Occurrence of Echinococcus felidis in Apex Predators and Warthogs in Tanzania: First Molecular Evidence of Leopards as a New, Definitive Host and Implications for Ecosystem Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
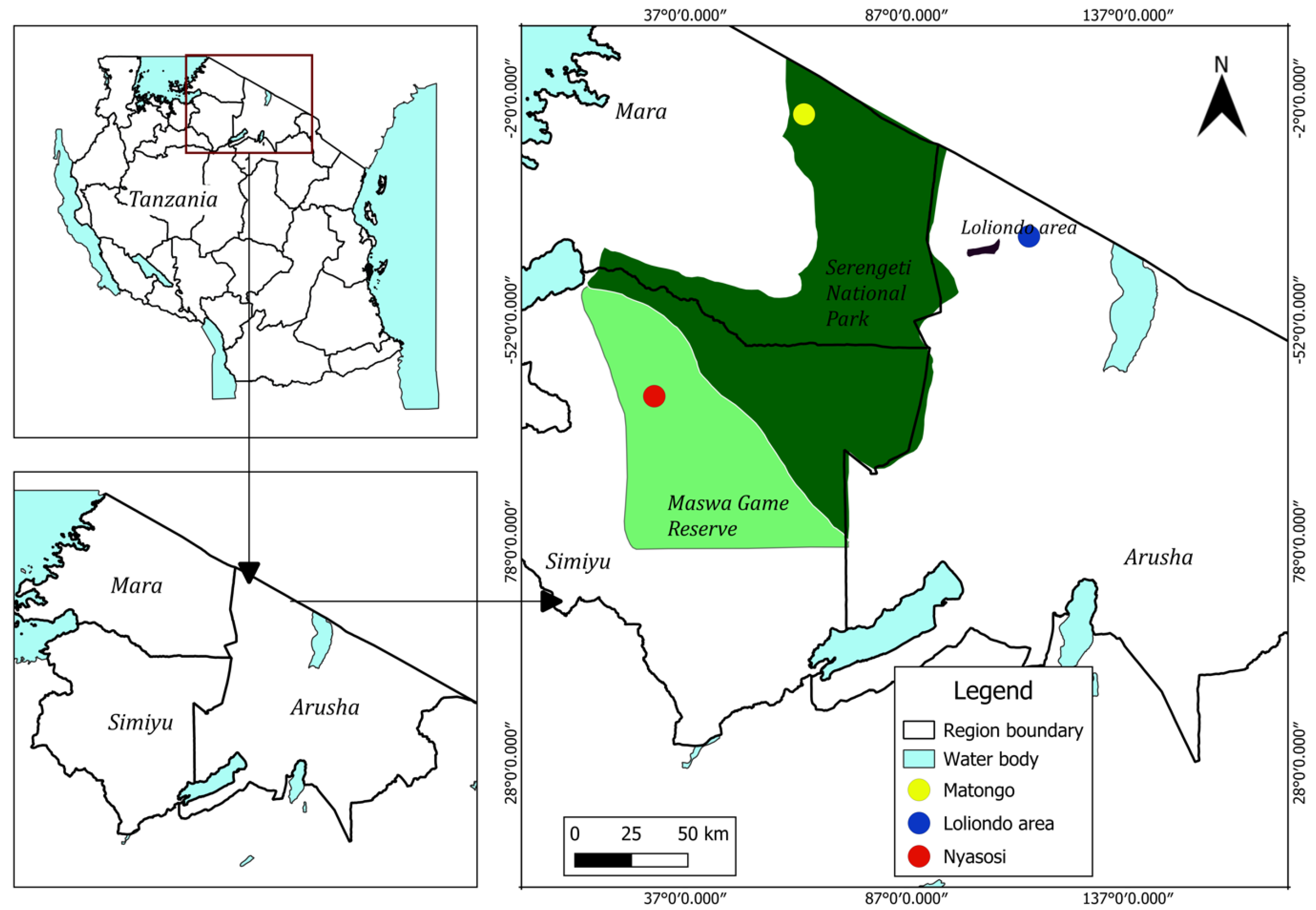
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Molecular Analysis
3. Results
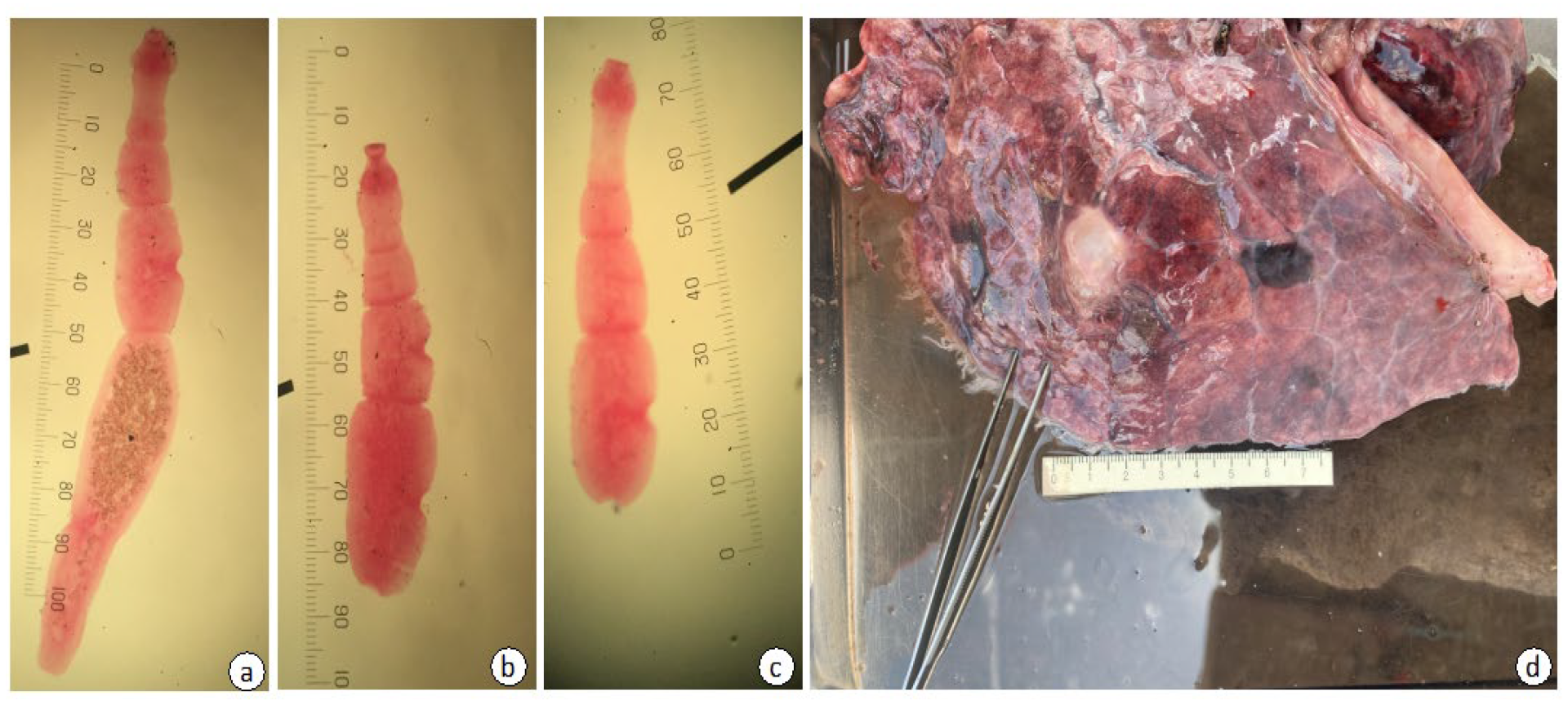
3.1. Morphological Identification of Echinococcus felidis
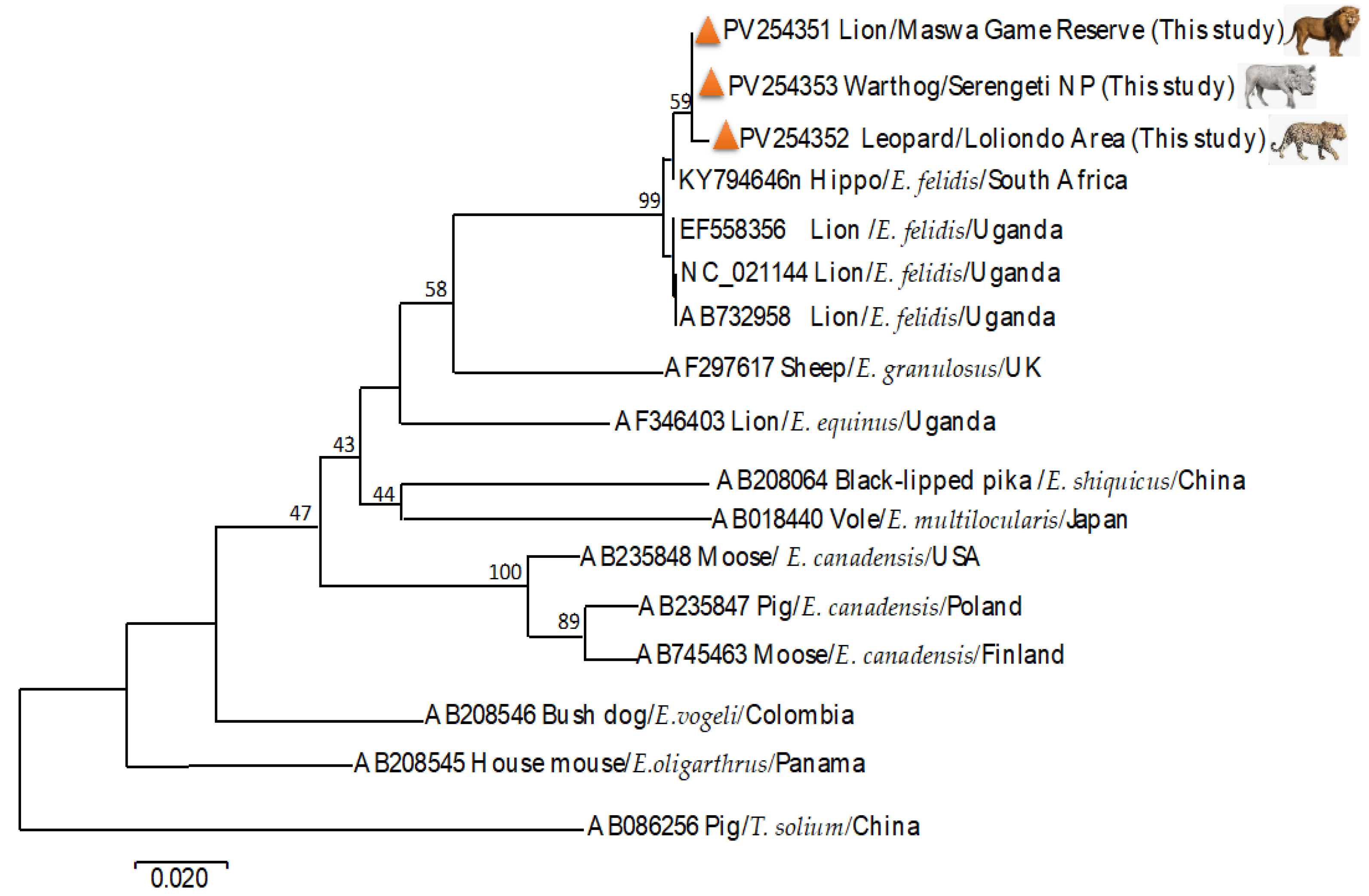
3.2. Molecular Identification of Echinococcus felidis and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yıldız, F. Echinococcus infection: The effects of echinococcosis on public health and economy. Int. J. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 2, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kakundi, E.M. Molecular Epidemiology of Echinococcus and Taenia Species in Dogs from Cystic Echinococcosis Endemic Areas in Kenya. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lymbery, A. Phylogenetic pattern, evolutionary processes and species delimitation in the genus Echinococcus. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 111–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.A.; McManus, D.P. Towards a taxonomic revision of the genus Echinococcus. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, A.; Massolo, A.; Saarma, U.; Umhang, G.; Santolamazza, F.; Santoro, A. Species and genotypes belonging to Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato complex causing human cystic echinococcosis in Europe (2000–2021): A systematic review. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Lavikainen, A.; Yanagida, T.; Ito, A. Phylogenetic systematics of the genus Echinococcus (Cestoda: Taeniidae). Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Yanagida, T.; Konyaev, S.; Lavikainen, A.; Odnokurtsev, V.; Zaikov, V.; Ito, A. Mitochondrial phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus (Cestoda: Taeniidae) with emphasis on relationships among Echinococcus canadensis genotypes. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuitton, D.; McManus, D.; Rogan, M.; Romig, T.; Gottstein, B.; Naidich, A.; Tuxun, T.; Wen, H.; Menezes da Silva, A. International consensus on terminology to be used in the field of Echinococcoses. Parasite 2020, 27, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, M.; Woldeyes, D.; Gerbi, B.; Ebi, D.; Zeyhle, E.; Mackenstedt, U.; Petros, B.; Tilahun, G.; Kern, P.; Romig, T. A novel zoonotic genotype related to Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto from southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurimaa, L. Echinococcus Multilocularis and Other Zoonotic Parasites in Estonian Canids. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moks, E.; Jõgisalu, I.; Valdmann, H.; Saarma, U. First report of Echinococcus granulosus G8 in Eurasia and a reappraisal of the phylogenetic relationships of ‘genotypes’ G5-G10. Parasitology 2008, 135, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.S.; Rausch, R.L. Echinococcus infections in man and animals in Kenya. