Sliding Mode Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based on Optimization of Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
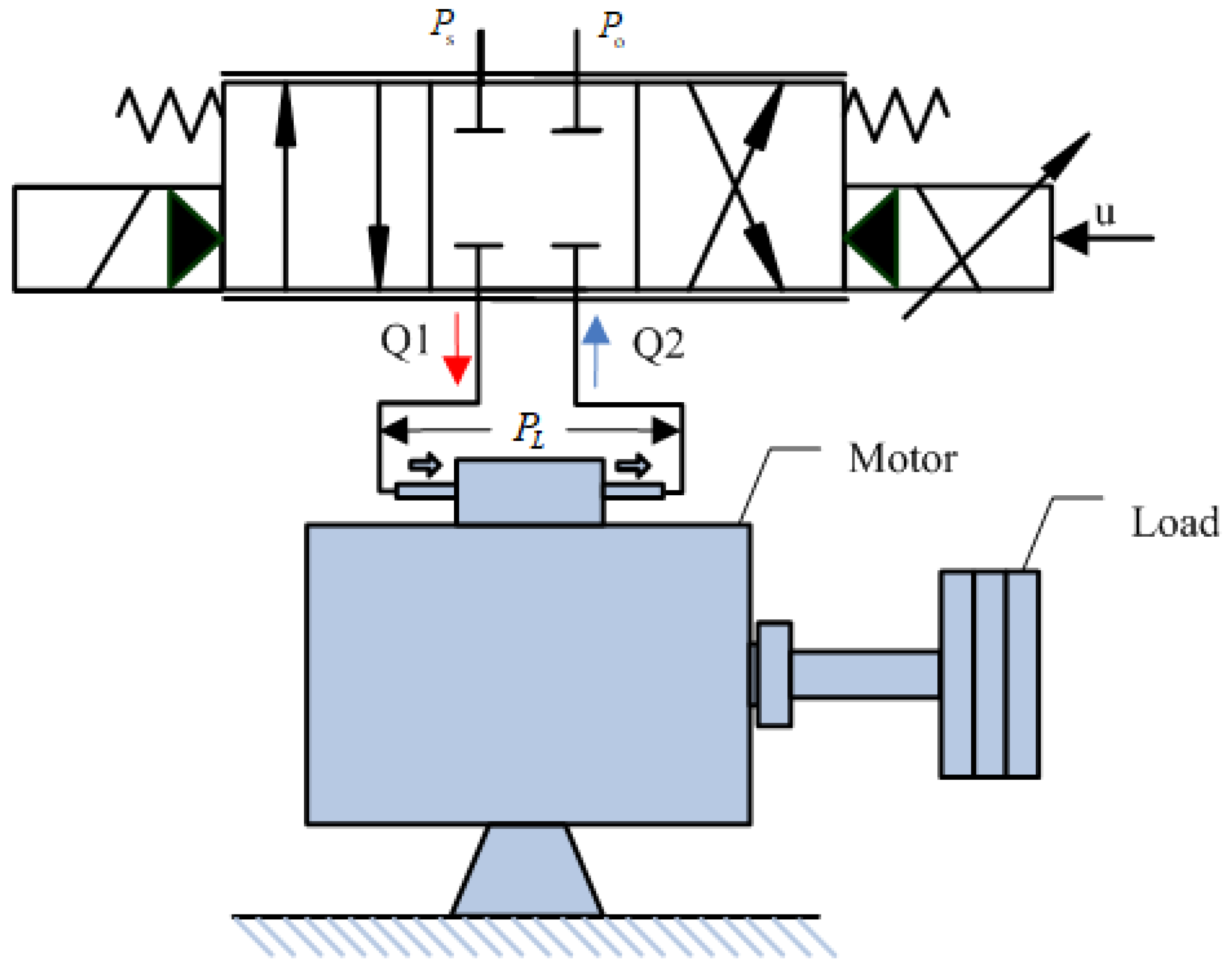
2. Mathematical Model and Problem Description
- The pressure in each chamber of the hydraulic rotary motor is equal everywhere.
- The total amount of liquid leakage is negligible that is = 0.
- Ignoring the non-linear interference such as friction and the influence of fluid quality.
3. Sliding Mode Controller Design
3.1. Design of Slide Surface
3.2. System Stability Analysis of Sliding Mode Control
4. Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm to Optimize Parameters
4.1. Evolution Equation of Particle Swarm Algorithm
4.2. Flow of Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm
- Setting the initial data, including population size, maximum number of iterations, dimension, parameter search range, range of scaling factors, etc.
- Calculating the average best position of the particle population according to Equation (28).
- Performing steps 4–7 for each particle.
- Calculating the adaptation value of the current position of particle i and update the individual best position of the particle according to Equation (23).
- Comparing the individual best position of particle i with the adaptation value of the global best position G(t−1). If , it is set , otherwise .
- Calculating the position of a random point according to Equation (27) for each dimension of particle i.
- Updating the new position of the particle according to Equation (26).
