Finite Element Modelling of a Composite Shell with Shear Connectors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
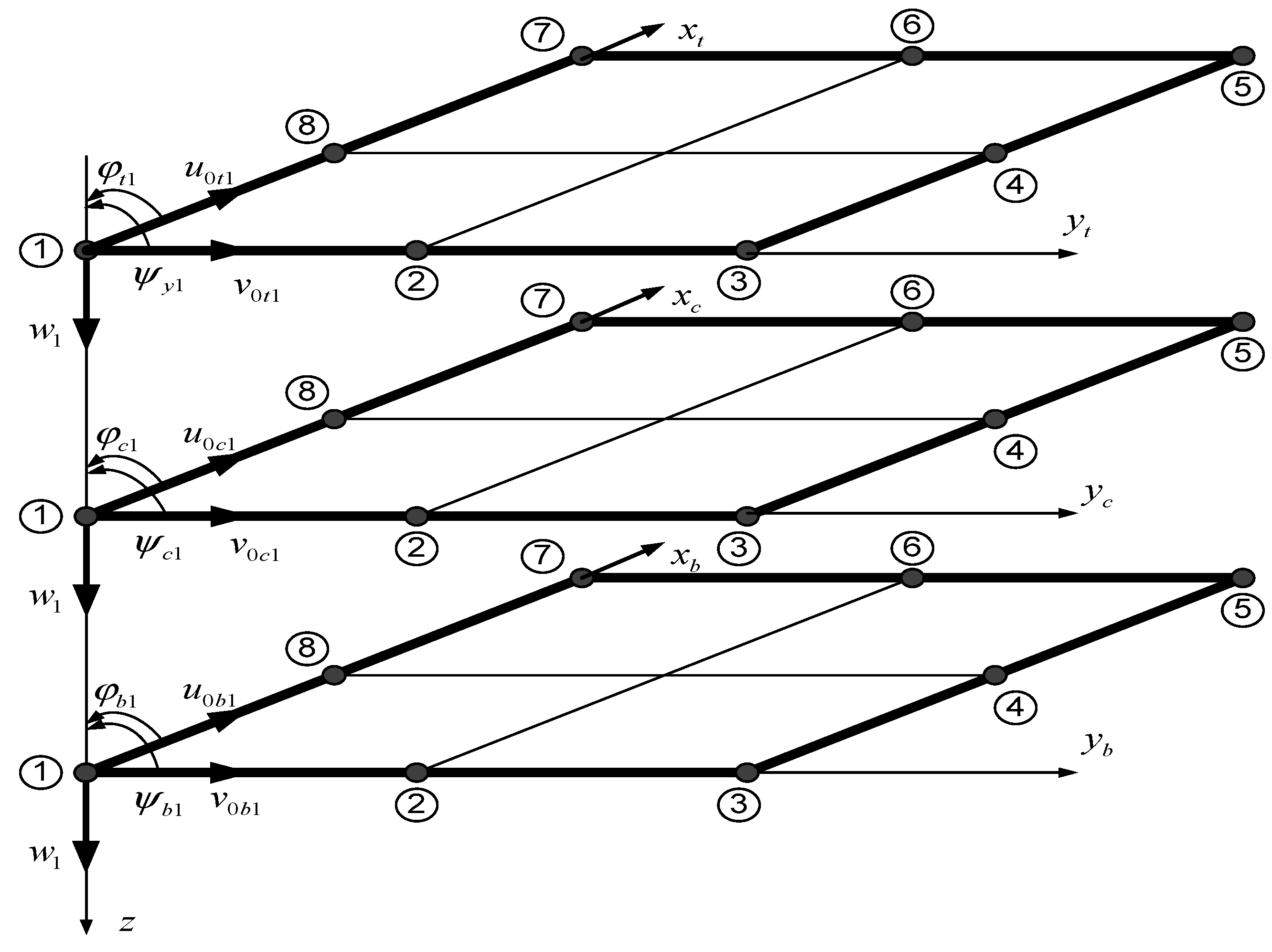
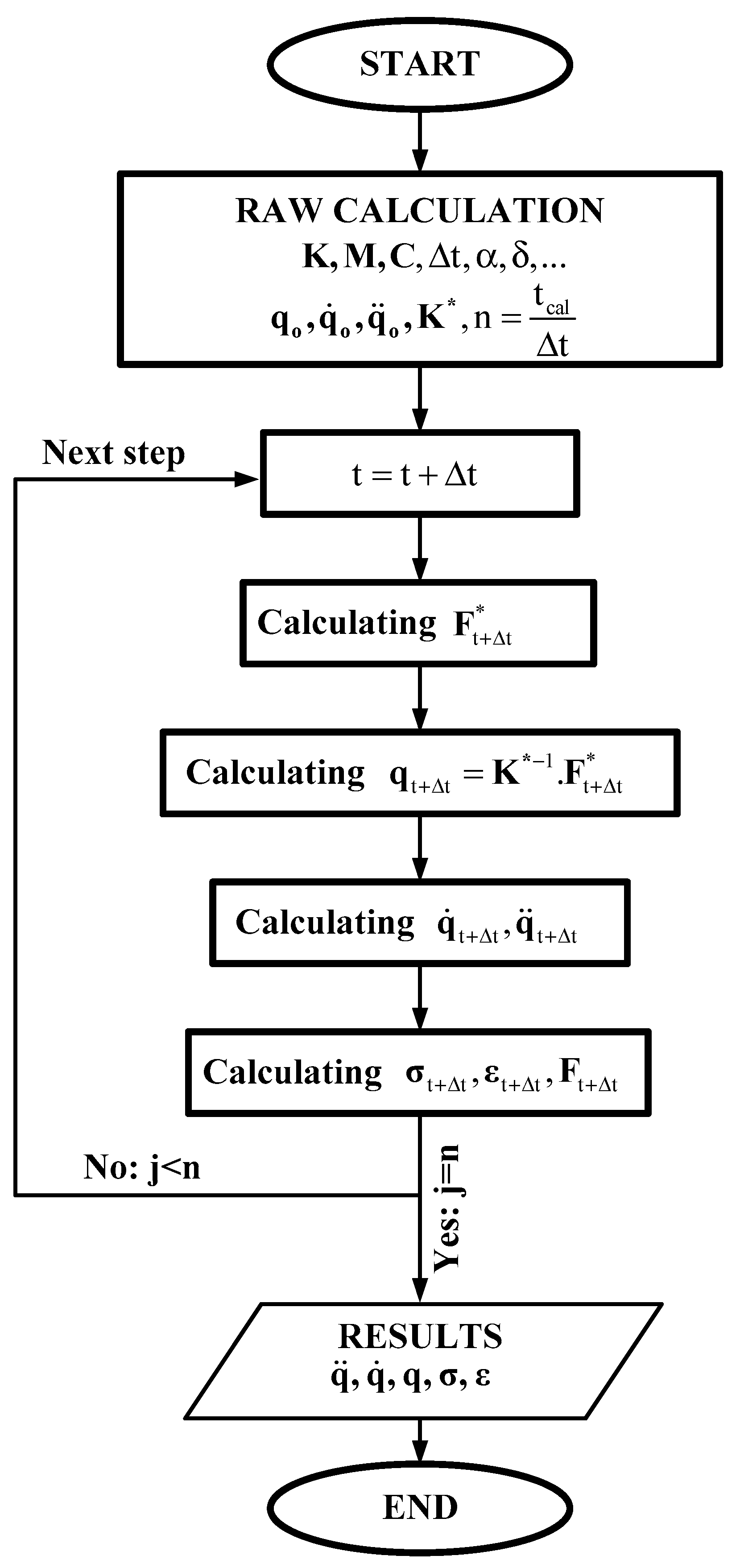
2. Finite Element Formulations
2.1. Equation of Motion of the Shell Element
2.2. The Differential Equation of Vibration
3. Numerical Results of Free Vibration Analysis of Three-Layer Composite Shells with Shear Connectors
3.1. Accuracy Studies
3.2. Effects of Some Parameters on Free Vibration of the Shell
3.2.1. Effect of Thickness h
3.2.2. Effect of the hc/ht Ratio (ht = hb)
3.2.3. Effect of the Length-to-Width Ratio a/b
3.2.4. Effect of the Shear Coefficient of Stub ks
4. Numerical Results of Forced Vibration Analysis of Three-Layer Composite Shells with Shear Connectors
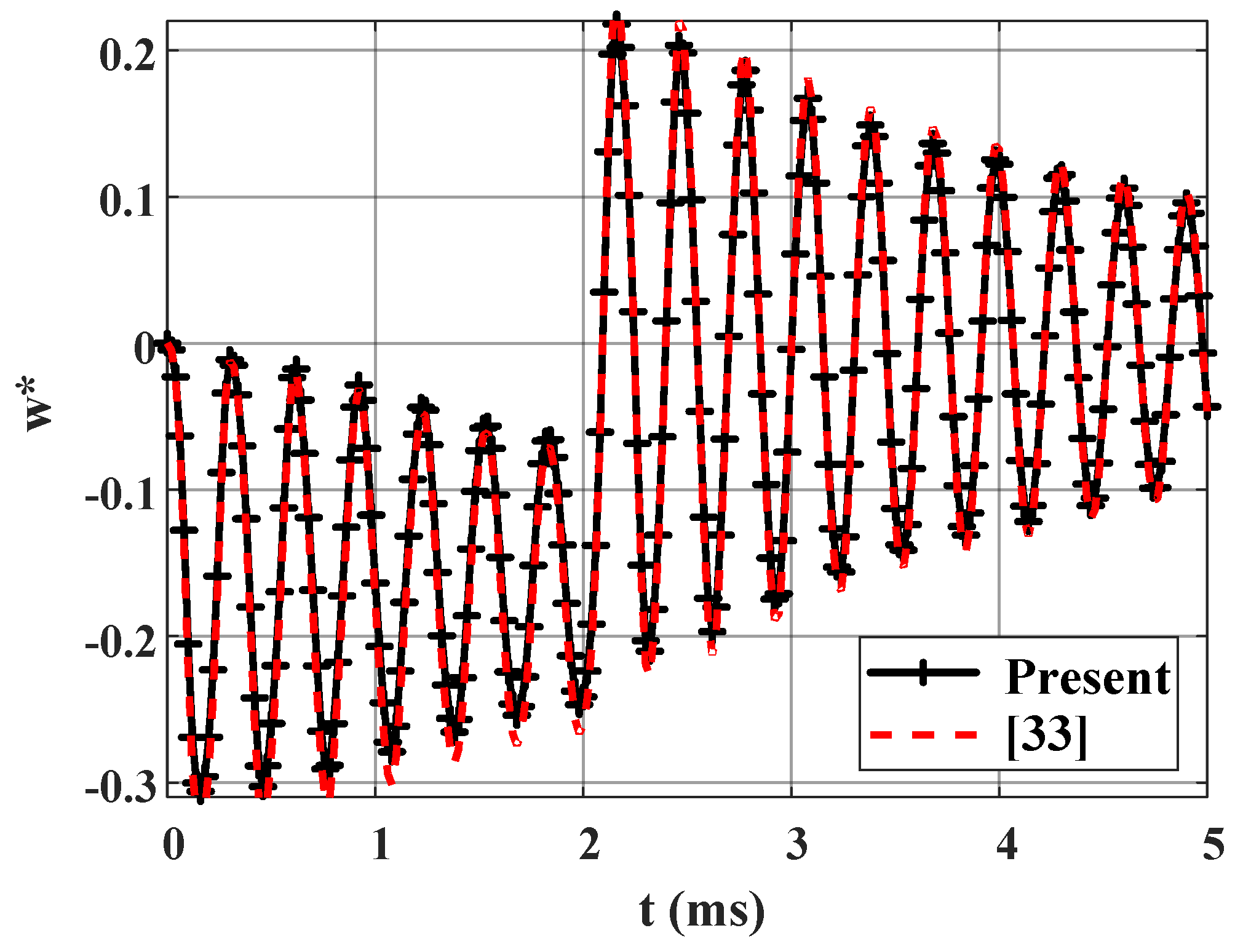
4.1. Accuracy Studies
4.2. Effect of Some Parameters on the Forced Vibration of the Shell
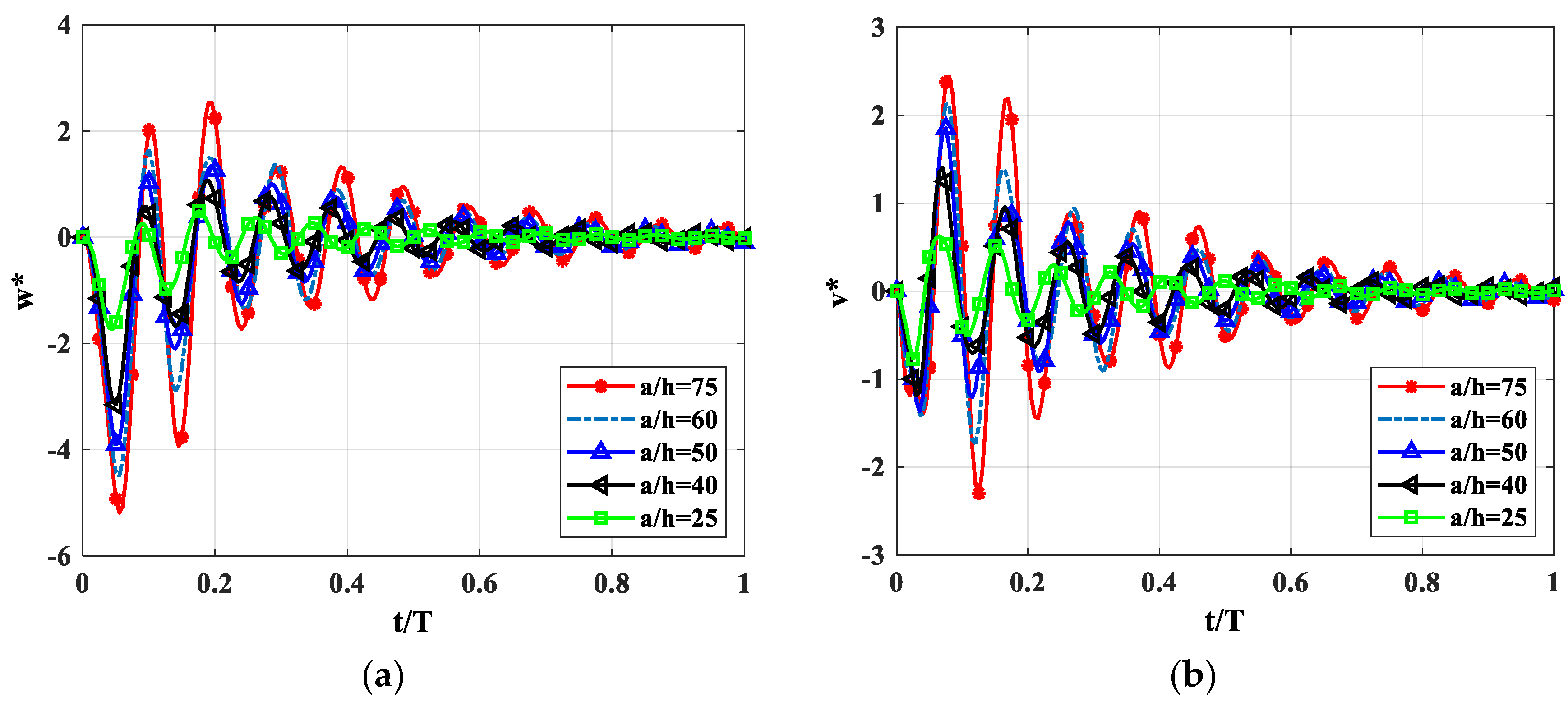
4.2.1. Effect of the Length-to-High Ratio a/h
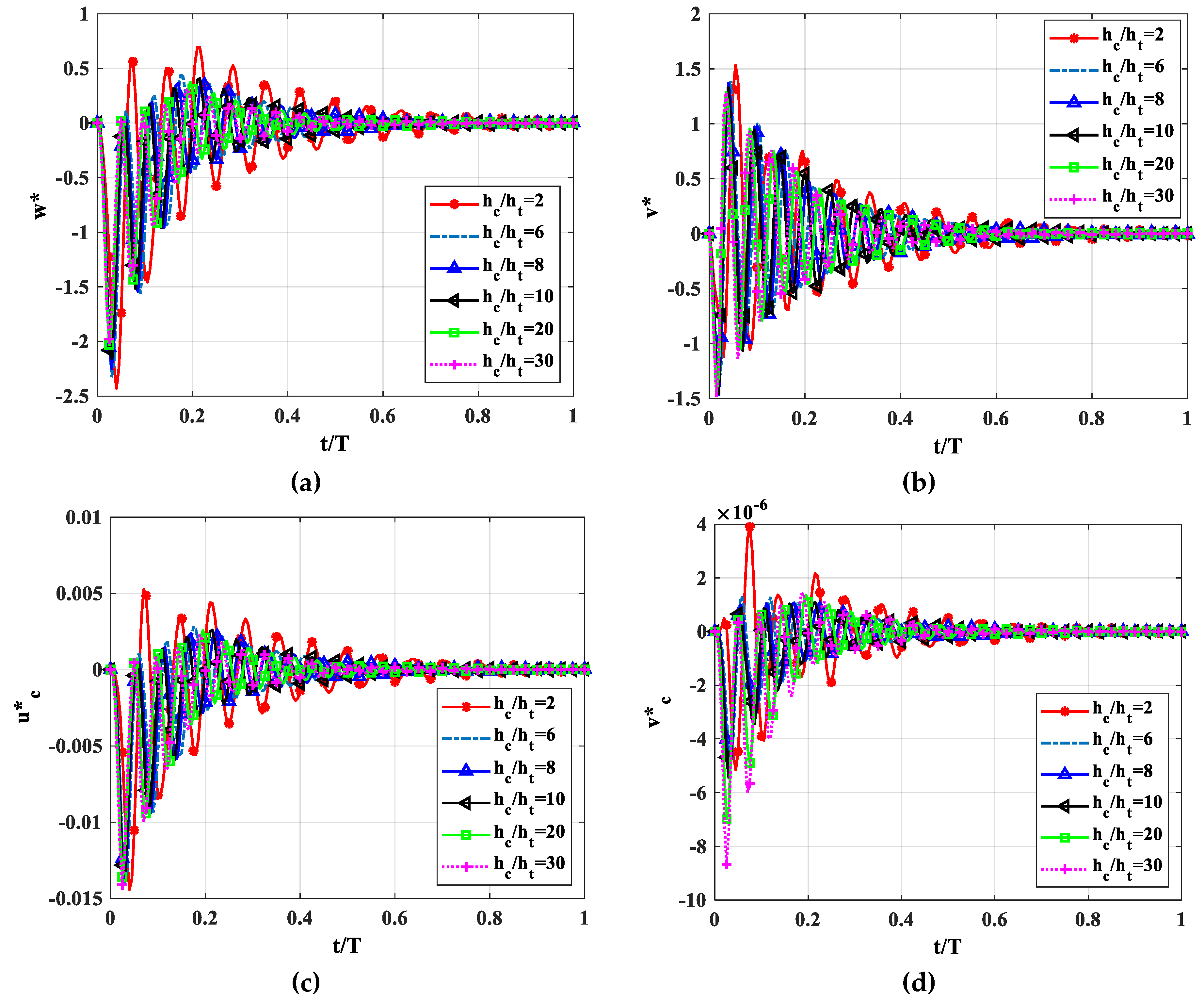
4.2.2. Effect of the hc/ht Ratio (ht = hb)
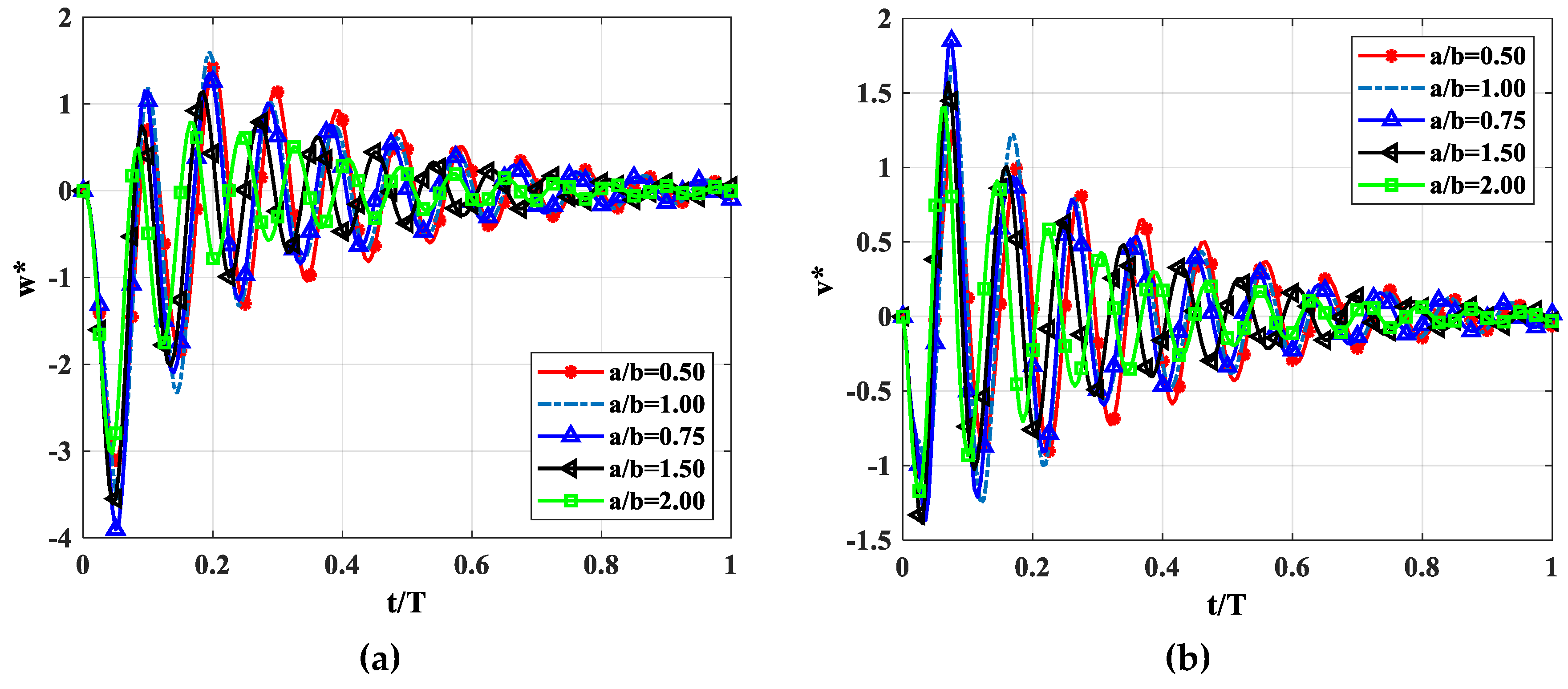
4.2.3. Effect of the Length-to-Width Ratio a/b
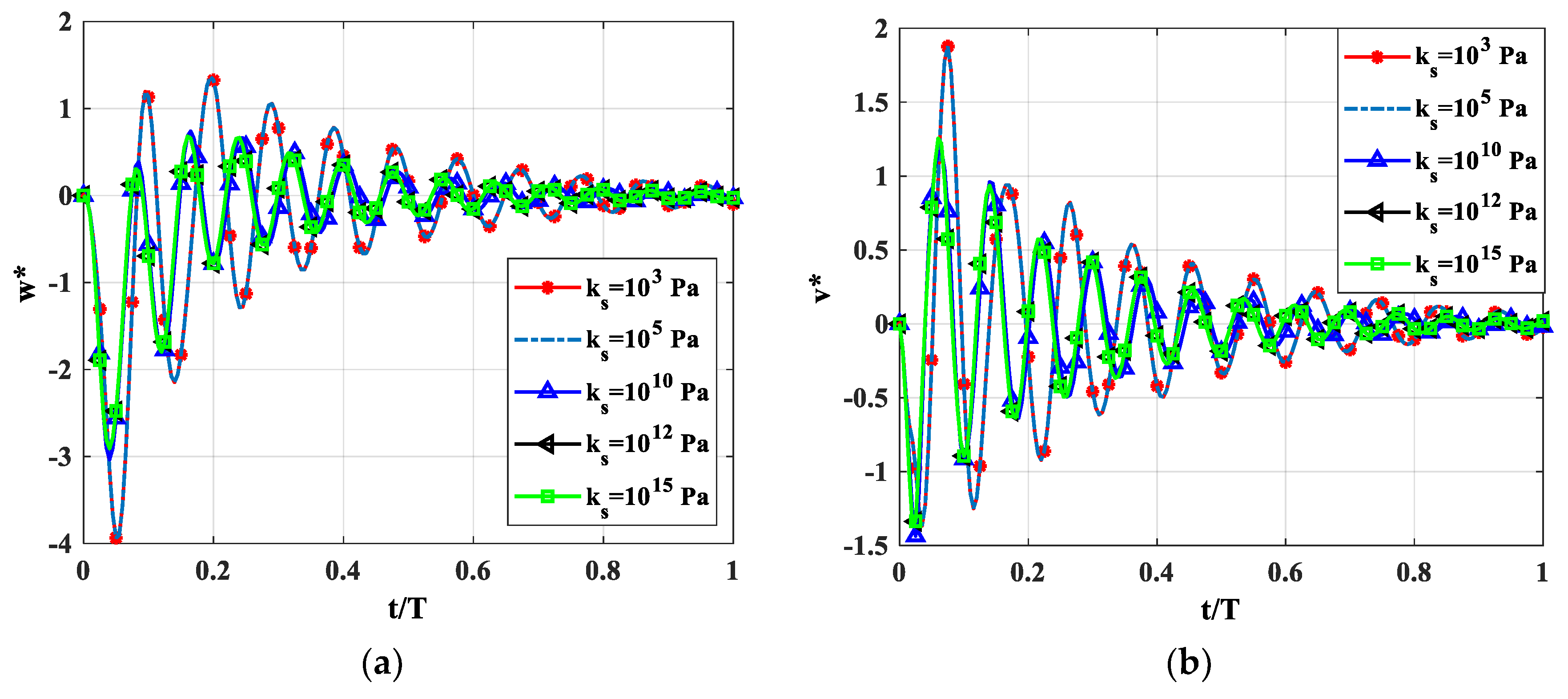
4.2.4. Effect of the Shear Coefficient of the Stub
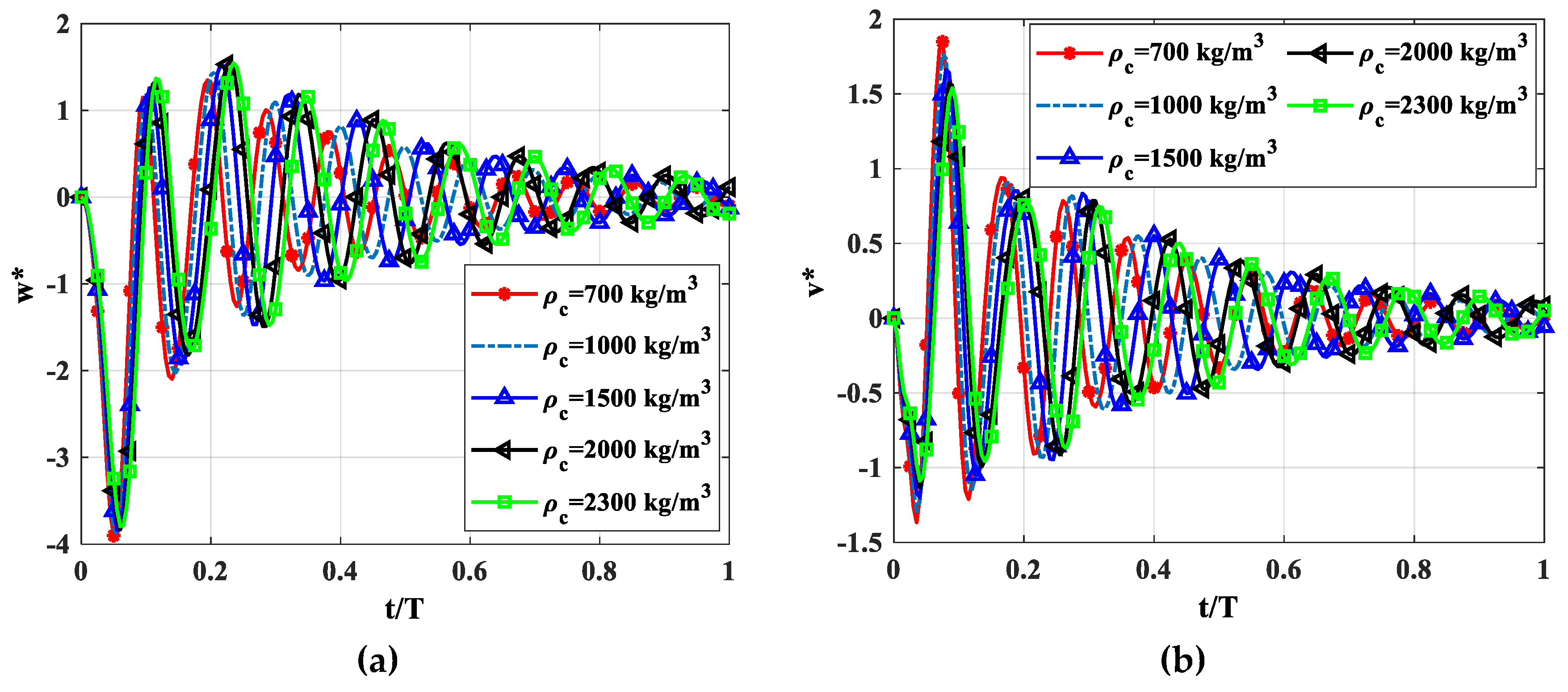
4.2.5. Influence of the Mass Density of the Core Layer
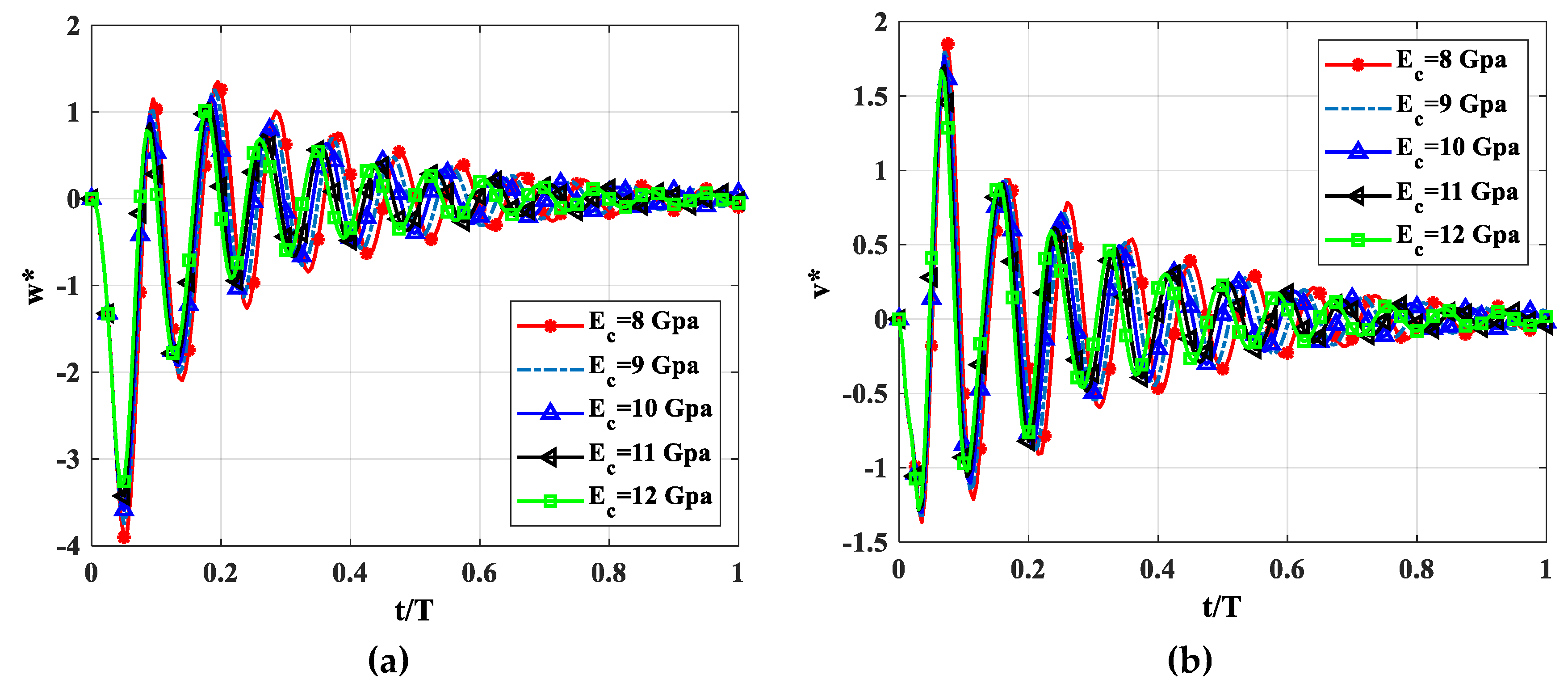
4.2.6. Influence of Modulus of Elasticity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Newmark, N.M.; Siess, C.P.; Viest, I.M. Test and analysis of composite beams with incomplete interaction. Proc. Soc. Exp. Stress Anal. 1951, 19, 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Yang, X. Finite element analysis for buckling of two-layer composite beams using Reddy’s higher order beam theory. