Generative AI for Architectural Façade Design: Measuring Perceptual Alignment Across Geographical, Objective, and Affective Descriptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Vision-Based Generative Design
2.2. Leveraging Urban Imagery for Human Perception Studies
2.3. Perceptual and Affective Quality of Our Environment
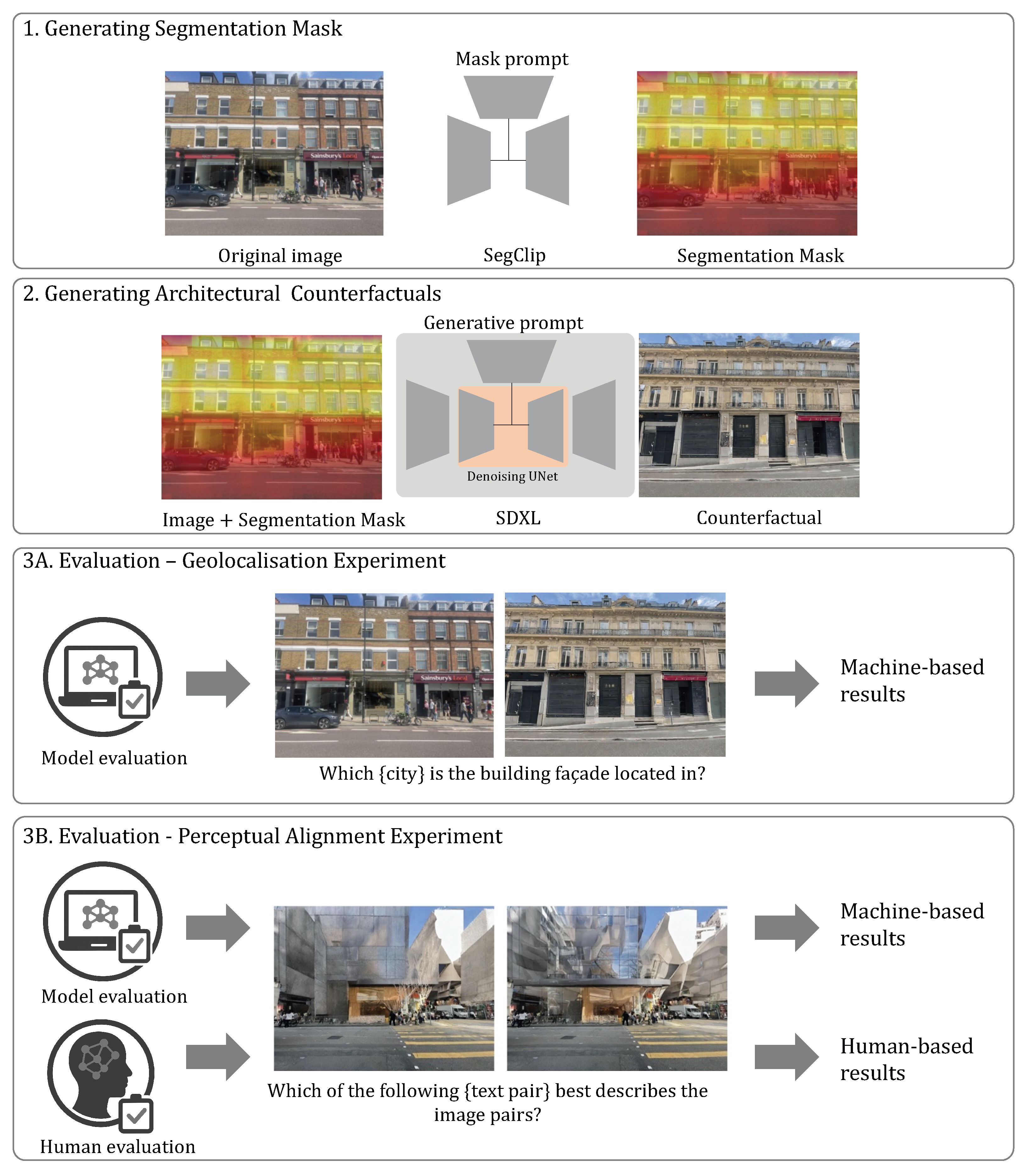
3. Methodology
Model Pipeline
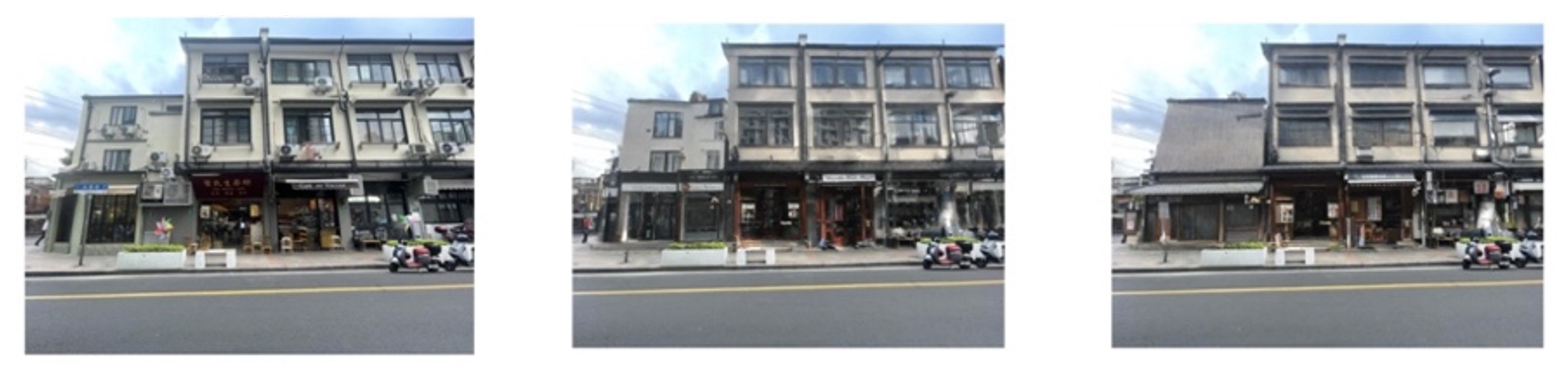
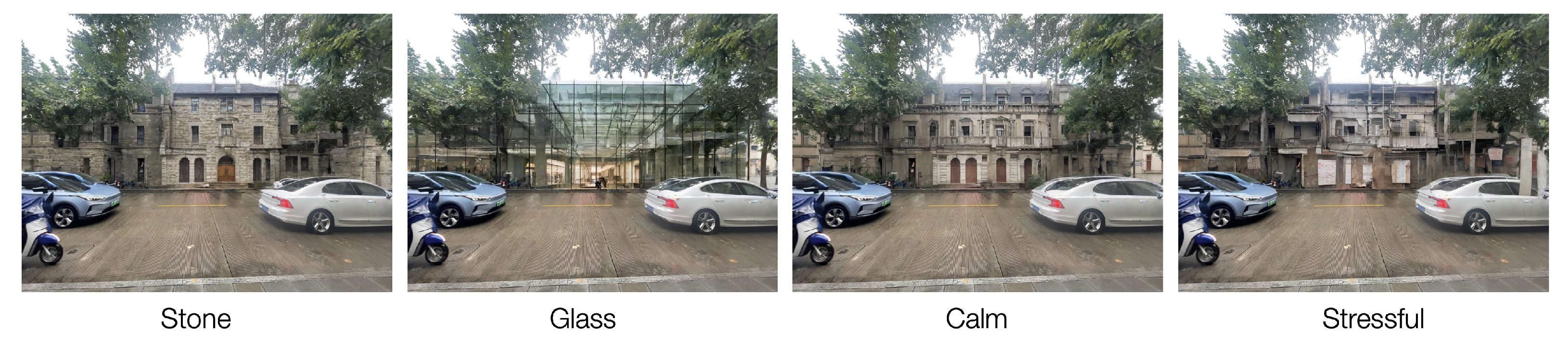
4. Parameter Analysis
4.1. Mask Prompt for Localised Inpainting
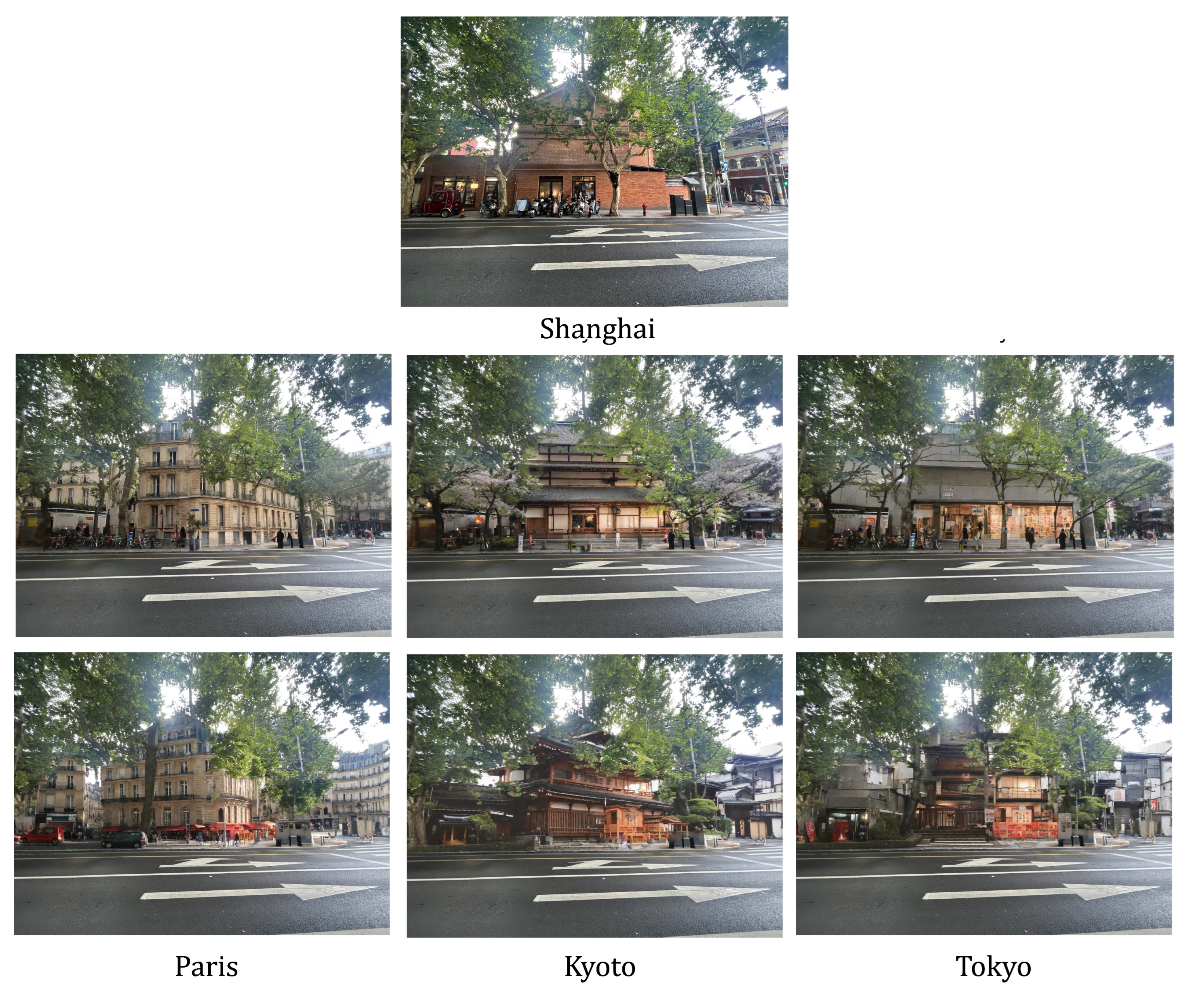
4.2. Image Diversity
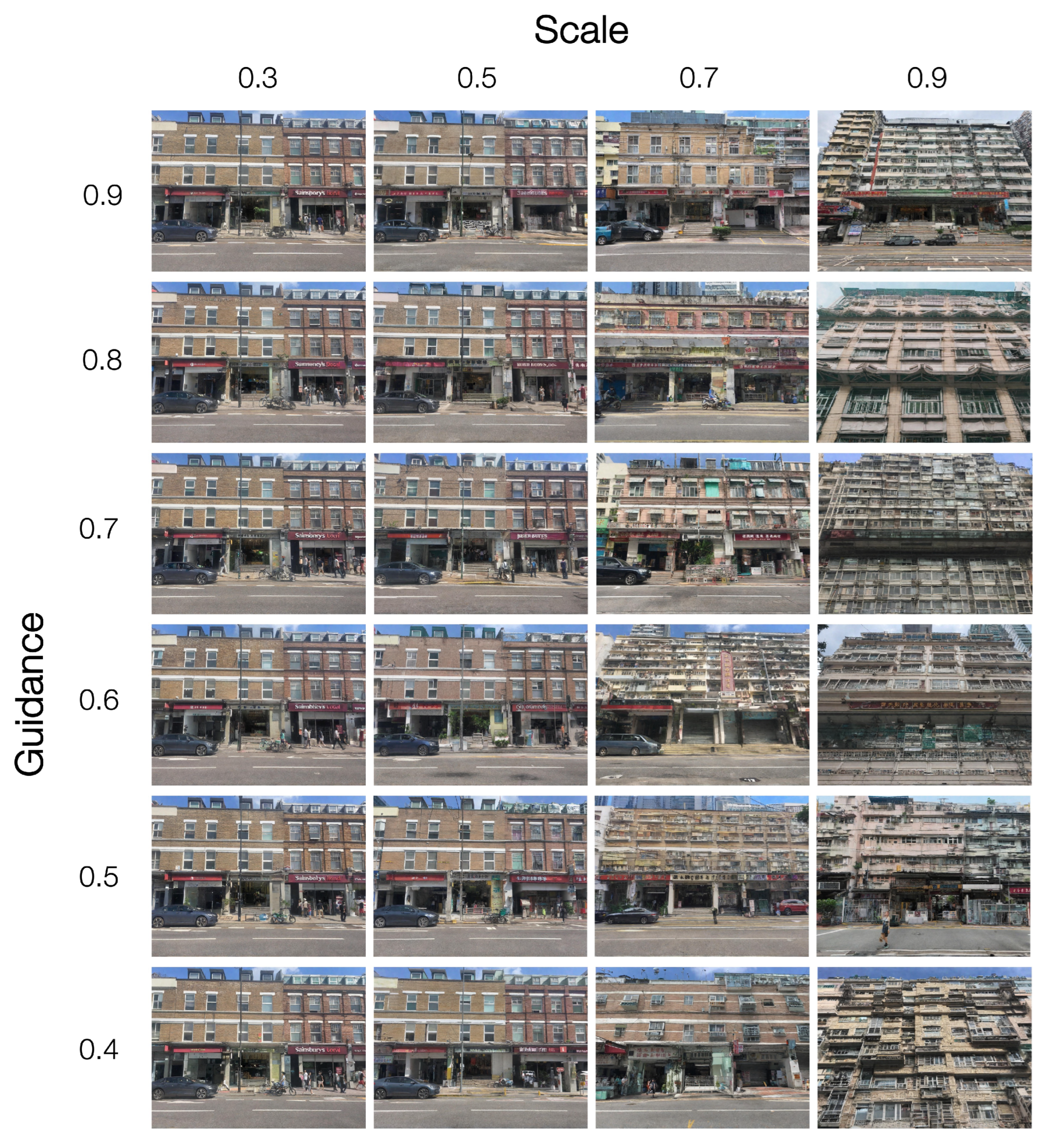
4.3. Guidance and Scale Parameters
5. Experiments
5.1. Geolocalisation Experiment

Model-Based Evaluations
5.2. Perceptual Alignment Experiment
5.2.1. Perceptual Text Prompts

5.2.2. Human-Based Evaluation
5.2.3. Model-Based Evaluations
6. Results
6.1. Geolocalisation Experiment
6.2. Perceptual Experiment
7. Discussion
7.1. Discrepancies Between Objective and Affective Alignment
7.2. Opportunities and Risks of Generative AI for Design
8. Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Perceptual Alignment—User Survey

| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utopian and dystopian | angular and curvy | safe and unsafe | Textured and Smooth |
| colorful and dull-color | Stimulating and Unstimulating | Utopian and dystopian | Relaxing and Tense |
| Relaxing and Tense | Welcoming and Uninviting | Utopian and dystopian | safe and unsafe |
| Textured and Smooth | colorful and dull-color | Welcoming and Uninviting | harmonious and discordant |
| Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Welcoming and Uninviting | harmonious and discordant | Textured and Smooth |
| Utopian and dystopian | Welcoming and Uninviting | safe and unsafe | Stimulating and Unstimulating |
| safe and unsafe | harmonious and discordant | Relaxing and Tense | Stimulating and Unstimulating |
| Stimulating and Unstimulating | angular and curvy | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Textured and Smooth |
| Relaxing and Tense | Textured and Smooth | Utopian and dystopian | harmonious and discordant |
| Welcoming and Uninviting | Textured and Smooth | safe and unsafe | Relaxing and Tense |
| Stimulating and Unstimulating | Relaxing and Tense | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Textured and Smooth |
