Effect of the Incorporation of 0.1 wt.% TiC on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 Samples Produced by Investment Casting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
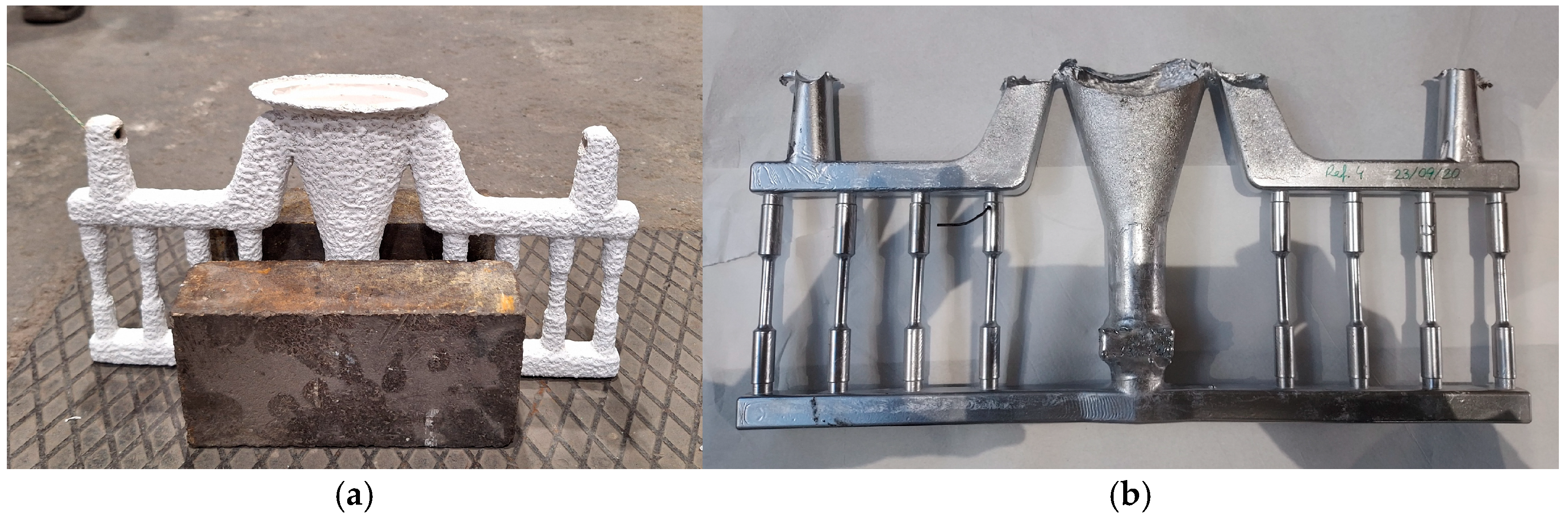
2.2. Samples Fabrication Procedure
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition
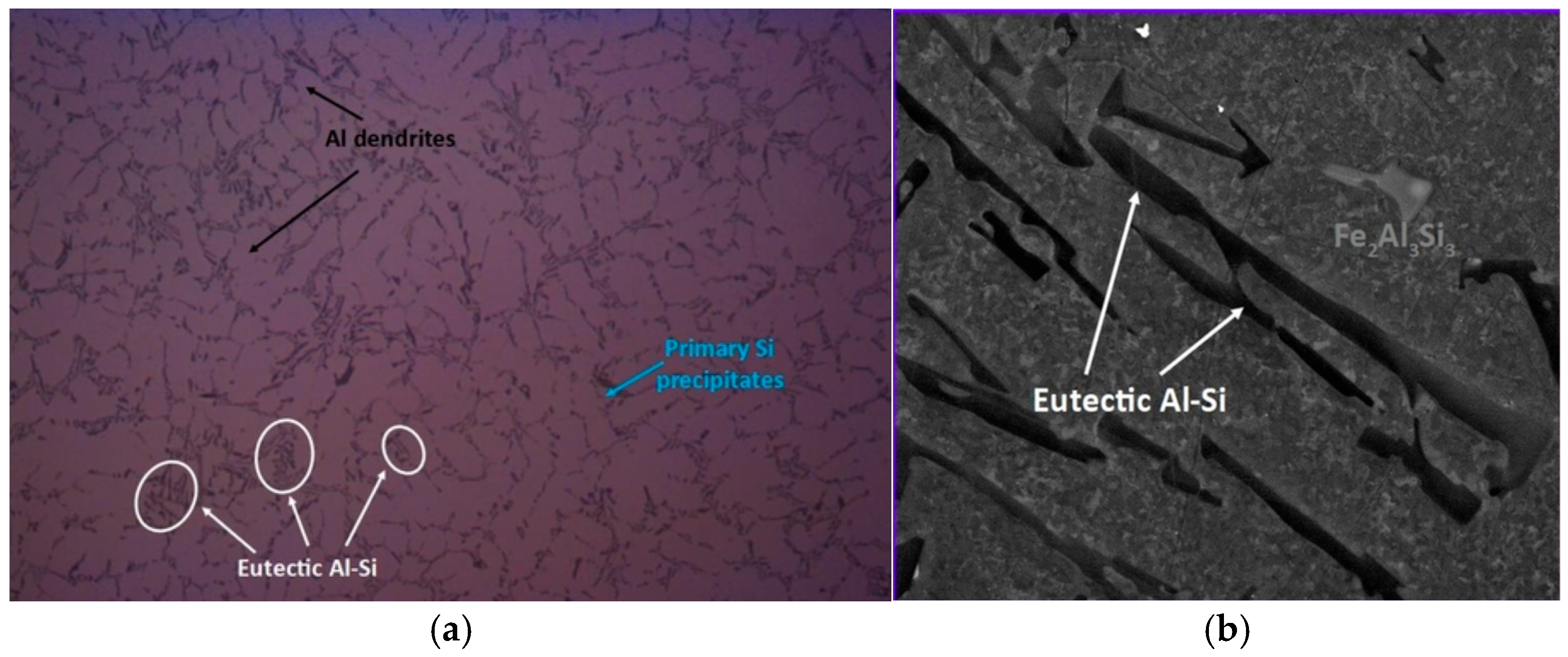
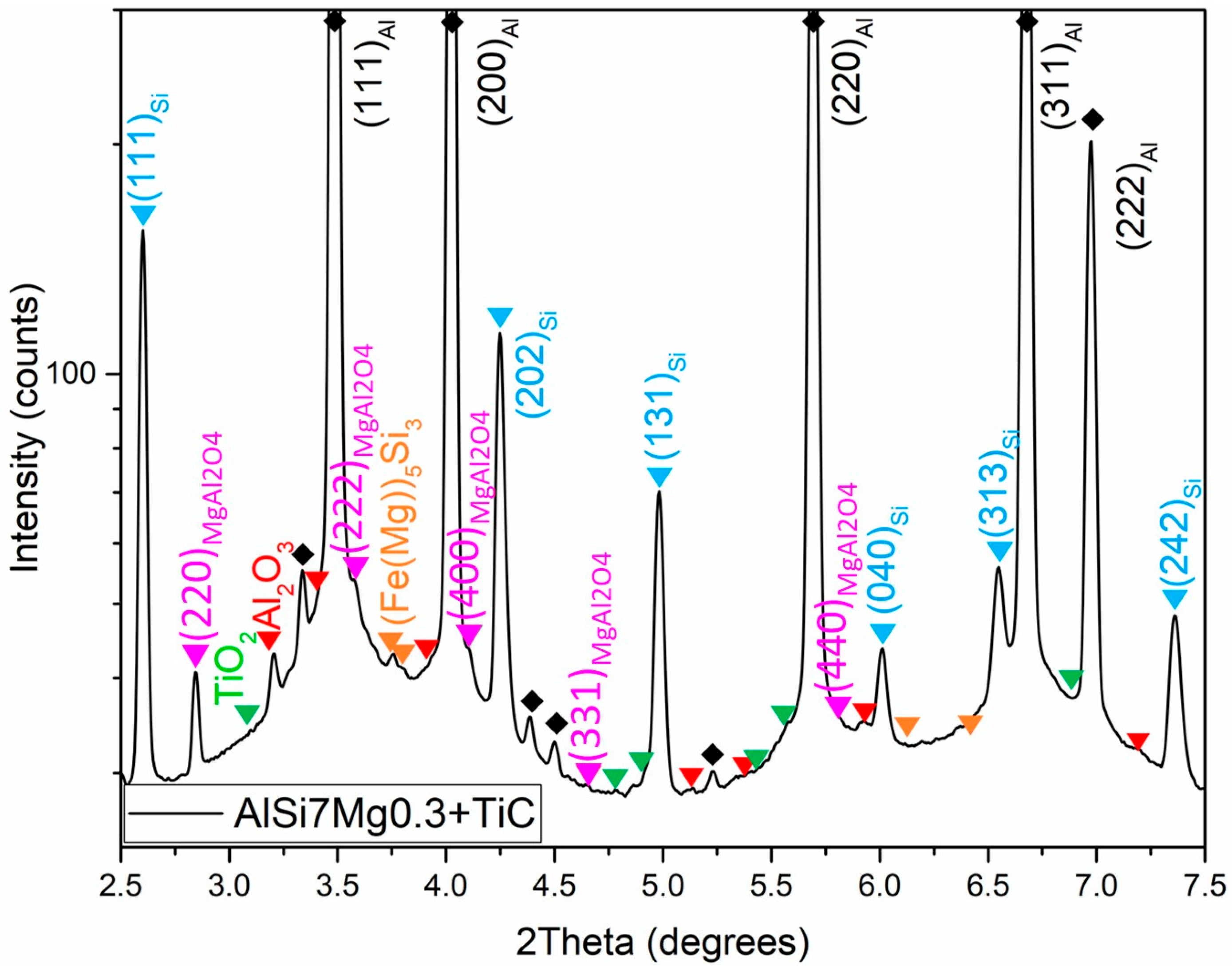
