An Image-Based Concrete-Crack-Width Measurement Method Using Skeleton Pruning and the Edge-OrthoBoundary Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of Existing Methods
2.1. The Orthogonal Projection Method
2.2. The OrthoBoundary Method
2.3. The Edge Shortest Distance Method
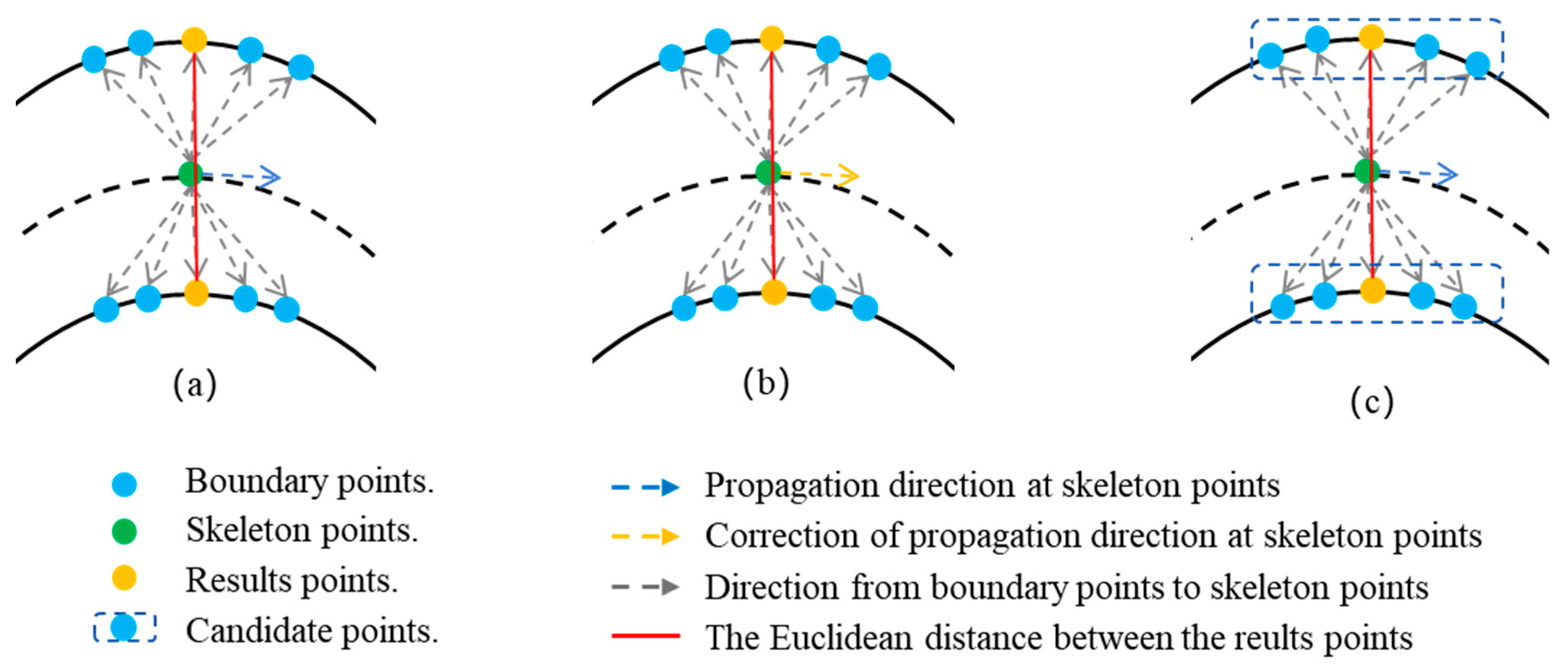
3. Methodology
3.1. Crack-Skeleton Extraction
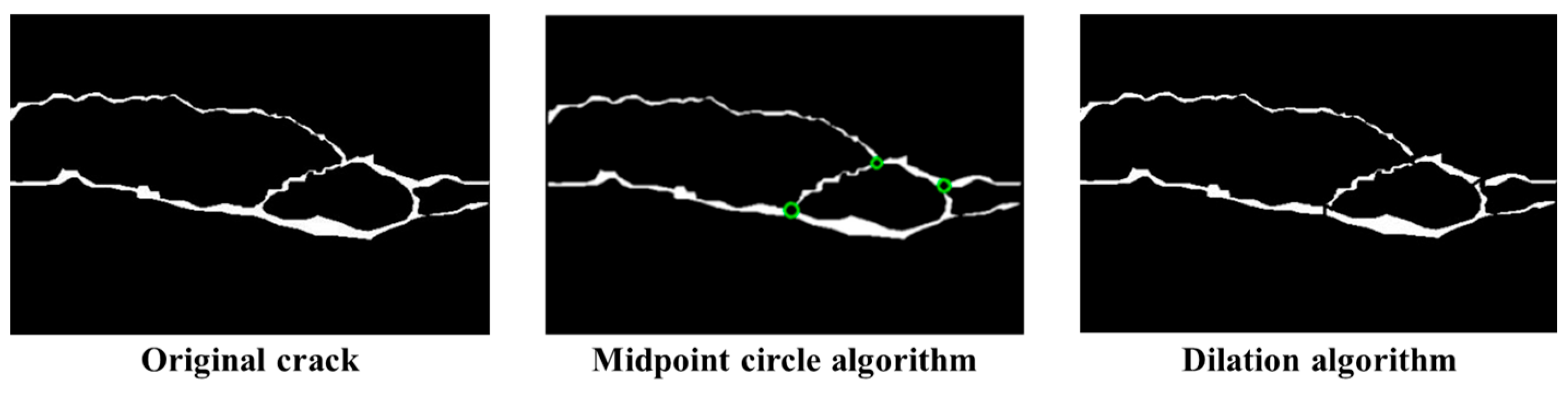
3.2. Intersection Removal
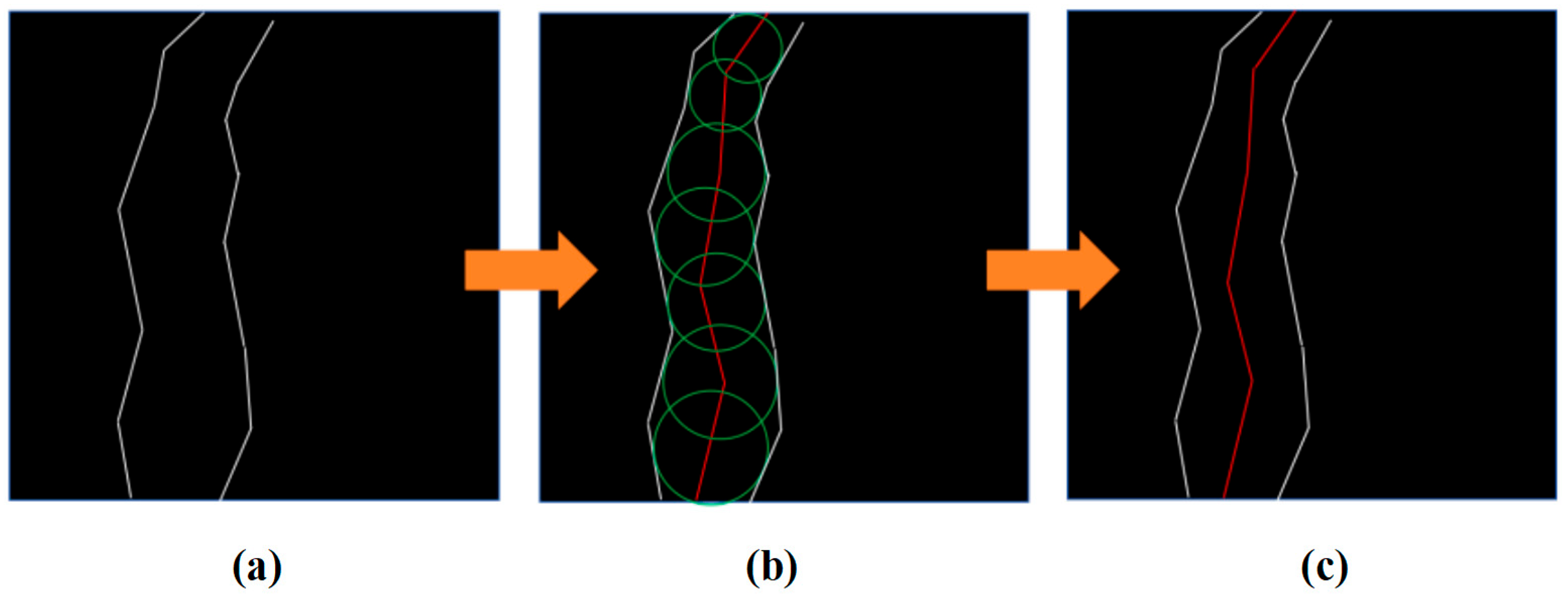
3.3. Skeleton Pruning
3.4. Crack-Width Measurement
4. Experiment Validation
4.1. Real Crack Measurement
4.2. Synthetic Crack Measurement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, X.W.; Liu, H.K.; Li, J.; Yu, P.D.; Zhang, J.F. Analysis of Filled Soil-Induced Pier Offset and Cracking in a Highway Bridge and Retrofitting Scheme Development: A Case Study. Buildings 2025, 15, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Han, Q.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, Z. A sugar-coated microbial agent for self-healing cracks in concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical Bulletin on the Development of Transportation Industry 2020. 2020. Available online: https://xxgk.mot.gov.cn/2020/jigou/zhghs/202105/t20210517_3593412.html (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- ARTBA. Bridge Conditions Report 2021; ARTBA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, M.; Sumathi, P. Crack detection using image processing: A critical review and analysis. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hashimoto, S. Practical image measurement of crack width for real concrete structure. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2009, 92, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.-G.; Lim, Y.-M.; Yun, K.-H.; Kim, G.-H. Monitoring Crack Changes in Concrete Structures. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2005, 20, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, K. A review of crack research in concrete structures based on data-driven and intelligent algorithms. Structures 2025, 75, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.T.; Luo, X.C.; Huang, T.; Yang, X. Automatic Pixel-Level Crack Detection and Measurement Using Fully Convolutional Network. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 1090–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Huang, Z.F.; Chen, Z.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.X.; Sun, J.B. Novel visual crack width measurement based on backbone double-scale features for improved detection automation. Eng. Struct. 2023, 274, 115158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Cho, S. Image-based concrete crack assessment using mask and region-based convolutional neural network. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.K.; Xue, X.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Luo, X.W.; Ru, X.W. An integrated approach to automatic pixel-level crack detection and quantification of asphalt pavement. Autom. Constr. 2020, 114, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flah, M.; Suleiman, A.R.; Nehdi, M.L. Classification and quantification of cracks in concrete structures using deep learning image-based techniques. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L. DSS-MobileNetV3: An Efficient Dynamic-State-Space- Enhanced Network for Concrete Crack Segmentation. Buildings 2025, 15, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, W. Crack detection on concrete composite slab using you only look once version 8 based lightweight system. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 108, 112974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mario, V.; Cardellicchio, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Nettis, A.; Renò, V.; Uva, G. Artificial intelligence in structural health management of existing bridges. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.C.H.; Ismadi, M.-Z.P.; Wang, X. A hybrid method for pavement crack width measurement. Measurement 2022, 197, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Miao, Y.; Torbaghan, M.E.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, J.P. Semi-automatic crack width measurement using an OrthoBoundary algorithm. Autom. Constr. 2024, 158, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Correia, P.L. Automatic Road Crack Detection and Characterization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 14, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Zheng, S.; Ou, J. A stereovision-based crack width detection approach for concrete surface assessment. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, M.R.; Masri, S.F. A new methodology for non-contact accurate crack width measurement through photogrammetry for automated structural safety evaluation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 035019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, K.C. Methodology for accurate AASHTO PP67-10–based cracking quantification using 1-mm 3D pavement images. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2017, 31, 04016056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, L.; Tang, C.S.; Shi, B.; Suo, W.B. Automatic quantification of crack patterns by image processing. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 57, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Ahn, E.; Cho, S.; Shin, M.; Sim, S.-H. Concrete Crack Identification Using a UAV Incorporating Hybrid Image Processing. Sensors 2017, 17, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, X.X.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, W.Z. Segment-based pavement crack quantification. Autom. Constr. 2019, 105, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, Y.Q.; Lu, S.U.; Mosalam, K.M. Multistage semisupervised active learning framework for crack identification, segmentation, and measurement of bridges. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 37, 1089–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Choi, I.Y.; Choi, Y. Estimation of crack width based on shape-sensitive kernels and semantic segmentation. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.J.; Zhen, G.B.; Guo, T.Q. A fast adaptive crack detection algorithm based on a double-edge extraction operator of FSM. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Zhang, A.; Wang, K.C.P.; Braham, A.F.; Qiu, S. Pavement Crack Width Measurement Based on Laplace’s Equation for Continuity and Unambiguity. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payab, M.; Abbasina, R.; Khanzadi, M. A Brief Review and a New Graph-Based Image Analysis for Concrete Crack Quantification. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Z.; Kang, F.; Li, J.J. Intelligent segmentation method for blurred cracks and 3D mapping of width nephograms in concrete dams using UAV photogrammetry. Autom. Constr. 2024, 157, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Hong, Y.; Pu, Q.H.; Wen, X.G. Neighborhood shortest distance method for concrete crack width detection in images. Eng. Struct. 2025, 326, 119519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Nie, X.; Fan, J.-S.; Liu, X.-G. Image-based crack assessment of bridge piers using unmanned aerial vehicles and three-dimensional scene reconstruction. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H.; Nagel, R.N. Shape description using weighted symmetric axis features. Pattern Recognit. 1978, 10, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Suen, C.Y. A fast parallel algorithm for thinning digital patterns. Commun. ACM 1984, 27, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Latecki, L.J. Discrete Skeleton Evolution. In Proceedings of the Energy Minimization Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Ezhou, China, 27–29 August 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 362–374. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Cui, L.; Qi, Z.; Meng, F.; Chen, Z. Automatic road crack detection using random structured forests. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 3434–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, C.; Pan, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. Three-Dimensional Crack Quantification Using Fused LiDAR Data and Optical Images. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2025, 39, 04025045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
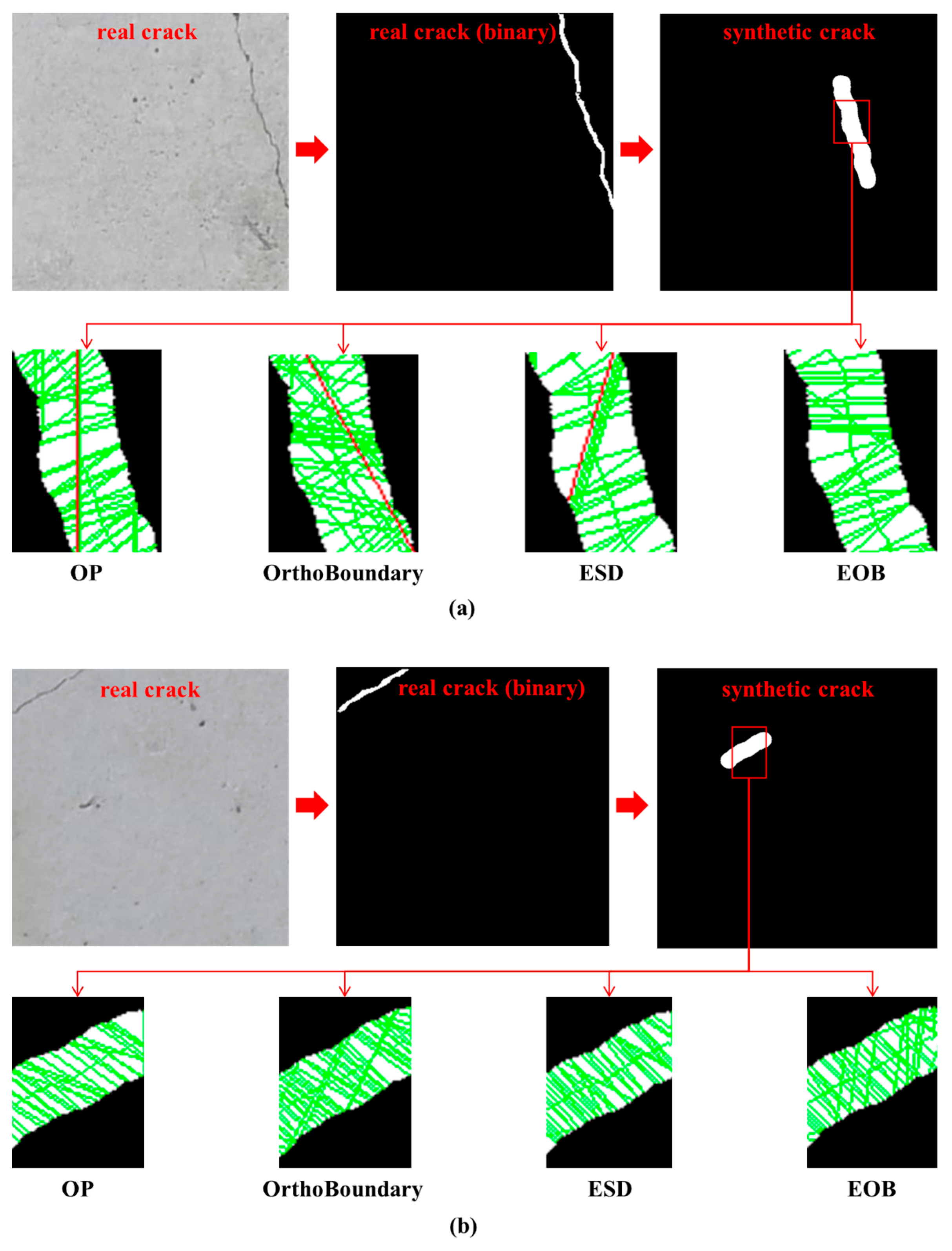










| Crack No. | Actual Width (Pixel) | OP (Pixel) | Relative Error (%) | OrthoBoundary (Pixel) | Relative Error (%) | ESD (Pixel) | Relative Error (%) | EOB (Pixel) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 23.35 | 1067.5% | 12.21 | 510.5% | 2.17 | 8.5% | 2.11 | 5.5% |
| 2 | 4 | 5.91 | 47.8% | 9.50 | 137.5% | 3.92 | −2.0% | 4.16 | 4.0% |
| 3 | 6 | 20.60 | 243.3% | 18.43 | 207.2% | 7.75 | 29.2% | 7.16 | 19.3% |
| 4 | 8 | 20.57 | 157.1% | 17.56 | 119.5% | 8.42 | 5.3% | 8.84 | 10.5% |
