Clinical Characteristics and Survival of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Analysis of the Serbian Cohort from the EMPIRE Registry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population, Inclusion Criteria, Baseline, and Follow-Up Assessment
2.2. Pulmonary Function Tests and Imaging
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Regional Subject Distribution
3.2. Follow-Up
3.3. Baseline Characteristic
3.4. Radiological Pattern
3.5. Comorbidities
3.6. Therapy
3.7. Pulmonary Function Tests
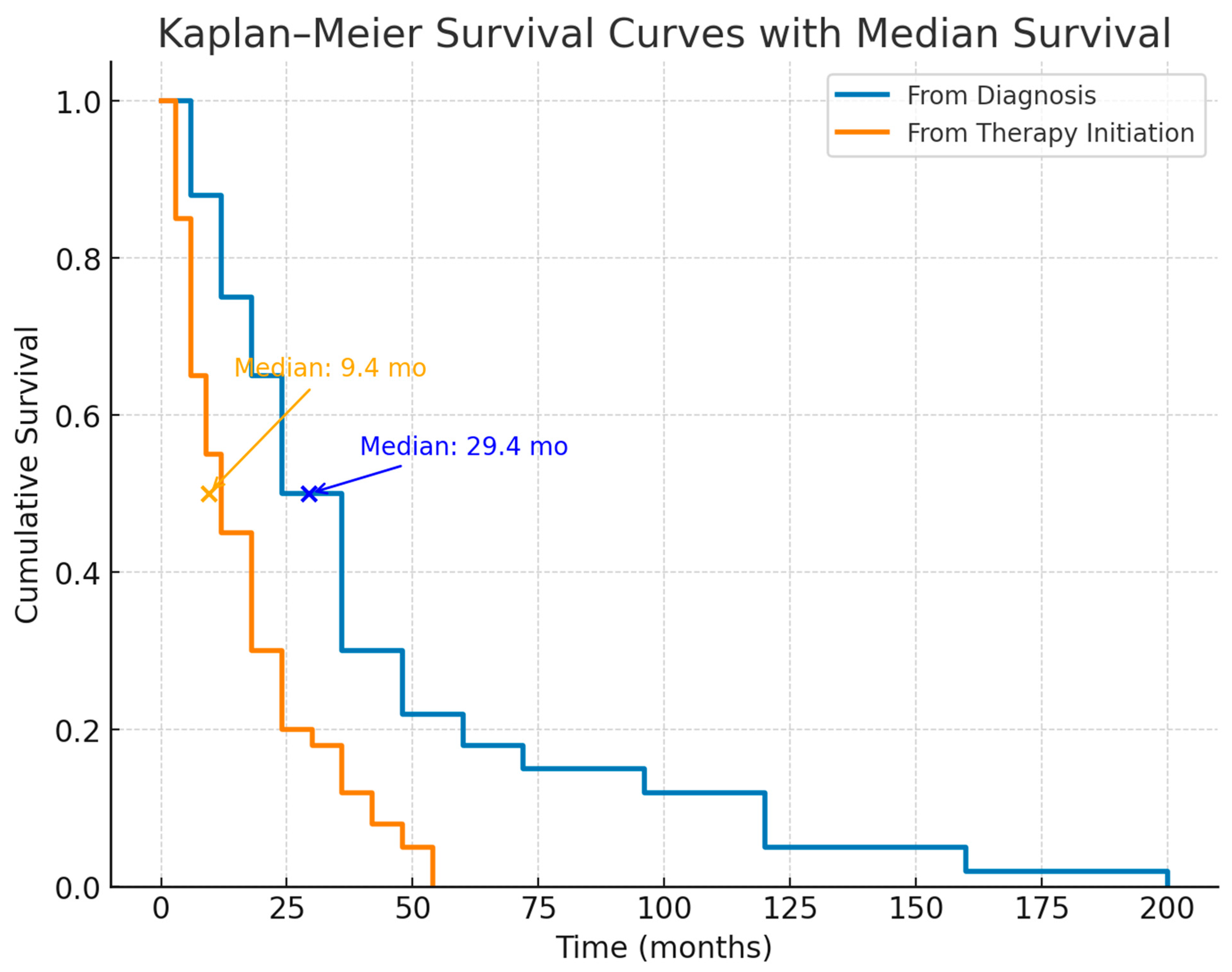
3.8. Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| FVC | forced vital capacity |
| FEV1 | forced expiratory volume in one second |
| DLco | diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide |
| 6MWDT | six-minute walk distance test |
| HRCT | high-resolution computed tomography |
| UIP | usual interstitial pneumonia |
| BMI | Body mass index. |
References
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; ILDs Study Group Sip/IRS; Bergantini, L.; D’Alessandro, M.; Pianigiani, T.; Simonetti, J.; Iovene, B.; Varone, F.; Sgalla, G.; Richeldi, L.; et al. The management of Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis in different medical settings: Where does that leave us? An Italian na-tionwide survey. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2024, 41, e2024047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Talwar, P. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF): Disease pathophysiology, targets, and potential therapeutic interventions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 479, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, I.; Afzal, M.; Islam, A.; Sohal, S.S.; Hassan, M.I. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Pathophysiology, cellular signaling, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Med. Drug Discov. 2023, 20, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokland, K.E.C.; Waters, D.W.; Schuliga, M.; Read, J.; Pouwels, S.D.; Grainge, C.L.; Jaffar, J.; Westall, G.; Mutsaers, S.E.; Prêle, C.M.; et al. Senescence of IPF Lung Fibroblasts Disrupt Alveolar Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Promote Migration in Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisman, M.; Nizamoglu, M.; Noordhoek, J.A.; Timens, W.; Burgess, J.K.; Heijink, I.H. Dysregulated cross-talk between alveolar epithelial cells and stromal cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis reduces epithelial regenerative capacity. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1182368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ling, F.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals special basal cells and fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzilas, V.; Koti, A.; Papandrinopoulou, D.; Tsoukalas, G. Prognostic factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 338, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Collard, H.R.; King, T.E. Clinical Course and Prediction of Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.E.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerty, J.P.; Ponnuswamy, A.; Dutta, P.; Abdelaziz, A.; Kamil, H. Efficacy of antifibrotic drugs, nintedanib and pirfenidone, in treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in both idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and non-IPF: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Cooper, B.G.; Jensen, R.; Kendrick, A.; MacIntyre, N.R.; Thompson, B.R.; Wanger, J. 2017 ERS/ATS standards for single-breath carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATS Statement. Guidelines for the Six-Minute Walk Test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2002, 166, 111–117. [CrossRef]
