Literature Review: Coinfection in Young Ruminant Livestock—Cryptosporidium spp. and Its Companions
Abstract
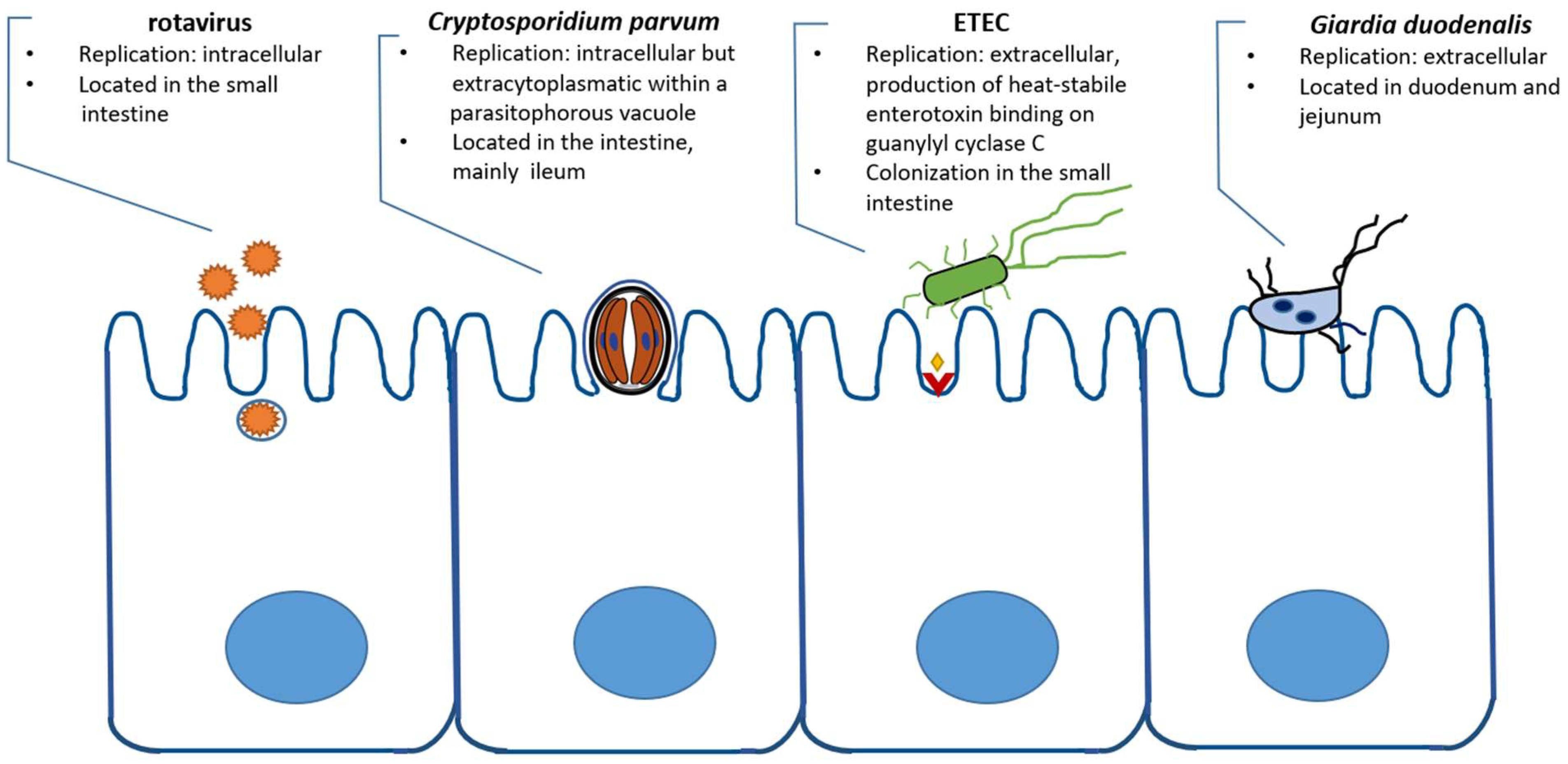
1. Introduction
2. Cryptosporidium and Viruses
2.1. Rotavirus
2.2. Coronavirus
2.3. Other Viruses
3. Cryptosporidium and Bacterial Infection
3.1. Escherichia coli
3.2. Clostridium
3.3. Salmonella
4. Cryptosporidium and Other Parasites
4.1. Protozoa
4.1.1. Giardia
4.1.2. Eimeria
4.2. Helminths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sweeny, J.P.A.; Ryan, U.M.; Robertson, I.D.; Jacobson, C. Prevalence and on-farm risk factors for diarrhoea in meat lamb flocks in Western Australia. Vet. J. 2012, 192, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.M.; Smith, G.W. Pathophysiology of diarrhea in calves. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2009, 25, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Tan, Z.; He, Z. Changes of Intestinal Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Gene Expression in Neonatal Diarrhoea Kids. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 598691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyzzer, E.E. A sporozoan found in the peptic glands of the common mouse. Exp. Biol. Med. 1907, 5, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Gregarine site-heterogeneous 18S rDNA trees, revision of gregarine higher classification, and the evolutionary diversification of Sporozoa. Eur. J. Protistol. 2014, 50, 472–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.; Paparini, A.; Monis, P.; Hijjawi, N. It’s official—Cryptosporidium is a gregarine. What are the implications for the water industry? Water Res. 2016, 105, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendner, M.; Etzold, M.; Daugschies, A. Kryptosporidiose—Ein Update. Berl. Und Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2011, 124, 473–484. [Google Scholar]
- Santín, M.; Trout, J.M.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, L.; Greiner, E.; Fayer, R. Prevalence and age-related variation of Cryptosporidium species and genotypes in dairy calves. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 122, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Zhang, K.; Huang, M.; Wang, S.; Xu, C.; Wang, T.; Jing, B.; Li, J. Longitudinal detection of Cryptosporidium spp. in 1-10-week-old dairy calves on a farm in Xinjiang, China. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3839–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayer, R.; Santín, M.; Trout, J.M.; Greiner, E. Prevalence of species and genotypes of Cryptosporidium found in 1-2-year-old dairy cattle in the eastern United States. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 135, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, T.; Koehler, A.V.; Hu, M.; Gasser, R.B. Molecular investigation of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in pre- and post-weaned calves in Hubei Province, China. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverlås, C.; Näslund, K.; Björkman, C.; Mattsson, J.G. Molecular characterisation of Cryptosporidium isolates from Swedish dairy cattle in relation to age, diarrhoea and region. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kváč, M.; Hromadová, N.; Květoňová, D.; Rost, M.; Sak, B. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in pre-weaned dairy calves in the Czech Republic. Absence of C. ryanae and management-associated distribution of C. andersoni, C. bovis and C. parvum subtypes. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 177, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieux, A.; Chartier, C.; Pors, I.; Paraud, C. Dynamics of excretion and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium isolates in pre-weaned French beef calves. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 195, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzhausen, I.; Lendner, M.; Göhring, F.; Steinhöfel, I.; Daugschies, A. Distribution of Cryptosporidium parvum gp60 subtypes in calf herds of Saxony, Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinari, M.; Lymbery, A.J.; Ryan, U.M. Cryptosporidium species in sheep and goats from Papua New Guinea. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 141, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanidakis, N.; Sotiraki, S.; Claerebout, E.; Ehsan, A.; Voutzourakis, N.; Kostopoulou, D.; Stijn, C.; Vercruysse, J.; Geurden, T. Occurrence and molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in sheep and goats reared under dairy husbandry systems in Greece. Parasite 2014, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaupke, A.; Michalski, M.M.; Rzeżutka, A. Diversity of Cryptosporidium species occurring in sheep and goat breeds reared in Poland. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroudi, D.; Hakem, A.; Adamu, H.; Amer, S.; Khelef, D.; Adjou, K.; Dahmani, H.; Chen, X.; Roellig, D.; Feng, Y.; et al. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium species and subtypes in lambs and goat kids in Algeria. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.; Navarro, E.; Prieto, A.; Pérez-Creo, A.; Viña, M.; Díaz-Cao, J.M.; López, C.M.; Panadero, R.; Fernández, G.; Díez-Baños, P.; et al. Cryptosporidium species in post-weaned and adult sheep and goats from N.W. Spain. Public and animal health significance. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 254, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quílez, J.; Torres, E.; Chalmers, R.M.; Hadfield, S.J.; del Cacho, E.; Sánchez-Acedo, C. Cryptosporidium genotypes and subtypes in lambs and goat kids in Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6026–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imre, K.; Luca, C.; Costache, M.; Sala, C.; Morar, A.; Morariu, S.; Ilie, M.S.; Imre, M.; Dărăbuş, G. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium parvum in Romanian newborn lambs (Ovis aries). Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 191, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, P.; Quílez, J.; Prieto, A.; Navarro, E.; Pérez-Creo, A.; Fernández, G.; Panadero, R.; López, C.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P. Cryptosporidium species and subtype analysis in diarrhoeic pre-weaned lambs and goat kids from north-western Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4099–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolopoulou, V.; Baroudi, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Papadopoulos, E.; Lafi, S.Q.; Abd El-Tawab, M.M.; Diakou, A.; Giadinis, N.D.; Feng, Y.; et al. Genotypes and subtypes of Cryptosporidium spp. in diarrheic lambs and goat kids in northern Greece. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessì, G.; Tamponi, C.; Varcasia, A.; Sanna, G.; Pipia, A.P.; Carta, S.; Salis, F.; Díaz, P.; Scala, A. Cryptosporidium infections in sheep farms from Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 4211–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Juárez, A.; Dashti, A.; Santín, M.; Köster, P.C.; López-López, P.; Risalde, M.A.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Frías, M.; et al. Diarrhoea-causing enteric protist species in intensively and extensively raised pigs (Sus scrofa domesticus) in Southern Spain. Part II: Association with Hepatitis E virus susceptibility. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, M.M.; Kirkland, P.D.; Mohler, V.L.; Perkins, N.R.; Gunn, A.A.; House, J.K. Prevalence of major enteric pathogens in Australian dairy calves with diarrhoea. Aust. Vet. J. 2011, 89, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, C.; Cooper, V.; Schwartz, K.; Engelken, T.; Yoon, K. Case-control study of microbiological etiology associated with calf diarrhea. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, V.; Malik, Y.P.S.; Kamdi, B.; Singh, R.; Kashyap, G. Immunohistochemical and molecular detection of natural cases of bovine rotavirus and coronavirus infection causing enteritis in dairy calves. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.E.; Weese, J.S. Viral enteritis in calves. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2017, 58, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Medina, A.; Schlafer, D.H.; Mebus, C.A. Rotaviral and coronaviral diarrhea. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1985, 1, 471–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramig, R.F. Pathogenesis of intestinal and systemic rotavirus infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10213–10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatek, D.L.; Palombo, E.A.; Lee, A.; Coventry, M.J.; Britz, M.L.; Kirkwood, C.D. Detection and analysis of bovine rotavirus strains circulating in Australian calves during 2004 and 2005. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebus, C.A.; Underdahl, N.R.; Rhodes, M.B.; Twiehaus, M.J. Further studies on neonatal calf diarrhea virus. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the United States Animal Health Association, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 12–17 October 1969; Volume 73, pp. 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Flewett, T.H.; Bryden, A.S.; Davies, H.; Woode, G.N.; Bridger, J.C.; Derrick, J.M. Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancet 1974, 2, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalov-Kovács, E.; Gellért, Á.; Marton, S.; Farkas, S.L.; Fehér, E.; Oldal, M.; Jakab, F.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K. Candidate new rotavirus species in sheltered dogs, Hungary. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bányai, K.; Kemenesi, G.; Budinski, I.; Földes, F.; Zana, B.; Marton, S.; Varga-Kugler, R.; Oldal, M.; Kurucz, K.; Jakab, F. Candidate new rotavirus species in Schreiber’s bats, Serbia. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2017, 48, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timurkan, M.Ö.; Alkan, F. Identification of rotavirus A strains in small ruminants. First detection of G8P1 genotypes in sheep in Turkey. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourasgari, F.; Kaplon, J.; Karimi-Naghlani, S.; Fremy, C.; Otarod, V.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Mirjalili, A.; Pothier, P. The molecular epidemiology of bovine rotaviruses circulating in Iran. A two-year study. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3483–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Cardiel, I.; Fernández-Jiménez, M.; Luján, L.; Buesa, J.; Espada, J.; Fantova, E.; Blanco, J.; Segalés, J.; Badiola, J.J. Novel group A rotavirus G8 P1 as primary cause of an ovine diarrheic syndrome outbreak in weaned lambs. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 149, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, H.; Malik, Y.S.; Farkas, S.L.; Jakab, F.; Martella, V.; Bányai, K. Rotavirus strains in neglected animal species including lambs, goats and camelids. Virusdisease 2014, 25, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Knutson, T.P.; Ciarlet, M.; Sturos, M.; Marthaler, D.G. Complete genome characterization of a rotavirus B (RVB) strain identified in Alpine goat kids with enteritis reveals inter-species transmission with RVB bovine strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaracco, A.; Garaicoechea, L.; Rodríguez, D.; Uriarte, E.L.; Odeón, A.; Bilbao, G.; Galarza, R.; Abdala, A.; Fernandez, F.; Parreño, V. Bovine rotavirus strains circulating in beef and dairy herds in Argentina from 2004 to 2010. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinsangaram, J.; Schore, C.E.; Guterbock, W.; Weaver, L.D.; Osburn, B.I. Prevalence of group A and group B rotaviruses in the feces of neonatal dairy calves from California. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 18, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; Orden, J.A.; Cid, D.; Sanz, R.; Gómez-Bautista, M.; de La Fuente, R. Rotavirus and concurrent infections with other enteropathogens in neonatal diarrheic dairy calves in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 23, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.C. Diagnostics of dairy and beef cattle diarrhea. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz Uhde, F.; Kaufmann, T.; Sager, H.; Albini, S.; Zanoni, R.; Schelling, E.; Meylan, M. Prevalence of four enteropathogens in the faeces of young diarrhoeic dairy calves in Switzerland. Vet. Rec. 2008, 163, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, R.; García, A.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; Luzón, M.; Cid, D.; García, S.; Orden, J.A.; Gómez-Bautista, M. Proportional morbidity rates of enteropathogens among diarrheic dairy calves in central Spain. Prev. Vet. Med. 1998, 36, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göhring, F.; Möller-Holtkamp, P.; Daugschies, A.; Lendner, M. Co-infections with Cryptosporidium parvum and other enteropathogenes support the occurrence and severity of diarrhoea in suckling calves. Tierarztl. Umsch. 2014, 69, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gillhuber, J.; Rügamer, D.; Pfister, K.; Scheuerle, M.C. Giardiosis and other enteropathogenic infections. A study on diarrhoeic calves in Southern Germany. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mawly, J.; Grinberg, A.; Prattley, D.; Moffat, J.; Marshall, J.; French, N. Risk factors for neonatal calf diarrhoea and enteropathogen shedding in New Zealand dairy farms. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzipori, S.; Sherwood, D.; Angus, K.W.; Campbell, I.; Gordon, M. Diarrhea in lambs. Experimental infections with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, rotavirus, and Cryptosporidium sp. Infect. Immun. 1981, 33, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruvinel, L.B.; Ayres, H.; Zapa, D.M.B.; Nicaretta, J.E.; Couto, L.F.M.; Heller, L.M.; Bastos, T.S.A.; Cruz, B.C.; Soares, V.E.; Teixeira, W.F.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors for agents causing diarrhea (Coronavirus, Rotavirus, Cryptosporidium spp., Eimeria spp., and nematodes helminthes) according to age in dairy calves from Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, E.W.; Kim, D. Causative agents and epidemiology of diarrhea in Korean native calves. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 20, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahzadeh, S.; Madadgar, O.; Reza Mohebbi, M.; Reza Mokhber Dezfouli, M.; George Watson, D. Bovine coronavirus in neonatal calf diarrhoea in Iran. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stair, E.L.; Rhodes, M.B.; White, R.G.; Mebus, C.A. Neonatal calf diarrhea. Purification and electron microscopy of a coronavirus-like agent. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1972, 33, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mebus, C.A.; White, R.G.; Stair, E.L.; Rhodes, M.B.; Twiehaus, M.J. Neonatal calf diarrhea. Results of a field trial using a reo-like virus vaccine. Vet. Med. Small Anim. Clin. 1972, 67, 173–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mebus, C.A.; Stair, E.L.; Rhodes, M.B.; Twiehaus, M.J. Neonatal calf diarrhea. Propagation, attenuation, and characteristics of a coronavirus-like agent. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1973, 34, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.A. Bovine coronavirus. Br. Vet. J. 1993, 149, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.W.; Herd, H.R.; Sorensen, N.J.; Confer, A.W.; Ritchey, J.W.; Ridpath, J.F.; Burge, L.J. Enteric disease in postweaned beef calves associated with Bovine coronavirus clade 2. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2015, 27, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, M.J.; Kapil, S. Bovine coronavirus associated syndromes. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.J.M.; Holzhauer, M.; Jorritsma, R.; Swart, W.A.J.M.; Lam, T.J.G.M. Prevalence, prediction and risk factors of enteropathogens in normal and non-normal faeces of young Dutch dairy calves. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 93, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, I.; Gottardo, F.; Contiero, B.; Dall Ava, B.; Bonfanti, L.; Stefani, A.; Barberio, A. Association between passive immunity and health status of dairy calves under 30 days of age. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 152, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschek, B.; Klein, D.; Benetka, V.; Herrera, C.; Sommerfeld-Stur, I.; Vilcek, S.; Moestl, K.; Baumgartner, W. Detection of bovine torovirus in neonatal calf diarrhoea in Lower Austria and Styria (Austria). J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.E.; Arroyo, L.G.; Poljak, Z.; Viel, L.; Weese, J.S. Detection of Bovine Coronavirus in Healthy and Diarrheic Dairy Calves. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, A.A.; Ribeiro, J.; de Carvalho Balbo, L.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.F. Dairy calf rearing unit and infectious diseases. Diarrhea outbreak by bovine coronavirus as a model for the dispersion of pathogenic microorganisms. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1937–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Alvarez, M.; Lanza, I.; Cármenes, P. Role of enteric pathogens in the aetiology of neonatal diarrhoea in lambs and goat kids in Spain. Epidemiol. Infect. 1996, 117, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, M.I.; Mohamed, A. Role of enteric pathogens in enteritis in lambs, goat kids and children and their zoonotic importance. Vet. Med. J. Giza 2004, 52, 41–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ozmen, O.; Yukari, B.A.; Haligur, M.; Sahinduran, S. Observations and immunohistochemical detection of Coronavirus, Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia intestinalis in neonatal diarrhoea in lambs and kids. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2006, 148, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tråvén, M.; Carlsson, U.; Lundén, A.; Larsson, B. Serum antibodies to bovine coronavirus in Swedish sheep. Acta Vet. Vet. Scand. 1999, 40, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burimuah, V.; Sylverken, A.; Owusu, M.; El-Duah, P.; Yeboah, R.; Lamptey, J.; Frimpong, Y.O.; Agbenyega, O.; Folitse, R.; Tasiame, W.; et al. Sero-prevalence, cross-species infection and serological determinants of prevalence of Bovine Coronavirus in Cattle, Sheep and Goats in Ghana. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 241, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumusova, O.; Yazici, Z.; Albayrak, H.; Çakiroglu, D. First report of bovine rotavirus and bovine coronavirus seroprevalance in goats in Turkey. Vet Glas 2007, 61, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chae, J.; Park, J.; Jung, S.; Kang, J.; Chae, J.; Choi, K. Acute phase response in bovine coronavirus positive post-weaned calves with diarrhea. Acta Vet. Scand. 2019, 61, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, H.M.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Shalaby, M.A.; Almajhdi, F.N.; Hufert, F.T.; Weidmann, M. A new approach for diagnosis of bovine coronavirus using a reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lojkić, I.; Krešić, N.; Šimić, I.; Bedeković, T. Detection and molecular characterisation of bovine corona and toroviruses from Croatian cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, M.; Alassia, M.; Frank, F.; Vega, C.G.; Wigdorovitz, A.; Parreño, V. Passive immunity to control Bovine coronavirus diarrhea in a dairy herd in Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Trent, A.M.; Goyal, S.M. Excretion and persistence of bovine coronavirus in neonatal calves. Arch. Virol. 1990, 115, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oma, V.S.; Tråvén, M.; Alenius, S.; Myrmel, M.; Stokstad, M. Bovine coronavirus in naturally and experimentally exposed calves; viral shedding and the potential for transmission. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de La Fuente, R.; Luzón, M.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; García, A.; Cid, D.; Orden, J.A.; García, S.; Sanz, R.; Gómez-Bautista, M. Cryptosporidium and concurrent infections with other major enterophatogens in 1 to 30-day-old diarrheic dairy calves in central Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 80, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfred, N.; Liu, H.; Li, M.L.; Hong, S.F.; Tang, H.B.; Wei, Z.Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, F.K.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Huang, W.J. Molecular epidemiology and phylogenetic analysis of diverse bovine astroviruses associated with diarrhea in cattle and water buffalo calves in China. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woode, G.N.; Bridger, J.C. Isolation of small viruses resembling astroviruses and caliciviruses from acute enteritis of calves. J. Med. Microbiol. 1978, 11, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woode, G.N.; Pohlenz, J.F.; Gourley, N.E.; Fagerland, J.A. Astrovirus and Breda virus infections of dome cell epithelium of bovine ileum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 19, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodgrass, D.R.; Gray, E.W. Detection and transmission of 30 nm virus particles (astroviruses) in faeces of lambs with diarrhoea. Arch. Virol. 1977, 55, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, D.R.; Angus, K.W.; Gray, E.W.; Menzies, J.D.; Paul, G. Pathogenesis of diarrhoea caused by astrovirus infections in lambs. Arch. Virol. 1979, 60, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, C.P.; Gregory, W.F.; Mason, C.; Barend, M.; Beard, P.M. High prevalence and diversity of bovine astroviruses in the faeces of healthy and diarrhoeic calves in South West Scotland. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.F.; Mansour, S.M.G.; El-Araby, I.E.; Mor, S.K.; Goyal, S.M. Molecular detection of enteric viruses from diarrheic calves in Egypt. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Ito, M.; Kabashima, Y.; Tsuzuki, H.; Fujiura, A.; Sakae, K. Isolation and characterization of a new species of kobuvirus associated with cattle. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 11, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamrin, P.; Maneekarn, N.; Peerakome, S.; Okitsu, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; Ushijima, H. Bovine kobuviruses from cattle with diarrhea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 985–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, A.F.; Ribeiro, J.; Alfieri, A.F.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Alfieri, A.A. First detection of kobuvirus in farm animals in Brazil and the Netherlands. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 1811–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeoung, H.; Lim, J.; Jeong, W.; Oem, J.; An, D. Three clusters of bovine kobuvirus isolated in Korea, 2008–2010. Virus Genes 2011, 42, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, B.; di Profio, F.; di Felice, E.; Ceci, C.; Pistilli, M.G.; Marsilio, F. Molecular detection of bovine kobuviruses in Italy. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 2393–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.F.; Mansour, S.M.G.; Orabi, A.; El-Araby, I.E.; Ng, T.F.F.; Mor, S.K.; Goyal, S.M. Detection and genetic characterization of bovine kobuvirus from calves in Egypt. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fredrickson, R.; Duncan, M.; Samuelson, J.; Hsiao, S. Bovine Kobuvirus in Calves with Diarrhea, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işidan, H.; Turan, T.; Atasoy, M.O.; Sözdutmaz, I.; Irehan, B. Detection and first molecular characterisation of three picornaviruses from diarrhoeic calves in Turkey. Acta Vet. Hung. 2019, 67, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas-Machado, U.; Saliki, J.T.; Sánchez, S.; Brown, C.C.; Zhang, J.; Keys, D.; Woolums, A.; Harvey, S.B. Pathogenesis of a bovine enterovirus-1 isolate in experimentally infected calves. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, N.M.; Mor, S.K.; Mohammed, M.E.M.; Bastawecy, I.M.; Fakhry, H.M.; Youssef, C.R.B.; Abouzeid, N.Z.; Goyal, S.M. Isolation and molecular characterization of bovine enteroviruses in Egypt. Vet. J. 2015, 206, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omatsu, T.; Tsuchiaka, S.; Hirata, T.; Shiroma, Y.; Okazaki, S.; Katayama, Y.; Oba, M.; Nishiura, N.; Sassa, Y.; Furuya, T.; et al. Detection of enterovirus genome sequence from diarrheal feces of goat. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, B.; di Profio, F.; Martella, V.; Ceci, C.; Marsilio, F. Evidence for recombination in neboviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, H.; Otto, P.; Heilmann, P. Diarrhea in young calves. 6. Determination of the pathogenicity of a bovine coronavirus and an unidentified icosahedral virus. Arch. Exp. Veterinarmed. 1984, 38, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Günther, H.; Otto, P. Diarrhea in young calves. 7. “Zackenvirus” (Jena agent 117/80)-a new diarrhea pathogen in calves. Arch. Exp. Veterinarmed. 1987, 41, 934–938. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, P.H.; Clarke, I.N.; Lambden, P.R.; Salim, O.; Reetz, J.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.M. Infection of calves with bovine norovirus GIII.1 strain Jena virus. An experimental model to study the pathogenesis of norovirus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12013–12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Scheuer, K.A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Pathogenesis of GIII.2 bovine norovirus, CV186-OH/00/US strain in gnotobiotic calves. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.L.; Wood, E.; Asobayire, E.; Wathes, D.C.; Brickell, J.S.; Elschner, M.; Otto, P.; Lambden, P.R.; Clarke, I.N.; Bridger, J.C. Serotype 1 and 2 bovine noroviruses are endemic in cattle in the United kingdom and Germany. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3050–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mauroy, A.; Scipioni, A.; Mathijs, E.; Saegerman, C.; Mast, J.; Bridger, J.C.; Ziant, D.; Thys, C.; Thiry, E. Epidemiological study of bovine norovirus infection by RT-PCR and a VLP-based antibody ELISA. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Jung, K.; Han, M.; Hoet, A.; Scheuer, K.