Robust Online Rotor Time Constant Tuning Method with High-Frequency Current Injection for Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drives
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Literature Reviews and Limitations
1.3. Paper Organization and Contribution
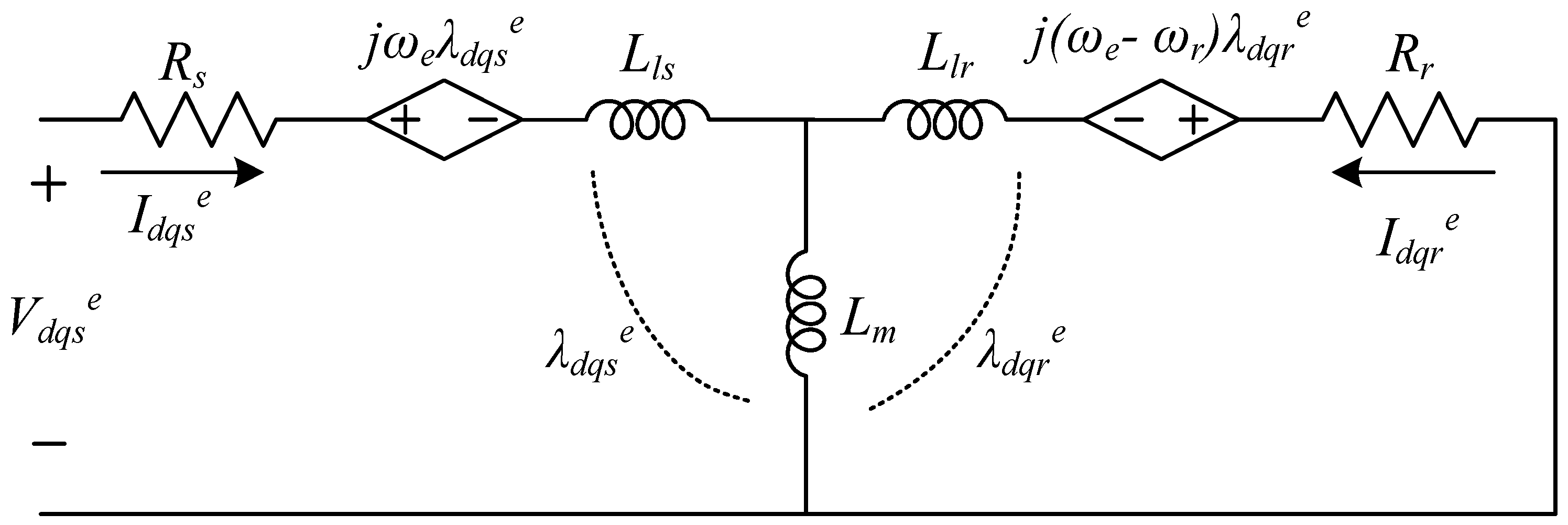
2. Conventional IFOC and Basic IM Equations
3. MRAS-Based Stator Resistance Estimation and Detection of Rotor Time Constant Variation
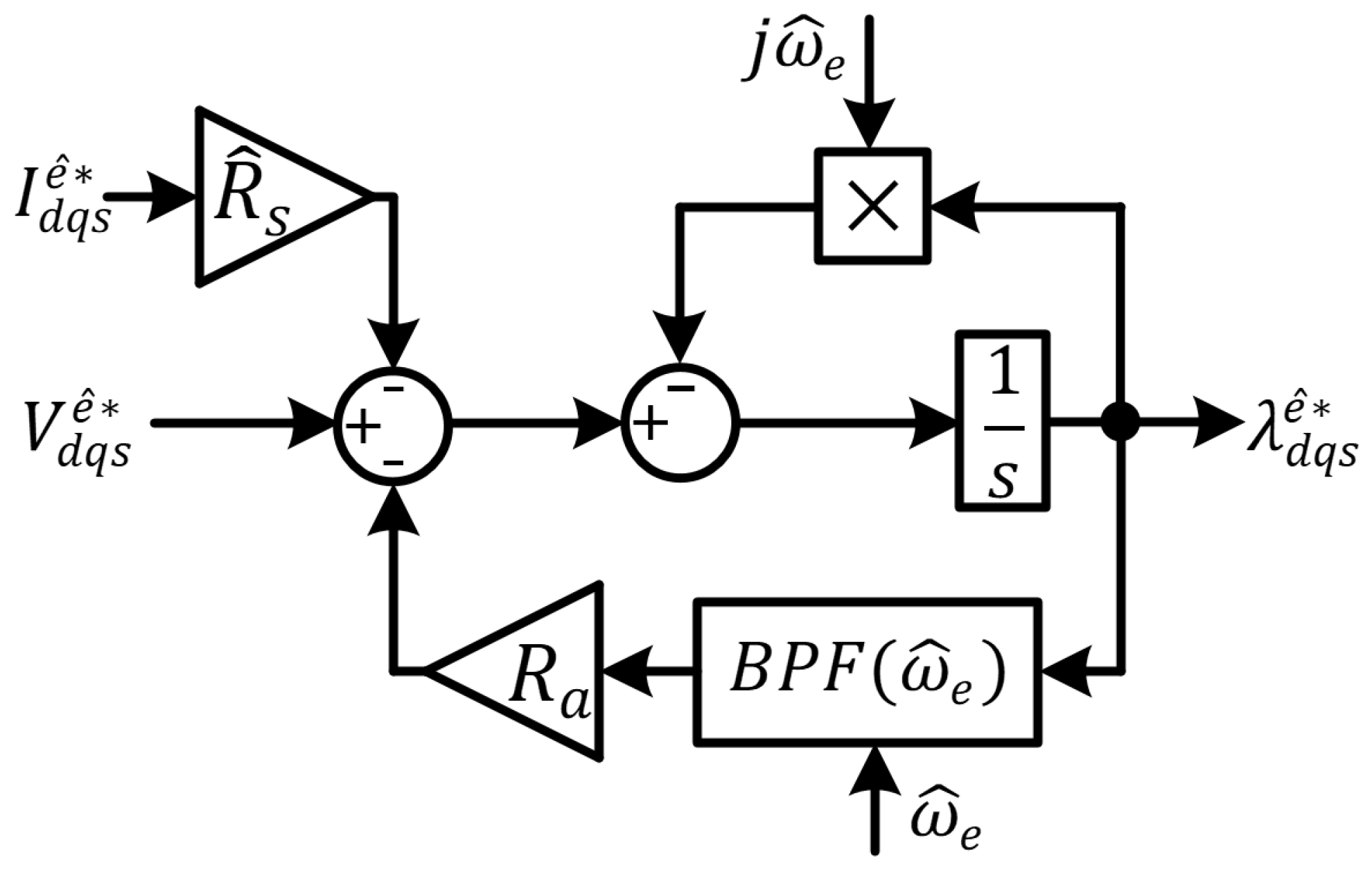
3.1. Selection of MRAS Model for Stator Resistance Estimation
3.2. Effects of Rotor Time Constant Error on MRAS-Based Stator Resistance Estimation
3.3. Proposed Method for Detecting Rotor Time Constant Variation
4. Simultaneous Estimation of Stator Resistance and a Rotor Time Constant Through High-Frequency Current Injection
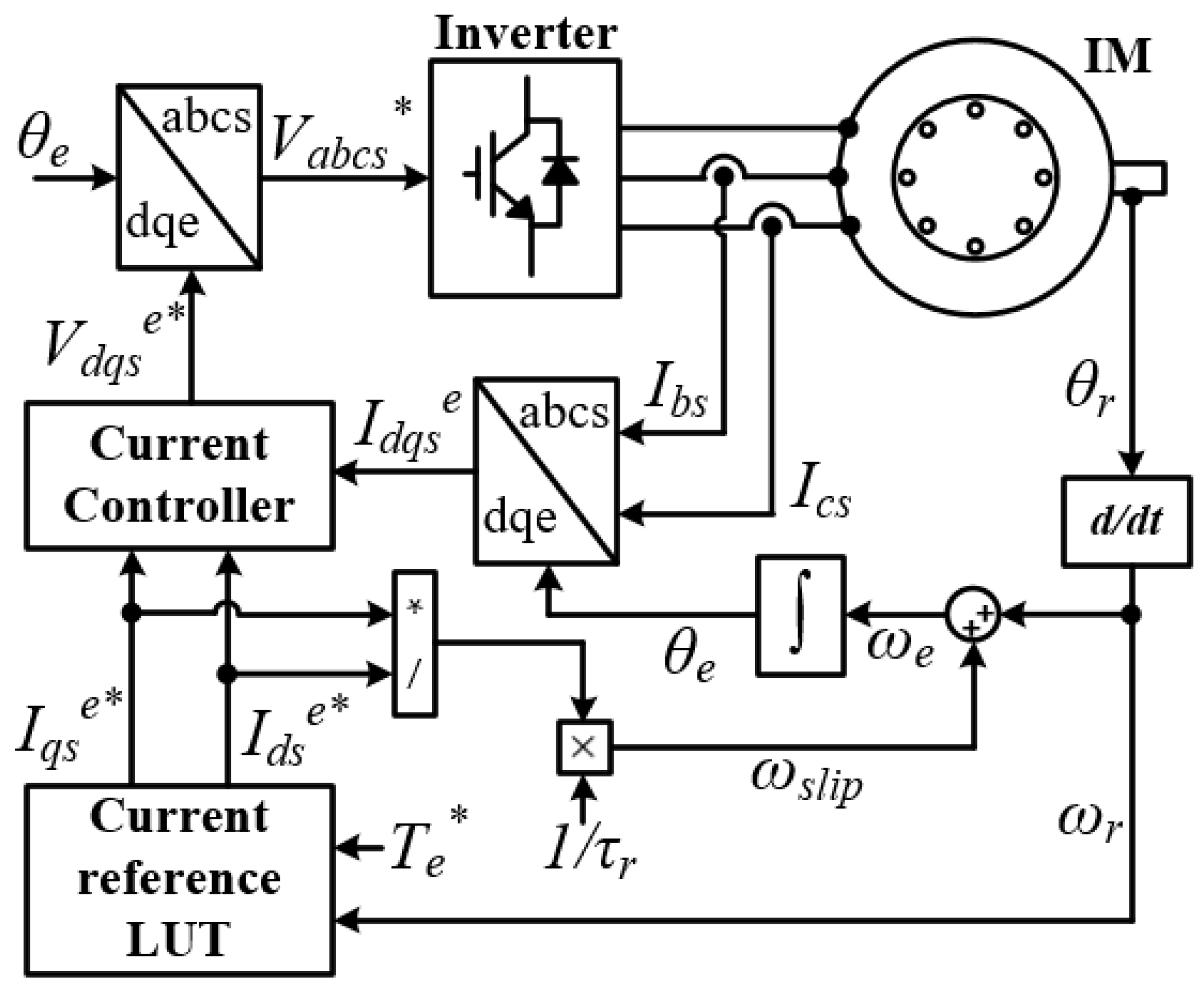
4.1. Overview
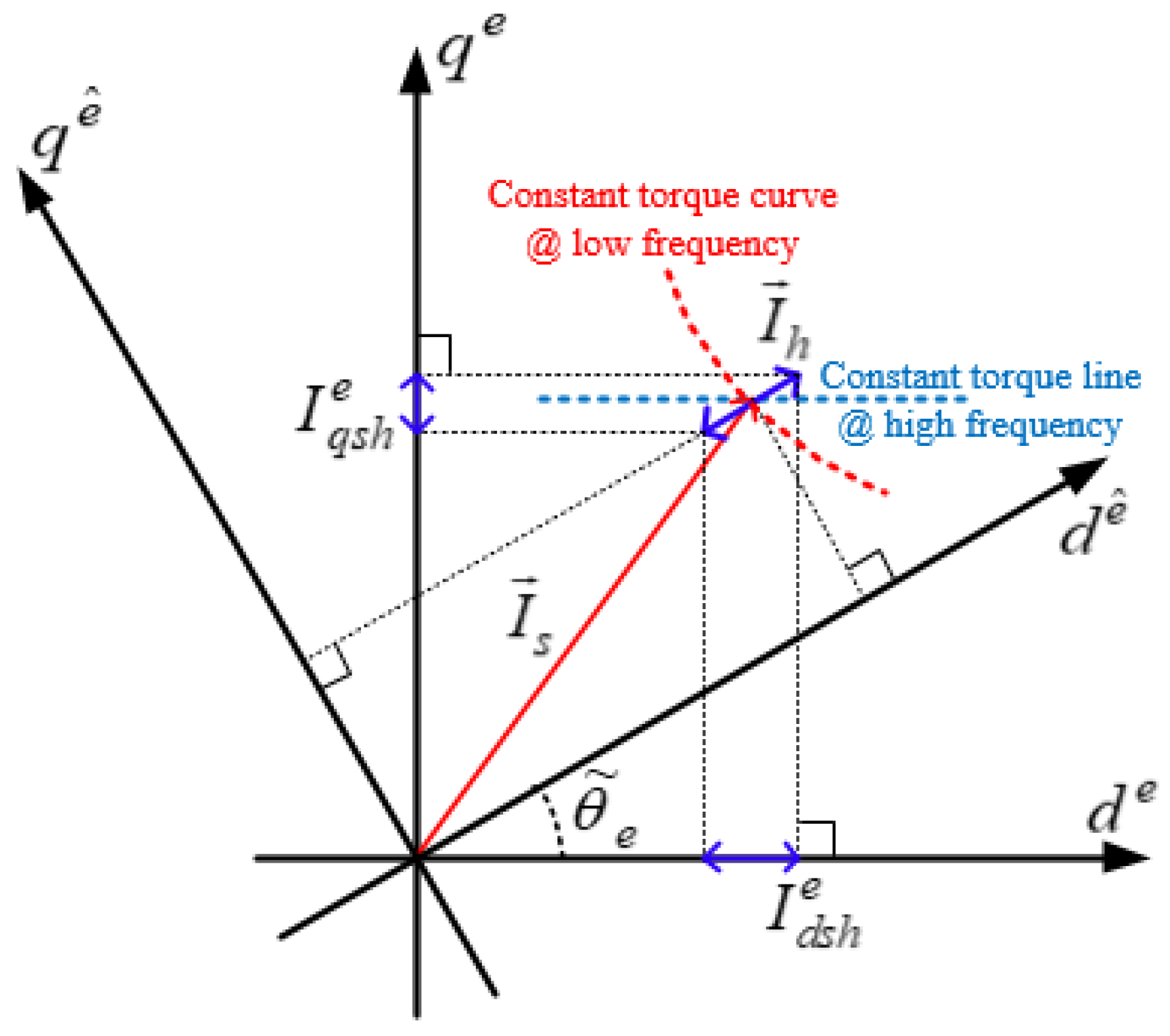
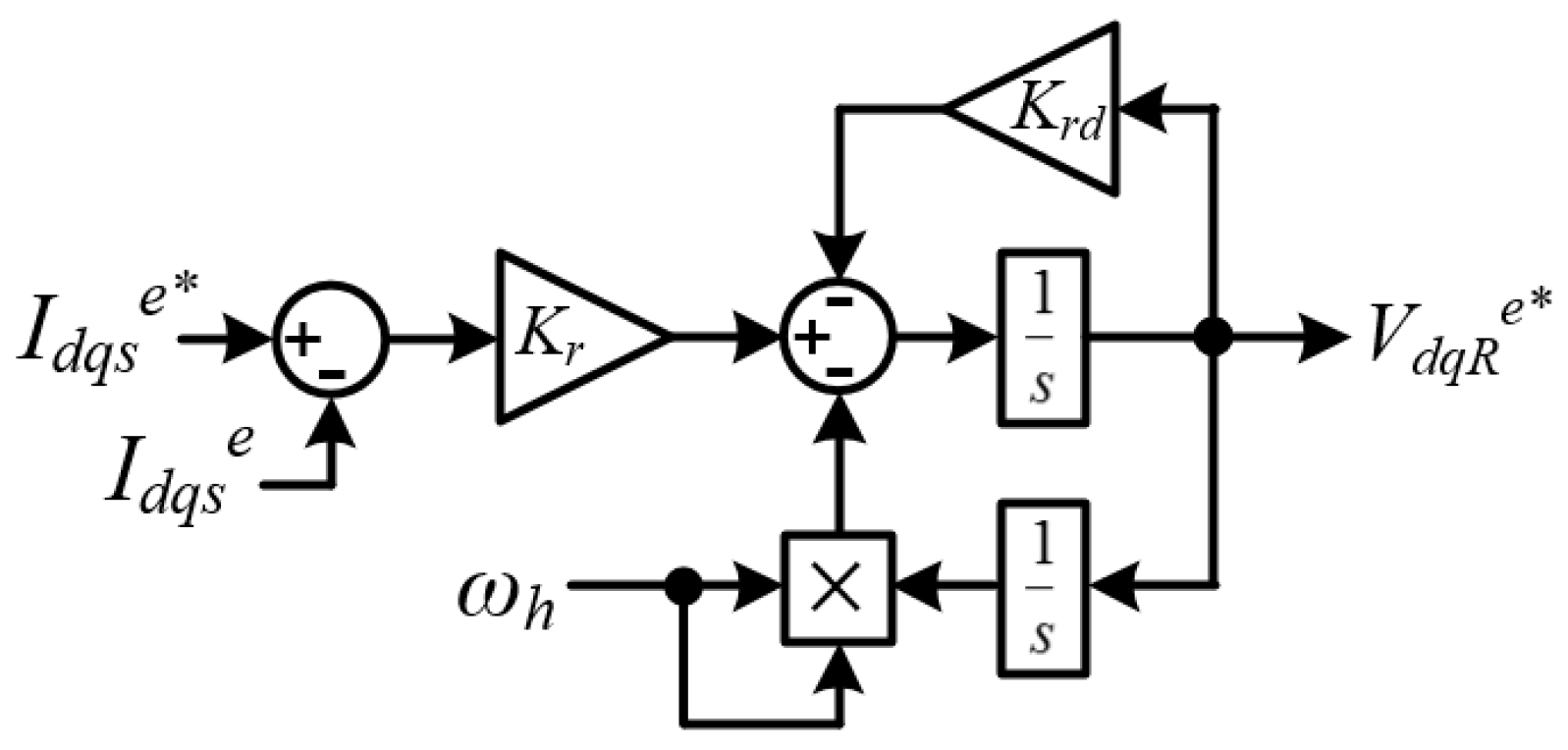
4.2. High-Frequency Current Injection and Rotor Time Constant Compensation
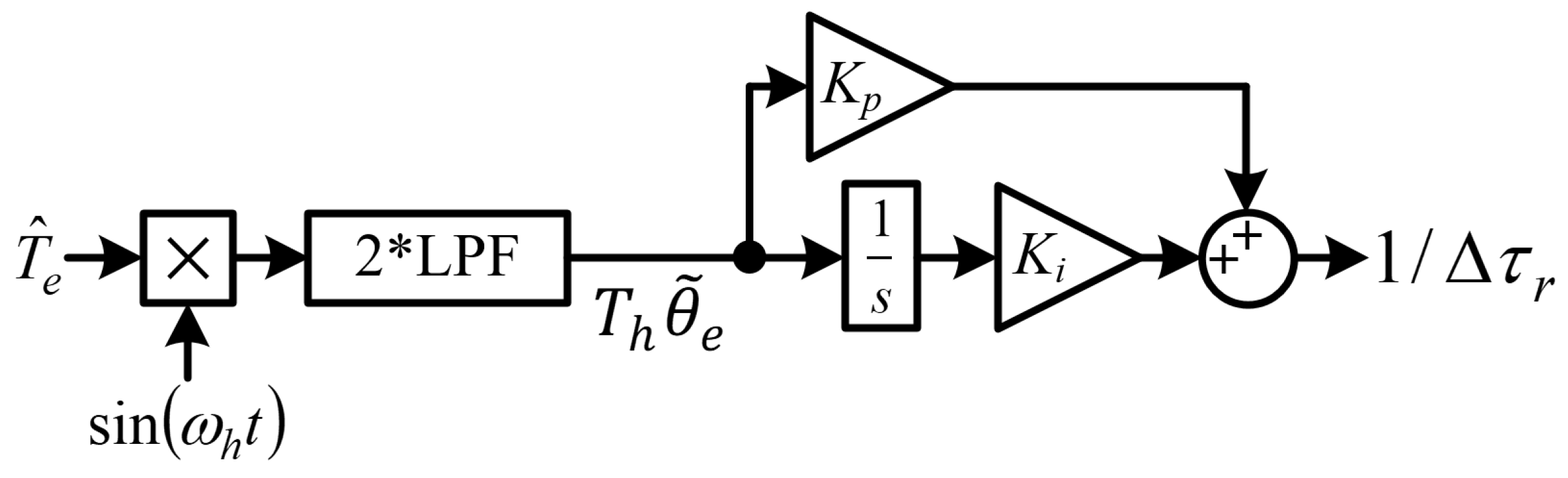
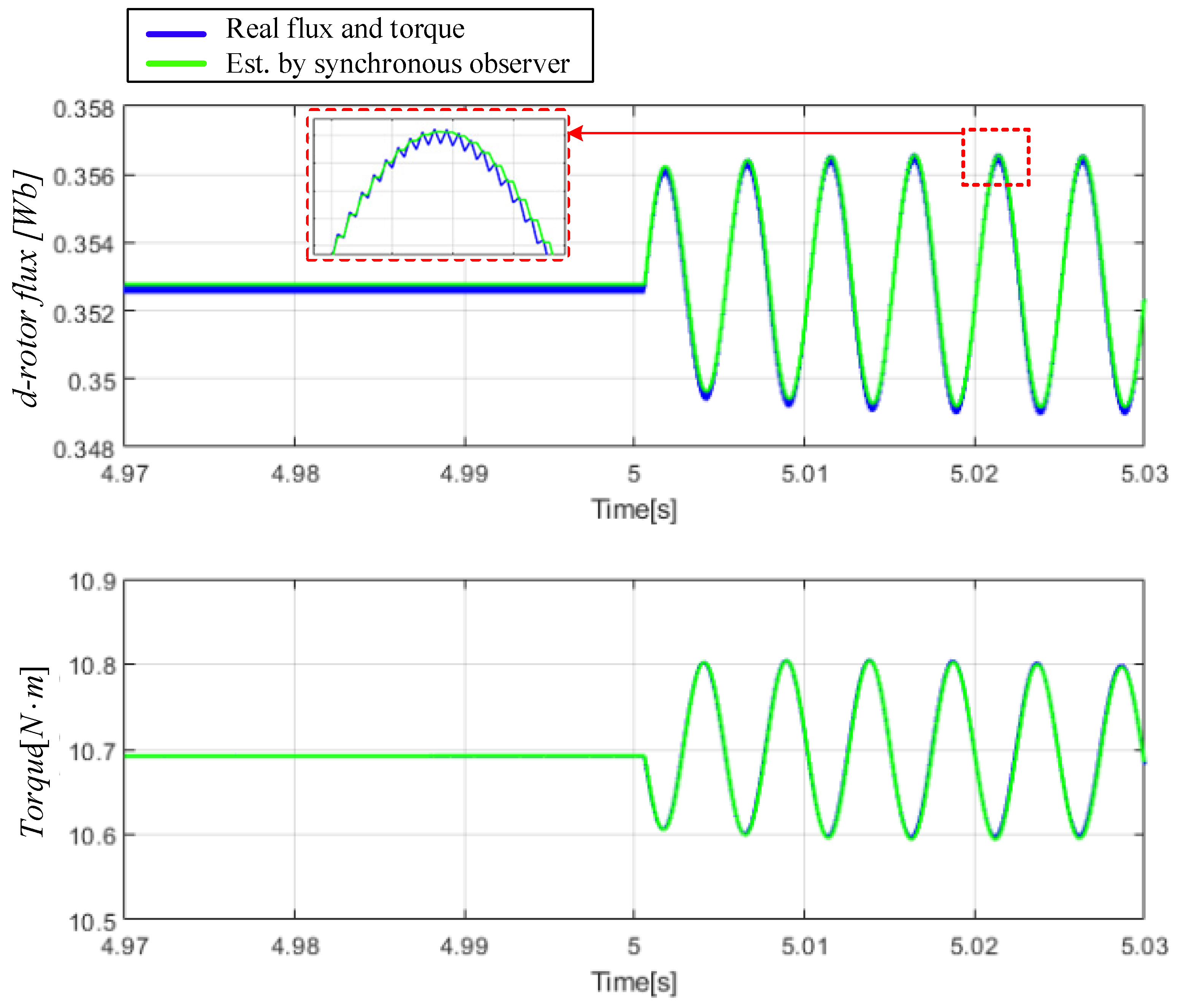
4.3. Torque Estimation with Zero Phase Delay and Decay [23]
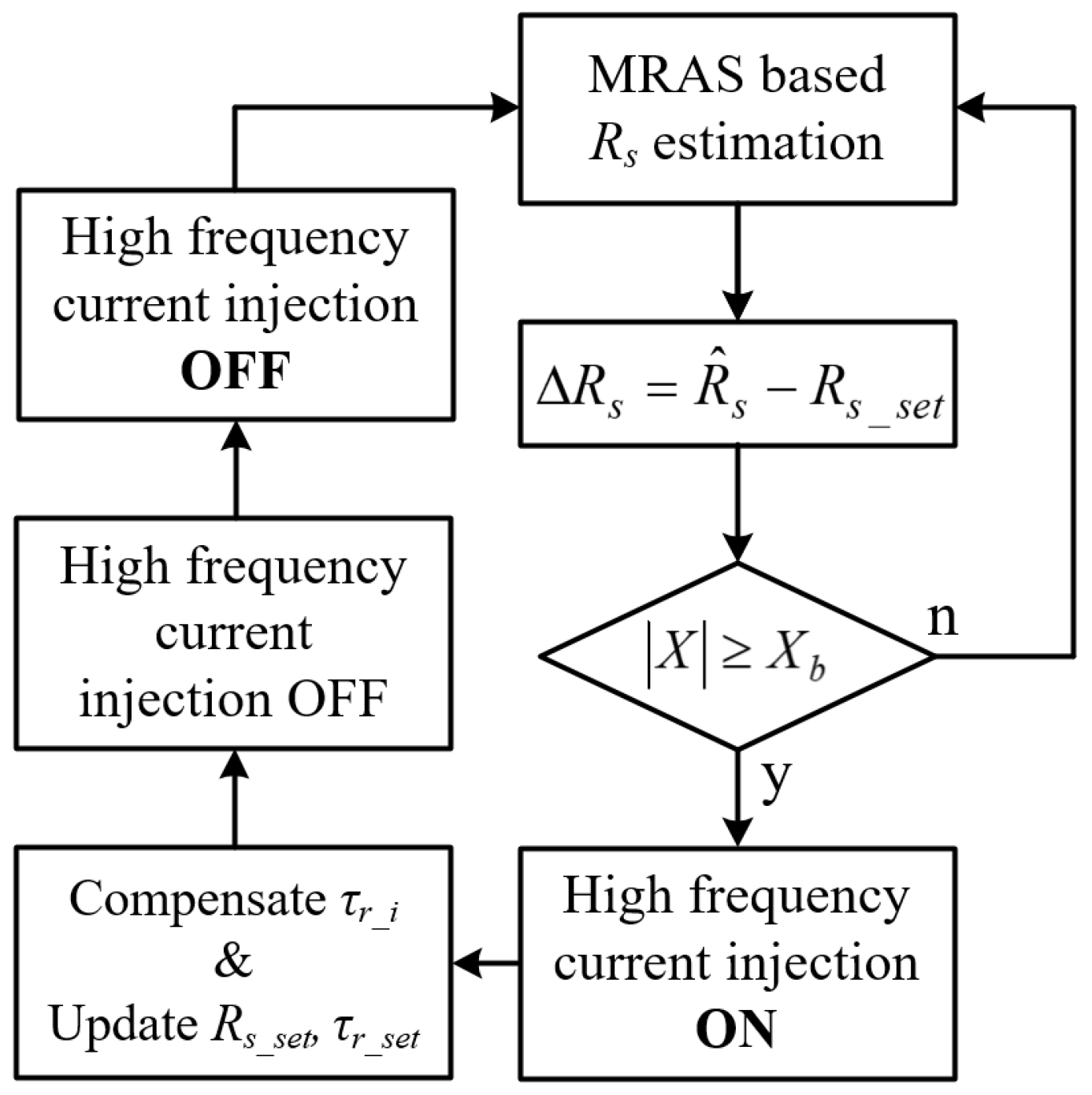
