Influence of Mucosal Thickness, Implant Dimensions and Stability in Cone Morse Implant Installed at Subcrestal Bone Level on the Peri-Implant Bone: A Prospective Clinical and Radiographic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Research Design
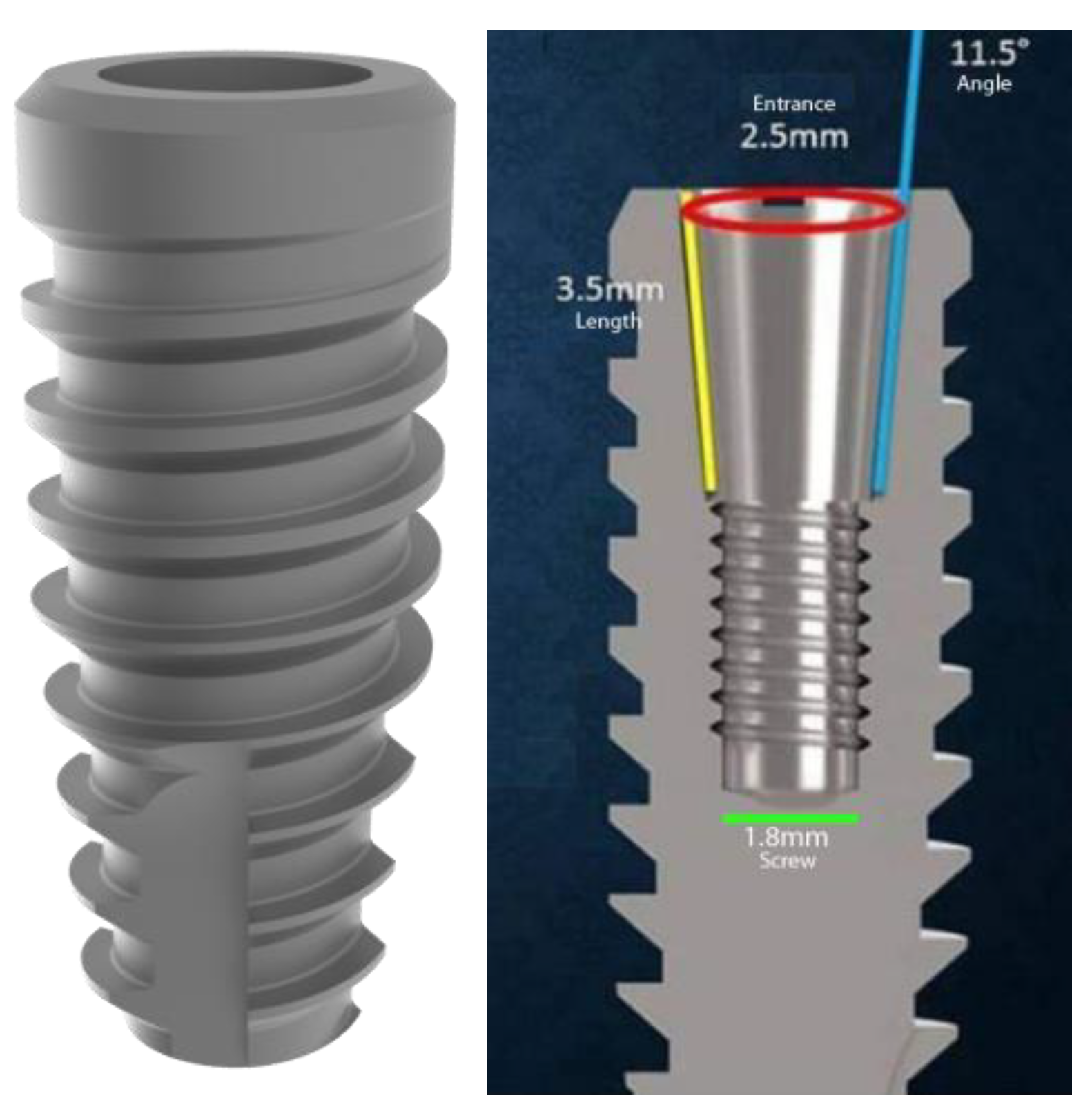
2.2. Dental Implant Surface Topography
2.3. Surgical Procedure of Implant Placement
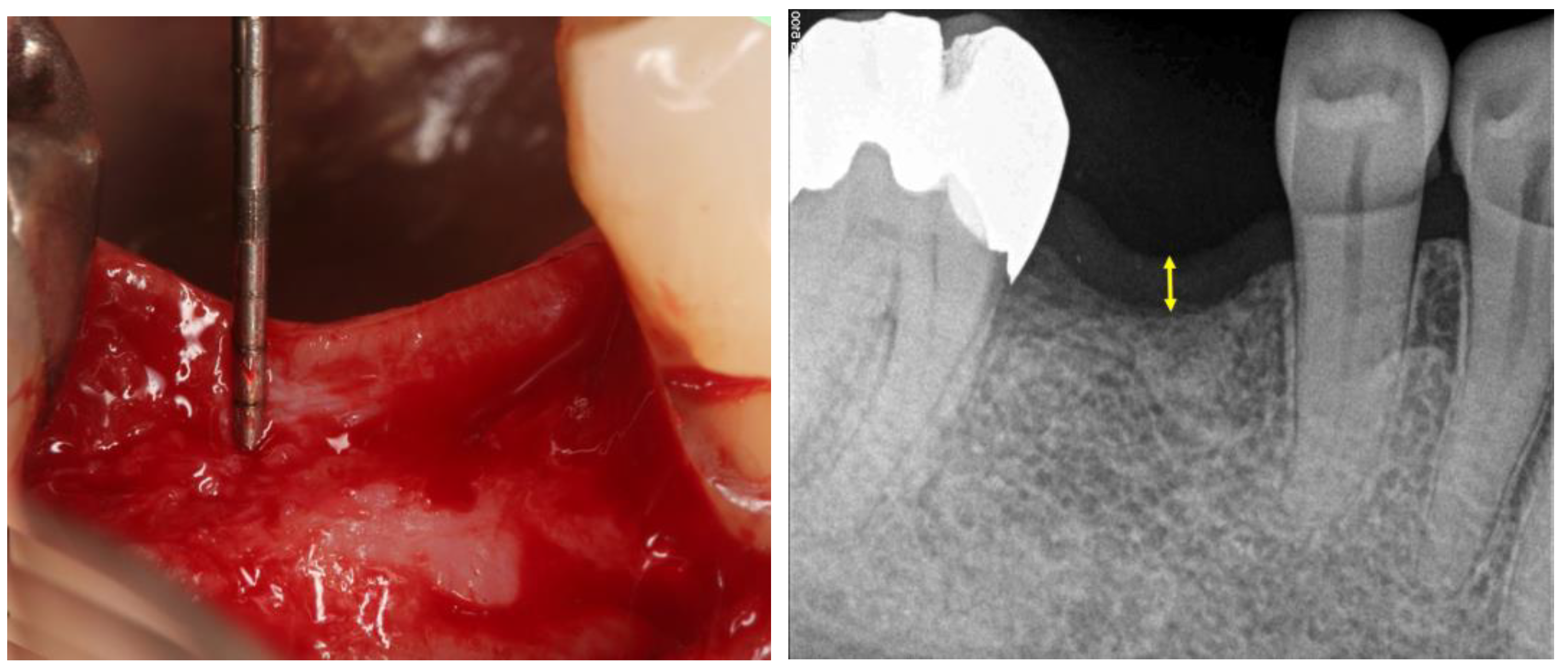
2.4. Clinical Stability and Radiographic Evaluations
2.5. Statistical Analyses
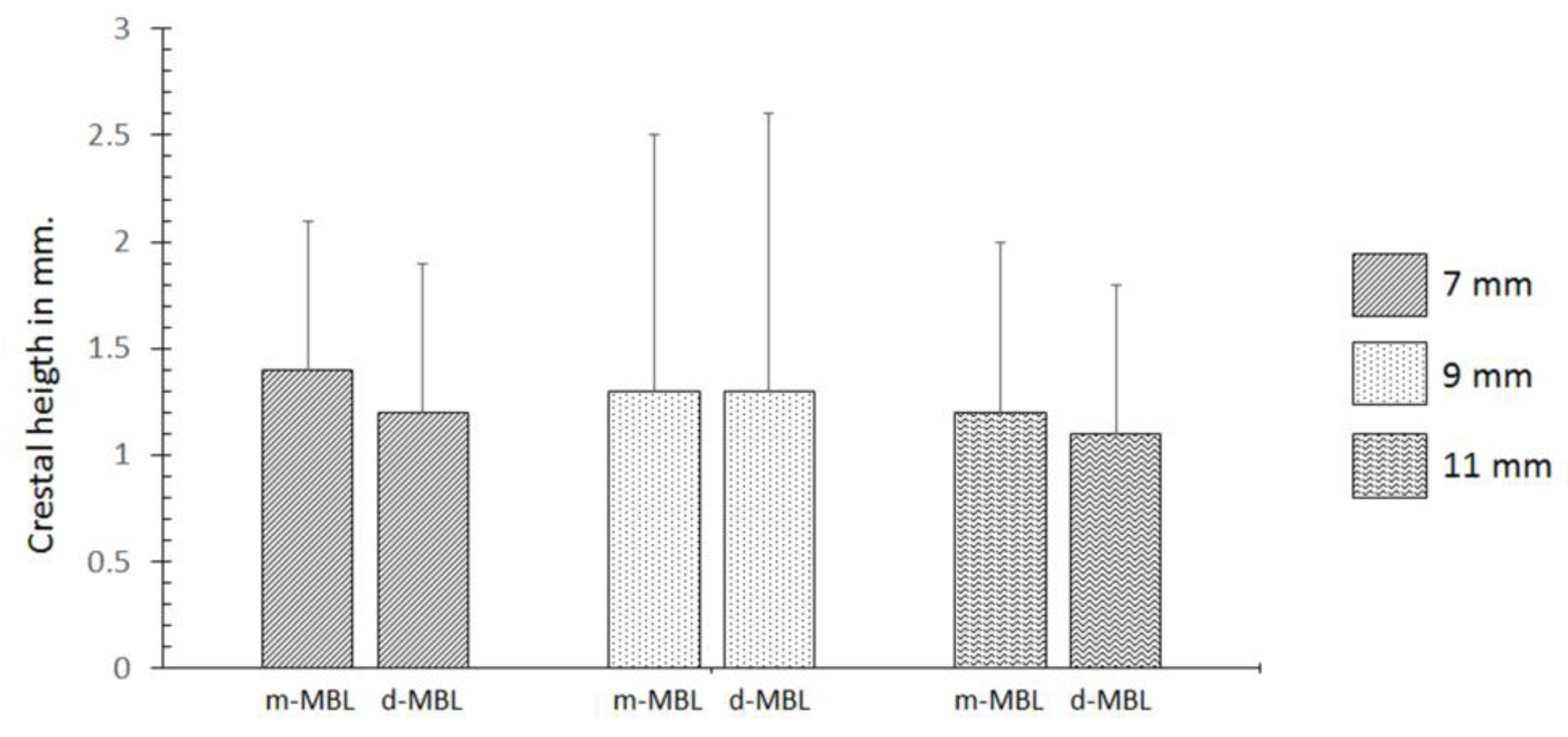
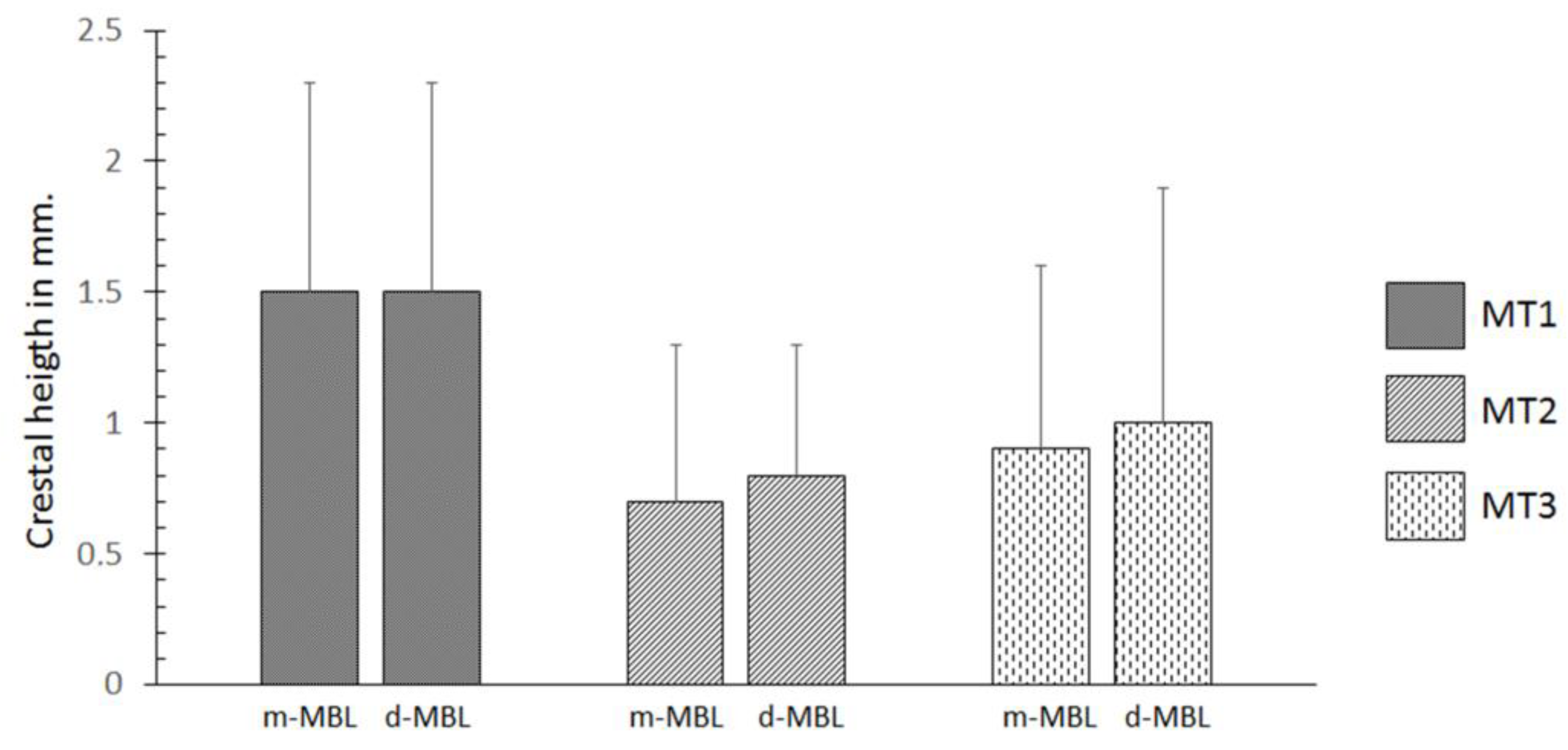
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Initial Implant Stability
4.2. Mucosal Thickness
4.3. Implant Dimensions (Diameter and Length)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. Dimension of the periimplant mucosa. Biological width revisited. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Apse, P.; Grybauskas, S.; Puisys, A. The influence of soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants: A 1-year prospective controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Linkevicius, T.; Apse, P.; Grybauskas, S.; Puisys, A. Influence of thin mucosal tissues on crestal bone stability around implants with platform switching: A 1-year pilot study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2272–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eekeren, P.; Tahmaseb, A.; Wismeijer, D. Crestal bone changes in macrogeometrically similar implants with the implant-abutment connection at the crestal bone level or 2.5 mm above: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Svediene, O.; Linkevicius, R.; Linkeviciene, L. Radiological comparison of laser-microtextured and platform-switched implants in thin mucosal biotype. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puisys, A.; Linkevicius, T. The influence of mucosal tissue thickening on crestal bone stability around bone-level implants. A prospective controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Steigmann, M.; Vindasiute, E.; Linkeviciene, L. Influence of Vertical Soft Tissue Thickness on Crestal Bone Changes Around Implants with Platform Switching: A Comparative Clinical Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; da Silva Neto, U.T. Evaluation of the Surface Treatment on Bone Healing in a Transmucosal 1-mm Area of Implant Abutment: An Experimental Study in the Rabbit Tibia. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eekeren, P.J.; Tahmaseb, A.; Wismeijer, D. Crestal Bone Changes Around Implants with Implant-Abutment Connections at Epicrestal Level or Above: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Hegewald, A.; Becker, J. Impact of implant-abutment connection and positioning of the machined collar/microgap on crestal bone level changes: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, J.S.; Schoolfield, J.D.; Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D.; Cochran, D.L. Influence of the size of the microgap on crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A histometric evaluation of unloaded non-submerged implants in the canine mandible. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, L.C.; Dib, L.L.; Gehrke, S.A. Photoelastic stress analysis surrounding different implant designs under simulated static loading. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.E.; McGlmphy, E.A.; Johnston, W.M.; Larsen, P.E. Effects of implant design and surface roughness on crestal bone and soft tissue levels in the esthetic zone. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 910–919. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, C.M.; Nogueira-Filho, G.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Lai, J.Y.; Brito, C.; Döring, H.; Nonhoff, J. Performance of conical abutment (Morse Taper) connection implants: A systematic review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 552–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, A.; Bolzoni, A.; Russillo, A.; Lauritano, D.; Palmieri, A.; Cura, F.; Silvestre, F.J.; Giannì, A.B. Cone-morse implant connection system significantly reduces bacterial leakage between implant and abutment: An in vitro study. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Prados Frutos, J.C.; Prados-Privado, M.; Dedavid, B.A.; Granero Marín, J.M.; Calvo Guirado, J.L. Misfit of Three Different Implant-Abutment Connections Before and After Cyclic Load Application: An in Vitro Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaoka, M.; Gehrke, S.A.; Mardegan, F.; Gennari, C.R.; Taschieri, S.; Del Fabbro, M.; Corbella, S. Influence of implant/abutment connection on stress distribution to implant-surrounding bone: A finite element analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2014, 23, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Chrcanovic, B.; Östman, P.O.; Sennerby, L. Initial and long-term crestal bone responses to modern dental implants. Periodontology 2000 2017, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasada, Y.; Cochran, D.L. Implant-Abutment Connections: A Review of Biologic Consequences and Peri-implantitis Implications. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Ramírez-Fernandez, M.P.; Granero Marín, J.M.; Barbosa Salles, M.; Del Fabbro, M.; Calvo Guirado, J.L. A comparative evaluation between aluminium and titanium dioxide microparticles for blasting the surface titanium dental implants: An experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salatti, D.B.; Pelegrine, A.A.; Gehrke, S.; Teixeira, M.L.; Moshaverinia, A.; Moy, P.K. Is there a need for standardization of tightening force used to connect the transducer for resonance frequency analysis in determining implant stability? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balleri, P.; Cozzolino, A.; Ghelli, L.; Momichioli, G.; Varriale, A. Stability measurements of osseointegrated implants using Osstell in partially edentulous jaws after one year of loading: A pilot study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2002, 4, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barewal, R.M.; Oates, T.W.; Meredith, N.; Cochran, D.L. Resonance frequency measurement of implant stability in vivo on implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 641–651. [Google Scholar]