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Retrospective serosurveillance of bovine norovirus (GIII.2) and nebovirus in cattle from selected feedlots and a veal calf farm in 1999 to 2001 in the United States. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Poel, W.H.M.; van der Heide, R.; Verschoor, F.; Gelderblom, H.; Vinjé, J.; Koopmans, M.P.G. Epidemiology of Norwalk-like virus infections in cattle in The Netherlands. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 92, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jor, E.; Myrmel, M.; Jonassen, C.M. SYBR Green based real-time RT-PCR assay for detection and genotype prediction of bovine noroviruses and assessment of clinical significance in Norway. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, B.; di Profio, F.; di Felice, E.; Melegari, I.; Ceci, C.; Mauroy, A.; Thiry, E.; Martella, V.; Marsilio, F. Genetic heterogeneity of bovine noroviruses in Italy. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Williamson, W.; Hewitt, J.; Lin, S.; Rivera-Aban, M.; Ball, A.; Scholes, P.; Savill, M.; Greening, G.E. Molecular detection of norovirus in sheep and pigs in New Zealand farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 133, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, E.B. Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2009). Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley, J.R.; Chang, K.O.; Hayes, J.; Vinjé, J.; Saif, L.J. Characterization of an enteropathogenic bovine calicivirus representing a potentially new calicivirus genus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10089–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.L.; Asobayire, E.; Dastjerdi, A.M.; Bridger, J.C. Genomic characterization of the unclassified bovine enteric virus Newbury agent-1 (Newbury1) endorses a new genus in the family Caliciviridae. Virology 2006, 350, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridger, J.C.; Hall, G.A.; Brown, J.F. Characterization of a calici-like virus (Newbury agent) found in association with astrovirus in bovine diarrhea. Infect. Immun. 1984, 43, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassine-Zaafrane, M.; Kaplon, J.; Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; Aouni, Z.; Pothier, P.; Aouni, M.; Ambert-Balay, K. Molecular prevalence of bovine noroviruses and neboviruses detected in central-eastern Tunisia. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplon, J.; Guenau, E.; Asdrubal, P.; Pothier, P.; Ambert-Balay, K. Possible novel nebovirus genotype in cattle, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1120–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, M.; Alencar, A.L.F.; Almeida-Queiroz, S.R.; Buzinaro, M.G.; Munin, F.S.; Godoy, S.H.S.; Livonesi, M.C.; Fernandes, A.M.; Sousa, R.L. First detection and molecular characterization of Nebovirus in Brazil. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourasgari, F.; Kaplon, J.; Sanchooli, A.; Fremy, C.; Karimi-Naghlani, S.; Otarod, V.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Mojgani, N.; Pothier, P. Molecular prevalence of bovine noroviruses and neboviruses in newborn calves in Iran. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, T.; Işıdan, H.; Atasoy, M.O.; Irehan, B. Detection and Molecular Analysis of Bovine Enteric Norovirus and Nebovirus in Turkey. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; He, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yue, H.; Tang, C. Detection and molecular characteristics of neboviruses in dairy cows in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayel-Hacioglu, I.; Alkan, F. Molecular characterization of bovine noroviruses and neboviruses in Turkey. Detection of recombinant strains. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woode, G.N.; Reed, D.E.; Runnels, P.L.; Herrig, M.A.; Hill, H.T. Studies with an unclassified virus isolated from diarrheic calves. Vet. Microbiol. 1982, 7, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoet, A.E.; Nielsen, P.R.; Hasoksuz, M.; Thomas, C.; Wittum, T.E.; Saif, L.J. Detection of bovine torovirus and other enteric pathogens in feces from diarrhea cases in cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2003, 15, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, F.B.; Wang, E.E.; Bain, C.; Good, J.; Duckmanton, L.; Petric, M. Human torovirus. A new nosocomial gastrointestinal pathogen. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoet, A.E.; Saif, L.J. Bovine torovirus (Breda virus) revisited. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2004, 5, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoet, A.E.; Smiley, J.; Thomas, C.; Nielsen, P.R.; Wittum, T.E.; Saif, L.J. Association of enteric shedding of bovine torovirus (Breda virus) and other enteropathogens with diarrhea in veal calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 64, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, M.; Cremers, H.; Woode, G.; Horzinek, M.C. Breda virus (Toroviridae) infection and systemic antibody response in sentinel calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1990, 51, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, E.; Kummeling, A.; Janssen, M.M.; Jiménez, C.; Alvarado, R.; Caballero, M.; Donado, P.; Dwinger, R.H. Infectious agents associated with diarrhoea of calves in the canton of Tilarán, Costa Rica. Prev. Vet. Med. 1998, 33, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aita, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Murayama, K.; Sasagawa, Y.; Yabe, S.; Higuchi, R.; Tamura, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Tsunemitsu, H. Characterization of epidemic diarrhea outbreaks associated with bovine torovirus in adult cows. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, J.S.; Asano, K.M.; de Souza, S.P.; Brandão, P.E.; Richtzenhain, L.J. First detection and molecular diversity of Brazilian bovine torovirus (BToV) strains from young and adult cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoet, A.E.; Cho, K.O.; Chang, K.O.; Loerch, S.C.; Wittum, T.E.; Saif, L.J. Enteric and nasal shedding of bovine torovirus (Breda virus) in feedlot cattle. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Okada, N.; Okawa, M.; Fukuyama, S.; Shimizu, M. Detection and characterization of bovine torovirus from the respiratory tract in Japanese cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kruiningen, H.J.; Castellano, V.P.; Koopmans, M.; Harris, L.L. A serologic investigation for coronavirus and Breda virus antibody in winter dysentery of dairy cattle in the northeastern United States. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1992, 4, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckmanton, L.; Carman, S.; Nagy, E.; Petric, M. Detection of bovine torovirus in fecal specimens of calves with diarrhea from Ontario farms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matiz, K.; Kecskeméti, S.; Kiss, I.; Adám, Z.; Tanyi, J.; Nagy, B. Torovirus detection in faecal specimens of calves and pigs in Hungary. Short communication. Acta Vet. Hung. 2002, 50, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülaçtı, I.; Işıdan, H.; Sözdutmaz, I. Detection of bovine torovirus in fecal specimens from calves with diarrhea in Turkey. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.W.; Beards, G.M.; Flewett, T.H. Detection of Breda virus antigen and antibody in humans and animals by enzyme immunoassay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, M.; van den Boom, U.; Woode, G.; Horzinek, M.C. Seroepidemiology of Breda virus in cattle using ELISA. Vet. Microbiol. 1989, 19, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebler, E.M.; Klüver, S.; Pohlenz, J.; Koopmans, M. Zur Bedeutung des Bredavirus als Durchfallerreger in niedersächsischen Kälberbeständen. DTW. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1992, 99, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara, M.; Wada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Miyazaki, A.; Tsunemitsu, H. First isolation of cytopathogenic bovine torovirus in cell culture from a calf with diarrhea. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escherich, T. The intestinal bacteria of the neonate and breast-fed infant. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.A. The Genus Escherichia; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; The Prokaryotes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxen, M.A.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janke, B.H.; Francis, D.H.; Collins, J.E.; Libal, M.C.; Zeman, D.H.; Johnson, D.D. Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli infections in calves, pigs, lambs, and dogs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1989, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, G.E.; Moxley, R.A.; Maddox, C.W.; Erickson, E.D. Enteric infection of a goat with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (O103:H2). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1992, 4, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drolet, R.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Vaillancourt, D. Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli in a goat with diarrhea. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 1994, 35, 122–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.J.; Ryu, S.J.; Chae, J.S.; Eo, S.K.; Woo, G.J.; Lee, J.H. Occurrence and characteristics of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 in calves associated with diarrhoea. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 98, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrani, M.; Dehkordi, F.S.; Momtaz, H. Characterization of Escherichia coli virulence genes, pathotypes and antibiotic resistance properties in diarrheic calves in Iran. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, I.; Thiry, D.; Duprez, J.-N.; Saulmont, M.; Iguchi, A.; Piérard, D.; Jouant, L.; Daube, G.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Identification of Shiga toxin-producing (STEC) and enteropathogenic (EPEC) Escherichia coli in diarrhoeic calves and comparative genomics of O5 bovine and human STEC. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 202, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.S.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Mohammed, F.F.; Bakry, N.M.; Abdou, N.M.I.; Kamel, M.S. Molecular characterization of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic and in-contact cattle and buffalo calves. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, R.; Garcia, S.; Orden, J.A.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; Diez, R.; Cid, D. Prevalence and characteristics of attaching and effacing strains of Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic and healthy sheep and goats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orden, J.A.; Cid, D.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; García, S.; Martínez, S.; de La Fuente, R. Verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC), enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) and necrotoxigenic E. coli (NTEC) isolated from healthy cattle in Spain. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolenda, R.; Burdukiewicz, M.; Schierack, P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of pathogenic Escherichia coli of calves and the role of calves as reservoirs for human pathogenic E. coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Ragione, R.M.; Best, A.; Woodward, M.J.; Wales, A.D. Escherichia coli O157:H7 colonization in small domestic ruminants. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Ragione, R.M.; Best, A.; Clifford, D.; Weyer, U.; Johnson, L.; Marshall, R.N.; Cooley, W.A.; Farrelly, S.; Pearson, G.R.; Woodward, M.J. Influence of colostrum deprivation and concurrent Cryptosporidium parvum infection on the colonization and persistence of Escherichia coli O157. H7 in young lambs. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55 Pt 7, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Orden, J.A.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; Cid, D.; García, S.; de La Fuente, R. Prevalence and characteristics of necrotoxigenic Escherichia coli (NTEC) strains isolated from diarrhoeic dairy calves. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 66, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bost, S.; Roels, S.; Mainil, J. Necrotoxigenic Escherichia coli type-2 invade and cause diarrhoea during experimental infection in colostrum-restricted newborn calves. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 81, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, J.E.; Ramos, J. Enterotoxigenic, verotoxigenic, and necrotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in Spain. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1993, 54, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, A.L.; Ball, H.J.; Finlay, D.A. CNF producing Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in Northern Ireland. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 49, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osek, J. Characterization of necrotoxigenic Escherichia coli (NTEC) strains isolated from healthy calves in Poland. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2001, 48, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naciri, M.; Paul Lefay, M.; Mancassola, R.; Poirier, P.; Chermette, R. Role of Cryptosporidium parvum as a pathogen in neonatal diarrhoea complex in suckling and dairy calves in France. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 85, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulliksen, S.M.; Jor, E.; Lie, K.I.; Hamnes, I.S.; Løken, T.; Akerstedt, J.; Osterås, O. Enteropathogens and risk factors for diarrhea in Norwegian dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 5057–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, A.P.S.; Sood, N.K.; Kaur, P.; Singla, L.D.; Sandhu, B.S.; Gupta, K.; Narang, D.; Singh, C.K.; Chandra, M. Periurban outbreaks of bovine calf scours in Northern India caused by Cryptosporidium in association with other enteropathogens. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2717–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouet, P.; Contrepois, M.; Dubourguier, H.C.; Riou, Y.; Scherrer, R.; Laporte, J.; Vautherot, J.F.; Cohen, J.; L’Haridon, R. The experimental production of diarrhoea in colostrum deprived axenic and gnotoxenic calves with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, rotavirus, coronavirus and in a combined infection of rotavirus and E. coli. Annales de recherches veterinaires. Ann. Vet. Res. 1978, 9, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori, S.R.; Makin, T.J.; Smith, M.L.; Krautil, F.L. Clinical manifestations of diarrhea in calves infected with rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1981, 13, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodgrass, D.R.; Smith, M.L.; Krautil, F.L. Interaction of rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in conventionally-reared dairy calves. Vet. Microbiol. 1982, 7, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R.G.; Bachmann, P.A.; Baljer, G.; Mayr, A.; Pospischil, A.; Schmid, G. Synergism in experimental mixed infections of newborn colostrum-deprived calves with bovine rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Zent. Veterinarmed. Reihe B J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1984, 31, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnels, P.L.; Moon, H.W.; Matthews, P.J.; Whipp, S.C.; Woode, G.N. Effects of microbial and host variables on the interaction of rotavirus and Escherichia coli infections in gnotobiotic calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1986, 47, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Kiu, R.; Hall, L.J. An update on the human and animal enteric pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, H.N. Clostridium perfringens as a pathogen of cattle. A literature review. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1967, 31, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Songer, J.G. Clostridial enteric diseases of domestic animals. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.M.; Callan, R.J.; van Metre, D.C. Clostridial Abomasitis and Enteritis in Ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, W.H.; Nuttall, G.H.F. A gas-producing bacillus (bacillus aerogenes capsulatas, nov. spec.) capable of rapid development in the blood vessels after death. John Hopkins Hosp. Bull. 1892, 3, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Rood, J.I.; Adams, V.; Lacey, J.; Lyras, D.; McClane, B.A.; Melville, S.B.; Moore, R.J.; Popoff, M.R.; Sarker, M.R.; Songer, J.G.; et al. Expansion of the Clostridium perfringens toxin-based typing scheme. Anaerobe 2018, 53, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteca, C.; Daube, G.; Pirson, V.; Limbourg, B.; Kaeckenbeeck, A.; Mainil, J.G. Bacterial intestinal flora associated with enterotoxaemia in Belgian Blue calves. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 81, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, T. Clostridium perfringens type A and beta2 toxin associated with enterotoxemia in a 5-week-old goat. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2004, 45, 251–253. [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa, M.E.F.; Saputo, J.; Leger, J.S.; Puschner, B.; Fisher, D.J.; McClane, B.A.; Uzal, F.A. Necrotizing enterocolitis and death in a goat kid associated with enterotoxin (CPE)-producing Clostridium perfringens type A. Can. Vet. J. = La Rev. Vet. Can. 2007, 48, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar]
