Diagnostics in Pleural Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pleural Fluid
3. Pleural Fluid Biochemistry
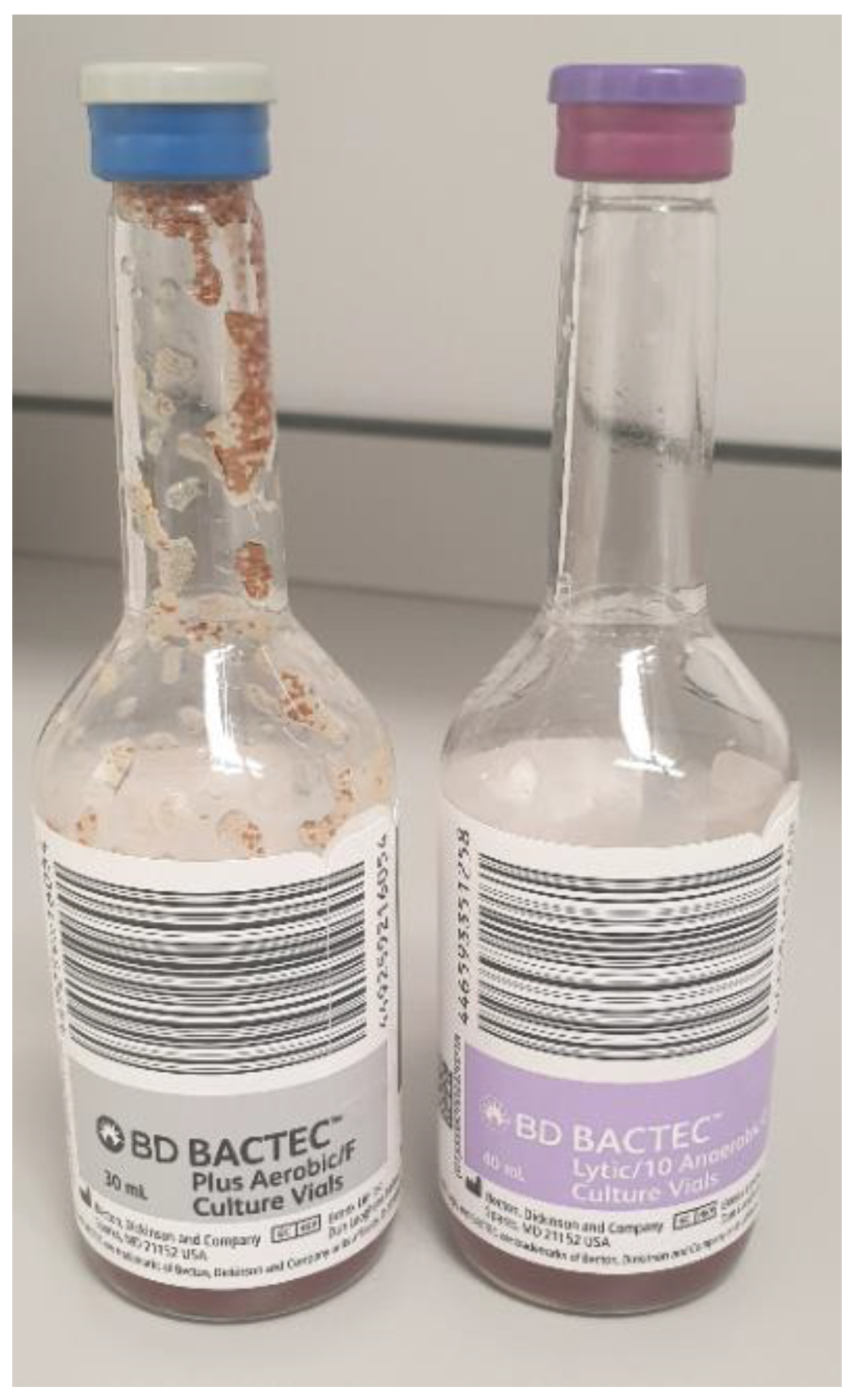
4. Pleural Fluid Microscopy Culture and Sensitivity (MCS)
5. Pleural Fluid Cytology
6. Pleural Biopsies
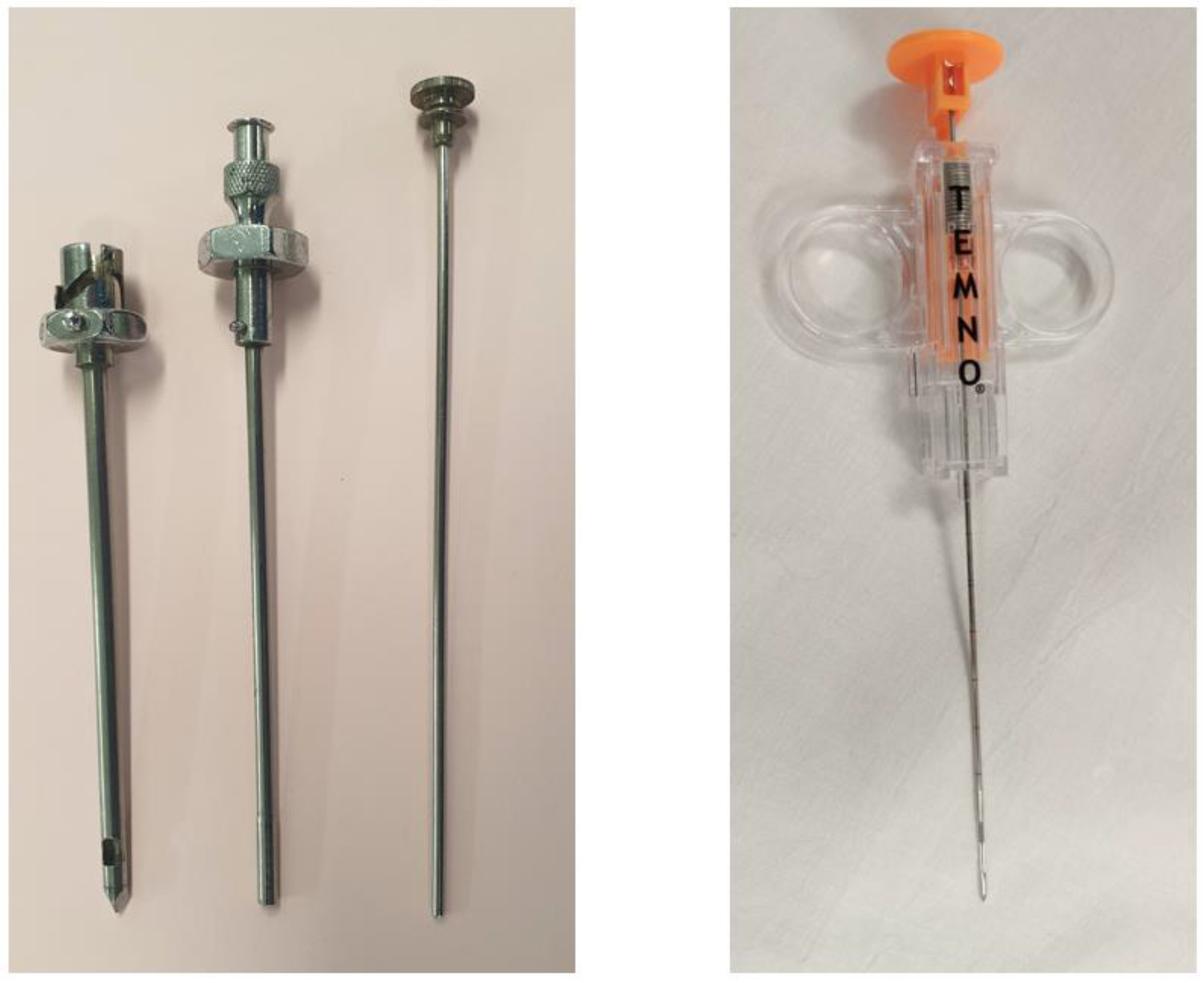
7. Closed Reverse-Bevel Needles (Abrams or Cope)
8. Core Cutting Needle Biopsy
9. Ultrasound vs. CT-Guided
10. Thoracoscopic Biopsies
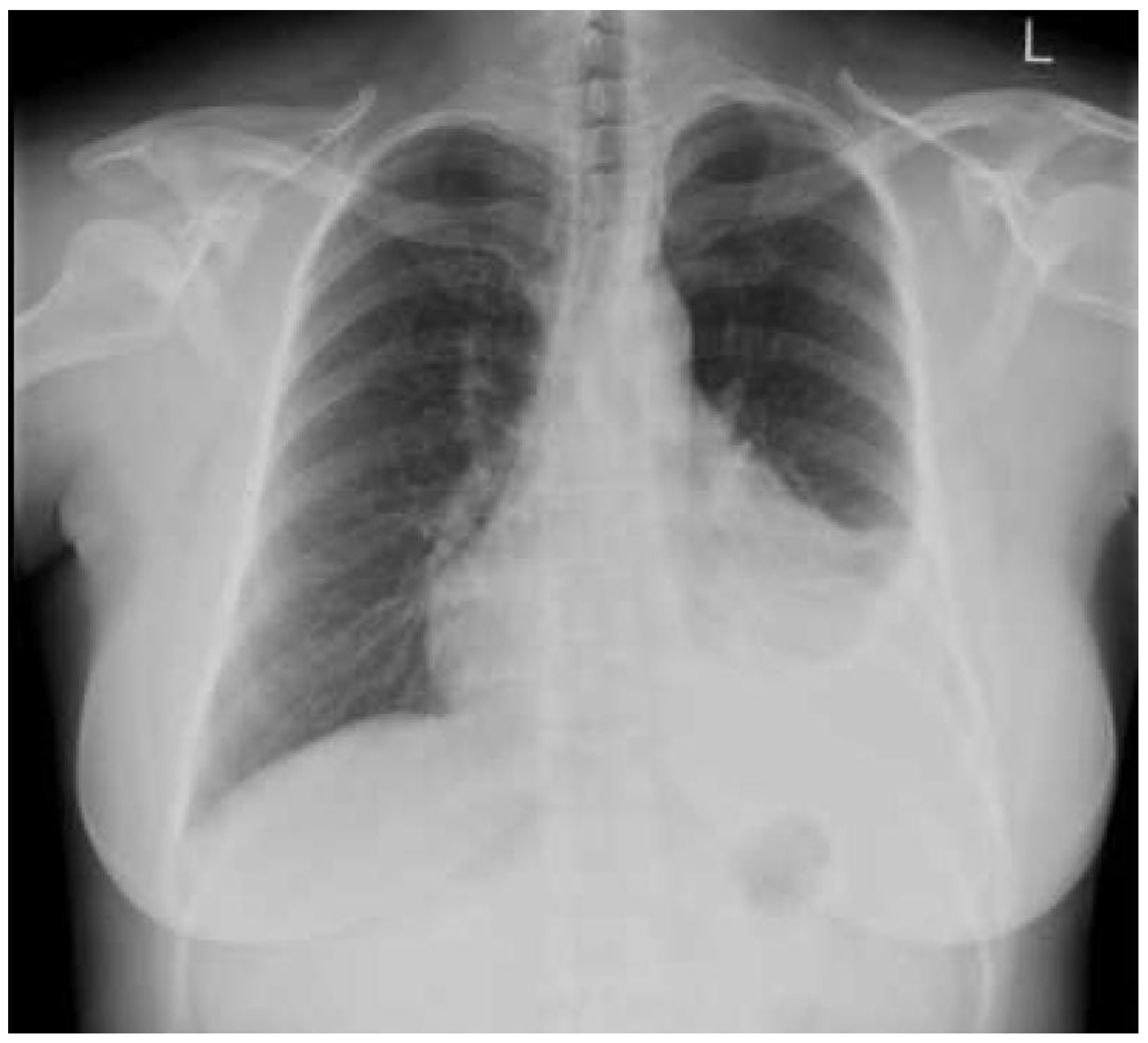
11. Imaging
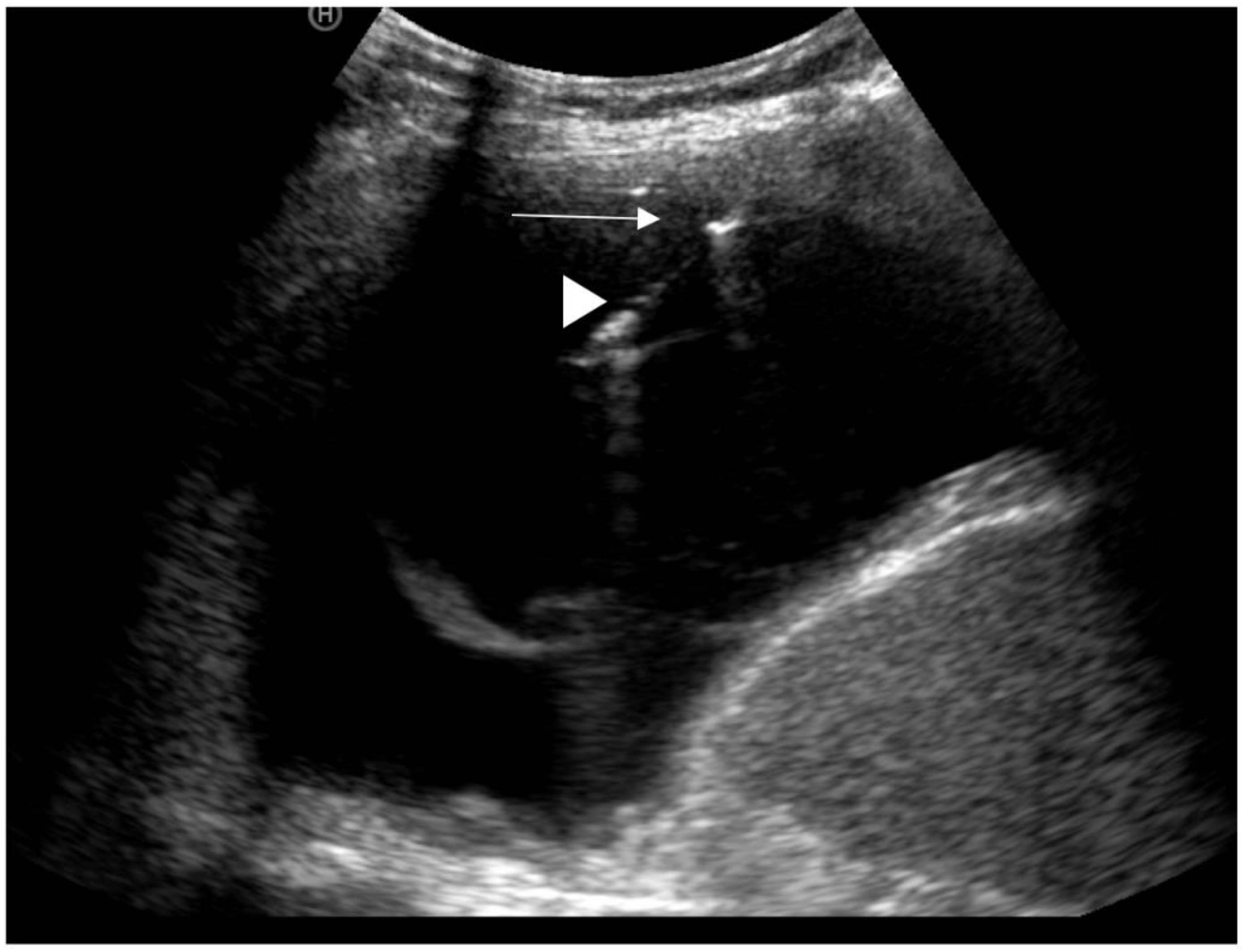
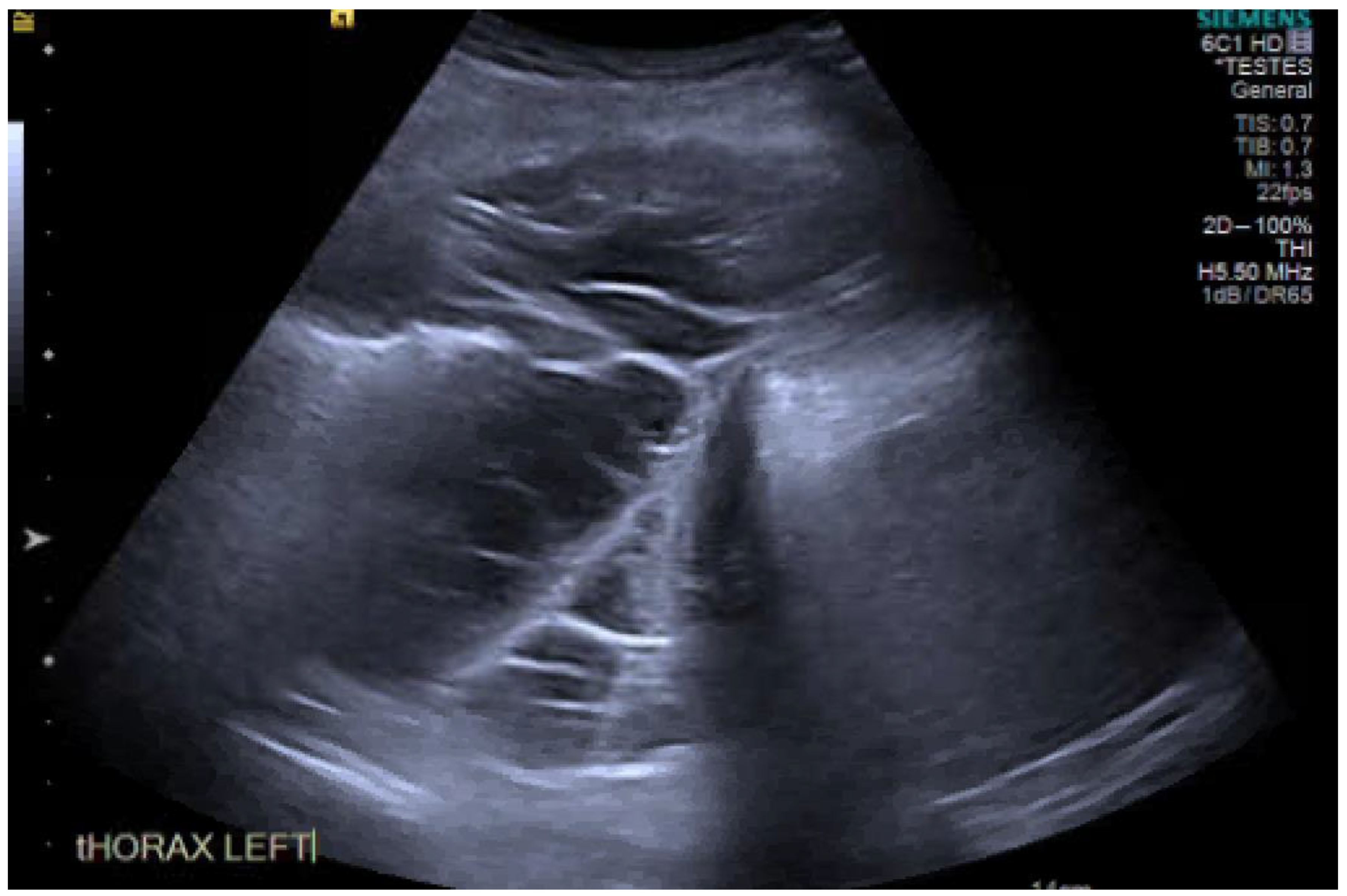
12. Chest Radiograph
13. Ultrasound
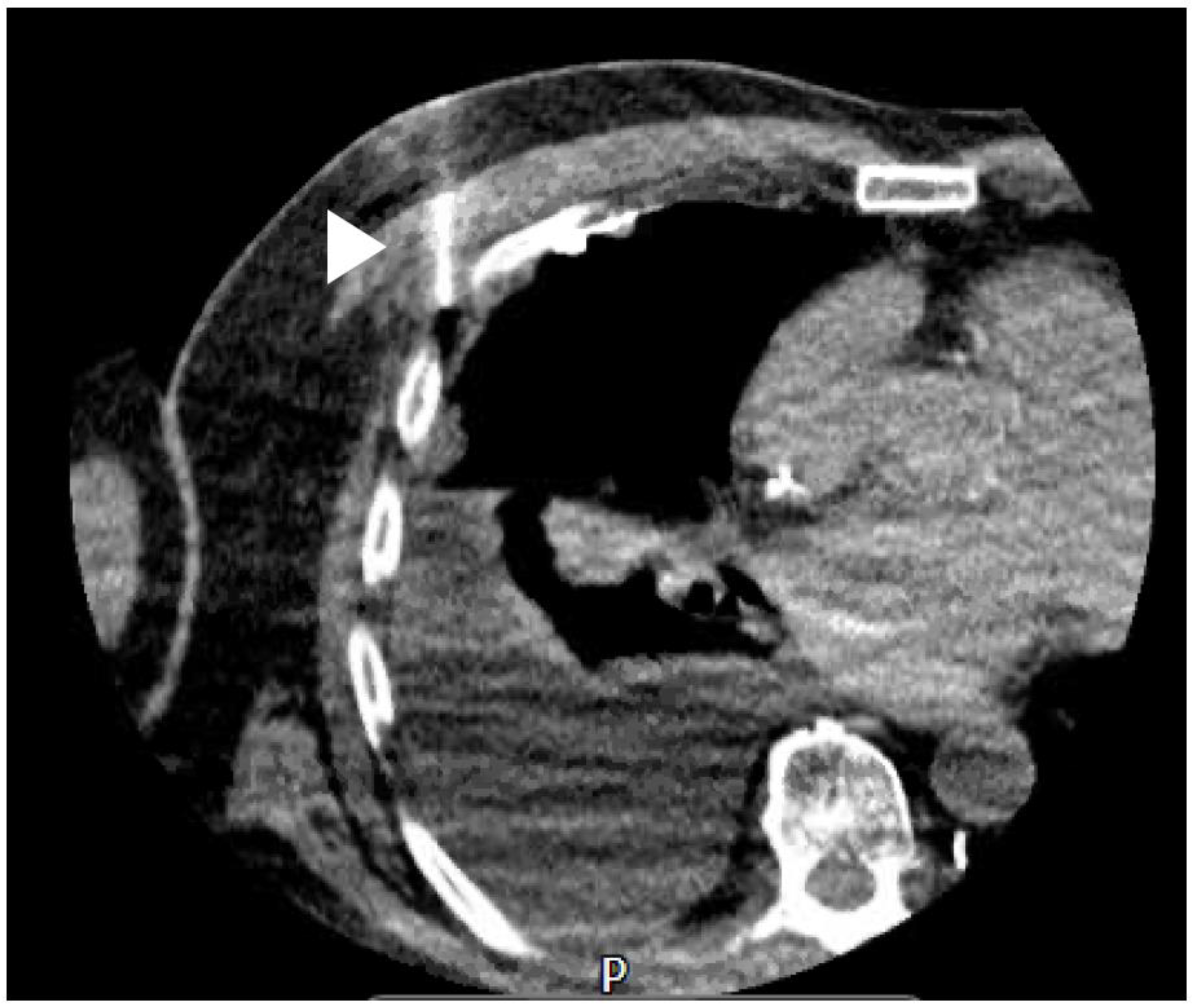
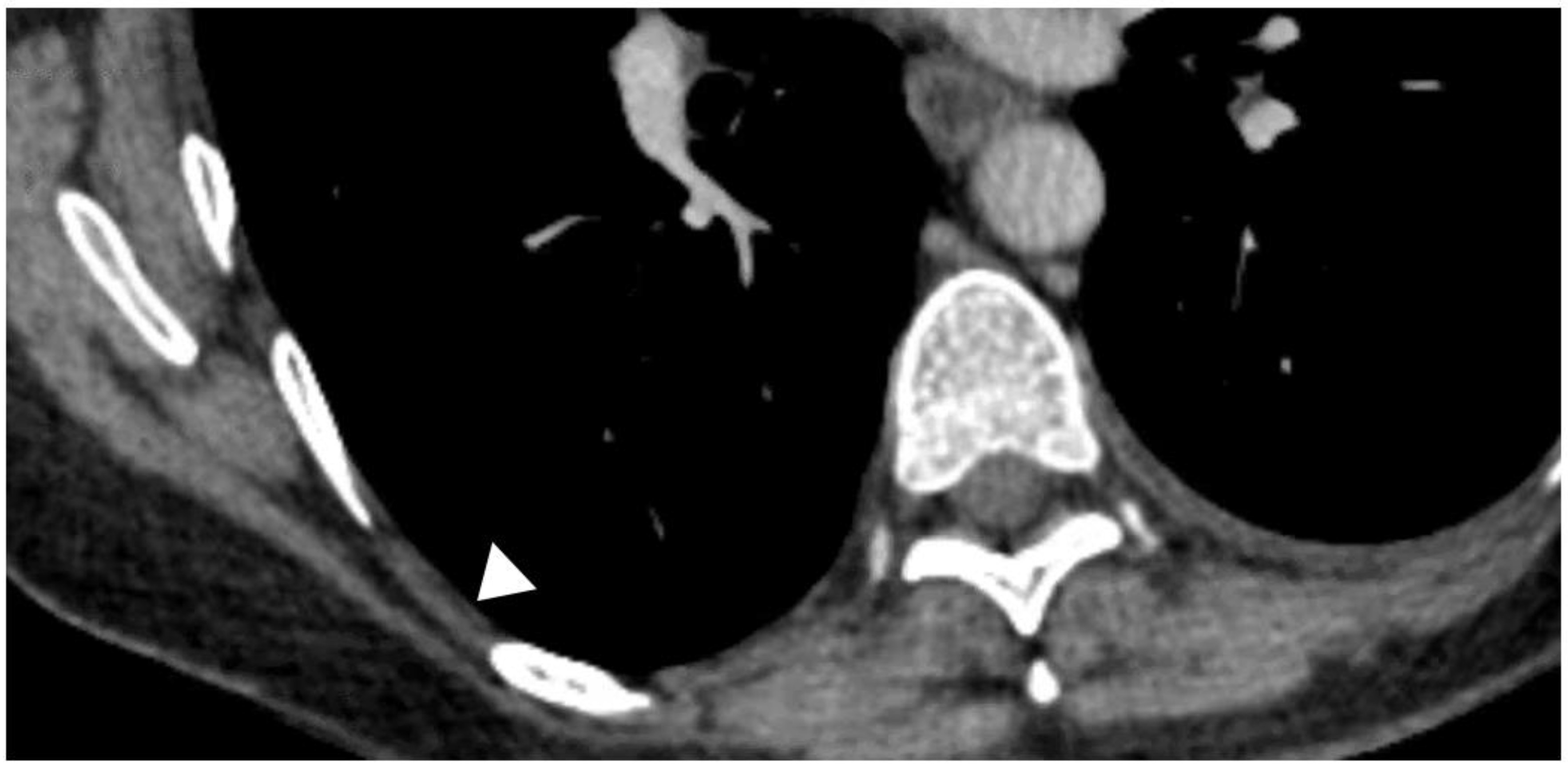
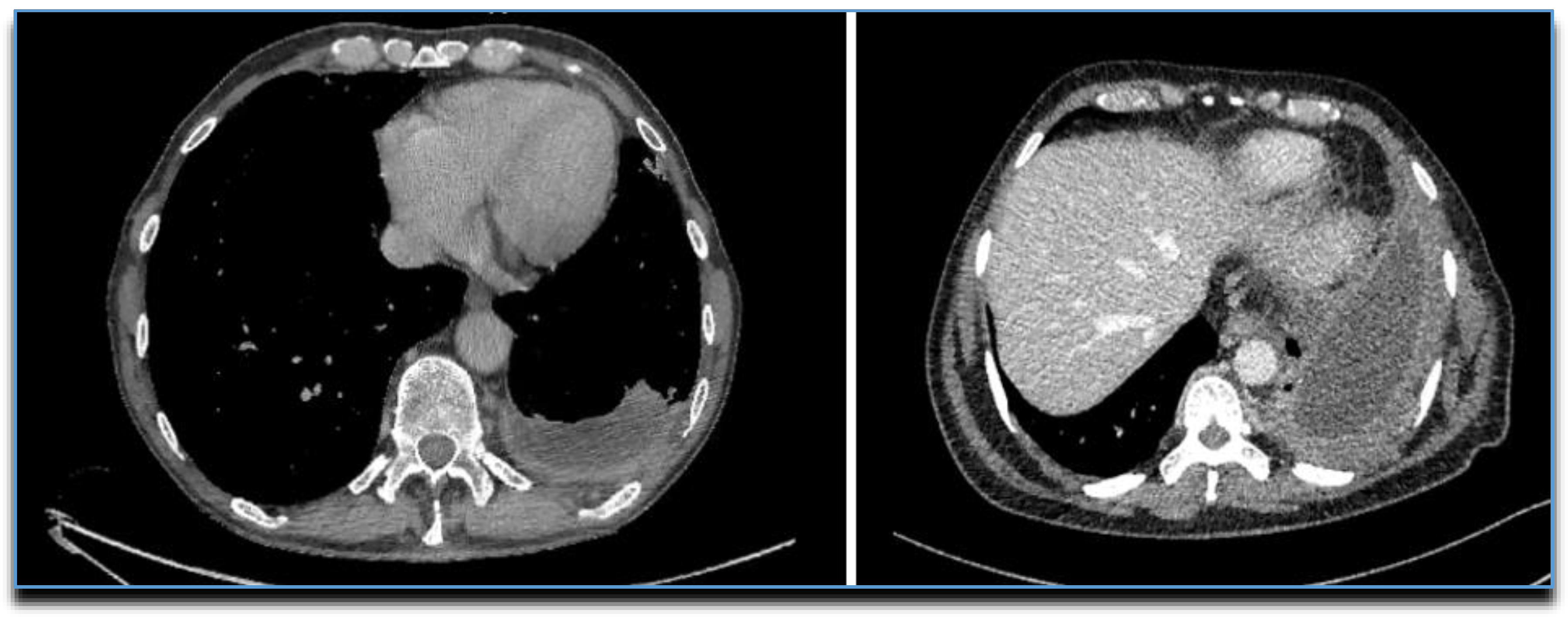
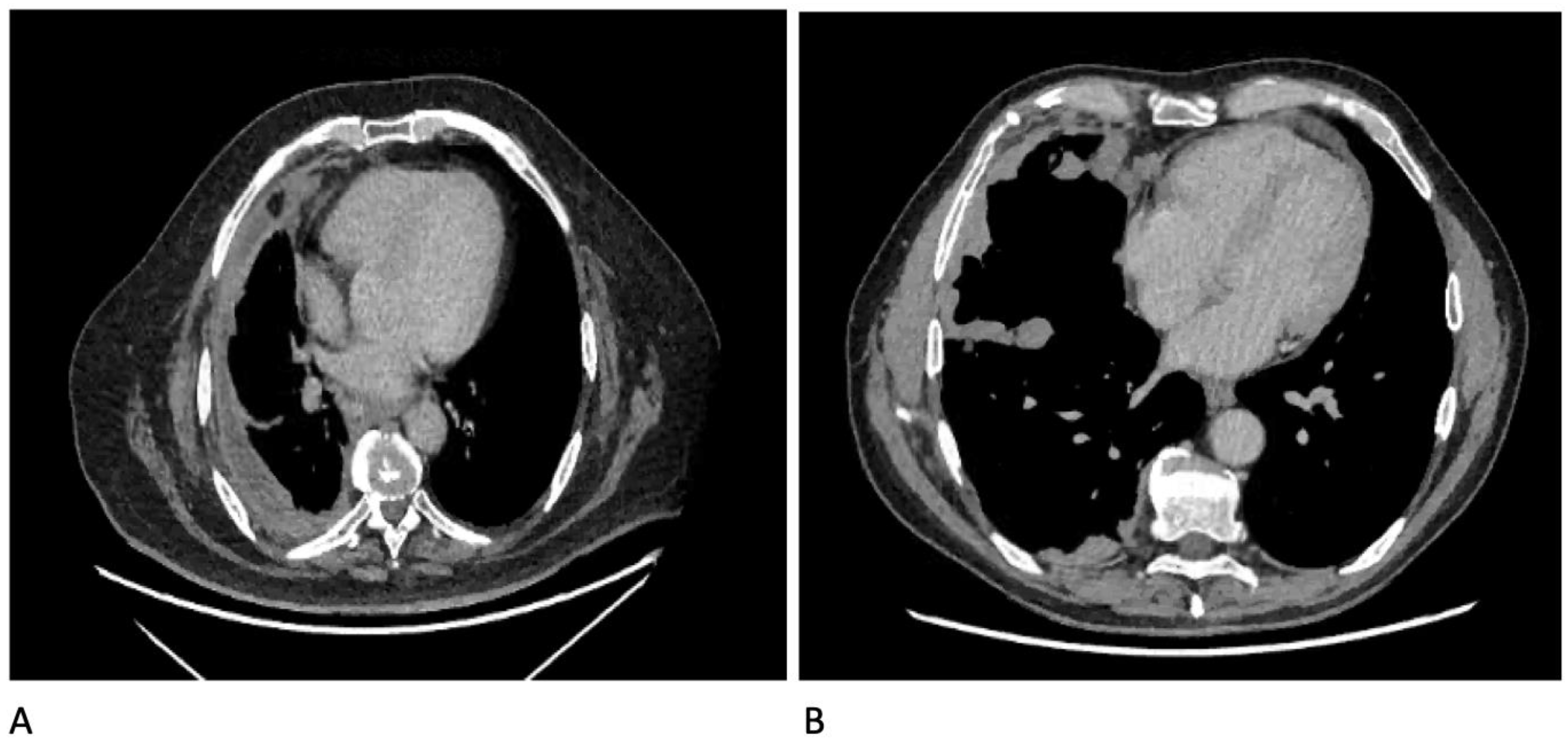
14. CT
15. Other Diagnostic Tests
16. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, N.S. Anatomy of the pleura. Clin. Chest Med. 1998, 19, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppen, M.; De Waele, M.; Li, R.; Gucht, K.V.; D’Haese, J.; Gerlo, E.; Vincken, W. Volume and Cellular Content of Normal Pleural Fluid in Humans Examined by Pleural Lavage. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, E.; D’Angelo, E. Thickness and pressure of the pleural liquid at various heights and with various hydrothoraces. Respir. Physiol. 1969, 6, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserocchi, G. Physiology and pathophysiology of pleural fluid turnover. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintcliffe, O.J.; Hooper, C.E.; Rider, I.J.; Finn, R.S.; Morley, A.J.; Zahan-Evans, N.; Harvey, J.E.; Skyrme-Jones, A.P.; Maskell, N.A. Unilateral Pleural Effusions with More Than One Apparent Etiology. A Prospective Observational Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broaddus, V.C.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P.; Staub, N.C. Clearance of lung edema into the pleural space of volume-loaded anesthetized sheep. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 68, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, M.G.; Feller-Kopman, D.; Maldonado, F. Pleural physiology: What do we understand and what should we measure in clinical practice? In Pleural Disease (ERS Monograph) [Internet]; Maskell, N.A., Laursen, C.B., Lee, Y.C.G., Rahman, N.M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2020; pp. 105–119. Available online: http://public.eblib.com/choice/PublicFullRecord.aspx?p=6181621 (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Mercer, R.M.; Corcoran, J.P.; Porcel, J.M.; Rahman, N.; Psallidas, I. Interpreting pleural fluid results. Clin. Med. 2019, 19, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahn, S.A. Pleural fluid analysis. In Textbook of Pleural Diseases, 2nd ed.; Light, R.W., Lee, Y.C.G., Eds.; Arnold Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Feller-Kopman, D.; Light, R. Pleural Disease. Ingelfinger JR, editor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, R.W. Pleural effusions. Med. Clin. North Am. 2011, 95, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Rull, J.L.; Bielsa, S.; Conde-Martel, A.; Aramburu-Bodas, O.; Llàcer, P.; Quesada, M.A.; Suárez-Pedreira, I.; Manzano, L.; Montero-Pérez-Barquero, M.; Porcel, J.M. Pleural effusions in acute decompensated heart failure: Prevalence and prognostic implications. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 52, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, C.; Lee, G.Y.C.; Maskell, N.A. Investigation of a unilateral pleural effusion in adults: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65 (Suppl. 2), ii4–ii17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.; Maskell, N. Identification and management of pleural effusions of multiple aetiologies. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2017, 23, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, R.W.; MacGregor, M.I.; Luchsinger, P.C.; Ball, W.C. Pleural Effusions: The Diagnostic Separation of Transudates and Exudates. Ann. Intern. Med. 1972, 77, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, R.W. Pleural Diseases; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vives, M.; Porcel, J.M.; De Vera, M.V.; Ribelles, E.; Rubio, M. A Study of Light’s Criteria and Possible Modifications for Distinguishing Exudative from Transudative Pleural Effusions. Chest 1996, 109, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotsman, I.; Fridlender, Z.; Meirovitz, A.; Dratva, D.; Muszkat, M. The evaluation of pleural effusions in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Med. 2001, 111, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.M.; Chorda, J.; Cao, G.; Esquerda, A.; Ruiz-González, A.; Vives, M. Comparing serum and pleural fluid pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels with pleural-to-serum albumin gradient for the identification of cardiac effusions misclassified by Light’s criteria. Respirology 2007, 12, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.; Alvarez, M.; Salud, A.; Vives, M. Should a Cytologic Study Be Ordered in Transudative Pleural Effusions? Chest 1999, 116, 1836–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashchi, M.; Golish, J.; Eng, P.; Oʼdonovan, P. Transudative malignant pleural effusions: Prevalence and mechanisms. South. Med J. 1998, 91, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addala, D.; Mercer, R.; Lu, Q.; Shepherd, G.; Castro, O.; Varatharajah, R.; Thayanandan, A.; Hassan, M.; Bedawi, E.; McCracken, D.; et al. P102 Discordant exudative pleural effusions: Demographics and aetiology. Malig. Pleural Dis. 2019, 74, A146. [Google Scholar]
- Assicot, M.; Bohuon, C.; Gendrel, D.; Raymond, J.; Carsin, H.; Guilbaud, J. High serum procalcitonin concentrations in patients with sepsis and infection. Lancet 1993, 341, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, G.; Lama-Lopez, A.; Bintcliffe, O.J.; Morley, A.; Hooper, C.E.; A Maskell, N. The role of serum procalcitonin in establishing the diagnosis and prognosis of pleural infection. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, R.W.; MacGregor, M.I.; Ball, W.C.; Luchsinger, P.C. Diagnostic Significance of Pleural Fluid pH and PCO2. Chest 1973, 64, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.E.; Davies, R.J.; Davies, C.W.H. Management of pleural infection in adults: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65 (Suppl. 2), ii41–ii53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffner, J.E.; Brown, L.K.; Barbieri, C.; DeLeo, J.M. Pleural fluid chemical analysis in parapneumonic effusions. A meta-analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, D.B.; Leong, S.L.; Budgeon, C.A.; Murray, K.; Rosenstengal, A.; Smith, N.A.; Porcel, J.M.; Lee, Y.C.G. Relationship of pleural fluid pH and glucose: A multi-centre study of 2971 cases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Maskell, N.; Gleeson, F.V.; Darby, M.; Davies, R.J.O. Diagnostically Significant Variations in Pleural Fluid pH in Loculated Parapneumonic Effusions. Chest 2004, 126, 2022–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, P.; Marples, L.; Breen, R.; Ahmed, L. The diagnostic utility of pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for tuberculosis in a low prevalence area. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2017, 21, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.A.; Ahmed, L.; Koegelenberg, C.F. Effusions related to TB. In Pleural Disease; European Respiratory Society (ERS): Sheffield, UK, 2020; pp. 