Dietary Soy Isoflavone Alleviates Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Growth Inhibition and Hepatic Injury in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus): Involvement of Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Function, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Feeds
2.2. Feeding Management
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Histological Preparation and Staining
2.5. Serum Biochemistry Indices Measurement
2.6. Biochemical Indices of Tissues
2.7. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time PCR
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Growth Result of M. albus
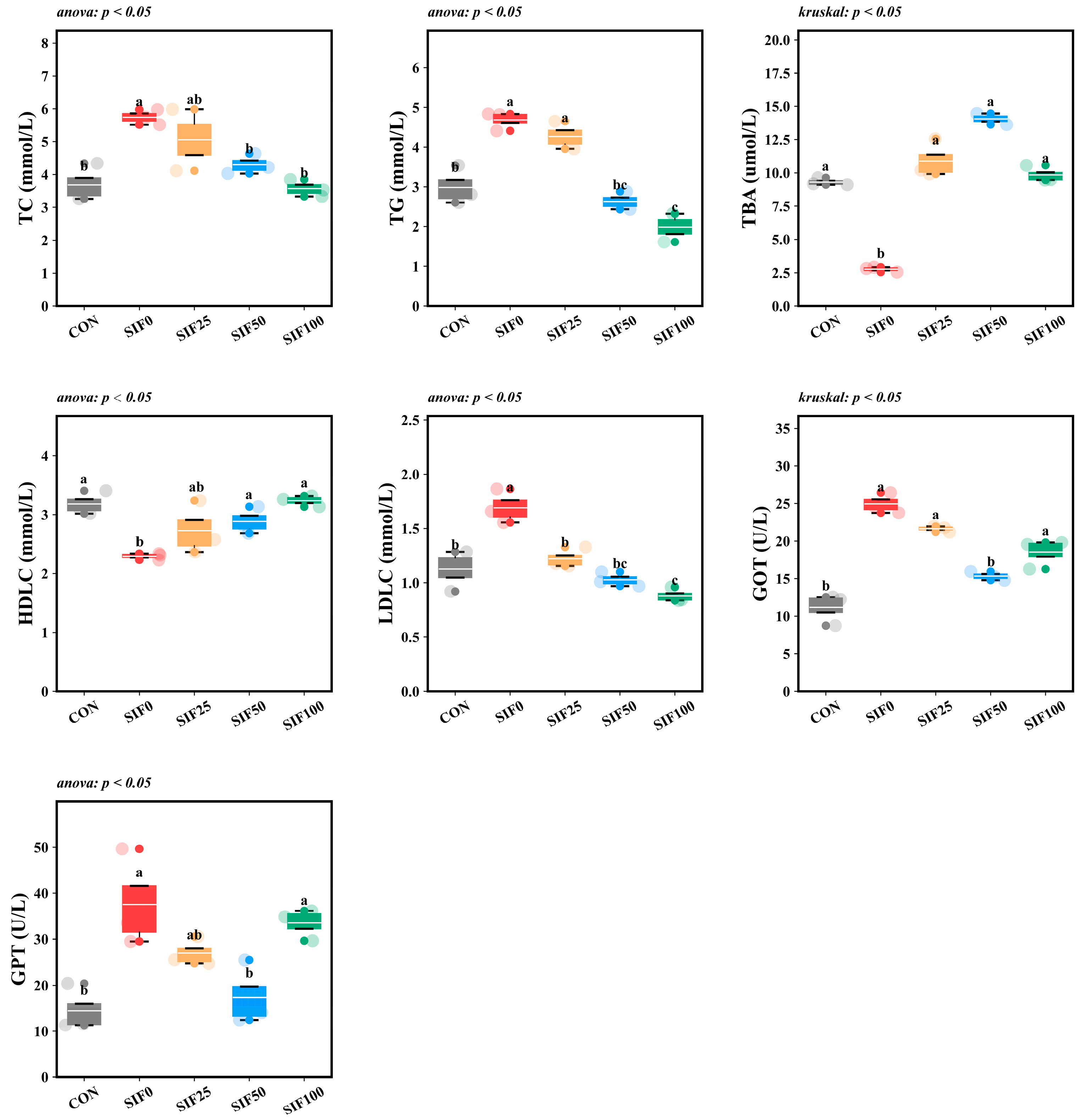
3.2. Analysis of Serum Biochemical Indices
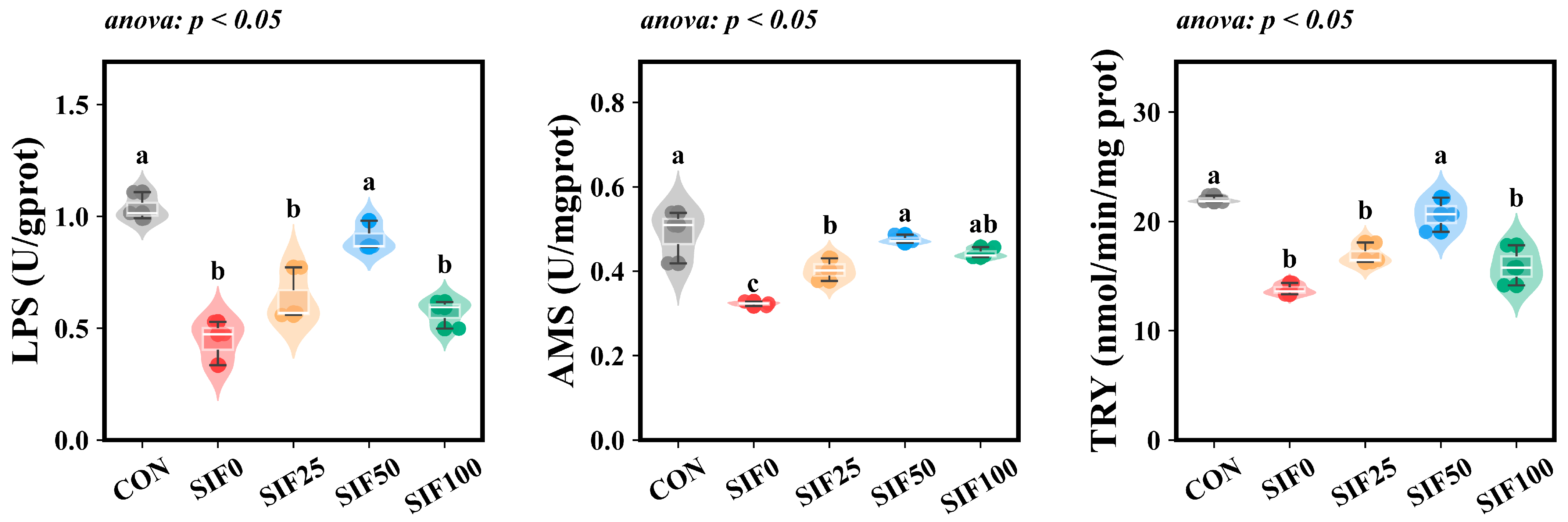
3.3. Intestinal Digestive Enzyme Activity
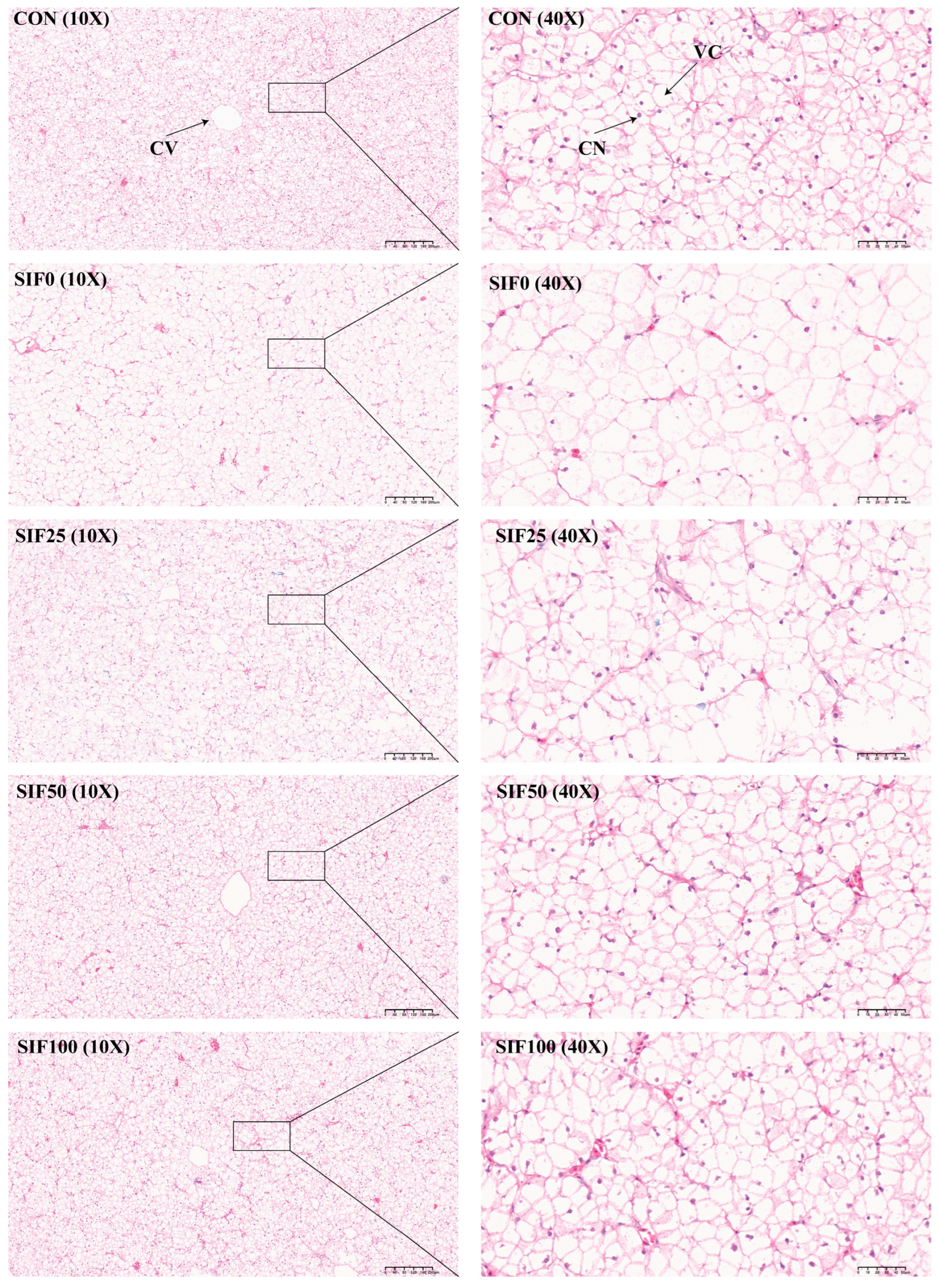
3.4. Histomorphological Analysis of the Liver
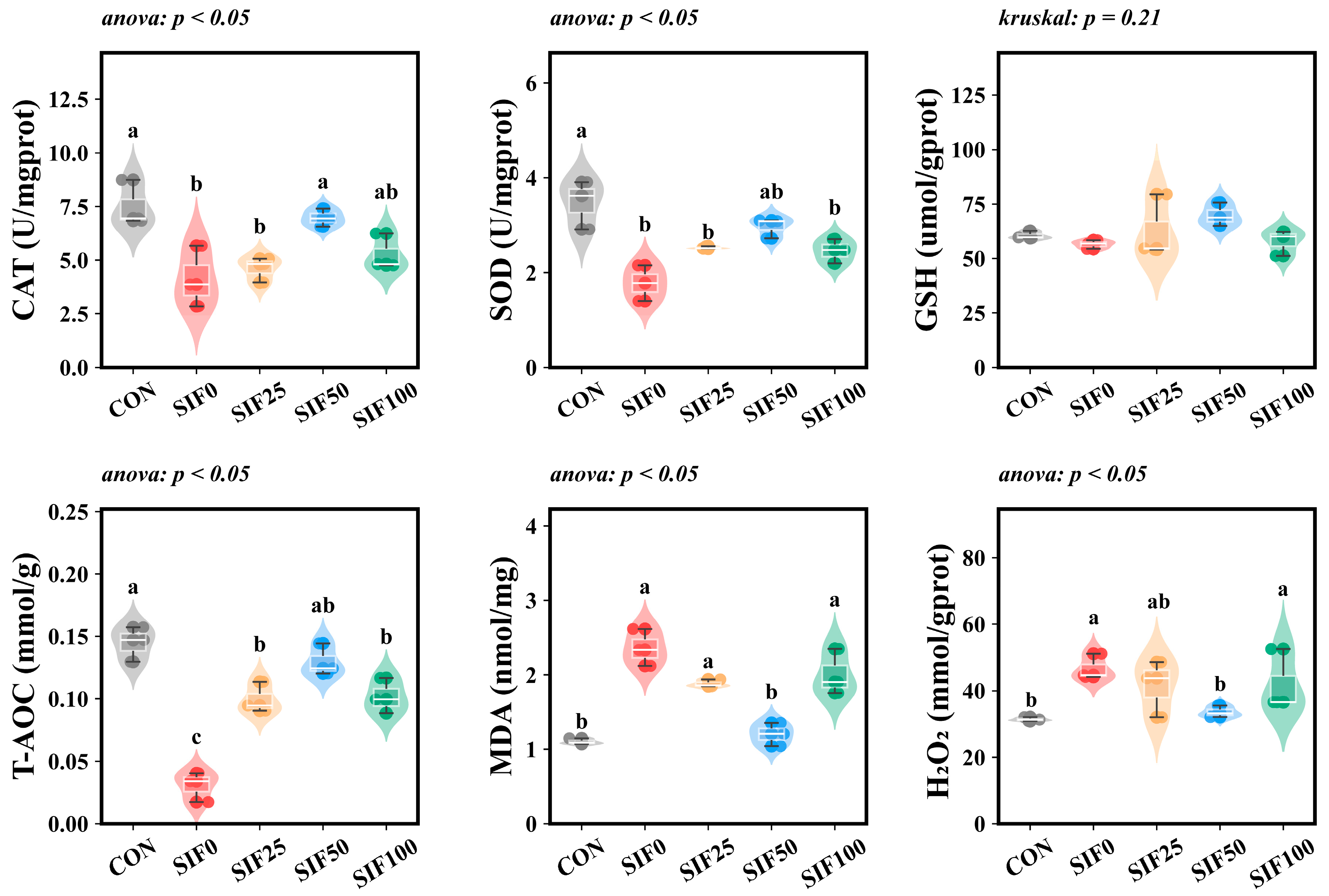
3.5. Biochemical Indicators of Hepatic Antioxidation
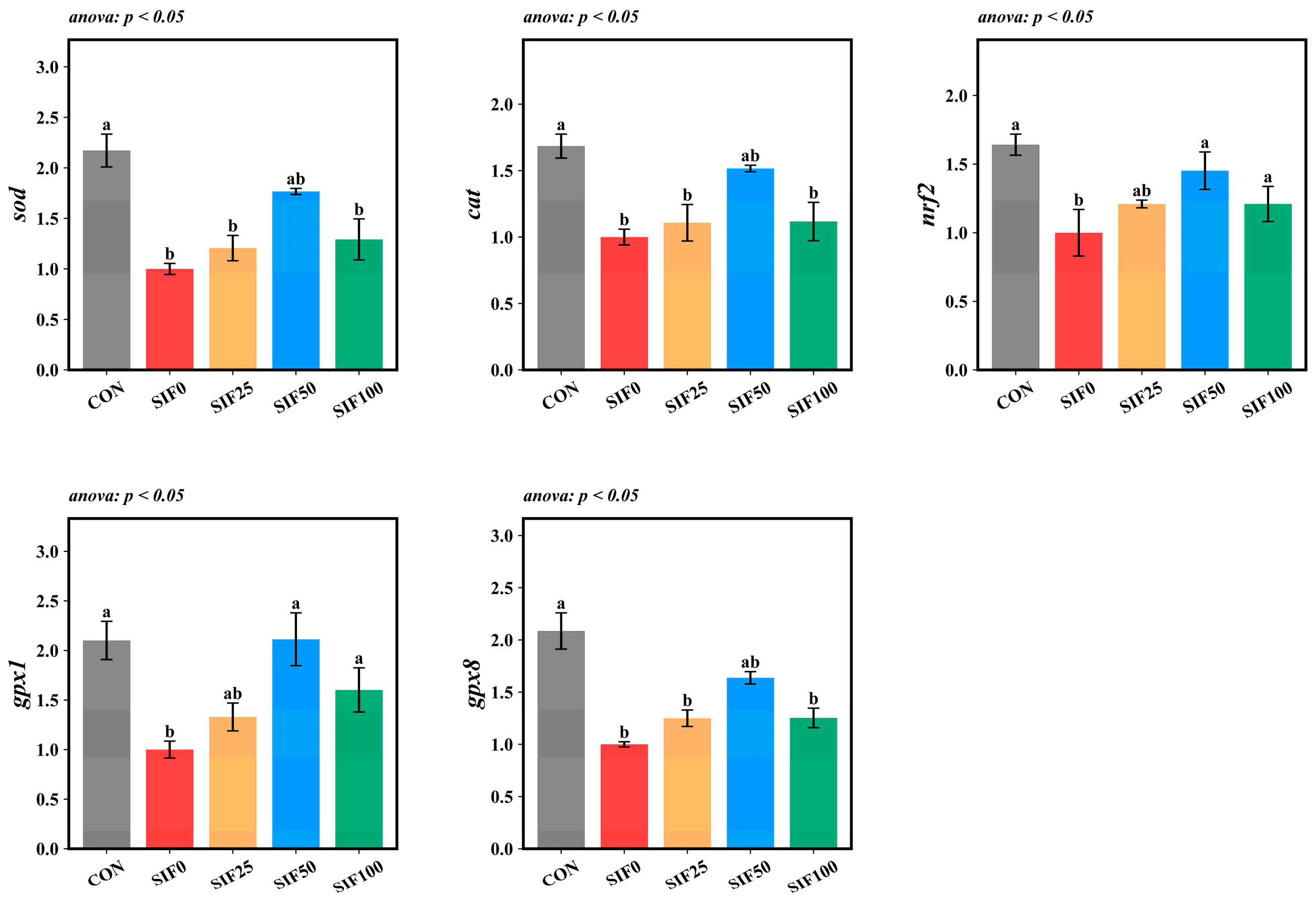
3.6. Relative Expression of Hepatic Antioxidant Genes
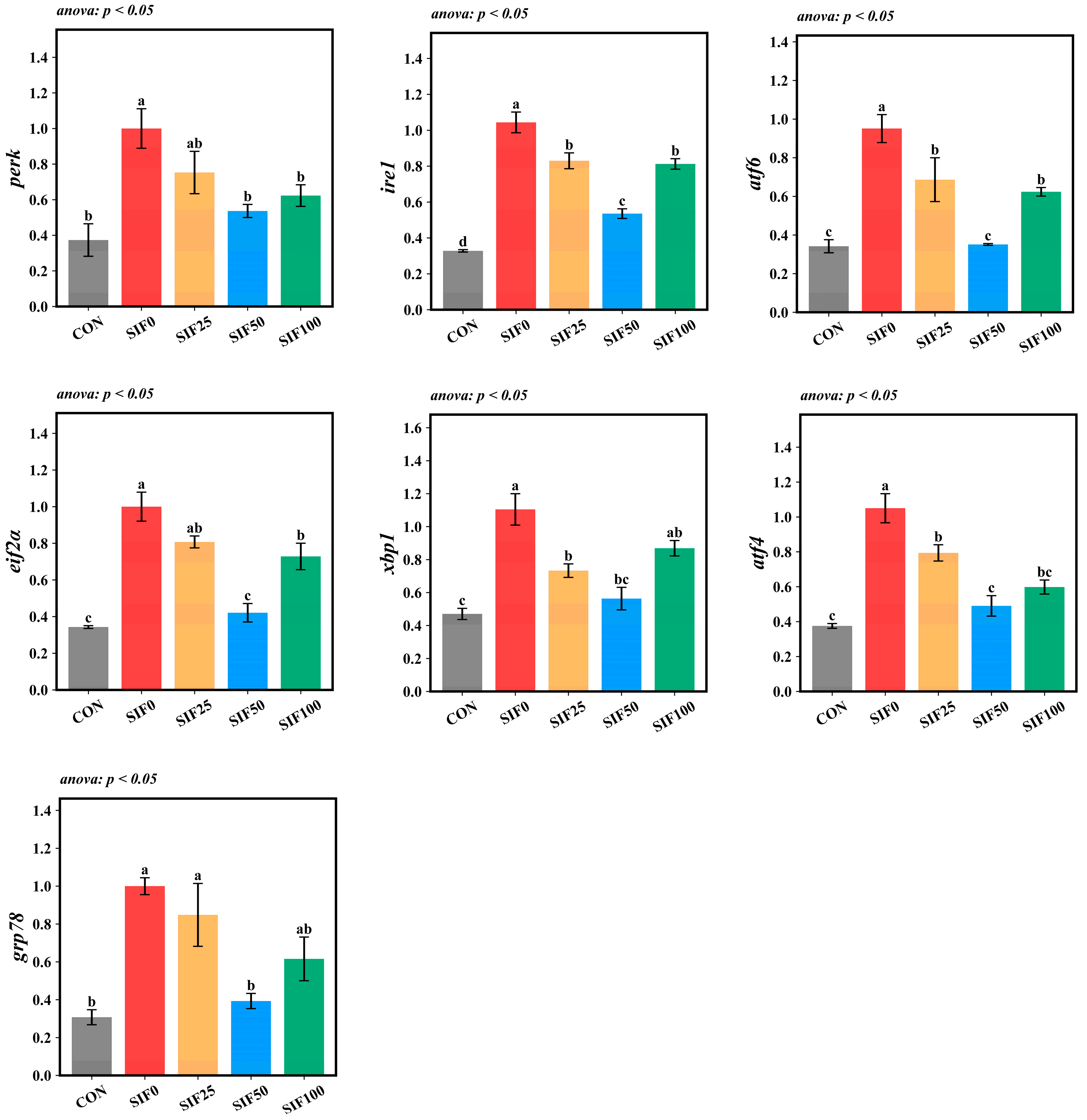
3.7. Hepatic Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Gene Relative Expression
3.8. Relative Expression of Hepatic Inflammatory Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, A.L.; Preta, G. Lipids in the cell: Organisation regulates function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1909–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Couto, A.; Peres, H. 8-Replacing fish meal and fish oil in industrial fish feeds. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; Davis, D.A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 231–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Luo, J.; Li, P.; Ruan, R.; Yang, J.; Xu, S.; Li, M.; et al. The Influence of Dietary n-3 Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids on Growth, Fatty Acid Profile, Lipid Metabolism, Inflammatory Response, and Intestinal Microflora in F2 Generation Female Yangtze Sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Animals 2024, 14, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Ye, R.; Chen, H.; Xie, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; You, C.; et al. Effects of dietary n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids levels on growth, lipid metabolism and innate immunity in juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xiong, W.