Recent Advances in Consumer Behavior Theory: Shocks from the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
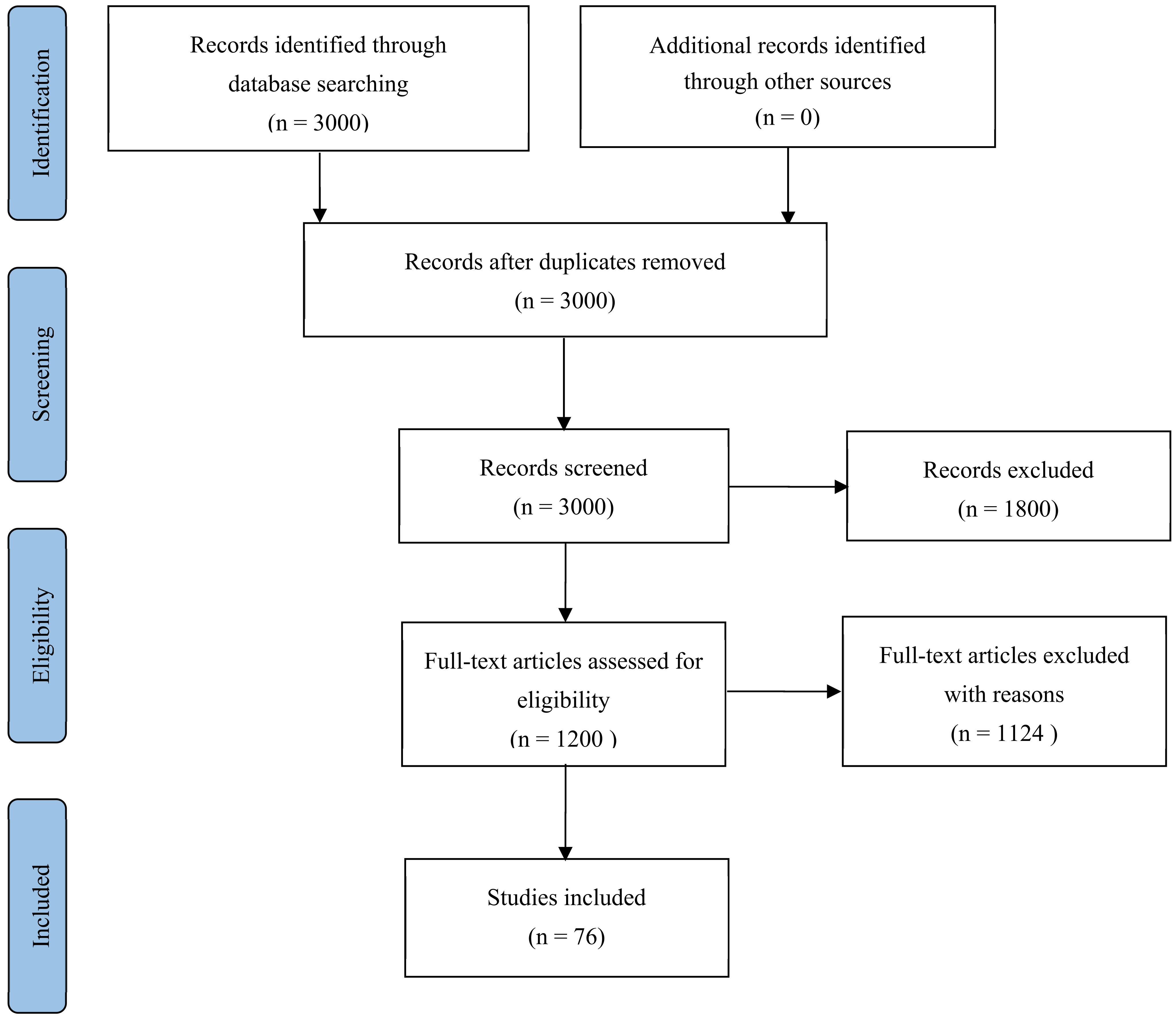
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Process
2.2. Inclusion Criteria, Extraction Process, and Quality Appraisal
3. Results
3.1. Advances in Theoretical Models
3.1.1. Early Research
3.1.2. Latest Research: Shocks from COVID-19
3.2. Consumption Willingness
3.2.1. Early Research
3.2.2. Latest Research: Shocks from COVID-19
3.3. Consumption Patterns
3.3.1. Early Research
3.3.2. Latest Research: Shocks from COVID-19
3.4. Consumption Object
3.4.1. Early Research
3.4.2. Latest Research: Shocks from COVID-19
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, L.; Meng, F.; Ji, X. Consumer Behavior; Economic Management Press: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Woods, W.A. Consumer Behavior; Elsevier North Holland: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 66. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Blackwell, R.; Miniard, P. Consumer Behavior; CBS College Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman, L.G.; Kanuk, L.L. Consumer Behavior; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Machine-buried analysis of mixed consumption behavior. Commer. Res. 2006, 17, 48–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, Y. An Economic Analysis of Consumer Behavior in the Sports Lottery Market. J. Beijing Sport Univ. 2004, 652, 605–606. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Kong, S. New Behavioral Economics Theory: An Extension of Expected Utility Theory and Prospect Theory. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2012, 32, 17–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T. 50 Years of Consumer Behavior: Evolution and Subversion. Foreign Econ. Manag. 2017, 39, 23–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. Promoting high-quality economic development through consumption upgrading. Proc. Financ. Expo 2021, 2, 12–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Research on System, Consumer Awareness and Consumer Purchase Decision. Bus. Econ. Res. 2020, 08, 109–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. Research on Marketing Strategy Based on Consumer Behavior. Natl. Circ. Econ. 2021, 9, 6–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X. How to express social concerns in consumer behavior research under emergent public health incidents: Status quo, perspective, thinking, logic. Soc. Sci. 2021, 04, 8–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F.D.; Bagozzi, R.P.; Warshaw, P.R. User Acceptance of Computer Technology: A Comparison of Two Theoretical Models. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 982–1003. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, Y. Ameta-analysis of the impact of price presentation on perceived savings. J. Retail. 2011, 78, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hern, A.; Koch, C.; Rangel, A. Consumers can make decisions in as little as a third of a second. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2011, 6, 5209530. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X. An Empirical Study on Consumers’ Willingness to Buy Tourism Products Using Mobile Payments—Based on the Technical Acceptance Model and the Theoretical Model of Planning Behavior. J. Sichuan Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2018, 6, 159–170. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, L. Nature and Operation of Attitudes. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvola, A.; Vassallo, M.; Dean, M. Predicting Intentions to Purchase Organic Food: The Role of Affective and Moral Attitudes in the Theory of Planned Behavior. Appetite 2008, 50, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.; Kerr, G.; Moore, K. Attitudes and Intentions Towards Purchasing GM Food. J. Econ. Psychol. 2002, 23, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.F.; Tung, P.J. Developing an extended Theory of Planned Behavior model to predict consumers’ intention to visit green hotels. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 36, 12–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. The theory of planned behavior and the green consumption behavior of Chinese consumers. China Circ. Econ. 2008, 8, 66–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Research on the Influencing Factors of Chinese Herbal Medicine Consumer Behavior—Taking Fujian Province as an Example; Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University: Fuzhou, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Asiah, O.N. The panic buying behavior of consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic: Examining the influences of uncertainty, perceptions of severity, perceptions of scarcity, and anxiety. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 62, 102600. [Google Scholar]