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouras, V.S.; Kalomenidis, I. Pleural fluid tests to diagnose tuberculous pleuritis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 22, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.T.; Hamilton, F.W.; Elvers, K.T.; Frankland, S.W.; Zahan-Evans, N.; Patole, S.; Medford, A.; Bhatnagar, R.; Maskell, N.A. Pleural Fluid suPAR Levels Predict the Need for Invasive Management in Parapneumonic Effusions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pachon, E.; Romero, S. Urinothorax: A new approach. Curr. Opin. Pulm Med. 2006, 12, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, S.; Swiston, J.R. Diagnostic accuracy of pleural fluid NT-pro-BNP for pleural effusions of cardiac origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2010, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Cargill, T.; Harriss, E.; Asciak, R.; Mercer, R.M.; Bedawi, E.O.; McCracken, D.J.; Psallidas, I.; Corcoran, J.P.; Rahman, N.M. The microbiology of pleural infection in adults: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, S.M.; Rahman, N.M.; Wrightson, J.M.; Davies, H.E.; Shorten, R.; Gillespie, S.H.; Davies, C.W.H.; Maskell, N.A.; Jeffrey, A.A.; Lee, Y.C.G.; et al. Blood culture bottle culture of pleural fluid in pleural infection. Thorax 2011, 66, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, L.; Alvarez, D.; San José, E.; Penela, P.; Valle, J.M.; García-Pazos, J.M.; Suárez, J.; Pose, A. Tuberculous pleurisy: A study of 254 patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopi, A.; Madhavan, S.M.; Sharma, S.K.; Sahn, S.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion in 2006. Chest 2007, 131, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, S.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, J.-W.; Chien, J.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Lee, L.-N.; Yu, C.-J.J. Revisiting tuberculous pleurisy: Pleural fluid characteristics and diagnostic yield of mycobacterial culture in an endemic area. Thorax 2012, 67, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maartens, G.; Bateman, E.D. Tuberculous pleural effusions: Increased culture yield with bedside inoculation of pleural fluid and poor diagnostic value of adenosine deaminase. Thorax 1991, 46, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcel, J.M.; Azzopardi, M.; Koegelenberg, C.F.; Maldonado, F.; Rahman, N.M.; Lee, Y.C.G. The diagnosis of pleural effusions. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2015, 9, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenke, R.; Nasilowski, J.; Korczynski, P.; Gorska, K.; Przybylowski, T.; Chazan, R.; Light, R.W. Incidence and aetiology of eosinophilic pleural effusion. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenke, R.; Light, R.W. Drug-induced eosinophilic pleural effusion. Eur Respir Rev. 2011, 20, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, Y.; Abu-Salah, T. The Prevalence and Diagnostic Significance of Eosinophilic Pleural Effusions: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Respiration 2012, 83, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, J.T.; Sahn, S.A. Drug-induced pleural disease. Clin. Chest Med. 2004, 25, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.T.; De Fonseka, D.; Perry, S.; Morley, A.; Harvey, J.E.; Medford, A.; Brett, M.; Maskell, N.A. Investigating unilateral pleural effusions: The role of cytology. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsim, S.; Paterson, S.; Cartwright, D.; Fong, C.J.; Alexander, L.; Kelly, C.; Holme, J.; Evison, M.; Blyth, K.G. Baseline predictors of negative and incomplete pleural cytology in patients with suspected pleural malignancy - Data supporting ’Direct to LAT’ in selected groups. Lung Cancer 2019, 133, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, R.M.; Varatharajah, R.; Shepherd, G.; Lu, Q.; Castro-Añón, O.; McCracken, D.; Dudina, A.; Addala, D.; Tsikrika, S.; George, V.; et al. Critical analysis of the utility of initial pleural aspiration in the diagnosis and management of suspected malignant pleural effusion. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2020, 7, e000701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooper, L.M.; Ali, S.Z.; Olson, M.T. A minimum fluid volume of 75 mL is needed to ensure adequacy in a pleural effusion: A retrospective analysis of 2540 cases. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, L.W.; Ducatman, B.S.; Wang, H.H. The value of multiple fluid specimens in the cytological diagnosis of malignancy. Mod. Pathol. 1994, 7, 665–668. [Google Scholar]