4.4. Proposed Method for Online Tuning of Rotor Time Constant
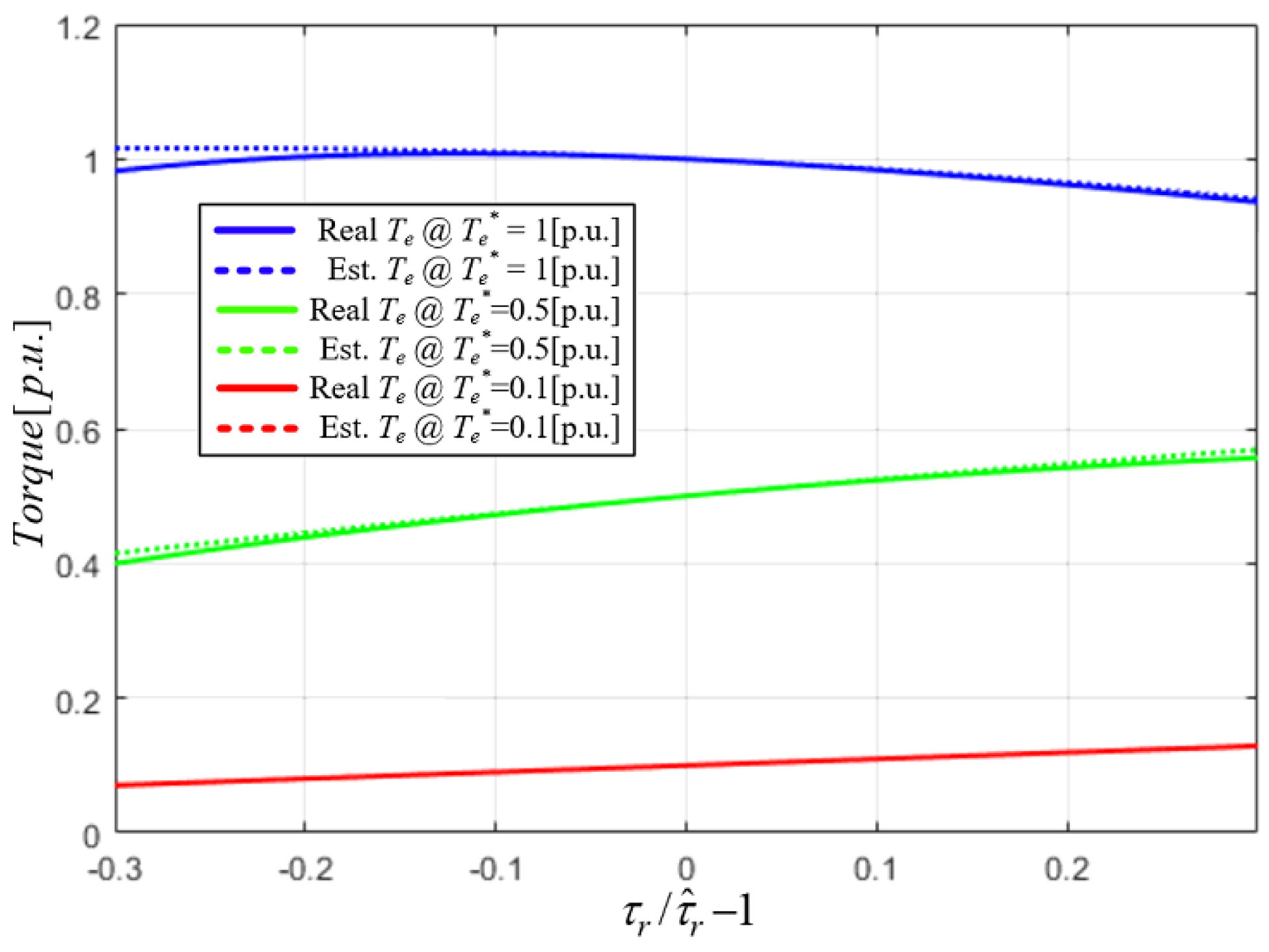
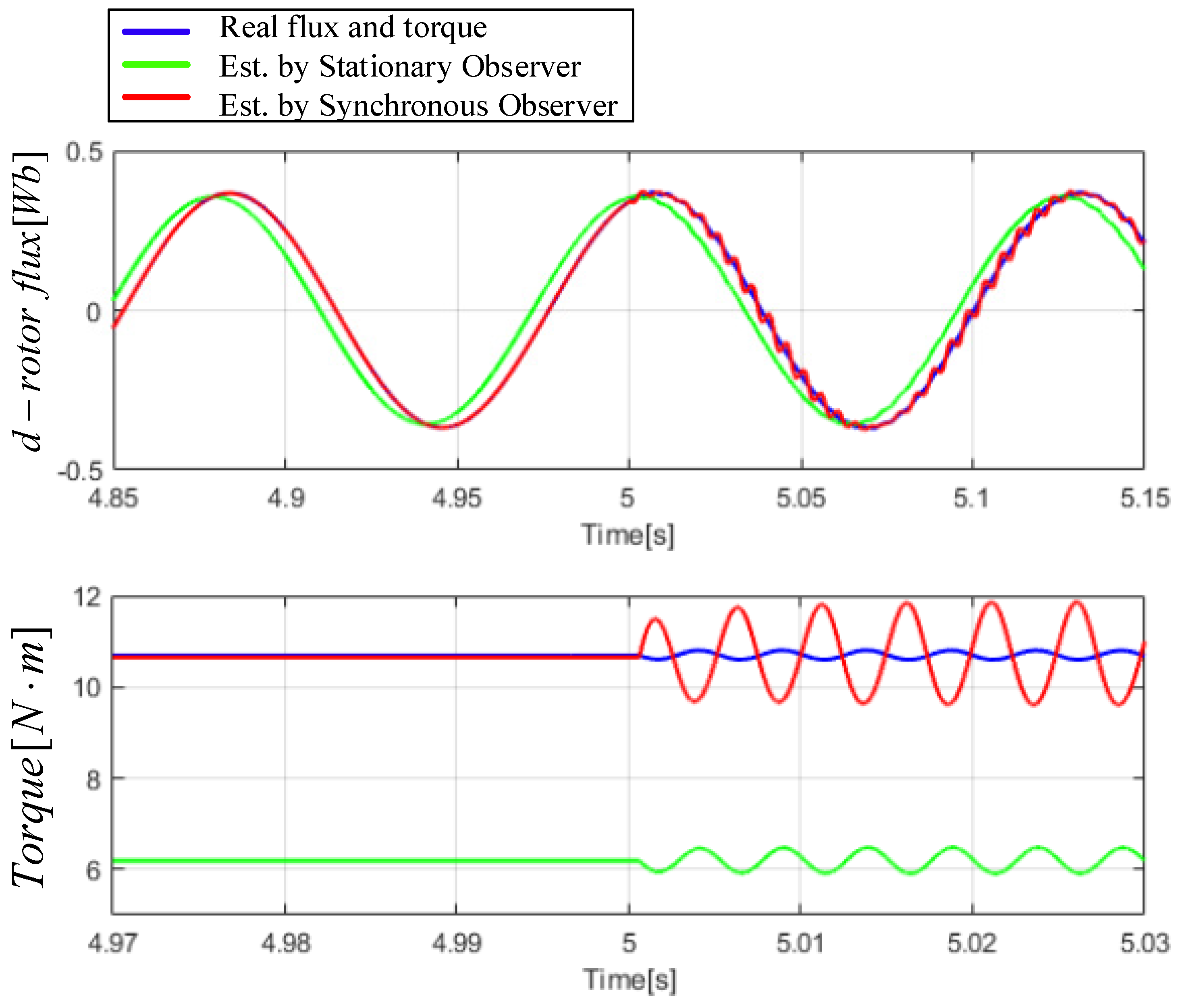
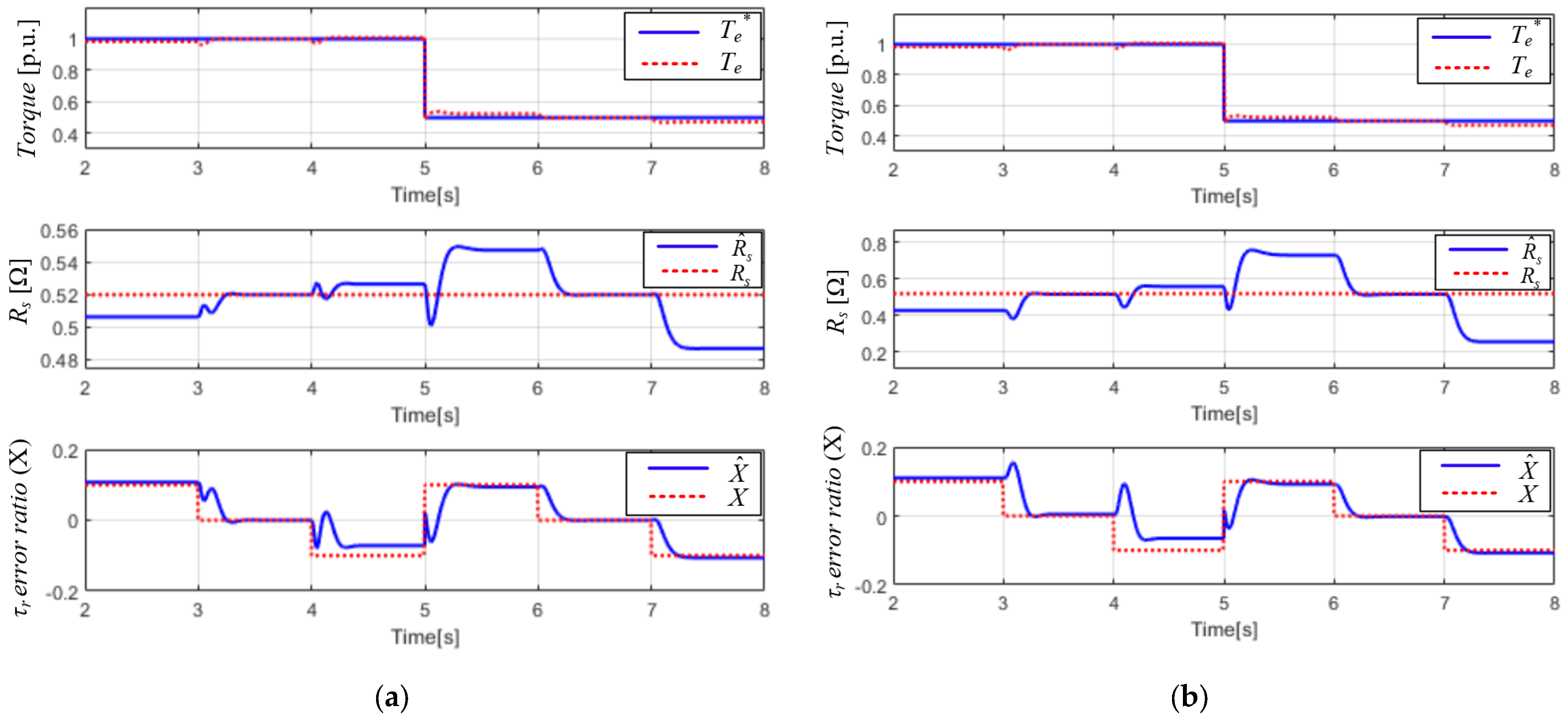
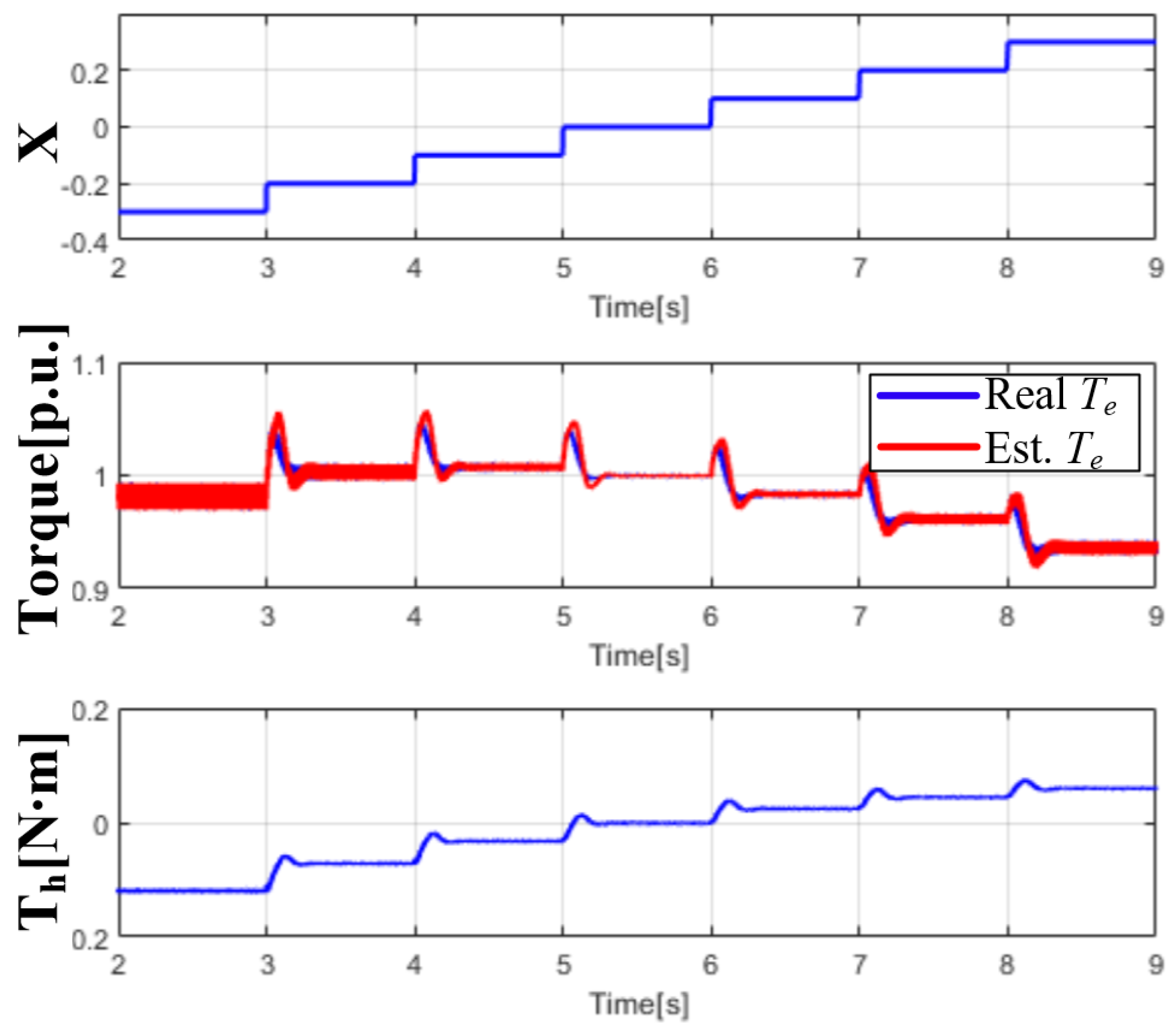
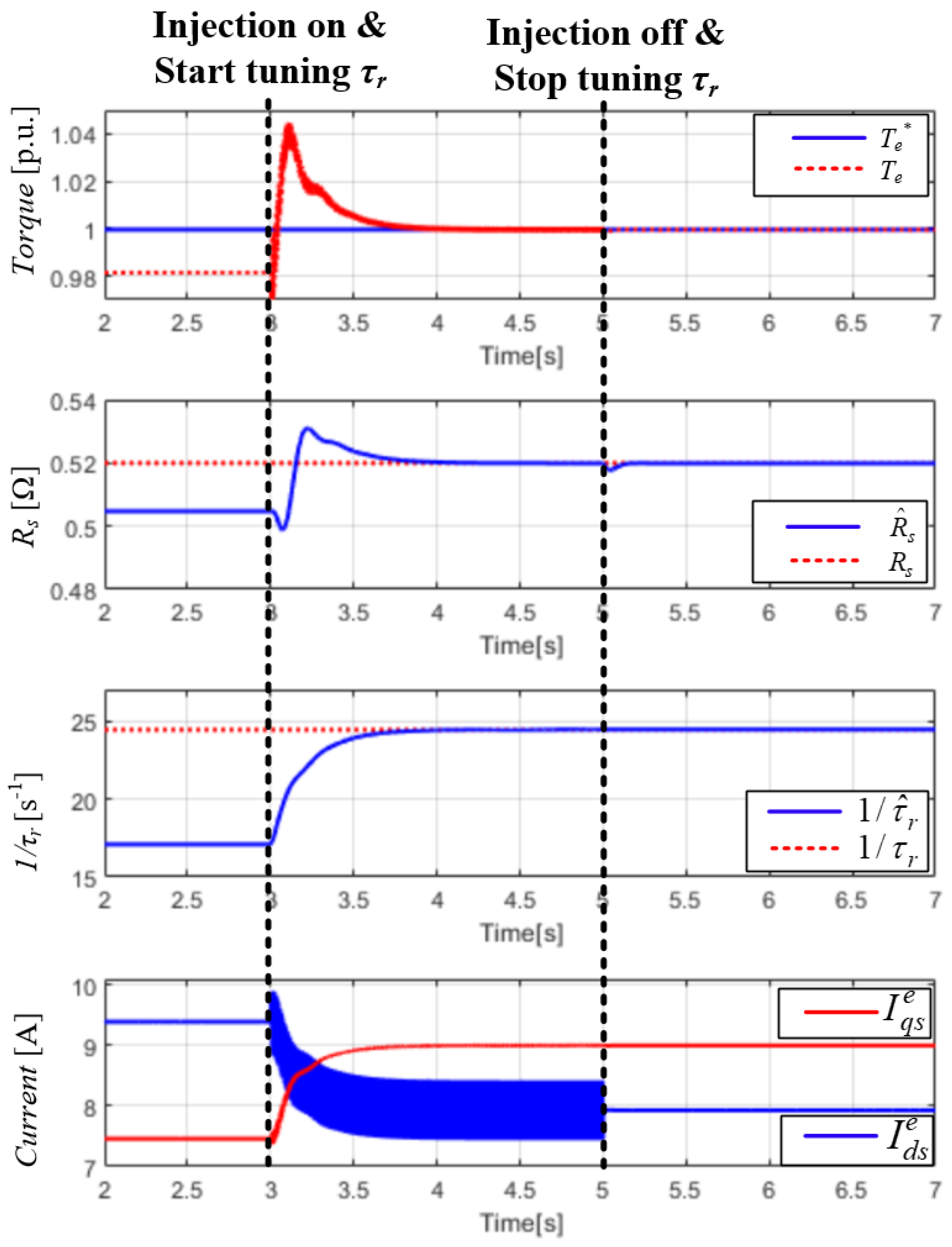
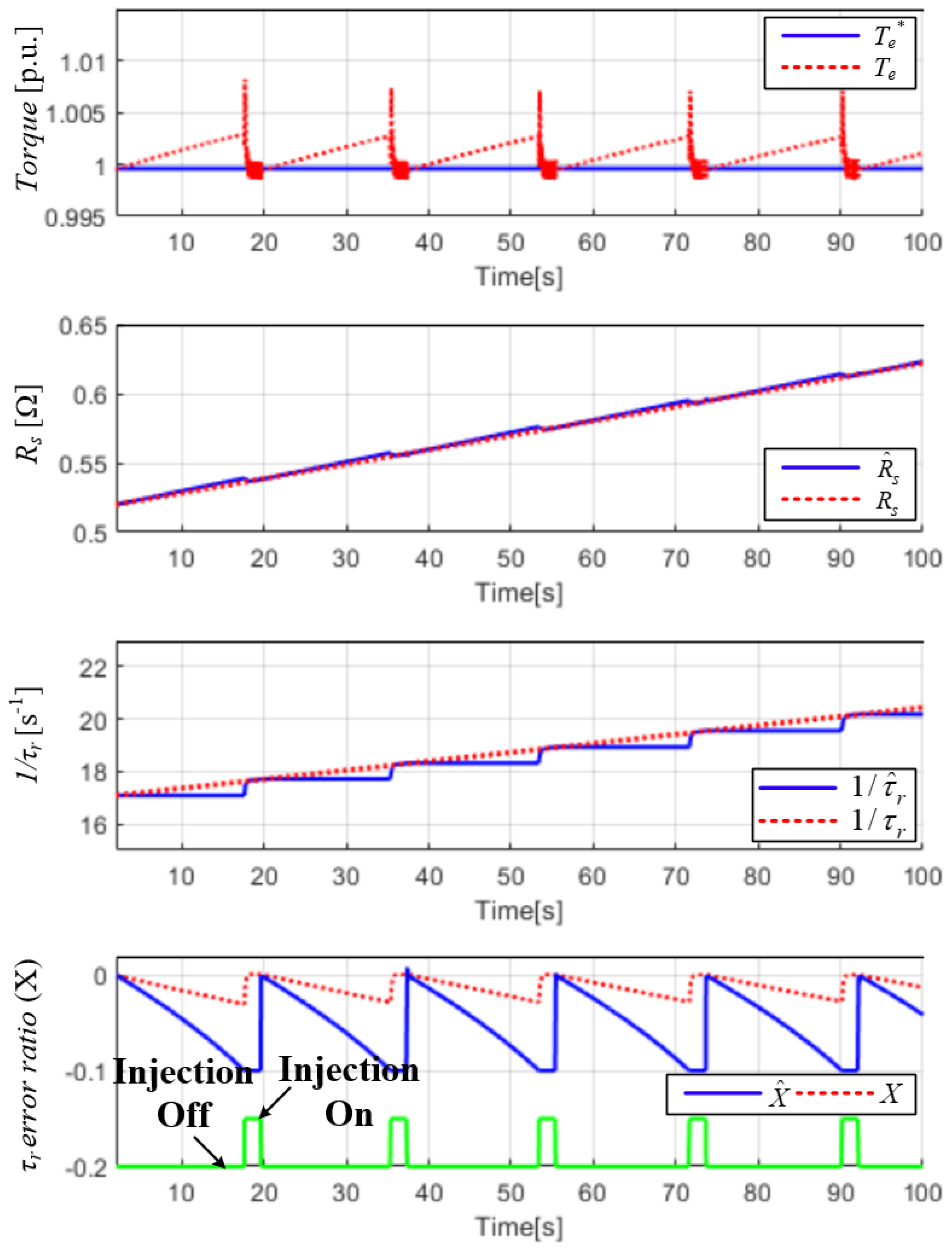
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IFOC | Indirect field-oriented vector control |
| IM | Induction machine |
| MRAS | Model reference adaptive system |
| PI | Proportional–integral |
References
- Mastorocostas, C.; Kioskeridis, I.; Margaris, N. Thermal and slip effects on rotor time constant in vector controlled induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2006, 21, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, S.; Dunnigan, W.; Williams, B.W. A new method of rotor resistance estimation for vector-controlled induction machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1997, 44, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba-Razzouk, A.; Cheriti, A.; Sicard, P. Implementation of a DSP based real-time estimator of induction motors rotor time constant. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Novotny, D.W.; Lipo, T.A. An automated rotor time-constant measurement system for indirect field-oriented drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 24, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, D.; Dunnigan, M.W.; Williams, B.W. Online identification of induction machine electrical parameters for vector control loop tuning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2003, 50, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, J. Stable simultaneous stator and rotor resistances identification for speed sensorless IM drives: Review and new results. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8695–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, O.; Bocker, J.; Bonifacio, J. Online-identification of the Induction Machine Parameters using the Extended Kalman Filter. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Chen, B.; Shen, G.; Yao, W.; Lee, K.; Lu, Z. Online updating of rotor time constant based on combined voltage and current mode flux observer for speed-sensorless AC drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 4583–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadoue, S.M.; Giaouris, D.; Finch, J.W. MRAS sensorless vector control of an induction motor using new sliding-mode and fuzzy-logic adaptation mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toliyat, H.A.; Arefeen, M.S.; Rahman, K.M.; Figoli, D. Rotor time constant updating scheme for a rotor flux-oriented induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1999, 14, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, S.-K. Control of Electric Machine Drive Systems, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S. A unified-model-based analysis of MRAS for online rotor time constant estimation in an induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xie, Z.; Cao, P. An improved MRAS for rotor time constant updating in induction motor drives utilizing dot product of stator current and rotor flux. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8905–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Chakraborty, C.; Hori, Y.; Ta, M.C. Model reference adaptive controller-based rotor resistance and speed estimation techniques for vector controlled induction motor drive utilizing reactive power. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y. Reactive-power-based MRAS for online rotor time constant estimation in induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10835–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A. Robust on-line rotor time constant estimation for induction machines. J. Power Electron. 2014, 14, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fot, S.; Testa, A.; De Caro, S.; Scimone, T.; Scelba, G.; Scarcella, G. Rotor Time Constant Identification on Sensorless Induction Motor Drives by Low Frequency Signal Injection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th International Symposium on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives (SLED), Helsinki, Finland, 13–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Foti, S.; Testa, A.; De Caro, S.; Scimone, T.; Pulvirenti, M. Rotor flux position correction and parameters estimation on sensorless multiple induction motors drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3759–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lorenz, R.D.; Baloch, N.A. Enhanced methodology for injection-based real-time parameter estimation to improve back EMF self-sensing in induction machine deadbeat-direct torque and flux control drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 6071–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, A.V.; Benedict, E.L.; John, V.; Lipo, T.A. A novel method for measuring induction machine magnetizing inductance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Omura, T.; Hiraishi, D. Direct Field-Oriented Control of Induction Motor with Iron-Core Loss Compensation and Robust Parameter Identification. In Proceedings of the IECON’01 Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (Cat. No. 37243), Denver, CO, USA, 29 November–2 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stojić, D.; Milinković, M.; Veinović, S.; Klasnić, I. Improved stator flux estimator for speed sensorless induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, K. Dual MRAS for robust rotor time constant compensation in IFOC IM drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 39, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D. A Model Reference Adaptive System-Based Online Rotor Time Constant Estimation Method for Induction Motor Field-Weakening Control Utilizing Dot Product of Stator Voltage and Stator Current. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 3576–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, N.; Das, D.; Goswami, G. Active Power Based MRAS for Estimation of Inverse Rotor Time Constant in Field-Oriented Control of Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. early access. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.; Poddar, G.; Muni, B. Parameter Estimation and Online Adaptation of Rotor Time Constant for Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 58, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F.; Borup, U.; Liserre, M. A New Control Structure for Grid-Connected LCL PV Inverters with Zero Steady-State Error and Selective Harmonic Compensation. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, APEC ‘04, Anaheim, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2004. [Google Scholar]

| MRAS Model | Reference Model | Adaptive Model | Required Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dot product of stator current and rotor flux [13] | , , | ||
| Active power [12] | |||
| Reactive power [12] |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Pole pairs | 3 |
| Base speed | 1000 r/min |
| Stator resistance (Rs) | 0.52 Ω |
| Rotor resistance (Rr) | 0.734 Ω |
| Mutual inductance (Lm) | 37.82 mH |
| Stator leakage inductance (Lls) | 2.3 mH |
| Rotor leakage inductance (Llr) | 5.128 mH |
| Rated stator current | 12 A |
| Rated rotor flux | 0.3 Wb |
| Rated torque | 10.7 N∙m |
| Inverter DC link voltage | 250 V |
| Inverter switching frequency | 10 kHz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y. Robust Online Rotor Time Constant Tuning Method with High-Frequency Current Injection for Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drives. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101729
Han Y. Robust Online Rotor Time Constant Tuning Method with High-Frequency Current Injection for Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drives. Symmetry. 2025; 17(10):1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yongsu. 2025. "Robust Online Rotor Time Constant Tuning Method with High-Frequency Current Injection for Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drives" Symmetry 17, no. 10: 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101729
APA StyleHan, Y. (2025). Robust Online Rotor Time Constant Tuning Method with High-Frequency Current Injection for Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drives. Symmetry, 17(10), 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101729