- Matheus, K.; José Alberto, F. Does the overweight epidemic cause energy consumption? A piece of empirical evidence from the European region. Energy 2021, 216, 119297. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Study on the mechanism of the impact of the COVID-19 pneumonia epidemic on the tourism industry in Guizhou Province. Mod. Bus. Trade Ind. 2021, 42, 16–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Ling, B.; Wang, L. Consumer psychology analysis of mask buying behavior under the epidemic. Mod. Bus. Trade Ind. 2021, 42, 42–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Li, H. Analysis of the influencing factors of individual panic buying behavior in emergencies—Taking mask consumption during the COVID-19 pneumonia epidemic as an example. Commer. Econ. 2021, 8, 66–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Eagly, A.H.; Shelly, C. The Psychology of Attitudes. Psychol. Inq. 1993, 4, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, C.; Robert, B.R.; Christo, K.; Managerial, B. Implications of Predicting Purchase Behavior From Purchase Intentions: A Retail Patronage Case Study. J. Serv. Mark. 2003, 17, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Shin, S. Effects of perceived interactivity on purchase intention of mobile fashion shopping malls. Res. J. Costume Cult. 2013, 21, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kim, M. Effect of On/off-line Acquaintance’s Recommendation Message on Product Attitude and Purchase Intention. J. Korean Soc. Cloth. Text. 2016, 40, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Sang, J.; Park, M. Comparison of fabric color, texture preference, and purchasing intention to fabrics recognized by smartphone displays—Focused on sensory test method. Res. J. Costume Cult. 2017, 25, 819–830. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, J.E.; Von Fricken, M.E.; Mesquita, S.V.D.O.; Diclemente, R.J. Willingness to pay for an Ebola vaccine during the 2014–2016 ebola outbreak in West Africa: Results from a U.S. National sample. J. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. The atypical impact of the epidemic on consumer behavior. Econ. Forum 2003, 16, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. The influence of consumer identity on brand purchase intention. Bus. Res. 2013, 11, 74–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L. Measurement of influencing factors of young consumers choosing online shopping based on SEM model. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Humanities Science, Management and Education Technology (HSMET 2018), International Conference on Humanities and Social Science Research, Nanjing, China, 8–10 June 2018. Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research VOL.237. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamoorthy, Y.; Radam, A.; Mohd, N. Willingness to pay for hepatitis B vaccination in Selangor, Malaysia: A cross-sectional household survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, X. Research on the Influence of the Change of Consumption Concept on the Development of Digital Products in the Post Epidemic Era. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 179, 02072. [Google Scholar]
- Bendau, A.; Petzold, M.B.; Pyrkosch, L.; Maricic, L.M.; Plag, J. Associations between COVID-19 related media consumption and symptoms of anxiety, depression and COVID-19 related fear in the general population in Germany. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 271, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Y. Effect of the event strength of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) on potential online organic agricultural product consumption and rural health tourism opportunities. Manag. Decis. Econ. MDE 2021, 42, 1156–1171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Mi, Y. The impact of consumer risk perception on consumer willingness in the post-epidemic era: An analysis of chain mediation effects based on negative emotions and safety motives. China Institute of Statistics Education. In Proceedings of the 2020 (seventh session)) National College Student Statistical Modeling Contest Outstanding Proceedings, Beijing, China, 10 December 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, F.; He, Z. An empirical study on the impact of major animal epidemics in China on consumption willingness. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, G. The impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on the consumption behavior of college students: Taking Jiangning University Town as an example. Mod. Bus. 2021, 10, 12–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N. Traditional consumer behavior and the transformation of consumption mode—A sociological perspective on expanding domestic demand. Guangdong Soc. Sci. 2003, 02, 148–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. The influence of web page background based on priming effect on online shopping behavior. Stat. Decis. 2008, 23, 103–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Demangeot, G.; Broderick, A.J. Exploration and its manifestations in the context of online shopping. J. Mark. Manag. 2010, 26, 1256–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwanho, K.; Yerim, C.; Jonghun, P. Pricing fraud detection in online shopping malls using a finite mixture mode. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2013, 12, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X. Research on the Factors Affecting Online Consumers’ Purchasing Behavior under the New Trend of E-commerce. J. Beijing Technol. Bus. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 93–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Suyanto, B.; Subiakto, H.; Srimulyo, K. Data of the patterns of youth local brand product consumption through online shopping. Data Brief 2019, 23, 2352–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H. Intelligent decision-making of online shopping behavior based on internet of things. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamunadevi, C. An empirical research on consumer online buying behaviour during the COVID-19 pandemic. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Erode, India, 15 December 2020; Volume 1055. [Google Scholar]
- Kien, P. A study on the COVID-19 awareness affecting the consumer perceived benefits of online shopping in Vietnam. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2020, 7, 1846882. [Google Scholar]
- Kostas, M.; Apostolos, P. COVID-19, internet, and mobility: The rise of telework, telehealth, e-learning, and e-shopping. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103182. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. Research on the Influencing Factors of College Students’ B2C Online Consumption Behavior Based on the Technology Acceptance Model; Yunnan University: Yunnan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Zhang, Y. Survey of mass consumption in the context of the epidemic. Shanghai Bus. 2020, 12, 175–177. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, P.; Zou, X. Study on the phenomenon of home cultural consumption under the COVID-19 epidemic. Bus. Econ. 2020, 11, 159–160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, X. The impact of the epidemic on the online and offline economy. Coop. Econ. Technol. 2021, 16, 9–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hua, X. Ablation and Transformation; Tongji University: Shanghai, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xian, L. Research on the Travel Consumption Preference of Contemporary College Students—Taking College Students in Chengdu as Research Objects. Mod. Mark. Xueyuan Ed. 2012, 7, 242–243. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Problems and Suggestions on Leisure Consumption of Urban and Rural Residents in my country. Coop. Econ. Technol. 2016, 21, 88–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chow, E.; Elkind, J. Hurricane Katrina and US Energy Security. Survivai 2005, 47, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H. Delayed epidemic peak of pandemic influenza A (H1N1-2009) among hospital workers: The association between hand hygiene behavior and the consumption of disposable hand paper. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, S55. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Wang, L. Exploration of the stock market response under sudden crisis—Based on the Banlangen panic buying incident. New West Theory Ed. 2014, 24, 62+45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lucie, D.; Konate, A.; Djossou, S.D.; Mensah, G.A.; Humle, T. Consumer perceptions and reported wild and domestic meat and fish consumption behavior during the Ebola epidemic in Guinea, West Africa. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9229. [Google Scholar]
