Interstitial Lung Diseases in Israel: Large Variability in Close Geographic Proximity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Periphery vs. Center of Israel
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DIP | Desquamative interstitial pneumonia |
| DLCO | Diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| HP | Hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| ILD | Interstitial lung diseases |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| MC | Medical center |
| MDD | Multidisciplinary discussion |
| NSIP | Non-specific interstitial pneumonia |
| OP | Organizing pneumonia |
| PLCH | Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RB-ILD | Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SSc | Scleroderma and systemic sclerosis |
References
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Suzuki, A.; Maher, T.M. Interstitial lung diseases. Lancet 2022, 400, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furini, F.; Carnevale, A.; Casoni, G.L.; Guerrini, G.; Cavagna, L.; Govoni, M.; Sciré, C.A. The Role of the Multidisciplinary Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Systematic Literature Review of the Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, J.S.; Morisset, J.; Fisher, J.H.; Churg, A.M.; Bilawich, A.M.; Ellis, J.; English, J.C.; Hague, C.J.; Khalil, N.; Leipsic, J.; et al. Role of a Regional Multidisciplinary Conference in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Baratella, E.; Confalonieri, P.; Wade, B.; Marrocchio, C.; Geri, P.; Busca, A.; Pozzan, R.; Andrisano, A.G.; Cova, M.A.; et al. High-Resolution Computed Tomography: Lights and Shadows in Improving Care for SSc-ILD Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Meyer, K.C. Review: Therapies for interstitial lung disease: Past, present and future. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2008, 2, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Ortega, P.; Molina-Molina, M. Interstitial Lung Diseases in Developing Countries. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, M.; Herth, F.J.F.; Wacker, M.; Leidl, R.; Hellmann, A.; Pfeifer, M.; Behr, J.; Witt, S.; Kauschka, D.; Mall, M.; et al. Exploring Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Rationale, Aims, and Design of a Nationwide Prospective Registry—The EXCITING-ILD Registry. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 123876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Sing, C.-W.; Hubbard, R.; Lam, D.C.L.; Li, H.-L.; Li, G.H.