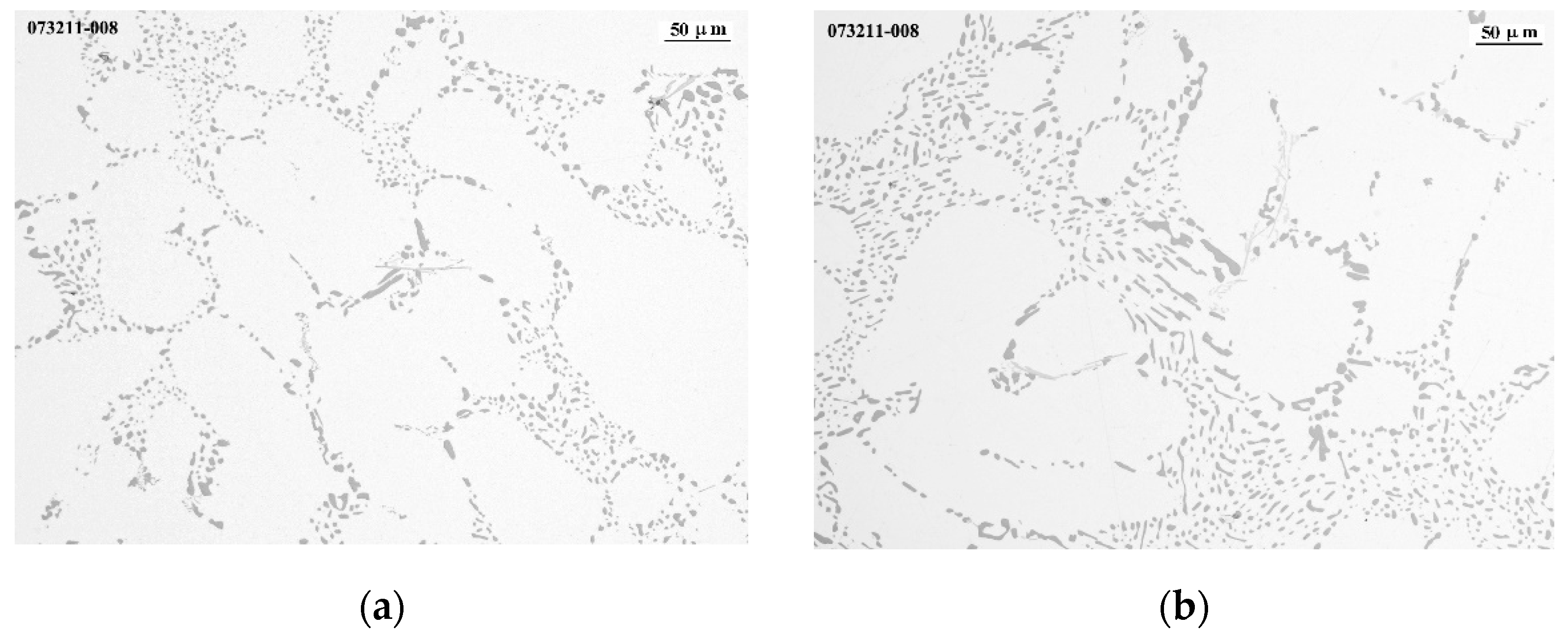
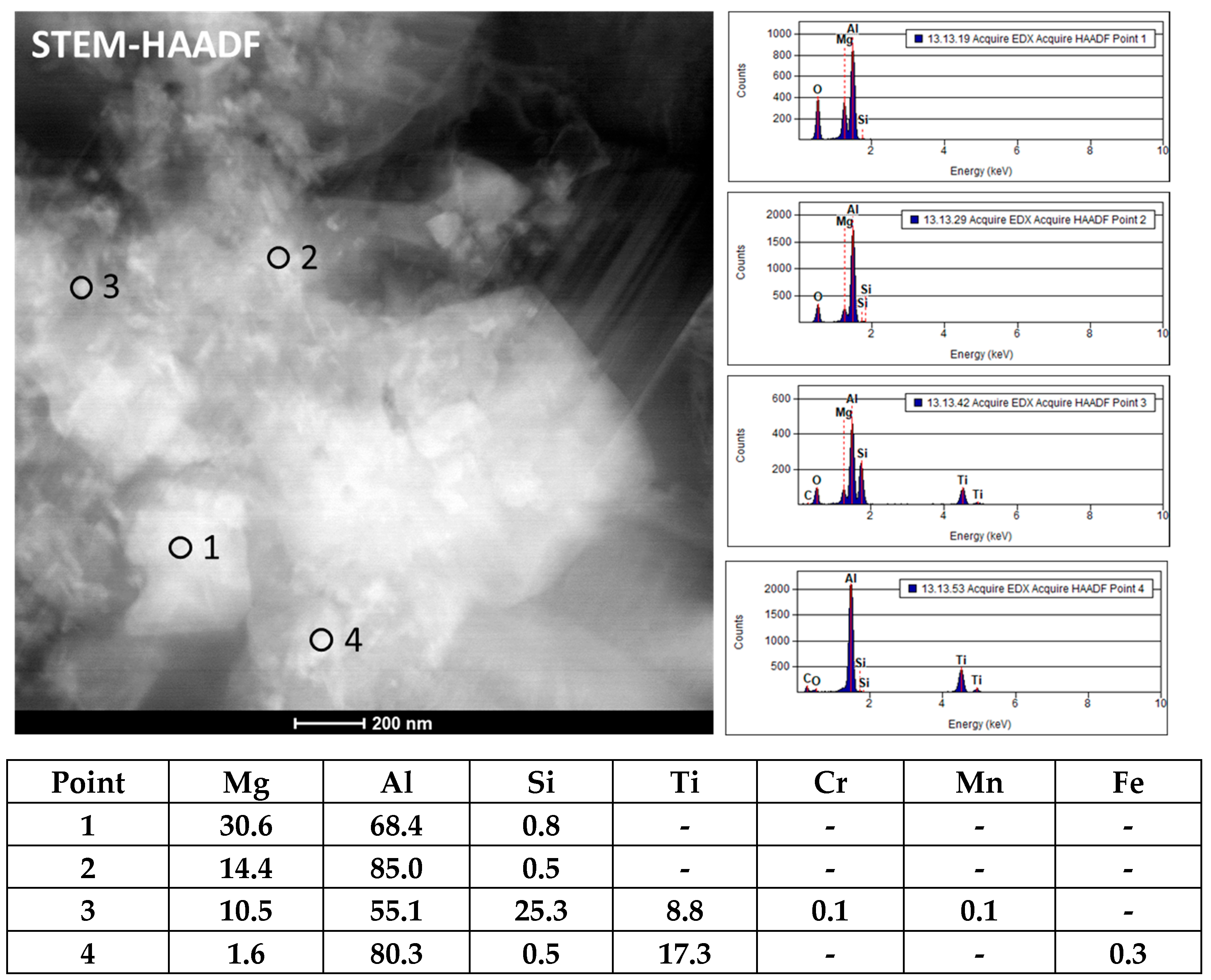
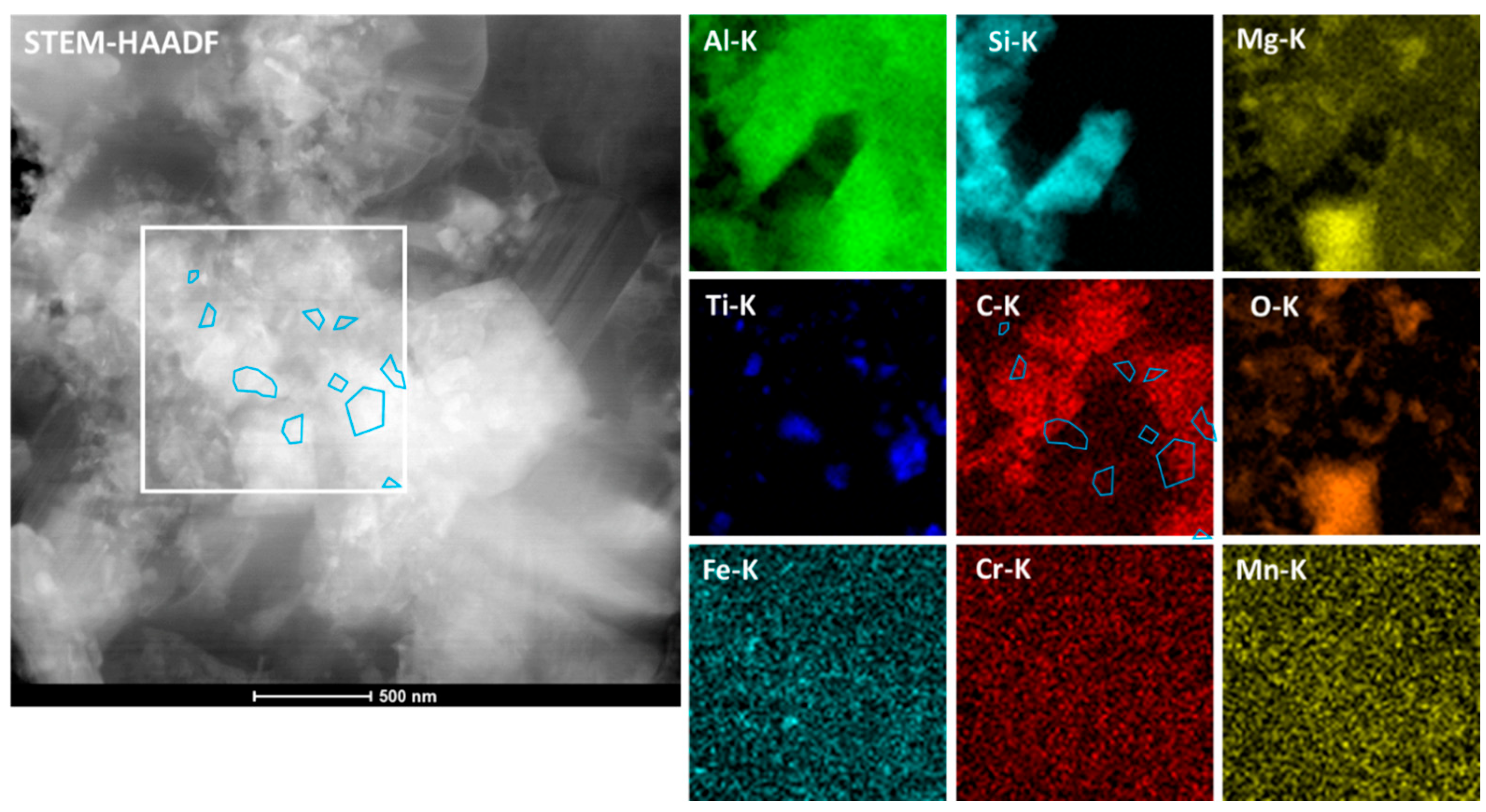
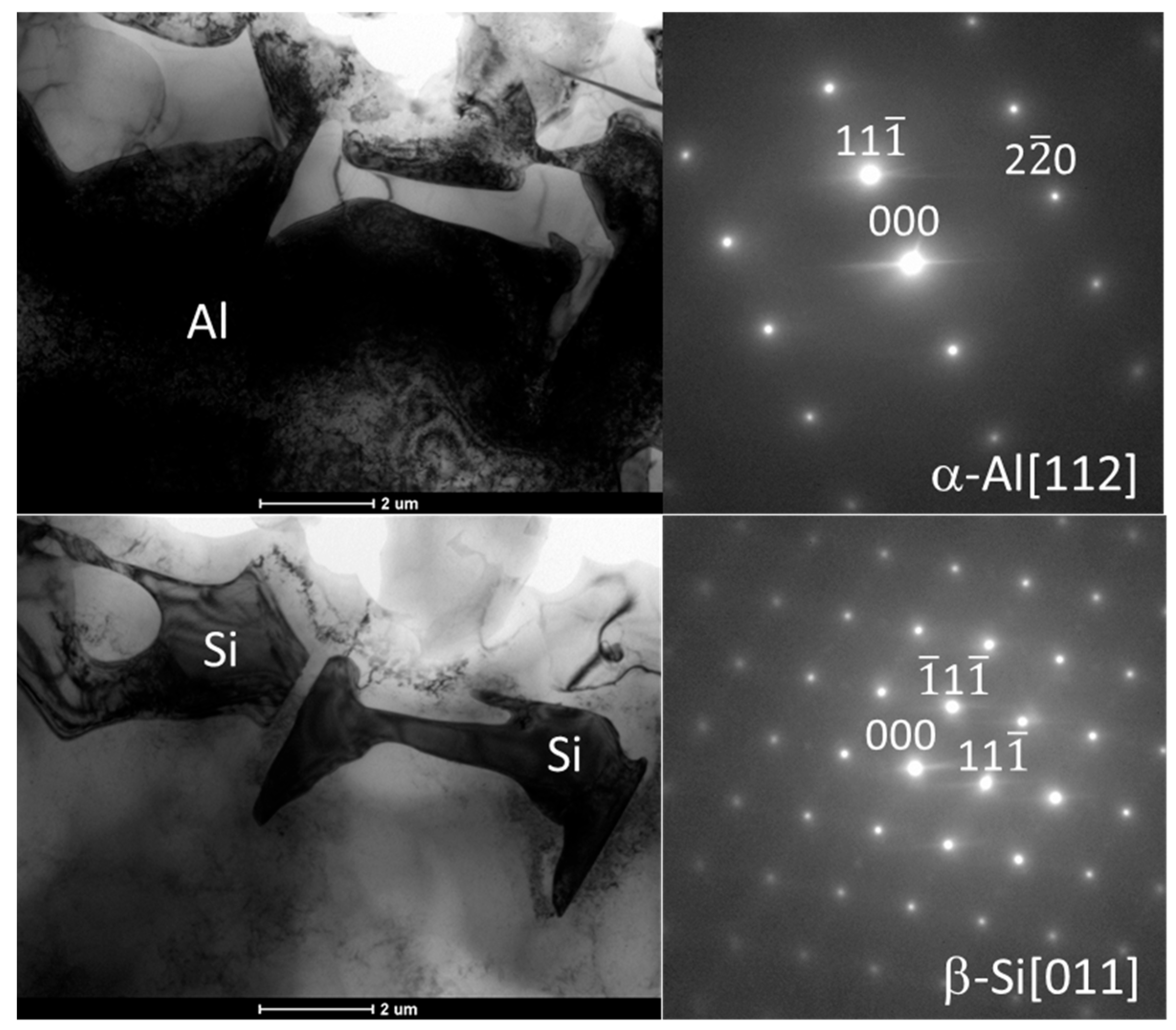
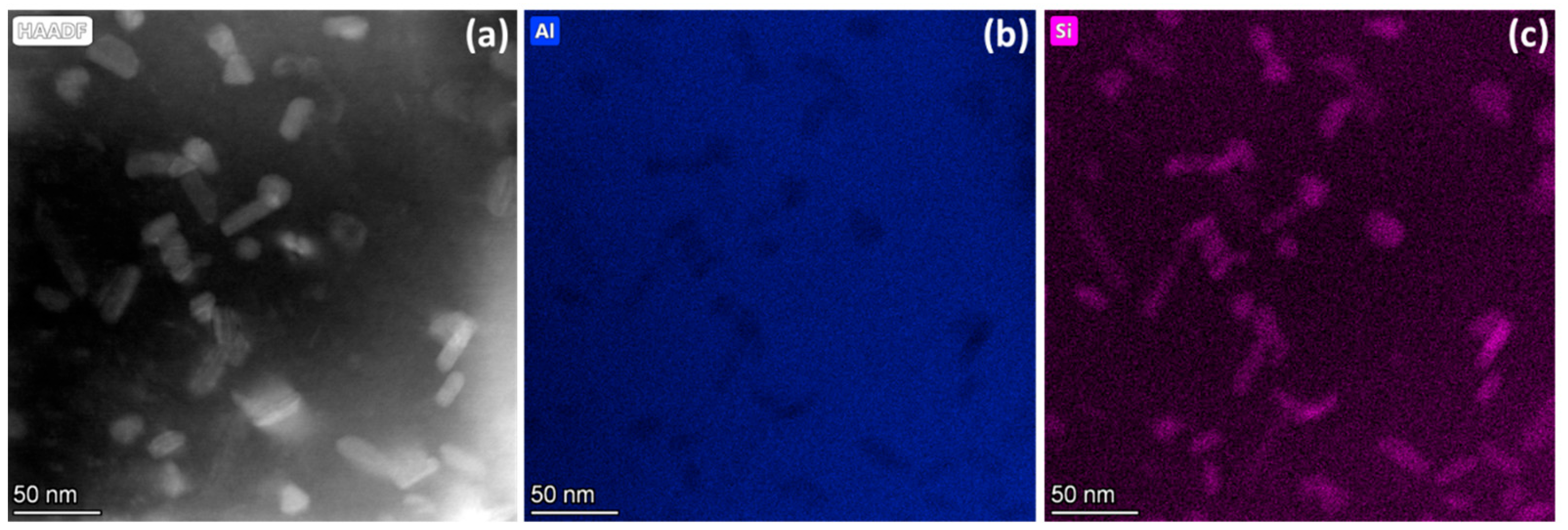
