Integrating Finite Element Death Technique and Bone Remodeling Theory to Predict Screw Loosening Affected by Radiation Treatment after Mandibular Reconstruction Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Finite Element Model Generation
2.2. Micro-Crack Propagation Simulation Using Element Death Analysis
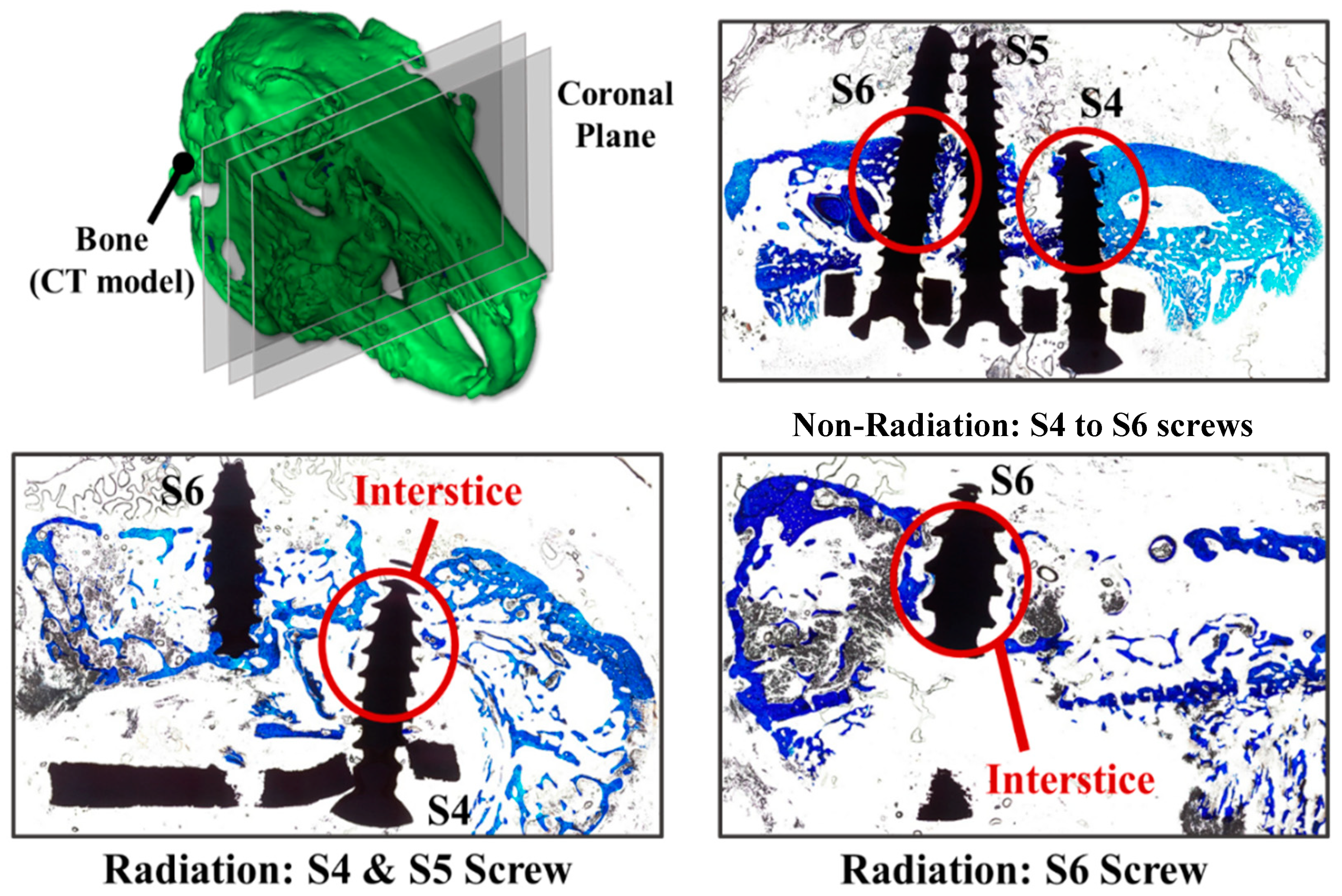
2.3. Mandibular Reconstruction Surgery and Radiation Treatment
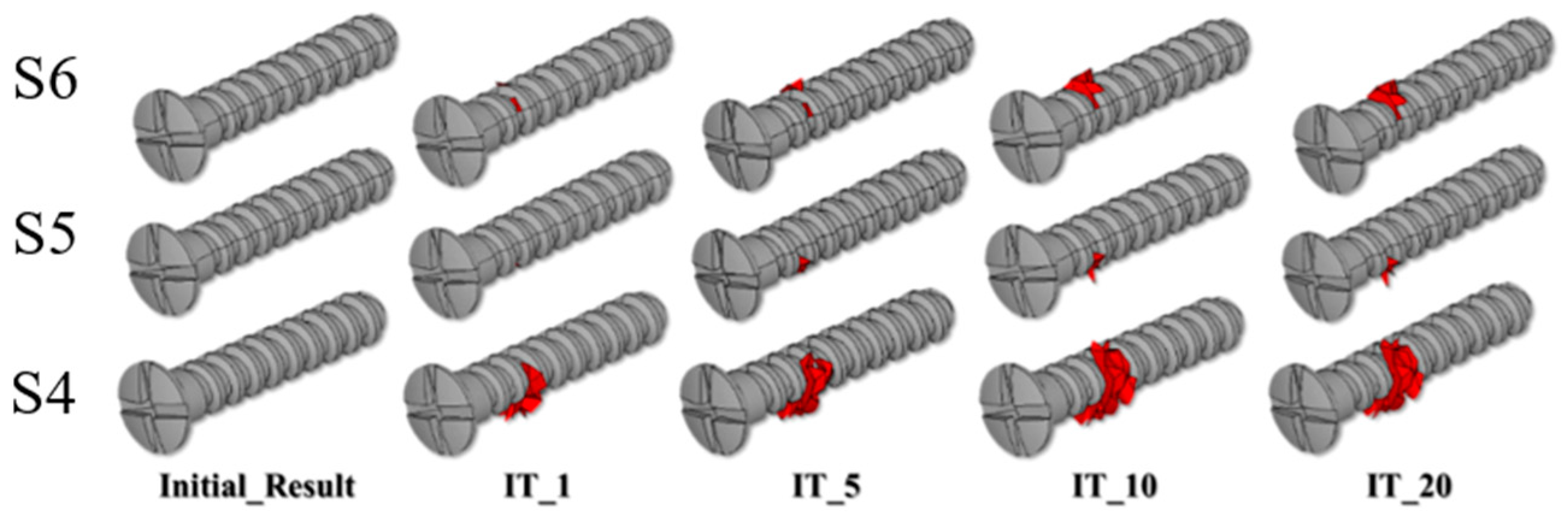
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.H.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, C.L. Design of a patient-specific mandible reconstruction implant with dental prosthesis for metal 3D printing using integrated weighted topology optimization and finite element analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 105, 103700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, H.G.; Ham, M.J.; Hong, D.G.K.; Kim, S.G.; Rotaru, H. Custom implant for reconstruction of mandibular continuity defect. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Harrison, P.; Cheng, A.; Bray, B.; Bell, R.B. Fibular reconstruction of the maxilla and mandible with immediate implant-supported prosthetic rehabilitation: JAW in a day. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 31, 369–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, G.; Gouet, E. Use of a 3-dimensional custom-made porous titanium prosthesis for mandibular body reconstruction with prosthetic dental rehabilitation and lipofilling. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapasco, M.; Colletti, G.; Romeo, E.; Zaniboni, M.; Brusati, R. Long-term results of mandibular reconstruction with autogenous bone grafts and oral implants after tumor resection. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajgel, A.; Camargo, I.B.; Willmersdorf, R.B.; de Melo, T.M.; Laureano Filho, J.R.; Vasconcellos, R.J. Comparative finite element analysis of the biomechanical stability of 2.0 fixation plates in atrophic mandibular fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujtár, P.; Simonovics, J.; Váradi, K.; Sándor, G.K.B.; Avery, C.M.E. The biomechanical aspects of reconstruction for segmental defects of the mandible: A finite element study to assess the optimization of plate and screw factors. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Shen, L.; Li, J.; Liang, R.; Tian, W.; Tang, W. Optimal design of an individual endoprosthesis for the reconstruction of extensive mandibular defects with finite element analysis. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.; Musio, D.; Tombolini, V. Osteoradionecrosis and intensity modulated radiation therapy: An overview. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 107, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Osteoradionecrosis: A new concept of its pathophysiology. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 41, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monika, D.P.; Both, S.; Alexander, C.W.; Amit, M.; Sunday, O.A. Onest of mandible and tibia osteoradionecrosis: A comparative pilot study in the rat. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Patrik, C.; Keita, I.; Rafaa, E.; Stephanie, B.; Elisabeth, S.R.; Roland, D.C.; Bert van, R. Bone remodeling in humans is load-driven but not lazy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4855. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, H.M. From Wolff’s law to the Utah paradigm: Insights about bone physiology and its clinical applications. Anat. Rec. 2001, 262, 398–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.M. On our age-related bone loss: Insights from a new paradigm. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; Grootenboer, H.J.; Dalstra, M.; Fudala, B.; Slooff, T.J. Adaptive bone-remodeling theory applied to prosthetic-design analysis. J. Biomech. 1997, 20, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; van Rietbergen, B. The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Lin, Y.H.; Chang, S.H. Multi-factorial analysis of variables influencing the bone loss of an implant placed in the maxilla: Prediction using FEA and SED bone remodeling algorithm. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.J.; Gröning, F.; Curtis, N.; Fitton, L.C.; Herrel, A.; McCormack, S.W.; Fagan, M.J. Masticatory biomechanics in the rabbit: A multi-body dynamics analysis. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atali, O.; Varol, A.; Basa, S.; Ergun, C.; Hartomacıoğlu, S. Comparison and validation of finite element analysis with a servo-hydraulic testing unit for a biodegradable fixation system in a rabbit model. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, P.J.; Taylor, D. Prediction of bone adaptation using gamage accumulation. J. Biomech. 1994, 27, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poort, L.J.; Ludlage, J.H.B.; Lie, N.; Böckmann, R.A.; Odekerken, J.C.E.; Hoebers, F.J.; Kessler, P.A.W.H. The histological and histomorphometric changes in the mandible after radiotherapy: An animal model. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Lin, C.-L.; Sun, M.T.; Chang, Y.H. 3D micro-crack propagation simulation at enamel/adhesive interface using FE submodeling and element death techniques. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciubba, J.J.; Goldenberg, D. Oral complications of radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Gao, H.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C. Effects of immediately static loading on osteointegration and osteogenesis around 3D-printed porous implant: A histological and biomechanical study. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 108, 110406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
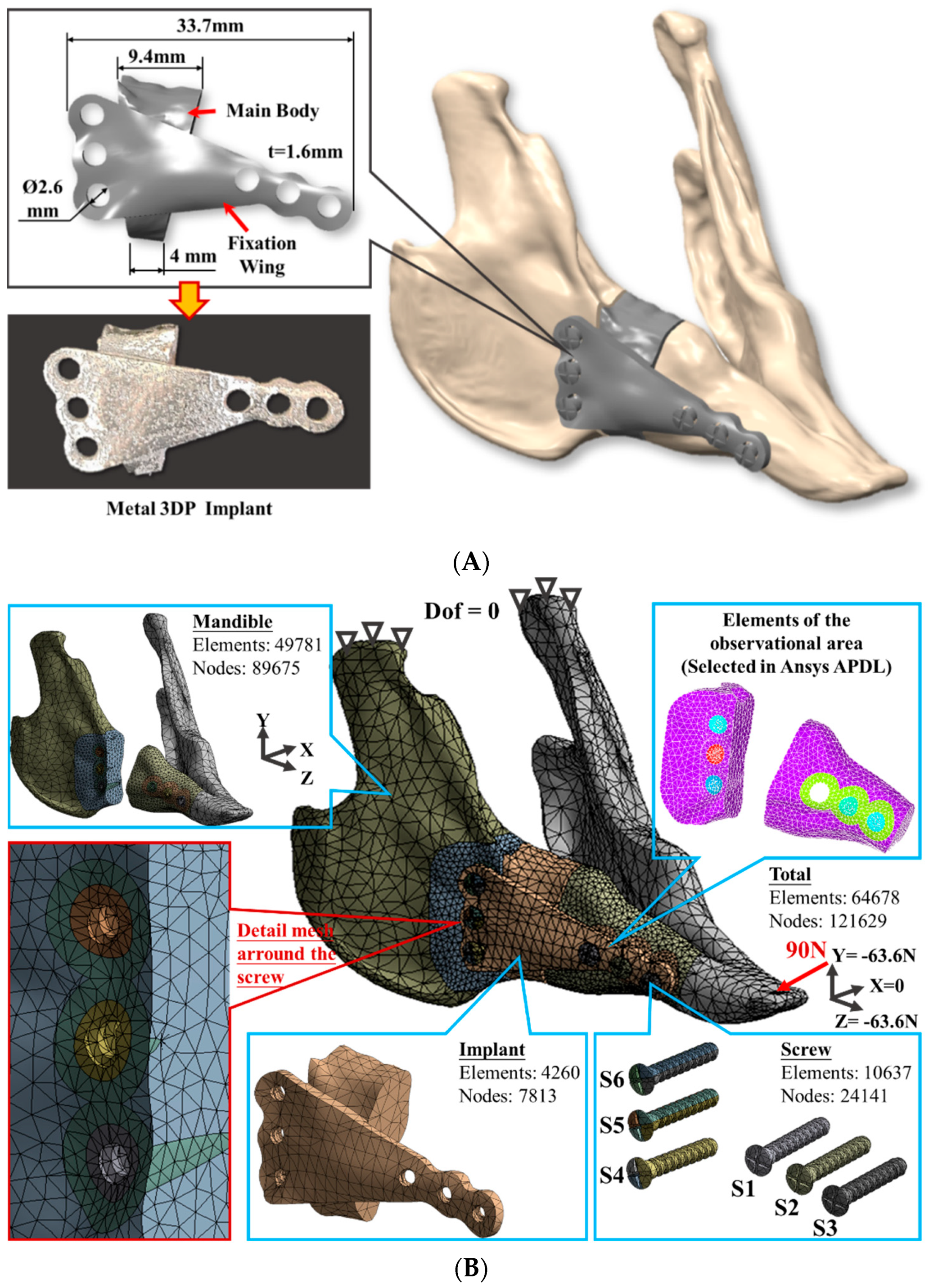
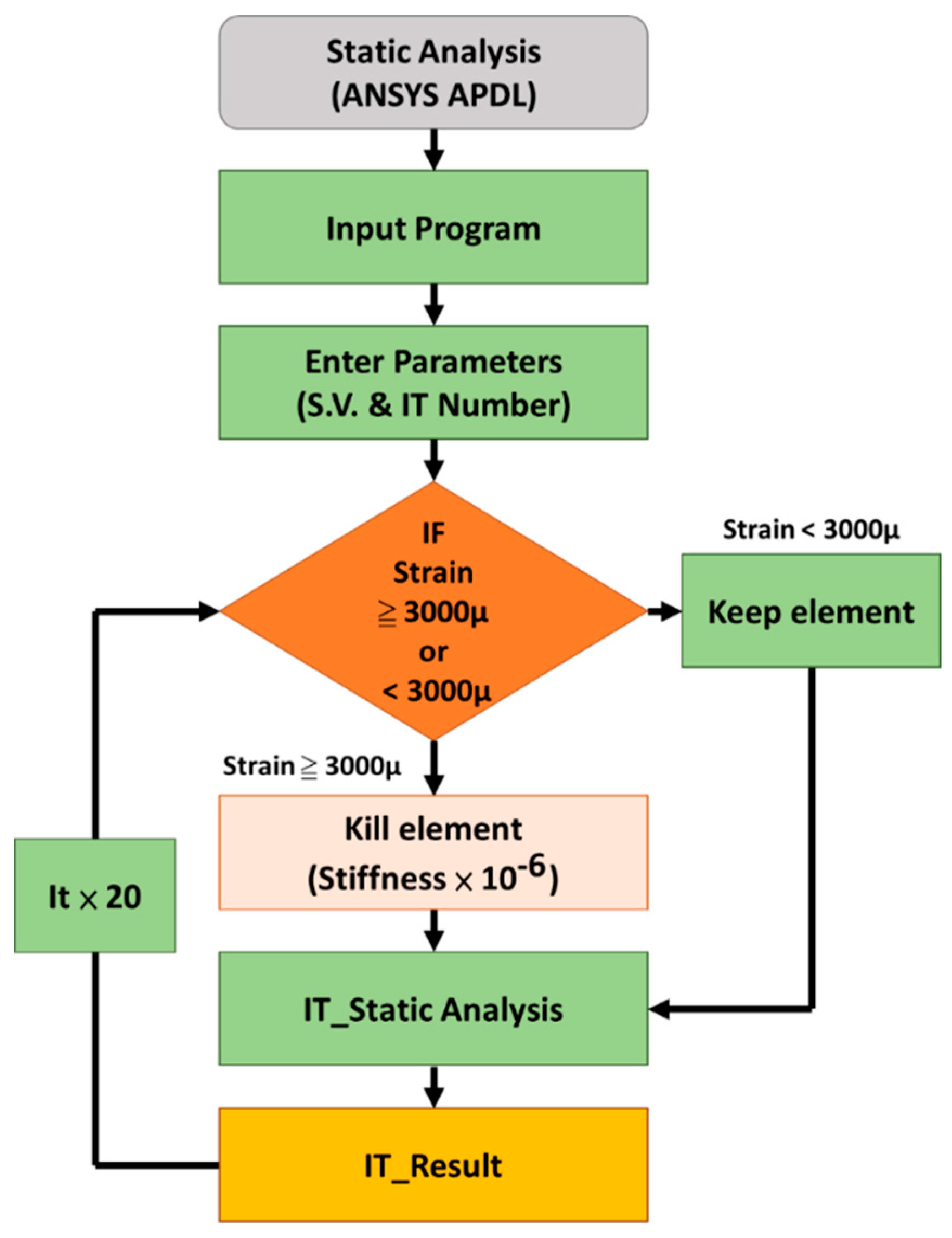

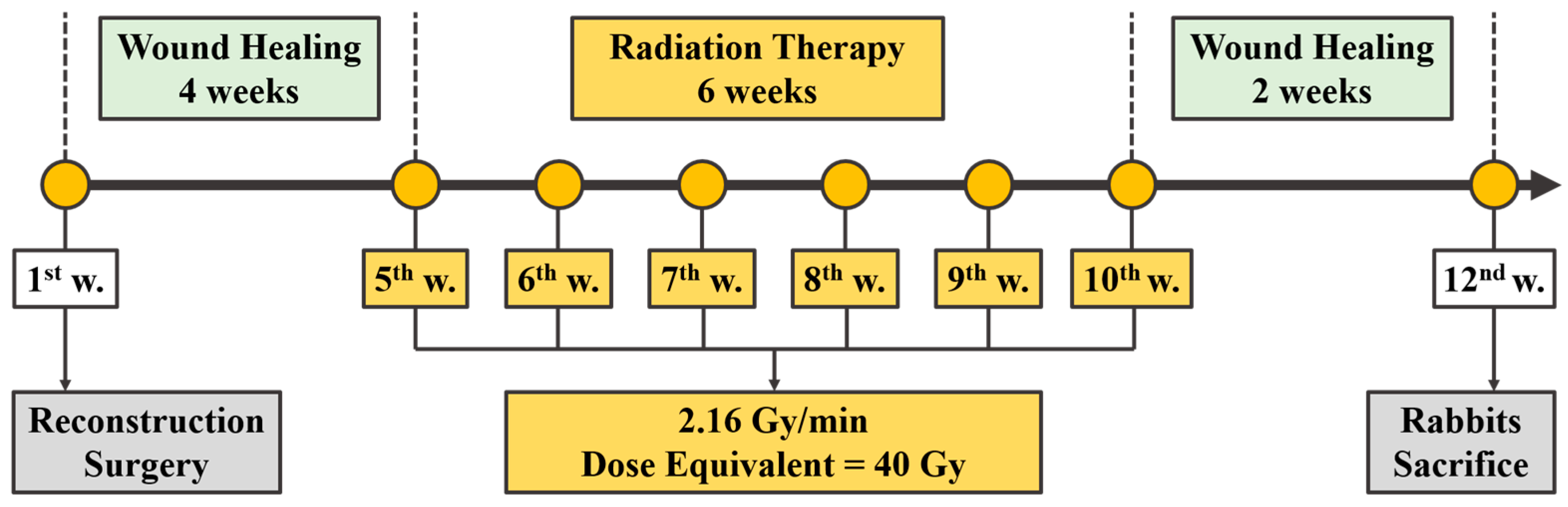

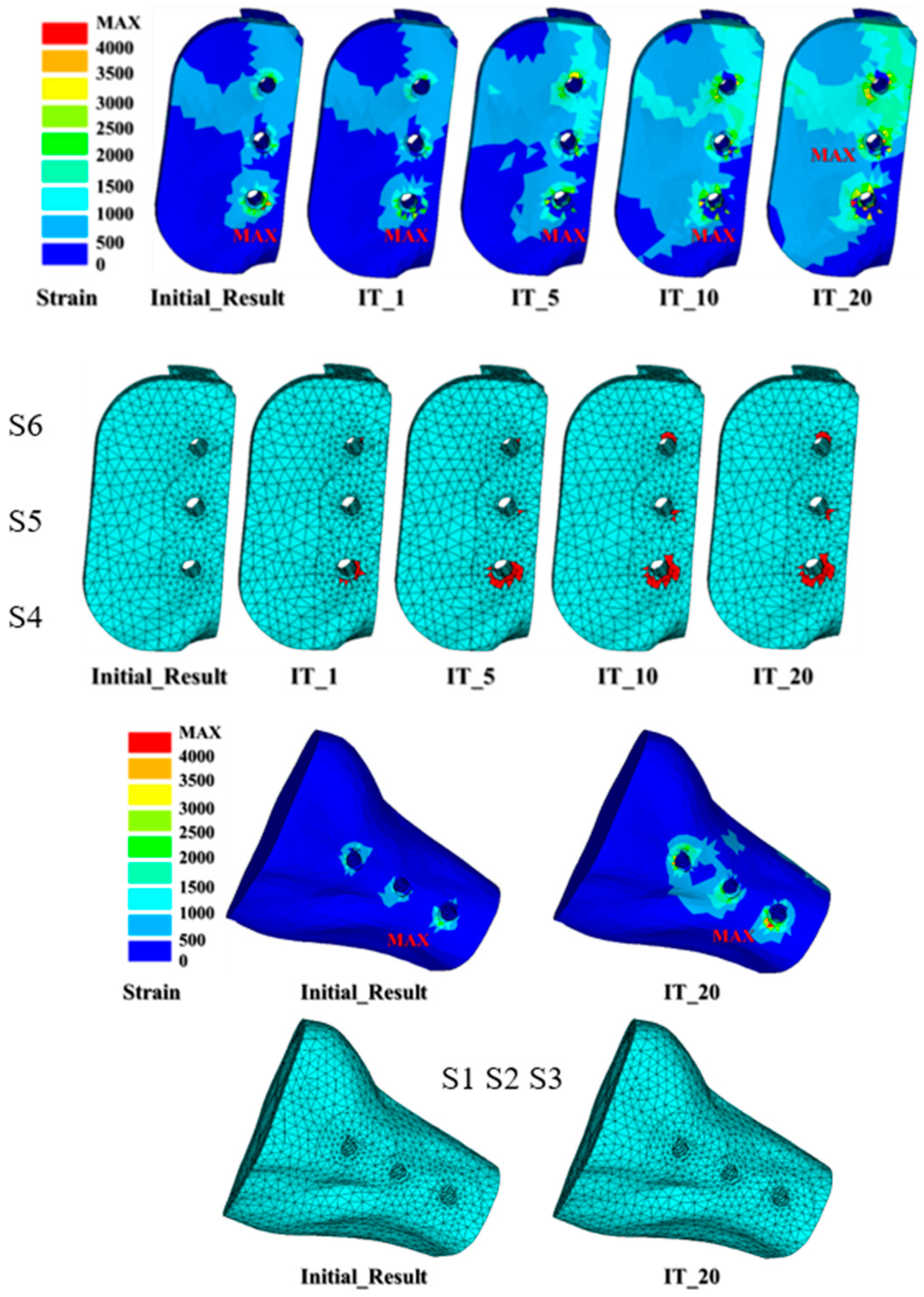