- Vasile, G.; Cernicova-Buca, M.; Fărcasiu, M.A.; Palea, A. Romanian Students’ Environment-Related Routines during COVID-19 Home Confinement: Water, Plastic, and Paper Consumption. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8209. [Google Scholar]
- Judit, R.; Bosque-Prous, M.; Colom, J.; Folch, C.; González-Casals, H.; Fernández, E.; Espelt, A. Consumption of Alcohol, Cannabis, and Tobacco in a Cohort of Adolescents before and during COVID-19 Confinement. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7849. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Azzam, S.; Mahmoud Mhaidat, N.; Banat, H.A.; Alfaour, M.; Ahmad, D.S.; Muller, A.; Al-Nuseirat, A.; Lattyak, E.A.; Conway, B.R.; Aldeyab, M.A. An Assessment of the Impact of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic on National Antimicrobial Consumption in Jordan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Man, C.W. Impact of COVID-19 on Urban Energy Consumption of Commercial Tourism City. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.09351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yao, H. Impacts and countermeasures of tourism crisis in post-epidemic era. Coop. Econ. Technol. 2021, 15, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Caso, D.; Guidetti, M.; Capasso, M.; Cavazza, N. Finally, the chance to eat healthily: Longitudinal study about food consumption during and after the first COVID-19 lockdown in Italy. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 95, 104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R. Changing residents’ consumption awareness and market response under the COVID-19 pneumonia epidemic. Coop. Econ. Technol. 2020, 23, 86–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M. Cognitive Improvement Brings about Behavior Changes. The Demand for Healthy Consumption Is Soaring. China Consumer News, 5 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, U.; Fülöp, M.T.; Tiron-Tudor, A.; Topor, D.I.; Căpușneanu, S. Impact of Digitalization on Customers’ Well-Being in the Pandemic Period: Challenges and Opportunities for the Retail Industry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, U.; Junaid, M.; Zafar, A.U.; Li, Z.; Fan, M. Online purchase intention in Chinese social commerce platforms: Being emotional or rational? J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 63, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, U.; Hui, P.; Khan, M.K.; Yan, C.; Akram, Z. Factors Affecting Online Impulse Buying: Evidence from Chinese Social Commerce Environment. Sustainability 2018, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Research Object | Analysis Method | Research Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kim M (2013) | Smartphone users aged 20–30 | Structural equation model | Perceived usefulness directly or indirectly affects purchase intention through purchase attitude |
| Lee J (2016) | Consumers at large | Confirmatory plant analysis, structural equation modeling | If the recommendation information of acquaintances acts as an intermediary, the recommendation information will increase the consumer’s intention to buy |
| Kim T (2017) | 80 volunteers | One-way analysis of variance, Duncan test | The phone does not represent the “real” fabric color |
| Painter J (2018) | U.S. residents | Investigation and analysis | The intention of US residents to pay for ebola vaccine increased significantly during the Ebola epidemic in West Africa |
| Yogam (2019) | 728 households in Serango | Malaysia Conditional Value Method | To explore and analyze the influencing factors of Malaysian Serango adults’ intention to consume hepatitis B vaccine |
| Zhang (2020) | Consumers at large | Questionnaire analysis | It is found that consumer risk perception during the epidemic period has a negative impact on consumer intention through the chain-like intermediary path of negative emotions and safety motives |
