The Role of Radiotherapy After Pleurectomy/Decortication for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
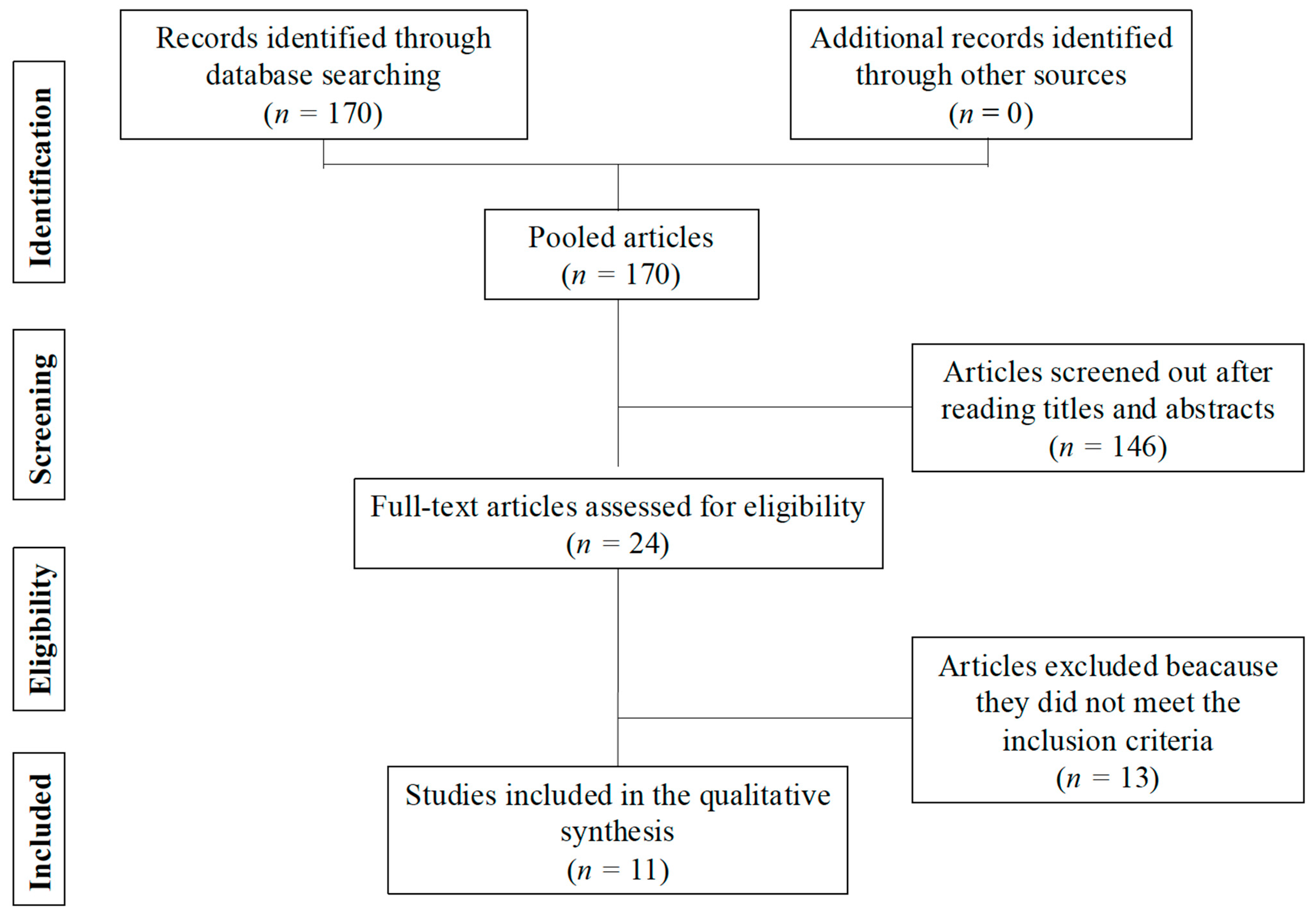
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popat, S.; Baas, P.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Girard, N.; Nicholson, A.G.; Nowak, A.K.; Opitz, I.; Scherpereel, A.; Reck, M.; on behalf of the ESMO Guidelines Committee. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 26, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasure, T.; Lang-Lazdunski, L.; Waller, D.; Bliss, J.M.; Tan, C.; Entwisle, J.; Snee, M.; O’Brien, M.; Thomas, G.; Senan, S.; et al. Extra-pleural pneumonectomy versus no extra-pleural pneumonectomy for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Clinical outcomes of the Mesothelioma and Radical Surgery (MARS) randomised feasibility study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Waller, D.; Lau, K.; Steele, J.; Pope, A.; Ali, C.; Bilancia, R.; Keni, M.; Popat, S.; O’Brien, M.; et al. Extended pleurectomy decortication and chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for pleural mesothelioma (MARS 2): A phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiameli, G.; Bottoni, E.; Cariboni, U.; Ferraroli, G.M.; Morenghi, E.; Giudici, V.M.; Voulaz, E.; Alloisio, M.; Testori, A. Single-Center 20-Year Experience in Surgical Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Krug, L.M.; Laser, B.; Hudka, K.; Flores, R.; Rusch, V.W.; Rosenzweig, K.E. Patterns of local and nodal failure in malignant pleural mesothelioma after extrapleural pneumonectomy and photon-electron radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Mesothelioma: Pleural. Version 2.2026. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/meso_pleural.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2025).
- Franceschini, D.; De Rose, F.; Cozzi, S.; Renna, I.; Franzese, C.; Di Brina, L.; Navarria, P.; D’Agostino, G.R.; Mancosu, P.; Tomatis, S.; et al. Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy After Lung Sparing Surgery for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Single Institution Experience. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, F.; Zauderer, M.G.; von Reibnitz, D.; Wu, A.J.; Yorke, E.D.; Foster, A.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; et al. Improved outcomes with modern lung-sparing trimodality therapy in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Mychalczak, B.; Krug, L.; Flores, R.; Bains, M.; Rush, V.W.; Rosenzweig, K.E. Hemithoracic radiation therapy after pleurectomy/decortication for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimner, A.; Zauderer, M.G.; Gomez, D.R.