| 5 | 10 | 22.41 | 124.1% | 15.73 | 57.3% | 13.58 | 35.8% | 12.78 | 27.8% |
| 6 | 12 | 34.95 | 191.3% | 24.39 | 103.3% | 15.02 | 25.2% | 14.52 | 21.0% |
| 7 | 14 | 40.49 | 189.2% | 27.52 | 96.6% | 18.51 | 32.2% | 16.76 | 19.7% |
| 8 | 16 | 32.25 | 101.6% | 24.76 | 54.8% | 17.79 | 11.2% | 17.52 | 9.5% |
| 9 | 18 | 34.23 | 90.2% | 39.11 | 117.3% | 20.16 | 12.0% | 20.85 | 15.8% |
| 10 | 20 | 28.62 | 43.1% | 44.84 | 124.2% | 21.14 | 5.7% | 22.90 | 14.5% |
| 11 | 22 | 55.19 | 150.9% | 36.48 | 65.8% | 27.53 | 25.1% | 25.48 | 15.8% |
| 12 | 24 | 45.63 | 90.1% | 43.68 | 82.0% | 25.20 | 5.0% | 25.53 | 6.4% |
| 13 | 26 | 30.21 | 16.2% | 37.57 | 44.5% | 26.40 | 1.5% | 27.00 | 3.8% |
| 14 | 28 | 30.32 | 8.3% | 30.85 | 10.2% | 27.53 | −1.7% | 29.13 | 4.0% |
| 15 | 30 | 44.30 | 47.7% | 40.41 | 34.7% | 34.98 | 16.6% | 31.08 | 3.6% |
| Method | RMS (Pixel) | MAE (Pixel) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| OP | 17.53 | 15.27 | 0.68 |
| OrthoBoundary | 13.51 | 12.20 | 0.87 |
| ESD | 2.73 | 2.08 | 0.98 |
| EOB | 2.00 | 1.72 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Qin, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Pan, S.; Liu, J.; Luo, W. An Image-Based Concrete-Crack-Width Measurement Method Using Skeleton Pruning and the Edge-OrthoBoundary Algorithm. Buildings 2025, 15, 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142489
Li C, Qin H, Tang Y, Zhao H, Pan S, Liu J, Luo W. An Image-Based Concrete-Crack-Width Measurement Method Using Skeleton Pruning and the Edge-OrthoBoundary Algorithm. Buildings. 2025; 15(14):2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142489
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunxiao, Hui Qin, Yu Tang, Hailiang Zhao, Shengshen Pan, Jinbo Liu, and Wenjiang Luo. 2025. "An Image-Based Concrete-Crack-Width Measurement Method Using Skeleton Pruning and the Edge-OrthoBoundary Algorithm" Buildings 15, no. 14: 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142489
APA StyleLi, C., Qin, H., Tang, Y., Zhao, H., Pan, S., Liu, J., & Luo, W. (2025). An Image-Based Concrete-Crack-Width Measurement Method Using Skeleton Pruning and the Edge-OrthoBoundary Algorithm. Buildings, 15(14), 2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142489