- Kolonics-Farkas, A.M.; Šterclová, M.; Mogulkoc, N.; Lewandowska, K.; Müller, V.; Hájková, M.; Kramer, M.; Jovanovic, D.; Tekavec-Trkanjec, J.; Studnicka, M.; et al. Differences in Baseline Characteristics and Access to Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Patients With IPF in the EMPIRE Countries. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 729203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.E.; Glaspole, I.; Grainge, C.; Goh, N.; Hopkins, P.M.A.; Moodley, Y.; Reynolds, P.N.; Chapman, S.; Walters, E.H.; Zappala, C.; et al. Baseline characteristics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Analysis from the Australian Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Šterclová, M.; Mogulkoc, N.; Lewandowska, K.; Müller, V.; Hájková, M.; Kramer, M.R.; Jovanović, D.; Tekavec-Trkanjec, J.; Studnicka, M.; et al. The European MultiPartner IPF registry (EMPIRE): Validating long-term prognostic factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Prasse, A.; Wirtz, H.; Koschel, D.; Pittrow, D.; Held, M.; Klotsche, J.; Andreas, S.; Claussen, M.; Grohé, C.; et al. Survival and course of lung function in the presence or absence of antifibrotic treatment in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Long-term results of the INSIGHTS-IPF registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1902279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunisto, J.; Salomaa, E.-R.; Hodgson, U.; Kaarteenaho, R.; Kankaanranta, H.; Koli, K.; Vahlberg, T.; Myllärniemi, M. Demographics and survival of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the FinnishIPF registry. ERJ Open Res. 2019, 5, 00170-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kalafatis, D.; Carlson, L.; Pesonen, I.H.A.; Li, C.-X.; Wheelock, Å.; Magnusson, J.M.; Sköld, C.M. Baseline characteristics and survival of patients of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A longitudinal analysis of the Swedish IPF Registry. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, D.; Yow, E.; Neely, M.; Belperio, J.; Bender, S.; Andrade, J.D.; Roman, J.; Whelan, T.; Palmer, S.; Conoscenti, C. Characteristics of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) in the us: Data from the ipf-pro registry. CHEST 2018, 154, 397A–398A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasakova, M.; Sterclova, M.; Mogulkoc, N.; Kus, J.; Müller, V.; Hajkova, M.; Jovanovic, D.; Tekavec-Trkanjec, J.; Kremer, M.; Svoboda, M.; et al. Real world idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the EMPIRE registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, PA2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukihara, J.; Kondoh, Y.; Brown, K.K.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Matsuda, T.; Yamano, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Furukawa, T.; Sumikawa, H.; et al. Probable usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on chest CT: Is it sufficient for a diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1802465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.B.; Pride, N.B. Examination of the carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (DL(CO)) in relation to its KCO and VA components. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, J.; Cascella, M. Diffusing Capacity of the Lungs for Carbon Monoxide. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556149/ (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. New. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, D.; Bengtson, L.G.S.; Conoscenti, C.S.; Anderson, A.J.; Brekke, L.; Shetty, S.S.; de Andrade, J. Impact of timing of nintedanib initiation among patients newly diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Med. Econ. 2022, 25, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, S.E.; Pavone, M.; Vancheri, A.; Vancheri, C. When to start and when to stop antifibrotic therapies. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, D.M.; Šterclová, M.; Mogulkoc, N.; Lewandowska, K.; Müller, V.; Hájková, M.; Studnicka, M.; Tekavec-Trkanjec, J.; Littnerová, S.; Vašáková, M. Comorbidity burden and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The EMPIRE registry study. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collum, S.D.; Amione-Guerra, J.; Cruz-Solbes, A.S.; DiFrancesco, A.; Hernandez, A.M.; Hanmandlu, A.; Youker, K.; Guha, A.; Karmouty-Quintana, H. Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Current and Future Perspectives. Can. Respir. J. 2017, 2017, 1430350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Bryant, A.J.; Sahay, S.; Wareing, N.; Zhou, Y.; Pandit, L.M.; Karmouty-Quintana, H. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension: Heracles meets the Hydra. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Value | %/IQR/sd |
