1. Introduction
Fractional differential equations have attracted considerable attention due to their many applications in science and engineering (see the monographs [
1,
2,
3,
4] and the references therein). The main advantage of fractional derivatives is that they can describe the properties of heredity and memory of many materials. There are various types of fractional derivatives known in the literature. One of the most important properties of the solutions is stability. There are various types of stability that describe different properties of the solutions. One of them is Lipschitz stability, defined and studied for ordinary differential equations in [
5]. Later, this type of stability was studied for various types of differential equations and problems, such as nonlinear differential systems [
6,
7,
8], impulsive differential equations with delays [
9], fractional differential systems [
10], Caputo fractional differential equations with non-instantaneous impulses [
11], a piecewise linear Schrödinger potential [
12], a hyperbolic inverse problem [
13], the electrical impedance tomography problem [
14], the radiative transport equation [
15] and neural networks with non-instantaneous impulses [
16].
In this paper we define and study Lipschitz stability for Riemann–Liouville (RL) fractional differential equations with non-instantaneous impulses. We will initially introduce the statement of the problem.
Let two sequences of points , , and be given such that and .
There are mainly two types of impulses involved in differential equations: instantaneous impulses (known as impulses), where time of action is negligibly small comparatively with the whole duration of the process and non-instantaneous impulses that start their actions abruptly and continue to act on a finite interval.
In this paper we will consider the non-instantaneous impulses starting at points and acting on intervals . The intervals will be called impulsive intervals. In addition, we will consider the RL fractional derivatives with changeable lower limits at each stop time point of the impulsive action.
The presence of the RL fractional derivative leads to two particular types of initial conditions that are equivalent (see the classical book [
2]):
- -
integral form of the initial condition - -
weighted form of the initial condition
Following the ideas of the impulses in ordinary differential equations, i.e., after the impulse the differential equation is the same with a new initial condition, the integral form and weighted form of the impulsive conditions can be defined.
In this paper we will use the integral form of both the initial condition and the impulsive conditions.
Keeping in mind the above description, in this paper we will study the initial value problem (IVP) for the following system of nonlinear RL fractional differential equations with non-instantaneous impulses (NIRLFDE) of fractional order
:
where
and
is the Riemann–Liouville fractional derivative.
Remark 1. Both given sequences and divide the positive real line into two types of intervals: the intervals on which the differential equation is given, and the impulsive intervals .
Remark 2. The equality could be replaced by
Remark 3. For the impulsive condition in Equation (1) is reduced to , which is an impulsive condition for ordinary differential equations with impulses (see the book [17]). Note that the solutions of the IVP for the NIRLFDE of Equation (
1) have singularities at each point
. This requires stability properties to be studied at intervals excluding these points. In this paper we will define a new type of Lipschitz stability for NIRLFDE of the type in Equation (
1), which is an appropriate generalization of the classical Lipschitz stability introduced in [
5]. It is called generalized Lipschitz stability in time. This type of stability is connected with the singularity of the solution at both the initial time point and the stop time points of impulses. In connection with this we consider an interval excluding these time points. We use Lyapunov functions and two types of derivatives of these Lyapunov functions among the studied RL fractional equation with non-instantaneous impulses. Several sufficient conditions for Lipschitz stability in time are obtained. Some examples illustrating the theoretical results and comparing the application of both fractional derivatives of Lyapunov functions are given.
We will use the following sets:
where
,
.
Remark 4. If then for any we get .
The main contributions of the paper can be summarized as follows:
- -
for a nonlinear system with RL fractional derivatives of order and non-instantaneous impulses we define in an appropriate way both the initial condition and the non-instantaneous impulsive conditions;
- -
generalized Lipschitz stability in time of the zero solution of a system of nonlinear RL fractional differential equations with non-instantaneous impulses is defined;
- -
two types of derivatives of Lyapunov functions among the RL fractional differential equations with non-instantaneous impulses are applied;
- -
comparison results with Lyapunov functions, scalar RL fractional equations with non-instantaneous impulses and both types of derivatives of Lyapunov functions are proved;
- -
sufficient conditions for generalized Lipschitz stability in time are obtained by the application of both types of derivatives of Lyapunov functions.
2. Preliminaries
In this section we will give the definitions of fractional derivatives used in the paper (see, for example, [
1,
2,
3]). These definitions are given for scalar functions but they also are easily generalized to the vector case by taking fractional derivatives component-wisely. Throughout the paper we will assume
.
- -
Riemann–Liouville (RL) fractional integral:
where
denotes the Gamma function;
- -
Riemann–Liouville fractional derivative: - -
The Grünwald–Letnikov fractional derivative is given by
and the Grünwald–Letnikov fractional Dini derivative by
where
and
denotes the integer part of the fraction
.
Remark 5. If , then hold (see Theorem 2.25 [2]). Proposition 1 (Lemma 2.3 [
18]).
