Abstract
The development of promising magnetic nanocatalysts is one of the key research topics in the field of catalysis. This is because of their versatile surface physicochemical, magnetic, and size-dependent catalytic properties. Herein, an optimization strategy for the synthesis of high-value fuel grade chemicals from hydro-deoxygenation of biomass-derived furfural and vanillin using a nanostructured magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst, synthesized by a facile one-pot procedure, was presented. Accordingly, effects of calcination temperature from 400, 500, 600 to 700 °C on the structure-activity properties of the magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst was systematically studied. The magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 500 °C exhibited the best catalytic performance, giving full conversions of vanillin and furfural, with good selectivity of 63 and 59% to cyclohexane and n-pentane (fuel grade chemicals), respectively. The prowess of this catalyst was attributed to its abundant acid properties in addendum to high BET surface area.
1. Introduction
Valorization of lignocellulosic biomass and its derived compounds into fuels and chemicals is a key research topic of the 21st century in view of finding sustainable alternatives to fossil fuel-derived products. Lignocellulosic biomass is abundantly produced via photosynthesis by means of water, sunlight, and atmospheric CO2. Hence, in addition to providing alternative fuels and chemicals, promising valorization of biomass could assist in reducing the net emissions of CO2 through the interplay chemistry of biorefinery and photosynthesis processes, which require economically viable processing methods [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts play a critical role in biomass processing towards high-value chemicals. However, efficient catalyst recovery/reusability remains a great challenge, especially in homogeneous catalysis in which both reactants and catalysts are in the same phase, mostly liquid phase. Although filtration or centrifugation are used for the recovery of heterogeneous catalysts (typically solids), these post-reaction steps are time-consuming, uneconomical, and generates huge amounts of solvent waste. In this context, the application of magnetically recoverable catalysts in biomass valorization would be a promising strategy as they not only enable the efficient catalyst recovery using external magnets, but also exhibit reasonably good catalytic performance because of their unique nanoscale properties [7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been widely used as the catalyst supports as well as the catalytic active components in many chemical reactions, such as oxidation, C−C and C−X (X = N, Cl, S, and O) coupling, and hydroprocessing [14,15,16]. However, relatively less attention has been paid towards the catalytic application of MNPs in biomass valorization reactions. This is because biomass valorization involves complex reactions, and, thus, understanding the structure-activity properties of MNPs-based catalysts is quite difficult and has not been investigated before. Although structure–activity relationships were proven for non-magnetic nanocatalysts, so far it has been for non-hydroprocessing reactions [17,18,19,20]. Therefore, understanding the structure-activity capability of MNPs-based catalysts for the hydrodeoxygenation reaction is necessary, especially for the production of fuel grade molecules from biomass-derived compounds.
In view of the above opportunities, the present work has been focused on modifying the properties of a magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst, synthesized by using a facile one-pot strategy. The effect of calcination temperature from 400 to 700 °C on the magnetic, textural, acid, and catalytic properties of the developed magnetic catalyst was thoroughly investigated. The catalytic efficiency of magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts was tested for hydro-deoxygenation of two biomass-derived compounds, such as furfural (hemicellulose-derived compound) and vanillin (lignin-derived compound). A handful of physicochemical characterization techniques were employed to obtain a clear insight into the textural, acid, and magnetic properties of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts. In this work, we mainly focused on achieving improved yields of saturated hydrocarbons from furfural and vanillin because saturated hydrocarbons can be used as potential fuel grade chemicals. Possible reaction pathways were proposed for the hydro-deoxygenation of furfural and vanillin over the magnetic nanocatalyst.