- Alì, G.; Bruno, R.; Fontanini, G. The pathological and molecular diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A literature review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S276–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, D.; Roberts, M.; Wahidi, M.; Bhatnagar, R. Optimal diagnosis and treatment of malignant disease: Challenging the guidelines. In Pleural Disease (ERS Monograph) [Internet]; Maskell, N.A., Laursen, C.B., Lee, Y.C.G., Rahman, N.M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2020; pp. 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.; Jackson, S.; Jones, J.; Holme, J.; Lyons, J.; Barrett, E.; Taylor, P.; Bishop, P.; Hodgson, C.; Green, M.; et al. Homozygous deletion of CDKN2A in malignant mesothelioma: Diagnostic utility, patient characteristics and survival in a UK mesothelioma centre. Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, I.; Bishop, L.; Darlison, L.; De Fonseka, D.; Edey, A.; Edwards, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; A Fennell, D.; Holmes, S.; Kerr, K.M.; et al. BTS guideline for the investigation and management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2018, 5, e000266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Munavvar, M.; Corcoran, J.P. Pleural interventions: Less is more. In Pleural Disease (ERS Monograph) [Internet]; Maskell, N.A., Laursen, C.B., Lee, Y.C.G., Rahman, N.M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2020; pp. 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.E. Cytologic and bacteriologic analysis of fluid and pleural biopsy specimens with Cope’s needle. Study of 414 patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metintas, M.; Yildirim, H.; Kaya, T.; Ak, G.; Dundar, E.; Ozkan, R.; Metintaş, S. CT Scan-Guided Abrams’ Needle Pleural Biopsy versus Ultrasound-Assisted Cutting Needle Pleural Biopsy for Diagnosis in Patients with Pleural Effusion: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Respir. 2016, 91, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.M.; O Davies, R.J. Relearning an old lesson: Stopping trials early. Thorax 2010, 65, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Koegelenberg, C.F.; Bolliger, C.T.; Theron, J.; Walzl, G.; Wright, C.A.; Louw, M.; Diacon, A.H. Direct comparison of the diagnostic yield of ultrasound-assisted Abrams and Tru-Cut needle biopsies for pleural tuberculosis. Thorax 2010, 65, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallifax, R.J.; Corcoran, J.P.; Ahmed, A.; Nagendran, M.; Rostom, H.; Hassan, N.; Maruthappu, M.; Psallidas, I.; Manuel, A.; Gleeson, F.V.; et al. Physician-Based Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy for Diagnosing Pleural Disease. Chest 2014, 146, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.-B.; Yang, P.-C.; Luh, K.-T.; Kuo, S.-H.; Yu, C.