-Y.; Ho, S.-C.; Cheung, C.L. Prevalence, incidence, and survival analysis of interstitial lung diseases in Hong Kong: A 16-year population-based cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2024, 42, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, O.; Hadad, Y.; Shalmon, T.; Wand, O.; Schneer, S.; Perluk, T.M.; Kleinhendler, E.; Hershko, T.; Tiran, B.; Aviram, G.; et al. Real-Life Diagnostic Performance of the Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Guidelines: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Myers, J.L.; Kreuter, M.; Vasakova, M.; Bargagli, E.; Chung, J.H.; Collins, B.F.; Bendstrup, E.; et al. Diagnosis of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Adults. An Official ATS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, e36–e69, Erratum in Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Perelas, A.; Yadav, R.; Kirby, D.F.; Singh, A. Viewpoint: A multidisciplinary approach to the assessment of patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perluk, T.M.; Regev, I.F.; Freund, O.; Kleinhendler, E.; Hershko, T.; Ben-Ami, S.; Bar-Shai, A.; Unterman, A. Importance of physician history taking in complementing patient-reported interstitial lung disease questionnaire. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel’s Central Bureau of Statistics. 2021 Israeli Population Report. Available online: https://www.cbs.gov.il/en/cbsNewBrand/Pages/community-new.aspx?inc=https://boardsgenerator.cbs.gov.il/pages/WebParts/YishuvimPage.aspx?mode=Machoz (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Bar-Shai, A.; Freund, O.; Ovdat, T.; Segel, M.J.; Klempfner, R.; Elis, A. Management of acute COPD exacerbations in the internal medicine departments in Israel–a national survey. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1174148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomi, D.; Galor, I.; More, A.; Oberman, B.; Fireman, L. Latent tuberculosis infection prevalence in second generation immigrants from high to low TB burden countries. Pulmonology 2023, 29, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broday, D.; Yuval, A. Air Pollution in the Haifa Bay Area in the Last Twenty Years. 2020. Available online: https://www.magazine.isees.org.il/?p=18614 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Yuval, A.; Broday, D. High-resolution spatial patterns of long-term mean concentrations of air pollutants in Haifa Bay area. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3653–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.I.; Hellman, S.; Brenner, S.; Egoz, N.; Rishpon, S. Prevalence of respiratory conditions among schoolchildren exposed to different levels of air pollutants in the Haifa Bay area, Israel. Environ. Health Perspect. 1990, 89, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Economy and Industry of Israel. Employment in Arab Society. 2008. Available online: https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/pmopolicy/dec550_2021/he/Gov_Docs_job071121.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Boyle, T.; Carey, R.N.; Glass, D.C.; Peters, S.; Fritschi, L.; Reid, A. Prevalence of occupational exposure to carcinogens among workers of Arabic, Chinese and Vietnamese ancestry in Australia. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2015, 58, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel’s Central Bureau of Statistics. The Face of Society in Israel. 2008. Available online: https://www.cbs.gov.il/he/publications/DocLib/2008/rep_01/pdf/h_print.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Moua, T.; Martinez, A.C.Z.; Baqir, M.; Vassallo, R.; Limper, A.H.; Ryu, J.H. Predictors of diagnosis and survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and connective tissue disease-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Strek, M.E.; Adegunsoye, A.; Wong, A.W.; Assayag, D.; Cox, G.; Fell, C.D.; Fisher, J.H.; Gershon, A.S.; Halayko, A.J.; et al. Inhalational exposures in patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease: Presentation, pulmonary function and survival in the Canadian Registry for Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respirology 2022, 27, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Feary, J.; Johannson, K.A. Environmental and occupational exposures in interstitial lung disease. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Adegunsoye, A.; Chung, J.H.; Ventura, I.B.; Jablonski, R.; Montner, S.; Vij, R.; Hines, S.E.; Strek, M.E. Characteristics and Prevalence of Domestic and Occupational Inhalational Exposures Across Interstitial Lung Diseases. Chest 2021, 160, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, S.; Murgia, N. Work-related interstitial lung disease: What is the true burden? Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2022, 26, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenbacher, W.L.; Kreiss, K.; Lougheed, M.D.; Pransky, G.S.; Day, B.; Castellan, R.M. Nylon Flock–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougheed, M.D.; Roos, J.O.; Waddell, W.R.; Munt, P.W. Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonitis and Diffuse Alveolar Damage in Textile Workers. Chest 1995, 108, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Olsen, J.H. Increased risk of lung cancer among different types of professional drivers in Denmark. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 55, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goon, S.; Bipasha, M.S. Prevalence and Pattern of Smoking among Bus Drivers of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Tob. Use Insights 2014, 7, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagabo, R.; Thiese, M.S.; Eden, E.; Thatcher, A.C.; Gonzalez, M.; Okuyemi, K. Truck Drivers’ Cigarette Smoking and Preferred Smoking Cessation Methods. Subst. Abus. Res. Treat. 2020, 14, 1178221820949262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEST Foundation. CHEST Interstitial and Diffuse Lung Disease Patient Questionnaire. 2020. Available online: https://www.chestnet.org/membership-and-community/philanthropy (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Thomeer, M.J.; Costabel, U.; Rizzato, G.; Poletti, V.; Demedts, M. Comparison of registries of interstitial lung diseases in three European countries. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 114S–118S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, B.; Cottin, V.; Collard, H.R.; Valenzuela, C. Variability in Global Prevalence of Interstitial Lung Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 751181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel’s Ministry of Health. The Minister of Health’s Report on Smoking in Israel for 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.il/en/pages/13122021-05 (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Croft, J.B.; Wheaton, A.G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; Lu, H.; Matthews, K.A.; Cunningham, T.J.; Wang, Y.; Holt, J.B. Urban-Rural County and State Differences in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease—United States, 2015. Mmwr-Morbidity Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.A.; Weinberger, A.H.; Eggers, E.M.; Parker, E.S.; Villanti, A.C. Trends in Rural and Urban Cigarette Smoking Quit Ratios in the US From 2010 to 2020. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2225326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa-Hadad, J.; Linn, S.; Rafaeli, S. A Web-Based Program to Increase Knowledge and Reduce Cigarette and Nargila Smoking Among Arab University Students in Israel: Mixed-Methods Study to Test Acceptability. J. Med Internet Res. 2015, 17, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalter-Leibovici, O.; Chetrit, A.; Avni, S.; Averbuch, E.; Novikov, I.; Daoud, N. Social characteristics associated with disparities in smoking rates in Israel. Isr. J. Health Policy Res. 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.R.; Blanc, P.D.; Fireman, E.; Amital, A.; Guber, A.; Rhahman, N.A.; Shitrit, D. Artificial Stone Silicosis. Chest 2012, 142, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
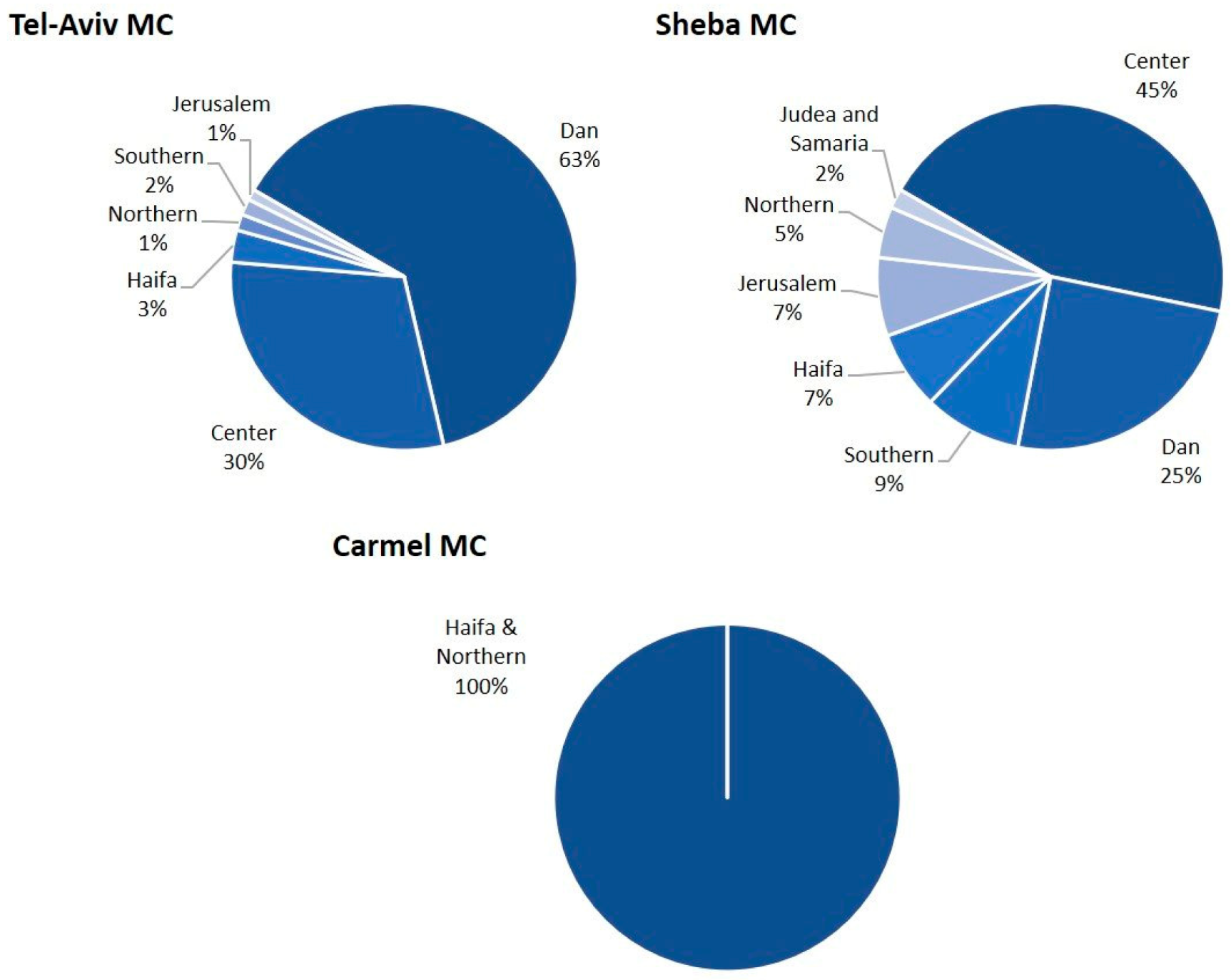
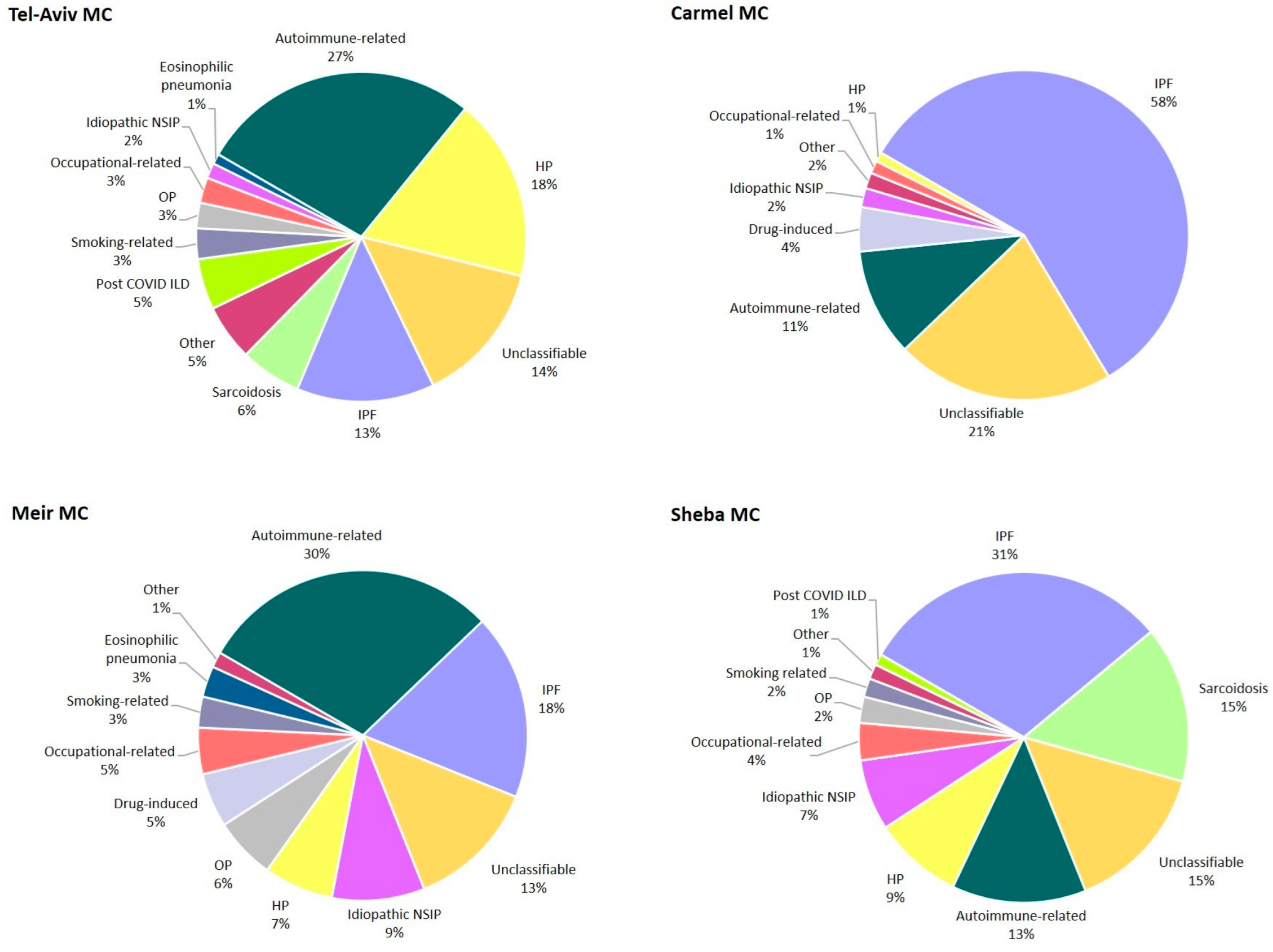

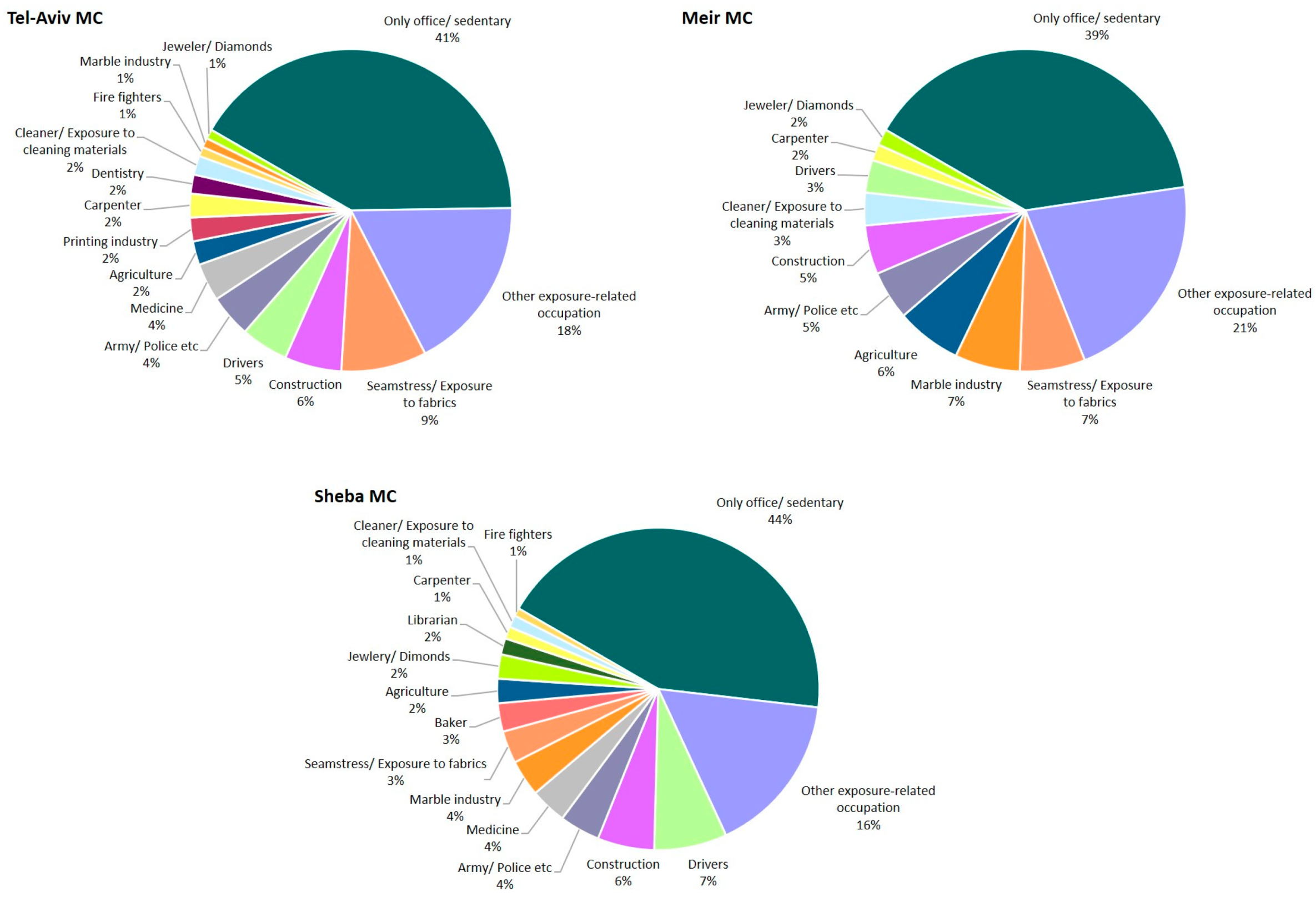
| Variable | S-MC | TA-MC | M-MC | C-MC | Total | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 232 (%) | N = 188 (%) | N = 132 (%) | N = 321 (%) | N = 873 (%) | ||
| Female sex | 96 (41) | 94 (50) | 58 (44) | 102 (32) | 350 (40) | <0.01 |
| Age, mean (SD) # | 63 (13) | 68 (12) | 65 (14) | 71 (11) | 67 (13) | <0.01 |
| Peripheral residence | 54 (23) | 12 (6) | N/A | 321 (100) | 387 (52) | <0.01 |
| Ever smoker | 126 (54) | 110 (59) | 68 (51) | 189 (59) | 493 (57) | 0.42 |
| Pack years, median (IQR) | 30 (15–50) | 26 (11–50) | 30 (20–40) | 35 (20–50) | 30 (18–50) | 0.07 |
| EO exposures ^ | 121 (52) | 145 (77) | 69 (52) | N/A | 335 (61) | <0.01 |
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Jews | 162 (82.2) | 182 (96.8) | N/A | 242 (75.3) | 321 (43) | <0.01 |
| Arabs | 28 (14.2) | 4 (2.1) | N/A | 79 (24.7) | ||
| Other | 7 (3.6) ¶ | 2 (1.1) | N/A | 0 | ||
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Non-ILD lung disease | 33 (14) | 42 (22) | 17 (13) | 28 (9) | 120 (14) | <0.01 |
| Hypertension | 67 (29) | 87 (46) | 53 (40) | 153 (48) | 360 (41) | <0.01 |
| Diabetes | 56 (24) | 52 (28) | 31 (24) | 85 (27) | 224 (26) | 0.77 |
| Dyslipidemia | 84 (36) | 84 (45) | 43 (33) | 151 (47) | 362 (42) | 0.01 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 51 (22) | 51 (27) | 32 (24) | 118 (37) | 252 (29) | <0.01 |
| Heart failure | 26 (11) | 26 (14) | 12 (9) | 49 (15) | 113 (13) | 0.26 |
| History of Cancer | 42 (18) | 31 (17) | 13 (10) | 51 (16) | 137 (16) | 0.21 |
| Pulmonary functions, mean (SD) # | ||||||
| FVC (% pred) ¶ | 72.5 (23) | 76.8 (19) | 75.7 (20) | 81.2 (21) | 77.1 (22) | <0.01 |
| DLCO (% pred) ¶ | 59.1 (19) | 53.6 (19) | 51.7 (18) | 60.9 (19) | 54.7 (20) | <0.01 |