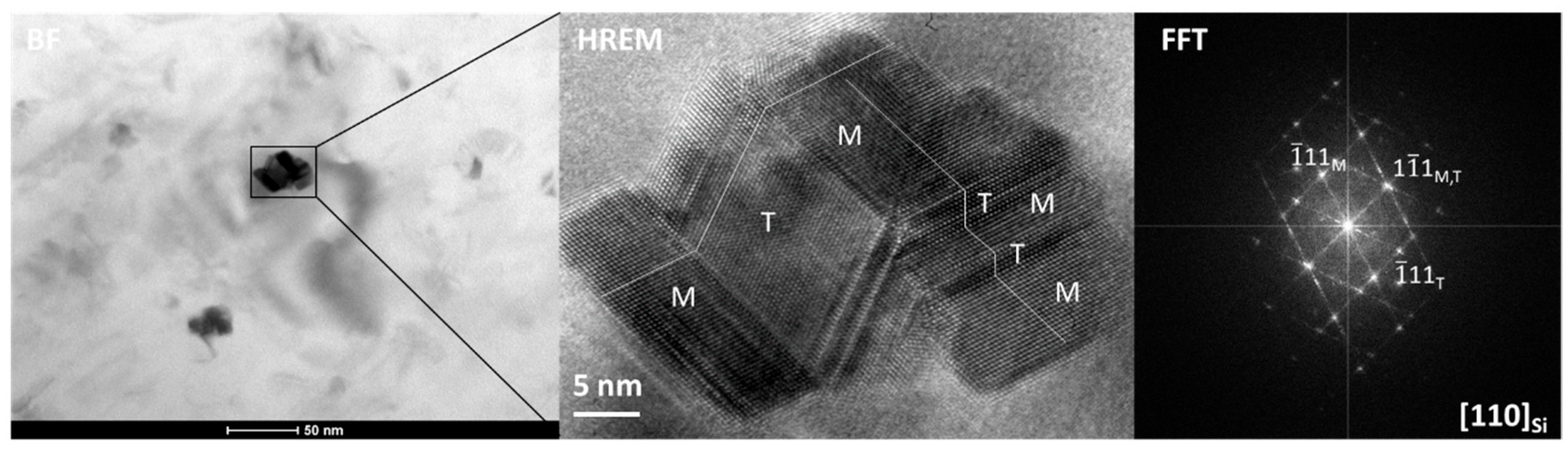
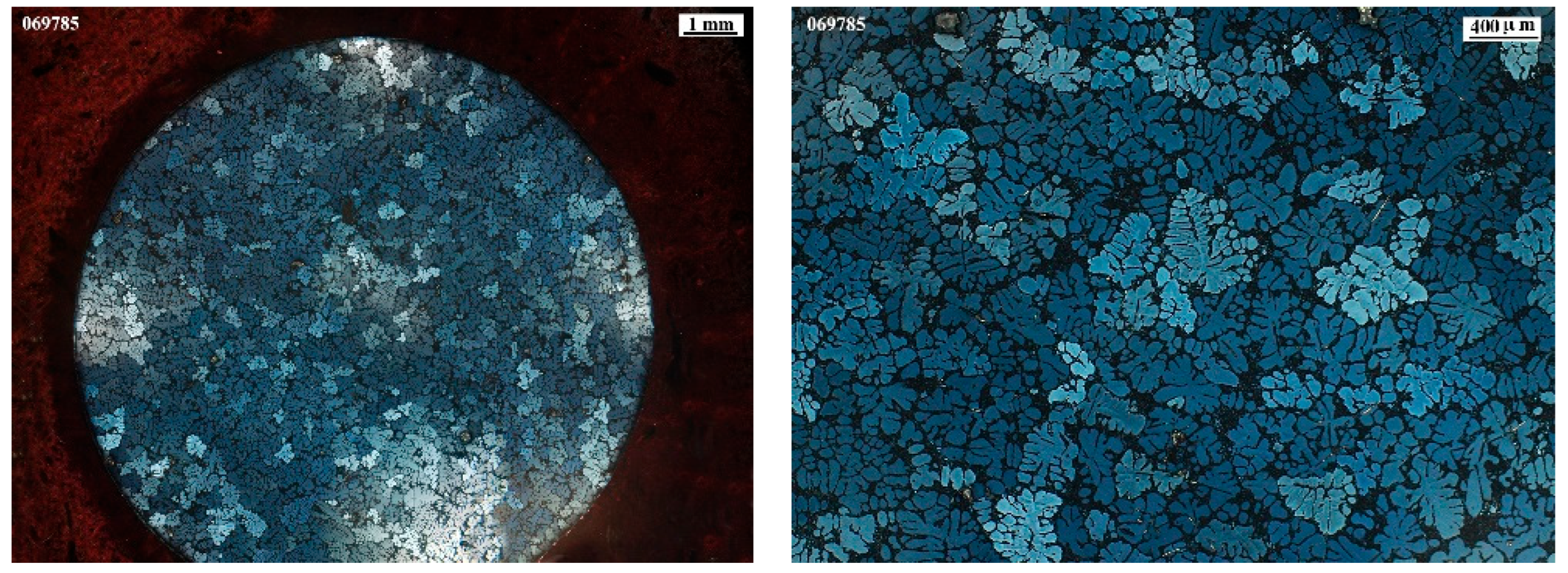
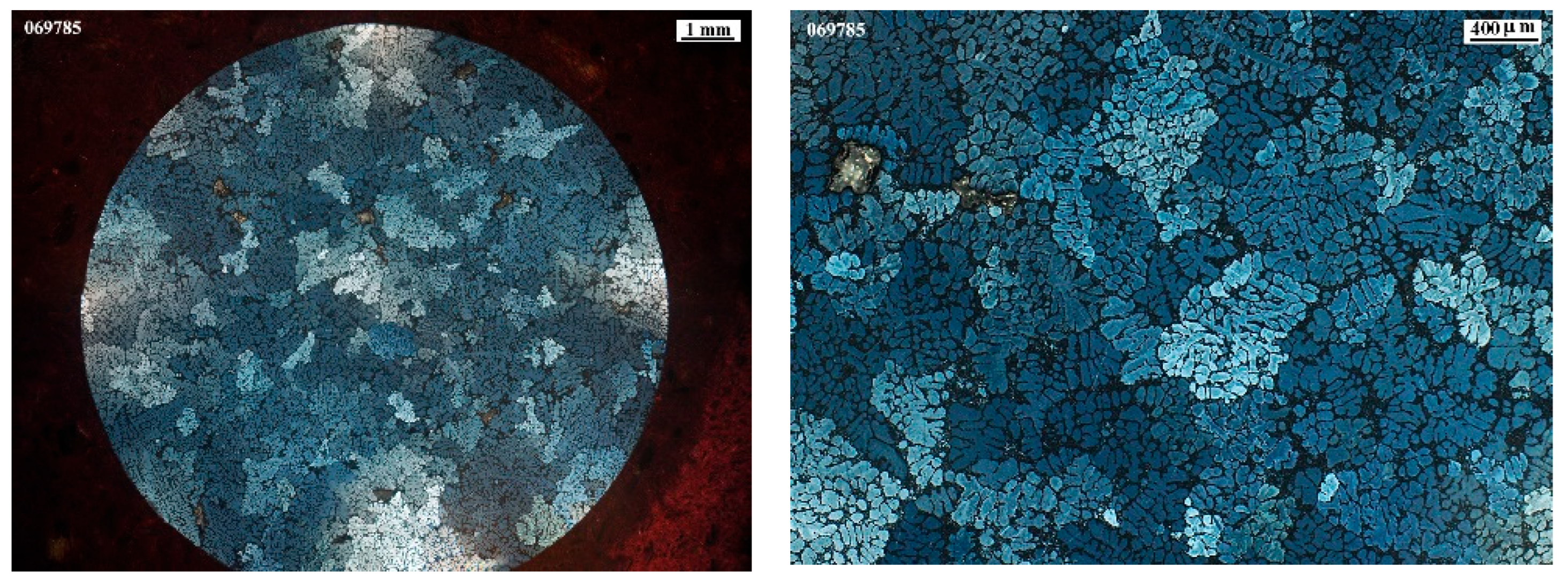
3.2. Microstructural Characterization
3.3. Grain Size Measurement
3.4. Mechanical Properties
