Comparative Proteomic Insights into the Immune Response of Conogethes punctiferalis Challenged with Beauveria bassiana
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Fungal Infection
2.3. Total Protein Extraction
2.4. Protein Quality Test
2.5. iTRAQ Labeling
2.6. Separation of Fractions
2.7. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis
2.8. Identification and Quantitation of Proteins
2.9. Functional Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
2.10. qRT-PCR Validation
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Quality Control of Proteome
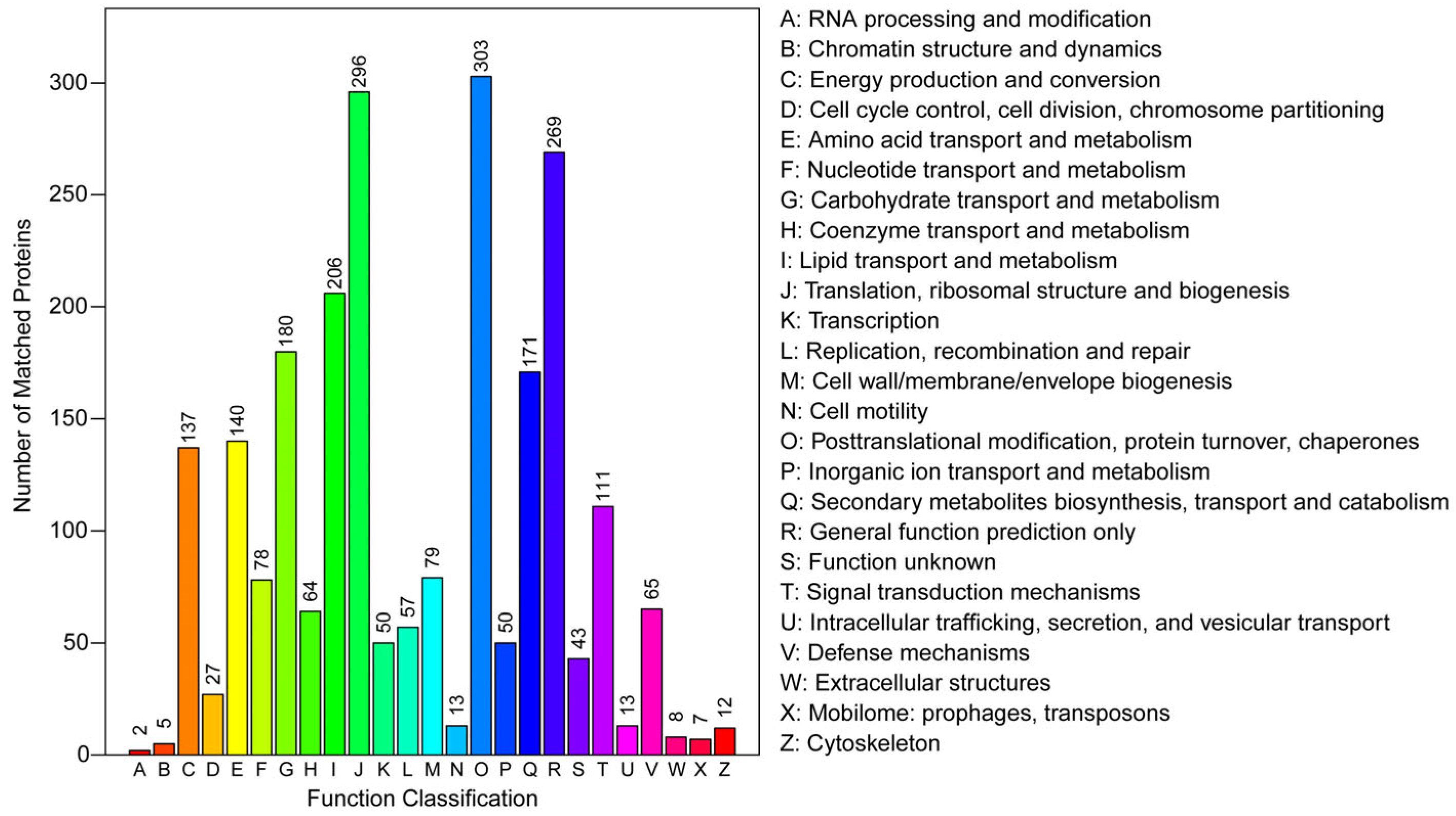
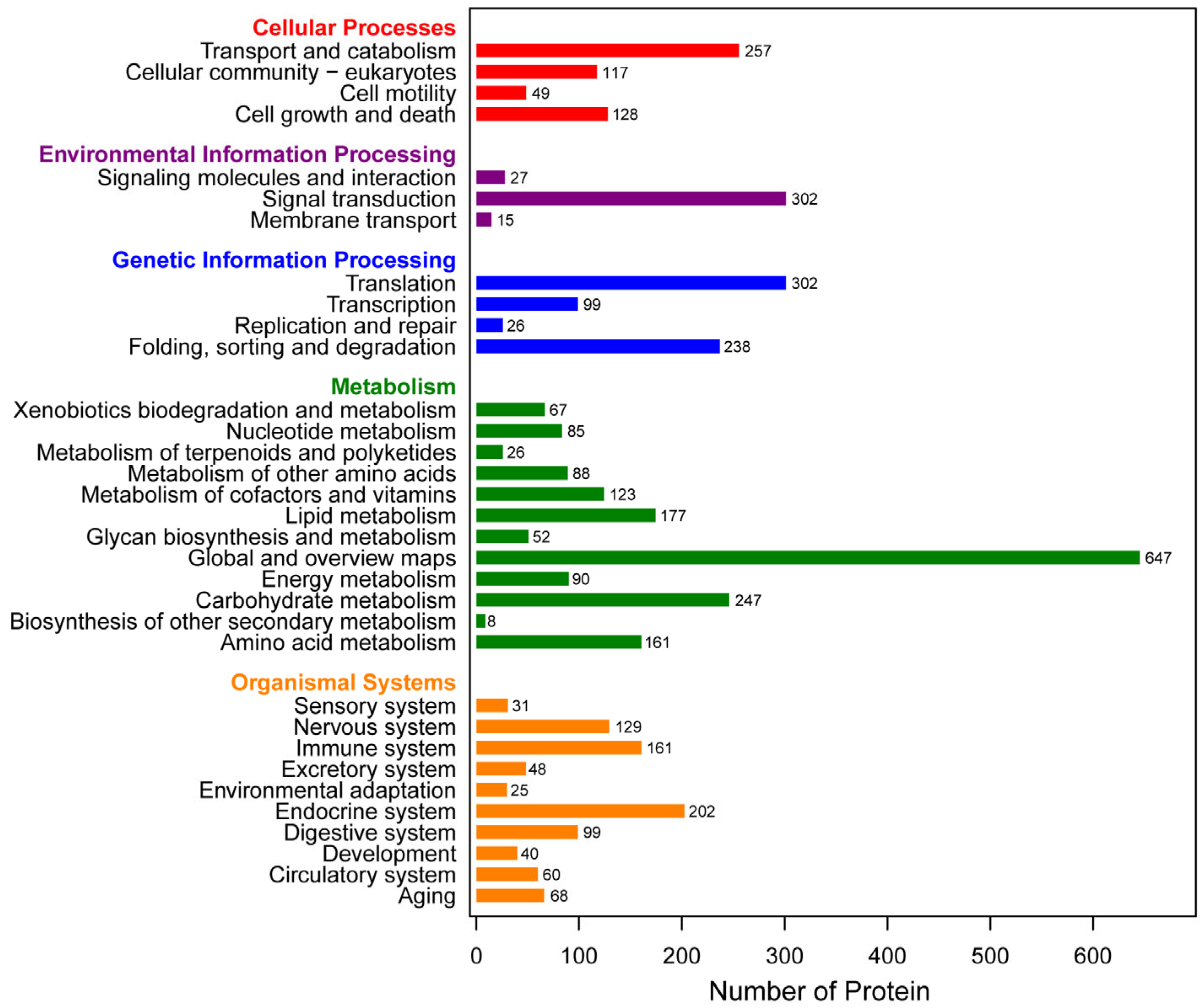
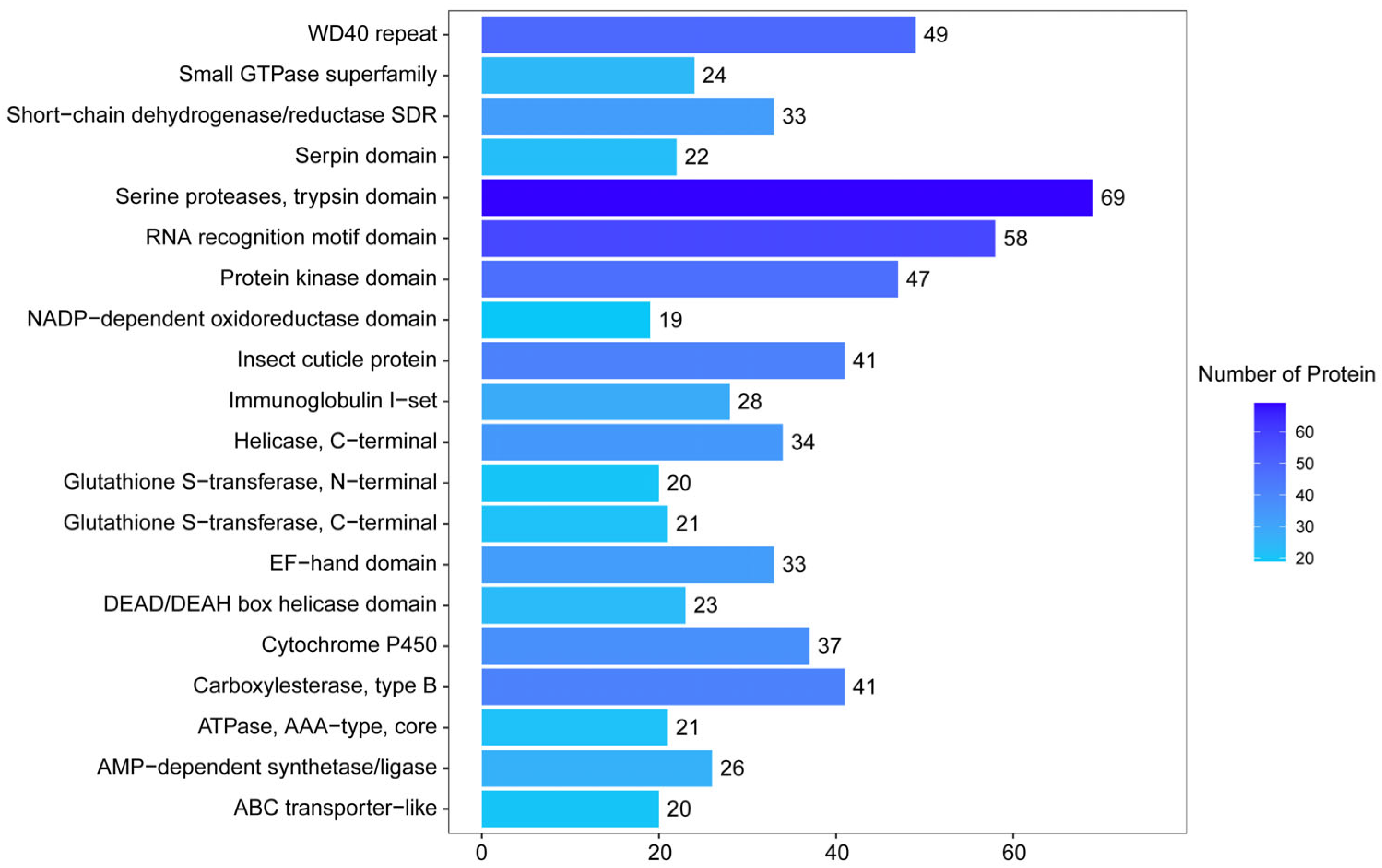
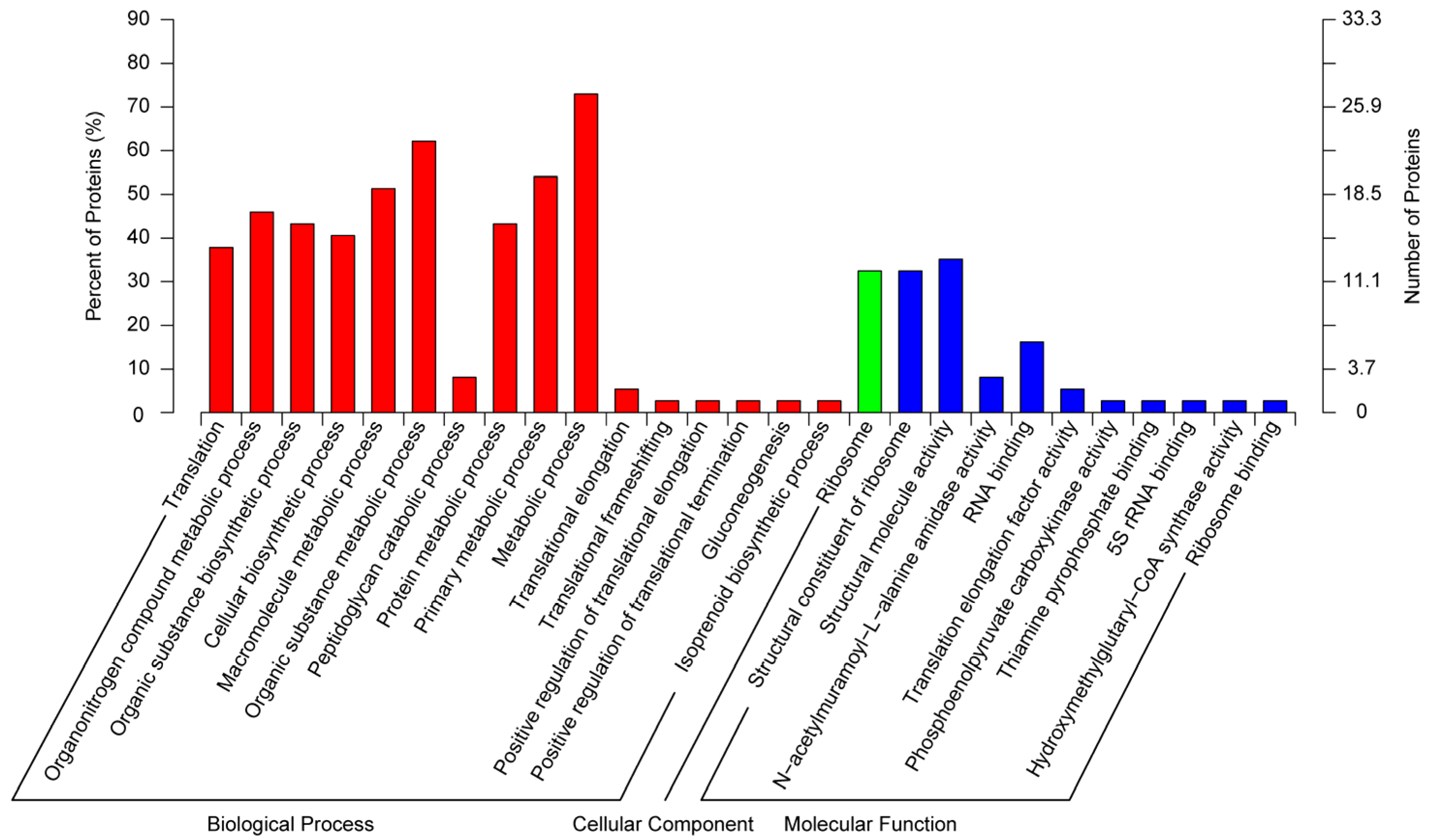
3.2. Functional Annotation and Classification of Proteome
3.3. Identification of the Immune-Related Proteins
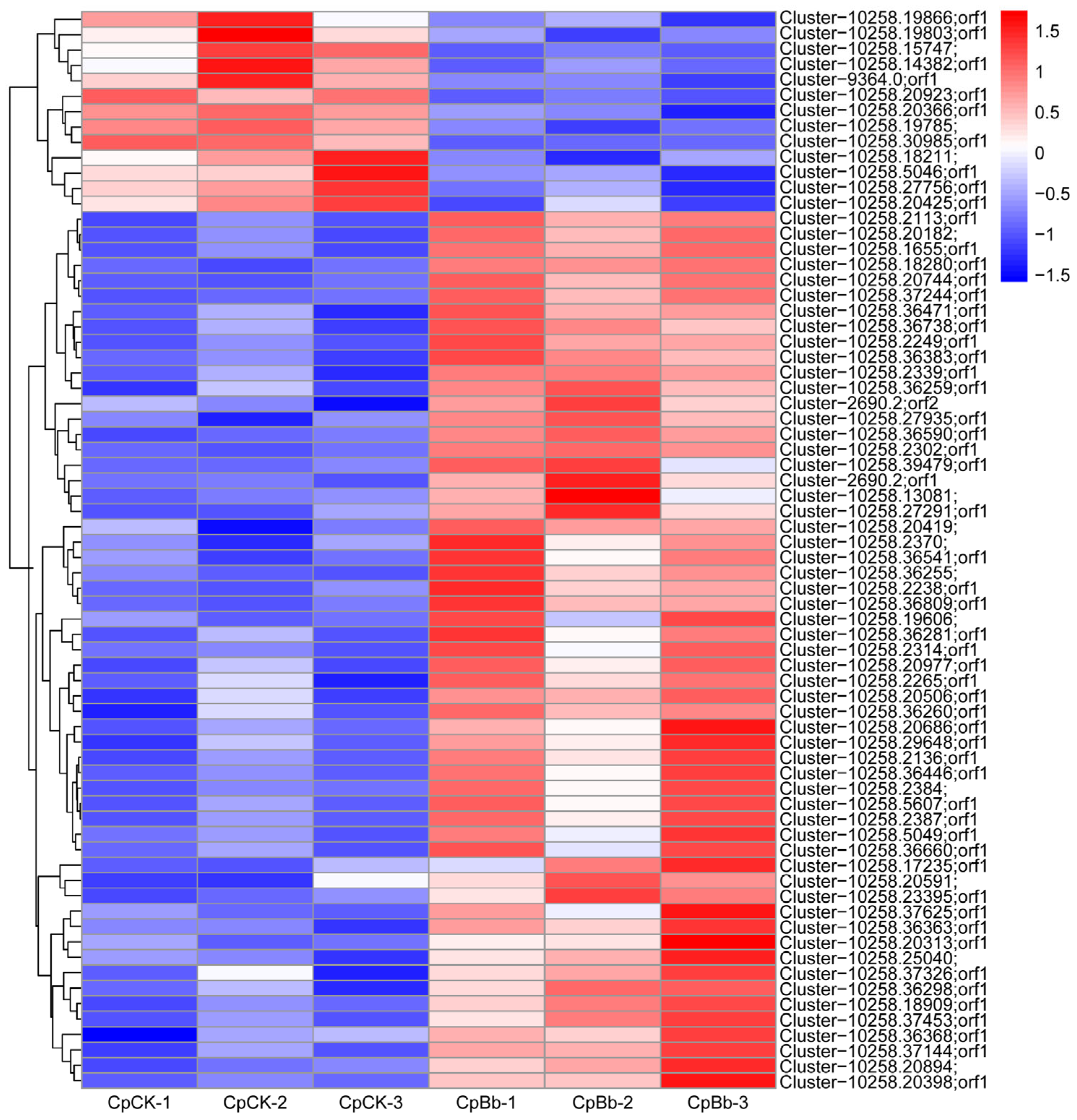
3.4. Statistics of DEPs
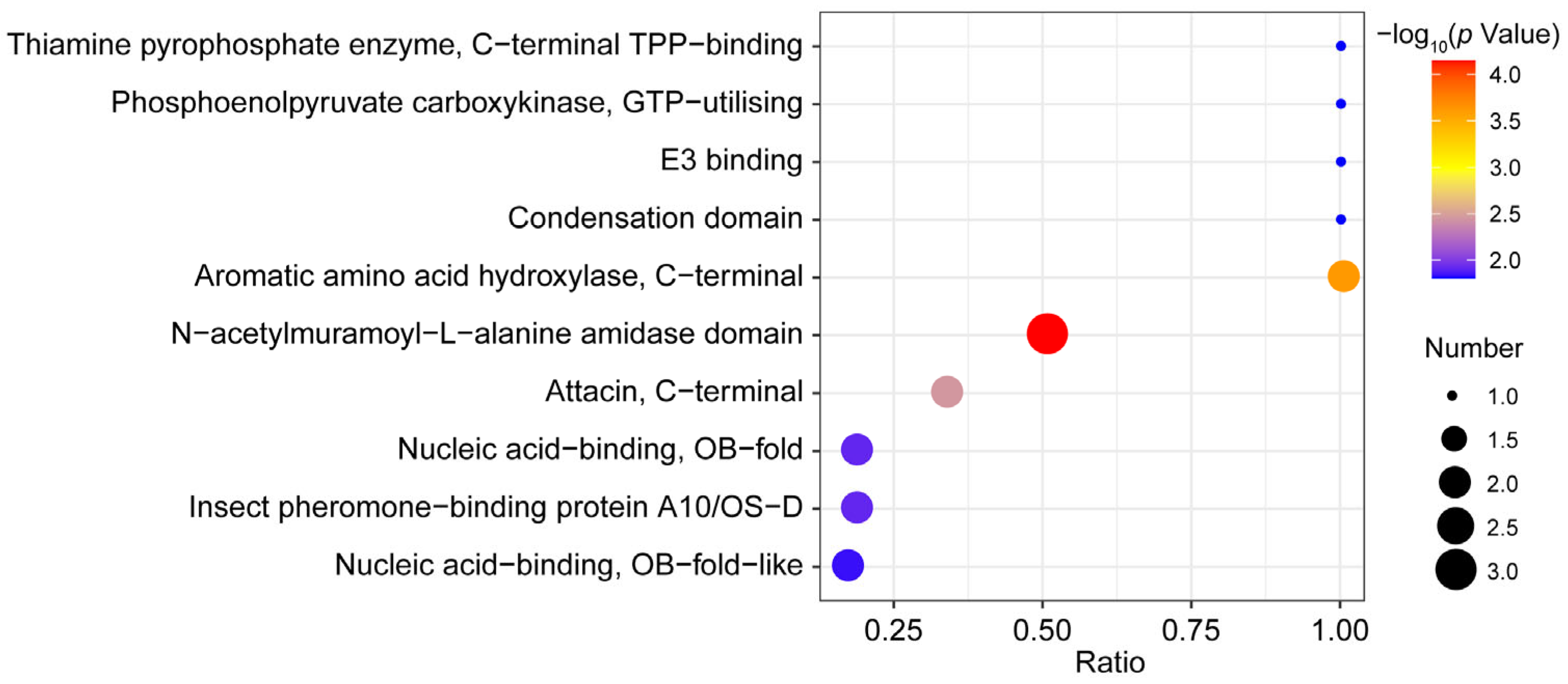
3.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEPs
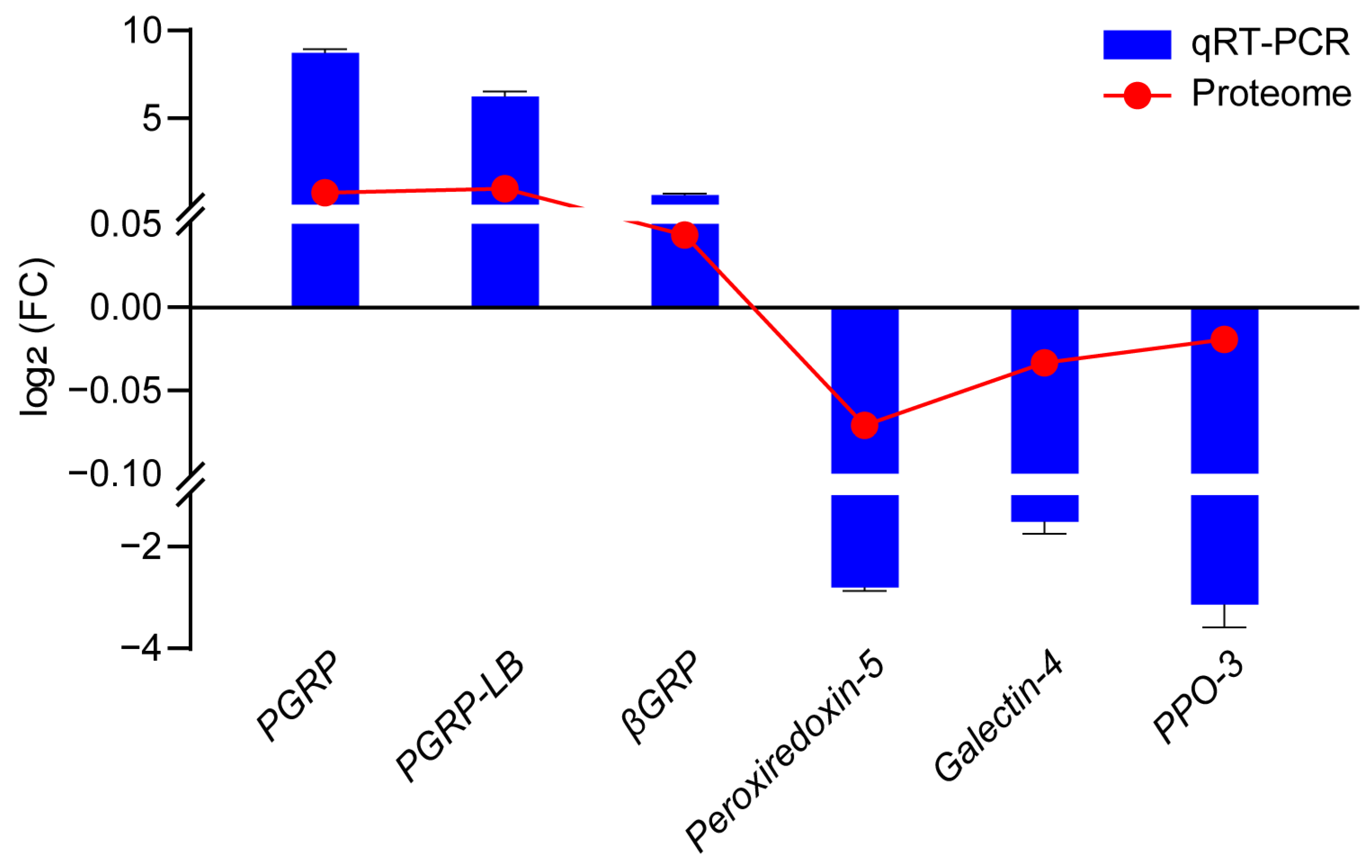
3.6. Validation of Several DEPs by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Y.L.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.Y. Research progress of Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in China. In The Black Spotted, Yellow Borer, Conogethes punctiferalis Guenée and Allied Species, 1st ed.; Chakravarthy, A.K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Sandoval, J. Conogethes punctiferalis (yellow peach moth). In CABI Compendium; CABI Digital Library: Wallingford, UK, 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Shi, J.; Ma, S.Y. Analysis of the heavy occurrence trend of the yellow peach moth in corn and its management strategies. Plant Prot. 2006, 32, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.F.; Qi, J.F.; He, K.L.; Wu, J.Q.; Bai, S.X.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhao, J.R.; Wang, Z.Y. The Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis feeding increases the direct and indirect defence of mid-whorl stage commercial maize in the field. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Baek, S.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, J.K.; Jung, C.; Lee, J.H. Efficiency of chemical and organic pesticides for Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in commercial chestnut and walnut fields. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2022, 25, 101897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, C.C.; Thomine, E.; Rusch, A.; Lavoir, A.V.; Wang, S.; Desneux, N. Crop diversification to promote arthropod pest management: A review. Agric. Commun. 