Dose–Response Functions for Assessing Corrosion Risks to Urban Heritage Materials from Air Pollution Under Climate Change: Insights from Europe and China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Impacts of Climate Change on Urban Heritage
2.1. Temperature and Thermal Stress
2.2. Humidity, Precipitation, and Time of Wetness
2.3. Extreme Weather and Disasters
2.4. Atmospheric Pollution
3. Development and Scientific Basis of Dose–Response Functions for Heritage Material Corrosion
3.1. Concept and Development
- (1)
- The first is based on a multilinear regression model, in which haze formation is treated as a time-dependent variable influenced by ambient concentrations of SO2, NO2, and PM10 (measured in μg/m3) (Lombardo et al., 2010) [48] (see Formula (13)).
- (2)
- The second utilizes a neural network model [49] (see Formulas (14)–(17)) that applies a nonlinear parametric regression using a hyperbolic tangent function. Once trained, the model is straightforward to use and offers flexibility in capturing complex environmental interactions.
3.2. Process of Assessing Heritage Degradation Using DRFs
4. Applications of Dose–Response Functions: Europe and China
4.1. Case Studies in Europe and China
4.2. Comparisons and Adaptation Challenges
5. Advantages, Disadvantages, and Complementarities of DRFs and Other Methods
5.1. Complementary to Other Advanced Methods
5.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of DRFs
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
- (1)
- DRFs provide a quantitative assessment of how major pollutants (SO2, NOx/HNO3, O3, PM) and climate variables (precipitation, humidity, temperature) affect the corrosion of materials such as limestone, sandstone, copper, and steel. By translating scientific data into management thresholds, DRFs support proactive conservation strategies ranging from pollution control to material-level interventions. European initiatives like ICP Materials and MULTI-ASSESS have incorporated multi-pollutant and climate factors, marking a transition from SO2-dominated models to more complex pollutant regimes. In China, localized adaptations, particularly in response to high particulate matter levels, have helped reduce corrosion risks and generate significant economic benefits.
- (2)
- Despite their strengths in quantification and simplicity, DRFs have limitations. They often overlook microclimatic effects and sudden damage from extreme events such as floods or heatwaves. Moreover, their material scope is limited, making them less effective for diverse heritage materials like marble, stained glass, or terracotta. These gaps highlight the need for model refinement and broader applicability.
- (3)
- Emerging technologies offer valuable support. Sensor networks allow real-time microclimate and corrosion tracking, remote sensing extends spatial coverage, and machine learning models help reveal complex environmental interactions. No single tool is sufficient—integrating DRFs with these technologies enables more responsive and precise risk management.
- (4)
- The comparison of European and Chinese experiences highlights the need for continuous model updates. In Europe, residual ozone and climate now play larger roles. In China, rapid pollution reduction and climate diversity demand recalibrated DRFs, tailored to local conditions through field validation—especially in monsoon, arid, and alpine zones.
- (1)
- Although DRFs have been developed, these models require further refinement and the inclusion of additional material types, particularly non-metallic and non-stone materials such as wood.
- (2)
- Integrate multivariable nonlinear modeling and machine learning. Combining physicochemical corrosion mechanisms with data-driven models (e.g., machine learning) can better capture complex, nonlinear interactions between multiple pollutants and climate factors, improving the accuracy of DRF-based risk predictions.
- (3)
- Expand empirical data collection across diverse climates. Long-term exposure studies should be extended to underrepresented climatic zones—such as monsoon, arid, and alpine regions—especially in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. This will support both regional adaptation and global applicability of DRFs.
