Water-Yield Variability and Its Attribution in the Yellow River Basin of China over Four Decades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
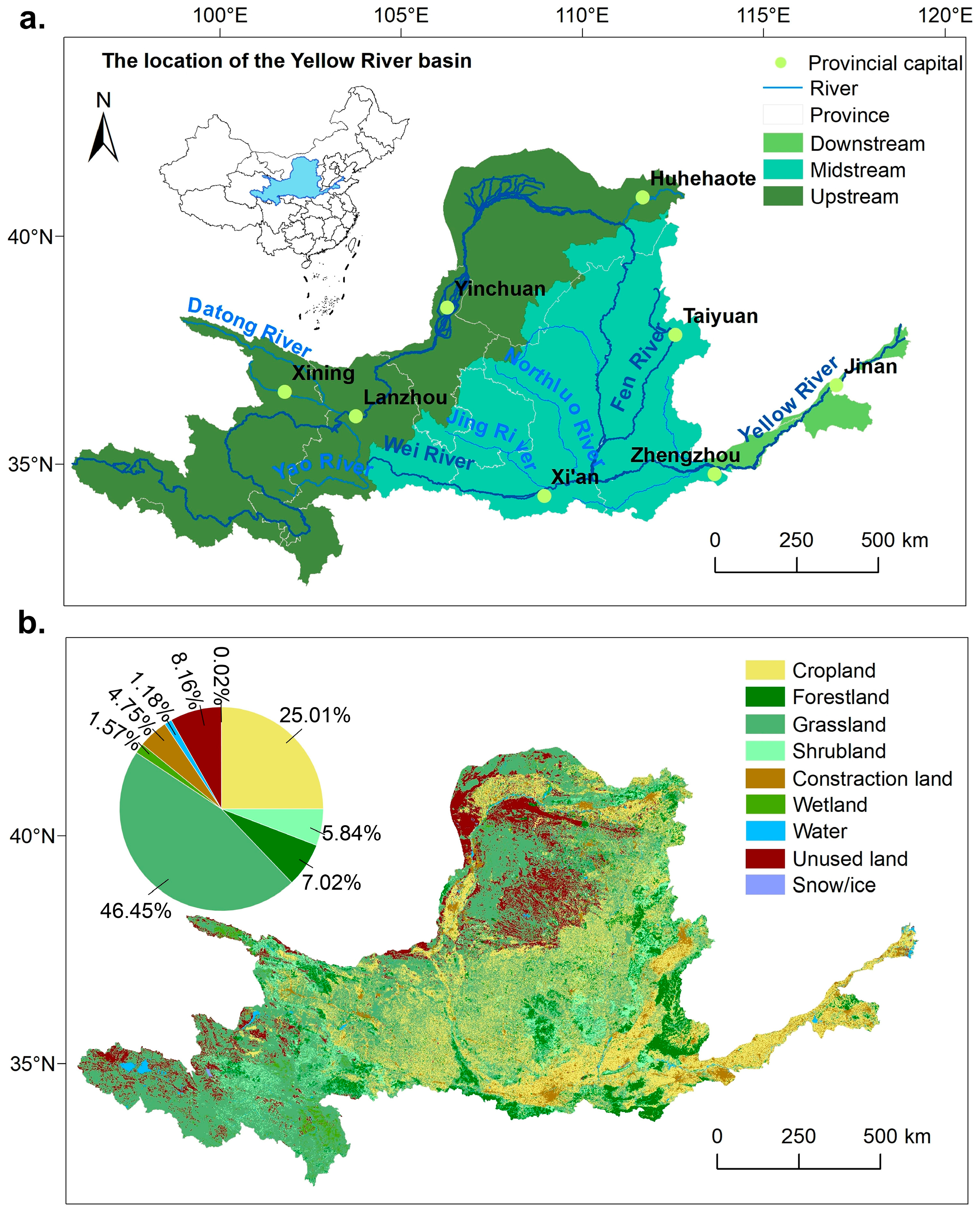
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. InVEST Model Input Data
2.2.2. Grid Datasets of Water Yield for Driving Factors
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. LULC Analysis Method
2.3.2. The InVEST Annual Water Yield Model
2.3.3. Temporal Trend Analysis Method
2.3.4. Spatial Hotspots Detection Method
2.3.5. Attribution Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. LUCC Analysis in the Yellow River Basin
3.2. Analysis of Surface Runoff Changes in the Yellow River Basin
3.2.1. Dynamic of Water Yield in Different LULCs in the Yellow River Basin
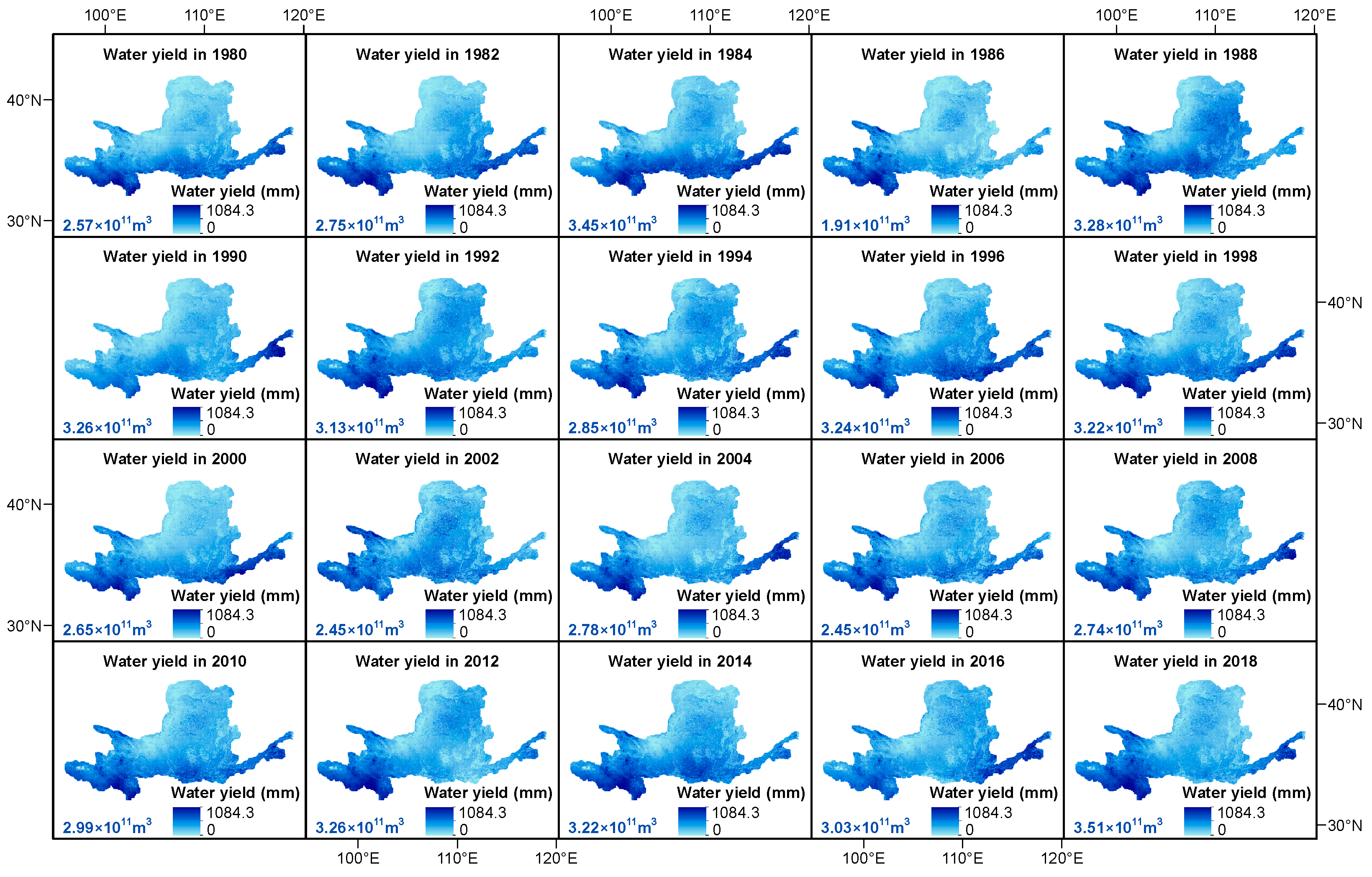
3.2.2. Temporal Variations of Water Yield at the Pixel Scale in the Yellow River Basin
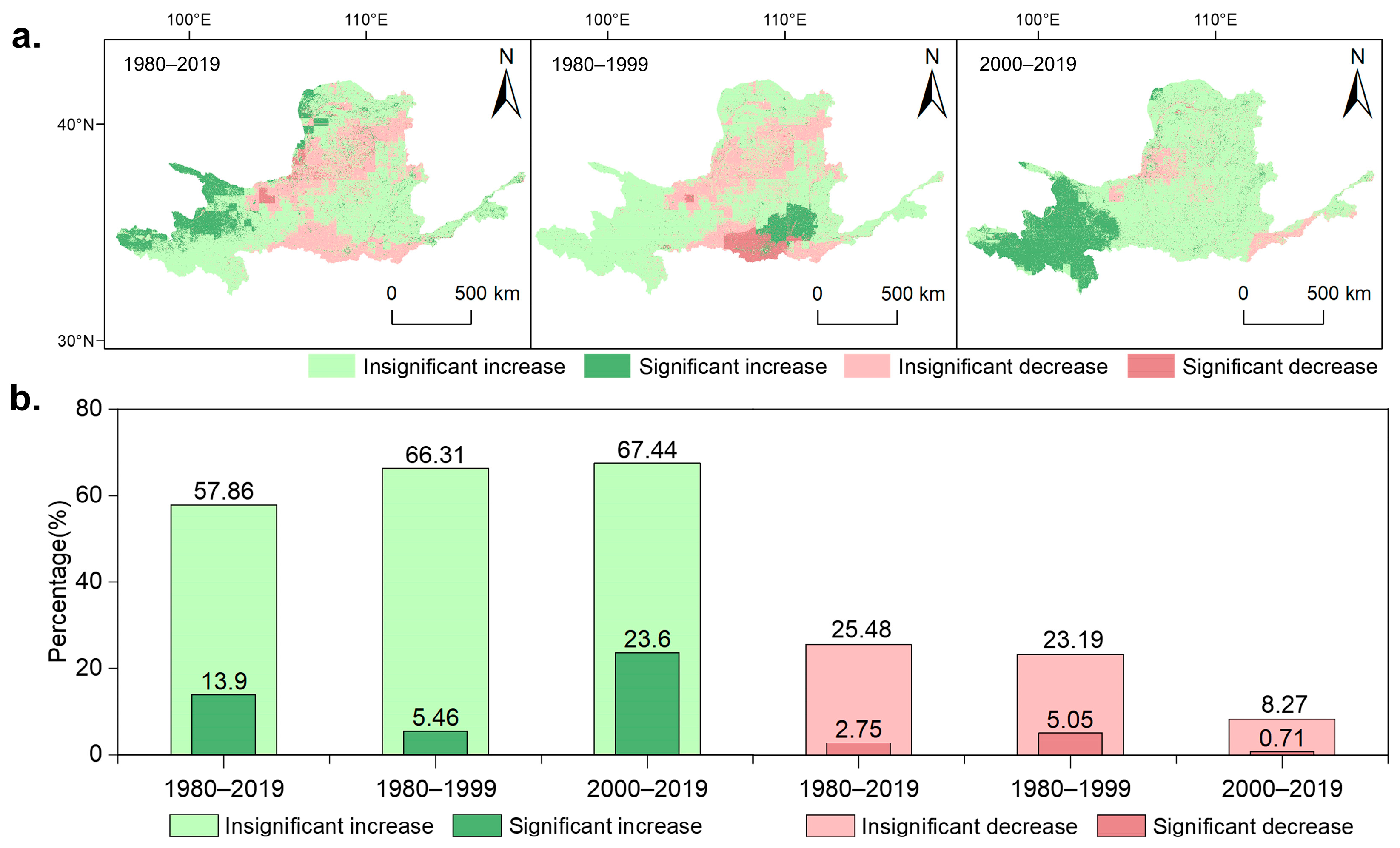
3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity of Water-Yield Changes in the Yellow River Basin
3.4. Driving Factors Influencing Water-Yield Changing Trends in the Yellow River Basin
3.4.1. Global Variable Analysis of Factors Influencing Water-Yield Changing Trends
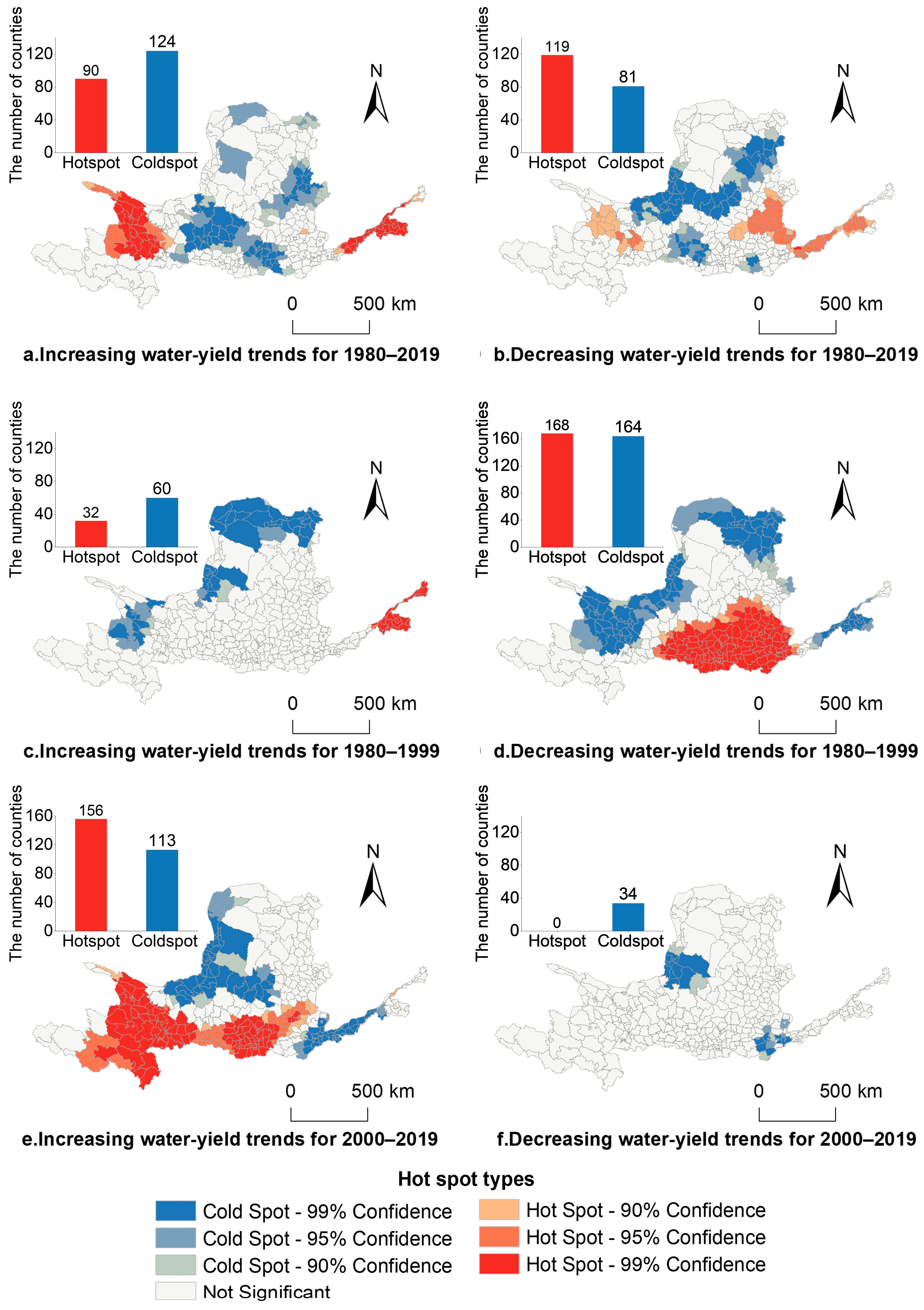
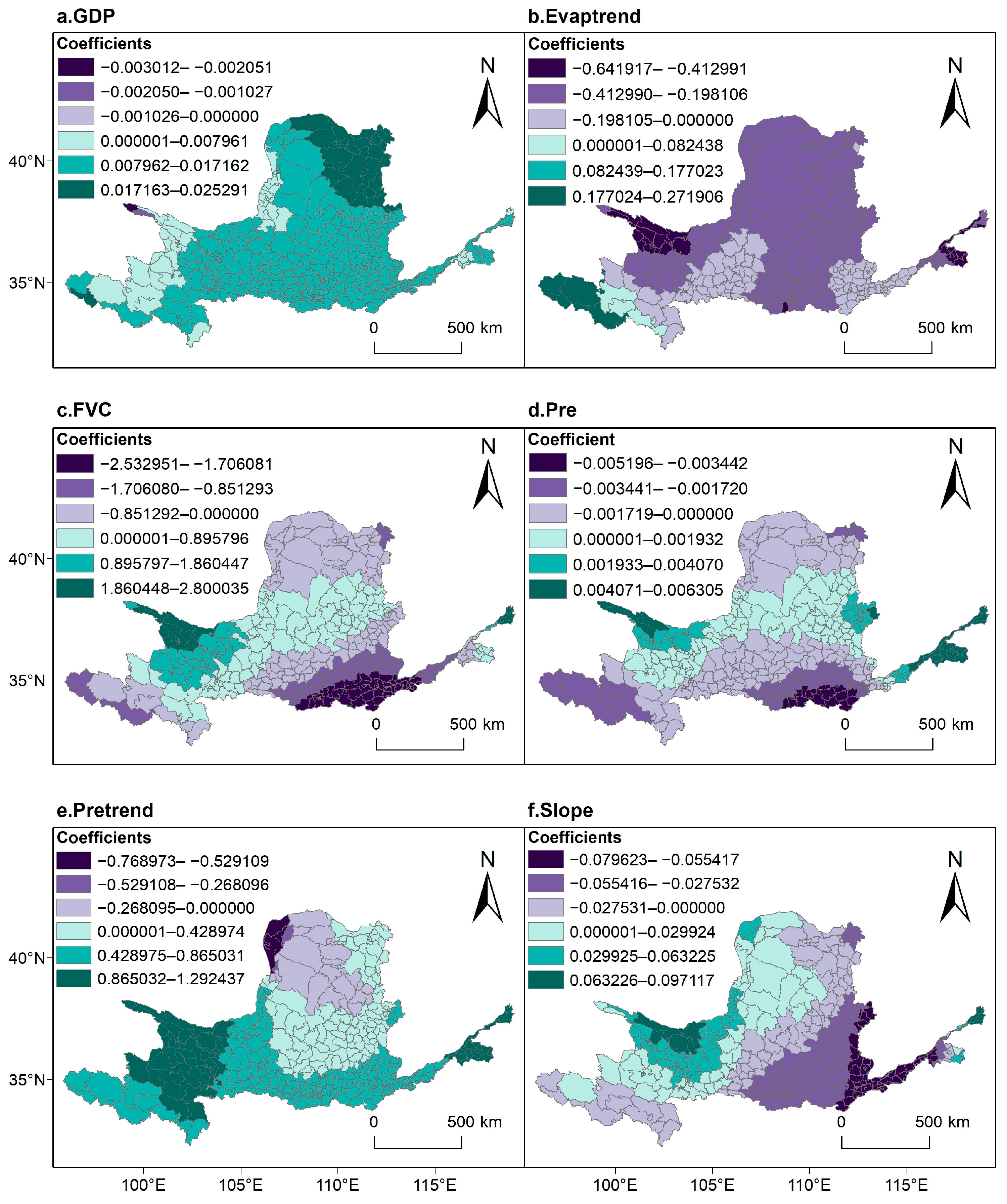
3.4.2. Local Variable Analysis of Water-Yield Change Drivers
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications of the Results
4.2. Uncertainties and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| YRB | Yellow River Basin |
| InVEST | Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Trade-offs |
| LULC | Land use and land cover |
| LUCC | Land use and land cover change |
| LULCs | Land use and land covers |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| GWR | Geographically Weighted Regression |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares |
Appendix A
References
