Symmetry-Aided Active RIS for Physical Layer Security in WSN-Integrated Cognitive Radio Networks: Green Interference Regulation and Joint Beamforming Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Resource Allocation Symmetry: Homogeneous PUs/SUs (similar channel conditions, identical QoS/SR requirements) justify uniform power allocation, avoiding redundant energy use.
- (2)
- Beamforming Structure Symmetry: Channel reciprocity and symmetric CBS/PBS antenna configurations allow derived precoding matrices, simplifying optimization.
- (3)
- RIS Reflection Matrix Symmetry: Uniform RIS arrays support block-diagonal reflection matrices, focusing green interference on Eves.
- A tripartite collaborative model in CRNs, integrating CBSs, PBSs, and active RIS, is set up. Supported by a software-defined architecture (SDA), this model leverages active RIS’ signal amplification capability to overcome the “double fading” bottleneck of passive RIS, enabling joint optimization of primary network SR and secondary network energy efficiency, filling the gap in active RIS applications for spectrum-sharing scenario.
- An alternating optimization algorithm is proposed based on SOC transformation. Unlike existing methods that either ignore non-convex SR constraints or rely on heuristic algorithms [24], our algorithm converts non-convex SR constraints into solvable SOC forms. By iteratively optimizing base station precoding and active RIS reflection matrices, it achieves directional “green interference” without artificial noise, reducing total transmission power while ensuring security.
- A dynamic interference regulation mechanism for active RIS is introduced. By adjusting reflection amplitudes and phases, targeted interference is generated to degrade eavesdropping links while enhancing legitimate signals. This mechanism avoids energy waste from traditional artificial noise methods [27], realizing dual gains in security and energy efficiency, distinct from existing active RIS studies that focus solely on signal amplification.
2. System Model
2.1. System Framework
2.2. Signal Model
- (1)
- Resource symmetry: Uniform power allocation for homogeneous PUs/SUs (e.g., ) to balance energy use.
- (2)
- Beamforming symmetry: Derive CBS precoding from PBS precoding via unitary transformation, exploiting channel reciprocity.
- (3)
- RIS symmetry: Block-diagonal reflection matrix for uniform RIS arrays, ensuring directional interference/signal amplification.
2.3. Signal Interference Noise Ratio
3. Problem Description and Algorithm Design
3.1. Problem Description
3.2. Problem Transformation
3.3. Subproblem 1
3.4. Subproblem 2
4. Simulation and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Parameters
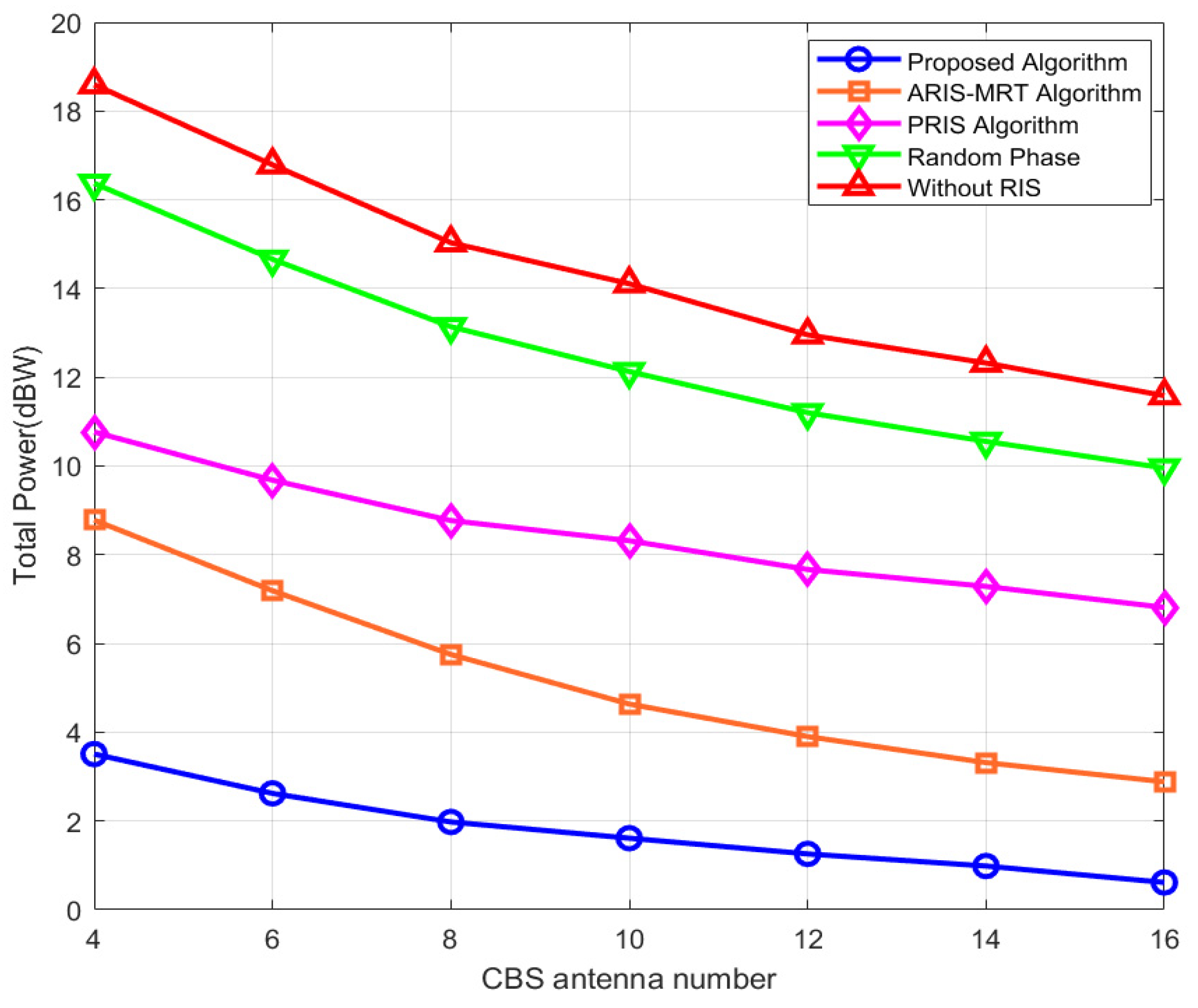
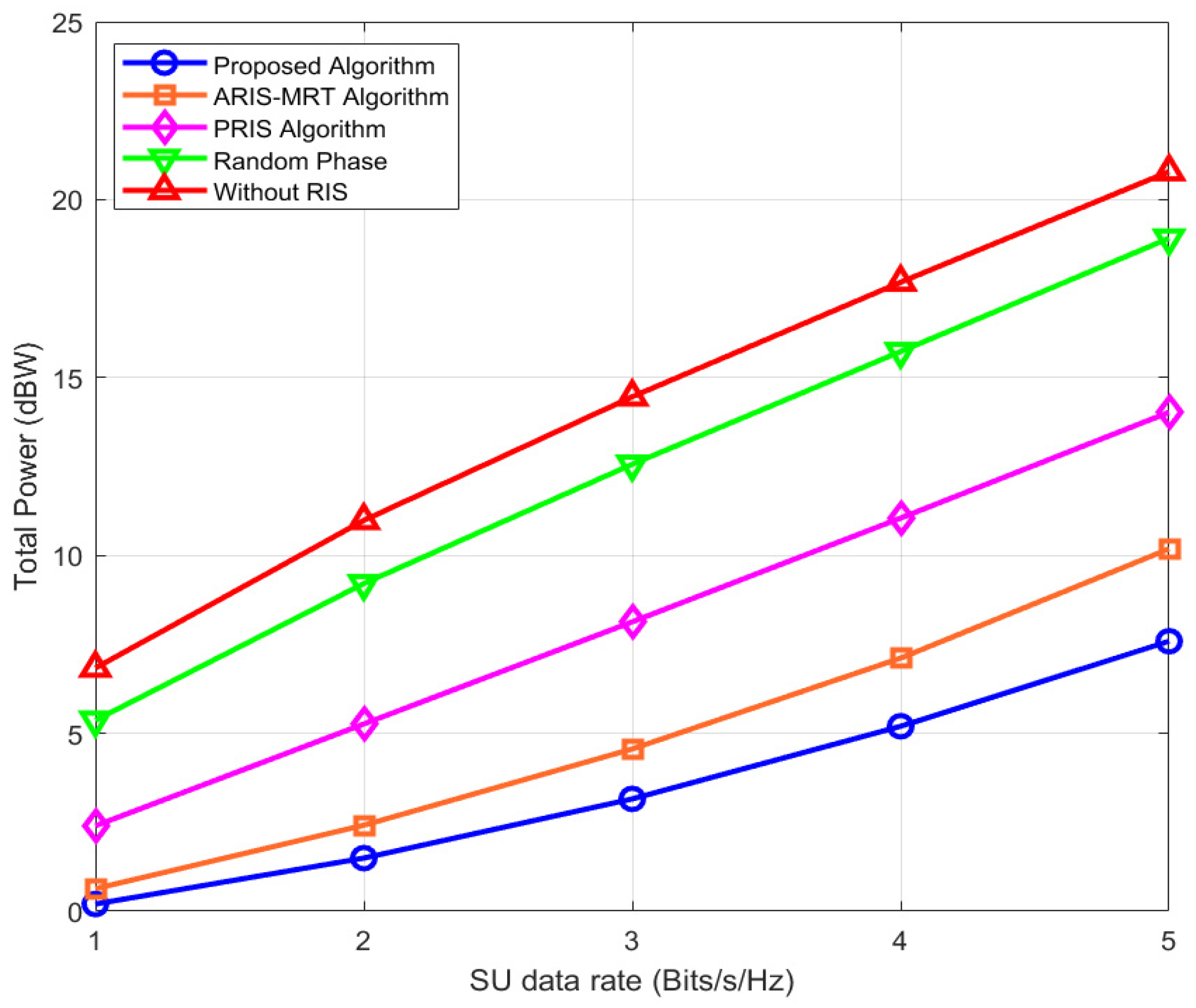
4.2. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wang, C.X.; You, X.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C. On the road to 6G: Visions, requirements, key technologies, and testbeds. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 905–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Towards Smart and Reconfigurable Environment: Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Wireless Network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Mu, X.; Hou, T.; Xu, J.; Di Renzo, M.; Al-Dhahir, N. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Principles and opportunities. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1546–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, E.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jin, S.; Yuen, C.; Dobre, O.A.; Schober, R. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for 6G: Emerging hardware architectures, applications, and open challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2024, 19, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.; Son, W.; Jung, B.C. Physical-layer security improvement with reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for 6G wireless communication systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.-M.; Wang, H.-M. Secure MIMO transmission via intelligent reflecting surface. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, R. Secure wireless communication via intelligent reflecting surface. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Sugiura, S. QoS-constrained optimization of intelligent reflecting surface aided secure energy-efficient transmission. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 5137–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Bansal, B.; Majhi, S.; Jain, S.; Huang, S.; Huang, C.; Yuen, C. A survey on reconfigurable intelligent surface for physical layer security of next-generation wireless communications. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2024, 5, 172–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, W.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Van Chien, T.; Kaleem, Z.; Lee, H.; Yu, H. Reconfigurable intelligent surface for physical layer security in 6G-IoT: Designs, issues, and advances. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 3599–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, W.; Song, F.; Zhang, H. Physical layer security in ris-noma-assisted iov systems with uncertain ris deployment. Electronics 2024, 13, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zappone, A.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Debbah, M.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Rani, S.; Alhudhaif, A.; Koundal, D.; Gunduz, E.S. An optimized scheme for energy efficient wireless communication via intelligent reflecting surfaces. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 190, 116106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Chen, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, C.; Fang, J.; Li, S. Joint power allocation and passive beamforming design for IRS-assisted physical-layer service integration. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 7286–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Joint power control and passive beamforming in RIS-assisted spectrum sharing. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Bai, J.; Yan, Q.; Wang, H.M. RIS-assisted green secure communications: Active RIS or passive RIS? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Xu, S.; Yang, F. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface: Fully-connected or sub-connected? IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Liang, Y.-C.; Pei, Y.; Larsson, E.G. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 4962–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Q. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface for energy efficiency in MU-MISO systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 4103–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, Y. Enhanced secure communication via novel double-faced active RIS. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 3497–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, J. Physical-layer secure wireless transmission via active reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Power Intelligent Computing Systems (ICPICS), Shenyang, China, 29–31 July 2022; pp. 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Paul, A.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, K.; Biswas, S. Robust transmission for energy-efficient sub-connected active RIS assisted wireless networks: DRL versus traditional optimization. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2024, 8, 1902–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Weng, R.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, C.; Wang, J. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface for mobile edge computing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 2482–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, W.; Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H. Covert transmission and physical-layer security of active RIS-RS-NOMA-aided communication systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 31507–31520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, H.-M.; Bai, J. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface aided secure transmission. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Lin, Z.; An, K.; Wang, J.; Zheng, G.; Al-Dhahir, N.; Wong, K.-K. Active RIS assisted rate-splitting multiple access network: Spectral and energy efficiency tradeoff. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 1452–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.F.J. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface enhanced secure and energy-efficient communication of jittering UAV. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 22386–22400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Xing, Z.; Gu, C.; Xue, X.; Zeng, X. Secure and energy efficient transmission for IRS-assisted cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakoca, H.; Namdar, M.; Aldirmaz-Colak, S.; Basaran, M.; Basgumus, A.; Durak-Ata, L.; Yanikomeroglu, H. Metasurface manipulation attacks: Potential security threats of RIS-aided 6G communications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2023, 61, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Pan, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, L. Adaptive and Robust Channel Estimation for Arbitrarily Shaped IRS-Aided Millimeter-Wave Communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 9411–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 5394–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Cheng, W.; Huo, Y. Robust and secure transmission over active reconfigurable intelligent surface aided multi-user system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 11515–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, R.; Du, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Geng, S.; Qin, P. Joint beamforming and reflecting elements optimization for segmented RIS assisted multi-user wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 3820–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, C.; Yuen, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, G. Energy-efficient maximization for RIS-aided MISO symbiotic radio systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 13689–13694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiriart-Urruty, J.-B.; Lemarechal, C. Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms I: Fundamentals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]







