Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome in Adult Farmed Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Historical Presentation of Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome (CMF)
2.2. Gross Pathology Description
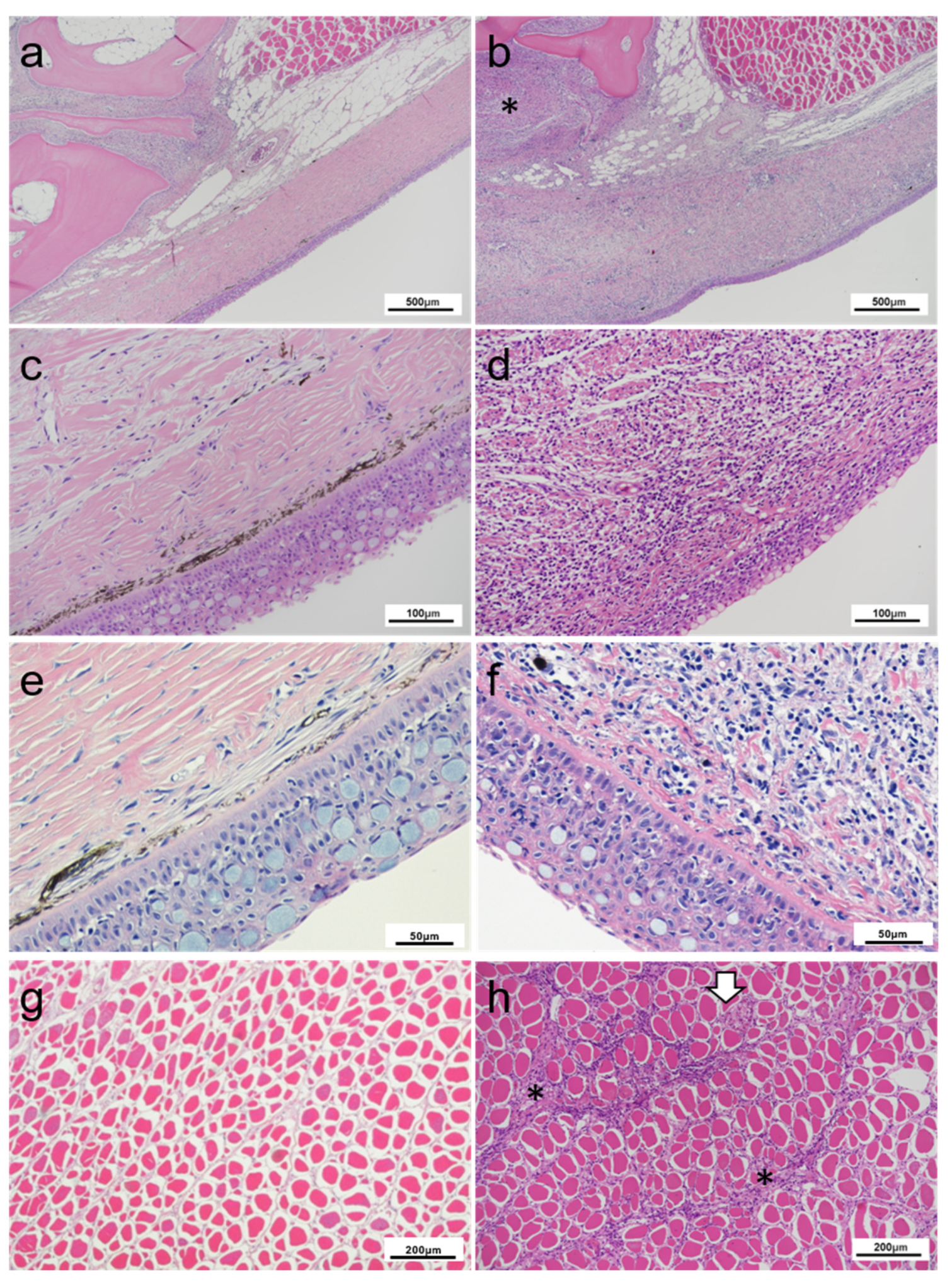
2.3. Histopathology Findings
2.4. Microbiology Findings
2.5. Molecular Tests
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.7. Host Response
2.8. Correlation of PKD with Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statement
4.2. Field Sample Collection and Histology
4.3. Bacteriology and Virology Examinations
4.4. PCR Detection of Viral Pathogens
4.5. Illumina MiSeq Next-Generation Sequencing
4.6. Taqman qPCR Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lafferty, K.D.; Harvell, C.D.; Conrad, J.M.; Friedman, C.S.; Kent, M.L.; Kuris, A.M.; Powell, E.N.; Rondeau, D.; Saksida, S.M. Infectious diseases affect marine fisheries and aquaculture economics. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shinn, A.; Pratoomyot, J.; Metselaar, M.; Gomes, G. Diseases in aquaculture—Counting the costs of the top 100. In Scientific Challenges and Oportunities in the Protein Economy; Binder, E.M., Rigl, A., Hines, R., Eds.; Biomin Holdings GmbH: Getzerdorf, Austria; Cape Town, South Africa, 2018; pp. 227–262. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B. The effects of pollution on fish health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 85, 2345–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, D.W. Jaw deformity associated with farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Vet. Rec. 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, J.; Pankhurst, P.M.; King, H.R. High prevalence of skeletal deformity and reduced gill surface area in triploid Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2001, 198, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatain, B. Abnormal swimbladder development and lordosis in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and sea bream (Sparus auratus). Aquaculture 1994, 119, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, G.; Adams, M.B.; Ventura, T.; Carter, C.G.; Cobcroft, J.M. Skeletal anomaly assessment in diploid and triploid juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) and the effect of temperature in freshwater. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, V.; Matousek, J.; Sebesta, R.; Prokesova, M.; Vanina, T.; Podhorec, P. Prevalence of deformities in intensively reared peled Coregonus peled and comparative morphometry with pond-reared fish. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeler, E.J.; Ryder, D.; Thrush, M.A.; Mewett, J.; Hulland, J.; Feist, S.W. Acute dermatitis in farmed trout: An emerging disease. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks, C.E.; Nolan, E.T.; Feist, S.W.; Crumlish, M.; Richards, R.H.; Williams, C.F. Puffy skin disease (PSD) in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum): A case definition. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, I.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Van Aerle, R.; Paley, R.K.; Peeler, E.J.; Green, M.; Rimmer, G.S.E.; Savage, J.; Joiner, C.L.; Bayley, A.E.; et al. Puffy skin disease is an emerging transmissible condition in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Pond, M.J.; Peeler, E.J.; Rimmer, G.S.E.; Oidtmann, B.; Way, K.; Mewett, J.; Jeffrey, K.; Bateman, K.; Reese, R.A.; et al. Emergence of cold water strawberry disease of rainbow trout Oncorynchus mykiss in England and Wales: Outbreak investigations and transmission studies. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2008, 79, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Bergmann, W.; Knüsel, R.; Heistinger, H.; Licek, E. Appearance of red mark syndrome/cold water strawberry disease in Switzerland and Austria. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 88, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, H.W.; Girons, A.; Rizgalla, G.; LaPatra, S.; Branson, E.J.; MacKenzie, K.; Davies, M.; Collins, R.O.; Diab, A.; Crumlish, M. Strawberry disease in rainbow trout in Scotland: Pathology and association with Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeotti, M.; Manzano, M.; Beraldo, P.; Bulfon, C.; Rossi, G.; Volpatti, D.; Magi, G.E. Ultrastructural and biomolecular detection of Rickettsiales-like organisms in tissues of rainbow trout with Red Mark Syndrome. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, T.A.; Senos, M.R.; Hansen, H.; Poppe, T.T. Red vent syndrome associated with Anisakis simplex diagnosed in Norway. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2010, 30, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Noguera, P.; Collins, C.; Bruno, D.; Pert, C.; Turnbull, A.; McIntosh, A.; Lester, K.; Bricknell, I.; Wallace, S.; Cook, P. Red vent syndrome in wild Atlantic salmon salmo salar in Scotland is associated with Anisakis simplex sensu stricto (Nematoda: Anisakidae). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2009, 87, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICES Report of the Working Group on North Atlantic Salmon (WGNAS); Robertson, M. (Ed.) International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Weichert, F.G.; Axén, C.; Förlin, L.; Inostroza, P.A.; Kammann, U.; Annikki, W.; Joachim, S.; Asker, N. A multi-biomarker study on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) affected by the emerging Red Skin Disease in the Baltic Sea. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J. Ulcerative dermal necrosis (UDN) in wild salmonids. Fish. Res. 1993, 17, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.G.; Thompson, K.D.; Padrós, F. Emerging skin diseases in aquaculture. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2018, 38, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, T.J. Inflammation. In General and Systemic Pathology; Underwood, J.C.E., Cross, S.S., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2009; pp. 199–219. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, G.; Athanikar, S.B.; Pai, V.V.; Naveen, K.N. Giant cells in dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. 2014, 59, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, K.L.; Holian, A. Multinucleated giant cell phenotype in response to stimulation. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groff, J.M. Cutaneous biology and diseases of fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2001, 4, 321–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Zusso, M.; Giusti, P. An inflammation-centric view of neurological disease: Beyond the neuron. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillig, P.M.; Sanders, R.D. The trigeminal (V) and facial (VII) cranial nerves: Head and face sensation and movement. Psychiatry 2010, 7, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran, E.; Grundon, R.; Stewart, J.; Biggi, M.; Holloway, A.; Freeman, C. Imaging diagnosis—Unilateral trigeminal neuritis mimicking peripheral nerve sheath tumor in a horse. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2016, 57, E1–E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swift, K.E.; McGrath, S.; Nolan, M.W.; Young, M.; Reese, M.; Rao, S.; Randall, E.; Leary, D.; LaRue, S. Clinical and imaging findings, treatments, and outcomes in 27 dogs with imaging diagnosed trigeminal nerve sheath tumors: A multi-center study. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2017, 58, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Lannes, B.; Goetz, J.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Lipsker, D.; Arnaud, L.; Martin, T.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Geny, B.; Sibilia, J. Inflammatory myopathies: A new landscape. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, Ú.; Casadei, E.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J. Red mark syndrome in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: Investigation of immune responses in lesions using histology, immunohistochemistry and analysis of immune gene expression. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenden, A.J.; Grayson, T.H.; Gilpin, M.L.; Munn, C.B. Renibacterium salmoninarum and bacterial kidney disease—The unfinished jigsaw. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1993, 3, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delghandi, M.R.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Waldner, K.; El-Matbouli, M. Renibacterium salmoninarum and Mycobacterium spp.: Two bacterial pathogens present at low levels in wild brown trout (Salmo trutta fario) populations in Austrian rivers. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loch, T.P.; Kumar, R.; Xu, W.; Faisal, M. Carnobacterium maltaromaticum infections in feral Oncorhynchus spp. (Family Salmonidae) in Michigan. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanong, R.P.E. Fungal diseases of fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2003, 6, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregeneda Grandes, J.M.; Fernández Díez, M.; Aller Gancedo, J.M. Experimental pathogenicity in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), of two distinct morphotypes of long-spined Saprolegnia isolates obtained from wild brown trout, Salmo trutta L., and river water. J. Fish Dis. 2001, 24, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; MacConnell, E.; de Kinkelin, P. Proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1993, 3, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Kallert, D.M.; Hedrick, R.P.; El-Matbouli, M. Whirling disease revisited: Pathogenesis, parasite biology and disease intervention. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2015, 114, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, T.J.; Vincent, E.R.; Silflow, R.M.; Stanek, D. Myxobolus cerebralis infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) exposed under natural stream conditions. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2000, 12, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaitetzidou, E.; Crespo, D.; Vraskou, Y.; Antonopoulou, E.; Planas, J.V. Transcriptomic Response of Skeletal Muscle to Lipopolysaccharide in the Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S3–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priante, G.; Ceol, M.; Terrin, L.; Gianesello, L.; Quaggio, F.; Del Prete, D.; Anglani, F. Understanding the pathophysiology of nephrocalcinosis. In Updates and Advances in Nephrolithiasis—Pathophysiology, Genetics, and Treatment Modalities; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Horst, R.L.; Goff, J.P.; Reinhardt, T.A. Calcium and Vitamin D Metabolism in the Dairy Cow. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 1936–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.G.; Richards, R.H. The pathology and histopathology of nephrocalcinosis in rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson in fresh water. J. Fish Dis. 1979, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, M.P.; Flik, G.; Wagner, G.F.; Balment, R.J. The corpuscles of stannius, calcium-sensing receptor, and stanniocalcin: Responses to calcimimetics and physiological challenges. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, H.; Sandoval, C. Nephrocalcinosis The Ureters are, of the Mycotic Infections Such as Exophiala. Fish—Gross Pathology. Available online: https://fishhistopathology.com/home/2019/08/22/nephrocalcinosis-in-fish-gross-pathology/#:~:text=Rainbowtroutwithseverenephrocalcinosis (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Hilton, J.W.; Hodson, P.V. Effect of increased dietary carbohydrate on selenium metabolism and toxicity in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Nutr. 1983, 113, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowey, C.B.; Knox, D.; Adron, J.W.; George, S.; Pirie, B. The production of renal calcinosis by magnesium deficiency in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Br. J. Nutr. 1977, 38, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch, H.; Atli, G.; Bonet, B.; Corcoll, N.; Leira, M.; Serra, A. Discharge