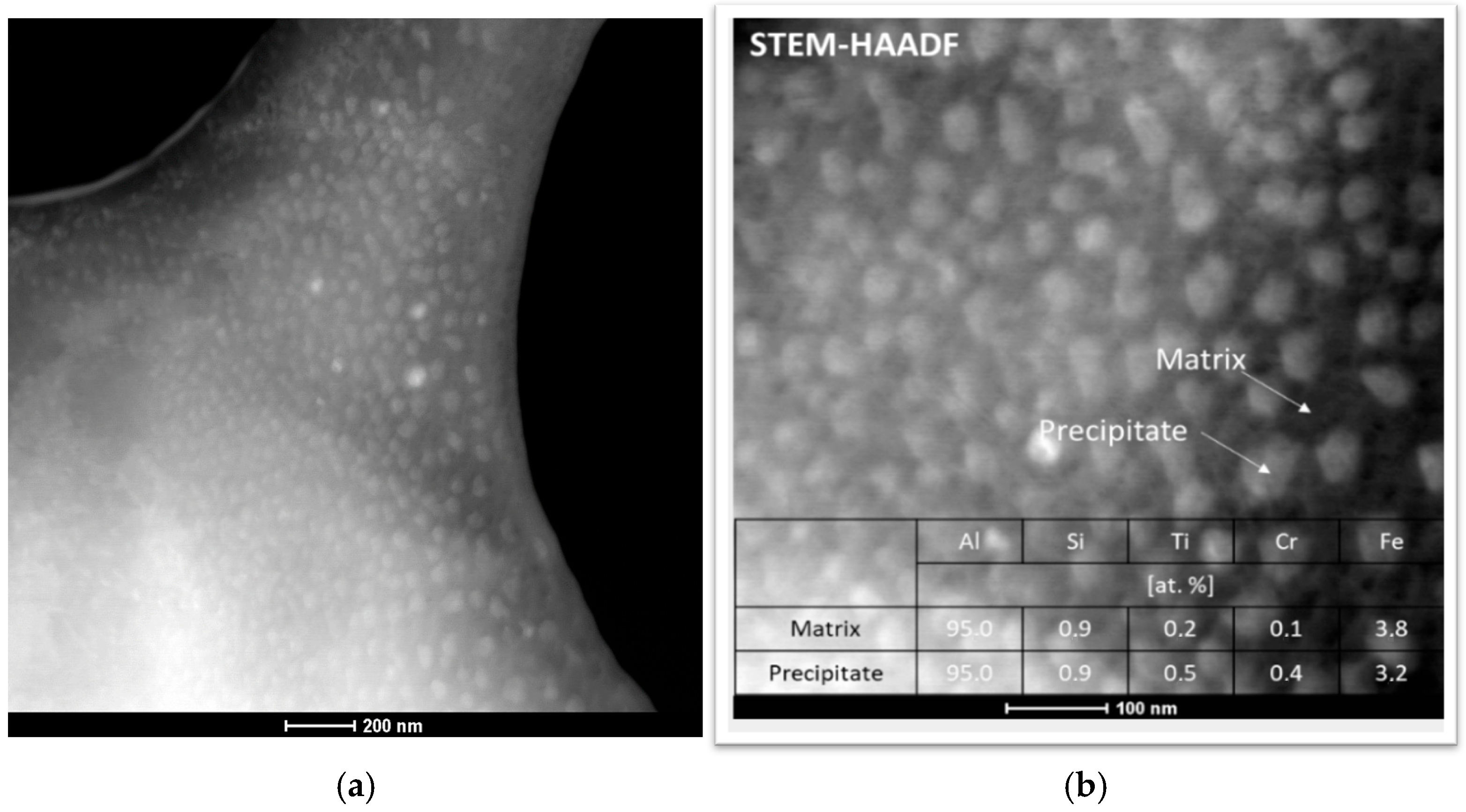
- Areas containing homogeneously distributed spherical precipitates, approximately 50 nm in size and enriched in Ti and Cr (Al 95.5%, Si 0.9%, Ti 0.5%, Cr 0.4%, and Fe 3.2%), were observed. The precise effect of such particle agglomeration on the properties of the final material was not determined; however, these regions may have acted as stress concentration sites (Figure 5).