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Ruan, R.; Fu, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Leng, X.; Li, P.; et al. The Effects of Dietary n-3 Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids on Growth, Antioxidant Capacity, Immunity, and Oxylipin Profiles in Acipenser dabryanus. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, M.; Mishra, H.N. Amelioration of the stability of polyunsaturated fatty acids and bioactive enriched vegetable oil: Blending, encapsulation, and its application. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6253–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, A.S.; Bannenberg, G.; Vigor, C.; Reversat, G.; Oger, C.; Roumain, M.; Galano, J.-M.; Durand, T.; Muccioli, G.G.; Ismail, A.; et al. Chemical Compositional Changes in Over-Oxidized Fish Oils. Foods 2020, 9, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Q.; Ye, Y.-T.; Cai, C.-F.; Wu, P.; Huang, Y.-W.; Wu, T.; Lin, X.-X.; Luo, Q.-G.; Zhang, B.-T.; Xiao, P.-Z. Effects of Dietary Oxidized Fish Oil on the Intestinal Structure and Permeability of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon Idellus). ACTA Hydrobiol. Sin. 2016, 40, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-G.; Zhao, T.; Hogstrand, C.; Ye, H.-M.; Xu, X.-J.; Luo, Z. Oxidized fish oils increased lipid deposition via oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and the CREB1-Bcl2-Beclin1 pathway in the liver tissues and hepatocytes of yellow catfish. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.S.; Blower, M.D. The endoplasmic reticulum: Structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, H.M.A.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, H.-R.; Chae, H.-J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Associated ROS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, X.; Ge, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, H.; Zhang, J. ER Stress Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome: A Novel Mechanism of Atherosclerosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 3462530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Iradukunda, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Gao, H.; Shi, G. Preparation of Electrospun Active Molecules Membrane Application to Atmospheric Free Radicals. Membranes 2022, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, S.; Fujita, M.; Kamei, Y. Health Promotion Effects of Soy Isoflavones. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2020, 66, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam Aliagan, A.; Madungwe, N.B.; Tombo, N.; Feng, Y.; Bopassa, J.C. Chronic GPER1 Activation Protects Against Oxidative Stress-Induced Cardiomyoblast Death via Preservation of Mitochondrial Integrity and Deactivation of Mammalian Sterile-20-Like Kinase/Yes-Associated Protein Pathway. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 579161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Jiang, S.Q.; Lin, Y.C.; Xi, P.B.; Yu, D.Q.; Wu, T.X. Effects of Soybean Isoflavone on Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Antioxidation in Male Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Lin, H.; Ge, X.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, Z.; Yu, W.; Tan, X. The Effects of dietary soybean isoflavones on growth, innate immune responses, hepatic antioxidant abilities and disease resistance of juvenile golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 43, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2024. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2024/indexch.htm (accessed on 21 September 2025).
- Batievskaya, N.; Yegorov, B. The Development Granulation Technology of Compound Feeds in the Form of Mixture Crumbs. Grain Prod. Mix. Fodder’s 2019, 19, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Cao, L.-P.; Du, J.-L.; He, Q.; Gu, Z.-Y.; Jeney, G.; Xu, P.; Yin, G.-J. Effects of high-fat diet on antioxidative status, apoptosis and inflammation in liver of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) via Nrf2, TLRs and JNK pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.-Q.; Ai, Q.-H.; He, Z.-G.; Feng, F.-X.; Lu, X.-Y. Effects of practical dietary protein to lipid levels on growth, digestive enzyme activities and body composition of juvenile rice field eel (Monopterus albus). Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS. Official Method Cd 8b-90: Peroxide Value Acetic Acid-Isooctane Method; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Urbana, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Latimer, G.W., Jr. AOAC Official Method 920.39Fat (Crude) or Ether Extract in Animal Feed. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, G.W., Jr. AOAC Official Method 979.09Protein in Grains. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Tan, B.