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punniyakotti, P.; Vinayagam, S.; Rajamohan, R.; Priya, S.D.; Moovendhan, M.; Sundaram, T. Environmental fate and ecotoxicological behaviour of pesticides and insecticides in non-target environments: Nanotechnology-based mitigation strategies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.L.; Lewis, L.C. Colonization of corn, Zea mays, by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2000, 66, 3468–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Wang, S.B. Insect pathogenic fungi: Genomics, molecular interactions, and genetic improvements. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, S.B. Interaction of entomopathogenic fungi with the host immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.J.; Chen, M.J.; Shang, Y.F.; Tang, G.R.; Tao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Huang, B.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhan, S.; Wang, C.S. Population genomics and evolution of a fungal pathogen after releasing exotic strains to control insect pests for 20 years. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z. History, progress and current status of the application of fungi against pest insects in China. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2015, 31, 699–711. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, C.M.; Jacob, T.K.; Devasahayam, S.; Geethu, C.; Hariharan, V. Characterization and biocontrol potential of a naturally occurring isolate of Metarhizium pingshaense infecting Conogethes punctiferalis. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 243, 126645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Liu, F.H.; Kang, Z.W.; Li, X.D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Pang, Y.S.; Zheng, F.Q.; Yin, X.C. Cellular immune responses of the yellow peach moth, Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), to the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2022, 194, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Q.; Wei, H.S.; Camara, I.; Jia, H.R.; Cao, K.L.; Shi, W.P. Symbiotic bacteria system of Locusta migratoria showed antifungal capabilities against Beauveria bassiana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.A. The immune response of Drosophila. Nature 2003, 426, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.C.; Reynolds, S.E.; Eleftherianos, I. Insect immune responses to nematode parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cao, X.L.; Li, K.; Hu, Y.X.; Chen, Y.R.; Blissard, G.; Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H.B. A genome-wide analysis of antimicrobial effector genes and their transcription patterns in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 62, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.H.; Xing, L.S.; Lin, Z.; Saha, T.T.; Wang, C.S.; Jiang, H.B.; Zou, Z. High throughput profiling of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera immunotranscriptome during the fungal and bacterial infections. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Zhu, S.J.; Mandal, S.D.; Gao, Y.F.; Yu, J.; Zeng, L.; Huang, J.L.; Zafar, J.; Jin, F.L.; Xu, X.X. Combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of developmental features in the immune system of Plutella xylostella during larva-to-adult metamorphosis. Genomics 2022, 114, 110381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.J.; Peng, Y.; Jin, M.H.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Wu, C.; Yuan, H.; Awawing, A.; Zheng, F.Q.; Li, X.D.; et al. Chromosome genome assembly and whole genome sequencing of 110 individuals of Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenée). Sci. Data 2023, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, D.D.; Xu, P.; Hou, C.X.; Li, R.L.; Hu, C.W.; Guo, X.J. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of silkworm infected with Beauveria bassiana. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 135, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhou, R.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Q.H.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.Q. IQuant: An automated pipeline for quantitative proteomics based upon isobaric tags. Proteomics 2014, 14, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.D.; Li, X.; Xu, W.B.; Han, Z.B.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Dong, J.; Wei, H.; Chen, Q.J. Comparative iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of the Chinese grass shrimp (Palaemonetes sinensis) infected with the isopod parasite Tachaea chinensis. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.Q.; Cen, X.F.; Chen, G.F.; Tang, M.L.; Mo, L.; Li, J.J. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis in liver of Pomacea canaliculata induced by oleanolic acid stress. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3467–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.Z.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Q.J.; Wang, S.L.; Crickmore, N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, Z.J. Critical analysis of multi-omic data from a strain of Plutella xylostella resistant to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11419–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Dong, Z.M.; Ren, X.; Zhao, D.C.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.Y.; Han, J.X.; Ye, L.; Zhao, P. Proteomic identification of immune-related silkworm proteins involved in the response to bacterial infection. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Yu, X.Q.; Wang, Q.; Tao, X.P.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Xia, X.F.; You, M.S. Immune responses to Bacillus thuringiensis in the midgut of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 107, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziarski, R.; Gupta, D. The peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs). Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.T.; Mei, X.H.; Li, R.X.; Xu, Y.Y.