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty Years of Ecosystem Services: How Far Have We Come and How Far Do We Still Need to Go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Zhang, L. Land-Use Change and Ecosystem Services: Concepts, Methods and Progress. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, S.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Dong, S.; Gong, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L. Simulation Study on Water Yield Service Flow Based on the InVEST-Geoda-Gephi Network: A Case Study on Wuyi Mountains, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egoh, B.; Rouget, M.; Reyers, B.; Knight, A.T.; Cowling, R.M.; Van Jaarsveld, A.S.; Welz, A. Integrating Ecosystem Services into Conservation Assessments: A Review. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Davis, K.F.; Rosa, L.; Carr, J.A.; Chiarelli, D.; Dell’Angelo, J.; Gephart, J.; MacDonald, G.K.; Seekell, D.A.; Suweis, S.; et al. The Global Food-Energy-Water Nexus. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 456–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, K.; Fuchs, R.; Rounsevell, M.; Herold, M. Global Land Use Changes are Four Times Greater than Previously Estimated. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.; Fu, B. Understanding the Impacts of Climate and Landuse Change on Water Yield. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Yan, T.; Sun, T. Growing Water Scarcity, Food Security and Government Responses in China. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 14, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; McNulty, S.G.; Vose, J.M. Potential Water Yield Reduction Due to Forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, K.; Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C. Drought and Crop Yield. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Sun, P.; Caldwell, P.V.; Harper, R.; Liu, S.; Sun, G. Trade-off between Watershed Water Yield and Ecosystem Productivity along Elevation Gradients on a Complex Terrain in Southwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessacg, N.; Flaherty, S.; Brandizi, L.; Solman, S.; Pascual, M. Getting Water Right: A Case Study in Water Yield Modelling Based on Precipitation Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 537, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, M.J.; Jiang, W.G.; Hou, P.; Li, Y. Change of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity in Yellow River Watersheds from 2001 to 2010 and Its Climatic Driving Factors Analysis. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2014, 25, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J. Speech at the Symposium on Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development of the Yellow River Basin. China Water Resour. 2019, 20, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, M.M.; Ma, J.; Wu, J.-H.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, H. Sustainable Development in the Yellow River Basin: Issues and Strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, H.; An, Z.; Sun, C.; Trouet, V.; Cai, Q.; Liu, R.; Leavitt, S.W.; Song, Y.; Li, Q. Recent Anthropogenic Curtailing of Yellow River Runoff and Sediment Load is Unprecedented over the Past 500 y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18251–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, B.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhen, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Wei, C.; Yang, L. Spatial–Temporal Evolution Patterns of Soil Erosion in the Yellow River Basin from 1990 to 2015: Impacts of Natural Factors and Land Use Change. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Mahmood, R.; Zheng, Z. Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Regional Climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001–2009. Part I: Observational Evidence. Clim. Change 2015, 129, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, J.W.; Stratford, C.; Sharps, K.; Jones, L.; Ziv, G.; Clarke, D.; Oliver, T.H.; Bullock, J.M. Empirical Validation of the InVEST Water Yield Ecosystem Service Model at a National Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chu, B.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, B.; Liu, S.; Jin, J. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors of Water Yield Services on the Qingzang Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Wood, S.; Guerry, A.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project: Standford, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Che, X.; Jiao, L.; Qin, H.; Wu, J. Impacts of Climate and Land Use/Cover Change on Water Yield Services in the Upper Yellow River Basin in Maqu County. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Qiu, D.; Gao, P.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G. Application of the InVEST Model for Assessing Water Yield and Its Response to Precipitation and Land Use in the Weihe River Basin, China. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Zhang, D.; Tao, W. Climate and Land Use Change Impacts on Water Yield Ecosystem Service in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tao, F.; Hu, J. A Coupled Human-Natural System Analysis of Water Yield in the Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Sato, Y.; Zhu, H. Simulating Spatial Urban Expansion Based on a Physical Process. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Hou, X.; An, Y.; Shen, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Yield Service and Its Response to Urbanisation in the Beiyun River Basin, Beijing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, H.; Lacayo, M.; Liu, J.; Lei, G. Impacts of Land-Use and Land-Cover Changes on Water Yield: A Case Study in Jing-Jin-Ji, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Hasi, E.; Dong, Z. Has the Three Norths Forest Shelterbelt Program Solved the Desertification and Dust Storm Problems in Arid and Semiarid China? J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y. Responses of the Water-Yield Ecosystem Service to Climate and Land Use Change in Sancha River Basin, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 2017, 101, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Xu, R.; Gao, P.; Mu, X. Effect of Vegetation Restoration Type and Topography on Soil Water Storage and Infiltration Capacity in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2024, 241, 108079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Xiang, W.; Ouyang, S.; Hu, Y.; Peng, C. Balancing Water Yield and Water Use Efficiency Between Planted and Natural Forests: A Global Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filoso, S.; Bezerra, M.O.; Weiss, K.C.; Palmer, M.A. Impacts of Forest Restoration on Water Yield: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.A.