Influence of Humic Acid on the Swelling Inhibition of Clay Minerals and Process Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Linear Swelling Experiment
2.2.2. Viscosity Measurement
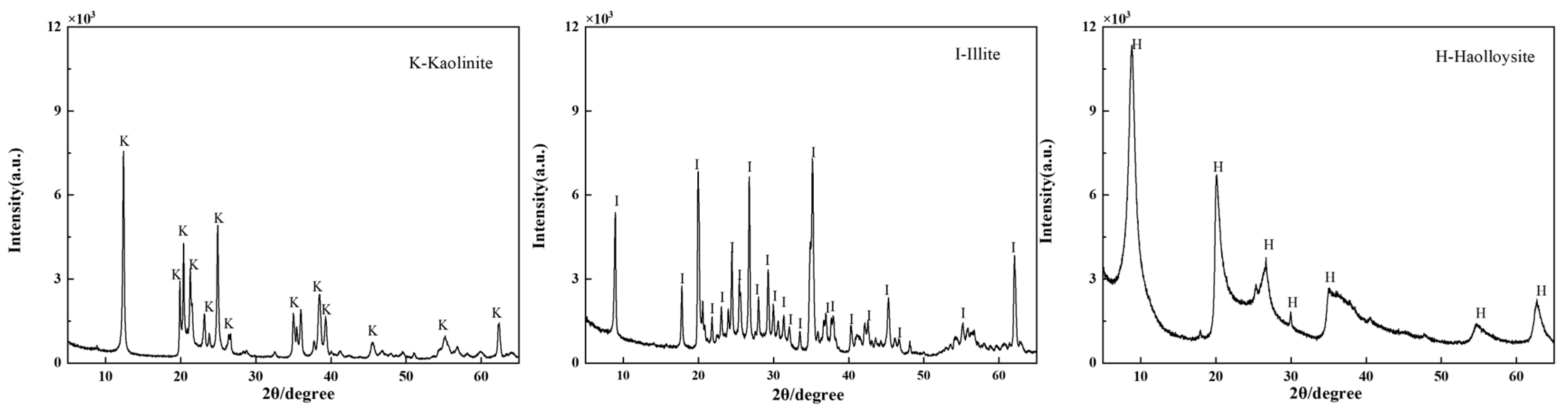
2.2.3. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.2.4. Zeta Potential Measurement
2.2.5. Infrared Spectrum Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Swelling Efficiency of Clay Minerals in Presence of HA
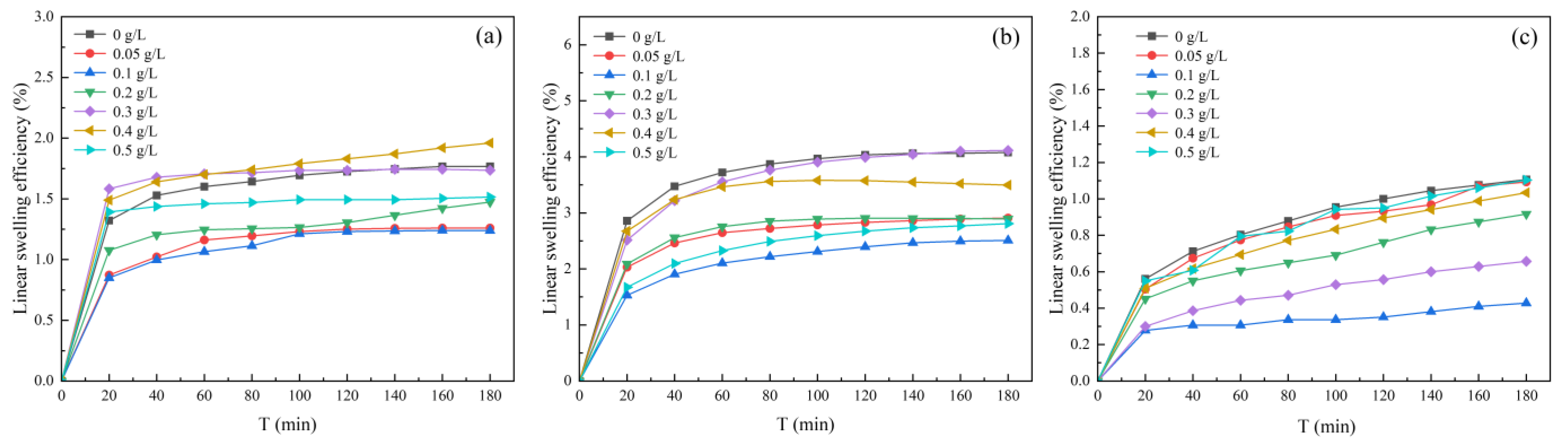
3.1.1. Effect of HA Concentration on Clay Minerals Swelling
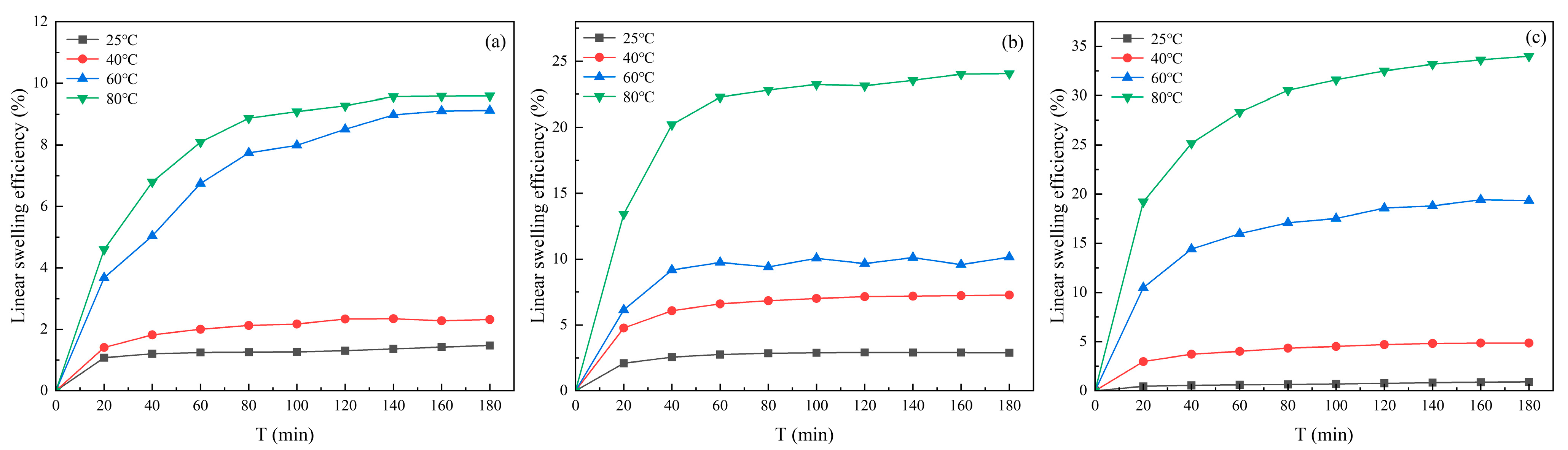
3.1.2. Effect of Temperature on Clay Minerals Swelling
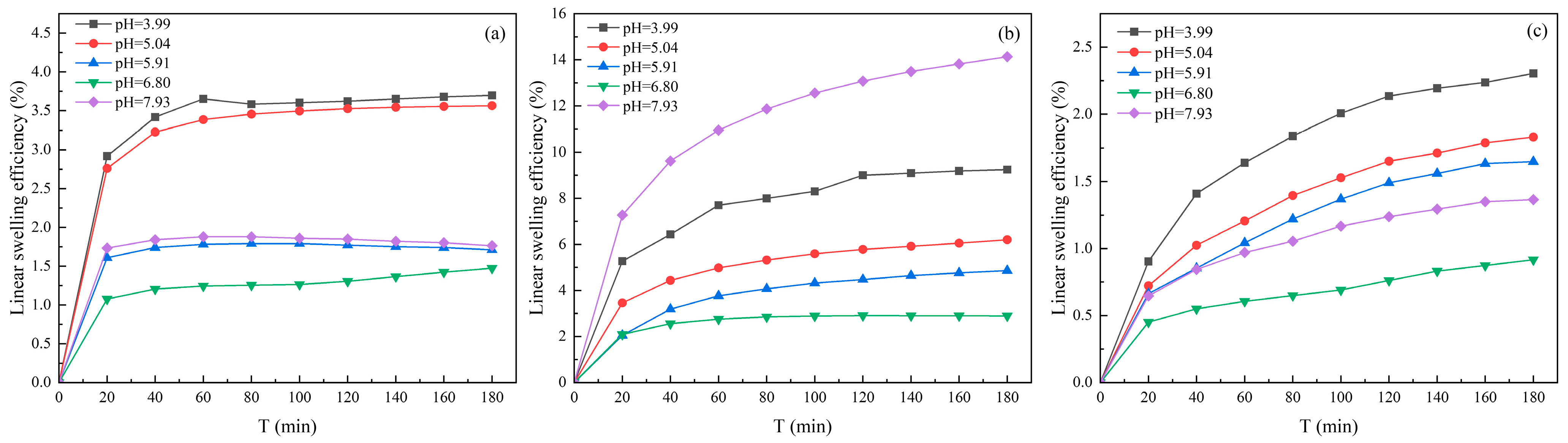
3.1.3. Effect of Solution pH on Clay Minerals Swelling
3.2. The Surface Hydration of Clay Minerals in Presence of HA
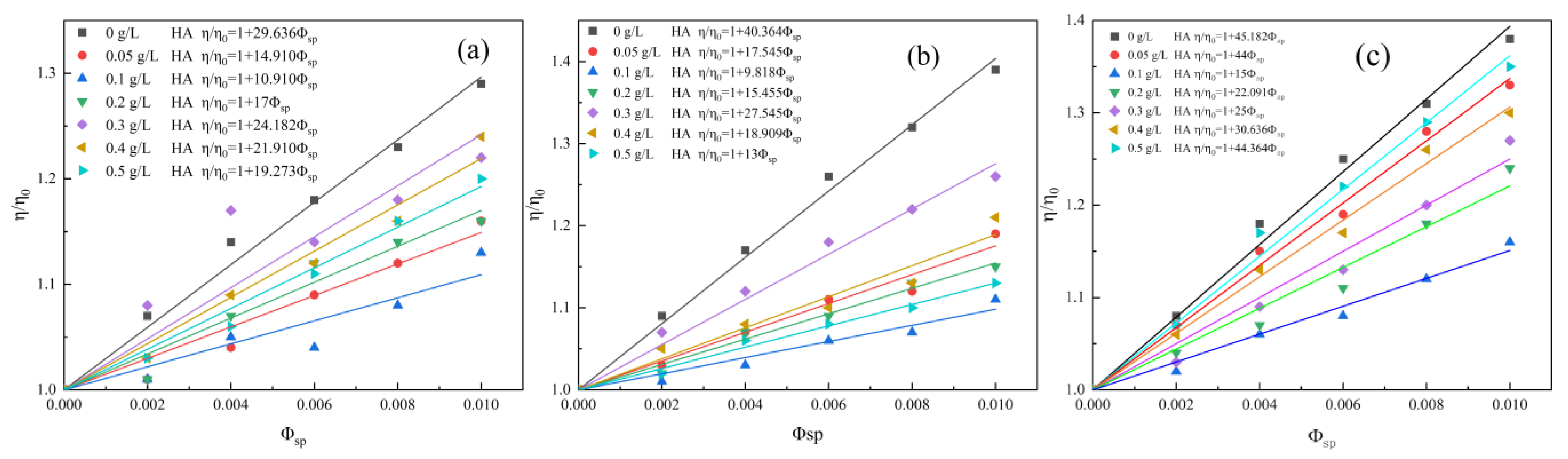
3.2.1. Effect of HA Concentration on Surface Hydration of Clay Mineral
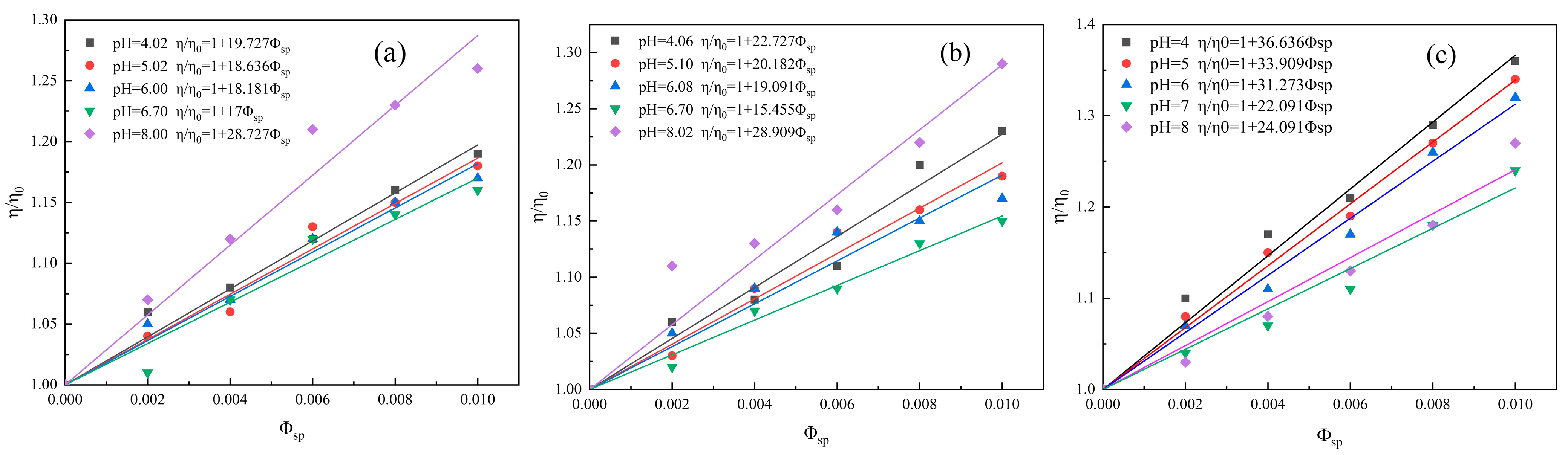
3.2.2. Effect of Solution pH on the Surface Hydration of Clay Minerals
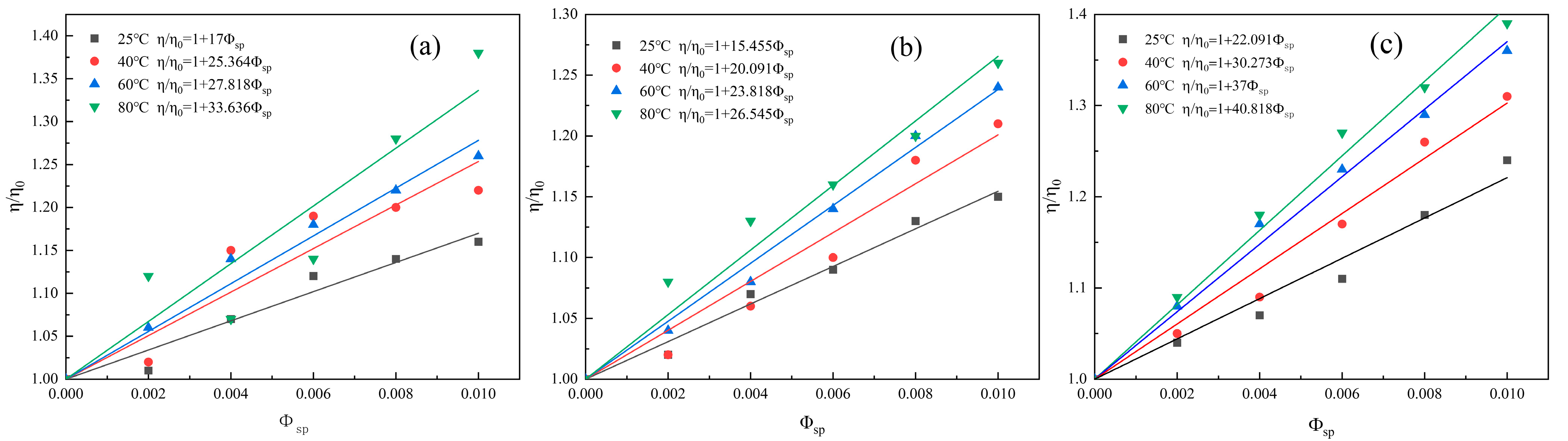
3.2.3. Effect of Temperature on the Surface Hydration of Clay Minerals
3.3. Inhibition Mechisom of HA on the Swelling of Clay Minerals
3.3.1. XRD Analysis of Clay Minerals in the Presence of HA
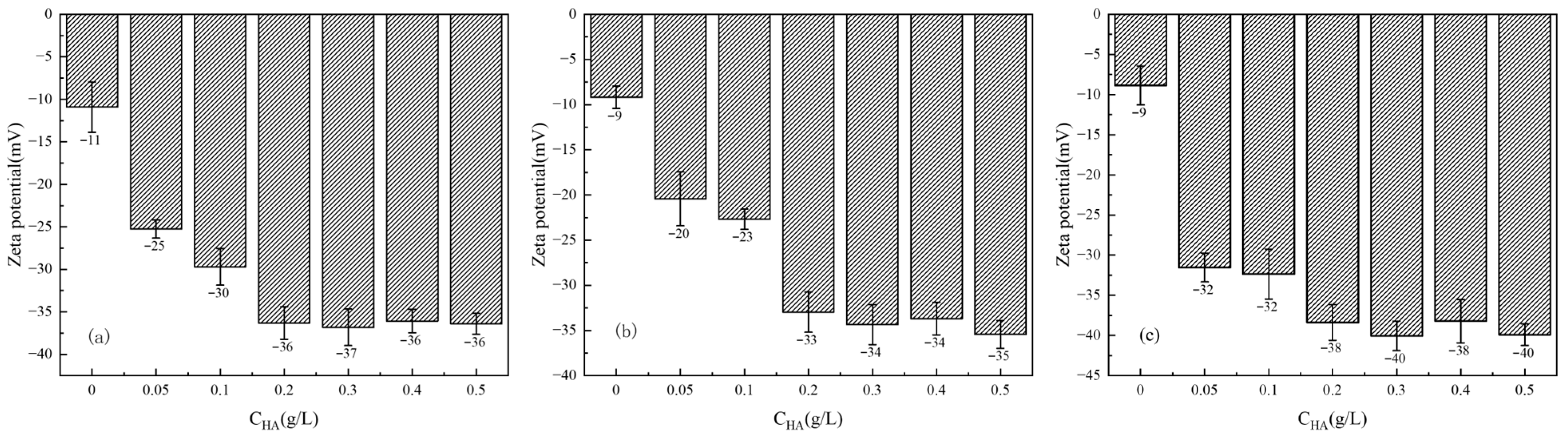
3.3.2. Effect of HA Concentration on Zeta Potential of Clay Minerals
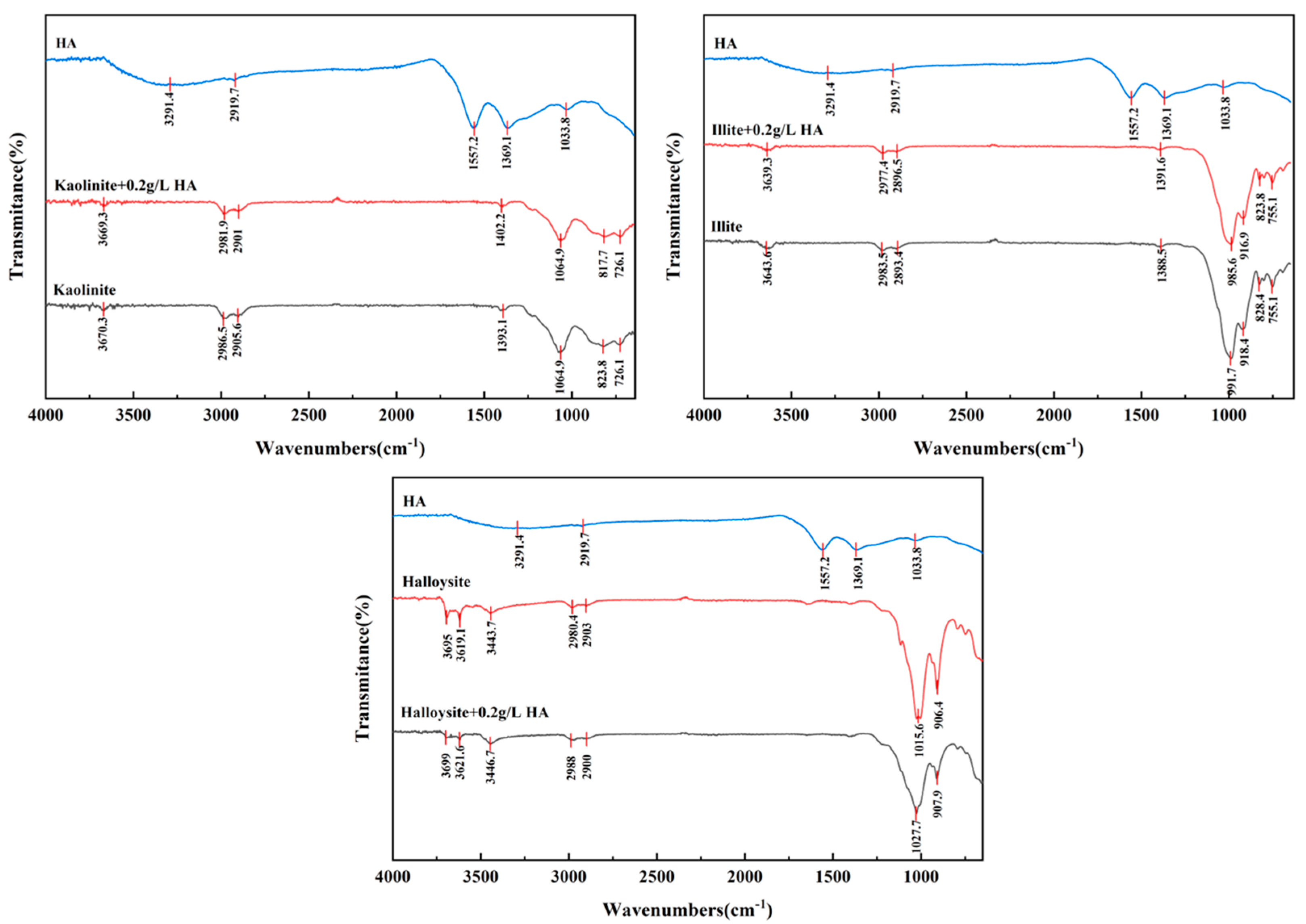
