Aichi Virus 1: Environmental Occurrence and Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
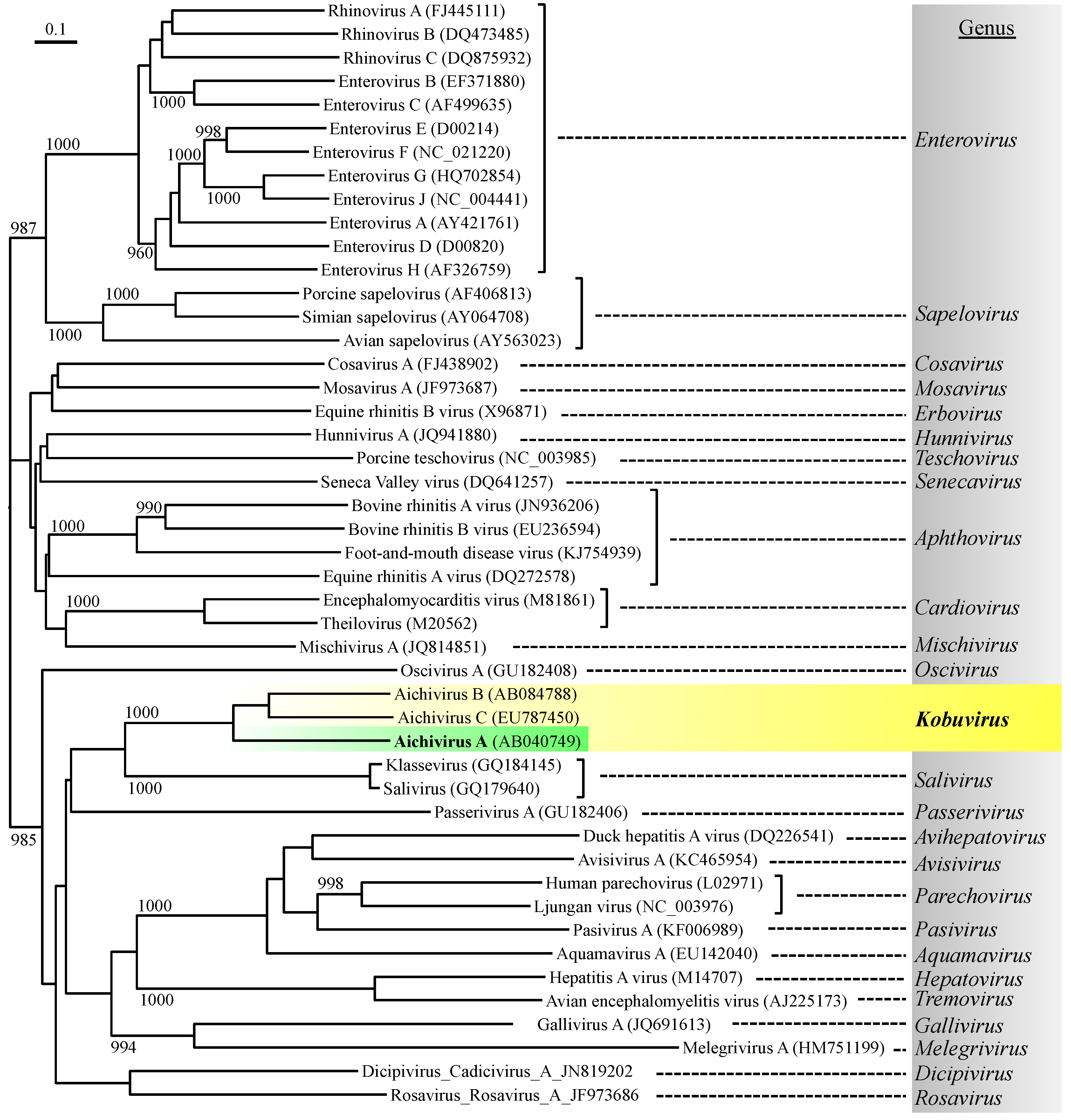
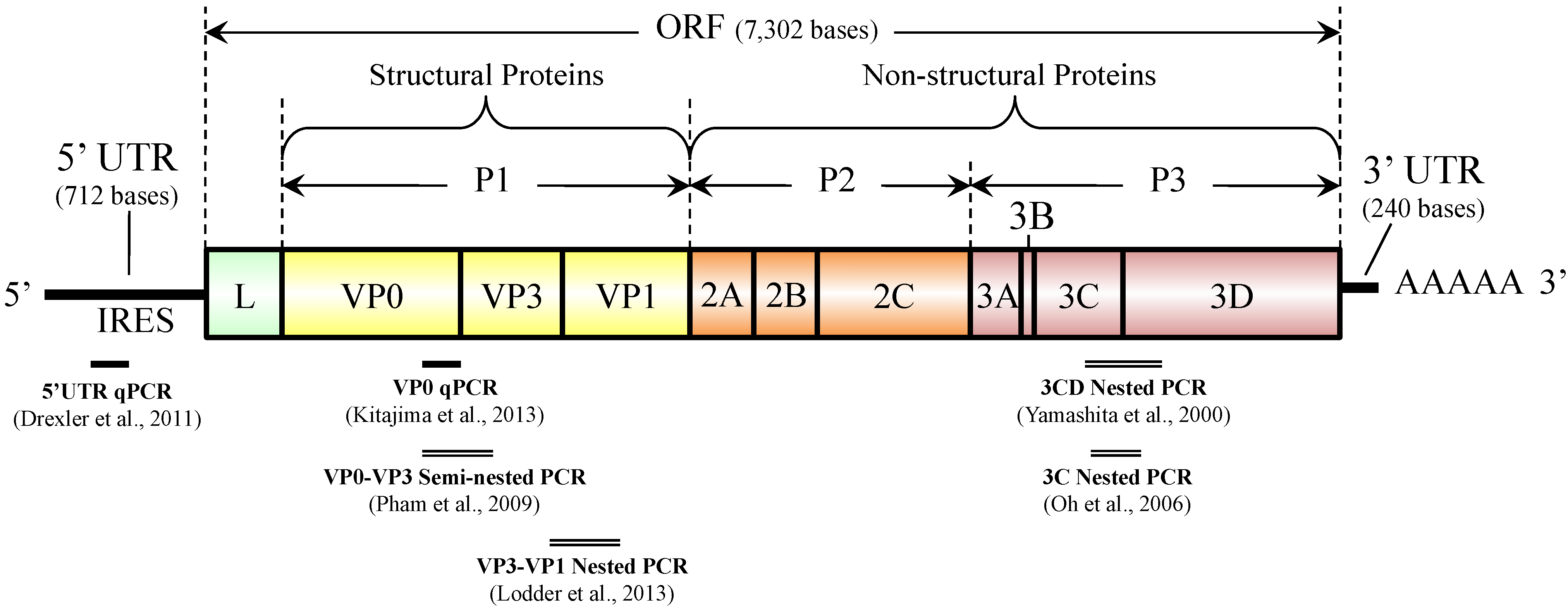
2. Detection Methods
3. Occurrence in the Environment
3.1. Sewage
| Sample | Detection Method | Positive Rate | Genotype | Concentration (copies/L) | Country | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Raw sewage | Nested PCR-cloning-sequencing | 100% (12/12) | A + B | ND | Japan | [31] |
| PCR-direct sequencing | 8% (10/125) | A | ND | Tunisia | [39] | ||
| qPCR | 100% (12/12) | A | 1.4 × 105 to 2.2 × 107 | Japan | [35] | ||
| Nested PCR-cloning-sequencing | 100% (16/16) | A + B | ND | Netherlands | [32] | ||
| PCR-direct sequencing | 12.5% (6/48) | B | ND | Italy | [43] | ||
| qPCR | 100% (24/24) | AiV-1 | 1.2 × 104 to 4.0 × 106 | US | [44] | ||
| Viral metagenomics | 50% (2/4) | AiV-1 | ND | Spain, US | [45] | ||
| Viral metagenomics | 75% (3/4) | AiV-1 | ND | Nepal, Thailand, US | [46] | ||
| PCR-cloning-sequencing | 66.2% (137/207) | A | ND | Japan | [42] | ||
| Treated sewage | Nested PCR-cloning-sequencing | 92% (11/12) | A | ND | Japan | [31] | |
| PCR-direct sequencing | 4% (4/125) | A | ND | Tunisia | [39] | ||
| qPCR | 92% (11/12) | A | Up to 1.8 × 104 | Japan | [35] | ||
| qPCR | 100% (24/24) | AiV-1 | 2.0 × 103 to 4.0 × 105 | US | [44] | ||
| qPCR | 61% (61/100) | AiV-1 | Up to 103 | France | [47] | ||
| Reclaimed water | Viral metagenomics | 50% (1/2) | AiV-1 | ND | US | [48] | |
| River water | PCR-direct sequencing | 45% (5/11) | B | ND | Venezuela | [38] | |
| Nested PCR-cloning-sequencing | 60% (36/60) | A + B | ND | Japan | [31] | ||
| Nested PCR-cloning-sequencing | 85% (12/14) | A + B | ND | Netherlands | [32] | ||
| qPCR | 100% (29/29) | AiV-1 | 8.6 × 102 to 2.0 × 104 | Japan | [36] | ||
| qPCR | 11% (20/175) | ND | Up to 102 | France | [47] | ||
| Biosolids | Viral metagenomics | 100% (1/1) | ND | ND | US | [49] | |
| Viral metagenomics | 25% (3/12) | ND | ND | US | [50] | ||
| Shellfish | Clam | PCR-direct sequencing | 33% (19/57) | A | ND | Japan | [40] |
| Oyster | Nested PCR-direct sequencing | 8% (5/62) | A | ND | France | [17] | |
| Mussel, clam, cockle | Nested PCR-hybridization | 0% (0/41) | ND | ND | Spain | [51] | |
| Shellfish | PCR-direct sequencing | 6.6% (4/60) | A | ND | Tunisia | [39] | |
| Oyster, clam, cockle | qPCR | 0% (0/77) | ND | ND | Morocco | [52] | |
3.2. River Water
3.3. Groundwater
3.4. Shellfish
3.5. Persistence
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tapparel, C.; Siegrist, F.; Petty, T.J.; Kaiser, L. Picornavirus and enterovirus diversity with associated human diseases. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, G.; Boros, A.; Pankovics, P. Kobuviruses—A comprehensive review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2011, 21, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.J.; King, A.M.Q.; Carstens, E.B. Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2013). Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Sakae, K.; Nakata, S.; Chiba, S.; Ishihara, Y.; Isomura, S. Isolation of cytopathic small round viruses with BS-C-1 cells from patients with gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 164, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Dubovi, E.J.; Qaisar, N.; Henriquez, J.A.; Medina, J.; Shields, S.; Lipkin, W.I. Characterization of a canine homolog of human Aichivirus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11520–11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.G.; Kapusinszky, B.; Wang, C.; Rose, R.K.; Lipton, H.L.; Delwart, E.L. The fecal viral flora of wild rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Sakae, K.; Tsuzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T.; Yamazaki, S. Complete nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of Aichi virus, a distinct member of the Picornaviridae associated with acute gastroenteritis in humans. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8408–8412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, J.; Kusuhara, Y.; Maeno, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Yamashita, T.; Sakae, K. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of Aichi virus (a new member of the family Picornaviridae) and mutational analysis of a stem-loop structure at the 5ʹ end of the genome. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8021–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Sakae, K. Molecular biology and epidemiology of Aichi virus and other diarrhoeogenic enteroviruses. In Perspectives in Medical Virology; Desselberger, U., Gray, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 645–657. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Tsuzuki, H.; Sakae, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Application of a reverse transcription-PCR for identification and differentiation of Aichi virus, a new member of the Picornavirus family associated with gastroenteritis in humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambert-Balay, K.; Lorrot, M.; Bon, F.; Giraudon, H.; Kaplon, J.; Wolfer, M.; Lebon, P.; Gendrel, D.; Pothier, P. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Aichi virus strains in stool samples from community and hospitalized patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.T.K.; Khamrin, P.; Nguyen, T.A.; Kanti, D.S.; Phan, T.G.; Okitsu, S.; Ushijima, H. Isolation and molecular characterization of Aichi viruses from fecal specimens collected in Japan, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Vietnam. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2287–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.T.K.; Trinh, Q.D.; Khamrin, P.; Nguyen, T.A.; Dey, S.K.; Phan, T.G.; Hoang, L.P.; Maneekarn, N.; Okitsu, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; et al. Sequence analysis of the capsid gene of Aichi viruses detected from Japan, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Vietnam. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 1227, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Sakae, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Ishihara, Y.; Miyake, T.; Mubina, A.; Isomura, S. Isolation of cytopathic small round virus (Aichi virus) from Pakistani children and Japanese travelers from Southeast Asia. Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 39, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Cui, L.; Hua, X. Aichi virus strains in children with gastroenteritis, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1703–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, S.; Räsänen, S.; Rämet, M. Aichi virus infection in children with acute gastroenteritis in Finland. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guyader, F.S.; le Saux, J.-C.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Krol, J.; Serais, O.; Parnaudeau, S.; Giraudon, H.; Delmas, G.; Pommepuy, M.; Pothier, P.; et al. Aichi virus, norovirus, astrovirus, enterovirus, and rotavirus involved in clinical cases from a French oyster-related gastroenteritis outbreak. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 4011–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.-Y.; Silva, P.A.; Hauroeder, B.; Diedrich, S.; Cardoso, D.D.P.; Schreier, E. Molecular characterization of the first Aichi viruses isolated in Europe and in South America. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, G.; Boldizsár, A.; Papp, G.; Pankovics, P. Detection of Aichi virus shedding in a child with enteric and extraintestinal symptoms in Hungary. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Räsänen, S.; Lappalainen, S.; Kaikkonen, S.; Hämäläinen, M.; Salminen, M.; Vesikari, T. Mixed viral infections causing acute gastroenteritis in children in a waterborne outbreak. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; Gharbi-Khélifi, H.; de Rougemont, A.; Chouchane, S.; Sakly, N.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Hassine, M.; Guédiche, M.N.; Aouni, M.; Pothier, P. Acute Infantile Gastroenteritis Associated with Human Enteric Viruses in Tunisia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; Hassine, M.; Gharbi-Khelifi, H.; Sakly, N.; Chouchane, S.; Guediche, M.N.; Pothier, P.; Aouni, M.; Ambert-Balay, K. Detection and Genomic Characterization of Aichi Viruses in Stool Samples from Children in Monastir, Tunisia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Sakae, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Isomura, S.; Utagawa, E. Prevalence of newly isolated, cytopathic small round virus (Aichi strain) in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goyer, M.; Aho, L.-S.; Bour, J.-B.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Pothier, P. Seroprevalence distribution of Aichi virus among a French population in 2006–2007. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribes, J.M.; Montava, R.; Téllez-Castillo, C.J.; Fernández-Jiménez, M.; Buesa, J. Seroprevalence of Aichi Virus in a Spanish Population from 2007 to 2008. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; Hassine, M.; Bour, J.-B.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Mastouri, M.; Aho, L.-S.; Gharbi-Khelifi, H.; Aouni, Z.; Sakly, N.; Chouchane, S.; et al. Aichi virus IgG seroprevalence in Tunisia parallels genomic detection and clinical presentation in children with gastroenteritis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Ito, M.; Tsuzuki, H. Identification of Aichi virus infection by measurement of immunoglobulin responses in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4178–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.T.K.; Trinh, Q.D.; Nguyen, T.A.; Dey, S.K.; Phan, T.G.; Hoang, L.P.; Khamrin, P.; Maneekarn, N.; Okitsu, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; et al. Development of genotype-specific primers for differentiation of genotypes A and B of Aichi viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 156, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, H.; Chitambar, S.D.; Gopalkrishna, V. Circulation of Aichi virus genotype B strains in children with acute gastroenteritis in India. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Baumgarte, S.; de Souza Luna, L.K.; Eschbach-Bludau, M.; Lukashev, A.N.; Drosten, C. Aichi virus shedding in high concentrations in patients with acute diarrhea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, M.; Haramoto, E.; Phanuwan, C.; Katayama, H. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Aichi viruses in wastewater and river water in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2184–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodder, W.J.; Rutjes, S.A.; Takumi, K.