- (4)
- Enhance DRF responsiveness through IoT and real-time monitoring. Sensor networks and IoT platforms can provide continuous microclimate and material condition data, allowing real-time comparison with DRF predictions. This enables the establishment of a dynamic “prediction–validation–adjustment” loop for responsive risk management. By integrating DRFs with machine learning and IoT feedback, the field can move from static, average-based models to dynamic systems that respond to rapidly changing urban environments, allowing for more precise, timely, and sustainable cultural heritage protection.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grossi, C.M.; Murray, M.; Butlin, R.N. Response of porous building stones to acid deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 2713–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalagli, N.; Kita, A.; Castaldo, V.; Pisello, A.; Ubertini, F.J.C.; Materials, B. Hierarchical environmental risk mapping of material degradation in historic masonry buildings: An integrated approach considering climate change and structural damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 215, 998–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Vicente, R.; Bastos, A.; Ferro Rocha, A.; Mendes Silva, J. Atmospheric corrosion in two different urban environments in Portugal: Results of one-year exposure. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Lefèvre, R.-A. Weathering of materials at Notre-Dame from changes in air pollution and climate in Paris, 1325–2090. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 50, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Sardella, A.; Kaiser, A.; Cacciotti, R.; De Nuntiis, P.; Hanus, C.; Maxwell, I.; Drdácký, T.; Drdácký, M. Safeguarding cultural heritage from climate change related hydrometeorological hazards in Central Europe. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 63, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, H.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhao, X.F. Quantifying the Potential Co-Benefit of Air Quality Improvement on Cultural Heritage in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, F. Mapping the corrosion impact of air pollution on the historical peninsula of Istanbul. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, J.; Jarrett, D.; Hamilton, R. Dose–response functions for the soiling of heritage materials due to air pollution exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanis, C.; Varotsos, C.; Christodoulakis, J.; Tidblad, J.; Ferm, M.; Ionescu, A.; Lefevre, R.-A.; Theodorakopoulou, K.; Kreislova, K. On the corrosion and soiling effects on materials by air pollution in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12039–12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.; Tzanis, C.; Cracknell, A. The enhanced deterioration of the cultural heritage monuments due to air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RISE Research Institutes of Sweden. ICP Materials. Available online: https://www.ri.se/en/icp-materials (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Visone, F.; Abate, N.; Sileo, M.; Masini, N. Assessing Stone Material Recession of Cultural Heritage: New Approach Based on Satellite-Based Rainfall Data and Dose-Response Functions—Case of UNESCO Site of Matera. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Bové, J.; Orr, S.A.; Thomas, H.; Andrews, M. Using damage functions to map heritage climatology at a global scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 963, 178350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Climate Change and World Heritage; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Fusion of multi source data for atmospheric corrosion evaluation using sensors and image recognition. npj Mater. Degrad. 2025, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, Y. A Review of Atmospheric Deterioration and Sustainable Conservation of Calcareous Stone in Historical Buildings and Monuments. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletti, C. Climate Change Threats to Stone Cultural Heritage: State of the Art of Quantitative Damage Functions and New Challenges for a Sustainable Future. Heritage 2024, 7, 3276–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, X.; Peng, N.; Sheng, Y.; Liang, Y. Experimental Study on Salt-Bearing Sandstone Samples Under the Change of Temperature and Humidity Cycle. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, F.; Frontera, P.; Malara, A.; Armocida, F. Materials and climate change: A set of indices as the benchmark for climate vulnerability and risk assessment for tangible cultural heritage in Europe. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanelli, E.; Quarta, G.; Masieri, M.; Calia, A. High temperature effects on the properties of a high porosity calcareous stone building material. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 6733–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, S.; Moj, M.; Banaszak, A.; Chowaniec-Michalak, A.; Jamroz, P.; Dzimitrowicz, A.; Sadowski, L. Mechanical and chemical wear of epoxy composites filled with waste bricks. Wear 2025, 571, 205815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, P.; Arshad, A.; Hussain, M. A review on environmental impacts of paints and strategies for producing eco-friendly-paints. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 22, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, V. Model for Multi-Pollutant Impact and Assessment of Threshold Levels for Cultural Heritage; Michael Melcher and Manfred Schreiner Institute of Sciences and Technologies in Art: Vienna, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Broomandi, P.; Tleuken, A.; Zhaxylykov, S.; Nikfal, A.; Kim, J.R.; Karaca, F. Assessment of potential benefits of traffic and urban mobility reductions during COVID-19 lockdowns: Dose-response calculations for material corrosions on built cultural heritage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 6491–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Yan, C.; Lv, S.; Sun, H.; Xue, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Edwing, D.; Edwing, K.; Geng, X. Synthetic aperture radar for geosciences. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, e2023RG000821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoncini, A.; Brattich, E.; Bernardi, E.; Chiavari, C.; Tositti, L. Safeguarding outdoor cultural heritage materials in an ever-changing troposphere: Challenges and new guidelines for artificial ageing test. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 59, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenel, C.; Raccurt, O.; Gardette, J.-L.; Therias, S. Review of accelerated ageing test modelling and its application to solar mirrors. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 186, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaskova, M.; Kotes, P.; Brodnan, M.J.P.E. Air pollution as an important factor in construction materials deterioration in Slovak Republic. Procedia Eng. 2015, 108, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Vega, J.M.; Viejo, F.; Díaz, I.; Morcillo, M. Mapping air pollution effects on atmospheric degradation of cultural heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-S.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Hsu, M.-F. Using heritage risk maps as an approach to estimating the threat to materials of traditional buildings in Tainan (Taiwan). J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J. Mapping Manual Ch 4 Final-Update; UBA: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- CULT-STRAT. Assessment of Air Pollution Effects on Cultural Heritage—Management Strategies; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Torkmahalleh, M.A.; Hopke, P.K.; Broomandi, P.; Naseri, M.; Abdrakhmanov, T.; Ishanov, A.; Kim, J.; Shah, D.; Kumar, P. Exposure to particulate matter and gaseous pollutants during cab commuting in Nur-Sultan city of Kazakhstan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferm, M.; De Santis, F.; Varotsos, C. Nitric acid measurements in connection with corrosion studies. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6664–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, V.; Tidblad, J.; Kreislova, K.; Knotkova, D.; Faller, M.; Reiss, D.; Snethlage, R.; Yates, T.; Henriksen, J.; Schreiner, M.; et al. UN/ECE ICP materials dose-response functions for the multi-pollutant situation. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2007, 7, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J.; Kucera, V.; Ferm, M.; Kreislova, K.; Brüggerhoff, S.; Doytchinov, S.; Screpanti, A.; Grøntoft, T.; Yates, T.; De La Fuente, D. Effects of air pollution on materials and cultural heritage: ICP materials celebrates 25 years of research. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 2012, 496321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomandi, P.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Fathian, A.; Darynova, Z.; Janatian, N.; Nikfal, A.; Kim, J.R.; Karaca, F. Impacts of ambient air pollution on UNESCO world cultural heritage sites in Eastern Asia: Dose-response calculations for material corrosions. Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Messina, P.; Sabbioni, C.; Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P. Mapping the impact of climate change on surface recession of carbonate buildings in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbioni, C.; Cassar, M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Tidblad, J.; Kozlowski, R.; Drdácký, M.; Sáiz-Jiménez, C.; Grøntoft, T.; Wainwright, I.; Ariño, X. Global climate change impact on built heritage and cultural landscapes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Heritage, Weathering and Conservation, HWC 2006, Madrid, Spain, 21–24 June 2006; pp. 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Harris, I. Predicting long term freeze–thaw risks on Europe built heritage and archaeological sites in a changing climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 377, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, C.; Brimblecombe, P.; Cassar, M. The Atlas of Climate Change Impact on European Cultural Heritage; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, S.A.; Costantini, I.; Etxebarria, I.; Madariaga, J.M.; Arana, G. Assessment of marine and urban-industrial environmental impact on stone acting as the base of a quaternary bronze sculpture. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 111187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, M.; Wiesinger, R.; Schreiner, M. Degradation of glass artifacts: Application of modern surface analytical techniques. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verney-Carron, A.; Sessegolo, L.; Lefèvre, R.-A.; Brimblecombe, P. Modelling the Alteration of Medieval Stained Glass as a Function of Climate and Pollution: Comparison between Different Methodologies. Heritage 2023, 6, 3074–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, T.; Ionescu, A.; Chabas, A.; Lefèvre, R.-A.; Ausset, P.; Candau, Y. Dose–response function for the soiling of silica–soda–lime glass due to dry deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verney-Carron, A.; Dutot, A.; Lombardo, T.; Chabas, A. Predicting changes of glass optical properties in polluted atmospheric environment by a neural network model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidović, K.; Hočevar, S.; Menart, E.; Drventić, I.; Grgić, I.; Kroflič, A. Impact of air pollution on outdoor cultural heritage objects and decoding the role of particulate matter: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46405–46437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brischke, C.; Rapp, A.O. Dose–response relationships between wood moisture content, wood temperature and fungal decay determined for 23 European field test sites. Wood Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brischke, C.; Alfredsen, G. Wood-water relationships and their role for wood susceptibility to fungal decay. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3781–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spezzano, P. Mapping the susceptibility of UNESCO World Cultural Heritage sites in Europe to ambient (outdoor) air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMEP. EMEP MSC-W Modelled Air Concentrations and Depositions. 2015. Available online: https://emep.int/mscw/mscw_moddata.html (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- UNECE. Transport Statistics Infocards. 2020. Available online: http://www.unece.org/trans/main/wp6/infocards.html (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Hettelingh, J.-P.; Posch, M. Critical load exceedances under equitable nitrogen emission reductions in the EU28. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Guo, M.; Cheng, M.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Chai, F. Prospect of China’s ambient air quality standards. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J.; Kreislová, K.; Faller, M.; De la Fuente, D.; Yates, T.; Verney-Carron, A.; Grøntoft, T.; Gordon, A.; Hans, U. ICP materials trends in corrosion, soiling and air pollution (1987–2014). Materials 2017, 10, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Xu, R.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, P.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X. Concentrations, sources, and influential factors of water-soluble ions of atmospheric particles in Dunhuang Mogao Grottoes, a world heritage site in China. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 1395–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosek, T.; Kouril, M.; Dubus, M.; Taube, M.; Hubert, V.; Scheffel, B.; Degres, Y.; Jouannic, M.; Thierry, D. Real-time monitoring of indoor air corrosivity in cultural heritage institutions with metallic electrical resistance sensors. Stud. Conserv. 2013, 58, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereszynski, E.W.; Dietterich, T.G. Spatiotemporal models for data-anomaly detection in dynamic environmental monitoring campaigns. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. (TOSN) 2011, 8, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, L.; Michalis, P.; Vlachos, M.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Tsiakos, C.; Amditis, A. Integrated sensing solutions for monitoring heritage risks. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024–2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 3352–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, L.; Calcerano, F.; Adinolfi, F.; Chianetta, D.; Gigliarelli, E. Open HBIM-IoT Monitoring Platform for the Management of Historical Sites and Museums. An Application to the Bourbon Royal Site of Carditello. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2025, 19, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, X.; Yang, M.; Tang, L.; Tang, B.-H. Evaluating the stability of architectural heritage from the perspective of InSAR: A practical study on Jianchuan Ancient Town. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moise, C.; Dana Negula, I.; Mihalache, C.E.; Lazar, A.M.; Dedulescu, A.L.; Rustoiu, G.T.; Inel, I.C.; Badea, A. Remote sensing for cultural heritage assessment and monitoring: The case study of Alba Iulia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoean, R.; Bacanin, N.; Stoean, C.; Ionescu, L.; Atencia, M.; Joya, G. Computational framework for the evaluation of the composition and degradation state of metal heritage assets by deep learning. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 64, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.B.; Zhang, D.; Van Ingelgem, Y.; Steckelmacher, D.; Nowé, A.; Terryn, H. Reviewing machine learning of corrosion prediction in a data-oriented perspective. npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Qiao, G.; Han, P. Machine learning algorithms in the environmental corrosion evaluation of reinforced concrete structures—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 133, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, B.; Screpanti, A.; De Marco, A. Corrosion on cultural heritage buildings in Jordan in current situation and in future climate scenarios. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neocleous, K.; Christofe, A.; Agapiou, A.; Evagorou, E.; Themistocleous, K.; Hadjimitsis, D. Digital mapping of corrosion risk in coastal urban areas using remote sensing and structural condition assessment: Case study in Cyprus. Open Geosci. 2016, 8, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbota, H.; Mitchell John, E.; Odlyha, M.; Strlič, M. Remote assessment of cultural heritage environments with wireless sensor array networks. Sensors 2014, 14, 8779–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, D.; Casas, A.; Escobar, C.A.; Perez, A.; Gonzalez, V. Advanced machine learning techniques for corrosion rate estimation and prediction in industrial cooling water pipelines. Sensors 2024, 24, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, H. Cultural Heritage Risk Assessment Based on Explainable Machine Learning Models: A Case Study of the Ancient Tea Horse Road in China. Land 2025, 14, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, E.; Sassoni, E. Correlation between microstructural characteristics and weight loss of natural stones exposed to simulated acid rain. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, B.; Choi, C.; Qiu, R.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Moon, S.; Son, G.; Kim, J.; Han, H.; Yeom, Y.S. Photon dose response functions for accurate skeletal dosimetry for Korean and Asian populations. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2024, 56, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøntoft, T.; Hallett, K.; Blades, N. Environmental dose-response functions of silk and paper exposed in museums. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 227, 110878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Ortiz, R.; Ortiz, P. Remote sensing to assess the risk for cultural heritage: Forecasting potential collapses due to rainfall in historic fortifications. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2024, 42, 92–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuca, B.; Zaina, F.; Tapete, D. Monitoring of damages to cultural heritage across Europe using remote sensing and earth observation: Assessment of scientific and grey literature. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-C. Environmental risk mapping of physical cultural heritage using an unmanned aerial remote sensing system: A case study of the Huang-Wei monument in Kinmen, Taiwan. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 39, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
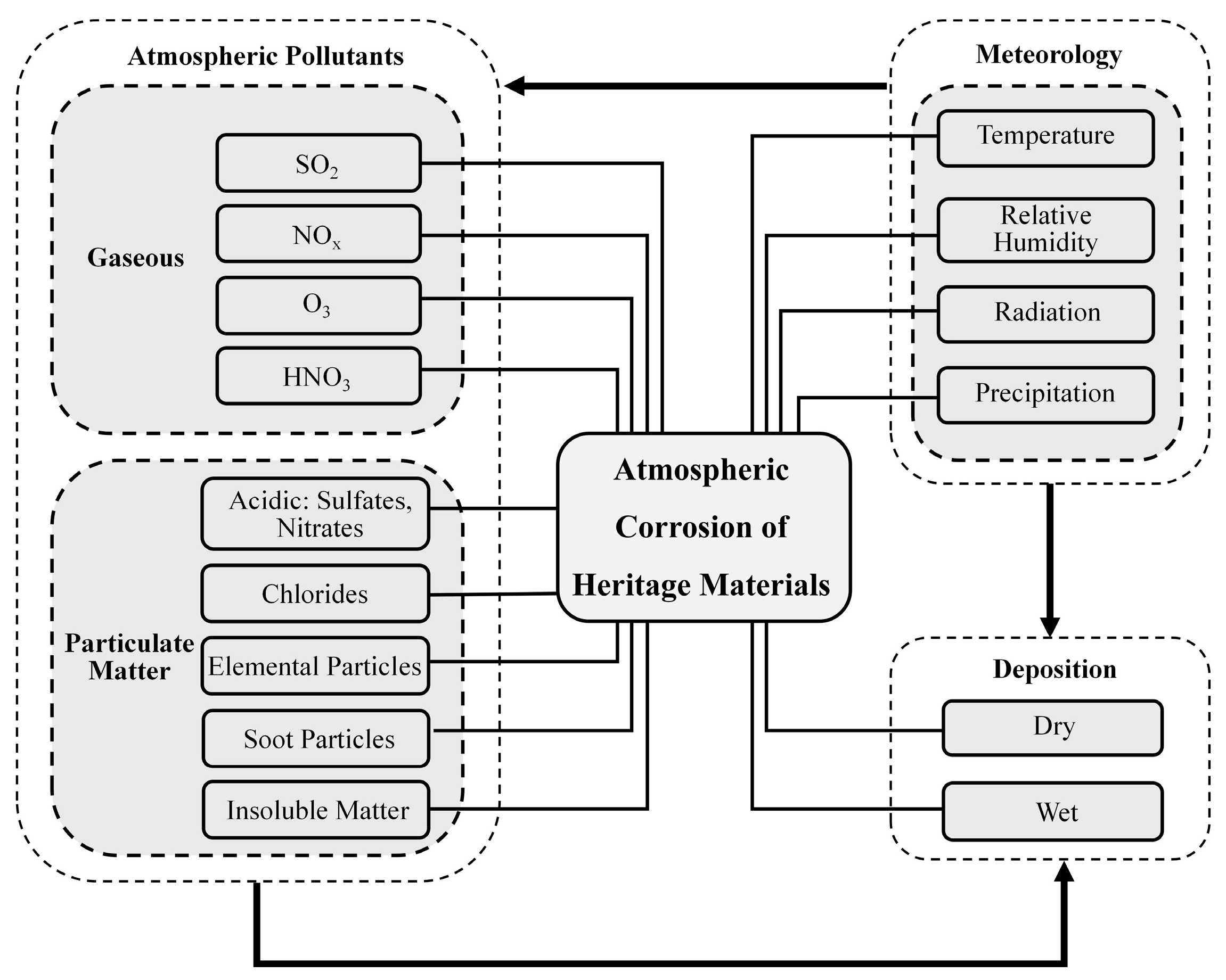
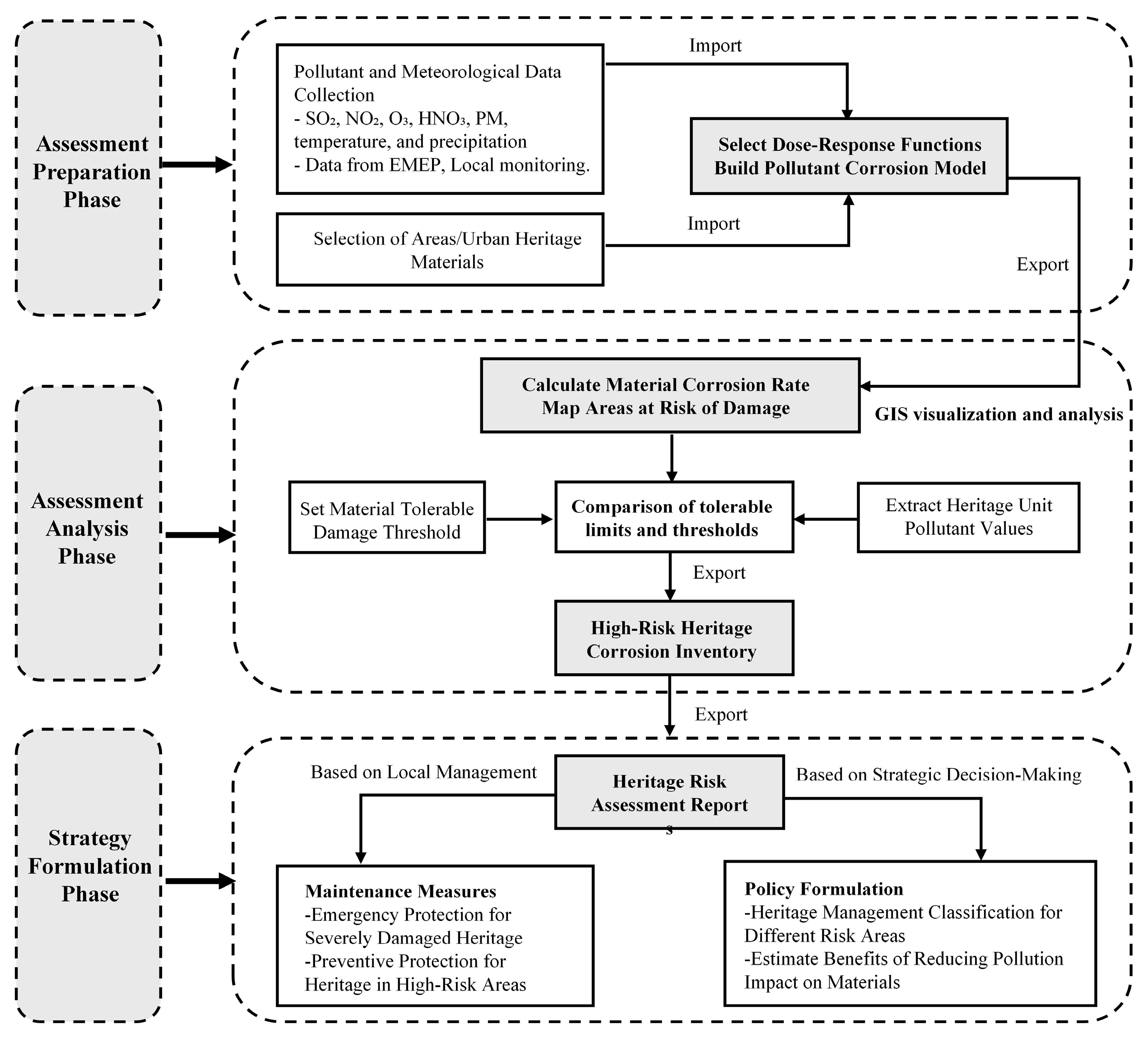

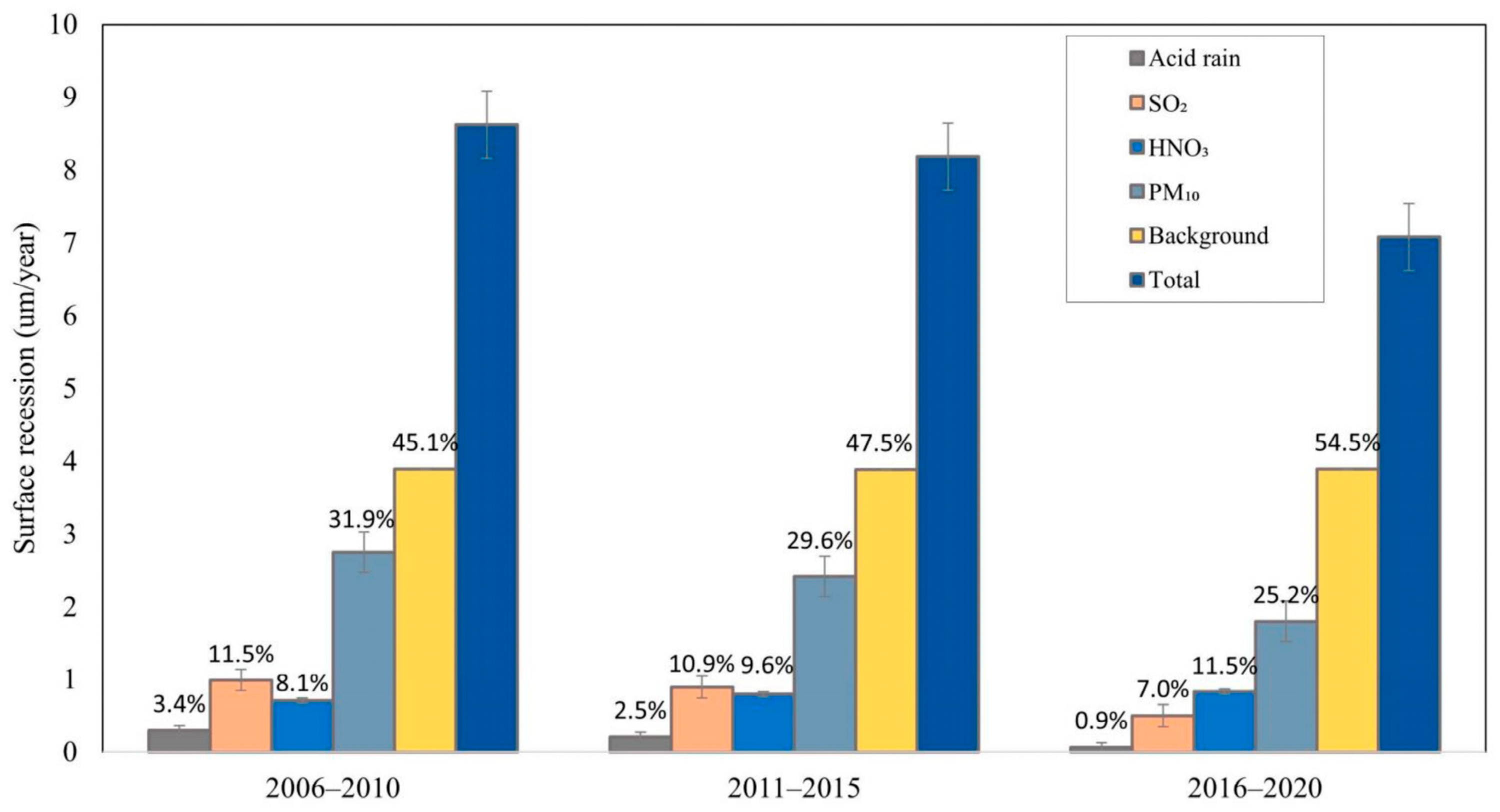
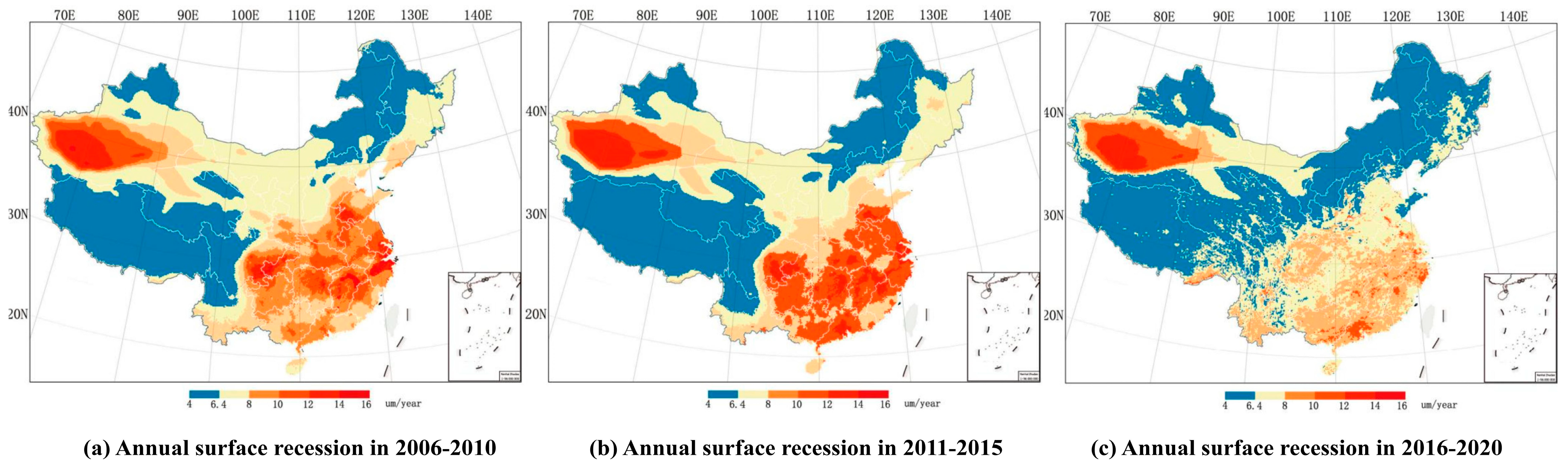
| Climate Indicator | Climate Change Risks | Physical, Social, and Cultural Impacts on Cultural Heritage |
|---|---|---|
| Humidity Changes | Floods; Heavy rainfall; Changes in soil chemistry; Groundwater changes; Humidity cycle changes | Floods erode heritage materials, causing cracks and expansion; Increased groundwater levels lead to instability of historical buildings; Drainage system failures; Humidity and drying affect the surface salt crystallization and dissolution of archaeological sites |
| Temperature Changes | Daily, seasonal, extreme events; Increased freeze-thaw, Wetting time | Thermal stress leads to the deterioration of building structures; Frost action after internal wetting of masonry materials |
| Wind Environment | Increased frequency of strong winds, gusts; Wind transport of salt; Wind transport of sand | Increased static and dynamic loads on historical buildings; Internal structural damage and collapse of buildings; Accelerated surface erosion of artifacts |
| Air Pollution | Changes in precipitation pH; Changes in pollutant deposition | Carbonating dissolution causing stone decay; Black crust formation on materials; Metal corrosion |
| Biological Effects | Spread of invasive species; Growth and increase of mold; Changes in lichen biology; Reduction of original plant species | Organic materials subjected to biological attack by insects, molds, fungi, termites, etc.; Structural timber and wood veneer decay |
| Scenario | Material | Dose–Response Function | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 Dominated Scenario | Carbon steel | (1) | |
| Zinc | (2) | ||
| Aluminum | (3) | ||
| Copper | (4) | ||
| Bronze | (5) | ||
| Limestone | (6) | ||
| Sandstone | (7) | ||
| Multi-Pollutant | Carbon Steel | (8) | |
| Zinc | (9) | ||
| Copper | (10) | ||
| Bronze | (11) | ||
| Limestone | (12) |
| Scenario | Material | Temperature (T) | Relative Humidity (Rh) | Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) | Ozone (O3) | Nitric Acid (HNO3) | Particulate Matter (PM10) | Precipitation (Prec) | pH | Chloride Ions (Cl−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2-Dominated Scenario | Carbon Steel | X | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Zinc | X | X | X | — | — | — | X | X | — | |
| Aluminum | X | X | X | — | — | — | X | — | X | |