Let . Suppose that for an arbitrary , we have and for . Then it follows that . Remark 6. From Remark 5 it follows that in Proposition 1 the fractional derivative could be replaced by .
The practical definition of the initial condition as well as the impulsive conditions of fractional differential equations with RL derivatives is based on the following result:
Proposition 2 ([
2])
. Let and , be a Lebesgue measurable function.- (a)
If there exists a.e. a limit , then there also exists a limit - (b)
If there exists a.e. and if there exists , then
Remark 7. According to Proposition 2 the initial condition and the impulsive conditions in Equation (1) could be replaced by the equalities and respectively. We introduce the assumptions:
(A1) The sequences , , and are such that and .
(A2) The function , for .
(
A3) The functions
for
. Let
and
be an interval. Defining the classes:
Remark 8. The function and . In addition, , is from the class with . The function is from the class with for .
We will generalize Lipschitz stability ([
5]) to systems of RL fractional differential equations with non-instantaneous impulses. In our further considerations below we will assume the existence of the solution of the IVP for the NIRLFDE of Equation (
1) and we will denote it by
.
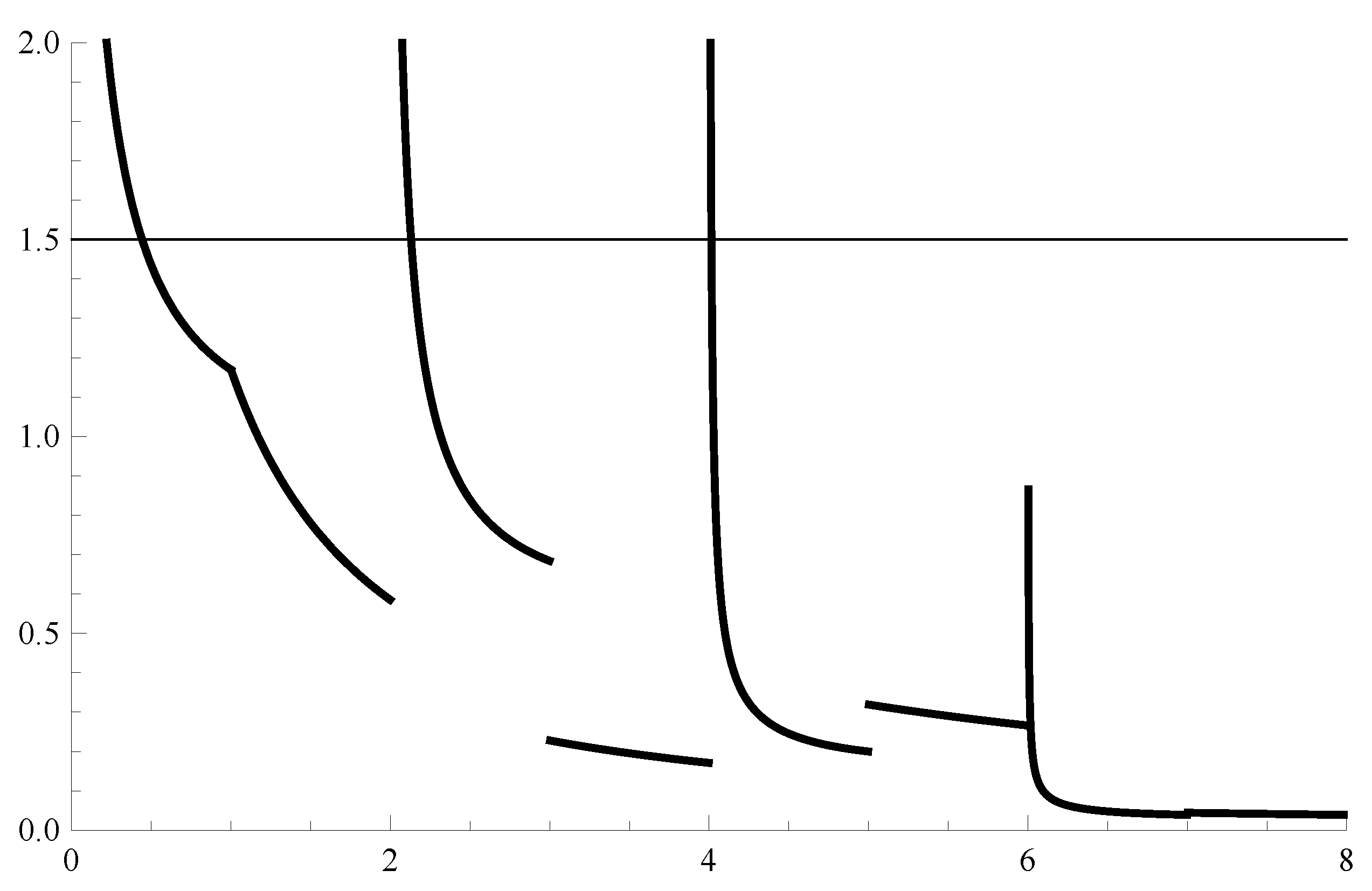
Example 1. Consider the IVP for the scalar linear NIRLFDE where , .