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Escobedo, F.J.; Cropper, W.P., Jr.; Martin, T.A.; Timilsina, N. Spatially-Explicit Modeling of Multi-Scale Drivers of Aboveground Forest Biomass and Water Yield in Watersheds of the Southeastern United States. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 199, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L. Variation of Precipitation and Temperature in Yellow River Basin during the Last 50 Years. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2012, 33, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, W.; Wei, J.; Wang, L. Water Demand Forecasting and Countermeasures across the Yellow River Basin: Analysis from the Perspective of Water Resources Carrying Capacity. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, L.; Peng, D.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Meng, R.; Xu, X.; Gong, P. Annual 30-m Land Use/Land Cover Maps of China for 1980–2015 from the Integration of AVHRR, MODIS and Landsat Data Using the BFAST Algorithm. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 1390–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 Km Monthly Temperature and Precipitation Dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, S. Spatiotemporal Change and Attribution of Potential Evapotranspiration over China from 1901 to 2100. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 145, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Cao, G.; Samson, E.L.; Zhang, J. Forecasting China’s GDP at the Pixel Level Using Nighttime Lights Time Series and Population Images. GIScience Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haklay, M.; Weber, P. Openstreetmap: User-Generated Street Maps. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2008, 7, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, W.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Y. China Regional 250m Fractional Vegetation Cover Data Set (2000–2022). Natl. Tibet. Plateau Data Cent. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Liu, T.; Yang, B.; et al. Habitat Quality Dynamics in China’s First Group of National Parks in Recent Four Decades: Evidence from Land Use and Land Cover Changes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boithias, L.; Acuña, V.; Vergoñós, L.; Ziv, G.; Marcé, R.; Sabater, S. Assessment of the Water Supply:Demand Ratios in a Mediterranean Basin under Different Global Change Scenarios and Mitigation Alternatives. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M. Water Yield of Xitiaoxi River Basin Based on InVEST Modeling. J. Resour. Ecol. 2012, 3, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Hao, J.; Tian, J.; Li, Z. Revealing Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Water Conservation and Its Drivers: Enlightenment to Water Ecology Protection and Restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Peng, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Tuo, Y. Assessing the Impacts of Climate and Land Use Change on Water Conservation in the Three-River Headstreams Region of China Based on the Integration of the InVEST Model and Machine Learning. Land. 2024, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, W.; Xu, C.; Tao, L.; Xu, X. Integrating the InVEST and SDSM Model for Estimating Water Provision Services in Response to Future Climate Change in Monsoon Basins of South China. Water 2020, 12, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hu, A.; Gan, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Trade-Off and Synergy Relationships in the Western Sichuan Plateau, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B. On the Calculation of the Evaporation from Land Surface. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 1981, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hickel, K.; Dawes, W.; Chiew, F.H.; Western, A.; Briggs, P. A Rational Function Approach for Estimating Mean Annual Evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W02502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, R.J.; Roderick, M.L.; McVicar, T.R. Roots, Storms and Soil Pores: Incorporating Key Ecohydrological Processes into Budyko’s Hydrological Model. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Hou, S.