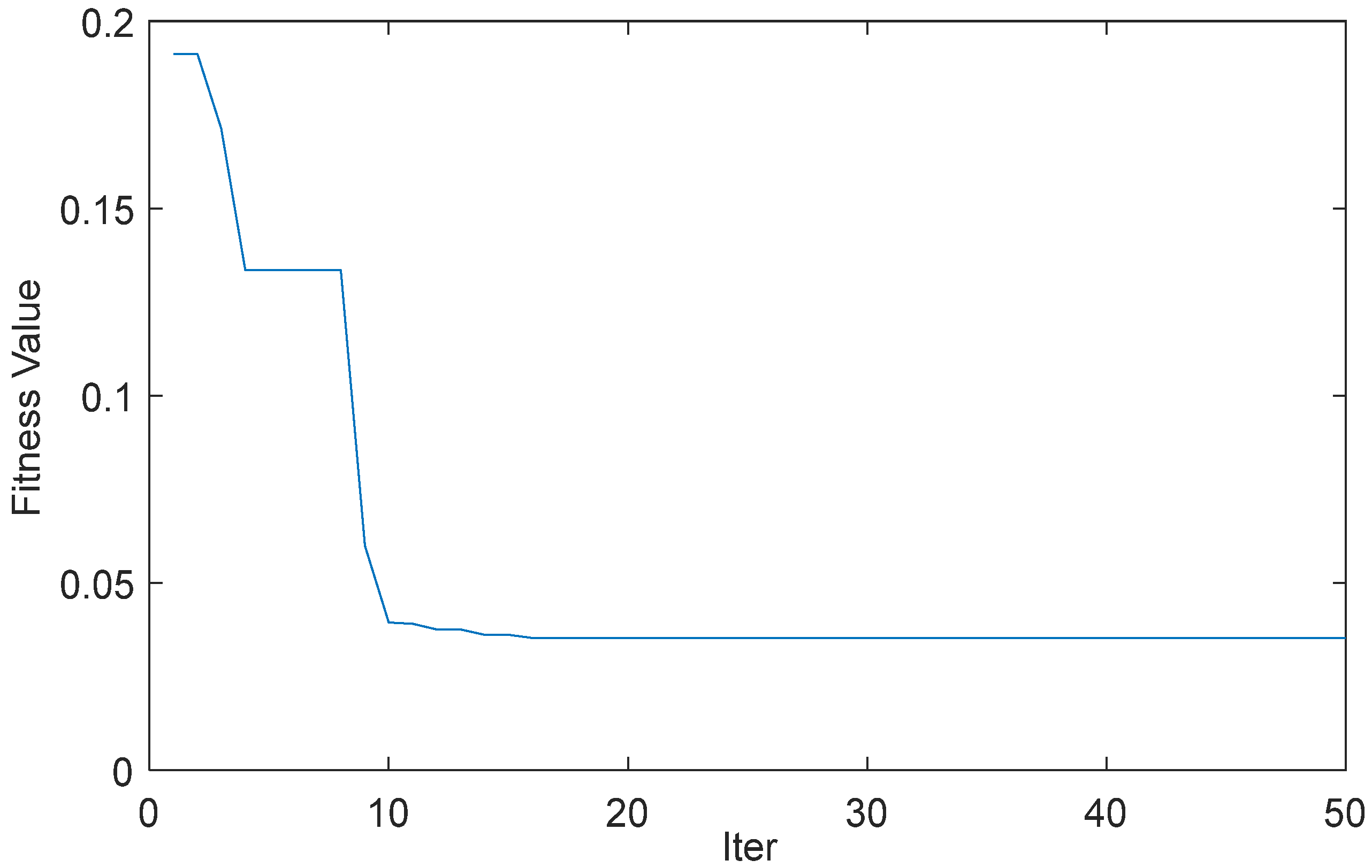
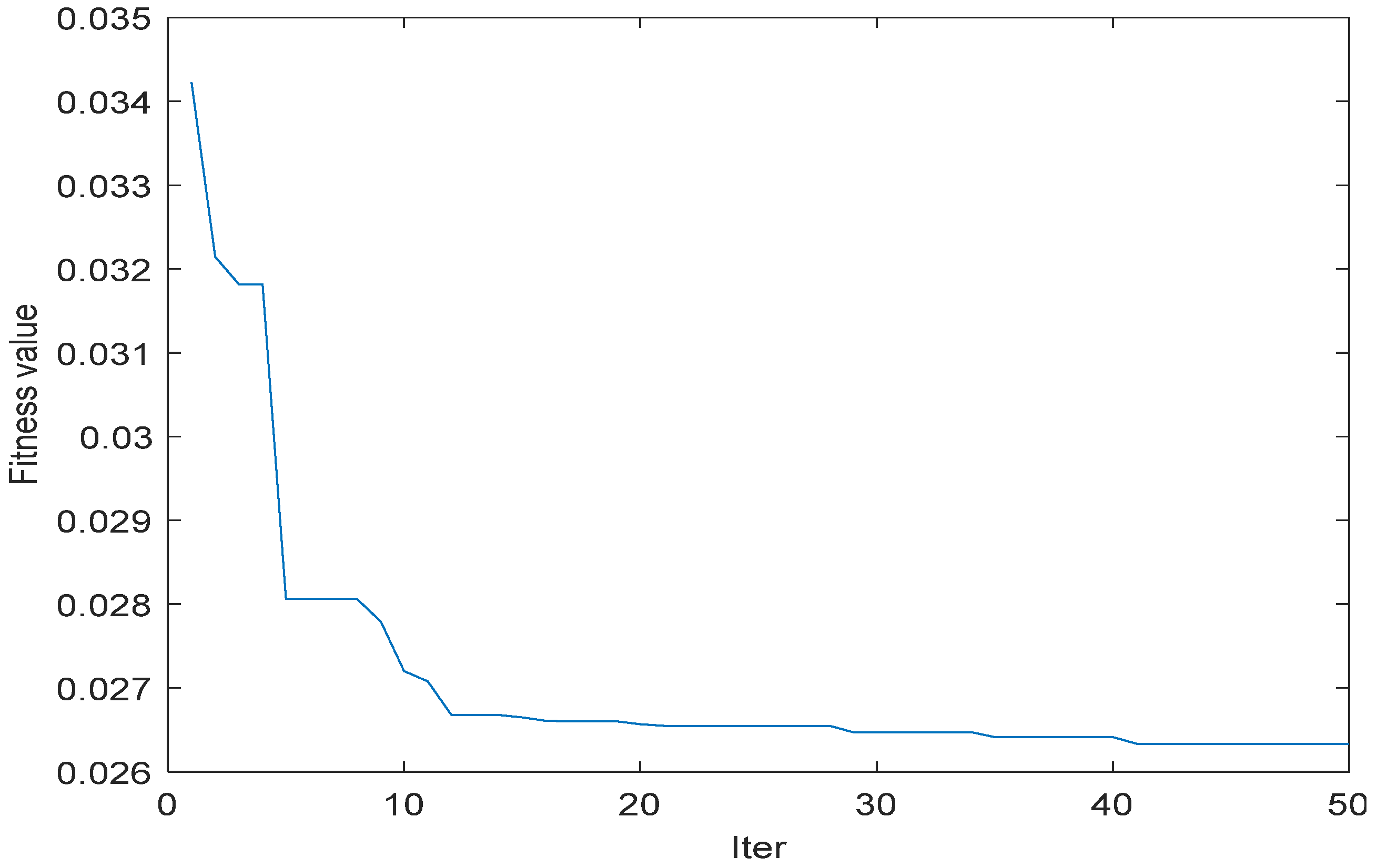
4.3. Fitness Function
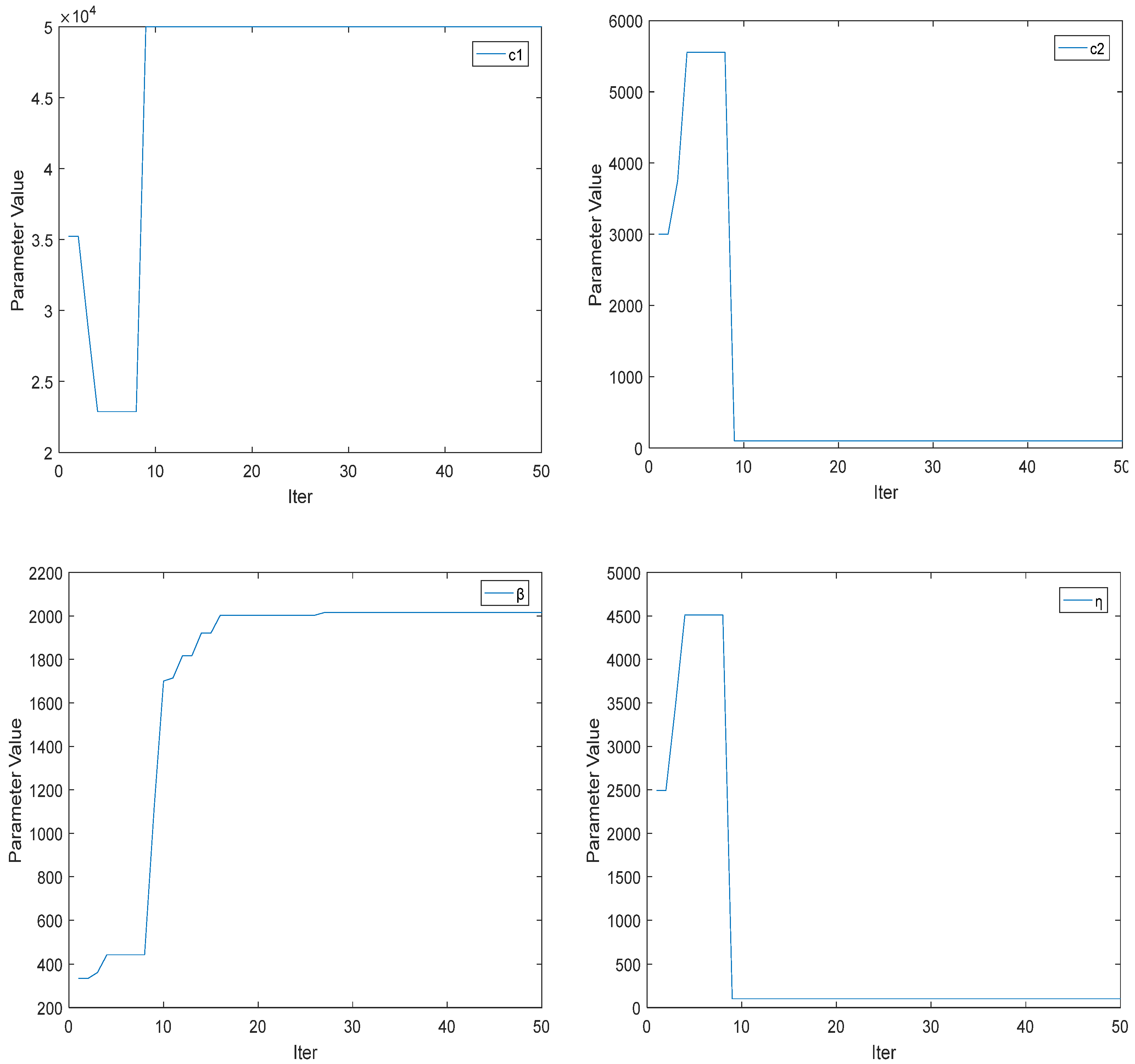
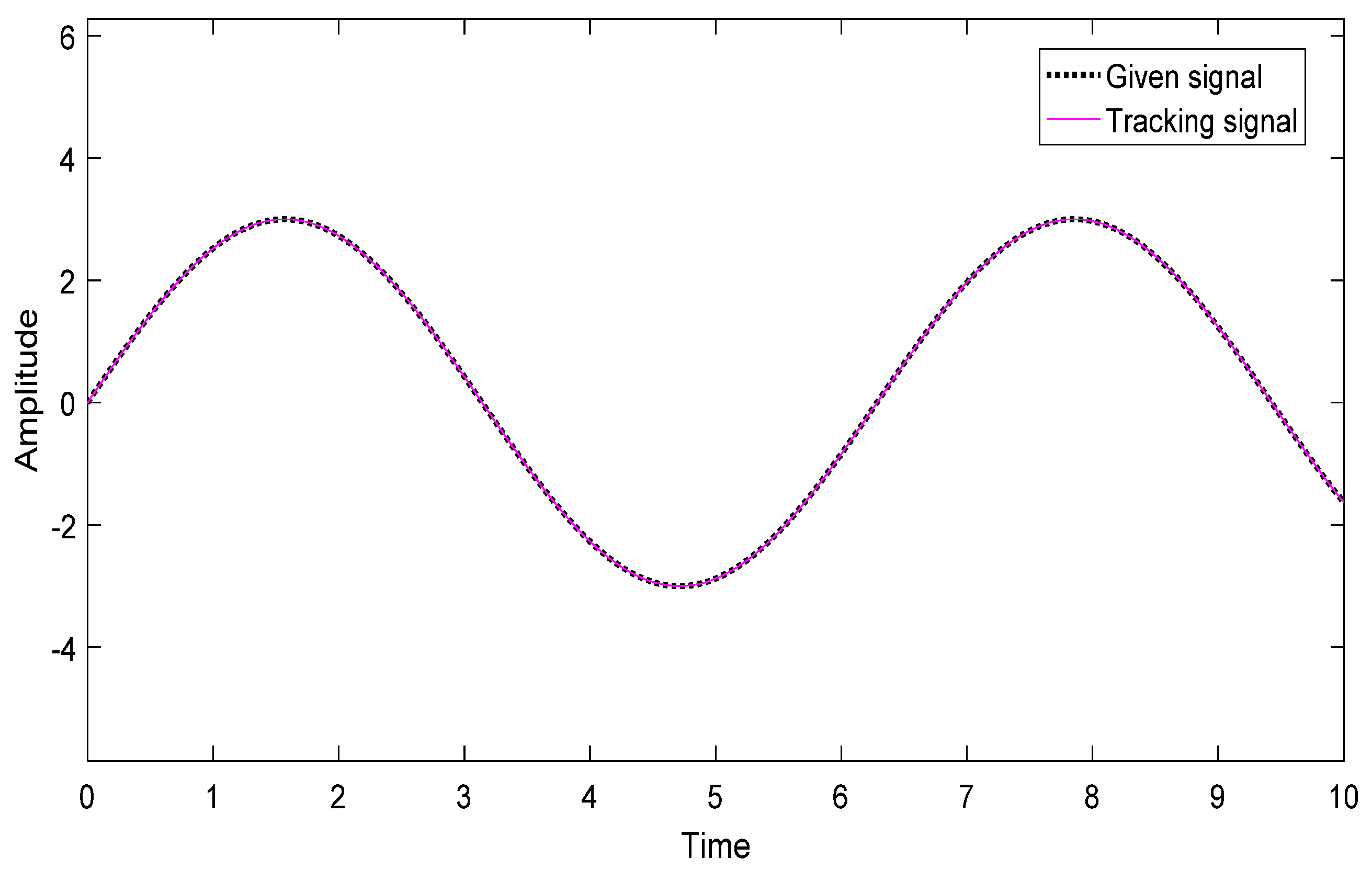
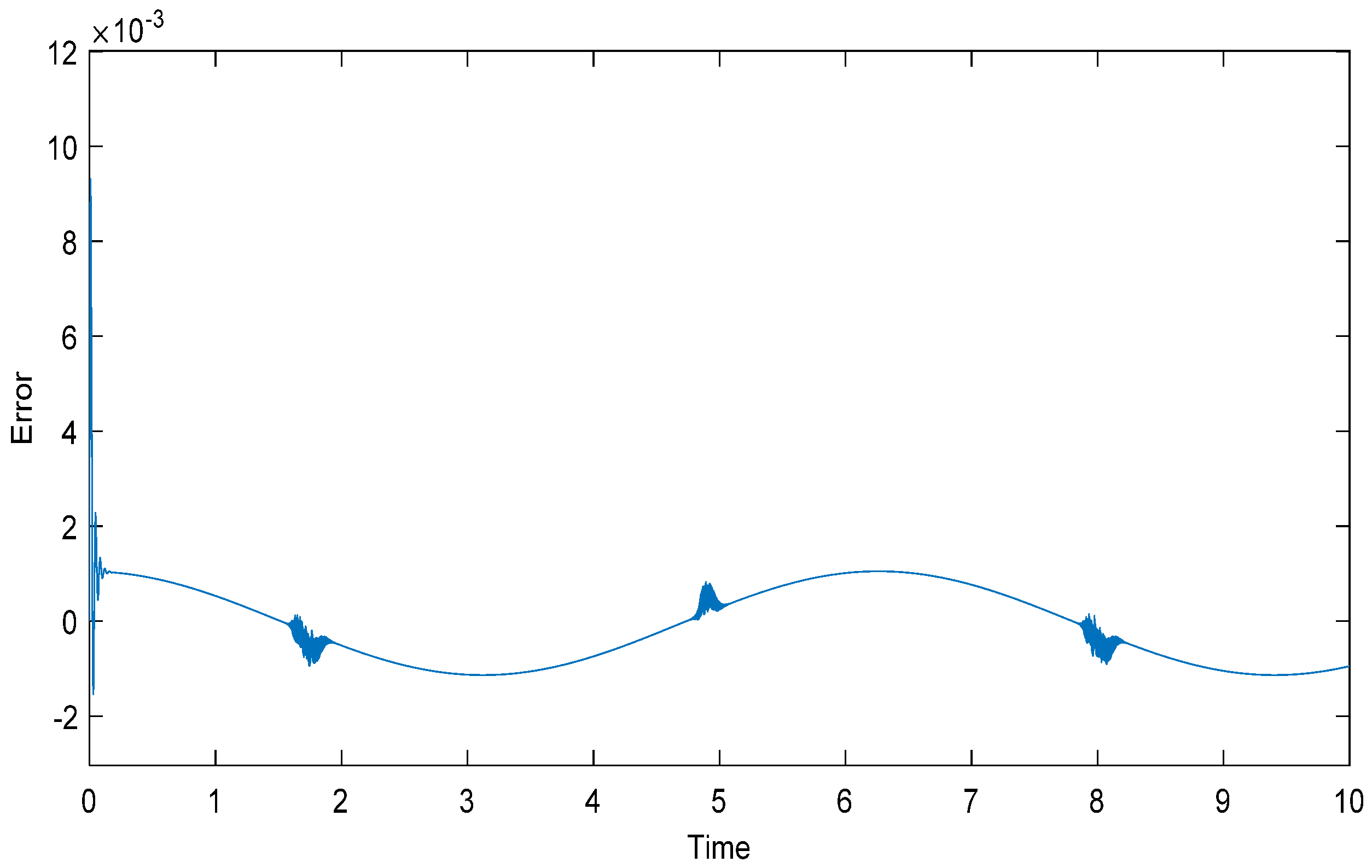
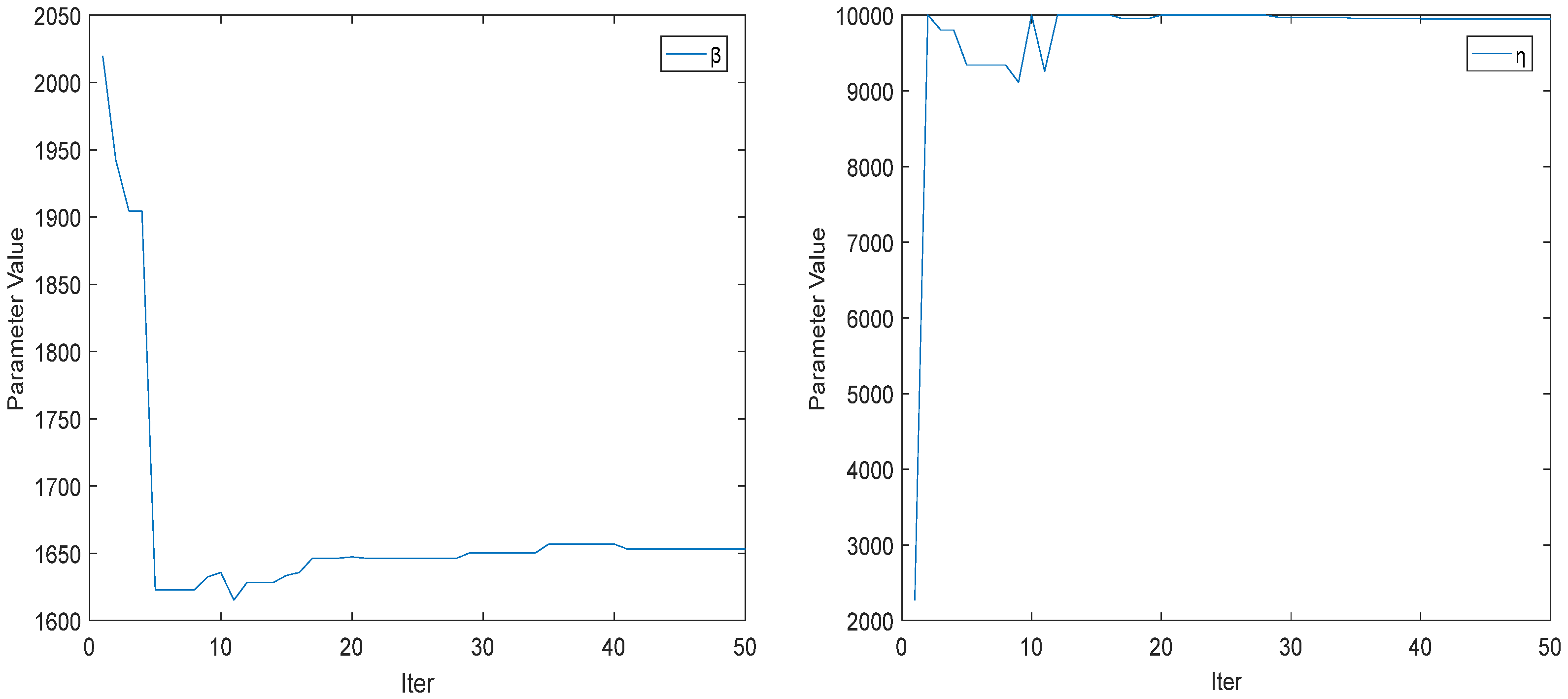
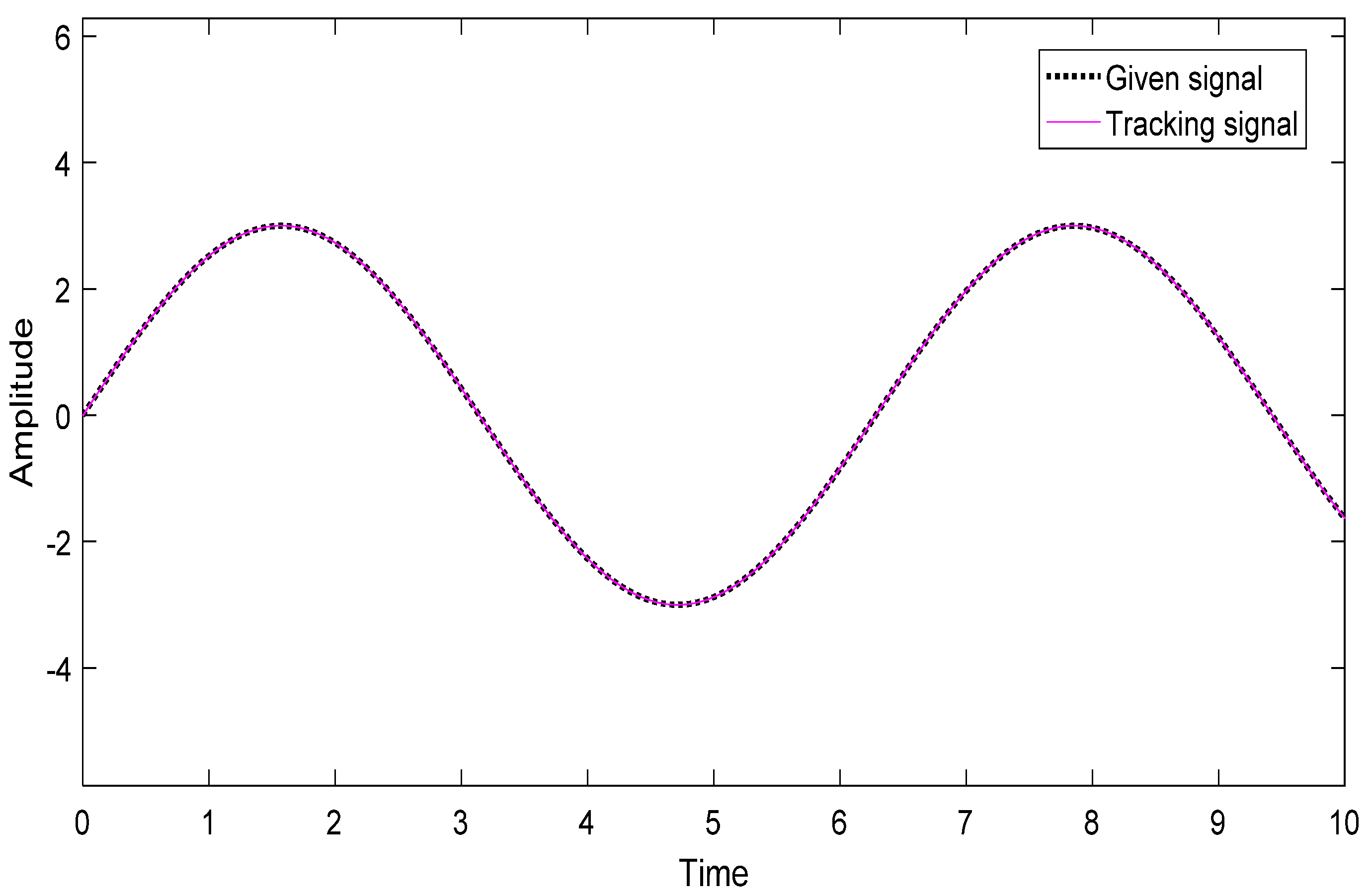
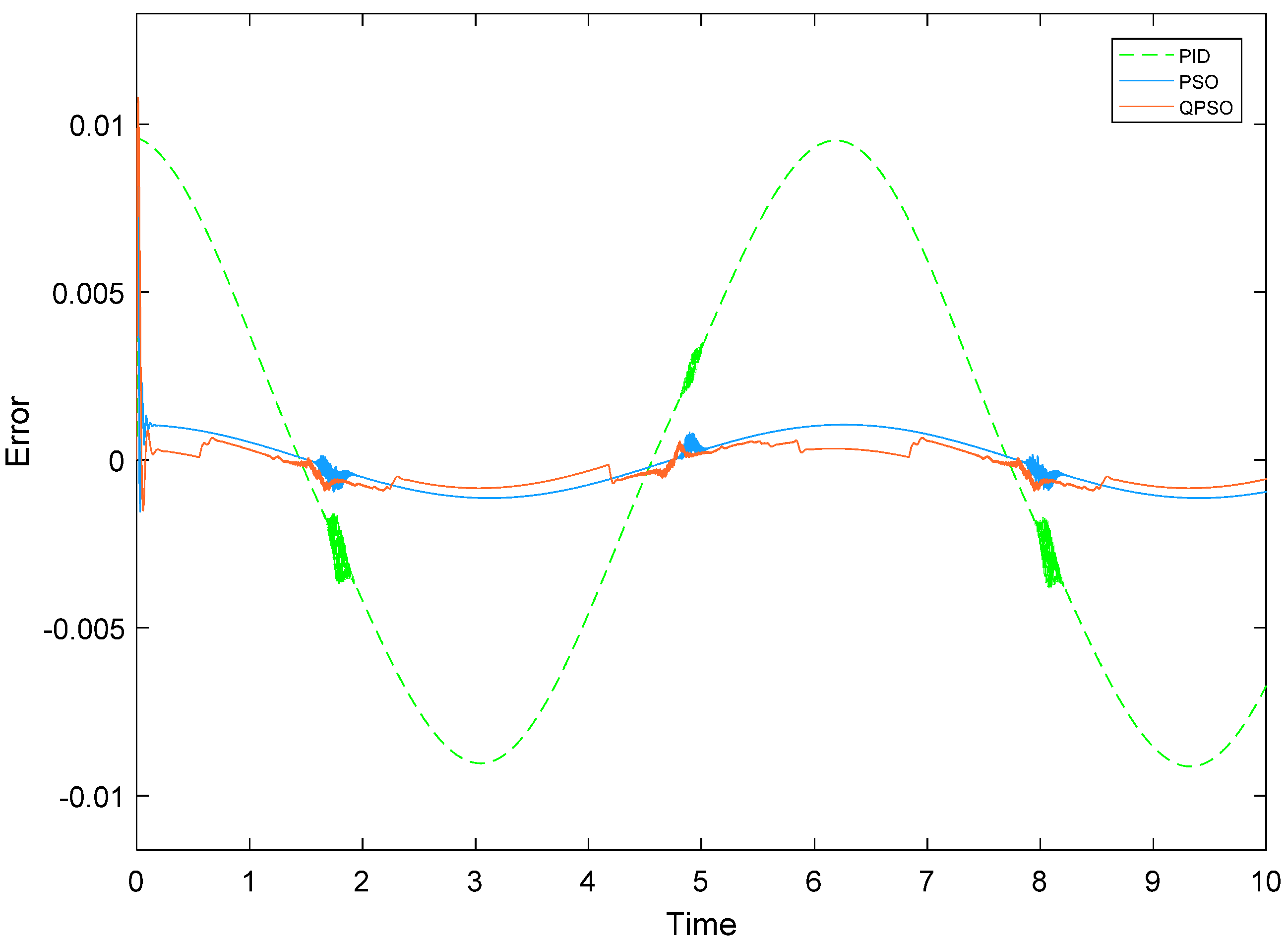
5. Simulation Analysis
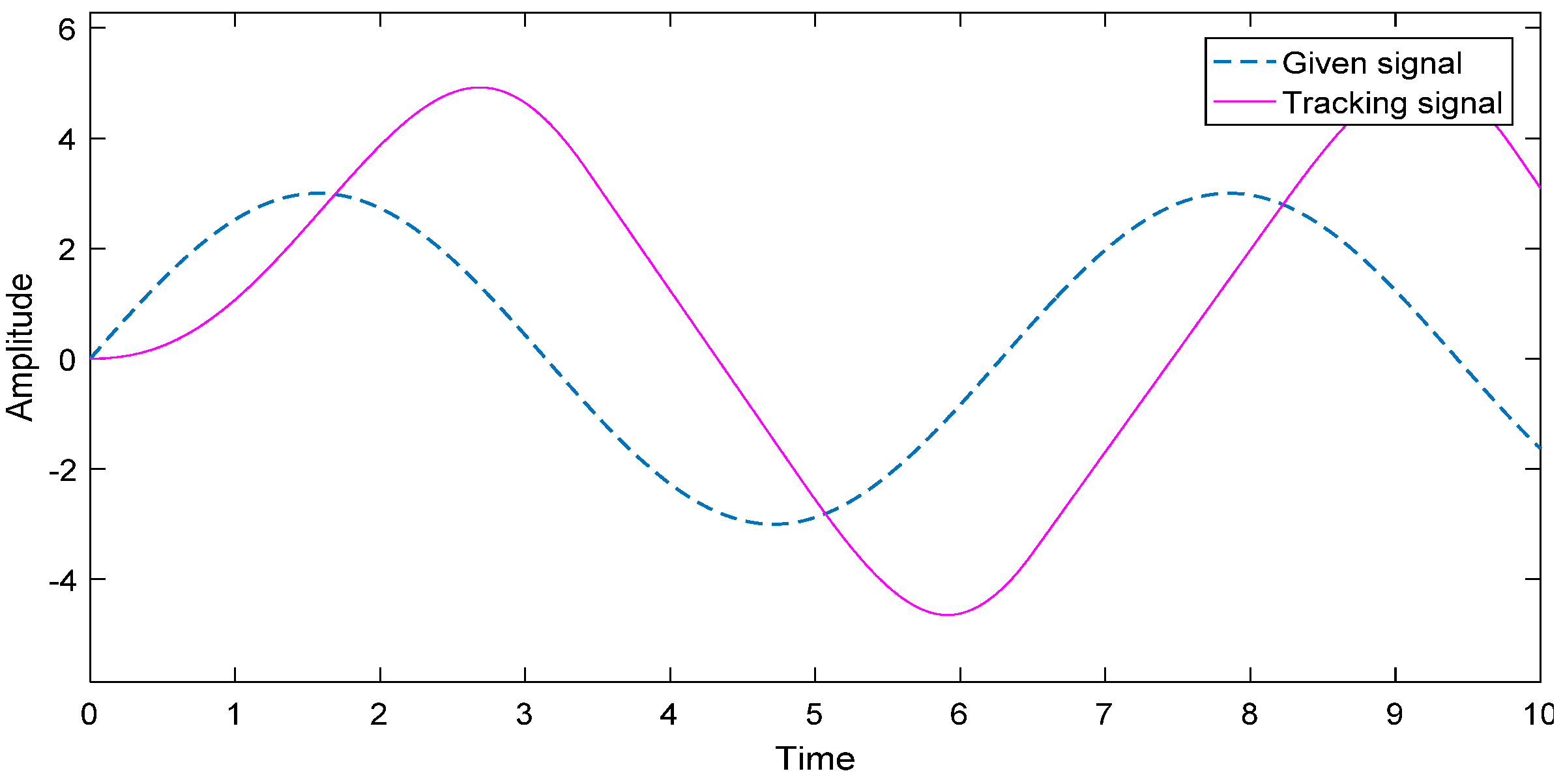
5.1. Working Condition I
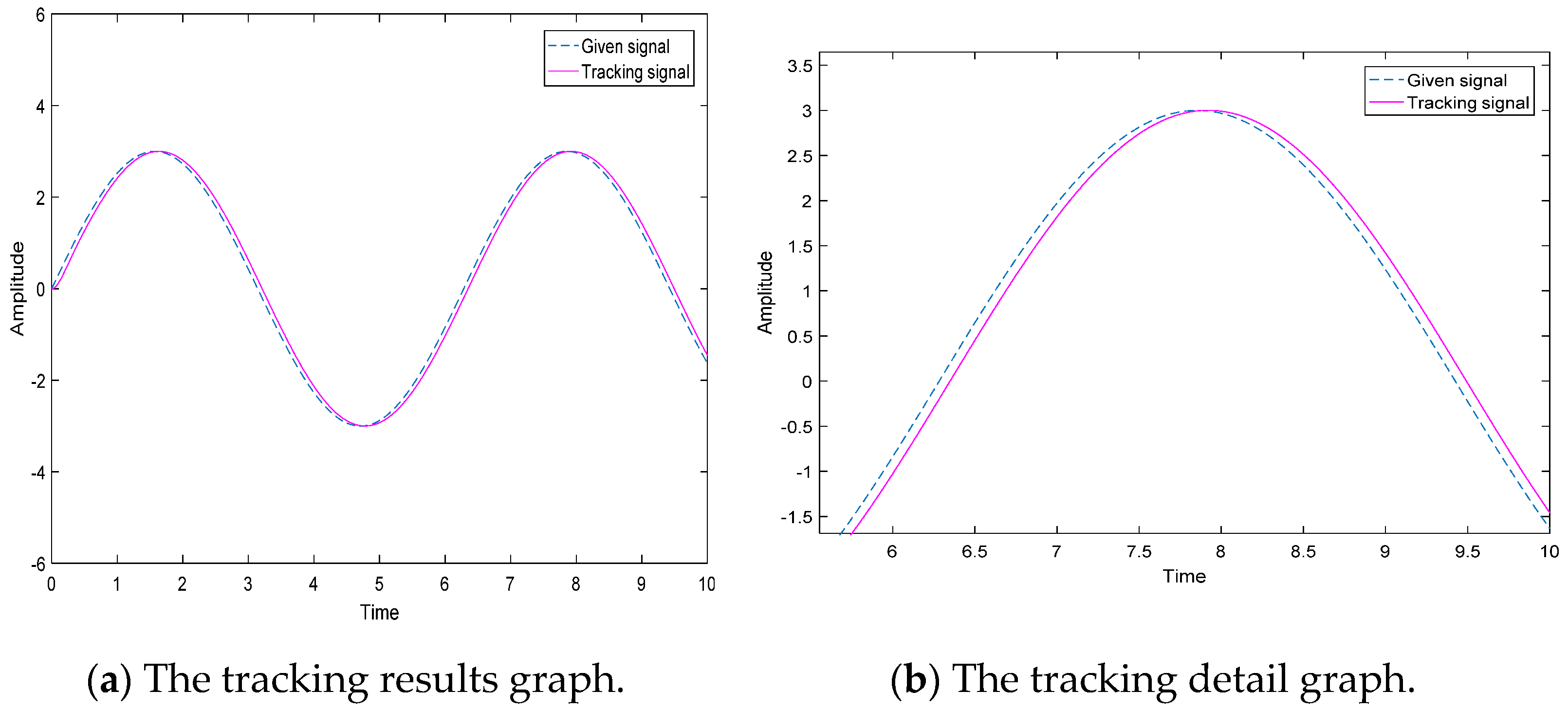
5.2. Working Condition II
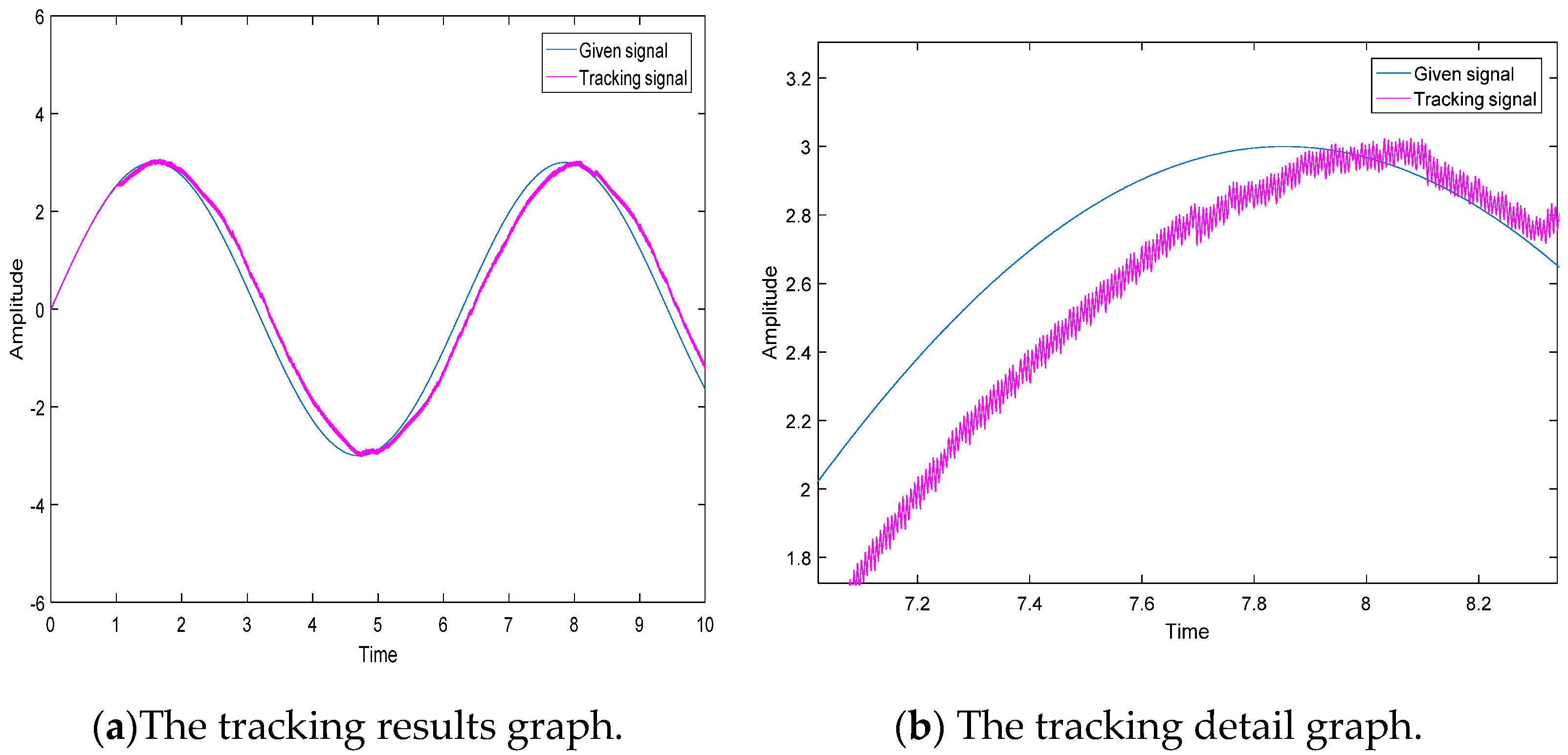
5.3. Working Condition III
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Pool, D.M.; Stroosma, O.; Chu, Q. Long-stroke hydraulic robot motion control with incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 304–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Pan, H.; Gao, H. Filter-based adaptive vibration control for active vehicle suspensions with electrohydraulic actuators. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 65, 4619–4626. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, M.; Seki, K.; Maeda, Y. High-precision motion control techniques: A promising approach to improving motion performance. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2012, 6, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Xu, G.; Zhang, S.; Jin, S.; Wang, R. Digital Twin-Driven Mating Performance Analysis for Precision Spool Valve. Machines 2021, 9, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Dao, H.V.; Ahn, K.K. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Position Tracking of Electro-Hydraulic Servo Systems under Modeling Uncertainty and External Load. Actuators 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Ma, W.; Yin, C.; Cao, D. Trajectory control of electro-hydraulic position servo system using improved PSO-PID controller. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103722. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.-K.; Zheng, J.-M.; Yuan, Q.-L.; Xiao, J.-M.; Li, Y. Fuzzy PID control for direct drive electro-hydraulic position servo system. In Proceedings of the 2011 International conference on consumer electronics, communications and networks (CECNet), Xianning, China, 16–18 April 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Milić, V.; Šitum, Ž.; Essert, M. Robust H∞ position control synthesis of an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Trans. 2010, 49, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Aela, A.; Mohamed, A.; Kenne, J.P.; Angue Mintsa, H. A novel adaptive and nonlinear electrohydraulic active suspension control system with zero dynamic tire liftoff. Machines 2020, 8, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Yan, H. Nonlinear adaptive robust control of the electro-hydraulic servo system. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4494. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Yao, J.