AI-Driven Rheological and Tribological Performance Modeling of Transmission Oil Blended with Castor Oil and Enhanced with CeO2 and MWCNTs Additives for Sustainable Lubrication Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
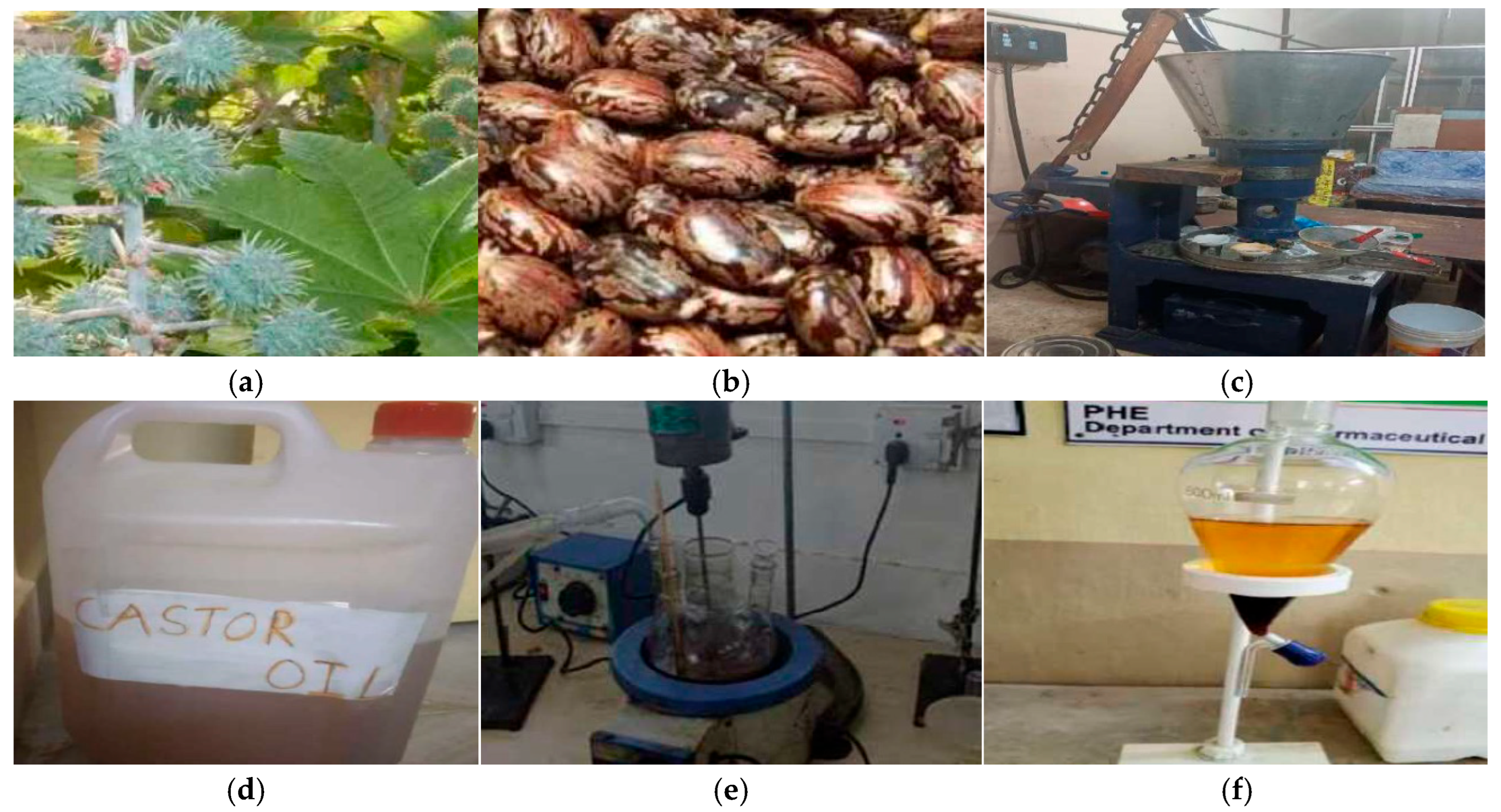
2.1. Extraction of Castor Oil
2.2. Transesterification of Castor Oil
2.3. Preparation of Bio-Nano Lubricants
2.3.1. CeO2-Based Nano-Lubricant
2.3.2. MWCNT-Based Nano-Lubricant
2.3.3. Blending with Transmission Oil
3. Experimentation
3.1. Rheology Tests
3.2. Tribology Tests
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Rheology Analysis
- CeO2-based lubricants (CCO) exhibit greater viscosity variation and are more sensitive to temperature and shear, indicative of strong particle clustering and potential for load-bearing applications.