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2014, 83, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, G. Variational principle of partial-interaction composite beams using Timoshenko’s beam theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2012, 60, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wu, Y. Static, dynamic, and buckling analysis of partial interaction composite members using Timoshenko’s beam theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2007, 49, 1139–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Hjiaj, M.; Grognec, P.L. Analytical approach for free vibration analysis of two-layer Timoshenko beams with interlayer slip. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 2949–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.R.; Sousa, J.B.M., Jr. A family of interface elements for the analysis of composite beams with interlayer slip. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2009, 45, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabl, S.; Saje, M.; Turk, G.; Planinc, I. Analytical solution of two-layer beam taking into account interlayer slip and shear deformation. J. Struct. Eng. 2007, 133, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Martinelli, E.; Hjiaj, M. Derivation of the exact stiffness matrix for a two-layer Timoshenko beam element with partial interaction. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Hjiaj, M.; Lai, V.-A. Force-based FE for large displacement inelastic analysis of two-layer Timoshenko beams with interlayer slips. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2014, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Su, Y.H. Dynamic characteristics of partial composite beams. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2008, 8, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Xu, R. Dynamic analysis of partial-interaction composite beams. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvin, H.; Bakhtiari-Nejad, F. Nonlinear free vibration analysis of rotating composite Timoshenko beams. Compos. Struct. 2013, 96, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Sheikh, A.H.; Griffith, M.; Oehlers, D.J. Dynamic response of composite beams with partial shear interaction using a higher-order beam theory. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Sheikh, A.H.; Griffith, M.; Oehlers, D.J. Analysis of composite beams with longitudinal and transverse partial interactions using higher order beam theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2012, 59, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Sheikh, A.H.; Griffith, M.; Oehlers, D.J. Analysis of composite beams with partial shear interactions using a higher order beam theory. Eng. Struct. 2012, 36, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P. Dynamic analysis of laminated composite beams using higher order theories and finite elements. Compos. Struct. 2006, 73, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, C.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Wu, W. Free vibration of axially loaded composite beams with general boundary conditions using hyperbolic shear deformation theory. Compos. Struct. 2013, 97, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.P.; Thai, H.-T. Static behavior of composite beams using various refined shear deformation theories. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarun, K.; Owen, D.R.J.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. A refined higher-order C0 plate bending element. Compos. Struct. 