2. Experimental
2.1. Catalyst Preparation and Heat Treatments
A magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst was prepared similarly to the method reported in the literature [5]. In a typical heat treatment experiment, 2 g of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 was placed in a P300 Nabertherm furnace coupled with a temperature controller. Heat treatments were conducted at set point temperature (SPTn; n = 1, 2, 3 & 4), i.e., SPT1 = 400 °C, SPT2 = 500 °C, SPT3 = 600 °C, and SPT4 = 700 °C under controlled temperature ramping of 1 °C/min starting from room temperature (RT). During heat treatments, where a ±T °C error drift was observed from the RT ~28 °C, the conversion factor t1 = T°Ramp/(SPTn − RT) was used so that 1 °C/min ramping is always maintained for the heat flow across the catalyst material under a static environment (t1 = ramping time). However, for RT ≠ 28 °C, SPTn is inserted together with the T°Ramp = 1 °C/min to compute t1.
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
N2 adsorption–desorption studies were carried out for the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst on Micromeritics TriStar II 3020 adsorption apparatus using the ASTM D 3663-03 test method. This was followed by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) on XRD Bruker D8 advance instrument. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) analysis of the 400 °C treated Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst was also performed on a JEOL JEM-3010. The magnetic properties of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts were measured using a Lakeshore 7400 series vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), coupled with an electromagnet field sweeping from −10 kOe to +10 kOe at room temperature. The NH3-TPD analysis of the catalysts was done on TPDRO 1100 series equipped with a TCD detector. The pyridine adsorption FTIR analysis of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts was done on a Bruker FTIR IFS 66/S instrument.
2.3. Catalytic Activity Studies
The catalytic performance of magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 nanocatalysts was investigated for the hydro-deoxygenation of furfural and vanillin in an automated 100 mL (42 mm ID) capacity autoclave reactor made of Hast-alloy C 276 material. Activated Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst amounting to 60 mg was introduced in 20% (v/v) furfural or 0.3 g vanillin reaction mixture from a catalyst bulb in heptane and heptane:H2O (95:5) solvents, respectively. The reaction was performed at 250 °C and 90 H2 bar for 4 h reaction time. After completion of the reaction, an Agilent 6890N with 5973 MSD analyzed the reaction mixture and further quantitative analysis was performed on an Agilent 6890N GC-FID with DB-wax column.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Temperature on Textural Properties of Fe(NiFe)O4−SiO2 Catalyst
Figure 1a shows XRD patterns of magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 nanocatalyst treated at various temperatures ranging from 400 °C, 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C. The noticed major reflections at 2θ values represented by 35.64°, 43.49°, 53.81°, 57.32°, and 63.11°, are assigned to Fe3O4 phase [21,22]. The average crystallite size of Fe3O4, estimated using Scherrer equation [21,22], increased with the increase of heat treatment from 400 to 600 °C and then decreased at 700 °C. The estimated average crystallite sizes for the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst were ~12.55 nm, ~14.53 nm, ~19.80 nm, and ~13.55 nm for 400 °C, 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C heat treatments, respectively. These values, irrespective of the temperature treatment, indicated that all catalysts are still in the super-paramagnetic domain as their crystallite sizes are below 20 nm [23,24]. High-resolution TEM images of the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 400 °C are shown in Figure 1b. Magnetic material exhibits crystalline phases and irregularly shaped particles in the nanoscale range (~8–23 nm). The estimated d-spacing (0.297 nm) corresponds to a Fe3O4 phase, in line with the XRD results (Figure 1a). N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts are shown in Figure 1c. The Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst treated at 400 °C exhibits type IV isotherm with a H3-type hysteresis loop, revealing the presence of slit-shaped pores (Figure 1c). In contrast, the H1-type hysteresis loop was noticed for 500, 600, and 700 °C treated Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts, indicating the formation of well-defined mesopores [25]. The hysteresis loop of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 material shifts to higher relative pressures with the increase of heat treatment from 400 to 500 °C and, then, there was no much difference in the shape of the hysteresis loop up to 700 °C. The shifting of the hysteresis loop towards higher relative pressures showed the formation of larger pores in the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst. The BET surface area values were 61.05 m2/g, 57.03 m2/g and 56.5 m2/g for 400 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C calcined Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts, respectively (Figure 1d). However, a superior BET surface area of ~259 m2/g was found for the 500 °C calcined Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst [5]. This suggested that the specific surface area was maximized for 500 °C calcined sample in order to compensate for surface atom energetics in contrast to 400, 600, and 700 °C calcined samples. Their BET surface areas were minimized to compensate for surface atom energetics. The pore volume and pore size of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts were found to be in the range of 0.21–0.9 cm3/g and 6.8–10.9 nm, respectively (Figure 1d).
