New Acoustic Features for Synthetic and Replay Spoofing Attack Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Classifiers
2.2. Features
3. New Cepstral Coefficients of Residual Signals
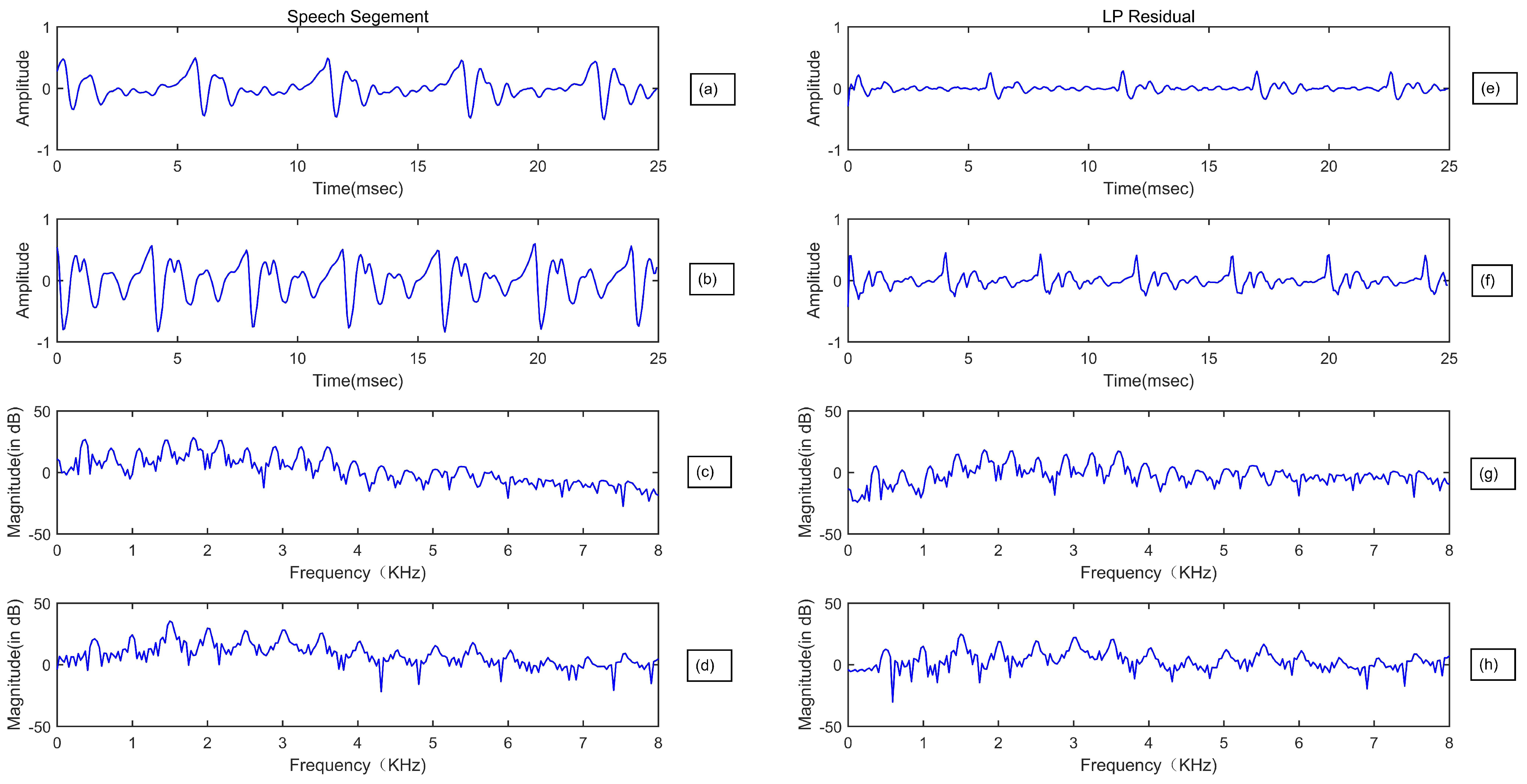
3.1. Linear Prediction Residual Modeling and Analysis
3.2. Conventional Cepstral Features
3.2.1. CQCC Features
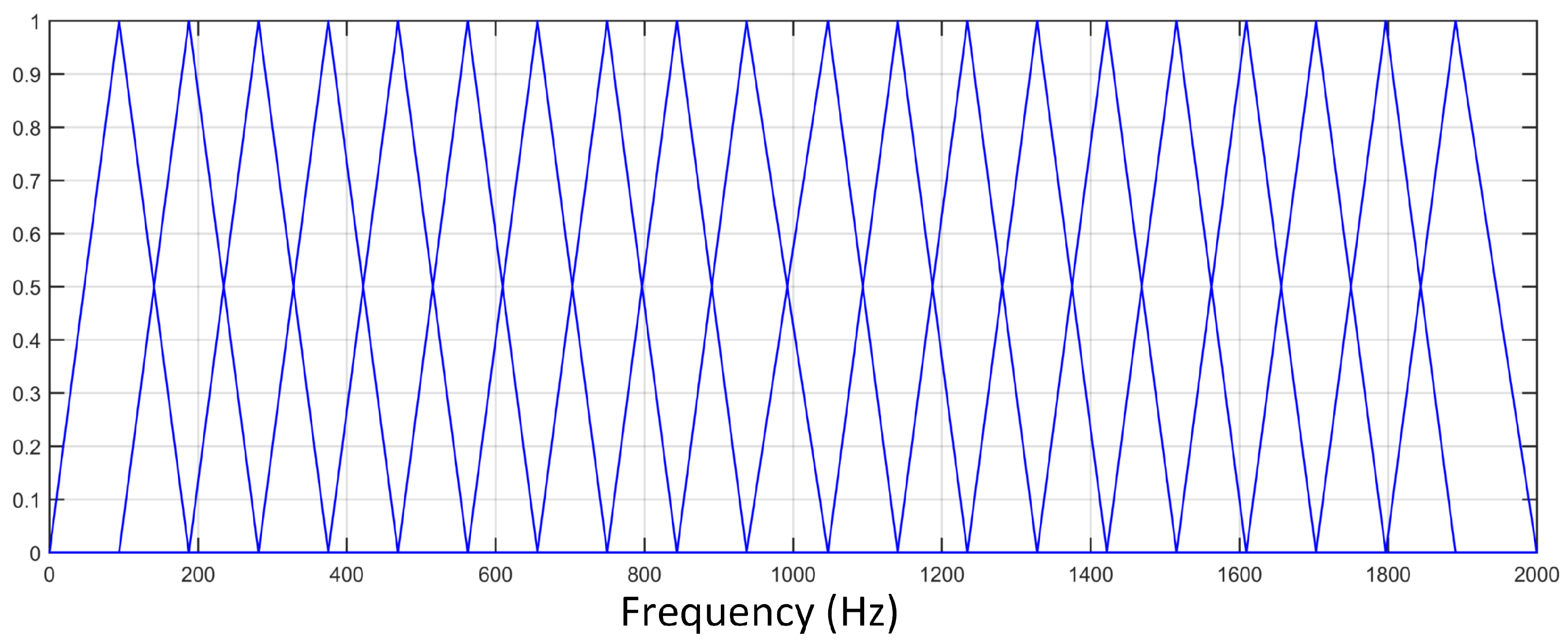
3.2.2. LFCC
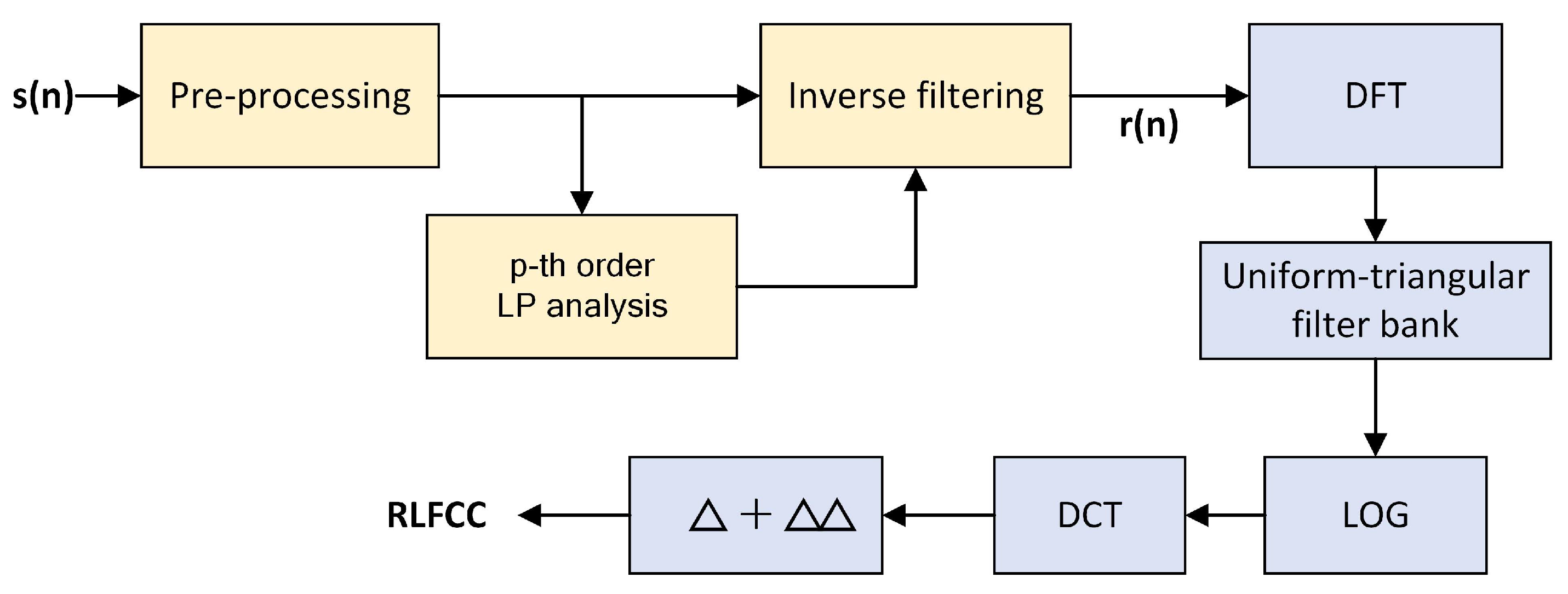
3.3. Residual Cepstral Coefficients
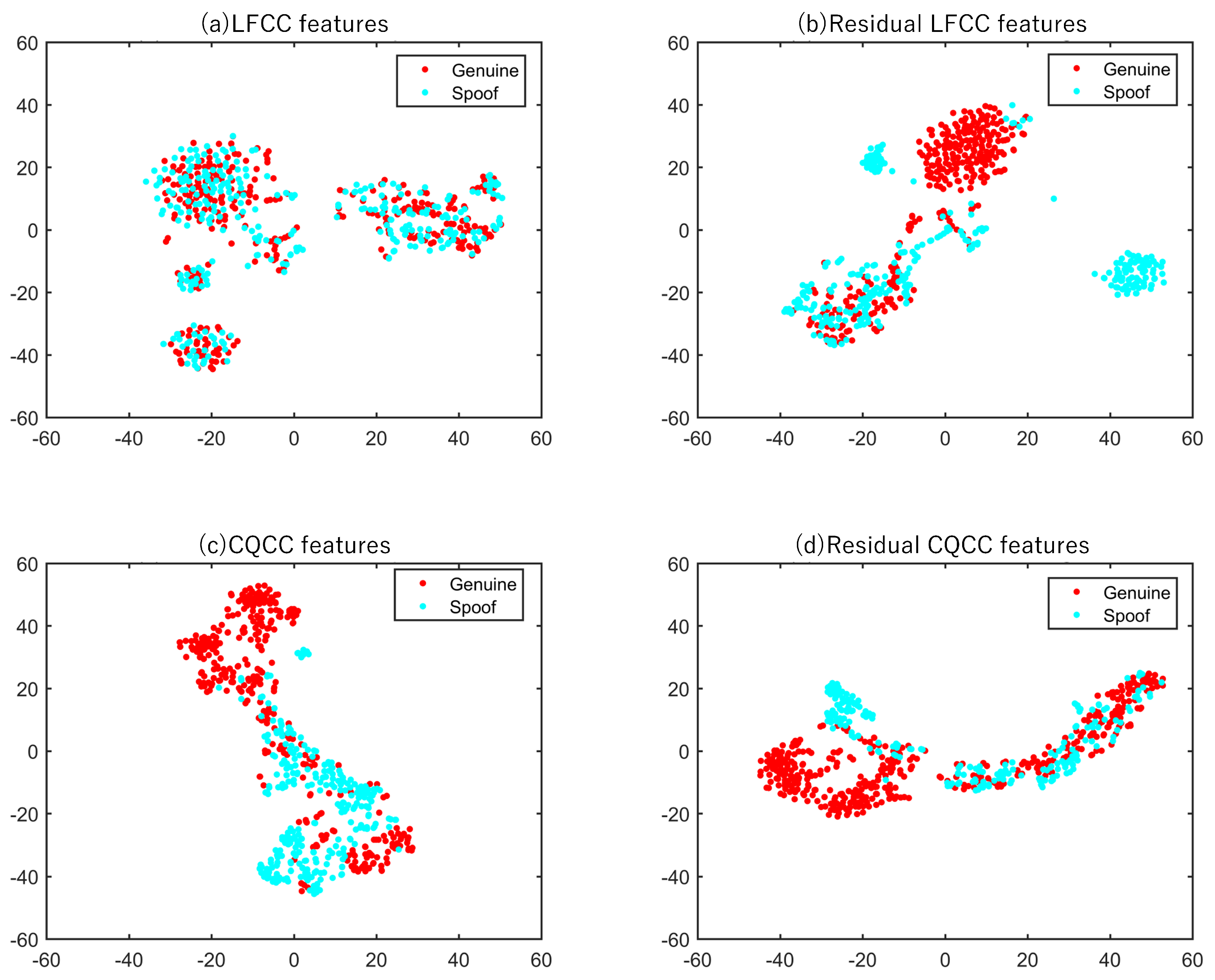
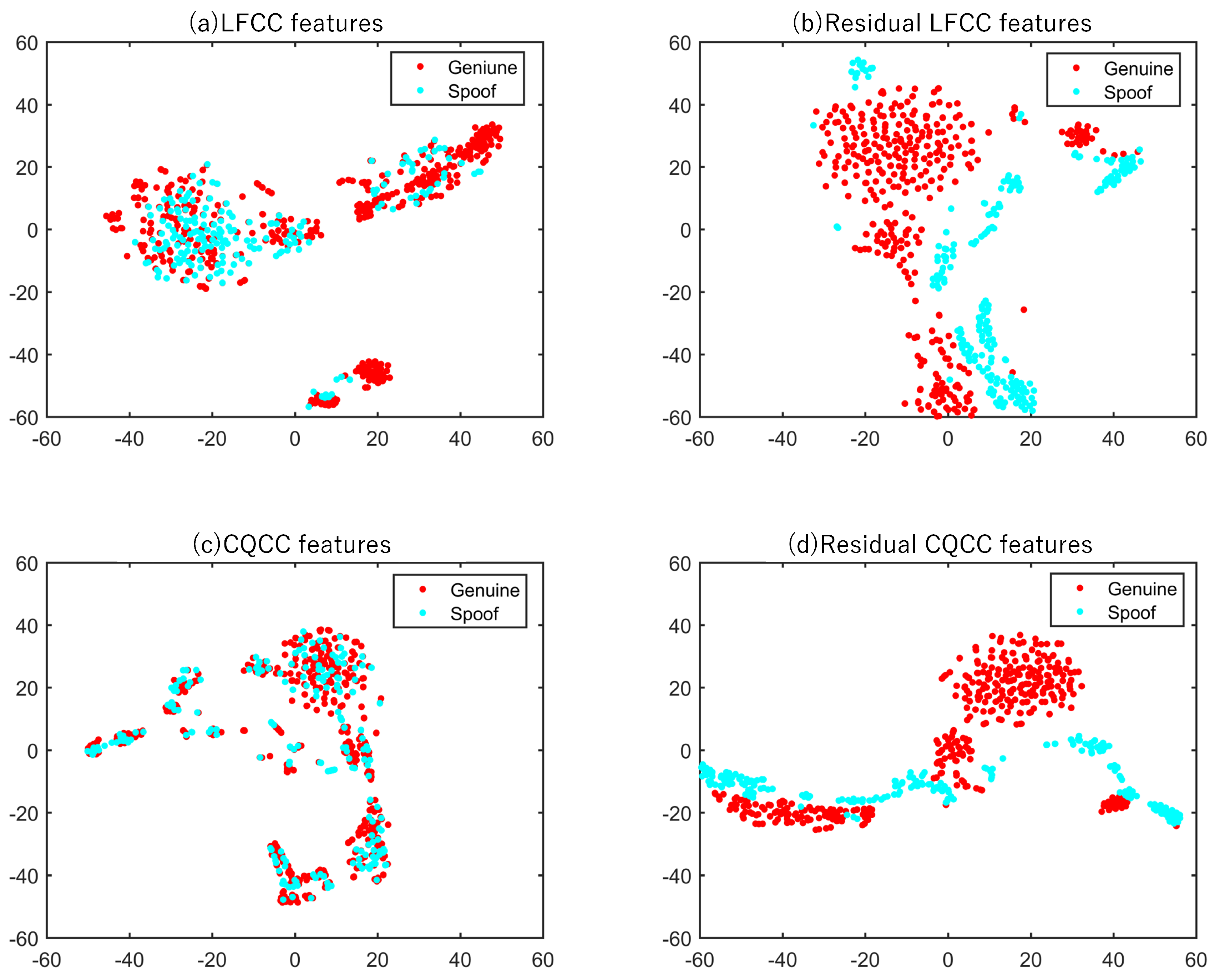
3.4. t-SNE Feature Visualization
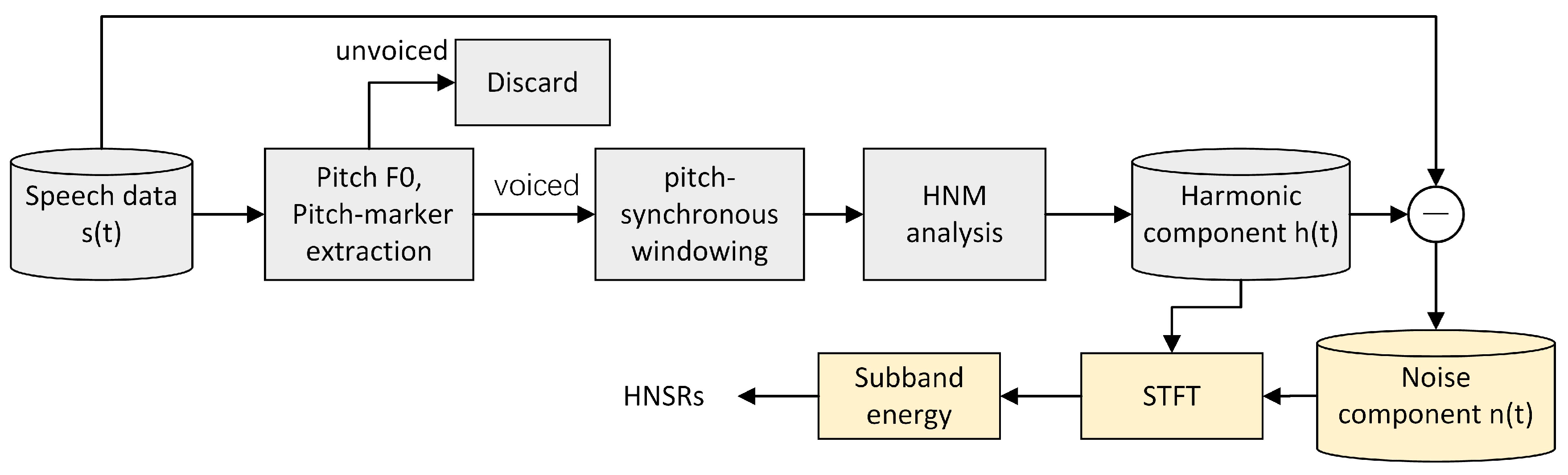
4. Harmonic and Noise Interaction Features
5. Experiments and Results
5.1. Dataset-ASVSpoof 2019
5.2. Experimental Configurations
5.2.1. Classifiers
5.2.2. Features
5.3. Evaluation Metrics
5.4. Results on LA Task
5.4.1. Detection Results of Single Systems
5.4.2. System Fusion
5.5. Results on PA Task
5.5.1. Detection Results of Single Systems
5.5.2. System Fusion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; Evans, N.; Kinnunen, T.; Yamagishi, J.; Alegre, F.; Li, H. Spoofing and countermeasures for speaker verification. Speech Commun. 2015, 66, 130–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yamagishi, J.; Todisco, M.; Delgado, H.; Nautsch, A.; Evans, N.; Sahidullah, M.; Vestman, V.; Kinnunen, T.; Lee, K.A.; et al. ASVspoof 2019: A large-scale public database of synthetized, converted and replayed speech. Comput. Speech Lang. 2020, 64, 101114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizada, A.; Jafarova, S.; Sultanov, E.; Rustamov, S. Development and Evaluation of Speech Synthesis System Based on Deep Learning Models. Symmetry 2021, 13, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, Y. Harmonic plus Noise Models for Speech, Combined with Statistical Methods, for Speech and Speaker Modification. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale Superieure des Telecommunications, Palaiseau, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Kinnunen, T.; Evans, N.; Yamagishi, J.; Hanilçi, C.; Sahidullah, M.; Sizov, A. ASVspoof 2015: The first automatic speaker verification spoofing and countermeasures challenge. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 2037–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, T.; Sahidullah, M.; Delgado, H.; Todisco, M.; Evans, N.; Yamagishi, J.; Lee, K.A. The ASVspoof 2017 challenge: Assessing the limits of replay spoofing attack detection. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yoshida, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Nakagawa, S. Relative phase information for detecting human speech and spoofed speech. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 2092–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M.; Paul, D.; Saha, G. Synthetic speech detection using fundamental frequency variation and spectral features. Comput. Speech Lang. 2018, 48, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, M.; Delgado, H.; Evans, N. Constant Q cepstral coefficients: A spoofing countermeasure for automatic speaker verification. Comput. Speech Lang. 2017, 45, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, M.; Wang, X.; Vestman, V.; Sahidullah, M.; Delgado, H.; Nautsch, A.; Yamagishi, J.; Evans, N.; Kinnunen, T.; Lee, K.A. ASVspoof 2019: Future Horizons in Spoofed and Fake Audio Detection. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 1008–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, J. On the use of fisher vector encoding for voice spoofing detection. Proceedings 2019, 31, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelil, S.; Das, R.K.; Prasanna, S.M.; Sinha, R. Spoof detection using source, instantaneous frequency and cepstral features. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Villalba, J.; Miguel, A.; Ortega, A.; Lleida, E. Spoofing detection with DNN and one-class SVM for the ASVspoof 2015 challenge. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 2067–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarsheth, P.; Khoury, E.; Patil, K.; Garland, M. Replay attack detection using DNN for channel discrimination. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Tan, Z.H.; Ma, Z.; Martin, R.; Guo, J. Spoofing detection in automatic speaker verification systems using DNN classifiers and dynamic acoustic features. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2017, 29, 4633–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, C.; Hansen, J. An investigation of deep-learning frameworks for speaker verification antispoofing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, D. Recurrent neural networks for automatic replay spoofing attack detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 2052–2056. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrentyeva, G.; Novoselov, S.; Malykh, E.; Kozlov, A.; Kudashev, O.; Shchemelinin, V. Audio replay attack detection with deep learning frameworks. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tak, H.; Patil, H.A. Novel linear frequency residual cepstral features for replay attack detection. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 726–730. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Tong, Q.; Long, Y.; Wei, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Q. SHNU Anti-spoofing Systems for ASVspoof 2019 Challenge. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Lanzhou, China, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 548–552. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, M.; Kacprzak, S.; Zelasko, P.; Kowalczyk, K.; Gałka, J. Audio replay attack detection using high-frequency features. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Xu, M.; Zheng, T. Replay detection using CQT-based modified group delay feature and ResNeWt network in ASVspoof 2019. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Lanzhou, China, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 540–545. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Pati, D. Usefulness of linear prediction residual for replay attack detection. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 110, 152837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Das, R. Low frequency frame-wise normalization over constant-Q transform for playback speech detetion. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 89, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, M.F.; Dey, P. End-to-end audio replay attack detection using deep convolutional networks with attention. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2018; pp. 681–685. [Google Scholar]
- Sriskandaraja, K.; Sethu, V.; Ambikairajah, E. Deep Siamese architecture based replay detection for secure voice biometric. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2018; pp. 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Chen, N.; Yu, K. Deep features for automatic spoofing detection. Speech Commun. 2016, 85, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xiao, X.; Chng, E.S.; Li, H. Synthetic speech detection using temporal modulation feature. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 7234–7238. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, T.; Patil, H. Cochlear filter and instantaneous frequency based features for spoofed speech detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 11, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahidullah, M.; Kinnunen, T.; Hanilci, C. A comparison of features for synthetic speech detection. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 2087–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Maaten, L.v.d.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Yan, Z.J.; Soong, F.K.; Dai, L.; Guo, W. Speaker characterization using spectral subband energy ratio based on harmonic plus noise model. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 4520–4523. [Google Scholar]
- Povey, D.; Ghoshal, A.; Boulianne, G.; Burget, L.; Glembek, O.; Goel, N.; Hannemann, M.; Motlicek, P.; Qian, Y.; Schwarz, P.; et al. The Kaldi speech recognition toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 11–15 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.; Cheng, M.; Rosenberg, A.; McGonegal, C. A comparative performance study of several pitch detection algorithms. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 2003, 24, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinier, W.; Kortekaas, L.; Kohlrausch, A. Psychoacoustical evaluation of the pitch-synchronous overlap-and-add speech-waveform manipulation technique using single-format stimuli. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, T.; Lee, K.A.; Delgado, H.; Evans, N.; Todisco, M.; Sahidullah, M.; Yamagishi, J.; Reynolds, D.A. t-DCF: A detection cost function for the tandem assessment of spoofing countermeasures and automatic speaker verification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.09618. [Google Scholar]
- Brümmer, N.; De Villiers, E. The bosaris toolkit: Theory, algorithms and code for surviving the new dcf. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1304.2865. [Google Scholar]




| Subset | Speakers | Utterances | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Logical Access | Physical Access | |||
| Bonafide | Spoof | Bonafide | Spoof | |||
| Training | 8 | 12 | 2580 | 22,800 | 5400 | 48,600 |
| Development | 4 | 6 | 2548 | 22,296 | 5400 | 24,300 |
| Evaluation | 21 | 27 | 7355 | 63,882 | 18,090 | 116,640 |
| Features | FL (LA/PA) | FS (LA/PA) | LP-Order | GMM (LA/PA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RLFCC | 30/25 | 15/12.5 | 12 | 512/256 |
| RCQCC | 30/30 | 15/15 | 12 | 256/128 |
| HNSR | 25/25 | 12.5/12.5 | - | 512/256 |
| RLogSpec | 25/20 | 10/10 | 12 | - |
| ID | Classifier | Features | Dev. | Eval. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EER | t-DCF | EER | t-DCF | |||
| L1 | GMM | CQCC | 0.43 | 0.0123 | 9.57 | 0.2359 |
| L2 | RCQCC | 0.40 | 0.0108 | 11.71 | 0.2817 | |
| L3 | LFCC | 2.71 | 0.0663 | 9.09 | 0.2115 | |
| L4 | RLFCC | 1.17 | 0.0358 | 6.84 | 0.1855 | |