1982, 15, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunatha, B.S.; Kant, T. New theories for symmetric/unsymmetric composite and sandwich beams with C0 finite elements. Compos. Struct. 1993, 23, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.B.; Zhang, W. Numerical analysis on steel-concrete-steel sandwich plates by damage plasticity model, Materials to structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E.; Petrolo, M.; Zappino, E. Performance of CUF Approach to Analyze the Structural Behavior of Slender Bodies. J. Struct. Eng. 2012, 138, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E. Theories and finite elements for multilayered, anisotropic, composite plates and shells. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2002, 9, 87–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinefra, M.; Kumar, S.K.; Carrera, E. MITC9 Shell elements based on RMVT and CUF for the analysis of laminated composite plates and shells. Compos. Struct. 2019, 209, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, A.A.; Nedelcu, M.; Gonçalves, R. GBT-based FE formulation to analyse the buckling behaviour of isotropic conical shells with circular cross-section. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 134, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schardt, R. Verallgemeinerte Technische Biegetheorie: Lineare Probleme; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fryba, L. Vibration of Solids and Structures under Moving Loads; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang-Nam, N.; Tan-Y, N.; Ke, V.T.; Thanh, T.T.; Truong-Thinh, N.; Van-Duc, P.; Thom, V.D. A Finite Element Model for Dynamic Analysis of Triple-Layer Composite Plates with Layers Connected by Shear Connectors Subjected to Moving Load. Materials 2019, 12, 598–617. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari Sadrabadi, S.; Rahimi, G.H.; Citarella, R.; Shahbazi Karami, J.; Sepe, R.; Esposito, R. Analytical solutions for yield onset achievement in FGM thick walled cylindrical tubes undergoing thermomechanical loads. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 116, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, K.J. Finite element Procedures; Prentice-Hall International Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, J.P. Dynamic Soil-Structure Interaction; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, J.N. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plate and Shell, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.F. Free and Forced Vibrations of Thick Rectangular Plates using Higher-Order Sheara and Normal Deformable Plate Theory and Meshless Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) Method. CMES 2003, 5, 519–534. [Google Scholar]

| a/h = 100 | This Work | Reddy [32] | |||||
| Meshes | 4 × 4 | 6 × 6 | 8 × 8 | 10 × 10 | 12 × 12 | ||
| R/a | 1 | 126.430 | 126.135 | 126.145 | 126.145 | 126.145 | 125.99 |
| 2 | 68.489 | 68.095 | 68.065 | 68.065 | 68.065 | 68.075 | |
| 3 | 47.432 | 47.316 | 47.369 | 47.369 | 47.369 | 47.265 | |
| 4 | 36.989 | 36.975 | 37.083 | 37.083 | 37.083 | 36.971 | |
| 5 | 31.188 | 30.908 | 31.030 | 31.030 | 31.030 | 30.993 | |
| 10 | 20.313 | 20.350 | 20.332 | 20.332 | 20.332 | 20.347 | |
| 1030 | 15.174 | 5.151 | 15.1457 | 15.1457 | 15.1457 | 15.183 | |
| a/h = 10 | This Work | Reddy [32] | |||||
| Meshes | 4 × 4 | 6 × 6 | 8 × 8 | 10 × 10 | 12 × 12 | ||
| R/a | 1 | 16.3576 | 16.3272 | 16.3226 | 16.3226 | 16.3226 | 16.115 |
| 2 | 12.9939 | 12.9811 | 12.978 | 12.978 | 12.978 | 13.382 | |
| 3 | 12.1582 | 12.1500 | 12.1488 | 12.1488 | 12.1488 | 12.731 | |