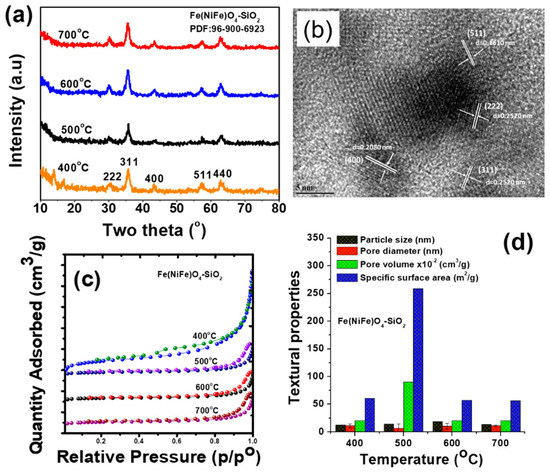
Figure 1.
Physicochemical properties of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts: (a) powder XRD patterns, (b) TEM image of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 calcined at 400 °C, (c) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, and (d) textural properties.
3.2. Effect of Calcination Temperature on Acid Properties of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 Catalysts
Figure 2 shows NH3-TPD and pyridine FT-IR profiles of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 magnetic catalysts. According to Figure 2a, the temperature at which NH3 molecules are desorbed from the catalyst surface reveals the acid strength of the catalysts. Generally, the peaks that was observed at <200 °C, 300–500 °C range and >500 °C can be assigned to NH3 molecules desorbed from surface weak, medium, and strong acid sites, respectively [25]. A higher intensity peak corresponding to strong acid sites was noticed at 554, 556, 552, and 554 °C for the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 400, 500, 600, and 700 °C, respectively (Figure 2a). Medium strength acid site peaks were noticed at 487, 485, 487, and 489 °C for the same range of temperature treatments (Figure 2a). Weak acid site peaks were also noticed at 152, 158, 146, and 142 °C for the same range of temperature treatments. These observations indicated that irrespective of the temperature treatment within the range of 400 °C to 700 °C, the catalyst contains weak, medium and strong acid sites on its surface. Additionally, pyridine adsorbed FT-IR studies reveal the presence of both Brönsted and Lewis acid sites on the catalyst surface (Figure 2b). The Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 700 °C exhibited several peaks due to strong Lewis acidic site-bonded pyridine at 1437 cm−1, weak Lewis acidic site-bonded pyridine at 1580 cm−1 and pyridinium ion on Brönsted acid sites at 1645 cm−1 as well as trivial peaks due to hydrogen bonded pyridine at 1597 cm−1. For the catalyst calcined at 600 °C, very low-intensity peaks were observed, corresponding to strong Lewis acidic site-bonded pyridine at 1439 cm−1 and pyridinium ion on Brönsted acidic sites at 1655 cm−1. The peak at 1482 cm−1 can be assigned to pyridine associated with both Brönsted and Lewis acid sites, whereas the peak at 1581 cm−1 is assigned to weak Lewis acidic site-bonded pyridine and the peak at 1437 cm−1 corresponds to strong Lewis acidic site-bonded pyridine for Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (calcined at 500 °C). The catalyst calcined at 400 °C exhibited very low-intensity peaks at 1439 cm−1 for strong Lewis acidic site-bonded pyridine and 1655 cm−1 for pyridinium ion on Brönsted acid sites. These observations are in line with previous reports [26,27,28]. Therefore, the developed magnetic catalysts exhibited considerable amounts of all types of acidic sites, which could play a key role in hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived compounds as discussed in the catalytic activity part.
