Improving Drying Shrinkage Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers by Adding Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Design of Mix Proportion
2.3. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Result Analysis
3.2. Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus
3.3. Reaction Heat Test Results
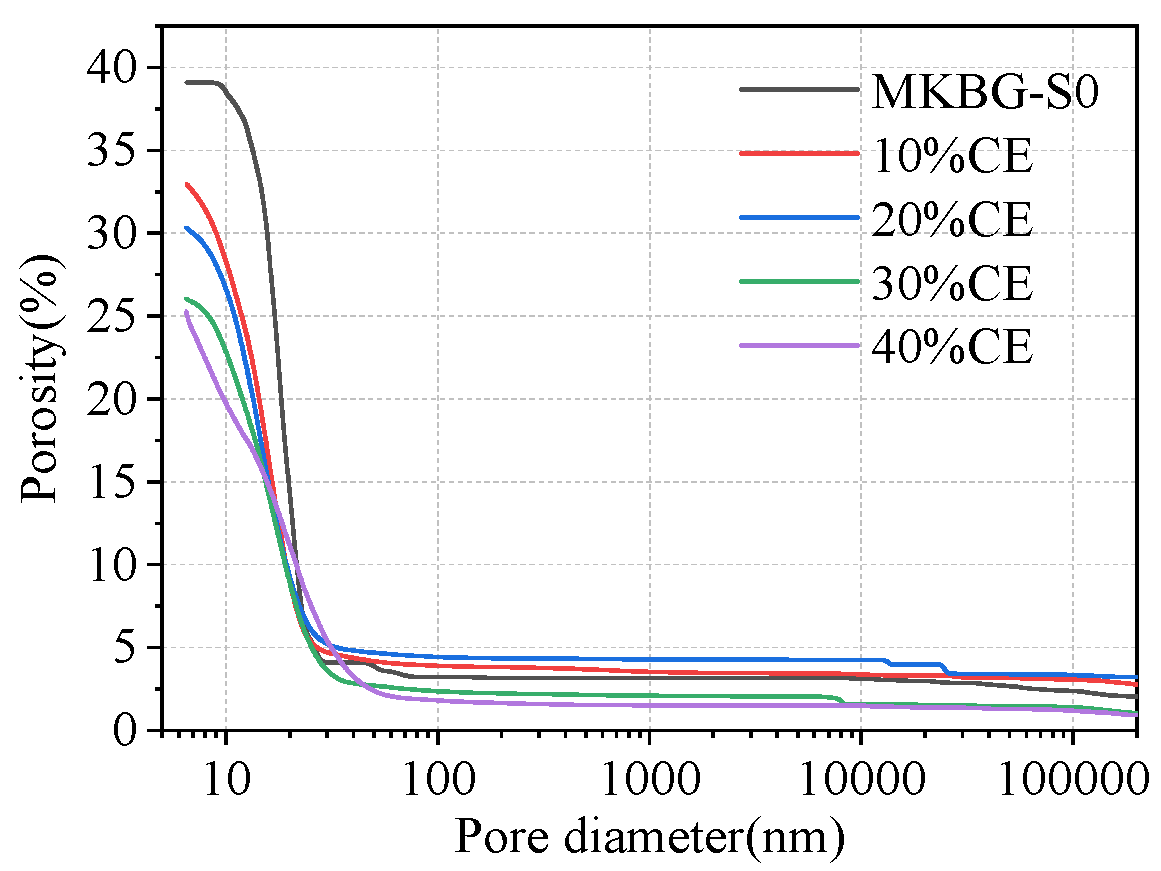
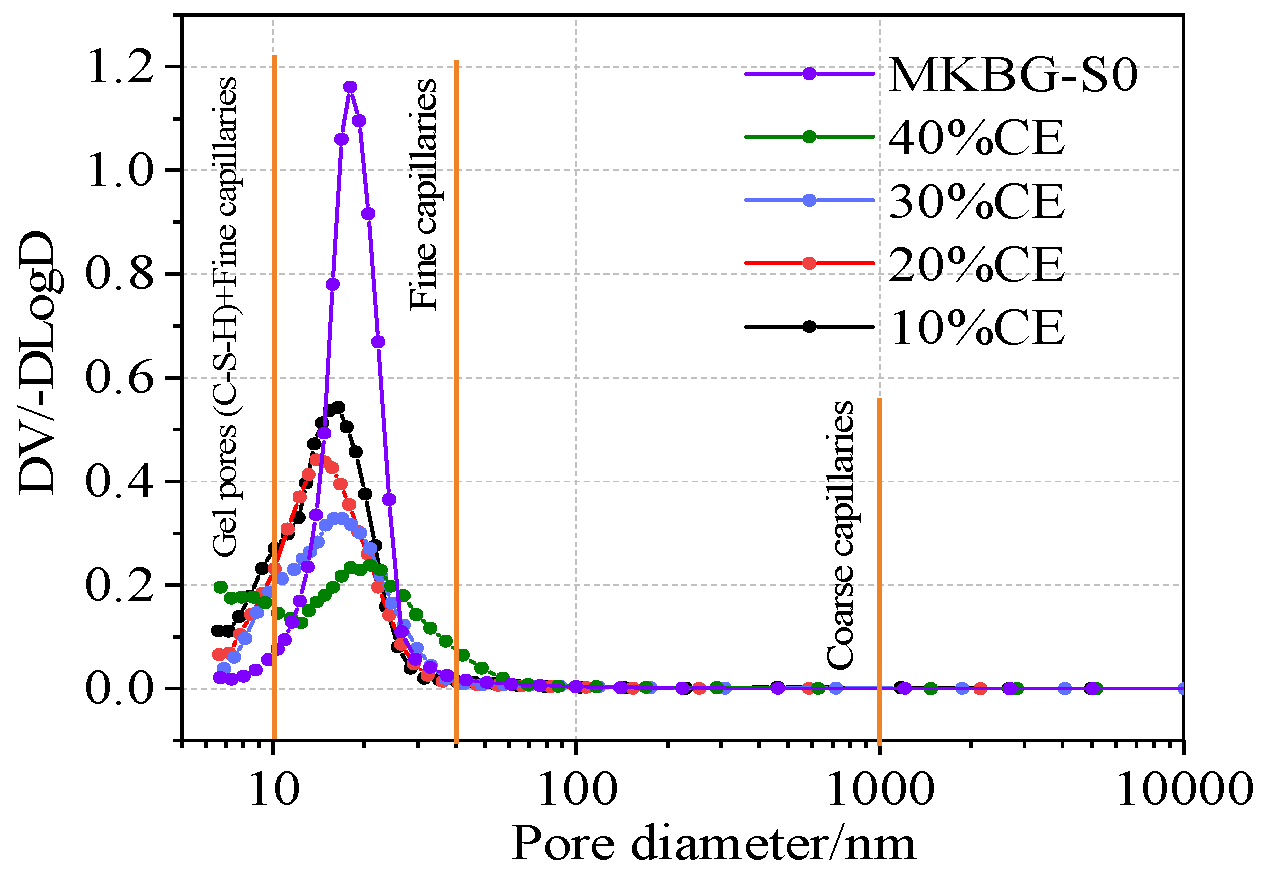
3.4. Pore Structure Characteristics
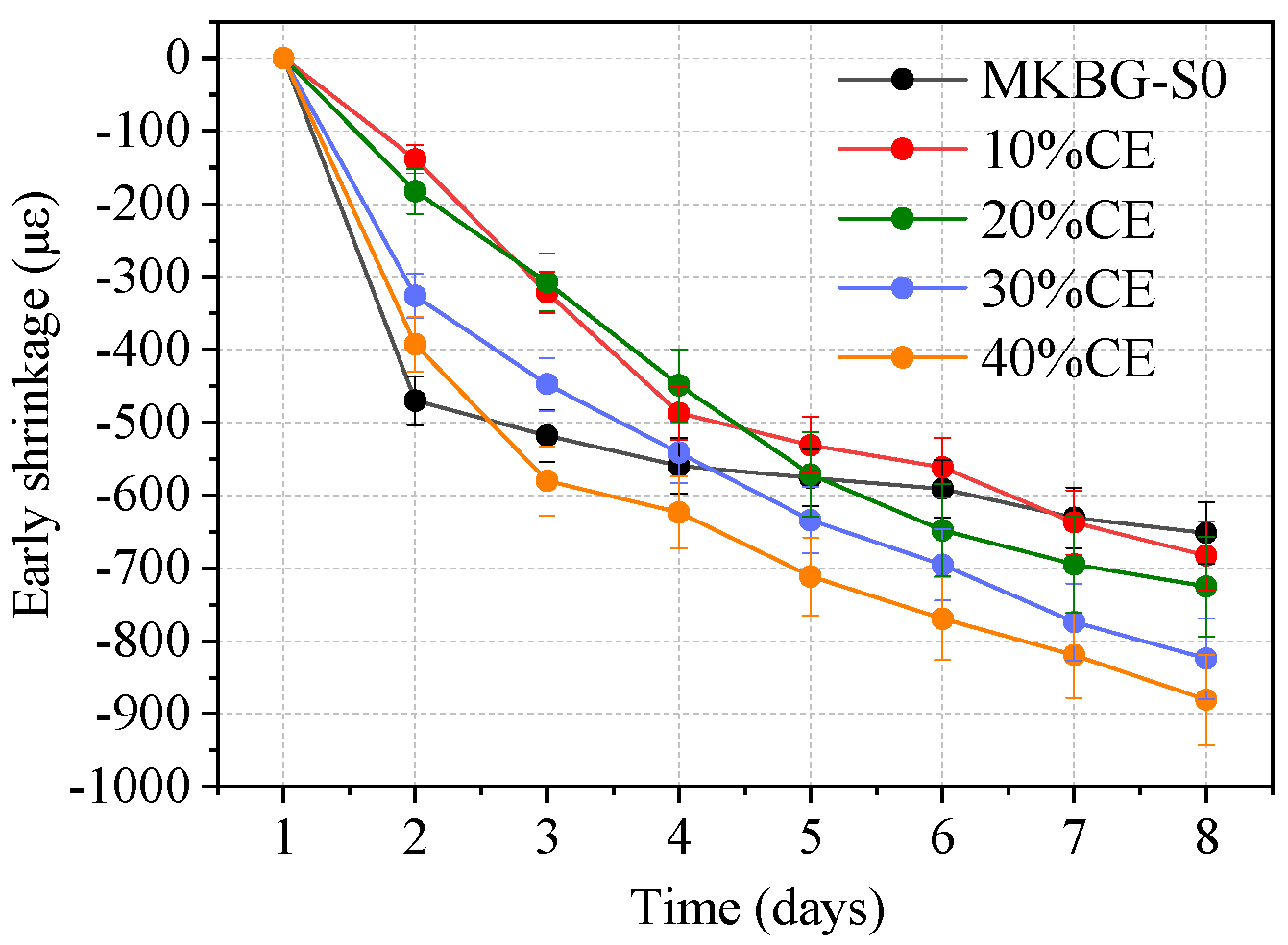
3.5. Early Shrinkage Results
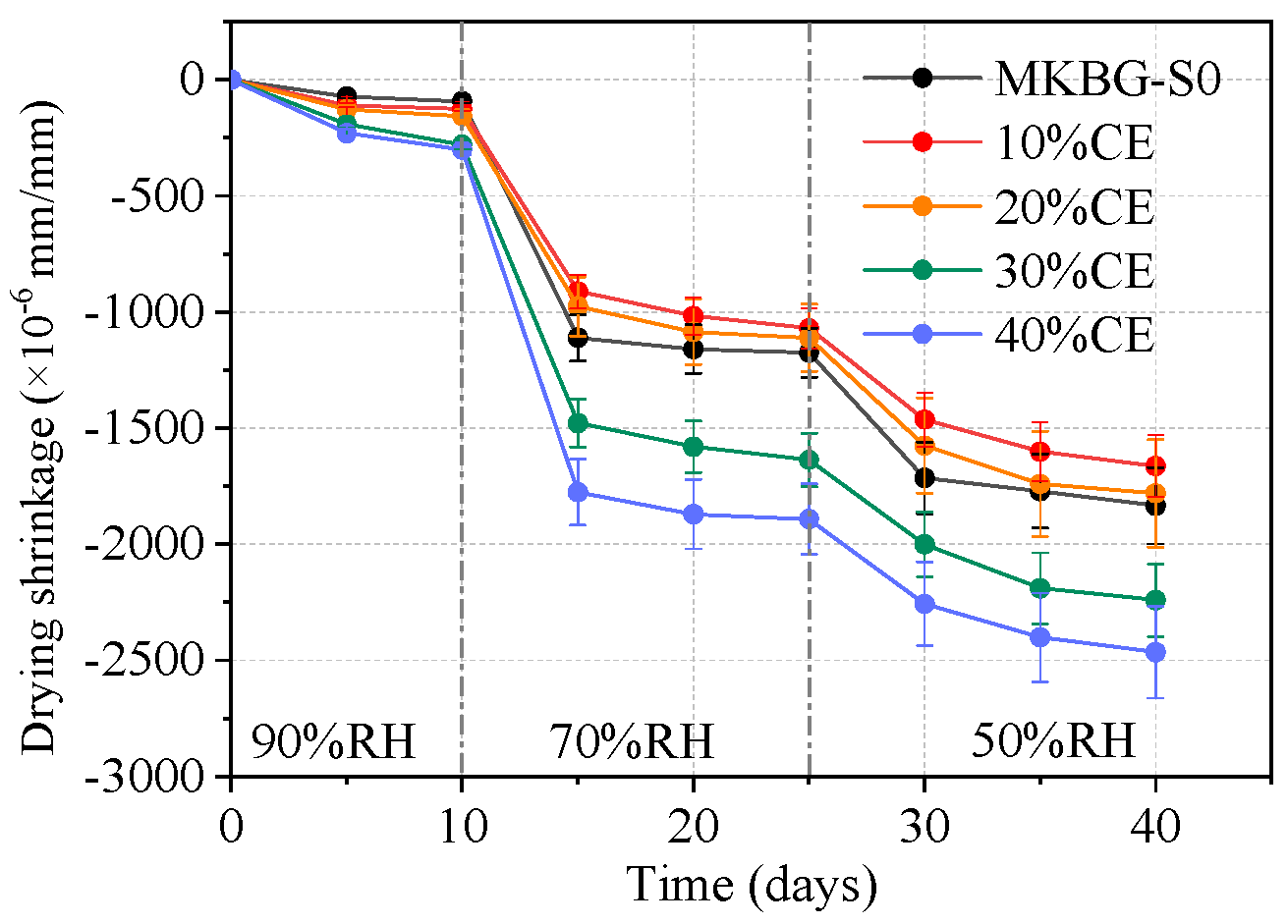
3.6. Dry Shrinkage Results Under Varying Humidity Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assi, L.N.; Deaver, E.E.; ElBatanouny, M.K.; Ziehl, P. Investigation of early compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesala, C.R.; Verma, N.K.; Kumar, S. Critical review on fly-ash based geopolymer concrete. Struct. Concr. 2020, 21, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T. Resistance of geopolymer materials to acid attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Mechanical activation of fly ash: Effect on reaction, structure and properties of resulting geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T.; Sanjayan, J.; Cheng, Y.