| L5 | HNSR | 13.34 | 0.3064 | 26.41 | 0.6403 | |
| L6 | LCNN | LogSpec | 0.20 | 0.0059 | 20.83 | 0.2971 |
| L7 | RLogSpec | 0.86 | 0.0286 | 10.07 | 0.1925 | |
| ID | Classifier | Features | Dev. | Eval. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EER | t-DCF | EER | t-DCF | |||
| LF1 | GMM | LFCC + CQCC | 0.04 | 0.000449 | 5.08 | 0.130134 |
| LF1-1 | LF1 + RLFCC | 0.04 | 0.000493 | 4.42 | 0.118015 | |
| LF1-2 | LF1 + RCQCC | 0.04 | 0.000404 | 5.11 | 0.130379 | |
| LF1-3 | LF1 + HNSR | 0.04 | 0.000404 | 5.05 | 0.132326 | |
| LF2 | RLFCC + RCQCC | 0.09 | 0.002972 | 6.46 | 0.168841 | |
| LF3 | LFCC + RLFCC | 1.01 | 0.032072 | 5.3 | 0.153161 | |
| LF4 | CQCC + RCQCC | 0.16 | 0.003633 | 5.92 | 0.15229 | |
| LF5 | LF1 + LF2 | 0.04 | 0.000628 | 4.57 | 0.118691 | |
| LF5-1 | LF5 + HNSR | 0.04 | 0.000493 | 4.49 | 0.118943 | |
| LF6 | LF3 + LF4 | 0.08 | 0.000897 | 4.53 | 0.119633 | |
| LF6-1 | LF6 + HNSR | 0.07 | 0.001121 | 4.5 | 0.120528 | |
| LF7 | LCNN | LogSpec + RLogSpec | 0.12 | 0.002854 | 9.67 | 0.180001 |
| LF8 | - | bestGMM + LF7 | 0 | 0 | 2.57 | 0.073931 |
| ID | Classifier | Features | Dev. | Eval. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EER | t-DCF | EER | t-DCF | |||
| P1 | GMM | CQCC | 10.57 | 0.2103 | 12.64 | 0.2916 |
| P2 | RCQCC | 16.96 | 0.3601 | 19.34 | 0.4463 | |
| P3 | LFCC | 9.97 | 0.2089 | 11.24 | 0.2494 | |
| P4 | RLFCC | 8.54 | 0.1921 | 10.45 | 0.2567 | |
| P5 | HNSR | 23.72 | 0.5839 | 29.54 | 0.6869 | |
| P6 | LCNN | LogSpec | 5.44 | 0.1795 | 6.59 | 0.1908 |
| P7 | RLogSpec | 2.96 | 0.0913 | 4.25 | 0.1345 | |
| ID | Classifier | Features | Dev. | Eval. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EER | t-DCF | EER | t-DCF | |||