- Ti particles associated with carbon and measuring 90–120 nm in size were observed. It was not clear whether these were Ti particles or TiC-type particles with different stoichiometry. However, their size was clearly smaller than the original TiC particles used in the study. It appears that the small TiC particles underwent diffusion processes, where Ti and C diffused into the liquid aluminum, affecting their geometrical stability (See Figure 7).
- The presence of primary nanometric β-Si crystals with an average size of 30 nm was confirmed (see Figure 11).
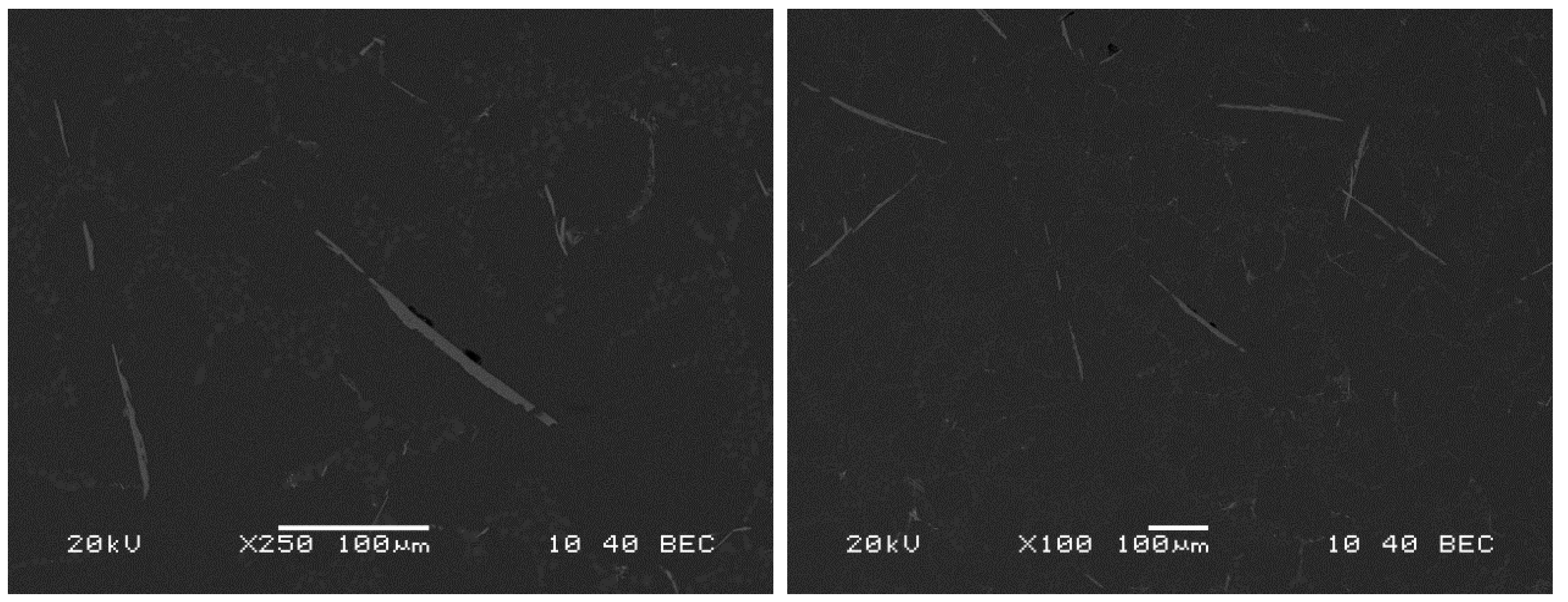
- Presence of complex Ti-Si-Cr-Mg phases with many needle-shaped structures that appear mainly located into the grain boundaries (See Figure 14 below).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koli, D.K.; Agnihotri, G.; Purohit, R. Advanced Aluminium Matrix Composites: The Critical Need of Automotive and Aerospace Engineering Fields. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosselle, F.; Timelli, G.; Bonollo, F. Doe applied to microstructural and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Cu-Mg casting alloys for automotive applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, A. Empirical models of mechanical behaviour of Al-Si-Mg cast alloys for high performance engine applications. Metall. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hockauf, M.; Wagner, M.F.-X.; Hände, M.; Lampke, T.; Siebeck, S.; Wielage, B. High-strength aluminum-based light-weight materials for safety components—Recent progress by microstructural refinement and particle reinforcement. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 103, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ma, Z.; Shan, S.F.; Jia, Y.Z.; Fan, C.Z.; Wang, W.K. Effect of cooling rate on solidified microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminium-A356 alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 207, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.O.; Mazahery, A. Prediction of mechanical properties of cast A356 alloy as a function of microstructure and cooling rate. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2011, 56, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, B.; Pocci, D.; Taccardo, C. Application of traditional investment casting process to aluminium matrix composites. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidari, S.; Patil, A.; Banapurmath, N.; Hallad, S. Effect of Nanoparticle Reinforcement in Metal Matrix for Structural Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 9552–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnamfard, S.; Khosroshahi, R.A.; Brabazon, D.; Mousavian, R.T. Study on the incorporation of ceramic nanoparticles into the semi-solid A356 melt. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 230, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-s.; Yuan, D.; Lü, S.-l.; Hu, K.; An, P. Nano-SiCP particles distribution and mechanical properties of Al-matrix composites prepared by stir casting and ultrasonic treatment. China Foundry 2018, 15, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Vedani, M. Metal matrix composites reinforced by Nano-Particles—A review. Metals 2014, 4, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschini, L.; Dahle, A.; Gupta, M.; Jarfors, A.E.W.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Morri, A.; Rotundo, F.; Toschi, S.; Singh, R.A. Aluminum and Magnesium Metal Matrix Nanocomposites; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodianskiy, K.; Zinigrad, M.; Gedanken, A. Aluminum A356 reinforcement by carbide nanoparticles. J. Nano Res. 2011, 13, 41–46. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JNanoR.13.41 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Ferreira, V.; Egizabal, P.; Popov, V.; de Cortázar, M.G.; Irazustabarrena, A.; López-Sabirón, A.M.; Ferreira, G. Lightweight automotive components based on nanodiamond-reinforced aluminium alloy: A technical and environmental evaluation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 92, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.T.; Koppad, V.; Raju, H.T. Fabrication of Stir Casting Setup for Metal Matrix Composite. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2017, 5, 944–949. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E8/E8M-24; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024; Volume 3, pp. 1–35. [CrossRef]
- UNE-EN ISO 643:2024; Aceros: Determinación Micrográfica del Tamaño de Grano Aparente. Comité Técnico CTN36 Siderurgia: Madrid, Spain, 2024.