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Effect of dietary oxidized fish oil on liver function in hybrid grouper (♀ Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × ♂ Epinephelus lanceolatus). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 101000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Che, C.; Cai, M.; Hu, Y. Taurine improves health of juvenile rice field eel (Monopterus albus) fed with oxidized fish oil: Involvement of lipid metabolism, antioxidant capacity, inflammatory response. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicas, J.L.; Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. Chapter 9—Generation of process-derived flavors and off-flavors. In Chemical Changes During Processing and Storage of Foods; Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B., Amaya-Farfan, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 385–451. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Xiao, H.; Lyu, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, F. Lipid oxidation in food science and nutritional health: A comprehensive review. Oil Crop Sci. 2023, 8, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; He, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Jia, L.; Chen, L.; Ye, J.; Qi, C. Effects of Soybean Isoflavones on the Growth Performance and Lipid Metabolism of the Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis. Fishes 2024, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M. Modulation of intestinal functions by dietary substances: An effective approach to health promotion. J. Tradit. Complement Med. 2012, 2, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Miyashita, K.; Nakajima, K.; Mabuchi, H. Hepatic Lipase: A Comprehensive View of its Role on Plasma Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chi, S.; Tan, B.; Dong, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Han, F.; He, Y. Effects of fish oil with difference oxidation degree on growth performance and expression abundance of antioxidant and fat metabolism genes in orange spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimnejad, S.; Dabrowski, K.; Izquierdo, M.; Hematyar, N.; Imentai, A.; Steinbach, C.; Policar, T. Effects of Vitamin C and E Supplementation on Growth, Fatty Acid Composition, Innate Immunity, and Antioxidant Capacity of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fed Oxidized Fish Oil. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 760587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.K.; Kashfi, K. Lipoproteins and cancer: The role of HDL-C, LDL-C, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 196, 114654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulpekova, Y.; Zharkova, M.; Tkachenko, P.; Tikhonov, I.; Stepanov, A.; Synitsyna, A.; Izotov, A.; Butkova, T.; Shulpekova, N.; Lapina, N.; et al. The Role of Bile Acids in the Human Body and in the Development of Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.G.; Kunz, W.S.; Lei, X.J.; Zito, E.; Zhao, T.; Xu, Y.C.; Wei, X.L.; Lv, W.H.; Luo, Z. Selenium Ameliorated Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Lipotoxicity via the Inhibition of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress, Remodeling of Usp4-Mediated Deubiquitination, and Stabilization of Pparα. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2024, 40, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Pang, D.; Luo, Q.; Chen, X.; Gao, Q.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Z. Soy Isoflavones Regulate Lipid Metabolism through an AKT/mTORC1 Pathway in Diet-Induced Obesity (DIO) Male Rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Das, A.; Chaffee, S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Chapter 4—Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage and Cell Death. In Immunity and Inflammation in Health and Disease; Chatterjee, S., Jungraithmayr, W., Bagchi, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, P.-P.; Jia, L.-S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, B.-H. Mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction mediated by ROS is a primary point of fluoride-induced damage in Hepa1-6 cells. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estévez, M.; Li, Z.; Soladoye, O.P.; Van-Hecke, T. Chapter Two—Health Risks of Food Oxidation. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Toldrá, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; Volume 82, pp. 45–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, Z. ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: Mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohnert, B.I.; Bernlohr, D.A. Protein carbonylation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin resistance. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdulSalam, S.F.; Thowfeik, F.S.; Merino, E.J. Excessive Reactive Oxygen Species and Exotic DNA Lesions as an Exploitable Liability. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5341–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Ge, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, P. Protective Effects of Emodin on Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Metabolic Disorder and Oxidative Stress through Notch-Nrf2 Crosstalk in the Liver of Teleost Megalobrama amblycephala. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.B. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irato, P.; Santovito, G. Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Molecules with Antioxidant Function. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.N.; Wang, S.W.; et al. Soybean isoflavones improve the health benefits, flavour quality indicators and physical properties of grass carp (Ctenopharygodon idella). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlach, A.; Bertram, K.; Hudecova, S.; Krizanova, O. Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yuan, M.; Guo, Y.S.; Shen, X.Y.; Gao, Z.K.; Bi, X. Mechanism of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Cerebral Ischemia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 704334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Jian, J.; Cai, S.; Yang, S. Sulforaphane alleviates oxidative stress induced by oxidized fish oil in Litopenaeus vannamei by involving antioxidant capacity, inflammation, autophagy, and apoptosis. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Ali, F.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A. Crosstalk between reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory markers in developing various chronic diseases: A review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.; Seo, J. ER Stress Activates the TOR Pathway through Atf6. J. Mol. Signal. 2018, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | CON | SIF0 | SIF25 | SIF50 | SIF100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Fish meal | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 |
| Soy protein concentrate | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 |
| Poultry by-product meal | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Beer yeast | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 2 Oxidized fish oil | 0.00 | 2.20 | 2.20 | 2.20 | 2.20 |
