An Asymptotic Test for Bimodality Using The Kullback–Leibler Divergence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bimodal Skew-Symmetric Normal Distribution
3. Information Measures
3.1. Shannon Entropy
- (i)
- : (real and equal roots). Thus, , with . However, for this case X does not present bimodality, so for all .
- (ii)
- : and , (complex and different roots). However, x is defined in the real line, .
3.2. Kullback-Leibler Divergence
- (i)
- , : and (real and equal roots). Thus, , with , and , with . However, neither densities presents bimodality. Thus, , for all , and , for all .
- (ii)
- , : and (complex and different roots). However, is defined in the real line, .
- (iii)
- , : , and (complex and different roots). Thus, , with . However, does not present bimodality and is defined in the real line, . So, , for all .
- (iv)
- , , : , and (complex and different roots). Hence, , with . However, does not present bimodality and is defined in the real line, . Therefore, , for all .
3.3. Jeffreys Divergence
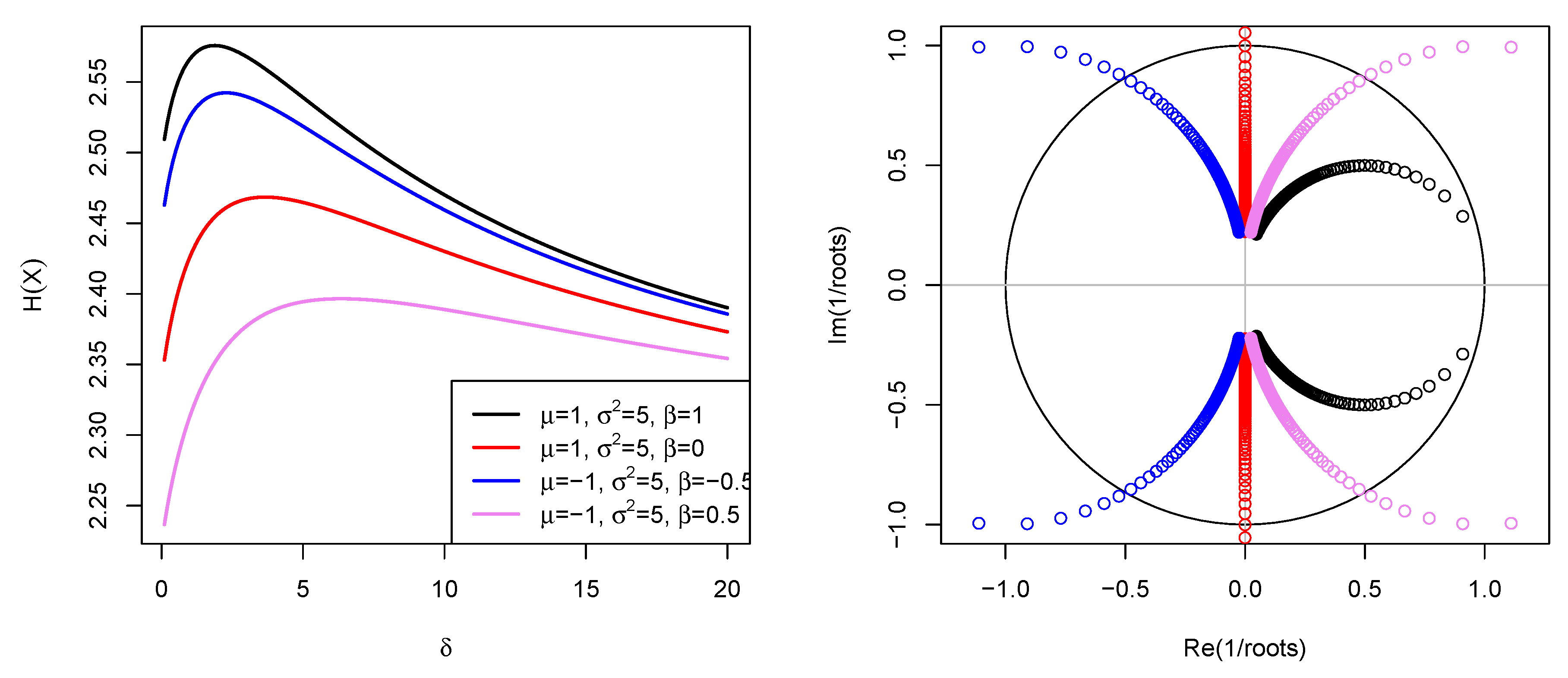
4. Bimodality Test
4.1. Bimodality
- (i)
- if , thus ;
- (ii)
- if , thus implies to find three roots, , and (), of the polynomial of degree three, , withFor given , and parameters, , the polynomial can be solved for in terms of and inequality can be used to determine . This implies thatTherefore, since , the upper bound given in Equation (15) can be used for detecting bimodality if for a given root of , , and , and parameters.