3.3.3. FTIR Analysis of Clay Minerals in Presence of HA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.Q.; Liang, T. Geochemical fractions of rare earth elements in soil around a mine tailing in Baotou, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.L.; Deng, Y.C.; Ye, D.X.; Chen, B.F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, J.G.; Wang, X.; Wang, W. Fine exploration and green development of ion-adsorption type REE deposits in South China using multi-geophysical technology. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.G.; Li, G.; Yang, H.F.; Sha, A.Y.; He, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.C.; Wu, M.; Qu, J. Development review on leaching technology and leaching agents of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores. Minerals 2023, 13, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Xi, G.S.; Yao, N.; Zhou, M.; Gao, X.J.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.X.; Pan, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.M. Spatiotemporal distribution of residual ammonium in a rare-earth mine after in-situ leaching: A modeling study with scarce data. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, G.A.; Papangelakis, V.G. Recovery of rare earth elements adsorbed on clay minerals: II. Leaching with ammonium sulfate. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 131–132, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Peng, C.; Song, S. Hydration Layers on Clay Mineral Surfaces In Aqueous Solutions: A Review. Arch. Min. Sci. 2014, 59, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.A.; Tian, J.; Li, Z.J.; Peng, C.; Wu, Y.X.; Li, S.R.; Wang, C.W.; Zhou, Z.A. Existing state and partitioning of rare earth on weathered ores. J. Rare Earths 2005, 23, 756–759+643. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, D.Y.; Zhuang, G.Z.; Li, X.L. Advanced development of chemical inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids to improve shale stability: A review. Pet. Sci. 2025, 22, 1977–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xu, Y.L.; Deng, X.Y.; Hu, S.M.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhou, F.; Chi, R.A. Effect of Potassium Salt on Swelling of Halloysite Clay Mineral during Leaching Process of Ionic Rare Earth Ore. Minerals 2023, 13, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; He, Z.Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhong, C.B.; Sun, N.J.; Chi, R.A. Swelling of clay minerals in ammonium leaching of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores. Rare Met. 2017, 37, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, D.F.; Chi, X.W.; Chen, W.D.; Chi, R. Swelling of clay minerals during the leaching process of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores by magnesium salts. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.; Sha, A.Y.; Zuo, Q.; Xu, Z.G.; Wu, M.; Chi, R.A. Anti-swelling mechanism of DMDACC on weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Sha, A.Y.; He, Z.Y.; Wu, M.; Qu, J.; Wu, C.J.; Xu, Z.G.; Chi, R.A. Swelling inhibition and infiltration promotion mechanism of polyethyleneimine. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.Y.; Yang, H.F.; He, Z.Y.; Zuo, Q.; Xu, Z.G.; Wu, C.J.; Wu, M.; Chi, R.A. Mechanisms of swelling inhibition and seepage promotion of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore by hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. Miner. Eng. 2023, 202, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xu, Y.L.; Jin, Z.Q.; Hu, S.M.; Pan, J.H.; Zhao, P.; Chi, R. Effect of sodium citrate on the expansion of clay minerals during leaching process of ionic rare-earth ores. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 726, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, B.A.G.d.; Motta, F.L.; Santana, M.H.A. Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, A.; Mindari, W. Effect of Humic Acid on Soil Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Embankment. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 58, 01028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Zhang, Y.B.; Su, Z.J.; Jiang, T. The NMR and spectral study on the structure of molecular size-fractionated lignite humic acid. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotzen, R.A.; Polubesova, T.; Chefetz, B.; Mishael, Y.G. Adsorption of soil-derived humic acid by seven clay minerals: A systematic study. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilin, L.; Tolpeshta, L.; Izosimova, Y.; Pozdnyakov, L.; Stepanov, A.; Salimgareeva, O. Thermal stability and resistance to biodegradation of humic acid adsorbed on clay minerals. Minerals 2023, 13, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yu, J.X.; Xiao, C.Q.; Chi, R.A. Influence of surfactant on clay swelling inhibition of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 677, 132435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhou, C.Y.; Chen, W.D.; Long, F.; Chen, Z.; Chi, R.A. Effects of Ammonium Salts on Rare Earth Leaching Process of Weathered Crust Elution-Deposited Rare Earth Ores. Metals 2023, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Wu, P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Stroet, M.; Liao, J.L.; Chai, Z.F.; Mark, A.E.; Liu, N.; Wang, D.Q. Understanding the effect of pH on the solubility and aggregation extent of humic acid in solution by combining simulation and the experiment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.K. Effect of pH on electric charges carried by clay particles. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1950, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokassidou, C.; Pashalidis, I.; Costa, C.N.; Efstathiou, A.M.; Buckau, G. Thermal stability of solid and aqueous solutions of humic acid. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 454, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Myshkin, V.F.; Khan, V.A.; Poberezhnikov, A.D.; Baraban, A.P. Effect of temperature on the diffusion and sorption of cations in clay vermiculite. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11596–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.T.; Zhang, B.; Kang, T.H. Monte carlo and molecular dynamic simulations of CH4 diffusion in kaolinite as functions of pressure and temperature. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 54, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Inhibitor Type | Swelling Efficiency | Advantages and Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| HA | 1.54%~2.51% | Environmentally friendly, cost-effective, relatively stable |
| Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide [21] | 0.45–0.82% | Strong inhibition, high cost, high toxicity, unfavorable for ecological restoration. |
| Ammonium chloride [22] | 2.50% | Soluble, economical, corrosive |
| Ammonium acetate [11] | 2.705% | Effective under specific conditions and low in price, unstable at high pH |
| Suspension | HA Concentration | Slope k | Surface Hydration Parameter f |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite | 0 g/L | 29.636 | 10.854 |
| 0.05 g/L | 14.910 | 4.964 | |
| 0.1 g/L | 10.910 | 3.364 | |
| 0.2 g/L | 17 | 5.800 | |
| 0.3 g/L | 24.182 | 8.673 | |
| 0.4 g/L | 21.910 | 7.764 | |
| 0.5 g/L | 19.273 | 6.709 | |
| Illite | 0 g/L | 40.364 | 15.146 |
| 0.05 g/L | 17.545 | 6.018 | |
| 0.1 g/L | 9.818 | 2.927 | |
| 0.2 g/L | 15.455 | 5.182 | |
| 0.3 g/L | 27.545 | 10.018 | |
| 0.4 g/L | 18.909 | 6.564 | |
| 0.5 g/L | 13 | 4.200 | |
| Halloysite | 0 g/L | 45.182 | 17.073 |
| 0.05 g/L | 44 | 16.6 | |
| 0.1 g/L | 15 | 5 | |
| 0.2 g/L | 22.091 | 7.836 | |
| 0.3 g/L | 25 | 9 | |
| 0.4 g/L | 30.636 | 11.254 | |
| 0.5 g/L | 44.364 | 16.746 |
| Suspension | pH | Slope k | Surface Hydration Parameter f |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite | 4.02 | 19.727 | 6.891 |
| 5.02 | 18.636 | 6.454 | |
| 6.00 | 18.181 | 6.272 | |
| 6.80 | 17 | 5.800 | |
| 8.00 | 28.727 | 10.491 | |
| Illite | 4.06 | 22.727 | 8.091 |
| 5.10 | 20.182 | 7.073 | |
| 6.08 | 19.091 | 6.636 | |
| 6.80 | 15.455 | 5.182 | |
| 8.02 | 28.909 | 10.564 | |
| Halloysite | 4 | 36.636 | 13.654 |
| 5 | 33.909 | 12.564 | |
| 6 | 31.273 | 11.509 | |
| 7 | 22.091 | 7.836 | |
| 8 | 24.091 | 8.636 |
| Suspension | Temperature | Slope k | Surface Hydration Parameter f |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite | 25 °C | 17 | 5.800 |