- MWCNT-based lubricants (MCO) maintain moderate, stable viscosities and superior thermal flowability, making them favorable for systems requiring low pumping losses.
- All formulations exhibit non-Newtonian, shear-thinning behavior, which is essential for energy-efficient performance under dynamic loading.
4.2. Tribological Analysis
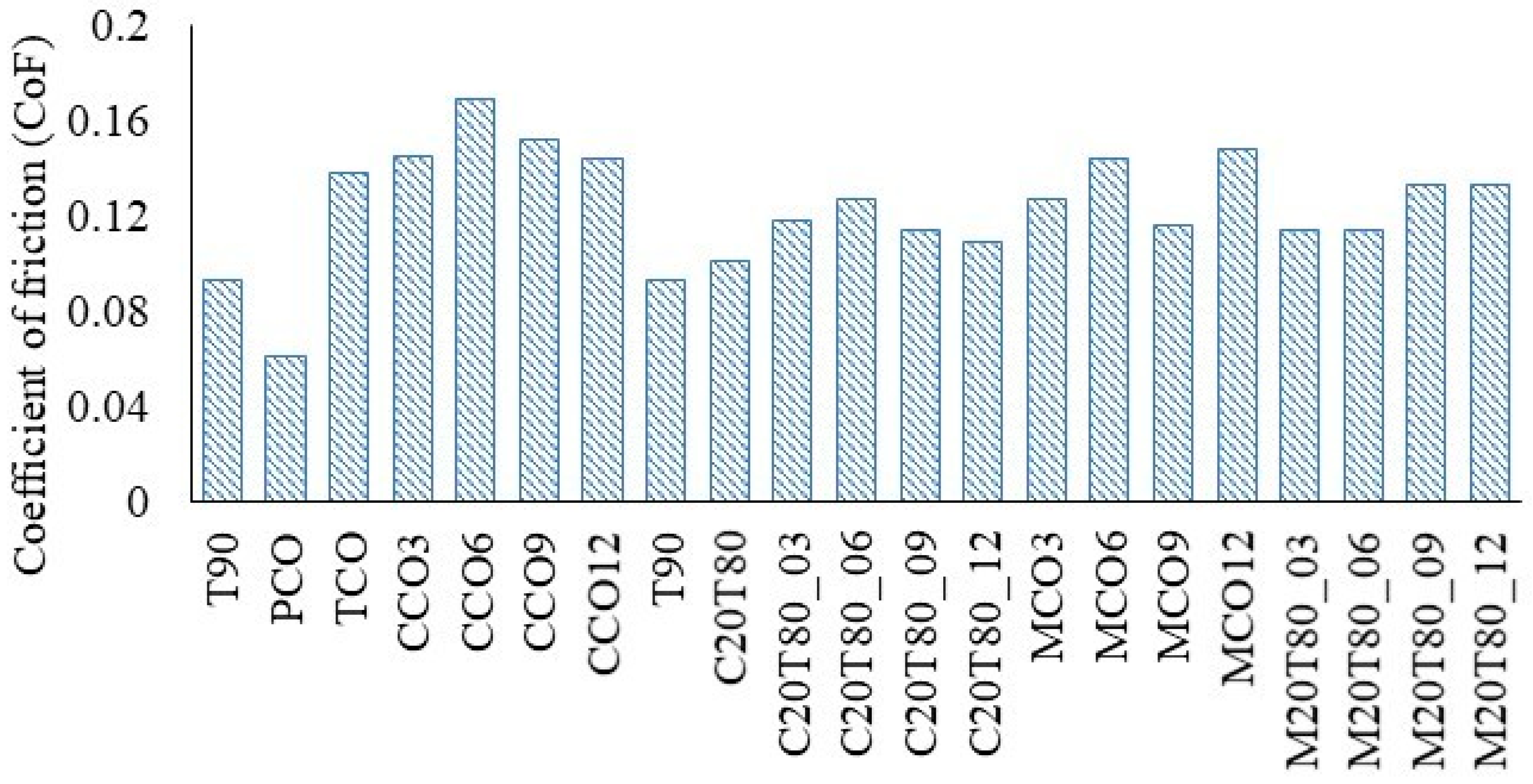
4.2.1. Coefficient of Friction (CoF)
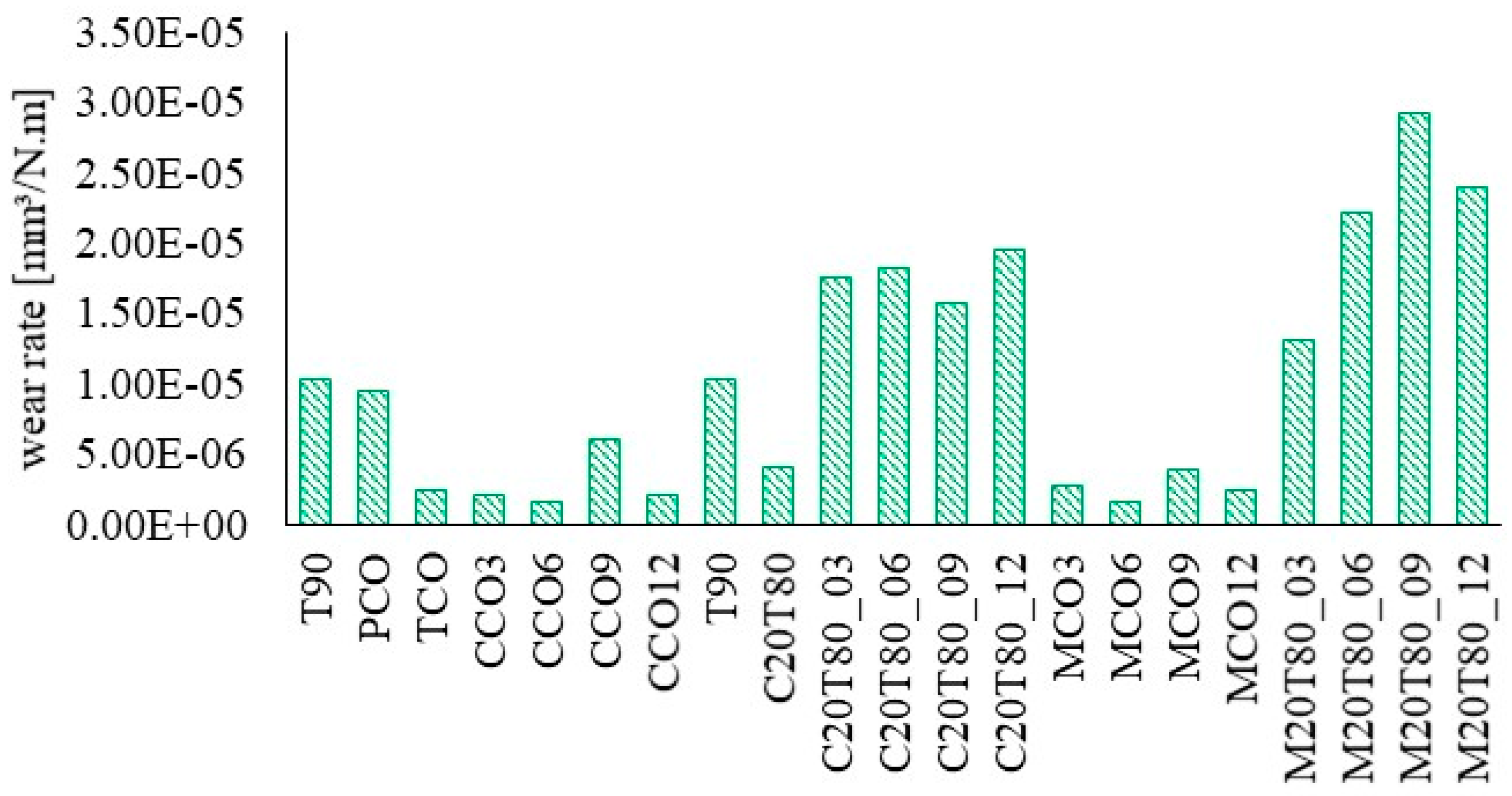
4.2.2. Wear Rate
5. Predictive Modeling
5.1. Model Selection Rationale
- Support Vector Regression (SVR);
- Artificial Neural Network (ANN)—specifically, a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP);
- Adaptive Boosting Regressor (AdaBoost).