| Copper | X | X | X | X | — | — | X | X | — | |
| Bronze | X | X | X | — | — | — | X | X | — | |
| Limestone | X | — | X | — | — | — | X | X | — | |
| Sandstone | X | — | X | — | — | — | X | X | — | |
| Multi-Pollutant Scenario | Carbon Steel | X | X | X | — | — | X | X | X | — |
| Zinc | X | X | X | — | X | — | — | — | — | |
| Bronze | X | X | X | — | — | X | X | X | — | |
| Limestone | — | X | X | — | X | X | X | X | — |
| Material | Tolerable Deterioration Rate | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 2020 (n = 2.5) | Year 2050 (n = 2) | ||
| Steel and Carbon Steel | 20 | 16 | µm, surface recession or corrosion depth per year |
| Zinc | 1.1 | 0.9 | |
| Aluminum | 0.22 | 0.18 | |
| Copper | 0.8 | 0.64 | |
| Bronze | 0.6 | 0.5 | |
| Limestone | 8 | 6.4 | |
| Sandstone | 7 | 5.5 | |
| Method | Cost (Hardware/Software and Maintenance) | Accuracy (Micro-Environment and Complex Interactions) | Scalability (Across Sites/Regions) | Responsiveness (Timeliness/Real-Time Feedback) | Practical Deployment (Equipment, Data Needs, Integration) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose–Response Functions (DRFs) | Low: Uses existing environmental data; requires minimal equipment | Moderate: Captures broad pollution–climate effects but misses microclimates and complex interactions | High: Easily applied via GIS; enables consistent regional corrosion risk mapping once data are available | Low: Based on long-term averages; not real-time; suited for planning, not immediate feedback | Easy: No hardware needed; uses existing data with simple software or spreadsheet-based formulas | [69] |
| Real-Time Sensor Monitoring | Moderate–High: Requires sensor installation and regular maintenance (e.g., batteries, calibration) | High: Offers sensitive in situ measurements at micro-scale; accuracy depends on sensor quality and placement | Moderate: Scalable with added sites, but expansion requires more devices and infrastructure; complexity grows with scale | High: Provides near real-time monitoring; logs data frequently and alerts to rapid environmental changes | Intermediate: Requires on-site hardware and network setup; signal issues possible; needs data management software | [71] |
| Remote Sensing and Imaging | Low–Moderate: Free data/software enable low-cost analysis; high-res imagery or drones increase cost | Moderate: Accurate for macro-scale mapping; limited micro-scale detection; captures indirect corrosion indicators | High: One satellite image covers large areas; ideal for multi-site comparison and long-term monitoring | Moderate: Suitable for seasonal tracking; not real-time—may miss sudden changes due to periodic satellite passes | Straightforward: No on-site setup; integrates via GIS with heritage data; requires validation and adequate resolution | [65,70] |
| Machine Learning Models | Moderate: Costs lie in data collection and model development; uses affordable computing and existing datasets | High: ML predicts corrosion more accurately than formulas; accuracy depends on training data quality | Moderate: Applicable across sites with similar data; can integrate with GIS for regional risk mapping | High: Ingests real-time data and provides instant risk forecasts, enabling proactive conservation | Challenging: Requires extensive data for training; user-friendly front end, but complex back-end development and validation | [72,73] |
| Approach | Principle & Data | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose-Response Functions (DRFs) | Empirical equations linking environmental dose (pollutant concentrations, rainfall, etc.) to material corrosion rate (µm/yr or mass loss); derived from multi-site exposure data | (1) Simple: Needs only standard environmental data (annual SO2, NOx, RH, etc.) to estimate decay (2) Validated: Built on decades of data, calibrated for common materials across climates (3) Mapping and Policy: Enables regional risk mapping and air quality policy thresholds (4) Scenario Testing: Predicts long-term impacts under future climate/pollution scenarios | (1) Limited scope: Only valid within the studied conditions, not for extreme climates or pollution (2) Simplified: Ignores microclimates and short-term spikes (uses annual averages) (3) One-material focus: Cannot directly assess combined effects (e.g., mortar-stone) (4) Static: Provides average corrosion rates, not real-time alerts or fine-scale mapping | [74,75,76] |