4.2. Asymptotic Test
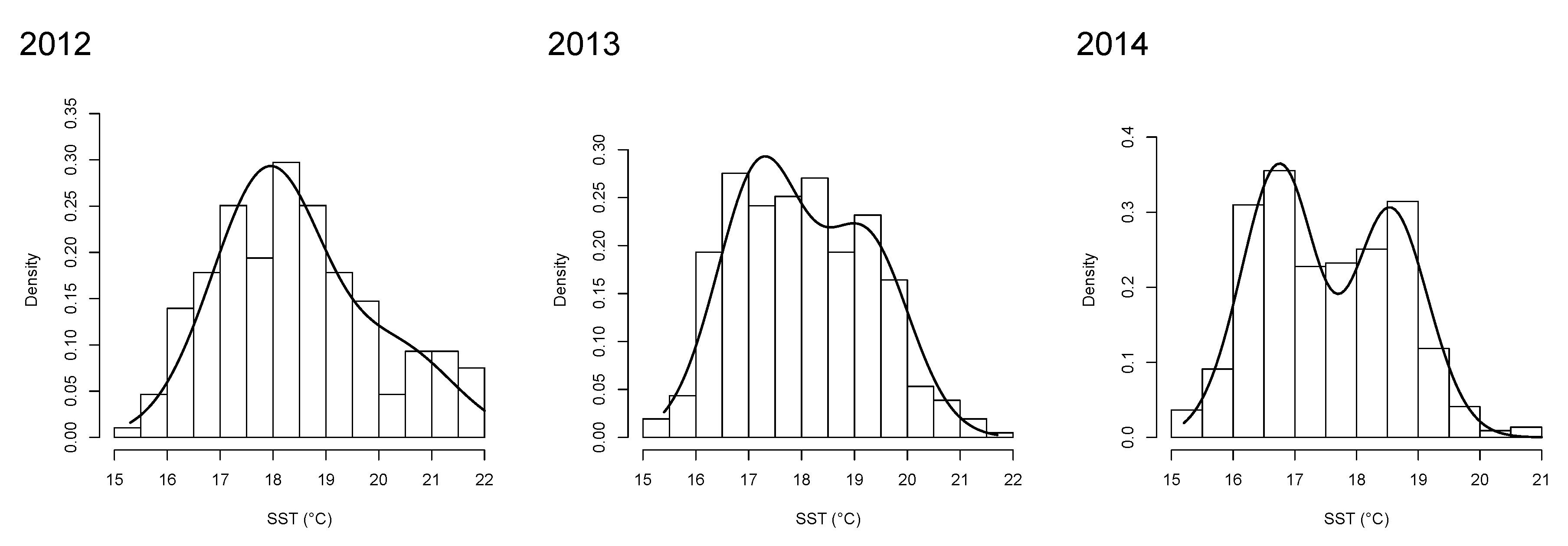
5. Application to Sea Surface Temperature Data
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyszomirski, T. Detecting and displaying size bimodality: Kurtosis, skewness and bimodalizable distributions. J. Theor. Biol. 1992, 158, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashman, K.M.; Bird, C.M.; Zepf, S.E. Detecting bimodality in astronomical datasets. Astr. J. 1994, 108, 2348–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosenfeld, B.; Van Der Maas, H.L.; Van den Boom, D.C. Detecting bimodality in the analogical reasoning performance of elementary schoolchildren. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 1997, 20, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Tang, O.; Ji, J. Applying the minimum relative entropy method for bimodal distribution in a remanufacturing system. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 113, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.B.; Dale, R. Assessing bimodality to detect the presence of a dual cognitive process. Behav. Res. Methods 2013, 45, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalek, A.K.; Satija, R.; Adiconis, X.; Gertner, R.S.; Gaublomme, J.T.; Raychowdhury, R.; Schwartz, S.; Yosef, N.; Malboeuf, C.; Lu, D.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals bimodality in expression and splicing in immune cells. Nature 2013, 498, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlington, R.B. Is kurtosis really “peakedness?”. Am. Stat. 1970, 24, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand, D.K. Kurtosis measures bimodality? Am. Stat. 1971, 25, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Hartigan, P.M. The dip test of unimodality. Ann. Stat. 1985, 13, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.Y.; El-Bassiouni, M.Y. Bimodal skew-symmetric normal distribution. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2016, 45, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.Y.; Hijazi, R. A bimodal exponential power distribution. Pak. J. Stat. 2010, 26, 379–396. [Google Scholar]
- Salicrú, M.; Menéndez, M.L.; Pardo, L.; Morales, D. On the applications of divergence type measures in testing statistical hypothesis. J. Multivar. Anal. 1994, 51, 372–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley & Son, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On information and sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Piessens, R.; deDoncker-Kapenga, E.; Uberhuber, C.; Kahaner, D. Quadpack: A Subroutine Package for Automatic Integration; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-Reyes, J.E. Asymptotic form of the Kullback–Leibler divergence