| colorful and dull-color | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Textured and Smooth | safe and unsafe |
| Textured and Smooth | angular and curvy | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Welcoming and Uninviting |
| harmonious and discordant | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Textured and Smooth | Stimulating and Unstimulating |
| Stimulating and Unstimulating | Textured and Smooth | Utopian and dystopian | Relaxing and Tense |
| Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Textured and Smooth | Welcoming and Uninviting | Stimulating and Unstimulating |
| Welcoming and Uninviting | harmonious and discordant | angular and curvy | Relaxing and Tense |
| Stimulating and Unstimulating | safe and unsafe | colorful and dull-color | Symmetrical and Asymmetrical |
| Textured and Smooth | safe and unsafe | harmonious and discordant | Relaxing and Tense |
| Welcoming and Uninviting | angular and curvy | Stimulating and Unstimulating | Relaxing and Tense |
| Utopian and dystopian | Relaxing and Tense | colorful and dull-color | Symmetrical and Assymetrical |
| Welcoming and Uninviting | Stimulating and Unstimulating | Symmetrical and Asymmetrical | angular and curvy |
| Textured and Smooth | Utopian and dystopian | harmonious and discordant | Symmetrical and Assymetrical |
| Welcoming and Uninviting | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Textured and Smooth | Relaxing and Tense |
| harmonious and discordant | colorful and dull-color | Relaxing and Tense | Utopian and dystopian |
| Relaxing and Tense | angular and curvy | harmonious and discordant | colorful and dull-color |
| Utopian and dystopian | angular and curvy | Textured and Smooth | harmonious and discordant |
| Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Symmetrical and Asymmetrical | Textured and Smooth | Stimulating and Unstimulating |
| angular and curvy | Textured and Smooth | Utopian and dystopian | Relaxing and Tense |
| harmonious and discordant | Symmetrical and Assymetrical | Stimulating and Unstimulating | Relaxing and Tense |
References