| PF1 | GMM | LFCC + CQCC | 9.22 | 0.180252 | 10.17 | 0.234929 |
| PF1-1 | PF1 + RLFCC | 8.22 | 0.175117 | 9.51 | 0.239068 | |
| PF1-2 | PF1 + RCQCC | 9.26 | 0.181334 | 10.18 | 0.236621 | |
| PF1-3 | PF1 + HNSR | 9.02 | 0.176851 | 10.11 | 0.235087 | |
| PF2 | RLFCC + RCQCC | 8.29 | 0.185531 | 10.38 | 0.267975 | |
| PF3 | LFCC + RLFCC | 8.17 | 0.191823 | 9.96 | 0.256397 | |
| PF4 | CQCC + RCQCC | 10.56 | 0.218662 | 11.56 | 0.286208 | |
| PF5 | PF1 + PF2 | 8.7 | 0.175911 | 9.55 | 0.238543 | |
| PF5-1 | PF5 + HNSR | 8.63 | 0.17278 | 9.54 | 0.238543 | |
| PF6 | PF3 + PF4 | 8.73 | 0.172954 | 9.51 | 0.23673 | |
| PF6-1 | PF6 + HNSR | 7.97 | 0.16983 | 9.51 | 0.236967 | |
| PF7 | LCNN | LogSpec + RLogSpec | 2.69 | 0.084703 | 3.93 | 0.13176 |
| PF8 | - | bestGMM + PF7 | 1.85 | 0.058915 | 2.47 | 0.073727 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Long, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, Y. New Acoustic Features for Synthetic and Replay Spoofing Attack Detection. Symmetry 2022, 14, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020274
Wei L, Long Y, Wei H, Li Y. New Acoustic Features for Synthetic and Replay Spoofing Attack Detection. Symmetry. 2022; 14(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Linqiang, Yanhua Long, Haoran Wei, and Yijie Li. 2022. "New Acoustic Features for Synthetic and Replay Spoofing Attack Detection" Symmetry 14, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020274
APA StyleWei, L., Long, Y., Wei, H., & Li, Y. (2022). New Acoustic Features for Synthetic and Replay Spoofing Attack Detection. Symmetry, 14(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020274