and the response of biofilms to metal exposure in Mediterranean rivers. Hydrobiologia 2010, 657, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.R.; Sánchez-Galán, S.; Izquierdo, J.I.; Arribas, P.; Marañón, E.; García-Vázquez, E. Brown trout as biomonitor of heavy metal pollution: Effect of age on the reliability of the assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 40, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümgüm, B.; Ünlü, E.; Tez, Z.; Gülsün, Z. Heavy metal pollution in water, sediment and fish from the Tigris River in Turkey. Chemosphere 1994, 29, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalaka, S.E. Heavy metals bioaccumulation and histopathological changes in Auchenoglanis occidentalis fish from Tiga dam, Nigeria. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapsenberg, M.L. Dendritic-cell control of pathogen-driven T-cell polarization. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Hikima, J.I.; Kono, T. Fish cytokines: Current research and applications. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.G.; Thomas, B.; Koff, J. TGF-β: Master regulator of inflammation and fibrosis. Respirology 2018, 23, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, L.J.; Laing, K.J.; Daniels, G.D.; Grabowski, P.S.; Cunningham, C.; Secombes, C.J. Isolation of the first piscine transforming growth factor β gene: Analysis reveals tissue specific expression and a potential regulatory sequence in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Cytokine 1998, 23, 1096–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Jimmy, K. Molecular isolation and characterisation of carp transforming growth factor β1 from activated leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2000, 10, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.O.; Flavell, R.A. Contextual Regulation of Inflammation: A Duet by Transforming Growth Factor-β and Interleukin-10. Immunity 2008, 28, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, B.; Dong, J.; Viswanathan, S.; Widjaja, A.A.; Paleja, B.S.; Adami, E.; Ko, N.S.J.; Wang, M.; Lim, S.; Tan, J.; et al. Fibroblast-specific IL11 signaling drives chronic inflammation in murine fibrotic lung disease. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 11802–11815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.P.; McGettigan, S.E.; Dang, V.D.; Kumar, A.; Cancro, M.P.; Nikbakht, N.; Stohl, W.; Debes, G.F. IgM Plasma Cells Reside in Healthy Skin and Accumulate with Chronic Inflammation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenback, B.A. Antimicrobial peptides as mediators of innate immunity in teleosts. Biology 2015, 4, 607–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masso-Silva, J.A.; Diamond, G. Antimicrobial peptides from fish. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 265–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peter Chiou, P.; Khoo, J.; Bols, N.C.; Douglas, S.; Chen, T.T. Effects of linear cationic alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides on immune-relevant genes in trout macrophages. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geering, B.; Stoeckle, C.; Conus, S.; Simon, H.U. Living and dying for inflammation: Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sziksz, E.; Pap, D.; Lippai, R.; Béres, N.J.; Fekete, A.; Szabó, A.J.; Vannay, Á. Fibrosis Related Inflammatory Mediators: Role of the IL-10 Cytokine Family. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaye, P.S.; Burgy, O.; Causse, S.; Garrido, C.; Bonniaud, P. Heat shock proteins in fibrosis and wound healing: Good or evil? Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, L.; van Aerle, R.; Paley, R.K.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Tidbury, H.; Green, M.; Feist, S.W.; Cano, I. The skin immune response of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), associated with puffy skin disease (PSD). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, A.S.; Sommerville, C.; Wootten, R. Molecular studies on the seasonal occurrence and development of five myxozoans in farmed Salmo trutta L. Parasitology 2006, 132, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, A.; de Coulon, P.; Bailey, C.; Segner, H.; Wahli, T.; Rubin, J.F. Keeping an Eye on Wild Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) Populations: Correlation Between Temperature, Environmental Parameters, and Proliferative Kidney Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotob, M.H.; Kumar, G.; Saleh, M.; Gorgoglione, B.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Differential modulation of host immune genes in the kidney and cranium of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and Myxobolus cerebralis co-infections. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, D.W.; Lewis, E.J.; Keller, B.J.; Smith, C.S. Histological Techniques for Marine Bivalve Mollusks and Crustaceans; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 5; NOAA/National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science: Oxford, MD, USA, 2004; 218p.
- MacFaddin, J.F. Media for Isolation-Cultivation-Identification-Maintenance of Medical Bacteria; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1985; ISBN 0683053167. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.H.; Hinton, J. A Protein-Free Medium for Primary Isolation of the Gonococcus and Meningococcus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1941, 48, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madetoja, J.; Dalsgaard, I.; Wiklund, T. Occurrence of Flavobacterium psychrophilum in fish-farming environments. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2002, 52, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, P.E.; Newman, M.W.; Sauber, J.H.; Owens, W.J. Isolation of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (serotype Ab) from diverse species of estuarine fish. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1984, 37, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wergeland, H.I.; Jakobsen, R.A. A salmonid cell line (TO) for production of infectious salmon anaemia virus (ISAV). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2001, 44, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, K.; Gravell, M.; Malsberger, R.G. Lymphocystis virus: Isolation and propagation in centrarchid fish cell lines. Science 1966, 151, 1004–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurtrie, J.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Cochrane-Dyet, T.; White, P.; van Aerle, R.; Ryder, D.; Stone, D.; Green, M.; Feist, S.W.; Cano, I. Health assessment of the cleaner fish ballan wrasse Labrus bergylta from the British south-west coast. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2019, 136, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamperin, G.; Lucas, P.; Cano, I.; Ryder, D.; Abbadi, M.; Stone, D.; Cuenca, A.; Vigouroux, E.; Blanchard, Y.; Panzarin, V. Sequencing of animal viruses: Quality data assurance for NGS bioinformatics. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorgoglione, B.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J.; Holland, J.W. Immune gene expression profiling of Proliferative Kidney Disease in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss reveals a dominance of anti-inflammatory, antibody and T helper cell-like activities. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grove, S.; Austbø, L.; Hodneland, K.; Frost, P.; Løvoll, M.; McLoughlin, M.; Thim, H.L.; Braaen, S.; König, M.; Syed, M.; et al. Immune parameters correlating with reduced susceptibility to pancreas disease in experimentally challenged Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chettri, J.K.; Kuhn, J.A.; Jaafar, R.M.; Kania, P.W.; Møller, O.S.; Buchmann, K. Epidermal response of rainbow trout to Ichthyobodo necator: Immunohistochemical and gene expression studies indicate a Th1-/Th2-like switch. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: http//www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 November 2020).