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1963, 57, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.N.L.; Karstad, L.; Stevenson, P.; Arundel, J.H. Hydatid disease in the Turkana District of Kenya: III. The significance of wild animals in the transmission of Echinococcus granulosus, with particular reference to Turkana and Masailand in Kenya. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1983, 77, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Alemu, H.H.; Marami, L.M.; Garedo, D.R.; Bodena, E.B. Cystic echinococcosis: A comprehensive review on life cycle, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical Spectrum, diagnosis, public health and economic implications, treatment, and control. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. Res. 2022, 6, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.; Macpherson, C. Transmission ecology of Echinococcus in wild-life in Australia and Africa. Parasitology 2003, 127, S63–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Abad, B.; Torgerson, P.R. A systematic review of the epidemiology of echinococcosis in domestic and wild animals. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, J.; Deplazes, P. Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 107–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R. Biology and systematics of Echinococcus. Adv. Parasitol. 1995, 95, 65–109. [Google Scholar]
- Deplazes, P.; Eckert, J. Veterinary aspects of alveolar echinococcosis—A zoonosis of public health significance. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 98, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo Higuita, N.I.; Brunetti, E.; McCloskey, C. Cystic echinococcosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.; Romig, T.; Thompson, R. Emergence/re-emergence of Echinococcus spp.—A global update. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, S.; Gottstein, B.; Haag, K.L.; Ma, S.; Colovic, I.; Benchikh-Elfegoun, M.C.; Knapp, J.; Piarroux, R. The EmsB tandemly repeated multilocus microsatellite: A new tool to investigate genetic diversity of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, R.; Dinkel, A.; Romig, T.; Mackenstedt, U.; Aradaib, I. Strain characterization of cystic echinococcosis in livestock in Sudan. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 293, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, R.A.; Dinkel, A.; Romig, T.; Mackenstedt, U.; Elnahas, A.; Aradaib, I.; Ahmed, M.; Elmalik, K.; Adam, A. A molecular survey of cystic echinococcosis in Sudan. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, S.; Benchikh-Elfegoun, M.C.; Knapp, J.; Bart, J.M.; Koskei, P.; Gottstein, B.; Piarroux, R. Taxonomic position and geographical distribution of the common sheep G1 and camel G6 strains of Echinococcus granulosus in three African countries. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigre, W.; Deresa, B.; Haile, A.; Gabriël, S.; Victor, B.; Van Pelt, J.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Vercruysse, J.; Dorny, P. Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus sl cysts from cattle, camels, goats and pigs in Ethiopia. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 215, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, J.; Blair, D.; McManus, D.P. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 54, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obwaller, A.; Schneider, R.; Walochnik, J.; Gollackner, B.; Deutz, A.; Janitschke, K.; Aspöck, H.; Auer, H. Echinococcus granulosus strain differentiation based on sequence heterogeneity in mitochondrial genes of cytochrome c oxidase-1 and NADH dehydrogenase-1. Parasitology 2004, 128, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachira, T. Host influence on the rate of maturation of Echinococcus granulosus in dogs in Kenya. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1993, 87, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkel, A.; Njoroge, E.M.; Zimmermann, A.; Wälz, M.; Zeyhle, E.; Elmahdi, I.E.; Romig, T. A PCR system for detection of species and genotypes of the Echinococcus granulosus-complex, with reference to the epidemiological situation in eastern Africa. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttner, M.; Siefert, L.; Mackenstedt, U.; Romig, T. A survey of Echinococcus species in wild carnivores and livestock in East Africa. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, A.; Zeyhle, E.; Brunetti, E.; Pozio, E.; Meroni, V.; Genco, F.; Filice, C. Molecular evidence of the camel strain (G6 genotype) of Echinococcus granulosus in humans from Turkana, Kenya. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, W. Weights, measurement and parasitic infestation of six lions from southern Tanzania. East Afr. Wildl. J. 1974, 12, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halajian, A.; Luus-Powell, W.J.; Roux, F.; Nakao, M.; Sasaki, M.; Lavikainen, A. Echinococcus felidis in hippopotamus, South Africa. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 243, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E. Echinococcosis (hydatodosis) in wild animals of the Kruger National Park. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1975, 46, 285–286. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner, M.; Nakao, M.; Wassermann, T.; Siefert, L.; Boomker, J.D.; Dinkel, A.; Sako, Y.; Mackenstedt, U.; Romig, T.; Ito, A. Genetic characterization and phylogenetic position of Echinococcus felidis (Cestoda: Taeniidae) from the African lion. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagendo, D.; Magambo, J.; Agola, E.L.; Njenga, S.M.; Zeyhle, E.; Mulinge, E.; Gitonga, P.; Mbae, C.; Muchiri, E.; Wassermann, M. A survey for Echinococcus spp. of carnivores in six wildlife conservation areas in Kenya. Parasitol. Int. 2014, 63, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulinge, E.; Magambo, J.; Odongo, D.; Njenga, S.; Zeyhle, E.; Mbae, C.; Kagendo, D.; Addy, F.; Ebi, D.; Wassermann, M. Molecular characterization of Echinococcus species in dogs from four regions of Kenya. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 255, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenborn, O.; Aschenborn, J.; Beytell, P.; Wachter, B.; Melzheimer, J.; Dumendiak, S.; Rüffler, B.; Mackenstedt, U.; Kern, P.; Romig, T. High species diversity of Echinococcus spp. in wild mammals of Namibia. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 21, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttner, M.; Romig, T. Echinococcus species in African wildlife. Parasitology 2009, 136, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y.; Rao, J.R.; Butchaiah, G.; Sharma, B. Random amplified polymorphic DNA for the specific detection of bubaline Echinococcus granulosus by hybridization assay. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 79, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, M.R.; Taghipour, N.; Nochi, Z.; Mojarad, E.N.; Mohebbi, S.; Harandi, M.F.; Zali, M. Molecular identification of animal isolates of Echinococcus granulosus from Iran using four mitochondrial genes. J. Helminthol. 2012, 86, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romig, T.; Omer, R.A.; Zeyhle, E.; Huettner, M.; Dinkel, A.; Siefert, L.; Elmahdi, I.E.; Magambo, J.; Ocaido, M.; Menezes, C.N. Echinococcosis in sub-Saharan Africa: Emerging complexity. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ernest, E.; Nonga, H.; Cleaveland, S. Prevalence of echinococcosis in dogs and wild carnivores in selected Serengeti ecosystem areas of Tanzania. Tanzan. Vet. J. 2013, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, E.; Kern, P.; Vuitton, D.A. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusano, A.; Bruschi, F. Cystic echinococcosis: Progress and limits in epidemiology and immunodiagnosis. Parassitologia 2006, 48, 65–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tamarozzi, F.; Kibona, T.; de Glanville, W.A.; Mappi, T.; Adonikamu, E.; Salewi, A.; Misso, K.; Maro, V.; Casulli, A.; Santoro, A. Cystic echinococcosis in northern Tanzania: A pilot study in Maasai livestock-keeping communities. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Deplazes, P.; Lymbery, A.J. Echinococcus and Echinococcosis, Part A. In Advances in Parasitology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 95, ISBN 9780128114714. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Deplazes, P.; Lymbery, A.J. Echinococcus and Echinococcosis, Part B. In Advances in Parasitology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 96, ISBN 9780128114721. [Google Scholar]