| Yin J (2021) | Consumers at large | Questionnaire analysis | Investigate the impact of COVID-19 on online organic agricultural product consumption and rural health tourism Consumption willingness |
| Sun (2021) | College students in Jiangning University Town | Investigation and analysis | It was found that during the epidemic period, college students’ intention to spend has not changed much compared with before, but there is some retaliatory consumption |
| Wang (2021) | The public residents | Structural equation model | gender, age, education level, etc. will change their intention to consume in some ways |
| Author | Research Object | Analysis Method | Research Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li (2008) | Consumers at large | Online experiment | Web page background has an impact on consumers’ online shopping behavior, and women’s online shopping behavior is more susceptible to the influence of web page background |
| Sun (2014) | Online consumer | Questionnaire and analytic hierarchy process | Online store reputation and product cost-effectiveness are key factors that affect consumers’ online buying behavior |
| Wu (2019) | Consumers at large | Technology acceptance model | Perceived usefulness, ease of use, and attitudes toward e-commerce platforms in online shopping all have a significant impact on consumers’ online shopping behavior |
| Pham Van Kien (2020) | 427 online Vietnamese respondents | Survey analysis method | COVID-19 encourages consumers to shop online |
| Xie (2020) | Consumers at large | Questionnaire | Most survey respondents are more inclined to online shopping and contactless delivery |
| Jamunadevi C (2021) | Online consumers during the COVID-19 epidemic | Model analysis | The COVID-19 virus has an important impact on consumers’ buying behavior, and it will change consumers’ future shopping habits |
| Mouratidis Kostas (2021) | Consumers across Greece | Investigation and analysis | The importance and frequency of online shopping has increased significantly during COVID-19 |
| Zhu (2021) | Economic development during the domestic epidemic | The theoretical analysis | The epidemic hinders offline consumption and promotes online consumption |
| Author | Research Object | Analysis Method | Research Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liu (2012) | College students from 3 universities in Chengdu | Questionnaire analysis | Exploring the Law of College Students’ Travel Consumption Preference |
| Duan (2014) | Banlangen objects to buy | Event research | Analyzed the reasons for the abnormal returns caused by the panic buying of Banlangen |
| Li (2016) | Urban and rural residents in 10 cities | Questionnaire analysis | Analyze the problems existing in the leisure consumption of Chinese residents |
| RogésJudit (2021) | The educated youth group in Central Catalonia | The empirical analysis | Analyzed the influence of individual factors and social factors on risk consumption during the epidemic |
| Zhang (2021) | Energy supply and demand before and after the epidemic | Statistical analysis | Reveals the impact of COVID-19 on energy consumption in commercial tourism cities |
| GherheșVasile (2021) | Romanian students | Survey analysis method | During the epidemic, water, plastic and paper consumption increased significantly |
| Al-Azzam Sayer (2021) | National Antibacterial Drugs | Empirical evaluation analysis | Increased use of certain antibiotics during a pandemic related to increased resistance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, B.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X. Recent Advances in Consumer Behavior Theory: Shocks from the COVID-19 Pandemic. Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11120171
Yin B, Yu Y, Xu X. Recent Advances in Consumer Behavior Theory: Shocks from the COVID-19 Pandemic. Behavioral Sciences. 2021; 11(12):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11120171
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Bibo, Yajing Yu, and Xiaocang Xu. 2021. "Recent Advances in Consumer Behavior Theory: Shocks from the COVID-19 Pandemic" Behavioral Sciences 11, no. 12: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11120171
APA StyleYin, B., Yu, Y., & Xu, X. (2021). Recent Advances in Consumer Behavior Theory: Shocks from the COVID-19 Pandemic. Behavioral Sciences, 11(12), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11120171