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Xia, D.G.; Zhao, Q.L.; Shen, D.X. Transcriptome analysis of immune-related genes of Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis [Guenée]) after oral bacterial infection. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 114, e22044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, M.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Xia, H.C.; Chen, K.P. Peptidoglycan recognition proteins in insect immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 106, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.Z.; Su, F.H.; Li, Q.L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.J.; Tang, T.; Hu, Q.H.; Yu, X.Q. Pattern recognition receptors in Drosophila immune responses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 102, 103468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Niu, J.L.; Feng, D.S.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, R. Immune functions of pattern recognition receptors in Lepidoptera. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1203061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, L.S.; Wu, J.L.; Wu, L.P. The peptidoglycan recognition protein PGRP-SC1a is essential for Toll signaling and phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus in Drosophila. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.X.; Ji, J.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Liu, J.H.; An, C.J. A short-type peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 (PGRP1) is involved in the immune response in Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Wang, D.Y.; Jiang, Y.R.; Shi, S.L.; Qin, L. Peptidoglycan recognition proteins regulate immune response of Antheraea pernyi in different ways. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 166, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Byun, M.; Oh, B.H. Crystal structure of peptidoglycan recognition protein LB from Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cera, E. Serine proteases. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H.B. Clip-domain serine proteases as immune factors in insect hemolymph. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillard, F.; Troxler, L.; Reichhart, J.M. Drosophila melanogaster clip-domain serine proteases: Structure, function and regulation. Biochimie 2016, 122, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.L.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Y.C.; Blissard, G.W.; Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H.B. Sequence conservation, phylogenetic relationships, and expression profiles of nondigestive serine proteases and serine protease homologs in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 62, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.B.; Kanost, M.R. The clip-domain family of serine proteinases in arthropods. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Xiao, K.R.; Wang, L.Z.; Wang, J.; Song, Q.S.; Stanley, D.; Wei, S.J.; Zhu, J.Y. Identification and expression profiling of serine protease-related genes in Tenebrio molitor. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 111, e21963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Heng, J.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Tang, X.; Guo, P.C.; Li, Y.S.; Xia, Q.Y.; Zhao, P. Identification, characterization, and expression analysis of clip-domain serine protease genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 105, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Zhang, W.; Heryanto, C.; Mohamed, A.; Contreras, G.; Tettamanti, G.; Wink, M.; Bassal, T. Diversity of insect antimicrobial peptides and proteins—A functional perspective: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulet, P.; Stöcklin, R.; Menin, L. Anti-microbial peptides: From invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Z.; Meng, G.L.; Zhu, L.; Ma, L.; Chen, K.K. Insect antimicrobial peptides as guardians of immunity and beyond: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedengren, M.; Borge, K.; Hultmark, D. Expression and evolution of the Drosophila attacin/diptericin gene family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, K.; Park, S.; Yoo, J.Y.; Cho, S. Characterization and expression of attacin, an antibacterial protein-encoding gene, from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesa, J.; Sadat, A.; Buccini, D.F.; Kati, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides from Bombyx mori: A splendid immune defense response in silkworms. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabel, D.; Charlet, M.; Ehret-Sabatier, L.; Cavicchioli, L.; Cudic, M.; Otvos, L.; Bulet, P. Primary structure and in vitro antibacterial properties of the Drosophila melanogaster attacin C pro-domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14853–14859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, L.; Ali, Y.M.; Seilly, D.; McCoy, R.; Owens, R.M.; Pipan, M.; Christie, G.; Grant, A.J. An attacin antimicrobial peptide, Hill_BB_C10074, from Hermetia illucens with anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa activity. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.R.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Toufeeq, S.; Huang, W.R. Immunometabolic regulation during the presence of microorganisms and parasitoids in insects. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 905467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, T.; Krejcova, G.; Bajgar, A.; Nedbalova, P.; Strasser, P. Molecular regulations of metabolism during immune response in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 109, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursać, S.; Brdovčak, M.C.; Pfannkuchen, M.; Orsolić, I.; Golomb, L.; Zhu, Y.; Katz, C.; Daftuar, L.; Grabušić, K.; Vukelić, I.; et al. Mutual protection of ribosomal proteins L5 and L11 from degradation is essential for p53 activation upon ribosomal biogenesis stress. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20467–20472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xiong, Y.H.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.; Wen, D.L. Comparative proteomics analysis of Spodoptera frugiperda cells during Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total Spectra | Matched Spectra | Peptides | Identified Proteins | All Quantifiable Proteins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 565,469 | 62,669 | 29,155 | 4197 | 4195 |
| Number of Total Proteins | Regulated Type | FC > 1.2 | FC > 1.3 | FC > 1.5 | FC > 2.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 565,469 | up-regulated | 126 | 92 | 57 | 11 |
| down-regulated | 72 | 47 | 13 | 0 |
| Protein | Description | Accession No. | FC | p Value | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster-10258.20366; orf1 | arylphorin subunit alpha-like | XP_028169947.1 | 0.62 | 0.0028 | down |
| Cluster-10258.18909; orf1 | protein henna | XP_026753049.1 | 1.57 | 0.0043 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20977; orf1 | peptidoglycan recognition protein B | ADU33185.1 | 1.97 | 0.0171 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20744; orf1 | GTP cyclohydrolase 1 isoform X1 | XP_028166842.1 | 1.63 | 6.01 × 10−4 | up |
| Cluster-10258.5049; orf1 | elongation factor 1-alpha | XP_022204799.1 | 1.85 | 0.0211 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20686; orf1 | pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase-like | XP_023935092.1 | 1.63 | 0.0258 | up |
| Cluster-10258.39479; orf1 | ribosomal L6 and ribosomal S8 and ribosomal S5 C and ribosomal S5 domain containing protein | CDW61069.1 | 2.15 | 0.0234 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20398; orf1 | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase isoform X1 | XP_028171956.1 | 1.72 | 0.0136 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20923; orf1 | hypothetical protein evm_001044 | RVE54217.1 | 0.61 | 6.82 × 10−4 | down |
| Cluster-10258.14382; orf1 | chemosensory protein 2 | AHX37219.1 | 0.63 | 0.0257 | down |
| Cluster-10258.2265; orf1 | heat shock protein 70-4 | AQP31364.1 | 1.56 | 0.0203 | up |
| Cluster-10258.5046; orf1 | hypothetical protein B5V51_858 | PCG72390.1 | 0.65 | 0.0305 | down |
| Cluster-10258.19866; orf1 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP]-like | XP_028168927.1 | 0.65 | 0.0316 | down |
| Cluster-10258.5607; orf1 | serine protease easter-like isoform X2 | XP_013184392.1 | 1.53 | 0.0136 | up |
| Cluster-10258.17235; orf1 | tryptase-like | XP_013193793.1 | 1.85 | 0.0448 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20506; orf1 | peptidoglycan recognition protein-like | XP_028160373.1 | 1.65 | 0.0114 | up |