- Alexander, C. A New Theory of Urban Design; Center for Environmental Structure: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1987; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B.; Hanson, J. The Social Logic of Space; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M.; Longley, P.A. Fractal Cities: A Geometry of Form and Function; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, R.; Miao, Y.; Aichinger, A.; Knecht, K.; Konieva, K. Integrating urban analysis, generative design, and evolutionary optimization for solving urban design problems. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2020, 47, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, T. Model-based Optimization for Architectural Design: Optimizing Daylight and Glare in Grasshopper. Technol.|Archit.+Des. 2017, 1, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, T.; Knopf-Lenoir, C.; Villon, P.; Beckers, B. Urban layout optimization framework to maximize direct solar irradiation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Roh, H.; Lee, G. Generative AI in architectural design: Application, data, and evaluation methods. Autom. Constr. 2025, 174, 106174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, Y.I.; Müller, P. Procedural modeling of cities. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 12–17 August 2001; pp. 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, P.; Wonka, P.; Haegler, S.; Ulmer, A.; Van Gool, L. Procedural modeling of buildings. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Papers; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM): New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 614–623. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, J.; Webster, C.J.; Chiaradia, A.J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X. Generative urban design: A systematic review on problem formulation, design generation, and decision-making. Prog. Plan. 2024, 180, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbei, M.; Cucuzzella, C. Revealing a Gap in Parametric Architecture’s Address of “Context”. Buildings 2023, 13, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8110–8119. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, S.; Weinmann, M.; Wessel, R.; Klein, R. Streetgan: Towards road network synthesis with generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conferences in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chaillou, S. Archigan: Artificial intelligence × architecture. In Architectural Intelligence, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Computational Design and Robotic Fabrication (CDRF 2019), Shanghai, China, 7–8 July 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Fu, X.M.; Tang, R.