- SVR is widely used for small- to medium-sized datasets and is effective in capturing non-linear relationships with kernel tricks (e.g., RBF kernel). Its generalization ability makes it suitable for rheological data with smooth, continuous variations.
- ANN (MLPRegressor) is well-suited for modeling complex, multi-dimensional, and non-linear patterns typical in nano-lubricant behavior. Given that nanoparticle interactions, thermal shear-thinning effects, and dispersion phenomena are inherently non-linear, ANN can extract meaningful relationships from such interdependencies.
- AdaBoost, an ensemble method, builds multiple weak learners (decision trees) and combines them into a strong regressor. It is known for its robustness against overfitting and superior performance with heterogeneous features—especially when the target variable (final viscosity) is affected by multiple interacting parameters such as temperature, concentration, and fluid type.
5.2. Input Features and Target Variable
- Nanoparticle Type (Categorical: CeO2 or MWCNT);
- Concentration (% weight);
- Temperature (°C);
- Initial Viscosity (mPa·s).
import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.svm import SVR from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostRegressor from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error # Manually input the experimental datadata = { "Sample": ["CCO-3 (40°C)", "CCO-3 (100°C)", "CCO-6 (40°C)", "CCO-6 (100°C)", "CCO-9 (40°C)", "CCO-9 (100°C)", "CCO-12 (40°C)", "CCO-12 (100°C)", "C20T80 (40°C)", "C20T80 (100°C)", "C20T80_03 (40°C)", "C20T80_03 (100°C)", "C20T80_06 (40°C)", "C20T80_06 (100°C)", "C20T80_09 (40°C)", "C20T80_09 (100°C)", "C20T80_12 (40°C)", "C20T80_12 (100°C)" ], "Temp_C": [40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100, 40, 100 ], "Conc_wv": [0.3, 0.3, 0.6, 0.6, 0.9, 0.9, 1.2, 1.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.3, 0.3, 0.6, 0.6, 0.9, 0.9, 1.2, 1.2 ], "Initial_Visc": [110, 298.58, 96.9, 275.06, 138.4, 402.6, 78.5, 27770, 3326.1, 2748.1, 117.5, 1840.3, 3700, 1420.8, 1074.7, 850.2, 623.4, 290 ], "Final_Visc": [110, 12, 95.5, 14, 113.5, 19.5, 78.5, 14, 125, 14, 117.5, 11.5, 116, 17, 96.5, 11, 103, 15 ] } df = pd.DataFrame(data) # Define features and targetX = df[["Temp_C", "Conc_wv", "Initial_Visc"]] y = df["Final_Visc"]# Scale featuresscaler = StandardScaler() X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X) # Split for evaluationX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42) # Initialize modelsmodels = {"SVR": SVR(kernel=‘rbf’), "ANN (MLPRegressor)": MLPRegressor(hidden_layer_sizes=(50, 50), max_iter=1000, random_state=42), "AdaBoost": AdaBoostRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42) } # Train and evaluateresults = [] for name, model in models.items(): model.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = model.predict(X_test) results.append({ "Model": name, "R2 Score": r2_score(y_test, y_pred), "MSE": mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred), "MAE": mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)}) |
6. Conclusions
- Both CeO2- and MWCNT-based nano-lubricants exhibited non-Newtonian, shear-thinning behavior, favorable for energy-efficient lubrication in dynamic systems.
- CeO2-based lubricants demonstrated very high viscosities at 40 °C (up to ~3700 mPa·s) with sharp shear-dependent thinning. They provided outstanding anti-wear performance, achieving the lowest wear rate of 1.66 × 10−6 mm3/N·m, albeit with slightly higher CoF values (0.144–0.169).
- MWCNT-based lubricants offered moderate initial viscosities (90–365 mPa·s at 40 °C) and excellent thermal flowability (8–18 mPa·s at 100 °C). They maintained lower and more consistent CoF values (0.116–0.148) and delivered comparable wear protection, with MCO-6 exhibiting a wear rate of 1.62 × 10−6 mm3/N·m.
- Ternary blends (C20T80 and M20T80) exhibited moderate frictional performance but significantly higher wear rates (up to 2.92 × 10−5 mm3/N·m), indicating that base oil dilution enhances dispersion but compromises tribo-film stability.
- From an application perspective, CeO2 nano-additives are better suited for high-load, wear-critical systems, whereas MWCNT-based lubricants are more appropriate for low-viscosity, friction-stable environments. Their complementary behaviors highlight the potential for developing hybrid nano-lubricant systems with tailored additive ratios for optimized performance.