-J. Ultrasound-Guided Pleural Biopsy with Tru-Cut Needle. Chest 1991, 100, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.P.; Tazi-Mezalek, R.; Maldonado, F.; Yarmus, L.B.; Annema, J.T.; Koegelenberg, C.F.N.; Noble, V.S.; Rahman, N.M. State of the art thoracic ultrasound: Intervention and therapeutics. Thorax 2017, 72, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psallidas, I.; Kanellakis, N.I.; Bhatnagar, R.; Ravindran, R.; Yousuf, A.; Edey, A.J.; Mercer, R.M.; Corcoran, J.P.; Hallifax, R.J.; Asciak, R.; et al. A Pilot Feasibility Study in Establishing the Role of Ultrasound-Guided Pleural Biopsies in Pleural Infection (The AUDIO Study). Chest 2018, 154, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, M. Diagnostic value of ultrasound-guided needle biopsy in undiagnosed pleural effusions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020, 99, e21076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sconfienza, L.M.; Mauri, G.; Grossi, F.; Truini, M.; Serafini, G.; Sardanelli, F.; Murolo, C. Pleural and Peripheral Lung Lesions: Comparison of US- and CT-guided Biopsy. Radiology 2013, 266, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fonseka, D.; Underwood, W.; Stadon, L.; Rahman, N.; Edey, A.; Rogers, C.; A Maskell, N. Randomised controlled trial to compare the diagnostic yield of positron emission tomography CT (PET-CT) TARGETed pleural biopsy versus CT-guided pleural biopsy in suspected pleural malignancy (TARGET trial). BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2018, 5, e000270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CCorcoran, J.P.; Psallidas, I.; Hallifax, R.J.; Talwar, A.; Sykes, A.; Rahman, N.M. Ultrasound-guided pneumothorax induction prior to local anaesthetic thoracoscopy: Table 1. Thorax 2015, 70, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medford, A.R.L.; Agrawal, S.; Bennett, J.A.; Free, C.M.; Entwisle, J.J. Thoracic ultrasound prior to medical thoracoscopy improves pleural access and predicts fibrous septation. Respiration 2010, 15, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.M.; Ali, N.J.; Brown, G.; Chapman, S.J.; O Davies, R.J.; Downer, N.J.; Gleeson, F.V.; Howes, T.Q.; Treasure, T.; Singh, S.; et al. Local anaesthetic thoracoscopy: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65, ii54–ii60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metintas, M.; Ak, G.; Dundar, E.; Yildirim, H.; Ozkan, R.; Kurt, E.; Erginel, S.; Metintas, S. Medical thoracoscopy vs CT scan-guided Abrams pleural needle biopsy for diagnosis of patients with pleural effusions: A randomized, controlled trial. Chest 2010, 137, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.U. Yield of Video Assisted Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions in South Indian Population. J. Med Sci. Clin. Res. 2015, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.J.; Kavuru, M.S.; Mehta, A.C.; Medendorp, S.V.; Wiedemann, H.P.; Kirby, T.J.; Rice, T.W.; Bice, T.W. The Impact of Thoracoscopy on the Management of Pleural Disease. Chest 1995, 107, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresler, C.M.; Olak, J.; Herndon, J.E.; Richards, W.G.; Scalzetti, E.; Fleishman, S.B.; Kernstine, K.H.; Demmy, T.; Jablons, D.M.; Kohman, L.; et al. Phase III Intergroup Study of Talc Poudrage vs Talc Slurry Sclerosis for Malignant Pleural Effusion. Chest 2005, 127, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.P.; Collier, G.; Astoul, P.; Tassi, G.F.; Noppen, M.; Rodriguez-Panadero, F.; Loddenkemper, R.; Herth, F.J.; Gasparini, S.; Marquette, C.H.; et al. Safety of pleurodesis with talc poudrage in malignant pleural effusion: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2007, 369, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medford, A.R.L.; Awan, Y.M.; Marchbank, A.; Rahamim, J.; Unsworth-White, J.; Pearson, P.J.K. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Performance of Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (Vats) in Investigation and Management of Pleural Exudates. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2008, 90, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McDonald, C.M.; Pierre, C.; De Perrot, M.; Darling, G.E.; Cypel, M.; Pierre, A.; Waddell, T.; Keshavjee, S.; Yasufuku, K.; Czarnecka-Kujawa, K. Efficacy and Cost of Awake Thoracoscopy and Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery in the Undiagnosed Pleural Effusion. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 106, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedawi, E.O.; Rahman, N.M. Rigid Mini-Thoracoscopy: The New Kid on the Block. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2020, 27, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.I.; Ambalavanan, S.; Thomson, D.; Miles, J.; Munavvar, M. A Comparison of the Diagnostic Yield of Rigid and Semirigid Thoracoscopes. J. Bronc- Interv. Pulmonol. 2012, 19, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, A.; Chandra, S.; Agarwal, D.; Naik, S.; Munavvar, M. Utility of semirigid thoracoscopy in the diagnosis of pleural effusions: A systematic review. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2010, 17, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Gupta, D. Diagnostic accuracy and safety of semirigid thoracoscopy in exudative pleural effusions: A meta-analysis. Chest 2013, 144, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Mittal, S.; Tiwari, P.; Jain, D.; Arava, S.; Hadda, V.; Mohan, A.; Malik, P.; Prabhat, R.M.; Khilnani, G.C.; et al. Rigid Mini-Thoracoscopy versus Semirigid Thoracoscopy in Undiagnosed Exudative Pleural Effusion: The MINT Randomized Controlled. Trial. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2020, 27, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, C.C.; Black, W.C.; Dallas, R.V.; Crow, H.C. Pleural fluid volume estimation: A chest radiograph prediction rule. Acad. Radiol. 1996, 3, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryminski, J.; Krakówka, P.; Lypacewicz, G. The Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion by Ultrasonic and Radiologic Techniques. Chest 1976, 70, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motogna, M.K.; Maratou, K.; Paianid, I.; Soldatos, T.; Antipa, E.; Tsikkini, A.; Baltas, C.S. Application of color Doppler ultrasound in the study of small pleural effusion. Med Ultrason. 2010, 12, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- McLoud, T.C.; Flower, C.D. Imaging the pleura: Sonography, CT, and MR imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 156, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.C.; Luh, K.T.; Chang, D.B.; Wu, H.D.; Yu, C.J.; Kuo, S.-H. Value of sonography in determining the nature of pleural effusion: Analysis of 320 cases. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 159, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asciak, R.; Hassan, M.; Mercer, R.M.; Hallifax, R.J.; Wrightson, J.M.; Psallidas, I.; Rahman, N.M. Prospective Analysis of the Predictive Value of Sonographic Pleural Fluid Echogenicity for the Diagnosis of Exudative Effusion. Respiration 2019, 97, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-J.; Tu, C.-Y.; Ling, S.-J.; Chen, W.; Chiu, K.-L.; Hsia, T.-C.; Shih, C.-M.; Hsu, W.-H. Sonographic Appearances in Transudative Pleural Effusions: Not Always an Anechoic Pattern. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banka, R.; Skaarup, S.; Mercer, R.; Laursen, C. Thoracic ultrasound: A key tool beyond procedure guidance. In Pleural Disease (ERS Monograph) [Internet]; Maskell, N.A., Laursen, C.B., Lee, Y.C.G., Rahman, N.M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2020; pp. 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.R.; Rahman, N.M.; Gleeson, F.V. Thoracic ultrasound in the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion. Thorax 2009, 64, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.N.; Müller, N.L.; Miller, R.R. CT in differential diagnosis of diffuse pleural disease. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1990, 154, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, J.; Hallifax, R.; Mercer, R.M.; Yousuf, A.; Asciak, R.; Hassan, M.; Piotrowska, H.E.; Psallidas, I.; Rahman, N. Thoracic Ultrasound as an Early Predictor of Pleurodesis Success in Malignant Pleural Effusion. Chest 2018, 154, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psallidas, I.; Piotrowska, H.E.G.; Yousuf, A.; I Kanellakis, N.; Kagithala, G.; Mohammed, S.; Clifton, L.; Corcoran, J.P.; Russell, N.; Dobson, M.; et al. Efficacy of sonographic and biological pleurodesis indicators of malignant pleural effusion (SIMPLE): Protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2017, 4, e000225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salamonsen, M.; Lo, A.K.C.; Ng, A.C.; Bashirzadeh, F.; Wang, W.Y.S.; Fielding, D. Novel Use of Pleural Ultrasound Can Identify Malignant Entrapped Lung Prior to Effusion Drainage. Chest 2014, 146, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerden, L.; Benamore, R.; Edey, A. Radiology: What is the role of chest radiographs, CT and PET in modern management. In Pleural Disease (ERS Monograph) [Internet]; Maskell, N.A., Laursen, C.B., Lee, Y.C.G., Rahman, N.M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2020; pp. 48–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsim, S.; Stobo, D.B.; Alexander, L.; Kelly, C.; Blyth, K.G. The diagnostic performance of routinely acquired and reported computed tomography imaging in patients presenting with suspected pleural malignancy. Lung Cancer 2017, 103, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, J.; García-Garrigós, E.; Escudero-Fresneda, C.; Sirera-Matilla, M.; García-Pastor, I.; Quirce-Vázquez, A.; Planells-Alduvin, M. Early and delayed phases of contrast-enhanced CT for evaluating patients with malignant pleural effusion. Results of pairwise comparison by multiple observers. Br. J. Radiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.P.; Acton, L.; Ahmed, A.; Hallifax, R.; Psallidas, I.; Wrightson, J.M.; Rahman, N.; Gleeson, F.V. Diagnostic value of radiological imaging pre- and post-drainage of pleural effusions. Respirol. 2015, 21, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, N.; Saraya, T.; Light, R.W.; Tsukahara, Y.; Koide, T.; Kurai, D.; Ishii, H.; Kimura, H.; Goto, H.; Takizawa, H. A Simple Method for Differentiating Complicated Parapneumonic Effusion/Empyema from Parapneumonic Effusion Using the Split Pleura Sign and the Amount of Pleural Effusion on Thoracic CT. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcel, J.M.; Pardina, M.; Alemán, C.; Pallisa, E.; Light, R.W.; Bielsa, S. Computed tomography scoring system for discriminating between parapneumonic effusions eventually drained and those cured only with antibiotics: CT for parapneumonic effusions. Respirology 2017, 22, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Shim, S.S.; Kim, Y.; Ryu, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. Chest CT findings of pleural tuberculosis: Differential diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis and malignant pleural dissemination. Acta Radiol. 2014, 55, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metintas, M.; Ucgun, I.; Elbek, O.; Erginel, S.; Metintas, S.; Kolsuz, M.; Harmanci, E.; Alataş, F.; Hillerdal, G.; Özkan, R.; et al. Computed tomography features in malignant pleural mesothelioma and other commonly seen pleural diseases. Eur. J. Radiol. 2002, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traill, Z.C.; Davies, R.J.; Gleeson, F.V. Thoracic Computed Tomography in Patients with Suspected Malignant Pleural Effusions. Clin. Radiol. 