- van Kruiningen, H.J.; Nyaoke, C.A.; Sidor, I.F.; Fabis, J.J.; Hinckley, L.S.; Lindell, K.A. Clostridial abomasal disease in Connecticut dairy calves. Can. Vet. J. = La Rev. Vet. Can. 2009, 50, 857–860. [Google Scholar]
- Savic, B.; Prodanovic, R.; Ivetic, V.; Radanovic, O.; Bojkovski, J. Enteritis associated with Clostridium perfringens type A in 9-month-old calves. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2012, 53, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, A.M.; Elhaig, M.M.; Zakaria, I.; Ali, A. Bacteriological and molecular studies of Clostridium perfringens infections in newly born calves. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkiourtzidis, K.; Frey, J.; Bourtzi-Hatzopoulou, E.; Iliadis, N.; Sarris, K. PCR detection and prevalence of alpha-, beta-, beta 2-, epsilon-, iota- and enterotoxin genes in Clostridium perfringens isolated from lambs with clostridial dysentery. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, J.S.; Bentall, H.; Aberdein, D.; Navarro, M.; Uzal, F.A.; Brown, S. Death of a neonatal lamb due to Clostridium perfringens type B in New Zealand. N. Zeal. Vet. J. 2020, 68, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niilo, L.; Harries, W.N.; Jones, G.A. Clostridium perfringens type C in hemorrhagic enterotoxemia of neonatal calves in Alberta. Can. Vet. J. = La Rev. Vet. Can. 1974, 15, 224–226. [Google Scholar]
- Uzal, F.A.; Songer, J. Glenn Diagnosis of Clostridium perfringens intestinal infections in sheep and goats. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Vet. Lab. Diagn. Inc. 2008, 20, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.P.; Anderson, M.; Blanchard, P.; Mete, A.; Uzal, F.A. The pathology of enterotoxemia by Clostridium perfringens type C in calves. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzal, F.A.; Kelly, W.R. Experimental Clostridium perfringens type D enterotoxemia in goats. Vet. Pathol. 1998, 35, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D.; Pawaiya, R.S.; Gururaj, K.; Gangwar, N.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Andani, D.; Singh, M.K.; Bhushan, S.; Kumar, A. Molecular detection of Clostridium perfringens toxinotypes, Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, rotavirus and coronavirus in diarrheic fecal samples of neonatal goat kids. Vet. Arhiv. 2018, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billington, S.J.; Wieckowski, E.U.; Sarker, M.R.; Bueschel, D.; Songer, J.G.; McClane, B.A. Clostridium perfringens type E animal enteritis isolates with highly conserved, silent enterotoxin gene sequences. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4531–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songer, J.G.; Miskimmins, D.W. Clostridium perfringens type E enteritis in calves. Two cases and a brief review of the literature. Anaerobe 2004, 10, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Byun, J.; Roh, I.; Bae, Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, B.; Songer, J.G.; Jung, B.Y. First isolation of Clostridium perfringens type E from a goat with diarrhea. Anaerobe 2013, 22, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Duffield, T.; Peregrine, A.S.; Trotz-Williams, L.A.; Arroyo, L.G.; Brazier, J.S.; Weese, J.S. Clostridium difficile PCR ribotypes in calves, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Stalker, M.; Duffield, T.; Weese, J.S. Natural and experimental infection of neonatal calves with Clostridium difficile. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammitt, M.C.; Bueschel, D.M.; Keel, M.K.; Glock, R.D.; Cuneo, P.; DeYoung, D.W.; Reggiardo, C.; Trinh, H.T.; Songer, J.G. A possible role for Clostridium difficile in the etiology of calf enteritis. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 127, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeberg, A.; Neubauer, H.; Schmoock, G.; Grossmann, E.; Seyboldt, C. Presence of Clostridium difficile PCR ribotype clusters related to 033, 078 and 045 in diarrhoeic calves in Germany. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62 Pt 8, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistrali, C.F.; Maresca, C.; Cucco, L.; Bano, L.; Drigo, I.; Filippini, G.; Dettori, A.; Broccatelli, S.; Pezzotti, G. Prevalence and risk factors associated with Clostridium difficile shedding in veal calves in Italy. Anaerobe 2015, 33, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, S.; Pusparajah, P.; Ab Mutalib, N.; Ser, H.; Chan, K.; Lee, L.S. A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschbach, C.L.; Peek, S.F. Salmonella in Dairy Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, G.M.; Gay, J.M.; Evermann, J.F. Biosecurity for neonatal gastrointestinal diseases. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2002, 18, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habing, G.G.; Neuder, L.M.; Raphael, W.; Piper-Youngs, H.; Kaneene, J.B. Efficacy of oral administration of a modified-live Salmonella Dublin vaccine in calves. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 238, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, C.; Sojka, W.J. Experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves. Res. Vet. Sci. 1978, 25, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, C.; Sojka, W.J. Salmonella dublin infection of calves. Use of small doses to simulate natural infection on the farm. J. Hyg. 1981, 87, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossler, C.P.; Wells, S.J.; Kaneene, J.B.; Ruegg, P.L.; Warnick, L.D.; Bender, J.B.; Eberly, L.E.; Godden, S.M.; Halbert, L.W. Herd-level factors associated with isolation of Salmonella in a multi-state study of conventional and organic dairy farms II. Salmonella shedding in calves. Prev. Vet. Med. 2005, 70, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, W.J.; Wray, C.; Shreeve, J.E.; Bell, J.C. The incidence of salmonella infection in sheep in England and Wales, 1975 to 1981. Br. Vet. J. 1983, 139, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methner, U.; Moog, U. Occurrence and characterisation of Salmonella enterica subspecies diarizonae serovar 61. K: 1, 5, (7) in sheep in the federal state of Thuringia, Germany. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harp, J.A.; Myers, L.L.; Rich, J.E.; Gates, N.L. Role of Salmonella arizonae and other infective agents in enteric disease of lambs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1981, 42, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.A. Salmonella arizonae in sheep. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 1990, 31, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, M.; Alvseike, O.; Skjerve, E. The prevalence and dynamics of Salmonella enterica IIIb 61:k:1,5,(7) in sheep flocks in Norway. Prev. Vet. Med. 2002, 52, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McOrist, S.; Miller, G.T. Salmonellosis in transported feral goats. Aust. Vet. J. 1981, 57, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, L.; Barlow, R.; Fegan, N.; Vanderlinde, P. Prevalence and serotypes of Salmonella associated with goats at two Australian abattoirs. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Habsi, K.; Jordan, D.; Harb, A.; Laird, T.; Yang, R.; O’Dea, M.; Jacobson, C.; Miller, D.W.; Ryan, U.; Abraham, S. Salmonella enterica isolates from Western Australian rangeland goats remain susceptible to critically important antimicrobials. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otesile, E.B.; Ahmed, G.; Adetosoye, A.I. Experimental infection of Red Sokoto goats with Salmonella typhimurium. Rev. D’elevage De Med. Vet. Des. Pays Trop. 1990, 43, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tripathi, B.N.; Verma, J.C.; Parihar, N.S. Experimental Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in Indian goats. Clinical, serological, bacteriological and pathological studies. Small Rumin. Res. 2001, 42, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinzoni, R.C.; Blackhall, J.; Terzolo, H.R.; Moreira, A.R.; Auza, N.; Mattion, N.; Micheo, G.L.; La Torre, J.L.; Scodeller, E.A. Microbiology of diarrhoea in young beef and dairy calves in Argentina. Rev. Argent Microbiol. 1990, 22, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, G.A.; Reynolds, D.J.; Parsons, K.R.; Bland, A.P.; Morgan, J.H. Pathology of calves with diarrhoea in southern Britain. Res. Vet. Sci. 1988, 45, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almawly, J.; Prattley, D.; French, N.P.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Hedgespeth, B.; Grinberg, A. Utility of halofuginone lactate for the prevention of natural cryptosporidiosis of calves, in the presence of co-infection with rotavirus and Salmonella Typhimurium. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama, V.A.; Mathison, B.A. Infections by Intestinal Coccidia and Giardia duodenalis. Clin. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, L.A.; Sartor, R. Balfour Advances in understanding Giardia. Determinants and mechanisms of chronic sequelae. F1000prime Rep. 2015, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurden, T.; Vercruysse, J.; Claerebout, E. Is Giardia a significant pathogen in production animals? Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Handley, R.M.; Cockwill, C.; McAllister, T.A.; Jelinski, M.; Morck, D.W.; Olson, M.E. Duration of naturally acquired giardiosis and cryptosporidiosis in dairy calves and their association with diarrhea. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 214, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Aloisio, F.; Filippini, G.; Antenucci, P.; Lepri, E.; Pezzotti, G.; Cacciò, S.M.; Pozio, E. Severe weight loss in lambs infected with Giardia duodenalis assemblage B. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 142, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeny, J.P.A.; Ryan, U.M.; Robertson, I.D.; Jacobson, C. Cryptosporidium and Giardia associated with reduced lamb carcase productivity. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurden, T.; Vanderstichel, R.; Pohle, H.; Ehsan, A.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Morgan, E.R.; Camuset, P.; Capelli, G.; Vercruysse, J.; Claerebout, E. A multicentre prevalence study in Europe on Giardia duodenalis in calves, with molecular identification and risk factor analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Certad, G.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabé, M.; Cacciò, S.M. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Jacobson, C.; Gordon, C.; Ryan, U. Prevalence and molecular characterisation of Cryptosporidium and Giardia species in pre-weaned sheep in Australia. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 161, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Yang, R.; McCarthy, S.; Gordon, C.; Hijjawi, N.; Ryan, U. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in pre-weaned calves in Western Australia and New South Wales. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 176, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.; Parrington, L.; Cook, A.; Pintar, K.; Pollari, F.; Kelton, D.; Farber, J. The potential for zoonotic transmission of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. from beef and dairy cattle in Ontario, Canada. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coklin, T.; Farber, J.; Parrington, L.; Dixon, B. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in dairy cattle in Ontario, Canada. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 150, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santín, M.; Trout, J.M.; Fayer, R. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium and Giardia species and genotypes in sheep in Maryland. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtmannsperger, K.; Hinney, B.; Joachim, A.; Wittek, T. Molecular characterization of Giardia intestinalis and Cryptosporidium parvum from calves with diarrhoea in Austria and evaluation of point-of-care tests. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 66, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, S.E.; Mohammed, H.O.; Schaaf, S.L. Prevalence of Giardia sp. Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium andersoni (syn. C. muris) correction of Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium muris (C. andersoni) in 109 dairy herds in five counties of southeastern New York. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, C.; Almeida, A.; Castro, A.; Lurdes Delgado, M.d.; Soares, S.; da Costa, J.M.C.; Canada, N. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium and Giardia isolates from cattle from Portugal. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, M.; Trout, J.M.; Fayer, R. A longitudinal study of Giardia duodenalis genotypes in dairy cows from birth to 2 years of age. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Hermida, J.A.; Carro-Corral, C.; González-Warleta, M.; Mezo, M. Prevalence and intensity of infection of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in dairy cattle in Galicia (NW Spain). J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Hermida, J.A.; Almeida, A.; González-Warleta, M.; Correia da Costa, J.M.; Rumbo-Lorenzo, C.; Mezo, M. Occurrence of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia duodenalis in healthy adult domestic ruminants. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huetink, R.E.; van der Giessen, J.W.; Noordhuizen, J.P.; Ploeger, H.W. Epidemiology of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis on a dairy farm. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 102, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, J.M.; Santín, M.; Greiner, E.; Fayer, R. Prevalence and genotypes of Giardia duodenalis in post-weaned dairy calves. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 130, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, K.A.; Robertson, I.D.; Fraser, D.M.; Palmer, D.G.; Thompson, R.C.A. Molecular epidemiology of Giardia and Cryptosporidium infections in dairy calves originating from three sources in Western Australia. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coklin, T.; Farber, J.M.; Parrington, L.J.; Coklin, Z.; Ross, W.H.; Dixon, B.R. Temporal changes in the prevalence and shedding patterns of Giardia duodenalis cysts and Cryptosporidium spp. oocysts in a herd of dairy calves in Ontario. Can. Vet. J. = La Rev. Vet. Can. 2010, 51, 841–846. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Herd, R.P. Infection pattern of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in calves. Vet. Parasitol. 1994, 55, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurden, T.; Thomas, P.; Casaert, S.; Vercruysse, J.; Claerebout, E. Prevalence and molecular characterisation of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in lambs and goat kids in Belgium. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 155, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, M.; Bajer, A.; Siński, E. Calves as a potential reservoir of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia sp. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 1998, 5, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Björkman, C.; Svensson, C.; Christensson, B.; de Verdier, K. Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia intestinalis in calf diarrhoea in Sweden. Acta Vet. Scand. 2003, 44, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, U.M.; Bath, C.; Robertson, I.; Read, C.; Elliot, A.; McInnes, L.; Traub, R.; Besier, B. Sheep may not be an important zoonotic reservoir for Cryptosporidium and Giardia parasites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4992–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.J.; Gjerde, B.K.; Furuseth Hansen, E. The zoonotic potential of Giardia and Cryptosporidium in Norwegian sheep. A longitudinal investigation of 6 flocks of lambs. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, Y.; Matsubayashi, M.; Nukata, S.; Shibahara, T.; Ayukawa, O.; Kondo, Y.; Matsuo, T.; Uni, S.; Furuya, M.; Tani, H.; et al. Report of fatal mixed infection with Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia intestinalis in neonatal calves. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugschies, A.; Najdrowski, M. Eimeriosis in cattle. Current understanding. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2005, 52, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangoura, B.; Daugschies, A. Coccidiosis in Cattle. Coccidiosis in Livestock, Poultry, Companion Animals and Humans; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780367265922. [Google Scholar]