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Parhar, P.K.; Wu, A.J.; Woo, K.M.; Shen, R.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Yorke, E.D.; et al. Phase II study of hemithoracic intensity-modulated pleural radiation therapy (IMPRINT) as part of lung-sparing multimodality therapy in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatel, E.; Trovo, M.; Bearz, A.; Di Maso, M.; Baresic, T.; Drigo, A.; Barresi, L.; Furlan, C.; Del Conte, A.; Bruschi, G.; et al. Radical radiation therapy after lung-sparing surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Survival, pattern of failure, and prognostic factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimner, A.; Spratt, D.E.; Zauderer, M.G.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Wu, A.J.; Foster, A.; Yorke, E.D.; Adusumilli, P.; Rusch, V.W.; Krug, L.M. Failure patterns after Hemithoracic Pleural Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.R.; Li, Y.R.; Busch, T.M.; Kim, M.M.; McNulty, S.; Dimofte, A.; Zhu, T.C.; Cengel, K.A.; Simone, C.B. 2nd. A novel prospective study assessing the combination of photodynamic therapy and proton radiation therapy: Safety and outcomes when treating malignant pleural mesothelioma. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatel, E.; Trovo, M.; Polesel, J.; Baresic, T.; Bearz, A.; Franchin, G.; Gobitti, C.; Rumeileh, I.A.; Drigo, A.; Fontana, P.; et al. Radical pleurectomy/decortication followed by high dose of radiation therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Final results with long-term follow-up. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, E.; Romeo, A.; Sarnelli, A.; Ghigi, G.; Bellia, S.R.; Neri, E.; Micheletti, S.; Dipalma, B.; Arpa, D.; Furini, G.; et al. High dose irradiation after pleurectomy/decortication or biopsy for pleural mesothelioma treatment. Cancer Radiother. 2017, 21, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrabi, S.B.; Koerber, S.A.; Adeberg, S.; Katayama, S.; Herfarth, K.; Debus, J.; Sterzing, F. Malignant pleural mesothelioma–pleural cavity irradiation after decortication with helical tomotherapy. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2017, 22, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, O.; Lozano-Ruiz, F.; Blake-Cerda, M.; Catalán, R.; Lara-Mejía, L.; Salinas, M.Á.; Maldonado-Magos, F.; Corona-Cruz, J.F. Locoregional control and toxicity after pleurectomy/decortication and intensity-modulated pleural radiation therapy in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 3448–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisma Statement. Available online: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on 10 September 2013).