2001, 56, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierholzer, J.; Luo, L.; Bittner, R.C.; Stroszczynski, C.; Schoenfeld, N.; Dorow, P.; Loddenkemper, R.; Grassot, A. MRI and CT in the differential diagnosis of pleural disease. Chest 2000, 118, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallifax, R.; Haris, M.; Corcoran, J.P.; Leyakathalikhan, S.; Brown, E.; Srikantharaja, D.; Manuel, A.; Gleeson, F.V.; Munavvar, M.; Rahman, N.M. Role of CT in assessing pleural malignancy prior to thoracoscopy: Table 1. Thorax 2014, 70, 192–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syer, T.; Arnold, D.T.; Patole, S.; Harvey, J.; Medford, A.; Maskell, N.A.; Edey, A. Investigation of a unilateral pleural effusion: What CT scan coverage is optimal? Thorax 2020, 75, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Judson, M.A.; Doelken, P.; Maldonado, F.; Rahman, N.M.; Huggins, J.T. The Relationship of Pleural Manometry With Postthoracentesis Chest Radiographic Findings in Malignant Pleural Effusion. Chest 2020, 157, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.A.; Tsim, S.; Kidd, A.C.; Foster, J.E.; McLoone, P.; Chalmers, A.; Blyth, K.G. Pre-EDIT: A Randomized Feasibility Trial of Elastance-Directed Intrapleural Catheter or Talc Pleurodesis in Malignant Pleural Effusion. Chest 2019, 156, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.J.; Lerner, A.D.; Pannu, J.K.; Merrick, C.M.; Roller, L.; Walston, C.; Valenti, S.; Goddard, T.; Chen, H.; Huggins, J.T.; et al. Routine monitoring with pleural manometry during therapeutic large-volume thoracentesis to prevent pleural-pressure-related complications: A multicentre, single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidecker, J.; Huggins, J.T.; Sahn, S.A.; Doelken, P. Pathophysiology of Pneumothorax Following Ultrasound-Guided Thoracentesis. Chest 2006, 130, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Chopra, A.; Huggins, J.T.; Nanchal, R. Pleural manometry: Techniques, applications, and pitfalls. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 2759–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Transudative Effusions | Exudative Effusions |
|---|---|
| Congestive cardiac failure | Parapneumonic |
| Cirrhosis | TB pleuritis |
| Nephrotic syndrome | Primary or secondary thoracic malignancy |
| Glomerulonephritis | Pulmonary embolism |
| Peritoneal dialysis | Pancreatitis |
| Hypoalbuminaemia | Post myocardial infarction |
| Cerebrospinal fluid leak | Collagen vascular disorders |
| Urinothorax | Drug-related |
| Haemothorax | |
| Chylothorax | |
| Benign asbestos-related pleural effusions |
| Assay |
|---|
| Biochemistry panel: Protein, LDH, Glucose, pH |
| Microbiology panel: Gram stain + Culture |
| Pathology panel: Cytology for differential cell count + abnormal cells |
| Condition | Typical PF Biochemical Patterns |
|---|---|
| Cardiac failure | Low Protein, Low LDH, N terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), but closely mirrors serum NT-proBNP |
| Pleural infection | High Protein, High LDH (>1000), very low Glucose, Low pH |
| Malignant pleural effusion | High Protein, High LDH, (Low Glucose) |
| Rheumatoid effusion | Very low Glucose |
| TB effusion | Very high Protein, low glucose |
| Dural leak | Very low Protein |
| Urinothorax | Very low Protein, PF/Serum creatinine ratio > 1, pH < 7.30 |
| Pancreatitis | PF/serum amylase ratio >1, PF amylase > upper limit of normal serum levels |
| Chylothorax | Elevated Triglycerides (>1.24 mmol/L), Chylomicrons |
| Pseudochylothorax | Elevated cholesterol (>5.18 mmol/L), cholesterol crystals |
| Haemothorax | PF haematocrit/Serum haematocrit > 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sundaralingam, A.; Bedawi, E.O.; Rahman, N.M. Diagnostics in Pleural Disease. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121046
Sundaralingam A, Bedawi EO, Rahman NM. Diagnostics in Pleural Disease. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121046
Chicago/Turabian StyleSundaralingam, Anand, Eihab O. Bedawi, and Najib M. Rahman. 2020. "Diagnostics in Pleural Disease" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121046
APA StyleSundaralingam, A., Bedawi, E. O., & Rahman, N. M. (2020). Diagnostics in Pleural Disease. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121046