for multivariate asymmetric heavy-tailed distributions. Phys. A 2014, 395, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, H. An invariant form for the prior probability in estimation problems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1946, 186, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.; Rigby, R.; Stasinopoulos, M. R Package Gamlssbssn: Bimodal Skew Symmetric Normal Distribution (Version 0.1.0). 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gamlssbssn/index.html (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Contreras-Reyes, J.E.; Maleki, M.; Cortés, D.D. Skew-Reflected-Gompertz information quantifiers with application to sea surface temperature records. Mathematics 2019, 7, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinzadeh, A.; Maleki, M.; Khodadadi, Z.; Contreras-Reyes, J.E. The Skew-Reflected-Gompertz distribution for analyzing symmetric and asymmetric data. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2019, 349, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraway, J.; Marsaglia, G.; Marsaglia, J.; Baddeley, A. R Package Goftest: Classical Goodness-of-Fit Tests for Univariate Distributions (Version 1.2-2). 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/goftest/index.html (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Maechler, M. R Package Diptest: Hartigan’s Dip Test Statistic for Unimodality—Corrected (Version 0.75-7). 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/diptest/index.html (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Lorentzen, T. Statistical analysis of temperature data sampled at Station-M in the Norwegian Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 130, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Reyes, J.E.; Canales, T.M.; Rojas, P.M. Influence of climate variability on anchovy reproductive timing off northern Chile. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 164, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Reyes, J.E.; Cortés, D.D. Bounds on Rényi and Shannon entropies for finite mixtures of multivariate skew-normal distributions: Application to swordfish (Xiphias gladius linnaeus). Entropy 2016, 18, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, O.; Salinas, H.S.; Gallardo, D.I.; Bolfarine, B.; Gómez, H.W. Bimodality based on the generalized skew-normal distribution. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2018, 88, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.5 | 25.40 | 17.63 | 19.78 | 34.31 | 59.97 | 75.69 | 86.49 |
| 2 | 44.27 | 30.19 | 23.01 | 21.39 | 33.61 | 48.22 | 65.56 | |
| 5 | 75.19 | 56.85 | 34.51 | 26.77 | 25.05 | 31.91 | 38.73 | |
| 7 | 84.04 | 70.12 | 40.21 | 32.34 | 23.00 | 26.96 | 34.07 | |
