Cytokines, Proliferation Markers, Antimicrobial Factors and Neuropeptide-Containing Innervation in Human Nasal Mucosa after Rhinoseptoplasty Procedure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Routine Changes
3.2. Immunohistochemical Changes. Innervation and Proliferation
3.3. Immunohistochemical Changes. Antimicrobial Factors and Interleukins
3.4. Statistics
3.5. Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klocke, R.A.; Siebens, A.A.; Heath, D.A.; Beers, M.F.; Burri, P.H.; Elliott, D.H.; Weibel, E.R.; Cherniack, N.S. Human respiratory system. In Encyclopedia Britannica; Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA; Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/human-respiratory-system (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Beule, A.G. Physiology and pathophysiology of respiratory mucosa of the nose and the paranasal sinuses. GMS Curr. Top. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.C.; Karp, D.A.; Kahwaji, C.I. Nasal Physiology. 2008. Available online: https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/ (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Scherzad, A.; Hagen, R.; Hackenberg, S. Current Understanding of Nasal Epithelial Cell Mis-Differentiation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mescher, A.L. The Respiratory System. In Junqueira’s Basic Histology: Text & Atlas; McGraw-Hill Education/Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Chapter 17; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D. (Eds.) The Olfactory Epithelium and Olfactory Receptor Neurons. In Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachostergios, P.J.; Papandreou, C.N. Neuroendocrine differentiation and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in cancer: Partners or enemies? World J. Exp. Med. 2011, 1, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, E.H.; Wu, E.; Curry, W.T.; Lin, D.T.; Schwob, J.E. Immunohistochemical characterization of human olfactory tissue. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1687–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellette, A.J. Paneth cell α-defensins in enteric innate immunity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2215–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freye, M.; Bargon, J.; Dauletbaev, N.; Weber, A.; Wagner, T.O.; Gropp, R. Expression of human alpha-defensin 5 (HD5) mRNA in nasal and bronchial epithelial cells. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 53, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanzadeh, R.; Hüttmann, G.; Gerdes, J.; Scholzen, T. Chromophore-assisted light inactivation of pKi-67 leads to inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell Prolif. 2007, 40, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrówka-Kata, K.; Namysłowski, G.; Stęplewska, K.; Gabriel, A.; Wysocka, A. Immunohistochemiczna ocena moleku?y Ki67 w tkance polipów nosa. Otolaryngol. Polska 2007, 61, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavello, W.; Viganò, P.; Romagnoli, M.; Sordo, L.; Berti, E.; Tredici, G.; Gaini, R.M. Expression of Cell Cycle Regulatory Proteins and Analysis of Apoptosis in Normal Nasal Mucosa and in Nasal Polyps. Am. J. Rhinol. 2005, 19, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Qurie, A. Interleukin; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, N.C.; Shayakhmetov, N.C.D.P.D.M. Interleukin 1α and the inflammatory process. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cánoves, P.; Scheele, C.; Pedersen, B.K.; Serrano, A.L. Interleukin-6 myokine signaling in skeletal muscle: A double-edged sword? FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4131–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Qu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Tan, M.; Jiang, J.; Qin, X. Role of epithelial chemokines in the pathogenesis of airway inflammation in asthma (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6935–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beste, M.T.; Lomakina, E.B.; Hammer, D.A.; Waugh, R.E. Immobilized IL-8 Triggers Phagocytosis and Dynamic Changes in Membrane Microtopology in Human Neutrophils. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, C.L.; Barton, G.M.; Farr, A.G.; Medzhitov, R. A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 9, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsias, D.I.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Veiopoulou, C.; Zintzaras, E.; Tassios, I.K.; Kogopoulou, O.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Thyphronitis, G. The Th1/Th2 cytokine balance changes with the progress of the immunopathological lesion of Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 128, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.L.; Goff, O.R.-L.; Huntington, N.D.; Sousa, A.P.; Ribeiro, V.S.G.; Bordack, A.; Vives, F.L.; Peduto, L.; Chidgey, A.; Cumano, A.; et al. Characterization of the thymic IL-7 niche in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikker, A.; Hack, C.E.; Lafeber, F.P.; Van Roon, J.A. Interleukin-7: A key Mediator in T Cell-driven Autoimmunity, Inflammation, and Tissue Destruction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkus, J.; Vaitkus, S.; Vitkauskienė, A. Changes of inflammatory markers IL-4, IL-5, IL-7, IL-21 of the nasal mucosa in patients with chronic odontogenic and fungal-allergic sinusitis. In Proceedings of the 5th Lithuanian—Polish ENT Congress, Druskininkai, Lithuania, 13–15 June 2019; pp. 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, B.; De Groot, E.J.J.; Kortekaas, I.J.M.; Fokkens, W.J.; Van Drunen, C.M. Nasal epithelial cells express IL-10 at levels that negatively correlate with clinical symptoms in patients with house dust mite allergy. Allergy 2007, 62, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, T.; Barnett, J.B.; Li, B. Interleukin 12 a Key Immunoregulatory Cytokine in Infection Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesdon, J.L.; Ternynck, T.; Avrameas, S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1979, 27, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilmane, M.; Rumba, I.; Sundler, F.; Luts, A. Patterns of distribution and occurrence of neuroendocrine elements in lungs of hu-mans with chronic lung diseases. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. 1998, 52, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Peebua, P.; Kruatrachue, M.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Kosiyachinda, P. Histological effects of contaminated sediments in Mae Klong River Tributaries, Thailand, on Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Sci. Asia 2006, 32, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichman, M.; Piedra Buena, I.T. Rhinoplasty; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, January 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558970/ (accessed on 27 June 2020).