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.H.; Liu, L. Data-driven interior plan generation for residential buildings. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.N.; Biljecki, F. GANmapper: Geographical data translation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 1394–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Hasegawa, R.; Paige, B.; Russell, C.; Elliott, A. Explaining holistic image regressors and classifiers in urban analytics with plausible counterfactuals. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2023, 37, 2575–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Zheng, H. Text Semantics to Image Generation: A method of building facades design base on Stable Diffusion model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Design and Robotic Fabrication, Shanghai, China, 24 July 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Li, H.; Hu, R.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Du, Z.; Xu, L. ControlCity: A Multimodal Diffusion Model Based Approach for Accurate Geospatial Data Generation and Urban Morphology Analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.17049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, H.; Ding, J.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Tian, L.; Li, Y. UrbanWorld: An Urban World Model for 3D City Generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Li, G.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Tian, R. TEXT-TO-CITY: Controllable 3D urban block generation with latent diffusion model. In Accelerated Design, Proceedings of the 29th International Conference of the Association for ComputerAided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA), Singapore, 20–26 April 2024; CAADRIA: Hong Kong, China, 2024; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Feng, X.; Sun, S. Learning to generate urban design images from the conditional latent diffusion model. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 89135–89143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R. Generating accessible multi-occupancy floor plans with fine-grained control using a diffusion model. Autom. Constr. 