| 50 | 0.5 | 18.14 | 16.64 | 47.95 | 72.14 | 93.58 | 97.52 | 99.23 |
| 2 | 62.58 | 35.97 | 23.89 | 33.05 | 59.77 | 77.14 | 87.29 | |
| 5 | 94.42 | 81.45 | 51.11 | 31.96 | 25.90 | 36.40 | 49.09 | |
| 7 | 97.68 | 87.83 | 64.03 | 47.04 | 26.01 | 26.72 | 36.61 | |
| 100 | 0.5 | 19.70 | 29.65 | 81.74 | 95.53 | 99.75 | 99.87 | 100.00 |
| 2 | 79.76 | 48.59 | 24.22 | 39.92 | 77.82 | 92.45 | 97.79 | |
| 5 | 99.90 | 96.20 | 69.70 | 43.40 | 26.03 | 36.60 | 59.50 | |
| 7 | 99.90 | 99.20 | 88.00 | 66.27 | 29.20 | 26.03 | 41.00 | |
| 200 | 0.5 | 21.37 | 53.33 | 95.04 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 2 | 95.80 | 70.10 | 24.92 | 51.30 | 93.20 | 99.30 | 100.00 | |
| 5 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 93.20 | 60.10 | 23.30 | 45.50 | 80.10 | |
| 7 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.40 | 88.90 | 38.80 | 24.20 | 45.60 | |
| Year | Param. | Estim. | (S.D) | AIC | BIC | K–S | A–D | C–V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 19.007 | 0.078 | −1396.1 | 2800.3 | 2818.9 | 0.042 | 1.760 | 0.233 | |
| () | 1.434 | 0.020 | (0.13) | (0.13) | (0.21) | ||||
| 19.670 | 0.151 | ||||||||
| 1.746 | 0.384 | ||||||||
| 2013 | 18.187 | 0.068 | −683.71 | 1375.4 | 1391.5 | 0.035 | 0.636 | 0.074 | |
| () | 0.886 | 0.044 | (0.68) | (0.61) | (0.73) | ||||
| 18.328 | 0.127 | ||||||||
| 1.026 | 0.310 | ||||||||
| 2014 | 17.628 | 0.040 | −643.62 | 1295.2 | 1311.6 | 0.043 | 0.518 | 0.070 | |
| () | 0.550 | 0.054 | (0.41) | (0.73) | (0.75) | ||||
| 17.682 | 0.058 | ||||||||
| 0.306 | 0.079 |
| Method | Quantifier | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | 1.613 | 1.634 | 1.455 | |
| 1.746 | 1.026 | 0.306 | ||
| 9.273 | 2.534 | 2.579 | ||
| 0.003 | 0.025 | 0.138 | ||
| Statistic | 556.657 | 21.425 | 121.087 | |
| p-value | 0.971 | 0.999 | 1.000 | |
| DIPtest | Statistic | 0.023 | 0.029 | 0.038 |
| p-value | <0.01 | 0.016 | <0.01 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contreras-Reyes, J.E. An Asymptotic Test for Bimodality Using The Kullback–Leibler Divergence. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12061013
Contreras-Reyes JE. An Asymptotic Test for Bimodality Using The Kullback–Leibler Divergence. Symmetry. 2020; 12(6):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12061013
Chicago/Turabian StyleContreras-Reyes, Javier E. 2020. "An Asymptotic Test for Bimodality Using The Kullback–Leibler Divergence" Symmetry 12, no. 6: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12061013
APA StyleContreras-Reyes, J. E. (2020). An Asymptotic Test for Bimodality Using The Kullback–Leibler Divergence. Symmetry, 12(6), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12061013