- Hong, H.R.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, Y.J. Aesthetic Motivation of Geriatric Rhinoplasty the Surgical Outcome. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2015, 26, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standring, S. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bradding, P.; Feather, I.H.; Wilson, S.; Bardin, P.G.; Heusser, C.H.; Holgate, S.T.; Howarth, P.H. Immunolocalization of cytokines in the nasal mucosa of normal and perennial rhinitic subjects. The mast cell as a source of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 in human allergic mucosal inflammation. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 3853–3865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Hong, S. Serum levels of IL-12, IL-4 and pathologic changes by scanning electron microscope of nasal mucous inflammation. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2010, 24, 913–917. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.D.; Christodoulopoulos, P.; Frenkiel, S.; Hamid, Q. Expression of interleukin (IL)-12 (p40) and IL-12 (beta 2) receptors in allergic rhinitis and chronic sinusitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J. Interleukin-10 polymorphisms, cancer susceptibility and prognosis. Fam. Cancer 2006, 5, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Han, R.; Kim, D.W.; Mo, J.-H.; Jin, Y.; Rha, K.-S.; Kim, Y.M. Role of Interleukin-10 on Nasal Polypogenesis in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-C.; Yao, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.-X.; Ma, J.; Chen, C.-L.; Deng, Y.-K.; Wang, M.-C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; et al. Deficiency in interleukin-10 production by M2 macrophages in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlgraf, K.G.; Pingel, L.C.; Dietrich, D.E.; Brogden, K.A. Defensins as anti-inflammatory compounds and mucosal adjuvants. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaní-Guerra, E.; Negrete-García, M.C.; Montes-Vizuet, R.; Asbun-Bojalil, J.; Terán, L.M. Human β-Defensin-2 Induction in Nasal Mucosa after Administration of Bacterial Lysates. Arch. Med Res. 2011, 42, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Shen, W.; Rowan, N.R.; Kulaga, H.; Hillel, A.; Jr, M.R.; Lane, A.P. Elevated ACE2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: Implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2001948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynes, D.M.; Lucas, G.H.; Beyak, M.J.; Lomax, A.E. Effects of Inflammation on the Innervation of the Colon. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gabory, L.; Deminière, C.; Stoll, D. Expression immunohistochimique de l’ACE, de l’UEA-I et du Ki-67 dans les papillomes inversés naso-sinusiens Immunohistochemistry expression of 3 markers (CEA, UEA-I and Ki-67) in nasal inverted papillo-mas. Rev. Laryngol. Otol. Rhinol. 2008, 129, 159–165. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Oncel, S.; Cosgul, T.; Calli, A.; Calli, C.; Pinar, E. Evaluation of P53, P63, P21, P27, Ki-67 in Paranasal Sinus Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Inverted Papilloma. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 63, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
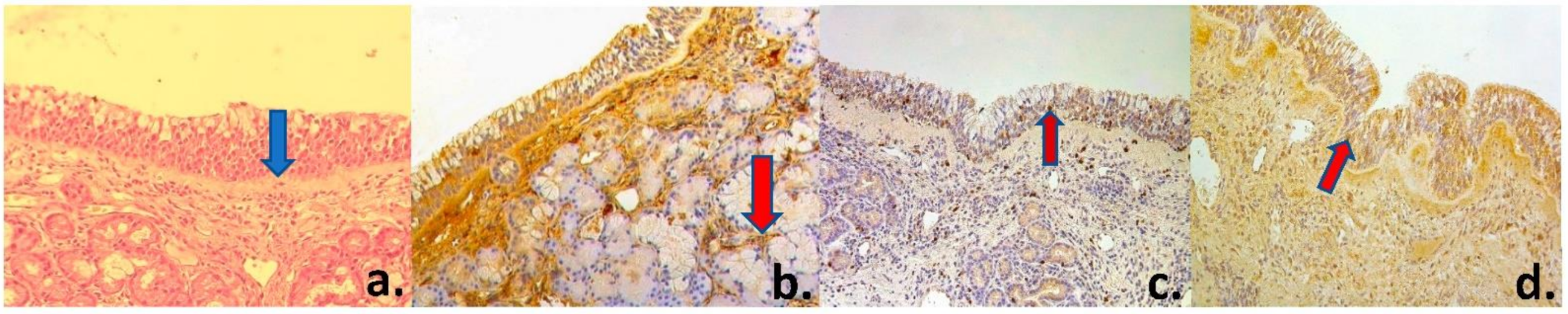
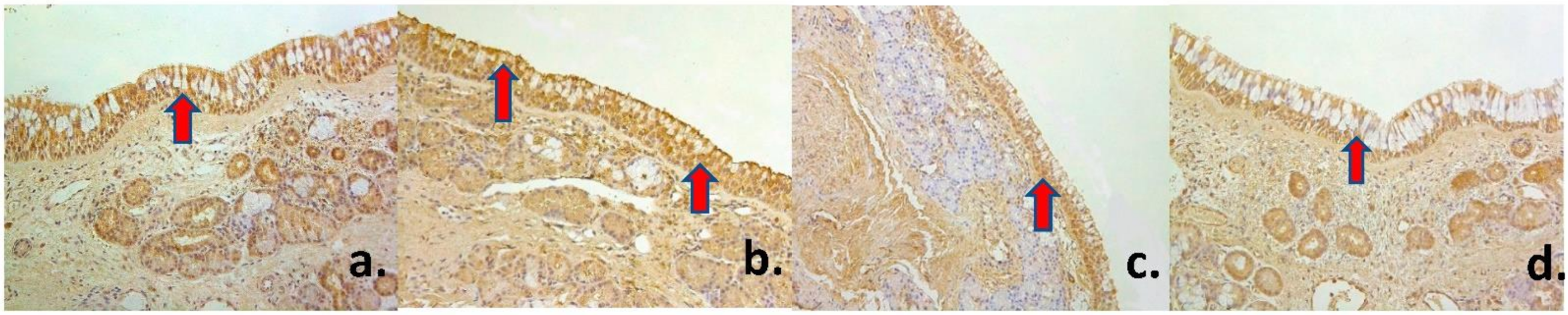
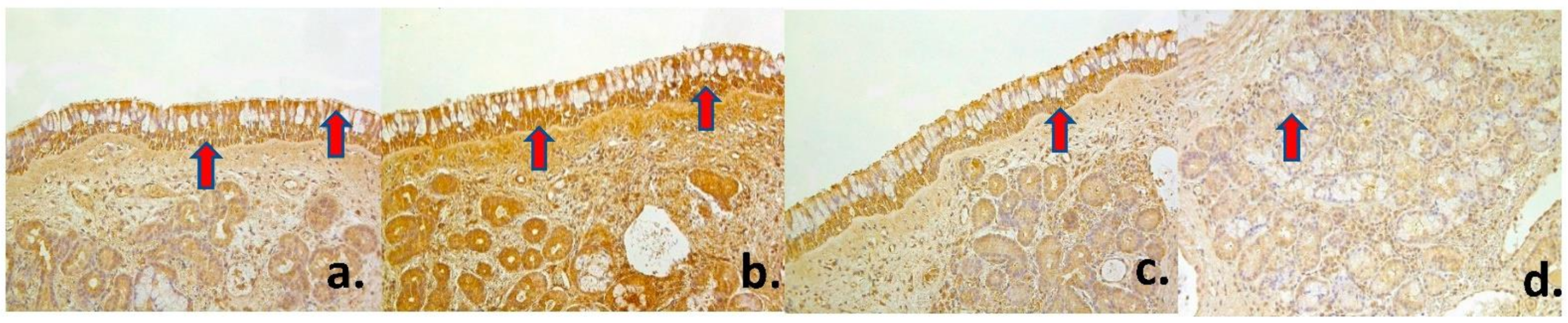
| Factors | PGP 9.5 | Ki-67 | β-Defensin 2 | IL-1 | IL-4 | IL-6 | IL-7 | IL-8 | IL-10 | IL-12 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject № | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Type of Tissue Nasal Mucosa | Nasal Mucosa | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | Superficial Epithelium | Glandular Epithelium | |
| 1 | ++ | ++/+++ | 0 | +++ | +/++ | +++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | |
| 2 | +++ | + | + | +++ | + | +++ | +/++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | +/++ | +++ | +/++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +/++ | |
| 3 | ++ | + | 0/+ | +++ | + | ++ | + | ++++ | ++ | ++/+++ | + | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +/++ | +++ | ++ | |
| 4 | ++ | + | 0 | +++ | + | +++ | + | +++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | |
| 5 | +++ | ++ | 0 | +++ | + | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | |
| 6 | + | 0/+ | 0/+ | ++++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | +/++ | ++++ | +/++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | + | +++ | + | |
| 7 | ++ | +/++ | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +/++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | ++ | + | |
| 8 | +++ | +/++ | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++/+++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | |
| 9 | +++ | + | 0 | ++ | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +/++ | |
| 10 | +++ | ++ | 0 | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | ++/+++ | ++++ | ++/+++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | + | |
| 11 | ++ | + | 0 | +++ | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++/+++ | |
| 12 | + | ++ | 0 | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | |
| 13 | + | ++/+++ | 0/+ | +++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | |
| 14 | ++ | ++/+++ | 0/+ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | |
| 15 | + | +++ | + | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | |
| 16 | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++ | |
| 17 | +/++ | ++ | 0 | +++ | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | |
| Average | ++ | +/++ | 0/+ | +++ | +/++ | +++ | ++/+++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++/++++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++ | |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | R | p- Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong positive correlation in superficial epithelium | |||
| PGP 9.5 | β-Defensin | 0.506 | 0.038 |
| PGP 9.5 | IL-10 | 0.539 | 0.026 |
| Ki-67 | IL-12 | 0.486 | 0.048 |
| β-Defensin 2 | IL-1 | 0.492 | 0.045 |
| IL-1 | IL-6 | 0.538 | 0.026 |
| IL-1 | IL-8 | 0.513 | 0.035 |
| IL-1 | IL-12 | 0.535 | 0.027 |
| IL-4 | IL-6 | 0.554 | 0.021 |
| IL-6 | IL-8 | 0.596 | 0.012 |
| IL-6 | IL-10 | 0.579 | 0.015 |
| IL-8 | IL-12 | 0.518 | 0.033 |
| Strong positive correlation in glandular epithelium | |||
| Ki-67 | IL-4 | 0.484 | 0.049 |
| β-Defensin 2 | IL-8 | 0.549 | 0.023 |
| A very strong positive correlation in superficial epithelium | |||
| PGP 9.5 | IL-12 | 0.628 | 0.007 |
| IL-8 | IL-10 | 0.741 | 0.001 |
| A very strong positive correlation in glandular epithelium | |||
| IL-1 | IL-8 | 0.638 | 0.006 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Podlesnaja, M.; Pilmane, M.; Sumeraga, G. Cytokines, Proliferation Markers, Antimicrobial Factors and Neuropeptide-Containing Innervation in Human Nasal Mucosa after Rhinoseptoplasty Procedure. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci9020025
Podlesnaja M, Pilmane M, Sumeraga G. Cytokines, Proliferation Markers, Antimicrobial Factors and Neuropeptide-Containing Innervation in Human Nasal Mucosa after Rhinoseptoplasty Procedure. Medical Sciences. 2021; 9(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci9020025
Chicago/Turabian StylePodlesnaja, Marija, Mara Pilmane, and Gunta Sumeraga. 2021. "Cytokines, Proliferation Markers, Antimicrobial Factors and Neuropeptide-Containing Innervation in Human Nasal Mucosa after Rhinoseptoplasty Procedure" Medical Sciences 9, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci9020025
APA StylePodlesnaja, M., Pilmane, M., & Sumeraga, G. (2021). Cytokines, Proliferation Markers, Antimicrobial Factors and Neuropeptide-Containing Innervation in Human Nasal Mucosa after Rhinoseptoplasty Procedure. Medical Sciences, 9(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci9020025