- Heritage, N. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation. UNESCO. 2014. Available online: https://ich.unesco.org/en/performing-arts-00054 (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Thaxton, M. Integrating population, health, and environment in Tanzania. Life 2004, 7, 285.7. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, A.R.; Mduma, S.A.; Hopcraft, J.G.C.; Fryxell, J.M.; Hilborn, R.; Thirgood, S. Long-term ecosystem dynamics in the Serengeti: Lessons for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 580–590. [Google Scholar]
- Avcioglu, H.; Guven, E.; Balkaya, I.; Kirman, R.; Akyuz, M.; Bia, M.M.; Gulbeyen, H.; Yaya, S. Echinococcus multilocularis in Red Foxes in Turkey: Increasing risk in urban. Acta Trop. 2021, 216, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, J.; Gemmell, M.; Meslin, F.-X.; Pawlowski, Z. WHO/OIE Manual on Echinococcosis in Humans and Animals: A Public Health Problem of Global Concern; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Thaenkham, U.; Chaisiri, K.; Hui En Chan, A. Parasitic helminth sample preparation for taxonomic Study. In Molecular Systematics of Parasitic Helminths; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, J.; Blair, D. Relative merits of nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and mitochondrial CO1 and ND1 genes for distinguishing among Echinostoma species (Trematoda). Parasitology 1998, 116, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, C.; Qaadri, K.; Moir, R.; Kearse, M.; Buxton, S.; Cheung, M. Geneious R7: A bioinformatics platform for biologists. In International Plant and Animal Genome Conference XXII; Biomatters, Inc.: Newark, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.-K.; Kim, K.-H.; Eom, K.S. Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Taenia saginata: Comparison with T. solium and T. asiatica. Parasitol. Int. 2007, 56, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Sako, Y.; Ito, A. The mitochondrial genome of the tapeworm Taenia solium: A finding of the abbreviated stop codon U. J. Parasitol. 2003, 89, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; McManus, D.; Schantz, P.; Craig, P.; Ito, A. A molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus inferred from complete mitochondrial genomes. Parasitology 2006, 134, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Yokoyama, N.; Sako, Y.; Fukunaga, M.; Ito, A. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the cestode Echinococcus multilocularis (Cyclophyllidea: Taeniidae). Mitochondrion 2002, 1, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Pearson, M.; Blair, D.; Dai, N.; Zhang, L.; McManus, D. Complete mitochondrial genomes confirm the distinctiveness of the horse-dog and sheep-dog strains of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitology 2002, 124, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verster, A.J.M. Review of Echinococcus species in South Africa. J. Vet. Res. 1965, 32, 7–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ortlepp, R. South African helminths Part I. J. Veterinalry Sci. Anim. Ind. 1937, 9, 311–336. [Google Scholar]