The solution of Equation (3) is given by It has singularities at the point which are the initial time and the end times of action of the non-instantaneous impulses at which the impulsive condition is switching to the differential equation (in the particular case , , the graph of the solution is given on Figure 1). Example 1 illustrates that the stability of the solution for non-instantaneous impulsive differential equations in the case of the RL fractional derivative has to be studied on intervals excluding from the right the points . In connection with this phenomenon we will define a new type of stability:
Definition 1. The zero solution of the IVP for the NIRLFDE of Equation (1) is said to begeneralized Lipschitz stable in timeif there exist a nonegative integer N, positive numbers and a sequence of positive numbers such that for any initial value the inequality holds for Remark 9. Note the generalized Lipschitz stability in time gives a bound of the solution to the right of an existing point and over intervals excluding to the right of any of the starting time points of the non-instantaneous impulses.
3. Lyapunov Functions and Comparison Results
Definition 2 ([
17])
. Let and . We will say that the function belongs to the class if , for , and it is locally Lipschitz with respect to its second argument. We will use two types of derivatives of Lyapunov functions from the class
to study the Lipschitz stability of the NIRLFDE of Equation (
1) (see Remark 1):
- -
The RL fractional derivative of the Lyapunov function
among the NIRLFDE of Equation (
1) is defined by
where
is a solution of Equation (
1).
- -
The Dini fractional derivative of the Lyapunov function
among the NIRLFDE of Equation (
1) is defined by:
Remark 10. The definition of the Dini fractional derivative of the Lyapunov function among the NIRLFDE of Equation (1) is similar to the Grünwald–Letnikov fractional Dini derivative in Equation (2). Remark 11. Let be a solution of Equation (1). Then for any the equalityholds. We will use as a comparison scalar equation the following equation:
where
.
We introduce the following conditions:
(A4) The function is decreasing w.r.t. its second argument and for .
(A5) The functions are increasing w.r.t. its second argument and for .
In our study we will use some comparison results with both defined above types of derivatives of Lyapunov functions.
3.1. Comparison Result with RL Fractional Derivative of Lyapunov Functions
Lemma 1. Assume the following conditions are satisfied:
- 1.
Conditions (A2)–(A5) are satisfied.
- 2.
The function is a solution of Equation (1). - 3.
The function is a solution of Equation (6).
- 4.
The function is such that
- (i)
- (ii)
For all the inequalitieshold. - (iii)
For all the inequalitieshold.
If then the inequalityholds. Proof. Let , .
Case 1. Let .
Let
be an arbitrary number. We will prove
From the choice of the initial point
we obtain
From inequalities (9) there exists a number such that for , i.e., Equation (8) is satisfied on .
If the inequality in Equation (8) is proved.
If we assume the inequality in Equation (8) is not true. Then there exists a point such that .
From condition (A4), equality
and Proposition 1 with
and
we obtain the inequality
The inequality of Equation (10) contradicts condition 4 (i). Therefore, the inequality in Equation (8) is true for any arbitrary number and thus Equation (7) holds for
Case 2. Let . Then from conditions 4(ii), (A5), and the inequality we get , i.e., the inequality of Equation (7) holds on .
Case 3. Let .
Let
be an arbitrary number. We will prove
From condition 4(iii) and the inequality
we obtain
From the inequality of Equation (12) there exists a number such that for , i.e., inequality holds, i.e., Equation (11) is satisfied on .
If the inequality of Equation (11) is proved.
If we assume the inequality of Equation (11) is not true. Then there exists a point such that .
From condition (A4), equality
and Proposition 1 with
and
we obtain the inequality
The inequality of Equation (13) contradicts condition 4(i). Therefore, the inequality of Equation (11) is true for any arbitrary number and thus Equation (7) holds for
Following the above procedure we prove the claim of Lemma 1. □
3.2. Comparison Result with Dini Fractional Derivative of Lyapunov Functions
Lemma 2. Assume:
- 1.
Conditions 1,2,3, 4(ii) and 4(iii) of Lemma 1 are satisfied.
- 2.
The function is such that the inequality holds.
If then the inequality for holds.
Proof. The proof is similar to the one in Lemma 1 where instead of the RL fractional derivative of the Lyapunov function we will use the Dini fractional derivative. The main difference between both proofs of Lemma 1 and Lemma 2, respectively, is connected with the inequalities of Equations (10) and (13) for and .
We will consider the general case of , i.e., assume that for a fixed non-zero integer k there exist and a point such that .
According to Remark 6 with
we obtain the inequality
For any fixed
we have (see Equation (2))
From Equation (
1) it follows
Therefore, where .
Therefore, for any
and
Thus, by
, i.e.,
, we obtain
From Equations (15)–(17) and condition 2 of Lemma 2 we get
The inequality of Equation (18) contradicts the inequality of Equation (14). □