- In addition to experimental evaluation, AI-based predictive models using Support Vector Regression (SVR), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), and AdaBoost were employed to forecast rheological and tribological behavior. The models demonstrated strong prediction accuracy, validating their use in reducing experimental burden, estimating performance under varying conditions, and supporting real-time decision-making in industrial applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neta, R.; Silva, T.; Santos, F. Sustainable alternatives to mineral oils: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138547. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, Z.; Khan, A.; Rehman, M. Advances in bio-lubricants: Environmental compliance and applications. Renew. Energy 2022, 196, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Petlyuk, A.M.; Adams, R.J. Oxidation Stability and Tribological Behavior of Vegetable Oil Hydraulic Fluids. Tribol. Trans. 2004, 47, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Bhuiya, M.M.K.; Mehat, H. Comparative tribological investigation of bio-lubricant formulated from a non-edible oil source (Jatropha oil). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 47, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, N.; Salimon, J.; Yousif, E. Improvement of oxidative stability of vegetable oils: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50384. [Google Scholar]
- Prasannakumar, S.; Rao, K.; Devi, P. Tribological properties of castor oil-based lubricants under high load conditions. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2025, 77, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Rheological properties of castor oil for lubrication applications. J. Renew. Mater. 2023, 11, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, A.; Wagner, H. Low-temperature challenges in vegetable oil lubricants. Lubricants 2021, 9, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Adhvaryu, A.; Erhan, S. Epoxidized vegetable oils as lubricant base oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 32, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Encinar, J.M.; Nogales-Delgado, S.; Sánchez, N.; González, J.F. Biolubricants from Rapeseed and Castor Oil Transesterification by Using Titanium Isopropoxide as a Catalyst: Production and Characterization. Catalysts 2020, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Sharma, R. Improved cold flow and oxidation stability of modified castor oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132544. [Google Scholar]
- Hamnas, A.; Unnikrishnan, S. Thermal stability of transesterified castor oil under tribological stress. Lubricants 2023, 516–517, 204545. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.K.; Adhvaryu, A.; Liu, Z.; Erhan, S.Z. Chemical modifications of vegetable oils for lubricant applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 7203–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppar, R.; Dinesha, P.; Kumar, S. Characterization of bio-lubricants with nanoparticles additives. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2024, 46, 3684–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M. Nanoparticle-enhanced lubricants: Mechanisms and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102552. [Google Scholar]
- Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M. Nanoparticles as additives in lubricants—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 82, 927–939. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.B.; Heris, S.Z.; Estellé, P. Experimental comparison between ZnO and MoS2 nanoparticles as additives on performance of diesel oil-based nano lubricant. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5813. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Chauhan, A. Role of WS2 nanoparticles in friction reduction. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Wei, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, F. Tribological properties of Al2O3 nanoparticles as lubricating oil additives. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 7143–7149. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, R.; Patel, D.; Yadav, S. Optimal nanoparticle loading in nanolubricants: A review. Tribol. Online 2023, 18, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Xu, L. Agglomeration issues in nanoparticle-based lubricants. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 646, 128918. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, K.; Low, K.; Ong, H. Eco-friendly tribological additives: Role of cerium oxide nanoparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 356, 131790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, W.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; He, K. Effect of CeO2 Content on Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser-Cladded Ni-Based Composite Coating. Lubricants 2024, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Sun, W.; Tang, W.; Wang, L. Tribological Performance of Nano-CeO2/BNH2 Compound Lubricant Additive. Coatings 2024, 14, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhou, H. Lubricant life extension with CeO2 nanoparticles. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2023, 75, 678–688. [Google Scholar]
- Uppar, V.; Joshi, R.; Kulkarni, M. Load-bearing capacity of gear lubricants with CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 340–346. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.; Varma, R. Sedimentation behavior of metal oxide nanoparticles in lubricants. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 606, 125451. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, M. Enhancing engine oil performance with carbon nanotube additives. Fuel 2022, 323, 124345. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.; Yu, N.; Zhang, R.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L. Tribological properties of lubricant-filled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 39, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Hassan, M.; Fathy, H. Optimal concentration of MWCNTs in engine oils for tribological improvement. Lubricants 2021, 472–473, 203712. [Google Scholar]
- Lijesh, K.; Rajendrakumar, P.; Binu, K. Effect of CNTs on thermal conductivity and viscosity of lubricants. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, A. Heat dissipation in CNT-reinforced lubricants. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 061401. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Gupta, V.; Mehta, S. Hybrid nanolubricants with CeO2 and CNTs: Synergistic tribological effects. Wear 2022, 490–491, 204163. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.; Chauhan, V.; Sinha, P. Comparative study of single and hybrid nanoparticle additives. Tribol. Int. 2023, 186, 107832. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Das, S. Performance of CNT-CeO2 hybrid nanoparticles in vegetable oil lubricants. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 5336–5342. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Q. Synergistic mechanisms of CNT and CeO2 in lubricants. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121754. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, X. Challenges in scaling nanoparticle-doped lubricants for industry. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111654. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Xu, L.; Lin, H. Real-world testing gaps in nanolubricants. Tribol. Lett. 2022, 70, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, K.; Fan, J.; Tang, Y. The tribological properties of nano-lubricants and their application on bearings: Recent research progress. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 3051–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qian, H. Comparative analysis of tribological studies on bio-based nanolubricants. Tribol. Int. 2021, 160, 107057. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Yadav, R.; Singh, D. Life-cycle analysis of bio-lubricants with nanomaterial additives. Renew. Energy 2022, 182, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, V.; Khan, S. Sustainability of nanostructured lubricants in modern machinery. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 380, 135193. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, G.; Navada, M.K.; Brahmavar, J.; Aroor, G. Machine Learning-Based Predictive Model to Assess Rheological Dynamics of Eco-Friendly Oils as Biolubricants Enriched with SiO2 Nanoparticles. Lubricants 2024, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Liu, W.; Wen, X.; Wei, P.; Cao, H.; Bai, P.; Tian, Y. Effective tribological performance-oriented concentration optimization of lubricant additives based on a machine learning approach. Tribol. Int. 2024, 197, 109770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Arif, S.; Raja, A.H.; Kouhia, R.; Almqvist, A.; Liwicki, M. Machine Learning Composite-Nanoparticle-Enriched Lubricant Oil Development for Improved Frictional Performance—An Experiment. Lubricants 2023, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.; Manat, R.; Xiaoxia, J.; Bo, Z.; Jamlos, M.F.; Ghazali, M.F. Performance enhancement and optimization of residential air conditioning system in response to the novel FAl2O3-POE nanolubricant adoption. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
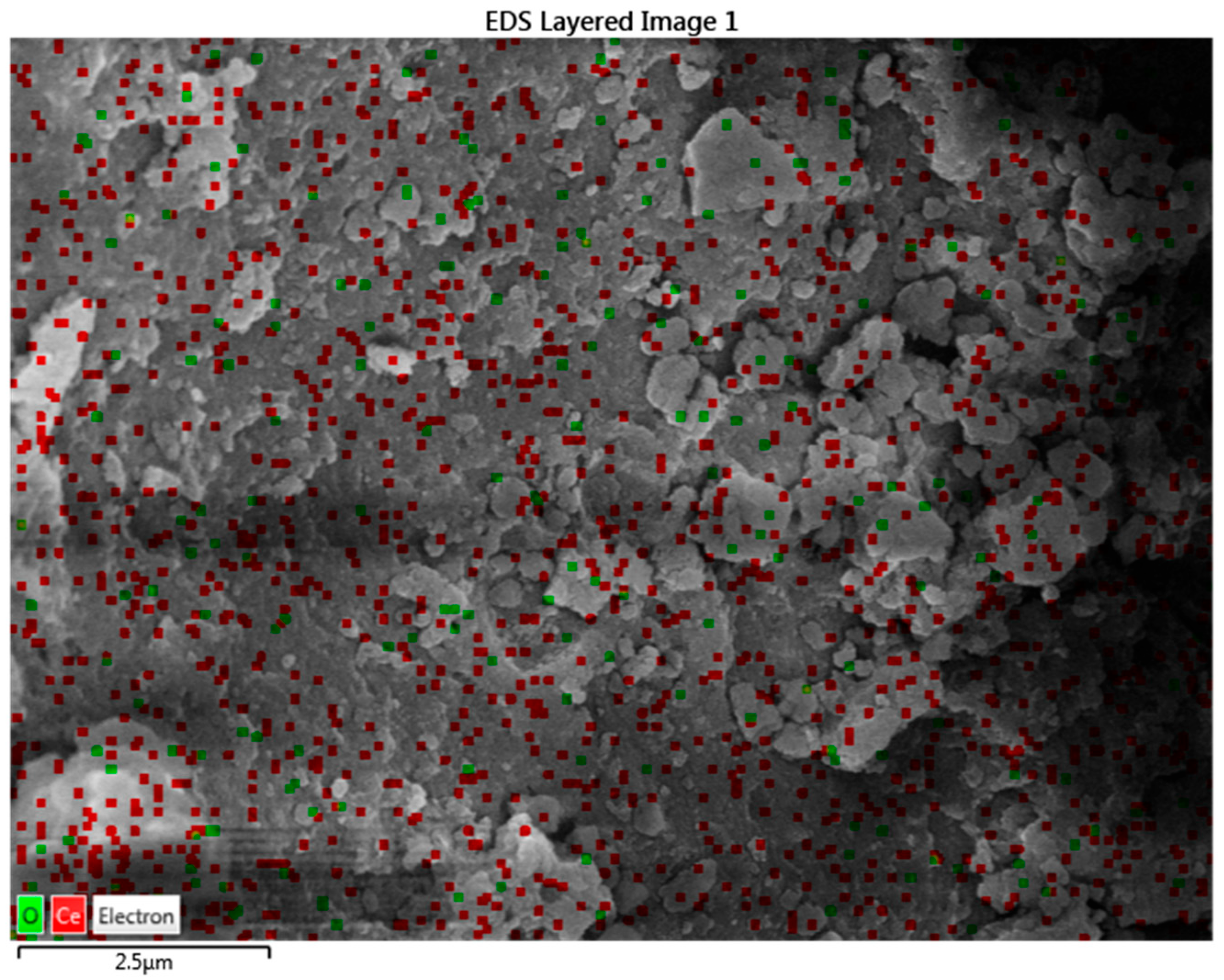
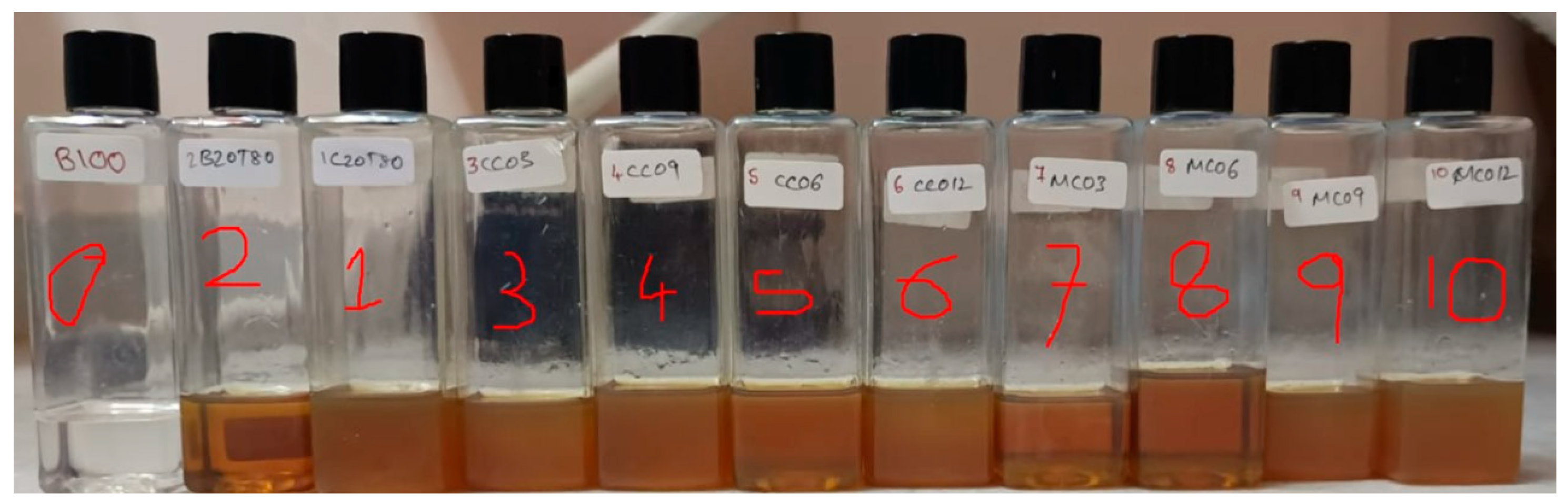



| Sample | Initial Viscosity (mPa·s) | Final Viscosity (mPa·s) | Shear Rate Range (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCO-3 (40 °C) | 105–115 | 105–115 | 0.01–600 |
| CCO-3 (100 °C) | 298.58 | 10–14 | 0.01–600 |
| CCO-6 (40 °C) | 96.9 | 90–101 | 12.3–600 |
| CCO-6 (100 °C) | 275.06 | 12–16 | 0.01–600 |
| CCO-9 (40 °C) | 138.4 | 111–116 | 12.3–600 |
| CCO-9 (100 °C) | 402.6 | 18–21 | 0.01–600 |
| CCO-12 (40 °C) | 72–85 | 72–85 | 0.01–600 |
| CCO-12 (100 °C) | 320 | 12–16 | 0.01–600 |
| C20T80 (40 °C) | 3326.1 | 120–130 | 0.01–600 |
| C20T80 (100 °C) | 2748.1 | 12–16 | 0.01–600 |
| C20T80_03 (40 °C) | 105–130 | 105–130 | 0.01–600 |