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, C.; Wu, H.; Gao, G.; et al. Unraveling Carbon Stock Dynamics and Their Determinants in China’s Loess Plateau over the Past 40 Years. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Sabnani, C.S.; Kapse, V.S. Hotspot Analysis of Structure Fires in Urban Agglomeration: A Case of Nagpur City, India. Fire 2021, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Croot, P.; Zhang, C. Discovering Hidden Spatial Patterns and Their Associations with Controlling Factors for Potentially Toxic Elements in Topsoil Using Hot Spot Analysis and K-Means Clustering Analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 151, 106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Qi, Q.; Wu, H.; Feng, D.; Zhu, E. Will the Landscape Composition and Socio-Economic Development of Coastal Cities Have an Impact on the Marine Cooling Effect? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, D.; Tsutsumida, N.; Yoshida, T.; Nakaya, T.; Lu, B. Scalable GWR: A Linear-Time Algorithm for Large-Scale Geographically Weighted Regression with Polynomial Kernels. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2020, 111, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, X.; Du, H.; Shi, H. Urban Water Resource Utilization Efficiency in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianhua, L.; Liangchao, H.; Qiting, Z. Evaluation of Harmonious Development of Economy-Population-Resource-Environment in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatyn, S.; Rotenberg, E.; Ramati, E.; Tatarinov, F.; Tas, E.; Yakir, D. Differential Impacts of Land Use and Precipitation on “Ecosystem Water Yield”. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5457–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Mu, X.; Li, R.; Fleskens, L.; Stringer, L.C.; Ritsema, C.J. Co-Evolution of Soil and Water Conservation Policy and Human–Environment Linkages in the Yellow River Basin since 1949. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Gu, C.-J.; Xiao, C. Multiple Scenarios Analysis on Land Use Simulation by Coupling Socioeconomic and Ecological Sustainability in Shanghai, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 95, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Coefficient | t Value | p Value | Relative Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | 2.11 × 10−2 | 17.42 | <2 × 1016 *** | 5.174 × 10−2 |