- Krug, L.M.; Pass, H.I.; Rush, V.W. Multicenter phase II trial of neo-adjuvant pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy and radiation for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schil, P.E.; Baas, P.; Gaafar, R. European Oragnization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Lung Cancer Group. Trimodality therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Results from a EORTC phase II multicenter trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Ludmir, E.B.; Miccio, J.A.; Menon, H.; Barsky, A.R.; Mesko, S.M.; Kodali, M.; Lautenschlaeger, T.; Adeberg, S.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; et al. Disease-Related Outcomes and Toxicities of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy After Lung-Sparing Pleurectomy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Systematic Review. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Perrot, M.; Wu, L.; Wu, M.; Cho, B.C.J. Radiotherapy for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e532–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, B.; Schwarz, S.; Cho, A.; Sinn, K.; Steindl, A.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Köstler, W.J.; Dieckmann, K.; Heilmann, M.; Widder, J.; et al. Impact of Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Pleural Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in Multimodality Treatment for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Thorac. Cancer 2025, 16, e70024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layer, J.P.; Fischer, P.; Dejonckheere, C.S.; Sarria, G.R.; Mispelbaum, R.; Hattenhauer, T.; Wiegreffe, S.; Glasmacher, A.R.; Layer, K.; Nour, Y.; et al. Safety and efficacy of helical tomotherapy following lung-sparing surgery in locally advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2023, 200, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, H.; Ozdemir, S.; Dogan, B.; Gunalp, G.; Ozden, A.S. Trimodality therapy of malignant pleural mesothelioma with helical tomotherapy. North. Clin. Istanb. 2023, 10, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, E.; Arpa, D.; Ghigi, G.; Fabbri, L.; Foca, F.; Tontini, L.; Neri, E.; Pieri, M.; Cima, S.; Burgio, M.A.; et al. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Preliminary Toxicity Results of Adjuvant Radiotherapy Hypofractionation in a Prospective Trial (MESO-RT). Cancers 2023, 15, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müdder, T.; Sarria, G.; Henkenberens, C.; Holz, J.; Garbe, S.; Röhner, F.; Stumpf, S.; Buchstab, T.; Giordano, F.; Leitzen, C. Dosimetric Comparison Between Helical Tomotherapy and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy in Patients With Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 34, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, G.G.; John, T.; Ball, D.L. Controversies in the role of radiotherapy in pleural mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.J.; Flores, R.M.; Wolf, A.S. Taken Together: Effective Multimodal Approaches for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2020, 30, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.M.; Voigt, S.L.; Jawitz, O.K.M.; Farrow, N.E.M.; Rhodin, K.E.; Yang, C.-F.J.; Tong, B.C.M.; D’aMico, T.A.; Harpole, D.H. The Impact of Adjuvant Hemithoracic Radiation on Outcomes in Patients With Stage I-III Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Ann. Surg. 2021, 277, e648–e656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Date, Journal and Country, Study Type (Level of Evidence) | Patient Group | Outcomes | Key Results | Dose Radiation | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Franceschini et al. (2019) [7] Clin. Lung Cancer, Italy (level II) | 49 patients underwent P/D and adjuvant RT with VMAT | LRC (2, 24, 36 months) | 75.2%, 67.4%, 56.5%. | 44 Gy (22–59.4 Gy) | Limited sample size. |