| ILD | Variable | Central | Peripheral | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | Older age | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | <0.01 | 1.04 (1.02–1.06) | <0.01 |
| Female sex | 0.44 (0.27–0.73) | <0.01 | 0.24 (0.15–0.38) | <0.01 | |
| Ever smoking | 1.56 (0.95–2.38) | 0.09 | 2.22 (1.49–3.35) | <0.01 | |
| Pack years | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.04 | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.04 | |
| CVD | 1.48 (0.89–2.51) | 0.14 | 1.61 (1.05–2.47) | 0.03 | |
| Autoimmune-related | Older age | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 0.01 | 0.95 (0.93–0.97) | <0.01 |
| Female sex | 4.13 (2.43–6.97) | <0.01 | 4.23 (2.36–7.49) | <0.01 | |
| Ever smoking | 0.61 (0.38–0.99) | 0.04 | 0.50 (0.29–0.88) | 0.03 | |
| Exposure related ^ | Older age | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.07 | 0.94 (0.87–0.94) | <0.01 |
| Female sex | 1.34 (0.79–2.30) | 0.36 | 0.74 (0.26–2.10) | 0.52 | |
| Ever smoker | 0.68 (0.39–1.16) | 0.16 | 0.67 (0.27–1.68) | 0.41 | |
| Interstitial Lung Disease | Living in Peripheral vs. Central Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis # | 2.95 | 2.12–4.11 | <0.01 |
| Autoimmune-related | 0.7 | 0.48–1.05 | 0.09 |
| Exposure-related ^ | 0.46 | 0.33–0.63 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hershko, T.; Freund, O.; Schneer, S.; Segel, M.J.; Wand, O.; Bar-Shai, A.; Shitrit, D.; Levy, L.; Adir, Y.; Unterman, A. Interstitial Lung Diseases in Israel: Large Variability in Close Geographic Proximity. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212780
Hershko T, Freund O, Schneer S, Segel MJ, Wand O, Bar-Shai A, Shitrit D, Levy L, Adir Y, Unterman A. Interstitial Lung Diseases in Israel: Large Variability in Close Geographic Proximity. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(21):2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212780
Chicago/Turabian StyleHershko, Tzlil, Ophir Freund, Sonia Schneer, Michael J. Segel, Ori Wand, Amir Bar-Shai, David Shitrit, Liran Levy, Yochai Adir, and Avraham Unterman. 2025. "Interstitial Lung Diseases in Israel: Large Variability in Close Geographic Proximity" Diagnostics 15, no. 21: 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212780
APA StyleHershko, T., Freund, O., Schneer, S., Segel, M. J., Wand, O., Bar-Shai, A., Shitrit, D., Levy, L., Adir, Y., & Unterman, A. (2025). Interstitial Lung Diseases in Israel: Large Variability in Close Geographic Proximity. Diagnostics, 15(21), 2780. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212780