| Disur | −4.83 × 10−3 | −1.62 | 0.11 | 9.441 × 10−3 |
| Roden | 1.81 × 10−4 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 3.408 × 10−3 |
| Evap | 3.44 × 10−5 | 0.14 | 0.89 | 8.298 × 10−3 |
| Evaptrend | −4.57 × 10−1 | −27.63 | <2 × 10−16 *** | 1.144 × 10−1 |
| FVC | 4.08 × 10−1 | 3.37 | 8.12 × 10−4 *** | 6.695 × 10−3 |
| Pre | 5.43 × 10−4 | 2.74 | 6.48 × 10−3 ** | 2.162 × 10−2 |
| Pretrend | 9.32 × 10−1 | 62.20 | <2 × 10−16 *** | 7.158 × 10−1 |
| Slope | −1.61 × 10−2 | −6.54 | 1.87 × 10−10 *** | 4.427 × 10−2 |
| Persand | 4.02 × 10−3 | 1.61 | 0.11 | 2.433 × 10−2 |
| (Intercept) | −3.74 × 10−1 | −2.07 | 0.04 * | |
| Multiple R2 | 0.92 | |||
| F-statistic | 490.90 | |||
| p-value | <2.2 × 10−16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Chen, X.; Che, Y.; Yang, H.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, T.; Du, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Water-Yield Variability and Its Attribution in the Yellow River Basin of China over Four Decades. Land 2025, 14, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081579
Li L, Chen X, Che Y, Yang H, Du Z, Wu Z, Liu T, Du Z, Li X, Li Y. Water-Yield Variability and Its Attribution in the Yellow River Basin of China over Four Decades. Land. 2025; 14(8):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081579
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Luying, Xin Chen, Yayuan Che, Hao Yang, Ziqiang Du, Zhitao Wu, Tao Liu, Zhenrong Du, Xiangcheng Li, and Yaoyao Li. 2025. "Water-Yield Variability and Its Attribution in the Yellow River Basin of China over Four Decades" Land 14, no. 8: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081579
APA StyleLi, L., Chen, X., Che, Y., Yang, H., Du, Z., Wu, Z., Liu, T., Du, Z., Li, X., & Li, Y. (2025). Water-Yield Variability and Its Attribution in the Yellow River Basin of China over Four Decades. Land, 14(8), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081579