| PFS (months) | 14.9 | Carboplatin- instead of cisplatin-based chemotherapy and R2 resection showed a negative correlation with OS. | |||
| OS (months) | 21.5 | The percentage of the heart receiving >20 Gy and >30 was associated with late pneumonitis. | |||
| Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 fatigue, lung fibrosis, RP, dyspnea) | 6.2%, 4.1%, 26.6%, 8.2% | A total of 47 patients (96%) treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. | |||
| Shaik et al. (2017) [8] J. Thorac. Oncol. USA (level II) | 209 patients underwent P/D and adjuvant RT (Group A[CONV] = 131, Group B[IMRT] = 78) | OS (months) | A: 12.3 B: 20.2 (p = 0.001) | [CONV]: >45 Gy: 11% pts [IMRT] >45 Gy: 65% pts | Long enrolment period (>40 years). |
| LRC (1- and 2-year rates) | A: 34%, 47% B: 42%, 60% (p = 0.08) | Association between adjuvant hemithoracic IMPRINT, chemotherapy, and P/D with promising OS rates and decreased toxicities. | |||
| PFS (1- and 2-year rates) | A: 47%, 69% B: 53%, 72% (p = 0.07) | 84 patients (41%) received chemotherapy (11% in group A and 90% in group B). | |||
| Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 esophagitis, fatigue, cough) | A: 47%, 16%, 2% B: 23%, 47%, 18% | No significant difference in grade 3/4 RP, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea and dermatitis | |||
| Gupta et al. (2005) [9] Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. USA (level II) | 123 patients underwent P/D and adjuvant external beam RT | OS (months) | 13.5 | 42.5 Gy (7.2–67.8 Gy) | Radiation dose <40 Gy, nonepithelioid histology, left-sided disease, and use of an implant are unfavorable for OS. 14 patients (11%) received chemotherapy (6 neoadjuvant and 8 adjuvant). |
| (2-year rate) | 23% | ||||
| LRC (1-year) | 42% | ||||
| Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 esophagitis, fatigue, RP, dyspnea) | 48.7%, 11.3%, 35.7%, 13.8% | ||||
| Rimner et al. (2016) [10] J. Clin. Oncol. USA (level II) | 27 patients underwent IMRT for MPM (Group A = 11 unresectable; Group B = 16 P/D and neoadjuvant chemotherapy) | Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 RP, esophagitis, fatigue, dyspnea) | 29.6%, 29.6%, 40.7%, 44.4% | 46.8 Gy (28.8–50.4 Gy) | Limited sample size. |
| PFS (months) | 12.4 | ||||
| OS (months) | 23.7 | ||||
| (1- and 2-year rates) | A: 74%, 25% B: 80%, 59% | ||||
| Minatel et al. (2015) [11] Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. Italy (level II) | 69 patients underwent IMRT after P/D (Group A = 35 extended P/D; Group B = 34 partial P/D) | OS (2–3 year) | A: 65%, 44% B: 58%, 36% (p = 0.94). | 50 Gy | Surgery elsewhere. Patients with immediate progression after surgery or chemotherapy were not enrolled. 19 patients (27.5%) developed distant metastases. Correlation between gross residual disease after surgery and OS. 69 patients (100%) received chemotherapy (8 neoadjuvant, 53 adjuvant, and 8 both). |
| LRC (2–3 year) | A: 65%, 58% B: 64%, 42% (p = 0.75). | ||||
| PFS (2–3 year) | A: 50%, 40% B: 40%, 38% (p = 0.76). | ||||
| Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 RP) | 20% | ||||