| C20T80_03 (100 °C) | 1840.3 | 8–15 | 0.01–600 |
| C20T80_06 (40 °C) | 3700 | 103–129 | 12.3–600 |
| C20T80_06 (100 °C) | 1420.8 | 16–18 | 12.3–600 |
| C20T80_09 (40 °C) | 1074.7 | 84–109 | 12.3–600 |
| C20T80_09 (100 °C) | 850.2 | 10–12 | 12.3–600 |
| C20T80_12 (40 °C) | 623.4 | 92–114 | 12.3–600 |
| C20T80_12 (100 °C) | 290 | 13–17 | 0.01–600 |
| Sample | Initial Viscosity (mPa·s) | Final Viscosity (mPa·s) | Shear Rate Range (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCO-3 (40 °C) | 101.81 | 95.77 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-3 (100 °C) | 364.75 | 162 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-6 (40 °C) | 140.84 | 128.31 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-6 (100 °C) | 74.94 | 25.61 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-9 (40 °C) | 328.52 | 222.01 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-9 (100 °C) | 240.14 | 35.32 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-12 (40 °C) | 364.75 | 162 | 12.3–600 |
| MCO-12 (100 °C) | 231.43 | 35.98 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80 (40 °C) | 90.51 | 107.34 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80 (100 °C) | 26.89 | 18.37 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_03 (40 °C) | 129.94 | 137.88 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_03 (100 °C) | 38.31 | 13.85 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_06 (40 °C) | 143.15 | 131.78 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_06 (100 °C) | 40.42 | 16.02 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_09 (40 °C) | 129.94 | 137.88 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_09 (100 °C) | 62.93 | 19.98 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_12 (40 °C) | 298.52 | 246.06 | 12.3–600 |
| M20T80_12 (100 °C) | 72.18 | 31.05 | 12.3–600 |
| Model | R2 Score | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | −0.188 | 41.83 | 2873.32 |
| ANN (MLP) | 0.980 | 8.82 | 120.74 |
| AdaBoost | 0.987 | 5.92 | 82.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Timmapuram, V.S.; Dogra, S.; Kotia, A. AI-Driven Rheological and Tribological Performance Modeling of Transmission Oil Blended with Castor Oil and Enhanced with CeO2 and MWCNTs Additives for Sustainable Lubrication Systems. Lubricants 2025, 13, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13120523
Timmapuram VS, Dogra S, Kotia A. AI-Driven Rheological and Tribological Performance Modeling of Transmission Oil Blended with Castor Oil and Enhanced with CeO2 and MWCNTs Additives for Sustainable Lubrication Systems. Lubricants. 2025; 13(12):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13120523
Chicago/Turabian StyleTimmapuram, Vijaya Sarathi, Sudhanshu Dogra, and Ankit Kotia. 2025. "AI-Driven Rheological and Tribological Performance Modeling of Transmission Oil Blended with Castor Oil and Enhanced with CeO2 and MWCNTs Additives for Sustainable Lubrication Systems" Lubricants 13, no. 12: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13120523
APA StyleTimmapuram, V. S., Dogra, S., & Kotia, A. (2025). AI-Driven Rheological and Tribological Performance Modeling of Transmission Oil Blended with Castor Oil and Enhanced with CeO2 and MWCNTs Additives for Sustainable Lubrication Systems. Lubricants, 13(12), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13120523