| 3 Fish oil | 2.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | 10.26 | 10.26 | 10.26 | 10.26 | 10.26 |
| Corn gluten meal | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 |
| Choline | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| 4 Premix | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 5 Antioxidants | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 6 Mold inhibitor | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 7 Soy isoflavones | 0.00 | 0.00 | 25.00 mg/kg | 50.00 mg/kg | 100.00 mg/kg |
| 8 Proximate composition (%) | |||||
| Crude protein | 41.36 | 40.74 | 40.91 | 41.45 | 41.17 |
| Crude lipid | 5.96 | 5.78 | 6.02 | 5.84 | 6.09 |
| Gene | Accession No. | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| rpl 17 | XM_020587712.1 | CGAGAACCCGACTAAATCA | GTTGTAGCGACGGAAAGG |
| gpx1 | XM_020607739.1 | AGATGTGAATGGGAAGGATGCC | AAACTTCGGGTCAGTCATCAGG |
| nrf2 | XM_020596408.1 | TCACAGACGAGAATGATGCC | CTGCTACTGGGAACTGAAACTG |
| gpx8 | XM_020593975.1 | ATCCTGCCTTCAGATTCCTCAC | TCATTTCTCGCACCAGCACT |
| sod | XM_020598412.1 | GTTGCCAAGATAGACATCACGG | TCATTGCCTCCTTTTCCCAG |
| cat | XM_020624985.1 | CATTGGGAAGACTACACCTATCGC | GATGAAGAAGATGGGGGTGTTG |
| grp78 | XM_020600810.1 | ACCTGACTGGCATCCCTCCTG | CTTGTTCTTGTTGCCTGTGCC |
| atf6 | XM_020607104.1 | AACCGTCGTGGTGACACTTTC | GTCCGTCACTTCACAGTCAATC |
| xbp1 | XM_020623950.1 | ATGGTGGTAGTAACAGCAGGGAC | CTGCGACTCTGTTCTTTAGTTTCC |
| atf4 | XM_020586222.1 | TCTTTCACGGGCATGGATTG | GAGAATCGTCGGATGAGCAAG |
| eif2α | XM_020603841.1 | AGCCCCTTCCTTTGTTCGTC | CTGCTGAGGCTTTCTTGTTCCAC |
| ire1 | XM_020619837.1 | TTCGAGAACGCAACCGTATCA | CATCATCCATACCGCTATCATTC |
| perk | XM_020604189.1 | CTCCCTACAGTCAAATGGAAGCC | AGGGGAAGTAGTAACCGTTGTC |
| pparγ | XM_020609689.1 | CAAAGCCTCTGGGTTTCACTAT | TTTGTTGCGGGACTTCTTGT |
| tgf-β1 | XM_020605575.1 | AAGTCCAGCAAGCAATCCCTAG | GAGATGCTTGTTGGGTCCTTG |
| tgf-β3 | XM_020590885.1 | GCCAAGAAAAACGAACAGAGG | TGTCACATCAAAGGAGACCCAC |
| nfkb | KC841853.1 | CTTCGTAACCCAGAGGATAAACC | CAGATAAACACTGCACAGCCAAG |
| il-1β | KM262825.1 | GTCAACCTCATTATCGCCACG | AAACTCCTCTTCTGGCTGTCG |
| il-8 | XM_020596483.1 | CAACTCCCACTGCAAAGATACTG | CGACTTTGCCAGTTTCCTTTC |
| tlr-8 | XM_020596483.1 | TTTGTCCTAACAGAGGGCTACG | CAGCATCAGCAGCACAATCAC |
| Item | CON | SIF0 | SIF25 | SIF50 | SIF100 | p_Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 IBW | 26.01 ± 0.02 | 25.97 ± 0.03 | 26.01 ± 0.01 | 25.98 ± 0.02 | 25.97 ± 0.01 | anova: p = 0.47 |