| Parameters | Units | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| - | Precoding matrix of PBS/CBS | |
| - | Reflection matrix of active RIS | |
| - | Channel matrix/vector from node x to node y (e.g., ): CBS→RIS) | |
| dBW | Transmit power of the i-th PU/SU | |
| dBm | Maximum total power consumption of active RIS | |
| - | SINR of SU/eavesdropper | |
| bit/s/Hz | Transmission rate of SU/secrecy rate of the p-th PU | |
| dBm | AWGN variance/dynamic noise variance of active RIS | |
| dBm | Interference temperature threshold of PU |
| Parameters | Value | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| CBS antenna number | 4 | Number of antennas equipped at the CBS |
| PBS antenna number | 4 | Number of antennas equipped at the PBS |
| RIS element number | 16 | Number of elements in the active RIS |
| SU transmission rate requirement | 4 bit/s/Hz | QoS rate requirement for SU |
| PU SR requirement | 1 bit/s/Hz | SR requirement for PU |
| Number of eavesdroppers | 2 | Number of Eves in the system |
| Number of primary users | 2 | Number of PUs in the primary network |
| Noise power | −90 dBm | Additive white Gaussian noise power at the receiver (SU, PU, eavesdropper) |
| RIS transmission power | 20 dBm | Transmission power configuration of active RIS |
| Interference threshold | −90 dBm | Maximum allowable interference temperature for Primary User (PU) |
| Rician K-factor | 7 dB | Quantitatively represents the power ratio of line-of-sight components to non-line-of-sight multipath components in the channel |
| Line-of-sight (LoS) path loss exponent | 2.2 | Path loss exponent for LoS links, used to simulate channel attenuation (e.g., CBS–RIS, RIS–SU links) |
| Non-LoS path loss exponent | 4.2 | Path loss exponent for non-LoS links, used to simulate channel attenuation in complex scattering environments (e.g., CBS–SU, PBS–SU links) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y. Symmetry-Aided Active RIS for Physical Layer Security in WSN-Integrated Cognitive Radio Networks: Green Interference Regulation and Joint Beamforming Optimization. Symmetry 2025, 17, 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122047
Wu Y. Symmetry-Aided Active RIS for Physical Layer Security in WSN-Integrated Cognitive Radio Networks: Green Interference Regulation and Joint Beamforming Optimization. Symmetry. 2025; 17(12):2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122047
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yixuan. 2025. "Symmetry-Aided Active RIS for Physical Layer Security in WSN-Integrated Cognitive Radio Networks: Green Interference Regulation and Joint Beamforming Optimization" Symmetry 17, no. 12: 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122047
APA StyleWu, Y. (2025). Symmetry-Aided Active RIS for Physical Layer Security in WSN-Integrated Cognitive Radio Networks: Green Interference Regulation and Joint Beamforming Optimization. Symmetry, 17(12), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122047