| 2018 (Spring) | 2018 (Autumn) | 2019 (Spring) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 4 | 10 | 16 |
| Jaw | Dermatitis, fibrosis (4/4) | Dermatitis, fibrosis (10/10) | Dermatitis, fibrosis (16/16) Epineurium infiltration and vasculitis (3/16) |
| Gill | Epithelial hyperplasia and eosinophil granule cells (2/4) Saprolegnia (1/4) | NAD | Epithelial hyperplasia (8/16) |
| Liver | Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (1/4) | Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (5/10) PKD (5/10) | Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (1/16) PKD (1/16) |
| Spleen | NAD | Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (3/10) PKD (5/10) | NAD |
| Kidney | Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (1/4) | Multifocal inflammatory cell infiltration (1/10) PKD (5/10) Nephrocalcinosis (1/10) Neutrophils (1/10) | Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (2/16) PKD (1/16) Nephrocalcinosis (1/16) |
| Heart | Mild myocarditis (2/4) | Myocarditis (1/10) Gram-positive bacteria infection (1/10) | NAD |
| Stomach | NAD | Lymphocytic infiltration (1/4) Calcinosis (1/4) | Calcinosis (2/16) |
| Gene | Gene Involvement | GenBank acc. no | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| vig1 | IFN inducible protein, antiviral | AF076620.1 | [83] |
| tlr3 | Innate sensing of viral dsRNA | NM_001124578.1 | [69] |
| tgf-b | Cell growth and proliferation | X99303 | [84] |
| tbx21 | Promotes Th1 polarization as a response of intracellular pathogens | FM863825 | [84] |
| igm | B cells antigen recognition | S63348.1 | [83] |
| lyz2 | Antibacterial protein | X59491 | [84] |
| il11 | Platelet and cell proliferation | AJ867256.1 | This study |
| il4/13a | Promotes Th2 polarization as response of extracellular parasites) | AB574337 | [84] |
| il1b | Pro-inflammatory cytokine, promotes Th17 polarization | NM_001124347.2 | [83] |
| ifn3 | Antival activity | NM_001160502.1 | [69] |
| hspa12a | Cellular stress and toxic chemicals | XM_021580438.1 | This study |
| gata3 | Promotes Th17 polarization | FM863826 | [84] |
| cath1 | Antimicrobial peptide, pro-inflammatory | AY382478.1 | This study |
| c3 | Complement system | AF271080 | [84] |
| il10 | Immunoregulatory | AB118099 | [84] |
| cd8 | Marker of cytotoxic T lymphocytes | AF178054 | [84] |
| Gene | Forward 5′-3′3′ | Reverse 5′-3′3′ | Probe (Fam) 5′-′3′ (BHQ-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| rpl18 | CACTGTTATTGCAGGGCTGTAGA | TGGAGCAGCACCAAAATACCT | AGGCCAGGGTTGC |
| il11 | TGAGTGTCTGTCTATCGTCACTATCAGT | AGGGCGAACAATCCAATAAAGA | TTTACGGAACAAAAAGTTTGGAG |
| cath1 | CTTTGCCTCAGCTGCTTCCT | TGGAGCTGGTTCAGAATTGGA | AGAGCAGGCTTTCC |
| hspa12a | AGCGGACGCCCCAAA | TCCTCAGGGTAGAAGCTCTTGGT | TGGAGGTTGAATACAAAG |
| b-actin | GAAATCGCCGCACTGGTT | CGGCGAATCCGGCTTT | TTGACAACGGATCCGGT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano, I.; Worswick, J.; Mulhearn, B.; Green, M.; Feist, S.W.; Clinton, M. Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome in Adult Farmed Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Pathogens 2021, 10, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050542
Cano I, Worswick J, Mulhearn B, Green M, Feist SW, Clinton M. Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome in Adult Farmed Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050542
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano, Irene, John Worswick, Brian Mulhearn, Matt Green, Stephen W. Feist, and Morag Clinton. 2021. "Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome in Adult Farmed Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050542
APA StyleCano, I., Worswick, J., Mulhearn, B., Green, M., Feist, S. W., & Clinton, M. (2021). Cranial Mandibular Fibrosis Syndrome in Adult Farmed Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Pathogens, 10(5), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050542