- Rausch, R.L. The Taxonomic Value and Variability of Certain Structures in the Cestode genus Echinococcus (Rudolphi, 1801) and a Review of Recognized Species; Thapar Commemoration; University of Nebraska: Lincoln, UK, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Mathis, A.; Deplazes, P.; Eckert, J. An improved test system for PCR-based specific detection of Echinococcus multilocularis eggs. J. Helminthol. 1996, 70, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.A.M.; Gray, D.J.; Clements, A.C.; Barnes, T.S.; McManus, D.P.; Yang, Y.R. Environmental changes impacting Echinococcus transmission: Research to support predictive surveillance and control. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Li, S.; Ma, B.; Di, X.; Li, Y.; An, B.; Jiang, W. How climate, landscape, and economic changes increase the exposure of Echinococcus Spp. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, I.M.; Abdel-Hafez, S.K.; Al-Yaman, F.M. Morphological variation of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces from hydatid cysts of human and various domestic animals in Jordan. Int. J. Parasitol. 1988, 18, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bia, M.M.; Choe, S.; Ndosi, B.A.; Park, H.; Kang, Y.; Eamudomkarn, C.; Nath, T.C.; Kim, S.; Jeon, H.-K.; Lee, D. Genotypes of Echinococcus species from cattle in Tanzania. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, L.L.; Assis, J.; Araújo, F.M.G.; Salim, A.C.; Macchiaroli, N.; Cucher, M.; Federico Camicia, F.; Fox, A.; Rosenzvit, M.; Oliveira, G.; et al. The Echinococcus canadensis (G7) genome: A key knowledge of parasitic platyhelminth human diseases. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Herwerden, L.; Gasser, R.B.; Blair, D. ITS-1 ribosomal DNA sequence variants are maintained in different species and strains of Echinococcus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.; Fields, P.D. Host–parasite co-evolution and its genomic signature. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosil, P.; Funk, D.J.; Ortiz-Barrientos, D. Divergent selection and heterogeneous genomic divergence. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doña, J.; Proctor, H.; Mironov, S.; Serrano, D.; Jovani, R. Host specificity, infrequent major host switching and the diversification of highly host-specific symbionts: The case of vane-dwelling feather mites. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, F.; Deplazes, P.; Rieffel, D.; Lambert, J.-C.; Giraudoux, P. Predator dietary response to prey density variation and consequences for cestode transmission. Oecologia 2010, 164, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budke, C.M.; Campos-Ponce, M.; Qian, W.; Torgerson, P.R. A canine purgation study and risk factor analysis for echinococcosis in a high endemic region of the Tibetan plateau. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 127, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziadinov, I.; Mathis, A.; Trachsel, D.; Rysmukhambetova, A.; Abdyjaparov, T.; Kuttubaev, O.; Deplazes, P.; Torgerson, P.R. Canine echinococcosis in Kyrgyzstan: Using prevalence data adjusted for measurement error to develop transmission dynamics models. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, R.E. Lion and Leopard Diet and Dispersal in Human-Dominated Landscapes. Master’s Thesis, Nelson Mandela University, Gqeberha, South Africa, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, C.J.; Myers, J.H. Population cycles in small mammals. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1974, 8, 267–399. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, F.K. East Coast Fever and Vaccination at the Livestock/Wildlife Interface. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh, Old College, South Bridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, K.; McCabe, J.T.; Estes, A.B.; Ogutu, J.O.; Rentsch, D.; Craft, M.; Hemed, C.B.; Ernest, E.; Hoare, R.; Kissui, B. Living in the Greater Serengeti Ecosystem: Human-Wildlife Conflict and Coexistence. Serengeti IV: Sustaining Biodiversity in a Coupled Humannatural System; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015; pp. 607–645. [Google Scholar]
- Kurpiers, L.A.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, B.; Ejotre, I.; Reeder, D.M. Bushmeat and emerging infectious diseases: Lessons from Africa. In Problematic Wildlife: A Cross-Disciplinary Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 24, pp. 507–551. [Google Scholar]
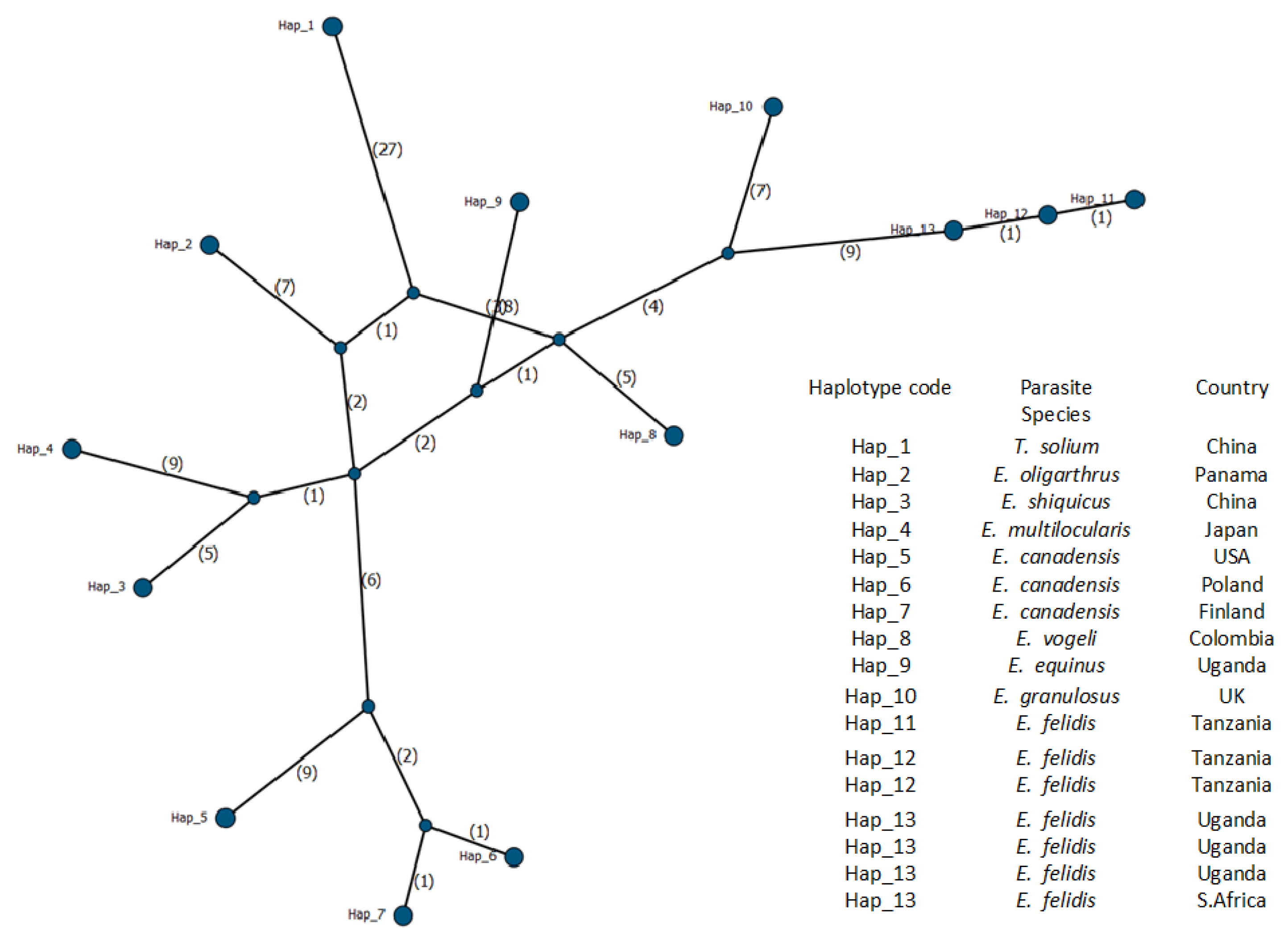

| Host Name | Scientific Name | Country | Parasite Species | Haplotype Code | Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pig | Sus scrofa | China | Taenia solium | Hap_1 | AB086256 | [62] |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Panama | E. oligarthrus | Hap_2 | AB208545 | [63] |
| Black-lipped pika | Ochotona curzoniae | China | E. shiquicus | Hap_3 | AB208064 | [63] |
| Vole | Craseomys rufocanus | Japan | E. multilocularis | Hap_4 | AB018440 | [64] |
| Moose | Alces alces | USA | E. canadensis | Hap_5 | AB235848 | [63] |
| Pig | Sus scrofa | Poland | E. canadensis | Hap_6 | AB235847 | [63] |
| Moose | Alces alces | Finland | E. canadensis | Hap_7 | AB745463 | [7] |
| Bush dog | Speothos venaticus | Colombia | E. vogeli | Hap_8 | AB208546 | [63] |
| African lion | Panthera leo | Uganda | E. equinus | Hap_9 | AF346403 | [65] |
| Sheep | Ovis aries | UK | E. granulosus | Hap_10 | AF297617 | [65] |
| African lion | Panthera leo | Tanzania | E. felidis | Hap_11 | PV254351 | This study |
| Leopard | Panthera pardus | Tanzania | E. felidis | Hap_12 | PV254352 | This study |