-B. Effect of admixtures on properties of alkali-activated slag concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, D.P.; Geiker, M.R.; Hansen, K.K. Shrinkage-reducing admixtures and early-age desiccation in cement pastes and mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radlinska, A.; Rajabipour, F.; Bucher, B.; Henkensiefken, R.; Sant, G.; Weiss, J. Shrinkage Mitigation Strategies in Cementitious Systems: A Closer Look at Differences in Sealed and Unsealed Behavior. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2008, 2070, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Lura, P.; Rajabipour, F.; Sant, G. Performance of Shrinkage-Reducing Admixtures at Different Humidities and at Early Ages. ACI Mater. J. 2008, 105, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R.A.; MacKenzie, K.J.; Nicholson, C.L.; Shimada, S. The composition range of aluminosilicate geopolymers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallah, S.E.; Rangan, B.V. Low-Calcium Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete: Long Term Properties; Research Report GC2; Faculty of Engineering, Curtin University of Technology: Perth, Australia, 2006; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11937/34322 (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Ding, Z.Y.; Sui, Z.T. Research on Shrinkage of Slag-based Geopolymer Concrete. Mater. Rev. 2010, 24, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Gu, K.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Strength and drying shrinkage of reactive MgO modified alkali-activated slag paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-H.; Chen, W.; Lu, Z.-A.; Chen, H. Shrinkage compensation of alkali-activated slag concrete and microstructural analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers and geopolymeric materials. J. Therm. Anal. 1989, 35, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadifar, M.; Ukrainczyk, N.; Koenders, E. Atomistic Insights into Silicate Dissolution of Metakaolinite under Alkaline Conditions: Ab Initio Quantum Mechanical Investigation. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2024, 40, 19332–19342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.M.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zuo, Y.B.; Chen, W.; Ye, G. Chemical deformation of metakaolin based geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 120, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudert, F.-X.; Cailliez, F.; Vuilleumier, R.; Fuchs, A.H.; Boutin, A. Water nanodroplets confined in zeolite pores. Faraday Discuss. 2009, 141, 377–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ/T 70-2009; Standard for Test Method of Basic Properties of Building Mortar. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 50081-2002; Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- ASTM C1698-09; Standard Test Method for Autogenous Strain of Cement Paste and Mortar. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- JC/T 603-2004; Standard Test Method for Drying Shrinkage of Cement Mortar. China Building Materials Academy Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Wang, Q.; Kang, S.R.; Wu, L.M.; Tang, N.; Zhang, Q. Molecular Simulation of N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H in Geopolymer Cementitious System. J. Build. Mater. 2020, 23, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, B.; San Nicolas, R.; Sani, M.-A.; Rees, G.J.; Hanna, J.V.; van Deventer, J.S.; Provis, J.L. Phase evolution of C- (N) -A-S-H/N-A-S-H gel blends investigated via alkali-activation of synthetic calcium aluminosilicate precursors. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, X. Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Features Different Pore Structure Characteristics from Ordinary Portland Cement Paste: A Mechanistic Study. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Chen, P.; Peng, H.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Su, M. A review and Comparison study on drying shrinkage prediction between alkali-activated fly ash/slag and ordinary Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, D.; Peng, H. Characterization and fractal analysis of drying shrinkage of MKBGs under gradually-decreasing humidity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Oxide/% | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | TiO2 | K2O | Na2O | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metakaolin | 52.53 | 45.42 | 0.26 | - | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.18 | - | 0.6 |
| Cement | 31.59 | 7.6 | 42.43 | 2.33 | - | - | 0.46 | 2.38 | 13.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dong, T.; Chen, Z. Improving Drying Shrinkage Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers by Adding Cement. Buildings 2025, 15, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101650
Li Z, Yang Y, Dong T, Chen Z. Improving Drying Shrinkage Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers by Adding Cement. Buildings. 2025; 15(10):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101650
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhichao, Yiwei Yang, Teng Dong, and Zhijun Chen. 2025. "Improving Drying Shrinkage Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers by Adding Cement" Buildings 15, no. 10: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101650
APA StyleLi, Z., Yang, Y., Dong, T., & Chen, Z. (2025). Improving Drying Shrinkage Performance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymers by Adding Cement. Buildings, 15(10), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101650