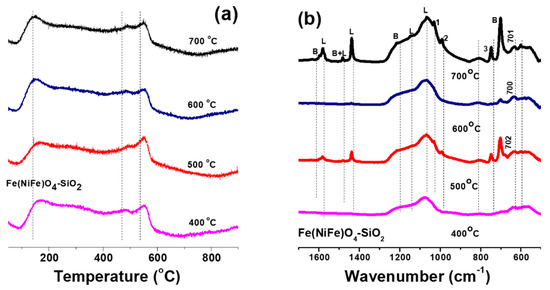
Figure 2.
Surface acidity analysis of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts: (a) NH3-TPD profiles and (b) pyridine adsorption FT-IR profiles.
3.3. Effect of Calcination Temperature on Magnetic Properties of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 Catalyst
The correlation of magnetic properties (magnetization, magnetic remanence, and coercivity) of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts with the calcination temperature is shown in Figure 3. Therein, the results revealed that all the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts exhibit considerable magnetization: 35.11 emu/g (700 °C), 32.75 emu/g (600 °C), 38.65 emu/g (500 °C), and 32.91 emu/g (400 °C), supporting their promising applications for facile catalyst recovery. On the other hand, lower coercivity and remanence values were found in the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst at all heat treatments in comparison to the magnetization.
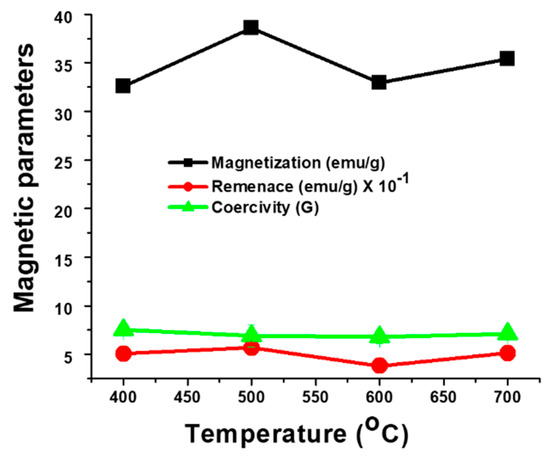
Figure 3.
Distribution of magnetic parameters (magnetization, magnetic remanence, and coercivity) for Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts.
3.4. Activity Studies of Magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 Catalyst
3.4.1. Hydrodeoxygenation of Vanillin
The catalytic efficiency of heat-treated magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts was studied for hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of vanillin and furfural at 250 °C and 90 H2 bar for 4 h. The main products in the HDO of vanillin were cyclohexane, cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone, phenol, 2-methoxyphenol, and 3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methoxyphenol (Table 1). Vanillin conversion was found to be 100% for all the calcined catalysts. In contrast, calcination temperature showed a noticeable effect on the catalyst’s performance in product selectivity. For the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (400 °C) catalyst, a high selectivity of vanillin HDO to cyclohexanone (~56%) was established, whereas only a 21% cyclohexane selectivity was achieved. Similarly, the catalyst treated at a higher temperature showed low selectivity to cyclohexanone, while the selectivity of cyclohexane was increased: Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (500 °C) = 63%, Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (600 °C) = 54%, and Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (700 °C) = 53%. In addition, considerable amounts of cyclohexanol and 2-methoxyphenol are formed over the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst at all calcination temperatures. Despite the calcination temperature applied, negligible amounts of phenol and 3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methoxyphenol were observed. In Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (500 °C) the catalyst showed high selectivity to cyclohexane (Table 1). These results are in accordance to the explanation given in Section 3.4.2 and Section 3.5 and to the fact that acidity and different acid sites of the catalyst can improve the cracking steps through dehydration, in line with the literature reports [29,30]. In addition, the catalyst calcined at 500 °C showed good reusability for at least four cycles (Figure 4).

Table 1.
Product distribution in HDO of vanillin over Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts at 250 °C and 90 bar H2 for 4 h.