| 2 FBW | 54.15 ± 2.21 a | 47.8 ± 0.46 b | 52.87 ± 0.15 a | 56.43 ± 0.8 a | 54.38 ± 0.18 a | anova: p < 0.05 |
| 3 WGR | 108.05 ± 8.62 a | 84.13 ± 1.62 b | 102.36 ± 1.13 ab | 111.8 ± 6.0 a | 106.76 ± 0.86 a | anova: p < 0.05 |
| 4 SR | 93.33 ± 1.76 | 93.0 ± 1.73 | 96.0 ± 0.0 | 97.0 ± 0.58 | 97.0 ± 0.58 | anova: p = 0.08 |
| 5 SGR | 1.3 ± 0.07 a | 1.09 ± 0.02 b | 1.26 ± 0.01 ab | 1.34 ± 0.05 a | 1.3 ± 0.01 a | anova: p < 0.05 |
| 6 CF | 0.11 ± 0.0 ab | 0.1 ± 0.0 b | 0.12 ± 0.0 a | 0.13 ± 0.0 a | 0.12 ± 0.0 a | kruskal: p < 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Wei, H.; Zhou, T.; Xie, K.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Dietary Soy Isoflavone Alleviates Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Growth Inhibition and Hepatic Injury in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus): Involvement of Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Function, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation. Animals 2025, 15, 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192839
Li Q, Wei H, Zhou T, Xie K, Hu Y, Zhang J. Dietary Soy Isoflavone Alleviates Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Growth Inhibition and Hepatic Injury in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus): Involvement of Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Function, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192839
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Quan, Huahong Wei, Tao Zhou, Kai Xie, Yi Hu, and Junzhi Zhang. 2025. "Dietary Soy Isoflavone Alleviates Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Growth Inhibition and Hepatic Injury in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus): Involvement of Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Function, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation" Animals 15, no. 19: 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192839
APA StyleLi, Q., Wei, H., Zhou, T., Xie, K., Hu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). Dietary Soy Isoflavone Alleviates Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Growth Inhibition and Hepatic Injury in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus): Involvement of Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Function, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation. Animals, 15(19), 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192839