| 4 | 11.8418 | 11.8354 | 11.8343 | 11.8343 | 11.8343 | 12.487 | |
| 5 | 11.6905 | 11.6851 | 11.6843 | 11.6843 | 11.6843 | 12.372 | |
| 10 | 11.4843 | 11.4799 | 11.4791 | 11.4791 | 11.4791 | 12.215 | |
| 1030 | 11.4141 | 11.4102 | 11.4095 | 11.4095 | 11.4095 | 12.165 | |
| R/a | a/h = 75 | a/h = 60 | a/h = 50 | a/h = 25 | a/h = 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48.9232 | 48.9329 | 48.9447 | 49.0591 | 49.8350 |
| 2 | 25.2821 | 25.3022 | 25.3267 | 25.5643 | 27.1440 |
| 3 | 16.9857 | 17.0161 | 17.0531 | 17.4099 | 19.6929 |
| 4 | 12.7982 | 12.8388 | 12.8881 | 13.3594 | 16.2390 |
| 5 | 10.2817 | 10.3324 | 10.3938 | 10.9744 | 14.3496 |
| 6 | 8.6065 | 8.6671 | 8.7403 | 9.4243 | 13.2070 |
| 7 | 7.4135 | 7.4838 | 7.5686 | 8.3498 | 12.4663 |
| 8 | 6.5225 | 6.6024 | 6.6983 | 7.5705 | 11.9605 |
| 9 | 5.8331 | 5.9222 | 6.0291 | 6.9856 | 11.6008 |
| 10 | 5.2847 | 5.3830 | 5.5004 | 6.5351 | 11.3363 |
| R/a | hc/ht = 2 | hc/ht = 4 | hc/ht = 8 | hc/ht = 20 | hc/ht = 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48.9447 | 49.6002 | 50.3956 | 51.3623 | 51.6856 |
| 2 | 25.3267 | 25.7143 | 26.2246 | 26.8744 | 27.0959 |
| 3 | 17.0531 | 17.3679 | 17.8202 | 18.4208 | 18.6285 |
| 4 | 12.8881 | 13.1816 | 13.6348 | 14.2529 | 14.4682 |
| 5 | 10.3938 | 10.6864 | 11.1625 | 11.8208 | 12.0502 |
| 6 | 8.7403 | 9.0417 | 9.5499 | 10.2558 | 10.5011 |
| 7 | 7.5686 | 7.8839 | 8.4277 | 9.1822 | 9.4432 |
| 8 | 6.6983 | 7.0301 | 7.6105 | 8.4117 | 8.6871 |
| 9 | 2.6219 | 6.3787 | 6.9948 | 7.8393 | 8.1278 |
| 10 | 2.5746 | 5.8683 | 6.5186 | 7.4026 | 7.7027 |
| R/a | a/b = 0.5 | a/b = 0.75 | a/b = 1 | a/b = 1.5 | a/b = 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 47.6987 | 48.3535 | 48.9447 | 49.8156 | 50.4172 |
| 2 | 25.1170 | 25.2201 | 25.3267 | 25.5626 | 25.9090 |
