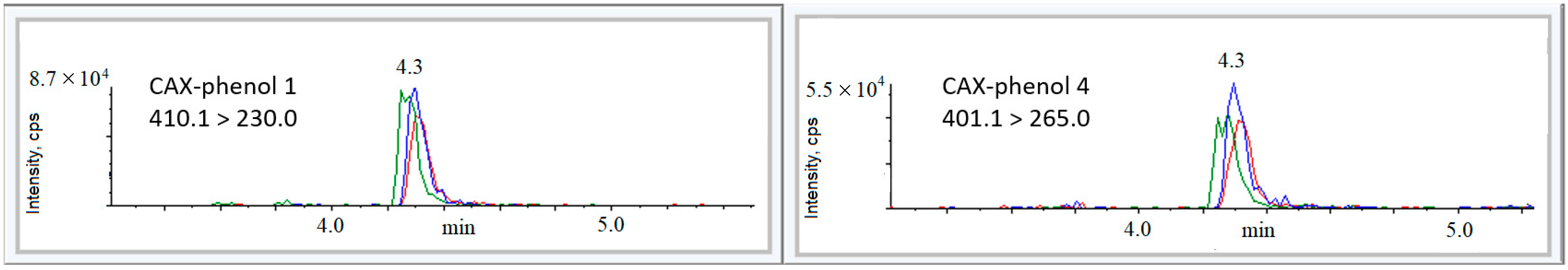
| 1 | C20H26NOBrCl+ | (+)410.1 | 230.0 195.1 165.1 100.1 | 40 | 30 45 58 47 | 3.2 3.0 2.4 1.0 | 4.3 |
| 2 | C22H32NOS+ | (+)358.2 | 257.1 209.1 181.1 141.1 | 40 | 28 33 38 30 | 1.0 5.1 5.7 4.6 | 4.2 |
| 3 | C21H29N2O3+ | (+)357.2 | 256.1 210.0 195.1 100.1 | 40 | 23 30 35 27 | 1.0 16.8 30.4 11.6 | 4.0 |
| 4 | C19H24N2OCl3+ | (+)401.1 | 300.0 265.0 229.0 201.0 100.1 | 30 | 25 35 42 40 52 | 6.3 7.3 2.2 1.3 1.0 | 4.3 |
| 5 | C20H27N2O3+ | (+)343.2 | 196.1 179.1 100.1 86.1 | 60 | 27 43 25 50 | 6.8 1.8 2.6 1.0 | 3.8 |
| 6 | C21H30NOS+ | (+)344.2 | 243.1 195.1 167.1 127.0 100.1 | 40 | 22 25 40 30 25 | 1.0 2.5 2.3 1.8 1.5 | 4.1 |
| 7 | C22H31N2O2+ | (+)355.2 | 254.1 212.1 184.1 167.0 100.1 | 50 | 25 30 42 42 27 | 4.2 3.4 1.0 1.3 1.4 | 3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weissberg, A.; Shamai Yamin, T.; Shifrovitch, A.; Tzadok, A.; Blanca, M.; Madmon, M. Enhancing the Detection and Identification Sensitivity of Organophosphorus Pesticide-Related Phenols via Derivatization and LC-ESI-MS/MS: A Straightforward Approach to Identify the Specific Pesticide Involved in Exposure. Environments 2025, 12, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060193
Weissberg A, Shamai Yamin T, Shifrovitch A, Tzadok A, Blanca M, Madmon M. Enhancing the Detection and Identification Sensitivity of Organophosphorus Pesticide-Related Phenols via Derivatization and LC-ESI-MS/MS: A Straightforward Approach to Identify the Specific Pesticide Involved in Exposure. Environments. 2025; 12(6):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060193
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeissberg, Avi, Tamar Shamai Yamin, Avital Shifrovitch, Adi Tzadok, Merav Blanca, and Moran Madmon. 2025. "Enhancing the Detection and Identification Sensitivity of Organophosphorus Pesticide-Related Phenols via Derivatization and LC-ESI-MS/MS: A Straightforward Approach to Identify the Specific Pesticide Involved in Exposure" Environments 12, no. 6: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060193
APA StyleWeissberg, A., Shamai Yamin, T., Shifrovitch, A., Tzadok, A., Blanca, M., & Madmon, M. (2025). Enhancing the Detection and Identification Sensitivity of Organophosphorus Pesticide-Related Phenols via Derivatization and LC-ESI-MS/MS: A Straightforward Approach to Identify the Specific Pesticide Involved in Exposure. Environments, 12(6), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060193