-Y. Adaptive Integral Robust Control of Electro-hydraulic Load Simulator. Chin. Hydraul. Pneum. 2016, 12, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Deng, W. Active disturbance rejection adaptive control of hydraulic servo systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8023–8032. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Huang, R.-N.; Gao, Y.-J. Adaptive Inversion Sliding Mode Control for Electro-hydraulic Servo Motion System. Chin. Hydraul. Pneum. 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-D.; Shi, G.-L. RBF Neural Network Sliding Mode Control for Electro Hydraulic Servo System. Chin. Hydraul. Pneum. 2019, 2, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazali, R.; Sam, Y.M.; Rahmat, M.F.; Hashim, A. Position tracking control of an electro-hydraulic servo system using sliding mode control. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Cerman, O.; Hušek, P. Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic servo mechanism. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10269–10277. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yao, J.Y.; Hu, J.; Ma, D.; Deng, W. Tracking Control for Electro-hydraulic Positioning Servo System Based on Disturbance Observer. Acta Armamentarii 2015, 11, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, S. Sliding Mode Control Parameters Tuning Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. Mech. Eng. Autom. 2019, 1, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, G.; Liu, X.; Luo, X.; Chen, H. Sliding Mode Control of Electro-hydraulic Position Servo System Optimized by Improved PSO Algorithm. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 8, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Lai, C.; Wu, X. Particle Swarm Optimisation: Classical and Quantum Perspectives; Taylor and Francis: Milton Park, UK, 2012; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, J. Robust backstepping sliding mode controller investigation for a port plate position servo system based on an extended states observer. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Shen, C. An extended state observer-based control design for electro-hydraulic position servomechanism. Control Eng. Pract. 2021, 109, 104730. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Xiong, S.; Cheng, H. Chattering inhibition of variable rate reaching law sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic position servo system. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 49, 163–169. [Google Scholar]


| System Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Dm | |
| J | |
| B | |
| Vt | |
| Kt | |
| βe | |
| Ct |
| Fitness Value | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Optimum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSO algorithm | 0.0548 | 0.0445 | 0.0353 |
| QPSO algorithm | 0.0271 | 0.0017 | 0.0263 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Su, X. Sliding Mode Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based on Optimization of Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm. Machines 2021, 9, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9110283
Zheng X, Su X. Sliding Mode Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based on Optimization of Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm. Machines. 2021; 9(11):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9110283
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xinyu, and Xiaoyu Su. 2021. "Sliding Mode Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based on Optimization of Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm" Machines 9, no. 11: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9110283
APA StyleZheng, X., & Su, X. (2021). Sliding Mode Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based on Optimization of Quantum Particle Swarm Algorithm. Machines, 9(11), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9110283