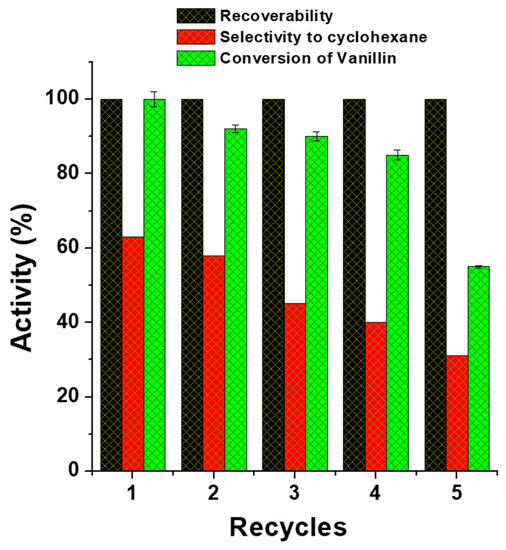
Figure 4.
Recovery and reusability of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts calcined at 500 °C in hydrodeoxygenation of vanillin at 250 °C and 90 bar H2 for 4 h.
3.4.2. Hydrodeoxygenation of Furfural
Furfural hydrodeoxygenation results reveal (Table 2) that the calcination temperature has a negligible influence towards furfural conversion. The furfural conversion was found to be 100% for all the catalysts. Three products, namely furfuryl alcohol, tetrahydrofuran, and n-pentane were formed in this reaction. The performance of magnetic catalysts and the effect of calcination temperature in hydrodeoxygenation of furfural are evaluated based on the selectivity of saturated hydrocarbon, i.e., n-pentane, which does not have any oxygen-containing groups. Among the products formed, very low selectivity of furfuryl alcohol was achieved for all the catalysts. The Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (700 °C) shows a high selectivity of tetrahydrofuran, i.e., 58%. Among the catalysts tested, Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (500 °C) catalyst showed 100% furfural conversion and 59% n-pentane selectivity. Hydrodeoxygenation is a typical acid-site driven reaction in which acid sites initiate the removal of oxygen via dehydration and the hydrogenation step is promoted by active phase Ni metal sites. It was obvious that Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (500 °C) showed the best catalytic performance in the HDO of furfural and vanillin. As shown in Figure 2, despite the calcination temperature employed, the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst exhibited a high-intensity peak at around 550 °C, indicating the presence of more number of strong acid sites. In addition, the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 500 °C showed superior BET surface area of ~259 m2/g compared to all the other catalysts. The catalytic materials with a high BET surface area can contain uniform dispersion of catalytic active phase species. Therefore, the high catalytic performance of the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 500 °C is likely to be due to the synergistic effect of its acid properties and larger BET surface area. Moreover, the catalyst calcined at 500 °C showed good reusability up to five cycles as shown in Figure 5.

Table 2.
Products distribution in hydrodeoxygenation of furfural over Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts, conducted at 250 °C and 90 bar H2 for 4 h.
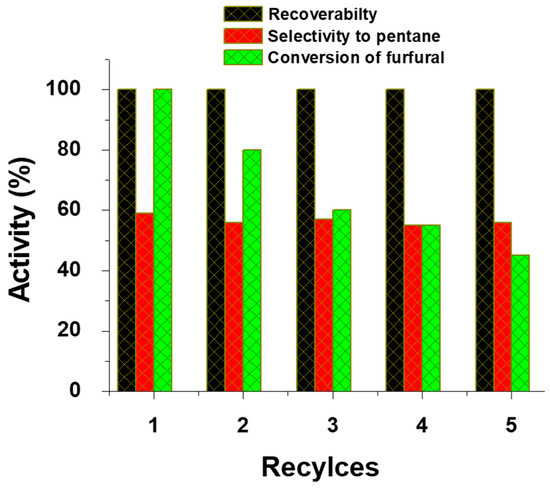
Figure 5.
Recovery and reusability of the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst calcined at 500 °C in hydrodeoxygenation of furfural at 250 °C and 90 bar H2 for 4 h.