| 3 | 16.9310 | 16.9833 | 17.0531 | 17.2818 | 17.7252 |
| 4 | 12.7690 | 12.8155 | 12.8881 | 13.1627 | 13.7259 |
| 5 | 10.2602 | 10.3104 | 10.3938 | 10.7236 | 11.4034 |
| 6 | 8.5872 | 8.6438 | 8.7403 | 9.1263 | 9.9146 |
| 7 | 7.3943 | 7.4584 | 7.5686 | 8.0095 | 8.8965 |
| 8 | 6.5025 | 6.5743 | 6.6983 | 7.1919 | 8.1678 |
| 9 | 5.8117 | 5.8914 | 6.0291 | 6.5726 | 7.6279 |
| 10 | 5.2618 | 5.3494 | 5.5004 | 6.0909 | 7.2169 |
| R/a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48.9437 | 48.9457 | 49.0792 | 49.3528 | 49.3628 |
| 2 | 25.3247 | 25.3288 | 25.6047 | 26.1739 | 26.1918 |
| 3 | 17.0500 | 17.0562 | 17.4689 | 18.3090 | 18.3350 |
| 4 | 12.8840 | 12.8922 | 13.4361 | 14.5187 | 14.5518 |
| 5 | 10.3887 | 10.3989 | 11.0674 | 12.3634 | 12.4024 |
| 6 | 8.7342 | 8.7463 | 9.5324 | 11.0130 | 11.0568 |
| 7 | 7.5615 | 7.5756 | 8.4716 | 10.1104 | 10.1582 |
| 8 | 6.6904 | 6.7062 | 7.7046 | 9.4781 | 9.5291 |
| 9 | 6.0202 | 6.0379 | 7.1307 | 9.0186 | 9.0722 |
| 10 | 5.4907 | 5.5100 | 6.6899 | 8.6749 | 8.7306 |
| Maximum Values | a/h = 75 | a/h = 60 | a/h = 50 | a/h = 40 | a/h = 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1866 | 4.5001 | 3.9020 | 3.1534 | 1.7250 | |
| 2.2997 | 1.7296 | 1.3653 | 1.1890 | 0.7686 |
| Maximum Values | hc/ht = 2 | hc/ht = 6 | hc/ht = 8 | hc/ht = 10 | hc/ht = 20 | hc/ht = 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4284 | 2.3267 | 2.2499 | 2.1578 | 2.0313 | 1.9787 | |
| 1.1921 | 1.8455 | 1.9861 | 1.990 | 2.1182 | 2.1605 | |
| 5.1472 | 4.8345 | 5.0843 | 5.4432 | 6.9771 | 8.6697 | |
| 1.1221 | 1.4232 | 1.4658 | 1.4525 | 1.4479 | 1.4879 |
| Maximum Values | a/b = 0.5 | a/b = 0.75 | a/b = 1 | a/b = 1.5 | a/b = 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1051 | 3.5580 | 3.9020 | 3.6051 | 3.0260 | |