| Warthog | Phacochoerus africanus | Tanzania | E. felidis | Hap_12 | PV254353 | This study |
| African lion | Panthera leo | Uganda | E. felidis | Hap_13 | NC_021144 | [7] |
| African lion | Panthera leo | Uganda | E. felidis | Hap_13 | AB732958 | [7] |
| African lion | Panthera leo | Uganda | E. felidis | Hap_13 | EF558356 | [36] |
| Hippopotamus | Hippopotamus amphibius | S. Africa | E. felidis | Hap_13 | KY794646 | [34] |
| Feature | E. felidis from Leopard (This Study) | E. felidis Verster, 1965 [66] | E. felidis Ortlepp, 1935 [67] | E. felidis Raush, 1953 [68] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body length (mm) | 1.65–3.10 (av.2.02) | 2.12–5.220 (av.3.239) ± 0.3 | 3.42–5.22 (av.4.21 ± 0.6) | 6 mm |
| Number of segments | 4.0–5.0 | 3 (18.5%), 4 (47.0%), 5 (34.5%) | 4–5 usually 4 | 3.0–4.0 |
| Number of hooklets | 28–32 | - | - | - |
| Number of testes | 12.0–60.0 | 28–45 (av.35.9 ± 3.5) | 30–46 (av.6 ± 4.2) | 32–46 |
| Cirrus sac | 69.13–188.89 (av.128.39 µm long, 49.38–164.19 µm (av.88.88 µm)) | Mt: 82.8–202.4 (129.4 ± 2.4) µm long, 46.0–105.8 (64.9 ± 99) µm with gravid segment 147.2–184 (159.9 ± 13.7 µm, 56.0–79.2 (717 ± 9.3)) | Mt: 115.0–174.8 (148.2 ± 15.5 µm long, 55.2–92.0 (77.3 + 133)) width. Gravid segment 142.6–207.0 (176.9 ± 21.6) µm, 64.4–96.6 (83.2 ± 10.2) µm | - |
| Egg size | 29.63 × 30.50 µm | - | - | 37–40.5 (32–35.5 µm) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndossi, B.A.; Mjingo, E.E.; Zebedayo, M.W.; Choe, S.; Park, H.; Dongmin, L.; Eom, K.S.; Bia, M.M. Occurrence of Echinococcus felidis in Apex Predators and Warthogs in Tanzania: First Molecular Evidence of Leopards as a New, Definitive Host and Implications for Ecosystem Health. Pathogens 2025, 14, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050443
Ndossi BA, Mjingo EE, Zebedayo MW, Choe S, Park H, Dongmin L, Eom KS, Bia MM. Occurrence of Echinococcus felidis in Apex Predators and Warthogs in Tanzania: First Molecular Evidence of Leopards as a New, Definitive Host and Implications for Ecosystem Health. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050443
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdossi, Barakaeli Abdieli, Eblate Ernest Mjingo, Mary Wokusima Zebedayo, Seongjun Choe, Hansol Park, Lee Dongmin, Keeseon S. Eom, and Mohammed Mebarek Bia. 2025. "Occurrence of Echinococcus felidis in Apex Predators and Warthogs in Tanzania: First Molecular Evidence of Leopards as a New, Definitive Host and Implications for Ecosystem Health" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050443
APA StyleNdossi, B. A., Mjingo, E. E., Zebedayo, M. W., Choe, S., Park, H., Dongmin, L., Eom, K. S., & Bia, M. M. (2025). Occurrence of Echinococcus felidis in Apex Predators and Warthogs in Tanzania: First Molecular Evidence of Leopards as a New, Definitive Host and Implications for Ecosystem Health. Pathogens, 14(5), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050443