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Aichi virus in sewage and surface water, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukashev, A.N.; Drexler, J.F.; Belalov, I.S.; Eschbach-Bludau, M.; Baumgarte, S.; Drosten, C. Genetic variation and recombination in Aichi virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.C.Y.; Gyhrs, M.L.; Nielsen, L.P.; Pedersen, C.; Böttiger, B. Gastroenteritis and the novel picornaviruses aichi virus, cosavirus, saffold virus, and salivirus in young children. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, M.; Hata, A.; Yamashita, T.; Haramoto, E.; Minagawa, H.; Katayama, H. Development of a reverse transcription-quantitative PCR system for detection and genotyping of Aichi viruses in clinical and environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3952–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Katayama, H.; Kojima, K.; Sano, S.; Kasuga, I.; Kitajima, M.; Furumai, H. Effects of rainfall events on the occurrence and detection efficiency of viruses in river water impacted by combined sewer overflows. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Katayama, H.; Kitajima, M.; Visvanathan, C.; Nol, C.; Furumai, H. Validation of internal controls for extraction and amplification of nucleic acids from enteric viruses in water samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4336–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalá, A.; Vizzi, E.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Zambrano, J.L.; Betancourt, W.; Liprandi, F. Molecular detection and characterization of Aichi viruses in sewage-polluted waters of Venezuela. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4113–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; Hassine, M.; Aouni, Z.; Gharbi-Khelifi, H.; Sakly, N.; Chouchane, S.; Guédiche, M.N.; Pothier, P.; Aouni, M.; Ambert-Balay, K. First molecular detection of Aichi virus in sewage and shellfish samples in the Monastir region of Tunisia. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Hansman, G.S.; Oka, T.; Li, T.-C.; Nishio, O.; Noda, M.; Takeda, N. Detection of human enteric viruses in Japanese clams. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, R.G.; Choi, C.Y.; Riley, M.R.; Gerba, C.P. Pathogen surveillance through monitoring of sewer systems. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 65, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Adachi, H.; Hirose, E.; Nakamura, N.; Ito, M.; Yasui, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Minagawa, H. Molecular detection and nucleotide sequence analysis of a new Aichi virus closely related to canine kobuvirus in sewage samples. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, B.; di Profio, F.; Ceci, C.; di Felice, E.; Marsilio, F. Molecular detection of Aichi virus in raw sewage in Italy. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2001–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, M.; Iker, B.C.; Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Relative abundance and treatment reduction of viruses during wastewater treatment processes—Identification of potential viral indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalupo, P.G.; Calgua, B.; Zhao, G. Raw sewage harbors diverse viral populations. MBio 2011, 2, e00180-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.F.F.; Marine, R.; Wang, C.; Simmonds, P.; Kapusinszky, B.; Bodhidatta, L.; Oderinde, B.S.; Wommack, K.E.; Delwart, E. High variety of known and new RNA and DNA viruses of diverse origins in untreated sewage. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12161–12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevost, B.; Lucas, F.S.; Goncalves, A.; Richard, F.; Moulin, L.; Wurtzer, S. Large scale survey of enteric viruses in river and waste water underlines the health status of the local population. Environ. Int. 2015, 79, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, K.; Nilsson, C.; Lim, Y.W.; Ruan, Y.; Breitbart, M. Metagenomic analysis of viruses in reclaimed water. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2806–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibby, K.; Viau, E.; Peccia, J. Viral metagenome analysis to guide human pathogen monitoring in environmental samples. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibby, K.; Peccia, J. Identification of viral pathogen diversity in sewage sludge by metagenome analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilariño, M.L.; le Guyader, F.S.; Polo, D.; Schaeffer, J.; Kröl, J.; Romalde, J.L. Assessment of human enteric viruses in cultured and wild bivalve molluscs. Int. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benabbes, L.; Ollivier, J.; Schaeffer, J.; Parnaudeau, S.; Rhaissi, H.; Nourlil, J.; le Guyader, F.S. Norovirus and other human enteric viruses in moroccan shellfish. Food Environ. Virol. 2013, 5, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancourt, W.Q.; Kitajima, M.; Wing, A.D.; Regnery, J.; Drewes, J.E.; Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Assessment of virus removal by managed aquifer recharge at three full-scale operations. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A 2014, 49, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Sims, J.T.; Kniel, K.E. Fate of human enteric viruses during dairy manure-based composting. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, D.H.; Chen, H.; Hoover, D.G. Inactivation of selected picornaviruses by high hydrostatic pressure. Virus Res. 2004, 102, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, D.H.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Temperature effects for high-pressure processing of Picornaviruses. Food Environ. Virol. 2014, 6, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromeans, T.; Park, G.W.; Costantini, V.; Lee, D.; Wang, Q.; Farkas, T.; Lee, A.; Vinjé, J. Comprehensive comparison of cultivable norovirus surrogates in response to different inactivation and disinfection treatments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5743–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Register; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 51850–51862.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitajima, M.; Gerba, C.P. Aichi Virus 1: Environmental Occurrence and Behavior. Pathogens 2015, 4, 256-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4020256
Kitajima M, Gerba CP. Aichi Virus 1: Environmental Occurrence and Behavior. Pathogens. 2015; 4(2):256-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4020256
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitajima, Masaaki, and Charles P. Gerba. 2015. "Aichi Virus 1: Environmental Occurrence and Behavior" Pathogens 4, no. 2: 256-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4020256
APA StyleKitajima, M., & Gerba, C. P. (2015). Aichi Virus 1: Environmental Occurrence and Behavior. Pathogens, 4(2), 256-268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens4020256