| 1.0248 | 1.2536 | 1.3653 | 1.3871 | 1.1701 |
| Maximum Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.9352 | 3.9352 | 3.0341 | 2.9070 | 2.9059 | |
| 1.3658 | 1.3658 | 1.4354 | 1.3657 | 1.3662 |
| Maximum Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.9020 | 3.8837 | 3.8403 | 3.8318 | 3.7942 | |
| 1.3653 | 1.2962 | 1.1985 | 1.1339 | 1.0871 |
| Mass Density of the Core Layer | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The mass ratio () | 65.21 | 71.73 | 82.60 | 93.44 | 100 |
| Reduced mass () | 34.79 | 28.27 | 17.40 | 6.56 | 0 |
| Maximum Values | Ec = 8 GPa | Ec = 9 GPa | Ec = 10 GPa | Ec = 12 GPa | Ec = 12 GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.9020 | 3.7494 | 3.5895 | 3.4252 | 3.3031 | |
| 1.3653 | 1.3375 | 1.2998 | 1.2841 | 1.2792 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.-N.; Canh, T.N.; Thanh, T.T.; Ke, T.V.; Phan, V.-D.; Thom, D.V. Finite Element Modelling of a Composite Shell with Shear Connectors. Symmetry 2019, 11, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040527
Nguyen H-N, Canh TN, Thanh TT, Ke TV, Phan V-D, Thom DV. Finite Element Modelling of a Composite Shell with Shear Connectors. Symmetry. 2019; 11(4):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040527
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Hoang-Nam, Tran Ngoc Canh, Tran Trung Thanh, Tran Van Ke, Van-Duc Phan, and Do Van Thom. 2019. "Finite Element Modelling of a Composite Shell with Shear Connectors" Symmetry 11, no. 4: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040527
APA StyleNguyen, H.-N., Canh, T. N., Thanh, T. T., Ke, T. V., Phan, V.-D., & Thom, D. V. (2019). Finite Element Modelling of a Composite Shell with Shear Connectors. Symmetry, 11(4), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040527