- Singh, S.; Pal, K. Influence of surface morphology and UFG on damping and mechanical properties of composite reinforced with spinel MgAl2O4-SiC core-shell microcomposites. Mater. Charact. 2017, 123, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, N.; Shi, C.; Liu, E.; Du, X.; He, C. Microstructure and properties of in situ generated MgAl2O4 spinel whisker reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, N.; Shi, C.; Liu, E.; Du, X.; He, C. In-situ processing and aging behaviors of MgAl2O4 spinel whisker reinforced 6061Al composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 598, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; García, R.; Verduzco, J.A. Efecto del Si en la estabilidad térmica del Tic en aluminio fundido. Rev. Latinoam. Metal. Mater. 2012, 32, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, H.; Xiao, W.; Li, H.; Fu, Y.; Yi, G.; Qie, J.; Ma, X.; Ma, C. Effects of submicron-sized TiC particles on the microstructure modification and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahallawi, I.; Abdelkader, H.; Yousef, L.; Amer, A.; Mayer, J.; Schwedt, A. Influence of Al2O3 nano-dispersions on microstructure features and mechanical properties of cast and T6 heat-treated Al Si hypoeutectic Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Awaji, H. Nanocomposites—A new material design concept. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahallawi, I.S.; Shash, Y.; Eigenfeld, K.; Mahmoud, T.S.; Ragaie, R.M.; Shash, A.Y.; El Saeed, M.A. Influence of nanodispersions on strength-ductility properties of semisolid cast A356 Al alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazahery, A.; Abdizadeh, H.; Baharvandi, H.R. Development of high-performance A356/nano-Al2O3 composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 518, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Ezatpour, H.R.; Beygi, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Al2O3 micro and nano composites fabricated by stir casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8765–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan Hamedan, A.; Shahmiri, M. Production of A356-1wt% SiC nanocomposite by the modified stir casting method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hu, M.; Shi, Q.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Ji, Z. Population dynamics behaviors of TiC and their effect on grain refinement in Al–Ti–C refiners: Growth, agglomeration, nucleation and precipitation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; Verduzco, J.; López, V.H.; García, R.; Verduzco, J.A. Reaction Kinetics for TiC Particles in Molten Aluminium. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332511019 (accessed on 1 October 2025).


| Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Ti | Other | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlSi7Mg0.3 | 7.26 | 0.105 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.262 | <0.1 | 0.12 | <0.02 | Bal. |
| Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Ti | Other | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlSi7Mg0.3 0.1 wt.% TiC | 7.42 | 0.11 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.32 | <0.1 | 0.23 | <0.02 | Bal. |
| Parameter | AlSi7Mg0.3 | AlSi7Mg0.3+TiC |
|---|---|---|
| Total grain area [mm2] | 11.63 | 7.69 |
| Total number of grains | 103 | 48 |
| N [grains per mm2] | 8.856 | 6.242 |
| Grain size number G | 0.147 | −0.358 |
| Material | UTS (MPa) | YS (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlSi7Mg0.3 | 303.25 (3.41) | 231.50 (4.5) | 6.35 (0.88) |
| AlSi7Mg0.3 + 0.1wt.% TiC | 287.0 (5.29) | 220.0 (5.58) | 5.68 (0.82) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Jimenez, A.; Wójcik, A.; Maziarz, W.; Merchán, M.; García de Cortázar, M. Effect of the Incorporation of 0.1 wt.% TiC on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 Samples Produced by Investment Casting. Metals 2026, 16, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16010034
Jimenez A, Wójcik A, Maziarz W, Merchán M, García de Cortázar M. Effect of the Incorporation of 0.1 wt.% TiC on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 Samples Produced by Investment Casting. Metals. 2026; 16(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleJimenez, Ane, Anna Wójcik, Wojciech Maziarz, Mikel Merchán, and Maider García de Cortázar. 2026. "Effect of the Incorporation of 0.1 wt.% TiC on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 Samples Produced by Investment Casting" Metals 16, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16010034
APA StyleJimenez, A., Wójcik, A., Maziarz, W., Merchán, M., & García de Cortázar, M. (2026). Effect of the Incorporation of 0.1 wt.% TiC on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 Samples Produced by Investment Casting. Metals, 16(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16010034