2025, 177, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.A.; Hosseini, S.; Furukawa, Y. Housediffusion: Vector floorplan generation via a diffusion model with discrete and continuous denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5466–5475. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Fort, J.M.; Mateu, L.G. Exploringthe potential of artificial intelligence as a tool for architectural design: A perception study using gaudí’sworks. Buildings 2023, 13, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Chen, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, H. Image inpainting using diffusion models to restore eaves tile patterns in Chinese heritage buildings. Autom. Constr. 2025, 171, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.R.; Haworth, J.; Cheng, T. Understanding cities with machine eyes: A review of deep computer vision in urban analytics. Cities 2020, 96, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Ito, K. Street view imagery in urban analytics and GIS: A review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 215, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Seresinhe, C.I.; Shen, Y.; Gutierrez-Roig, M. Street-Frontage-Net: Urban image classification using deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 681–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salesses, P.; Schechtner, K.; Hidalgo, C.A. The collaborative image of the city: Mapping the inequality of urban perception. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, N.; Philipoom, J.; Raskar, R.; Hidalgo, C. Streetscore-predicting the perceived safety of one million streetscapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 779–785. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, A.; Naik, N.; Parikh, D.; Raskar, R.; Hidalgo, C.A. Deep learning the city: Quantifying urban perception at a global scale. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, Proceedings of the 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016, Proceedings, Part I 14; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, R.; Kaplan, S. The Experience of Nature: A Psychological Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, R.S. Aesthetic and affective response to natural environment. In Behavior and the Natural Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 85–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, R.L. The Intelligent Eye; Weidenfeld & Nicolson: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Neisser, U. Cognitive Psychology: Classic Edition; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, K.R. Appraisal theory. In Handbook of Cognition and Emotion; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Salingaros, N.A.; Mehaffy, M.W. A Theory of Architecture; Umbau-Verlag Harald Püschel: Solingen, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Podell, D.; English, Z.; Lacey, K.; Blattmann, A.; Dockhorn, T.; Müller, J.; Penna, J.; Rombach, R. Sdxl: Improving latent diffusion models for high-resolution image synthesis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmann, C.; Beaumont, R.; Vencu, R.; Gordon, C.; Wightman, R.; Cherti, M.; Coombes, T.; Katta, A.; Mullis, C.; Wortsman, M.; et al. Laion-5b: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing System, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Volume 35, pp. 25278–25294. [Google Scholar]
- Labs, B.F. FLUX. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/black-forest-labs/flux (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Lüddecke, T.; Ecker, A. Image segmentation using text and image prompts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7086–7096. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; et al. Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024, Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024, Proceedings, Part XLVII; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 38–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Rao, A.; Agrawala, M. Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3836–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, L.; Skreta, M.; Alberti, S.; Finn, C. Pigeon: Predicting image geolocations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 12893–12902. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, N.; Kalogeiton, V.; Picard, D.; Landrieu, L. Around the world in 80 timesteps: A generative approach to global visual geolocation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 10–17 June 2025; pp. 23016–23026. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Chi, Z.; Dong, L.; Wei, F. Optimizing prompts for text-to-image generation. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023; Volume 36, pp. 66923–66939. [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco Cepeda, V.; Nayak, G.K.; Shah, M. Geoclip: Clip-inspired alignment between locations and images for effective worldwide geo-localization. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023; Volume 36, pp. 8690–8701. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.S.B.; Stanovich, K.E. Dual-process theories of higher cognition: Advancing the debate. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 8, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wason, P.C.; Evans, J.S.B. Dual processes in reasoning? Cognition 1974, 3, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D. Thinking, Fast and Slow; Farrar, Straus and Giroux: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, H. The Production of Space; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Mustafa, B.; Kolesnikov, A.; Beyer, L. Sigmoid loss for language image pre-training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11975–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models from Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.A.; Weiss, A.; Mendelsohn, G.A. Affect grid: A single-item scale of pleasure and arousal. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1989, 57, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillion, D.; Tandon, N.; Gu, Y.; Gray, K. Can AI language models replace human participants? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2023, 27, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doersch, C.; Singh, S.; Gupta, A.; Sivic, J.; Efros, A.A. What makes paris look like paris? Commun. ACM 2015, 58, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, M.; Nasar, J.L. Physical upkeep, perceived upkeep, fear of crime and neighborhood satisfaction. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 38, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.; Dang, M.; Rafailov, R.; Zhou, L.; Lou, A.; Purushwalkam, S.; Ermon, S.; Xiong, C.; Joty, S.; Naik, N. Diffusion model alignment using direct preference optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 8228–8238. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, B.S.; Zhu, K.; Horton, J.J. Automated Social Scientific Hypothesis Generation and Testing with LLMs; Technical Report Working Paper 32381; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
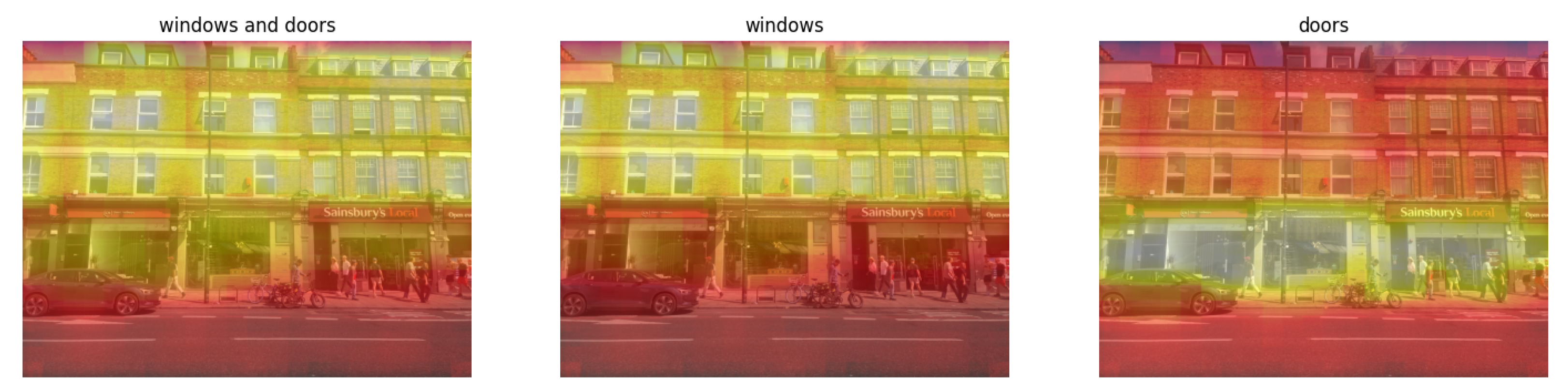
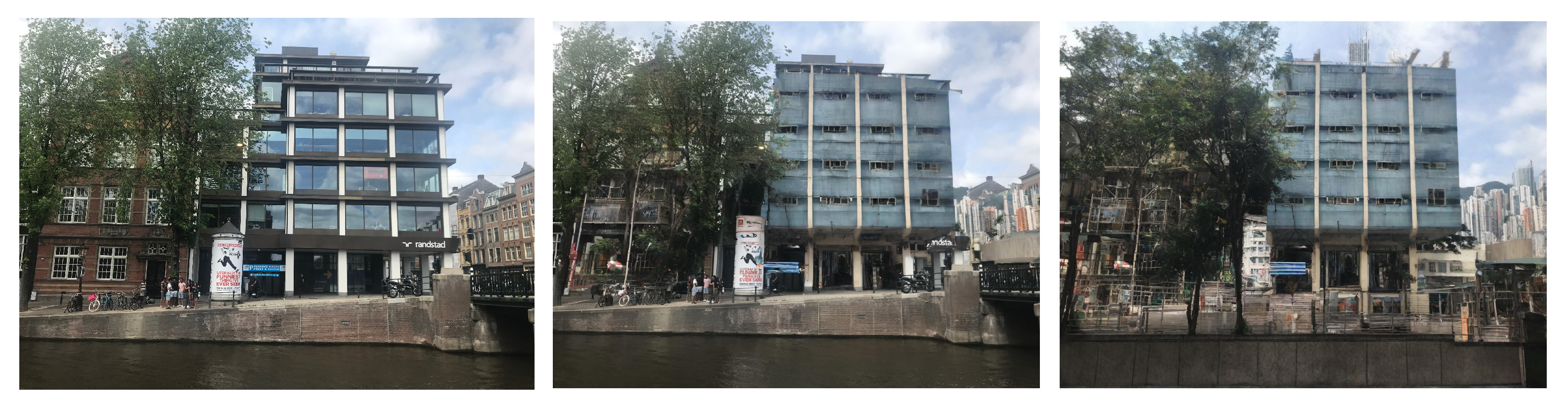
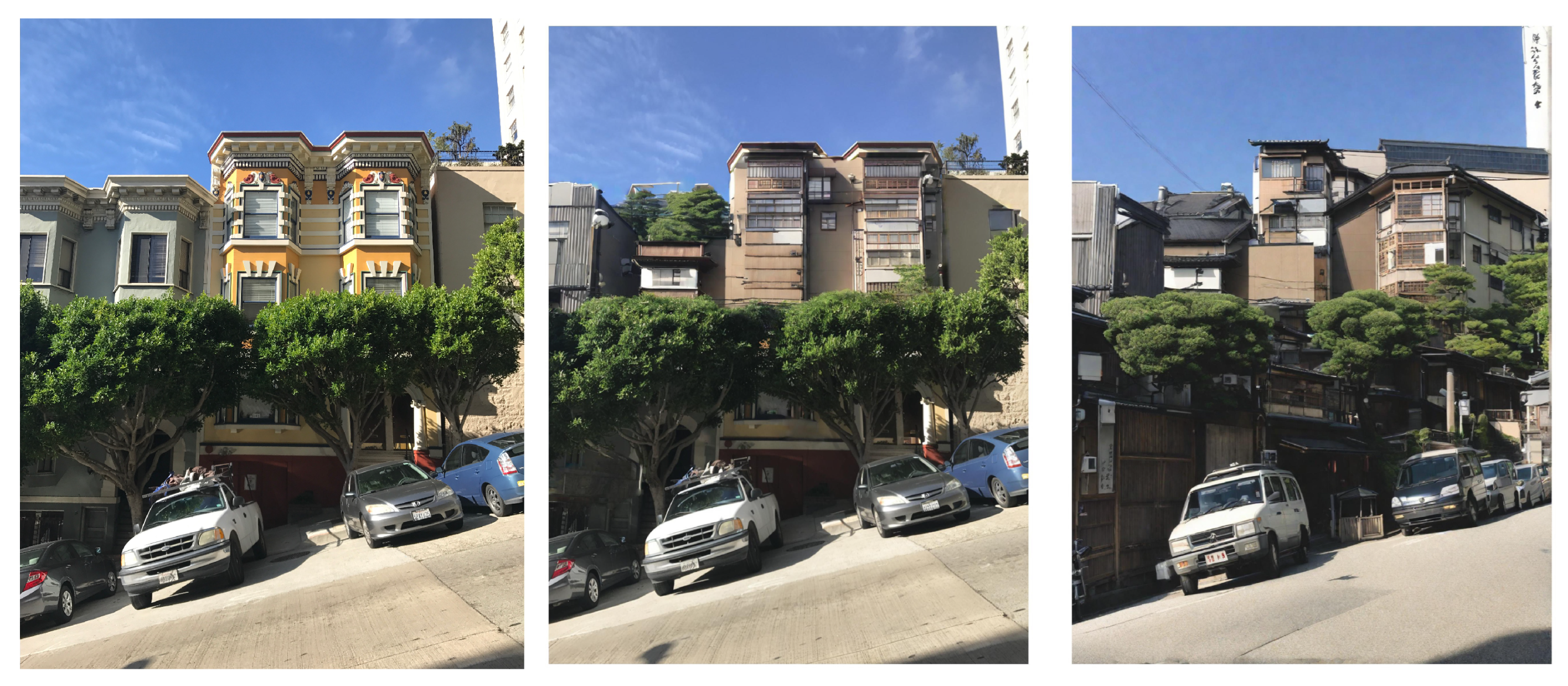