| Rimner et al. (2014) [12] Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. USA (level II) | 67 patients underwent IMRT after P/D (Group A = 28 extended P/D; Group B = 39 partial P/D or unresectable) | LRC (1–2 year in field local failure) | 56%, 74% A: 43%, 60% B: 66%, 83% (p = 0.03) | 46.8 Gy (45–50.4 Gy) | 43 patients (64%) experienced in-field local failure; 13 (19%) a marginal failure; 25 (37%) had out-of-field failure, and 32 patients (48%) had distant failure. 57 patients (85%) received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. No data regarding acute and late toxicities was reported. |
| (1–2 year distant failure) | 40%, 55% | ||||
| OS (months) | 24 | ||||
| (1–2 year rates) | 85%, 50% | ||||
| Rice et al. (2019) [13] Photochem. Photobiol. USA (level II) | 10 patients underwent chemotherapy, P/D/proton therapy and photodynamic therapy | LRC (1–2 year rates) | 90%, 90% | 55 CGE (50–75 CGE) | Limited sample size. 70% of patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. |
| OS (months) | 30.3 | ||||
| (1–2 year rates) | 58%, 29% | ||||
| Toxicity (Grade 2 RP, cough, dyspnea, dysphagia) | 10%, 10%, 20%, 10% | ||||
| Minatel et al. (2014) [14] Lung Cancer Italy (level II) | 20 patients underwent P/D and adjuvant RT | OS (months) | 33 | 46 Gy | Surgery elsewhere. 7 patients (35%) had distant failure; 3 patients (15%) had an isolated loco-regional recurrence. 19 patients (95%) received chemotherapy (11 adjuvant and 8 both neoadjuvant and adjuvant). |
| (1–3 year rates) | 70%, 49% | ||||
| PFS (months) | 29 | ||||
| (2–3 year rates) | 65%, 46% | ||||
| LRC (2–3 year rates) | 68%, 59% | ||||
| Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 RP, pericardial effusion) | 25%, 10% | ||||
| Parisi et al. (2017) [15] Cancer/Radiothérapie Italy (level II) | 36 patients received IMRT (Group A = 19 P/D; Group B = 17 biopsy) | Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 RP, dyspnea, cough) | 9%, 14%, 17% | 25 Gy (25–30 Gy) | 29 patients (80%) received chemotherapy (no data regarding the timing). |
| OS (months) | 21.6 | ||||
| (1–2 year rates) | A: 85%, 40% | ||||
| Harrabi et al. (2017) [16] Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. Germany (level II) | 10 patients underwent P/D and adjuvant IMRT | Toxicity (Grade ≥ 2 RP) | 20% | 52.2 Gy (40–54 Gy) | Limited sample size. 10 patients (100%) received chemotherapy (2 neoadjuvant and 8 adjuvant). |
| PFS (months) | 13 | ||||
| OS (months) | 19 | ||||
| Arrieta et al. (2020) [17] Thorac. Cancer Mexico (level II) | 15 patients underwent trimodal therapy (chemotherapy, P/D, and adjuvant IMRT) | Toxicity (Grade ≥ 3 RP, esophagitis, fatigue) | 2%, 2%, 3% | 48.7 Gy (23.4–54 Gy) | Limited sample size. Pulmonary function tests were not performed |
| PFS (months) | 18.9 | ||||
| OS (months) | 23.6 | ||||
| LRC (2year rate) | 75.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andolfi, M.; Salati, M.; Refai, M. The Role of Radiotherapy After Pleurectomy/Decortication for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120585
Andolfi M, Salati M, Refai M. The Role of Radiotherapy After Pleurectomy/Decortication for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(12):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120585
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndolfi, Marco, Michele Salati, and Majed Refai. 2025. "The Role of Radiotherapy After Pleurectomy/Decortication for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 12: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120585
APA StyleAndolfi, M., Salati, M., & Refai, M. (2025). The Role of Radiotherapy After Pleurectomy/Decortication for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(12), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120585