|---|---|---|
| Patient status | Newly diagnosed | 162 (86.2) |
| Diagnosed before database implementation | 26 (13.8) | |
| Gender | Male | 63.8 |
| Female | 36.2 | |
| Median age at diagnosis (years) | 65 | (60–72.2) |
| Median duration of symptoms | 12 months | |
| <6 months | 23.1 | |
| 6–11 months | 22.0 | |
| 12–17 months | 22.0 | |
| 18–23 months | 4.9 | |
| 24–29 months | 9.9 | |
| 30–35 months | 0.0 | |
| 36–41 months | 6.6 | |
| ≥42 months | 11.5 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | Median | 26.8 |
| <20 | 3.2 | |
| 20–24 | 33.5 | |
| 25–29 | 41.1 | |
| 30–34 | 16.8 | |
| 35–39 | 4.9 | |
| Smoking status | Ever-smoker | 51.0 |
| Nonsmoker | 49.0 | |
| NYHA class | I | 8.0 |
| II | 59.0 | |
| III | 27.0 | |
| IV | 5.0 | |
| Main signs/symptoms | Dyspnea | 91 (n = 169) |
| Cough | 58 (n = 107) | |
| Crepitation | 92 (n = 171) | |
| Lung function (% predicted) | FVC | 73.7 (62.4–90.9) |
| FEV1 | 79.8 (66.4–91.4) | |
| DLco | 38.0 (26.9–49.3) |
| Duration of Antifibrotic Therapy (Pirfenidone and Nintedanib) in Months | Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|
| For all patients | 10.6 (3.7–21.1) | 0.598 |
| Deceased | 10.7 (5.3–20.4) | |
| Alive | 10.5 (2.3–21.1) |
| Parameter | Overall Median (IQR) | Alive Median (IQR) | Deceased Median (IQR) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FVC (% predicted) | 73.2 (62.7–88.3) | 75.8 (65.7–88.1) | 71.5 (53.9–92.9) | 0.455 |
| FEV1 (% predicted) | 79.8 (67.2–93.1) | 79.3 (69.9–96.4) | 78.4 (53.9–93.1) | 0.307 |
| DLco (% predicted) | 33.8 (17.2–46.8) | 35.6 (24.3–47.1) | 19.9 (unmeasurable–37.5) | 0.046 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimic-Janjic, S.; Stjepanovic, M.; Belic, S.; Vukosavljevic, D.; Milivojevic, I.; Trboljevac, N.; Nikolic, N.; Stamenic, S.; Stojanovic, M.; Stosic, K.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Survival of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Analysis of the Serbian Cohort from the EMPIRE Registry. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172121
Dimic-Janjic S, Stjepanovic M, Belic S, Vukosavljevic D, Milivojevic I, Trboljevac N, Nikolic N, Stamenic S, Stojanovic M, Stosic K, et al. Clinical Characteristics and Survival of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Analysis of the Serbian Cohort from the EMPIRE Registry. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172121
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimic-Janjic, Sanja, Mihailo Stjepanovic, Slobodan Belic, Dragan Vukosavljevic, Ivan Milivojevic, Nikola Trboljevac, Nikola Nikolic, Slavko Stamenic, Maja Stojanovic, Kristina Stosic, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Characteristics and Survival of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Analysis of the Serbian Cohort from the EMPIRE Registry" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172121
APA StyleDimic-Janjic, S., Stjepanovic, M., Belic, S., Vukosavljevic, D., Milivojevic, I., Trboljevac, N., Nikolic, N., Stamenic, S., Stojanovic, M., Stosic, K., Vasakova, M. K., Stevic, R., Colic, N., Lukic, K., Ilic, M., Isovic, L., Maric, N., Popevic, S., Vucinic-Mihailović, V., ... the Serbian EMPIRE Investigators. (2025). Clinical Characteristics and Survival of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Analysis of the Serbian Cohort from the EMPIRE Registry. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172121