3.5. Possible Reaction Pathways
Scheme 1 and 2 show the possible reaction pathways for the HDO of vanillin and furfural at 250 °C and 90 bar H2, respectively. The active metal Ni and acid properties of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts could play a key role in the production of fuel grade chemicals from the HDO of vanillin and furfural. As shown in Scheme 1, transformation of vanillin can be initiated with four potential C-O bonds having different bond dissociation energies (BDEs): C(sp3)–OAr (~262–276 kJ/mol), C(sp2)–OMe (~409–421 kJ/mol), C(sp2)–OH (~466 kJ/mol), and C(Sp2)–O (~732 kJ/mol). As shown earlier, the magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst surface can possess non-hydrogen spillover attributes [5]. Therefore, on the basis of BDEs over the catalyst surface, bond cleavage likely follows the order during vanillin HDO: C(sp3)–OAr < C(sp2)–OMe < C(sp2)–OH < C(Sp2)–O. Most probably, the bond cleavage of vanillin will follow the direct C–O cleavage with the attack of hydrogen at the ipso position (–OH) and at the meso (–OCH3) position followed by hydrogenation on the metal site at the ortho position and then dehydration step over acid sites. This reaction pathway is initiated by tautomerization (Scheme 1). Accordingly, the cyclohexane is formed through a series of reactions from vanillin. By implication, phenol is transformed to phenoxide ion in the presence of acid sites. The phenoxide species can diffuse towards the Ni metal active phase to attack electrophiles, such as H+ obtained from the dissociation of H2 over the metal active phase in the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst, giving cyclohexanone product [31]. In continuation, cyclohexanone is then directly hydrogenated to form cyclohexanol. The magnetic attributes of the catalysts then induce electron mobility that can enhance the adsorption of cyclohexanol on the catalyst acid sites at the OH terminal, giving cyclohexene through dehydration step. Finally, the cyclohexene is hydrogenated to yield cyclohexane.
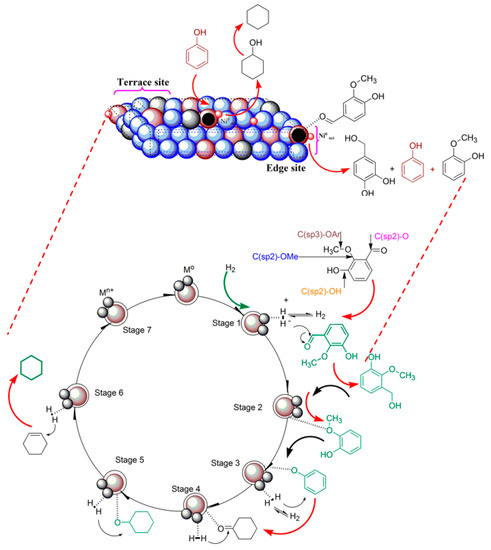
Scheme 1.
Possible reaction pathway for HDO of vanillin over Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts.
As observed in the HDO of vanillin, similar trends are also possible for the HDO of furfural by considering the fact that the electron density distribution around the carbonyl functionality stimulates the furfural molecules for hydrogen attack and subsequent decarbonylation at 250 °C and 90 bar H2 conditions. As shown in Scheme 2, adsorption and reaction steps initiating the formation of tetrahydrofuran from furfural was due to the presence of adequate acidic sites, active metal phase, and magnetic functions of the catalysts. The formed tetrahydrofuran is directly hydrogenated over the metal active phase in Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst, giving furfuryl alcohol. Finally, pentane is formed via the ring opening of furfuryl alcohol and the subsequent dehydration step.
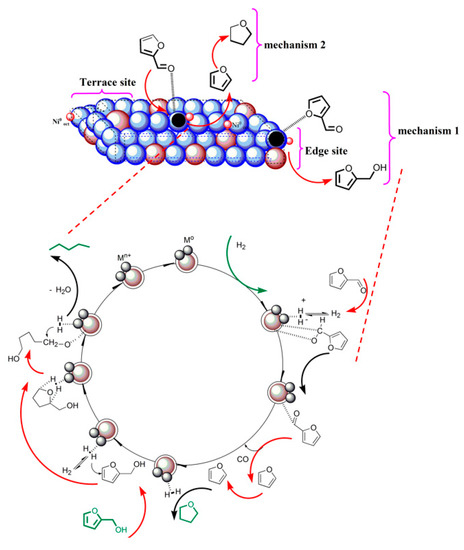
Scheme 2.