- Keeton, S.T.N.; Navarre, C.B. Coccidiosis in Large and Small Ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodakaram-Tafti, A.; Hashemnia, M. An overview of intestinal coccidiosis in sheep and goats. Rev. Med. Vet. 2017, 168, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bangoura, B.; Mundt, H.; Schmäschke, R.; Westphal, B.; Daugschies, A. Prevalence of Eimeria bovis and Eimeria zuernii in German cattle herds and factors influencing oocyst excretion. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109 (Suppl. S1), S129–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enemark, H.L.; Dahl, J.; Enemark, J.M.D. Eimeriosis in Danish dairy calves--correlation between species, oocyst excretion and diarrhoea. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112 (Suppl. S1), 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.; Chae, M.J.; Oh, S.I.; Kim, J.H.; Rhee, M.H.; Kwon, O.D.; et al. Eimeria species in cattle with diarrhoea in the Republic of Korea regarding age, season and nature of diarrhoea. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Epe, C.; Wirtherle, N.; Heyden, V.v.; Welz, C.; Radeloff, I.; Beening, J.; Carr, D.; Hellmann, K.; Schnieder, T.; et al. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of Eimeria infections in first-year grazing cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 136, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratsis, A.; Joachim, A.; Alexandros, S.; Sotiraki, S. Lamb coccidiosis dynamics in different dairy production systems. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratsis, A.; Karagiannis, I.; Brozos, C.; Kiossis, E.; Tzanidakis, N.; Joachim, A.; Sotiraki, S. Lamb eimeriosis. Applied treatment protocols in dairy sheep production systems. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Rodrigues, F.; Cezar, A.S.; Menezes, F.R.d.; Sangioni, L.A.; Vogel, F.S.F.; de Avila Botton, S. Efficacy and economic analysis of two treatment regimens using toltrazuril in lambs naturally infected with Eimeria spp. on pasture. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudela, B.; Boková, A. Coccidiosis in goats in the Czech Republic. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 76, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, M.; Tao, J.P. Pathogenic effects of the coccidium Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae in goats. Vet. Res. Commun. 2006, 30, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; González, J.F.; Rodríguez, E.; Martín, S.; Hernández, Y.I.; Almeida, R.; Molina, J.M. Influence of climatic and management factors on Eimeria infections in goats from semi-arid zones. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutny, H.; Joachim, A.; Tichy, A.; Baumgartner, W. Bovine Eimeria species in Austria. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, B.; Prosl, H.; Cieslicki, M.; Joachim, A. Epidemiology of Eimeria infections in an Austrian milking sheep flock and control with diclazuril. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 129, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, K.; Mundt, H.; Grzonka, E.; Daugschies, A.; Bangoura, B. Ovine coccidiosis in housed lambs in Saxony-Anhalt (central Germany). Berl. Und Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2010, 123, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, E.S.E.; Smith, R.P.; Ellis-Iversen, J. Husbandry risk factors associated with subclinical coccidiosis in young cattle. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppä-Lassila, L.; Orro, T.; Lassen, B.; Lasonen, R.; Autio, T.; Pelkonen, S.; Soveri, T. Intestinal pathogens, diarrhoea and acute phase proteins in naturally infected dairy calves. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 41, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczak, M.; Sadowska, N.; Udała, J. Parasites of the digestive tract of sheep and goats from organic farms in Western Pomerania, Poland. Ann. Parasitol. 2019, 65, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, B.; Viltrop, A.; Raaperi, K.; Järvis, T. Eimeria and Cryptosporidium in Estonian dairy farms in regard to age, species, and diarrhoea. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 166, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, G.S.; Gitau, G.K.; Mulei, C.M.; Vanleeuwen, J.; Richards, S.; Wichtel, J.; Uehlinger, F.; Mainga, O. Prevalence of Cryptosporidia, Eimeria, Giardia, and Strongyloides in pre-weaned calves on smallholder dairy farms in Mukurwe-ini district, Kenya. Vet. World 2015, 8, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, A.W.C.A.; Verstegen, R.; van den Brand, H.; Perie, N.M.; Eysker, M.; Lam, T.J.G.M.; Pijpers, A. An observational study of Eimeria species in housed cattle on Dutch dairy farms. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 56, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeny, J.P.A.; Robertson, I.D.; Ryan, U.M.; Jacobson, C.; Woodgate, R.G. Impacts of naturally acquired protozoa and strongylid nematode infections on growth and faecal attributes in lambs. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, M.; Gauly, M.; Bauer, C.; Failing, K.; Erhardt, G.; Zahner, H. Endoparasites in calves of beef cattle herds. Management systems dependent and genetic influences. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 131, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.M.; Miller, J.E.; Mosjidis, J.A.; Terrill, T.H. Use of a mixed sericea lespedeza and grass pasture system for control of gastrointestinal nematodes in lambs and kids. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, W.M.D.; do Amarante, A.F.T.; Bresciani, K.D.S. Occurrence of gastrointestinal parasites in goat kids. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Vet. Braz. J. Vet. Parasitol. Orgao Do Col. Bras. De Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeber, F.; Jex, A.R.; Campbell, A.J.D.; Nielsen, R.; Anderson, G.A.; Stanley, K.K.; Gasser, R.B. Establishment of a robotic, high-throughput platform for the specific diagnosis of gastrointestinal nematode infections in sheep. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S.A.; Sörensen, C.R.L.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Enemark, H.L. Gastrointestinal nematodes and anthelmintic resistance in Danish goat herds. Parasite 2014, 21, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramenko, R.W.; Redman, E.M.; Lewis, R.; Bichuette, M.A.; Palmeira, B.M.; Yazwinski, T.A.; Gilleard, J.S. The use of nemabiome metabarcoding to explore gastro-intestinal nematode species diversity and anthelmintic treatment effectiveness in beef calves. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busato, A.; Lentze, T.; Hofer, D.; Burnens, A.; Hentrich, B.; Gaillard, C. A case control study of potential enteric pathogens for calves raised in cow-calf herds. Zent. Veterinarmed. Reihe B J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1998, 45, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorsich, E.E.; Ezenwa, V.O.; Jolles, A.E. Nematode-coccidia parasite co-infections in African buffalo. Epidemiology and associations with host condition and pregnancy. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2014, 3, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, S.C.L.; Fenton, A.; Petchey, O.L.; Jones, T.R.; Barber, R.; Pedersen, A.B. Stability of within-host-parasite communities in a wild mammal system. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20130598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, M.; Fenton, A.; Babayan, S.A.; Pedersen, A.B. Parasitic nematodes simultaneously suppress and benefit from coccidian coinfection in their natural mouse host. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, S.; Hudson, P.J.; Thakar, J.; Saric, J.; Harvill, E.; Albert, R.; Perkins, S.E. Generating super-shedders. Co-infection increases bacterial load and egg production of a gastrointestinal helminth. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, M.; Devevey, G.; Fenton, A.; Pedersen, A.B. Antibodies and coinfection drive variation in nematode burdens in wild mice. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, M.; Lariviee, S.; Lallier, R.; Begin, M.E.; Ethier, R.; Roy, R.S.; Tremblay, A. Diarrhoea of newborn calves. II. Agents responsible for the disease on Quebec dairy farms. Med. Vet. Quebec. 1980, 10, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, D.J.; Morgan, J.H.; Chanter, N.; Jones, P.W.; Bridger, J.C.; Debney, T.G.; Bunch, K.J. Microbiology of calf diarrhoea in southern Britain. Vet. Rec. 1986 119, 34–39. [CrossRef]
- Salgame, P.; Yap, G.S.; Gause, W.C. Effect of helminth-induced immunity on infections with microbial pathogens. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Gross, K.; Kendig, A.E.; Lacroix, C.; Mitchell, C.E.; Mordecai, E.A.; Power, A.G. The community ecology of pathogens. Coinfection, coexistence and community composition. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delling, C.; Daugschies, A. Literature Review: Coinfection in Young Ruminant Livestock—Cryptosporidium spp. and Its Companions. Pathogens 2022, 11, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010103
Delling C, Daugschies A. Literature Review: Coinfection in Young Ruminant Livestock—Cryptosporidium spp. and Its Companions. Pathogens. 2022; 11(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010103
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelling, Cora, and Arwid Daugschies. 2022. "Literature Review: Coinfection in Young Ruminant Livestock—Cryptosporidium spp. and Its Companions" Pathogens 11, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010103
APA StyleDelling, C., & Daugschies, A. (2022). Literature Review: Coinfection in Young Ruminant Livestock—Cryptosporidium spp. and Its Companions. Pathogens, 11(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010103