- Bischof, M.; Nedir, R.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Bernard, J.P.; Samson, J. Implant stability measurement of delayed and immediately loaded implants during healing. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedir, R.; Bischof, M.; Szmulzkler-Moncler, S.; Bernard, J.P.; Samson, J. Predicting osseointegration by means of implant primary stability: A resonance frequency analysis with delayed and immediately loaded ITI SLA implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, T.W.; Valderrama, P.; Bischof, M.; Nedir, R.; Jones, A.; Simpson, J.; Toutenburg, H.; Cochran, D.L. Enhanced implant stability with a chemically modified SLA surface: A randomized pilot study. Int. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 755–760. [Google Scholar]
- Meredith, N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1998, 11, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, K.; Bäckström, M.; Sennerby, L. Immediate and early loading of oxidized tapered implants in the partially edentulous maxilla: A 1-year prospective clinical, radiographic, and resonance frequency analysis study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.; Book, K.; Friberg, B.; Jemt, T.; Sennerby, L. Resonance frequency measurements of implant stability in vivo. A crosssectional and longitudinal study of resonance frequency measurements on implants in the edentulous and partially dentate maxilla. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1997, 8, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; da Silva Neto, U.T.; Rossetti, P.H.; Watinaga, S.E.; Giro, G.; Shibli, J.A. Stability of implants placed in fresh sockets versus healed alveolar sites: Early findings. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Tavares da Silva Neto, U. Does the time of osseointegration in the maxilla and mandible differ? J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, B.; Sennerby, L.; Linden, B.; Gröndahl, K.; Lekholm, U. Stability measurements of one-stage Branemark implants during healing in mandibles. A clinical resonance frequency analysis study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 28, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zix, J.; Hug, S.; Kessler-Liechti, G.; Mericske-Stern, R. Measurement of dental implant stability by resonance frequency analysis and damping capacity assessment: Comparison of both techniques in a clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2008, 23, 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Neto, U.T.; Joly, J.C.; Gehrke, S.A. Clinical analysis of the stability of dental implants after preparation of the site by conventional drilling or piezosurgery. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 52, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.A.; da Silva, U.T.; Del Fabbro, M. Does Implant Design Affect Implant Primary Stability? A Resonance Frequency Analysis-Based Randomized Split-Mouth Clinical Trial. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, e281–e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzis, T.; Neiva, R.; Nair, M.; Nonhoff, J.; Lundgren, T. Cone beam computed tomographic evaluation of implants with platform-switched Morse taper connection with the implant-abutment interface at different levels in relation to the alveolar crest. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutouzis, T.; Neiva, R.; Nonhoff, J.; Lundgren, T. Placement of implants with platform-switched Morse taper connections with the implant-abutment interface at different levels in relation to the alveolar crest: A short-term (1-year) randomized prospective controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetner, M.; Fetner, A.; Koutouzis, T.; Clozza, E.; Tovar, N.; Sarendranath, A.; Coelho, P.G.; Neiva, K.; Janal, M.N.; Neiva, R. The Effects of Subcrestal Implant Placement on Crestal Bone Levels and Bone-to-Abutment Contact: A Microcomputed Tomographic and Histologic Study in Dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, M.; Wallet, S.; Koutouzis, T.; Lundgren, T. Bacterial colonization of the dental implant fixture-abutment interface: An in vitro study. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welander, M.; Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T. Subcrestal placement of two-part implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.H.; Bell, M.; Bosco, A.F.; de Melo, L.G.N.; Richter, E.-J. Influence of microgap location and configuration on the periimplant bone morphology in submerged implants. An experimental study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.H.; Leite, C.M.; de Melo, L.G.N.; Bosco, A.F. Influence of microgap location and configuration on radiographic bone loss in nonsubmerged implants: An experimental study in dogs. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 24, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Pilliar, R.M.; Deporter, D.A.; Watson, P.A.; Valiquette, N. Dental implant design: Effect on bone remodeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunski, J.B. Biomechanical considerations in dental implant design. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1988, 5, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren, E.P.; Seckinger, R.J.; Kilgren, L.M.; Mante, F. Evaluating parameters of osseointegrated dental implants using finite element analysis—A two-dimensional comparative study examining the effects of implant diameter, implant shape, and load direction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1998, 24, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, H.J.; Kuiper, J.H.; Starmans, F.J.; Bosman, F. Stress distribution around dental implants: Influence of superstructure, length of implants, and height of mandible. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 68, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iplikcioglu, H.; Akca, K. Comparative evaluation of the effect of diameter, length and number of implants supporting three-unit fixed partial prostheses on stress distribution in the bone. J. Dent. 2002, 30, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmlova, L.; Dostalova, T.; Kacovsky, A.; Konvickova, S. Influence of implant length and diameter on stress distribution: A finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, S.; Morris, H.F.; Ochi, S. Implant survival to 36 months as related to length and diameter. Ann. Periodontol. 2000, 5, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misch, C.E. Divisions of available bone. In Contemporary Implant Dentistry, 2nd ed.; Mosby: St Louis, MO, USA, 1999; pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Koutouzis, T.; Fetner, M.; Fetner, A.; Lundgren, T. Retrospective evaluation of crestal bone changes around implants with reduced abutment diameter placed non-submerged and at subcrestal positions: The effect of bone grafting at implant placement. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Todo, M.; Matsushita, Y.; Koyano, K. Effects of implant diameter, insertion depth, and loading angle on stress/strain fields in implant/ jawbone systems: Finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 877–886. [Google Scholar]






| ISQ Value | Baseline | 90 Days | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median | Mean ± SD | Median | |
| Mesio-distal | 63.4 ± 2.94 | 63.75 | 68.0 ± 3.85 | 69.53 |
| Vestibule-lingual | 63.7 ± 2.89 | 64.45 | 69.9 ± 4.14 | 70.80 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gehrke, S.A.; Bercianos, M.; Aguerrondo, J.G.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Prados-Frutos, J.C. Influence of Mucosal Thickness, Implant Dimensions and Stability in Cone Morse Implant Installed at Subcrestal Bone Level on the Peri-Implant Bone: A Prospective Clinical and Radiographic Study. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091138
Gehrke SA, Bercianos M, Aguerrondo JG, Calvo-Guirado JL, Prados-Frutos JC. Influence of Mucosal Thickness, Implant Dimensions and Stability in Cone Morse Implant Installed at Subcrestal Bone Level on the Peri-Implant Bone: A Prospective Clinical and Radiographic Study. Symmetry. 2019; 11(9):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091138
Chicago/Turabian StyleGehrke, Sergio Alexandre, Mauro Bercianos, Jorge Gonzalo Aguerrondo, José Luis Calvo-Guirado, and Juan Carlos Prados-Frutos. 2019. "Influence of Mucosal Thickness, Implant Dimensions and Stability in Cone Morse Implant Installed at Subcrestal Bone Level on the Peri-Implant Bone: A Prospective Clinical and Radiographic Study" Symmetry 11, no. 9: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091138
APA StyleGehrke, S. A., Bercianos, M., Aguerrondo, J. G., Calvo-Guirado, J. L., & Prados-Frutos, J. C. (2019). Influence of Mucosal Thickness, Implant Dimensions and Stability in Cone Morse Implant Installed at Subcrestal Bone Level on the Peri-Implant Bone: A Prospective Clinical and Radiographic Study. Symmetry, 11(9), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091138