Possible reaction pathway for hydro-deoxygenation of furfural over Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalysts.
4. Conclusions
This study rationalized a systematic heat treatment of a magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst for vanillin and furfural HDO to produce fuel grade chemicals. The magnetic Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst is suitable for hydrodeoxygenation reactions due to the presence of optimized amounts of metal (Ni) and acid active sites. The 500 °C was found to be a suitable calcination temperature for treating the Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 catalyst for hydro-processing reactions, evidenced from the selectivity of 63% cyclohexane and 59% n-pentane fuel grade hydrocarbons from HDO of vanillin and furfural at 250 °C and 90 H2 bar for 4 h, respectively. The catalytic efficiency of Fe(NiFe)O4-SiO2 (500 °C) was due to the optimized acid sites, superior surface area, and unique magnetization property.
Author Contributions
A.H. has conducted the experiments and the manuscript was written through the contribution of all authors.
Funding
This work was supported by the High Impact Research (HIR) grant number F-00032, Universiti Malaya (UM) and the National Research Institute for Chemical Technology (NARICT), Nigeria through the collaboration on renewable energy.
Acknowledgments
The authors dedicate this study to Late Sharifah Bee Abd Hamid, the founder of Nanotechnology and Catalysis Research Center (NANOCAT), Malaysia. The authors also appreciate the initiative of Idris M. Bugaje on the collaboration with NANOCAT.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Halilu, A. Is there a realistic solution to upgrading bio-oil to fuel and chemicals? Inform 2017, 28, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Zhong, R.; van den Bosch, S.; Coman, S.M.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Sels, B.F. Functionalised heterogeneous catalysts for sustainable biomass valorisation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8349–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambursa, M.M.; Sudarsanam, P.; Voon, L.H.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Bhargava, S.K. Bimetallic Cu-Ni catalysts supported on MCM-41 and Ti-MCM-41 porous materials for hydrodeoxygenation of lignin model compound into transportation fuels. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 162, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambursa, M.M.; Ali, T.H.; Lee, H.V.; Sudarsanam, P.; Bhargava, S.K.; Hamid, S.B.A. Hydrodeoxygenation of dibenzofuran to bicyclic hydrocarbons using bimetallic Cu–Ni catalysts supported on metal oxides. Fuel 2016, 180, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halilu, A.; Ali, T.H.; Atta, A.Y.; Sudarsanam, P.; Bhargava, S.K.; Hamid, S.B.A. Highly Selective Hydrogenation of Biomass-Derived Furfural into Furfuryl Alcohol Using a Novel Magnetic Nanoparticles Catalyst. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 2216–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Peeters, E.; Makshina, E.V.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Sels, B.F. Advances in porous and nanoscale catalysts for viable biomass conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polshettiwar, V.; Luque, R.; Fihri, A.; Zhu, H.; Bouhrara, M.; Basset, J.-M. Magnetically recoverable nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3036–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Wang, L. A recyclable magnetic nanoparticles supported palladium catalyst for the Hiyama reaction of aryltrialkoxysilanes with aryl halides. Catal. Sci. Tech. 2012, 2, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Branco, P.S.; Varma, R.S. Nano-magnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for recyclable catalysts in the development of sustainable methodologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3371–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. Fast-Growing Field of Magnetically Recyclable Nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6949–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Dutta, S.; Sharma, S.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S.; Gawande, M.B. Fe3O4 (iron oxide)-supported nanocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization and applications in coupling reactions. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3184–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Monga, Y.; Zboril, R.; Sharma, R.K. Silica-decorated magnetic nanocomposites for catalytic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 288, 118–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Rathi, A.K.; Branco, P.S.; Nogueira, I.D.; Velhinho, A.; Shrikhande, J.J.; Indulkar, U.U.; Jayaram, R.V.; Ghumman, C.A.A.; Bundaleski, N.; et al. Regio- and Chemoselective Reduction of Nitroarenes and Carbonyl Compounds over Recyclable Magnetic Ferrite–Nickel Nanoparticles (Fe3O4–Ni) by Using Glycerol as a Hydrogen Source. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 12628–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Varma, R.S. Magnetically retrievable catalysts for organic synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, S.; Ramezani, Z. Synthesis of arylphosphonates catalyzed by Pd-imino-Py-[gamma]-Fe2O3 as a new magnetically recyclable heterogeneous catalyst in pure water without requiring any additive. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29237–29244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, S.B.A.; Halilu, A.; Gbadamasi, S.; Hakim, L. Opportunities in Utilization of Lignocellulosic Biomass Oil to Bio-Esters. In Renewable Energy and Sustainable Developments; Al-Douri, Y., Ed.; Scientific & Academic Publishing: Rosemead, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.H.; Putla, S.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Bhargava, S.K. Understanding the role of lanthanide promoters on the structure–activity of nanosized Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalysts in carbon dioxide reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 492, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, K.-i.; Cui, Y.; Buru, C.T.; Li, Z.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Single-Atom-Based Vanadium Oxide Catalysts Supported on Metal–Organic Frameworks: Selective Alcohol Oxidation and Structure–Activity Relationship. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8652–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, M.; Sprick, R.S.; Pearce, D.; Hillman, S.A.; Monti, A.; Guilbert, A.A.; Brownbill, N.J.; Dimitrov, S.; Shi, X.; Blanc, F. Understanding structure-activity relationships in linear polymer photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, B.; Sudarsanam, P.; Amin, M.H.; Bhargava, S.K. Nanoscale Cobalt–Manganese Oxide Catalyst Supported on Shape-Controlled Cerium Oxide: Effect of Nanointerface Configuration on Structural. Redox, and Catalytic Properties. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Hillary, B.; Mallesham, B.; Rao, B.G.; Amin, M.H.; Nafady, A.; Alsalme, A.M.; Reddy, B.M.; Bhargava, S.K. Designing CuOx Nanoparticle-Decorated CeO2 Nanocubes for Catalytic Soot Oxidation: Role of the Nanointerface in the Catalytic Performance of Heterostructured Nanomaterials. Langmuir 2016, 32, 2208–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Hillary, B.; Amin, M.H.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Bhargava, S.K. Structure-activity relationships of nanoscale MnOx/CeO2 heterostructured catalysts for selective oxidation of amines under eco-friendly conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 185, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, R. Influence of particle size on the coercive force of barium ferrite powders. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 1267–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, C.E.; Johansson, C.; Nævestad, A.; Sontum, P.C.; Briley-Sæbø, K.; Fahlvik, A.K. Crystal size and properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) particles. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 15, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistura, G.; Pozzato, A.; Grenci, G.; Bruschi, L.; Tormen, M. Continuous adsorption in highly ordered porous matrices made by nanolithography. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farneth, W.; Gorte, R. Methods for characterizing zeolite acidity. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J.; Lee, D.F. Control of product selectivity for the epoxidation of allyl alcohol by variation of the acidity of the catalyst TS-1. Chem. Commun. 1994, 9, 1095–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiya, S.; Oumi, Y.; Uozumi, T.; Sano, T. Characterization of AlSBA-15 prepared by post-synthesisalumination with trimethylaluminium. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.S.; Srinivas, B.N.; Maity, S.K.; Dhar, G.M.; Rao, T.S.R.P. Origin of Cracking Functionality of Sulfided (Ni) CoMo/SiO2–ZrO2 Catalysts. J. Catal. 2000, 195, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinghua, Z.; Tiejun, W.; Longlong, M.; Chuangzhi, W. Aqueous-phase catalytic process for production of pentane from furfural over nickel-based catalysts. Fuel 2010, 89, 2697–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, P.M.; Grunwaldt, J.-D.; Jensen, P.A.; Jensen, A.D. Screening of Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of Phenol as a Model Compound for Bio-oil. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).