| Real-Time Sensor Monitoring | In situ sensors measuring environmental parameters and corrosion proxies (e.g., electrical resistance probes, atmospheric corrosion monitors for metal loss, pollutant gas sensors) | (1) Direct measurement: Tracks actual material corrosion or gas levels on-site (2) High temporal resolution: Detects diurnal or episodic changes (e.g., overnight corrosion) (3) Preventive insight: Gives immediate feedback for quick mitigation (e.g., ventilation) (4) Local accuracy: Captures microclimate effects at specific site points (e.g., showcases, shelters) | (1) Coverage: Limited range—many sensors needed for large sites, costly to deploy (2) Maintenance: Needs power, calibration, and replacements; drift may degrade data (3) Data interpretation: Large datasets require expert or automated analysis; raw data needs conversion to material loss units (4) Specificity: Sensors (e.g., silver) target specific materials; hard to generalize results to others | [62,63] |
| Remote Sensing and Imaging | Remote data assess heritage environments (satellite climate/pollution) or material condition (high-res damage imaging); techniques: satellite Earth observation, drones, laser scanning, spectral imaging | (1) Broad coverage: Satellites offer uniform pollution/climate data, enabling global heritage risk maps (2) Non-contact: LiDAR/photogrammetry creates 3D models to assess erosion/cracks without touching the site (3) Change detection: Comparing images over time reveals subtle changes (mm-scale loss, color, structure) | (1) Resolution: Satellite data is often too coarse for microclimates (e.g., 10 km grid can’t resolve street-level variations) (2) Indirect: Remote sensing sees symptoms (like discoloration), needing expert interpretation to link to actual corrosion (3) Technical needs: Specialized skills for data processing (LiDAR, SAR, etc.), not always available to heritage teams (4) Costs: High-end imaging (e.g., satellite tasking, LIDAR flights) can be costly | [77,78,79] |
| Machine Learning Models | Data-driven models use historical data to predict corrosion; inputs are environmental time series; outputs are past corrosion data; methods: neural networks, random forests, etc. | (1) Complexity: Models non-linear interactions (thresholds, synergies) missed by linear DRFs (2) Adaptive: Learns and improves with more data, tailored to site or material (3) High-dimensional: Can include new data types (spectral data, images) for holistic predictions (4) Scenario flexibility: Once trained, can test any hypothetical scenario rapidly | (1) Data hungry: Needs lots of historical corrosion data, often missing for heritage sites (2) Black box: Hard to explain predictions, less intuitive than formulas—can reduce trust (3) Overfitting: Risks poor performance in new conditions if it learns spurious patterns (4) Limited adoption: Still experimental, not yet part of standards for cultural heritage | [66,67,68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Z.; Yan, Y. Dose–Response Functions for Assessing Corrosion Risks to Urban Heritage Materials from Air Pollution Under Climate Change: Insights from Europe and China. Buildings 2025, 15, 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132271
Bai Z, Yan Y. Dose–Response Functions for Assessing Corrosion Risks to Urban Heritage Materials from Air Pollution Under Climate Change: Insights from Europe and China. Buildings. 2025; 15(13):2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132271
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Zhe, and Yu Yan. 2025. "Dose–Response Functions for Assessing Corrosion Risks to Urban Heritage Materials from Air Pollution Under Climate Change: Insights from Europe and China" Buildings 15, no. 13: 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132271
APA StyleBai, Z., & Yan, Y. (2025). Dose–Response Functions for Assessing Corrosion Risks to Urban Heritage Materials from Air Pollution Under Climate Change: Insights from Europe and China. Buildings, 15(13), 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132271