| Cluster-10258.37244; orf1 | 60S ribosomal protein L13 | XP_008552884.1 | 2.02 | 5.25 × 10−4 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20313; orf1 | uncharacterized protein LOC114360519 | XP_028171047.1 | 1.57 | 0.0475 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36590; orf1 | 40S ribosomal protein S4-like, partial | XP_021339550.1 | 1.62 | 2.55 × 10−4 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36281; orf1 | hypothetical protein DDB_G0285741 | XP_638067.1 | 1.64 | 0.0211 | up |
| Cluster-10258.19803; orf1 | chemosensory protein | APG32552.1 | 0.57 | 0.0455 | down |
| Cluster-10258.36541; orf1 | S10 | AAX48886.1 | 1.86 | 0.0158 | up |
| Cluster-10258.18280; orf1 | uncharacterized protein LOC114364556 | XP_028176547.1 | 1.74 | 7.80 × 10−5 | up |
| Cluster-9364.0; orf1 | endocuticle structural glycoprotein ABD-4-like | XP_028173253.1 | 0.58 | 0.0124 | down |
| Cluster-10258.27935; orf1 | peptidoglycan-recognition protein LB-like | XP_013143081.1 | 1.94 | 0.0049 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36298; orf1 | uncharacterized protein LOC111678542 | XP_023295698.1 | 1.58 | 0.0112 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2249; orf1 | 60S ribosomal protein L2-A-like | XP_021339551.1 | 1.80 | 0.0019 | up |
| Cluster-10258.30985; orf1 | venom serine carboxypeptidase-like | XP_028155892.1 | 0.60 | 6.37 × 10−4 | down |
| Cluster-10258.23395; orf1 | defense protein 3-like | XP_023937619.1 | 2.45 | 0.0072 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2238; orf1 | elongation factor, putative | XP_002783366.1 | 1.69 | 0.0073 | up |
| Cluster-10258.1655; orf1 | ribonucleoprotein, putative | ELP90168.1 | 2.29 | 9.19 × 10−4 | up |
| Cluster-2690.2; orf2 | uncharacterized protein LOC111689114 | XP_023307388.1 | 1.65 | 0.0198 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36368; orf1 | 60S ribosomal protein L7-like | XP_028405051.1 | 1.52 | 0.0338 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2136; orf1 | elongation factor 1-beta-like | XP_022205053.1 | 1.67 | 0.0090 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36383; orf1 | predicted protein | XP_001625520.1 | 1.52 | 0.0025 | up |
| Cluster-10258.37625; orf1 | pyruvate dehydrogenase complex dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase | XP_013761136.1 | 2.84 | 0.0303 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2339; orf1 | hypothetical protein | AIU94794.1 | 1.97 | 0.0024 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36446; orf1 | 60S ribosomal protein L10-like | XP_015760823.1 | 2.30 | 0.0114 | up |
| Cluster-2690.2; orf1 | uncharacterized protein LOC111689114 | XP_023307388.1 | 3.72 | 0.0123 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36809; orf1 | 40S ribosomal protein S14 | KXJ11429.1 | 2.14 | 0.0036 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36363; orf1 | 60S ribosomal protein L5-like, partial | XP_021339565.1 | 1.87 | 0.0078 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2314; orf1 | stress-70 protein, mitochondrial | RDD38839.1 | 1.74 | 0.0143 | up |