| 40 °C | 25.364 | 9.146 | |
| 60 °C | 27.818 | 10.127 | |
| 80 °C | 33.636 | 12.454 | |
| Illite | 25 °C | 15.455 | 5.518 |
| 40 °C | 20.091 | 7.036 | |
| 60 °C | 23.818 | 8.527 | |
| 80 °C | 26.545 | 9.618 | |
| Halloysite | 25 °C | 22.091 | 7.836 |
| 40 °C | 30.273 | 11.109 | |
| 60 °C | 37 | 13.8 | |
| 80 °C | 40.818 | 15.327 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Chi, R.; Deng, B.; Zhou, F. Influence of Humic Acid on the Swelling Inhibition of Clay Minerals and Process Optimization. Minerals 2025, 15, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101062
Cheng Y, Zhang D, Gao X, Yu J, Chi R, Deng B, Zhou F. Influence of Humic Acid on the Swelling Inhibition of Clay Minerals and Process Optimization. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101062
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Ying, Dandan Zhang, Xing Gao, Junxia Yu, Ruan Chi, Bona Deng, and Fang Zhou. 2025. "Influence of Humic Acid on the Swelling Inhibition of Clay Minerals and Process Optimization" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101062
APA StyleCheng, Y., Zhang, D., Gao, X., Yu, J., Chi, R., Deng, B., & Zhou, F. (2025). Influence of Humic Acid on the Swelling Inhibition of Clay Minerals and Process Optimization. Minerals, 15(10), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101062