| Material | Young’s Modulus | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical Bone | 13,700 MPa | 0.3 |
| Cancellous Bone | 1370 MPa | 0.3 |
| Implants (Ti-6Al-4V) | 110,000 MPa | 0.35 |
| Bone Screw (Ti-6Al-4V) | 110,000 MPa | 0.35 |
| S4_Dis. | S5_Dis. | S6_Dis. | S4_% | S5_% | S6_% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial results | 0.000683 | 0.000596 | 0.000522 | |||
| IT_1 | 0.000685 | 0.000597 | 0.000522 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.00 |
| IT_5 | 0.000687 | 0.000598 | 0.000523 | 0.59 | 0.34 | 0.19 |
| IT_10 | 0.000688 | 0.000598 | 0.000523 | 0.73 | 0.34 | 0.19 |
| IT_20 | 0.000688 | 0.000598 | 0.000523 | 0.73 | 0.34 | 0.19 |
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial results | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IT_1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 1 | 5 |
| IT_5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 121 | 6 | 10 |
| IT_10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 160 | 9 | 23 |
| IT_20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 164 | 10 | 23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.-J.; Hsieh, K.-H.; Lin, C.-L. Integrating Finite Element Death Technique and Bone Remodeling Theory to Predict Screw Loosening Affected by Radiation Treatment after Mandibular Reconstruction Surgery. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100844
Wu L-J, Hsieh K-H, Lin C-L. Integrating Finite Element Death Technique and Bone Remodeling Theory to Predict Screw Loosening Affected by Radiation Treatment after Mandibular Reconstruction Surgery. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(10):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100844
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Le-Jung, Kai-Hung Hsieh, and Chun-Li Lin. 2020. "Integrating Finite Element Death Technique and Bone Remodeling Theory to Predict Screw Loosening Affected by Radiation Treatment after Mandibular Reconstruction Surgery" Diagnostics 10, no. 10: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100844
APA StyleWu, L.-J., Hsieh, K.-H., & Lin, C.-L. (2020). Integrating Finite Element Death Technique and Bone Remodeling Theory to Predict Screw Loosening Affected by Radiation Treatment after Mandibular Reconstruction Surgery. Diagnostics, 10(10), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100844