| Cluster-10258.27756; orf1 | uncharacterized protein LOC114364166 | XP_028175991.1 | 0.60 | 0.0126 | down |
| Cluster-10258.2302; orf1 | guanine nucleotide-binding protein | XP_004343796.1 | 1.98 | 3.34 × 10−5 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36260; orf1 | fatty acid-binding protein-like | XP_022204143.1 | 1.54 | 0.0127 | up |
| Cluster-10258.20425; orf1 | uncharacterized protein LOC114366599 | XP_028179325.1 | 0.59 | 0.0242 | down |
| Cluster-10258.36738; orf1 | K+ channel protein | KJE97207.1 | 1.72 | 0.0054 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36471; orf1 | 40S ribosomal protein S24 | XP_013405352.1 | 1.53 | 0.0059 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2113; orf1 | 60S ribosomal protein L25-B-like | XP_022204254.1 | 2.46 | 0.0014 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36660; orf1 | hypothetical protein pdam_00013747 | RMX60612.1 | 1.54 | 0.0269 | up |
| Cluster-10258.27291; orf1 | putative ferric-chelate reductase 1 homolog | XP_028167929.1 | 1.52 | 0.0127 | up |
| Cluster-10258.36259; orf1 | transaldolase | OQV22424.1 | 1.78 | 0.0086 | up |
| Cluster-10258.37144; orf1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 | XP_015794685.1 | 1.57 | 0.0052 | up |
| Cluster-10258.2387; orf1 | ribosomal protein L17 | ABO26685.1 | 1.56 | 0.0107 | up |
| Cluster-10258.37453; orf1 | trichothecene biosynthesis protein 14 OS | G0KYA7 | 1.93 | 0.0096 | up |
| Cluster-10258.37326; orf1 | hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase 1-like | XP_027216736.1 | 1.55 | 0.0400 | up |
| Cluster-10258.29648; orf1 | hypothetical protein evm_006310 | RVE49064.1 | 1.59 | 0.0257 | up |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Kang, Z.; Li, X.; Wei, H.; Yin, X.; Zheng, F.; Liu, F. Comparative Proteomic Insights into the Immune Response of Conogethes punctiferalis Challenged with Beauveria bassiana. Insects 2025, 16, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070667
Li S, Kang Z, Li X, Wei H, Yin X, Zheng F, Liu F. Comparative Proteomic Insights into the Immune Response of Conogethes punctiferalis Challenged with Beauveria bassiana. Insects. 2025; 16(7):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070667
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shaohua, Zhiwei Kang, Xiangdong Li, Hailei Wei, Xiangchu Yin, Fangqiang Zheng, and Fanghua Liu. 2025. "Comparative Proteomic Insights into the Immune Response of Conogethes punctiferalis Challenged with Beauveria bassiana" Insects 16, no. 7: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070667
APA StyleLi, S., Kang, Z., Li, X., Wei, H., Yin, X., Zheng, F., & Liu, F. (2025). Comparative Proteomic Insights into the Immune Response of Conogethes punctiferalis Challenged with Beauveria bassiana. Insects, 16(7), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070667