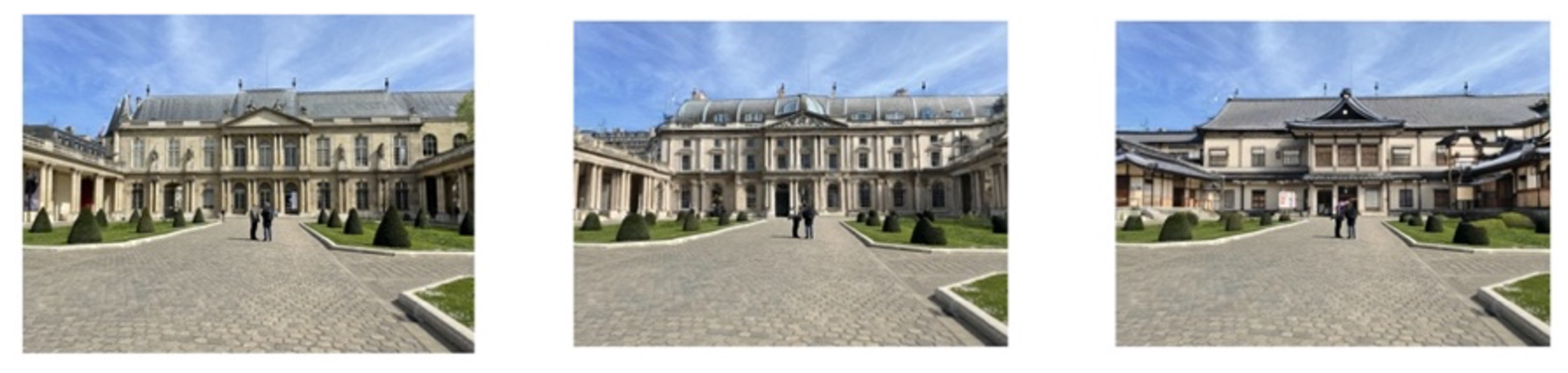




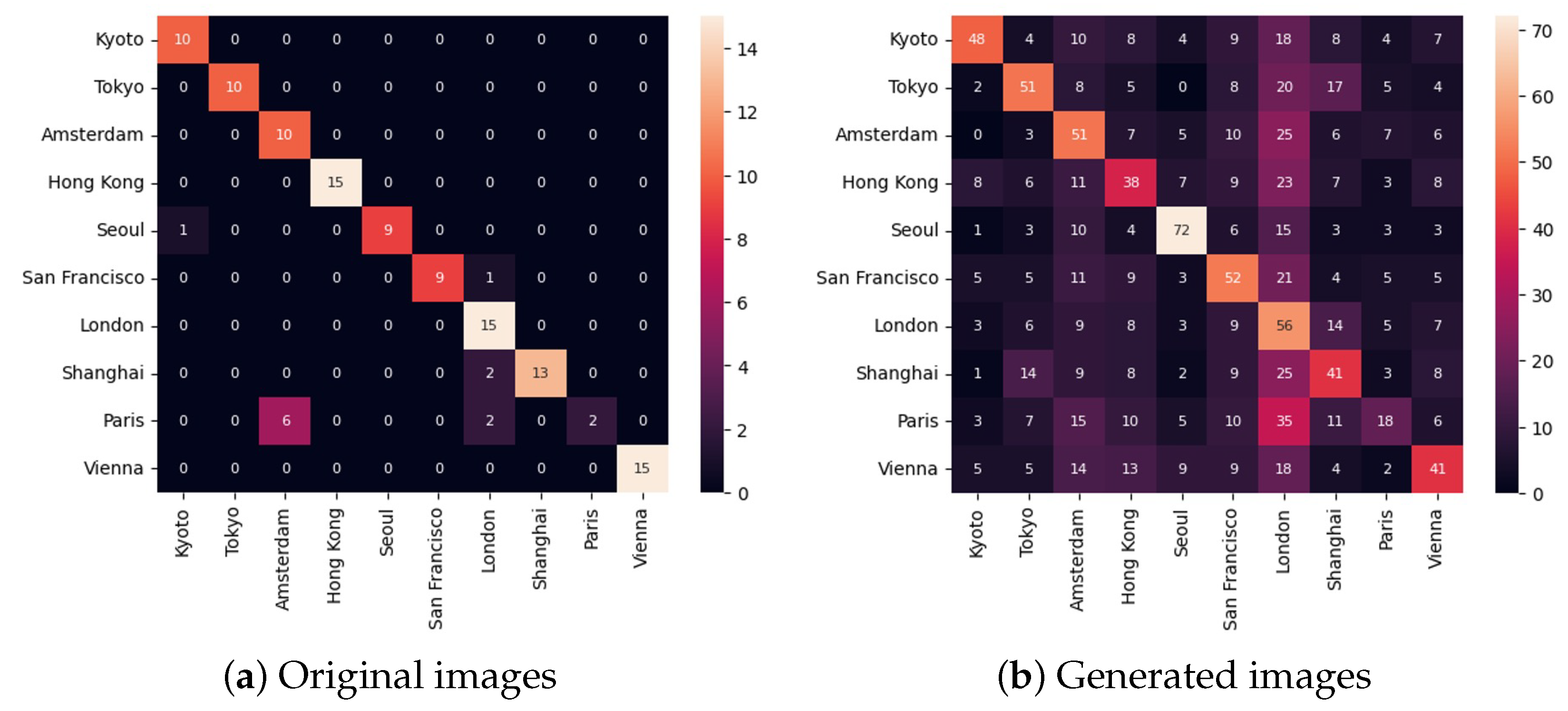





| Model/Subset | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Baseline images (existing) | 0.90 |
| Generative images (all cities) | 0.39 |
| Western cities (subset) | 0.58 |
| East Asian cities (subset) | 0.43 |
| Type | Contrastive Attribute | N | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obj | Colorful vs. Dull-color | 0.85 | 0.58 | 72 |
| Obj | Angular vs. Curvy | 0.72 | 0.38 | 73 |
| Obj | Symmetrical vs. Asymmetrical | 0.64 | 0.23 | 71 |
| Obj | Textured vs. Smooth | 0.65 | 0.30 | 70 |
| Aff | Welcoming vs. Uninviting | 0.64 | 0.35 | 72 |
| Aff | Safe vs. Unsafe | 0.55 | 0.24 | 72 |
| Aff | Relaxing vs. Tense | 0.54 | 0.12 | 73 |
| Aff | Stimulating vs. Not Stimulating | 0.53 | 0.27 | 74 |
| HiA | Utopian vs. Dystopian | 0.59 | 0.24 | 72 |
| HiA | Harmonious vs. Discordant | 0.58 | 0.28 | 71 |
| Type | Multi-Class Category | |
|---|---|---|
| Obj | Red–green–blue–yellow–purple–orange | 0.86 |
| Obj | Brick–glass–stone–wood | 0.65 |
| Aff | Exciting–depressing–calm–stressful | 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Law, S.; Valentine, C.; Kahlon, Y.; Seresinhe, C.I.; Tang, J.; Morad, M.G.; Fujii, H. Generative AI for Architectural Façade Design: Measuring Perceptual Alignment Across Geographical, Objective, and Affective Descriptors. Buildings 2025, 15, 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173212
Law S, Valentine C, Kahlon Y, Seresinhe CI, Tang J, Morad MG, Fujii H. Generative AI for Architectural Façade Design: Measuring Perceptual Alignment Across Geographical, Objective, and Affective Descriptors. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaw, Stephen, Cleo Valentine, Yuval Kahlon, Chanuki Illushka Seresinhe, Jason Tang, Michal Gath Morad, and Haruyuki Fujii. 2025. "Generative AI for Architectural Façade Design: Measuring Perceptual Alignment Across Geographical, Objective, and Affective Descriptors" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173212
APA StyleLaw, S., Valentine, C., Kahlon, Y., Seresinhe, C. I., Tang, J., Morad, M. G., & Fujii, H. (2025). Generative AI for Architectural Façade Design: Measuring Perceptual Alignment Across Geographical, Objective, and Affective Descriptors. Buildings, 15(17), 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173212








