Comparison between Hyperspectral and Multispectral Retrievals of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Rivers
Abstract
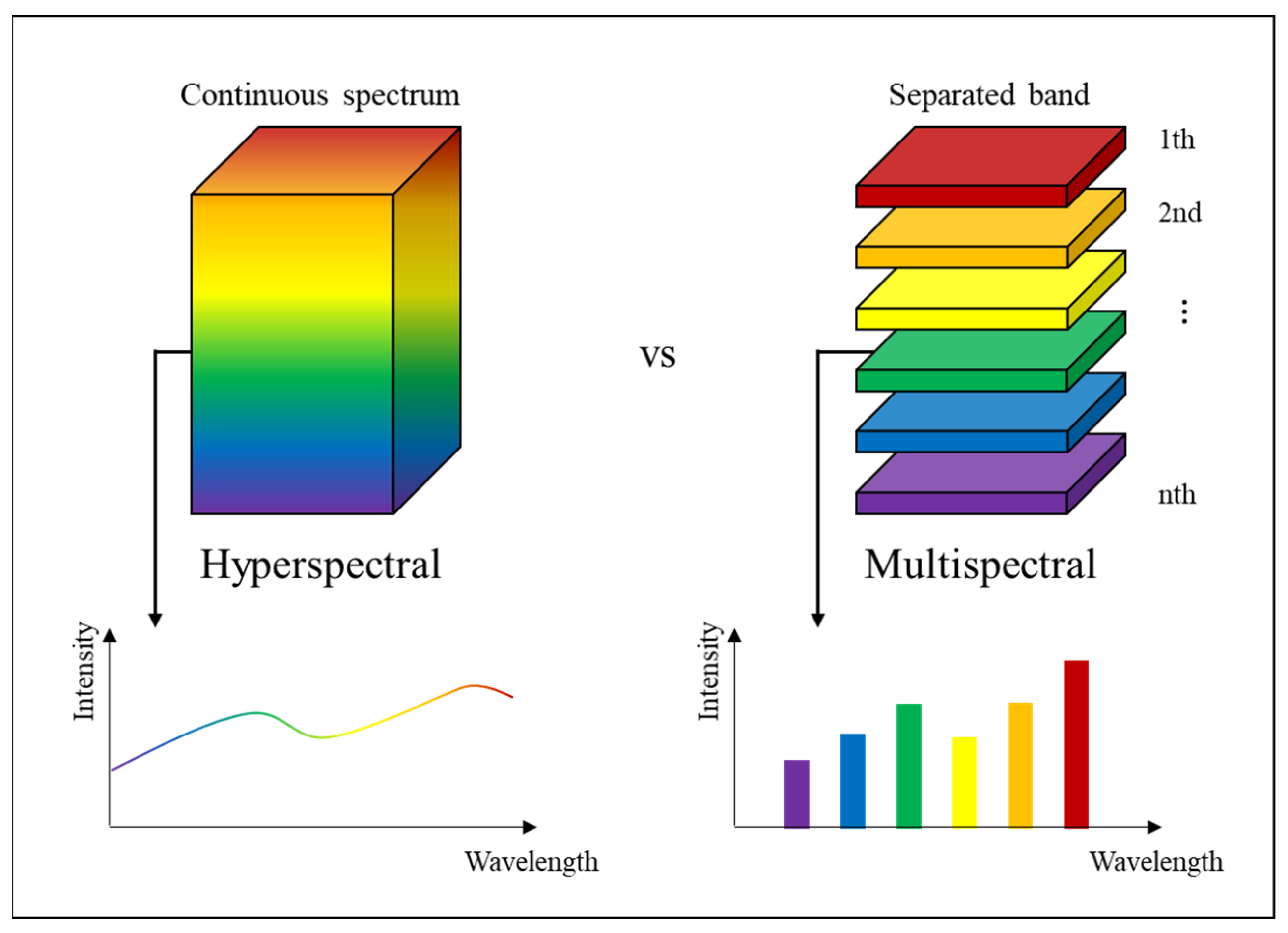
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment
2.2. Optimal Band Ratio Algorithm
3. Results and Discussion
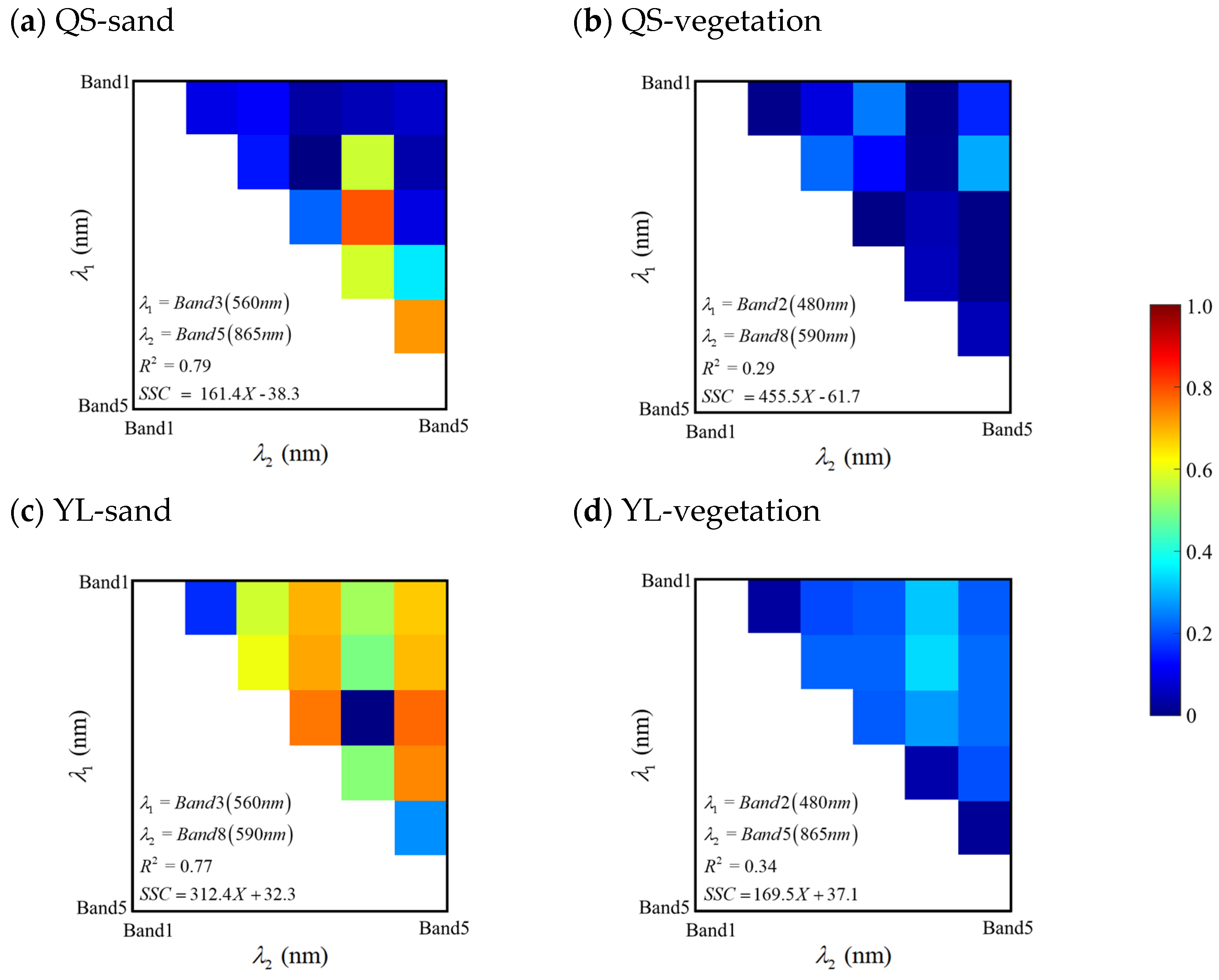
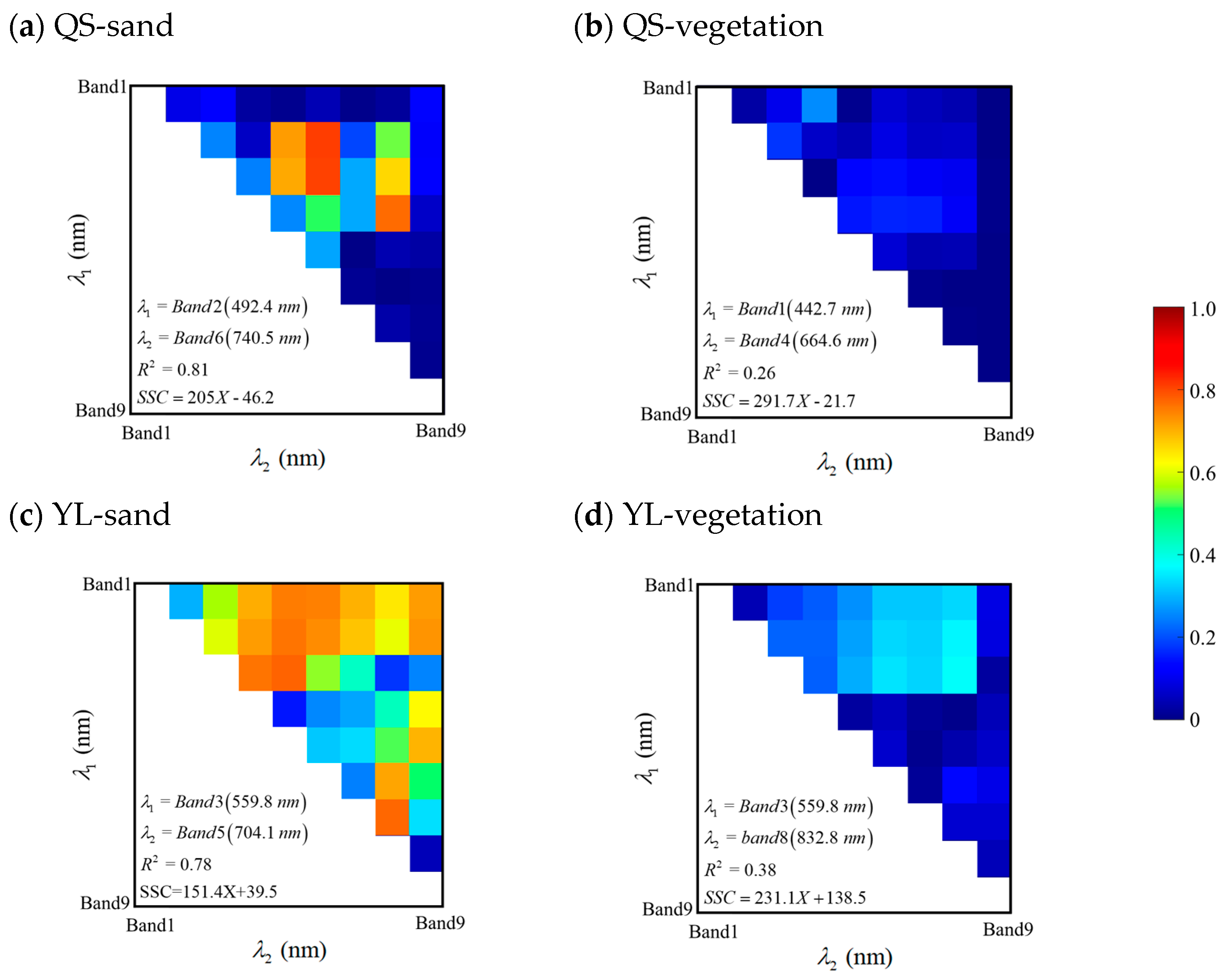
3.1. Multispectral Retrieval of SSC
3.2. Hyperspectral Retrieval of SSC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szupiany, R.N.; Amsler, M.L.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L. Morphology, flow structure, and suspended bed sediment transport at two large braid-bar confluences. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W05415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Grabowski, R.C.; Rickson, R.J. Suspended sediment transport dynamics in rivers: Multi-scale drivers of temporal variation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 166, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Seo, I.W.; Lyu, S. Investigating mixing patterns of suspended sediment in a river confluence using high-resolution hyperspectral imagery. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minella, J.P.; Merten, G.H.; Reichert, J.M.; Clarke, R.T. Estimating suspended sediment concentrations from turbidity measurements and the calibration problem. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haun, S.; Rüther, N.; Baranya, S.; Guerrero, M. Comparison of real time suspended sediment transport measurements in river environment by LISST instruments in stationary and moving operation mode. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2015, 41, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y. Estimation of suspended sediment concentration in the yangtze main stream based on sentinel-2 MSI data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Pierson, D.C.; Tranvik, L.; Reinart, A.; Sobek, S.; Kallio, K. Using satellite remote sensing to estimate the colored dissolved organic matter absorption coefficient in lakes. Ecosystem 2005, 8, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, V.; Silvestri, S.; Marani, M. Remote sensing retrieval of suspended sediment concentration in shallow waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Seo, I.W.; Baek, D. Modeling spatial variability of harmful algal bloom in regulated rivers using a depth-averaged 2D numerical model. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2018, 20, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legleiter, C.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Marcus, W.A.; Fonstad, M.A. Passive optical remote sensing of river channel morphology and in-stream habitat: Physical basis and feasibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.M.; Castaing, P.A. reflectance band ratio used to estimate suspended matter concentrations in sediment-dominated coastal waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 5079–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Retrieval of suspended sediment concentrations in the Pearl River estuary using multi-source satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, Q.; Cui, T.; Xue, C.; Zhang, S. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River estuary from Landsat TM and ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 146, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.V.; Ha, N.T.T.; Pahlevan, N.; Oanh, L.T.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, N.T. Using Landsat-8 images for quantifying suspended sediment concentration in Red River (Northern Vietnam). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudela, R.M.; Palacios, S.L.; Austerberry, D.C.; Accorsi, E.K.; Guild, L.S.; Torres-Perez, J. Application of hyperspectral remote sensing to cyanobacterial blooms in inland waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Shin, J.; Seo, I.W.; Noh, H.; Jung, S.H.; You, H. Measurement of suspended sediment concentration in open channel flows based on hyperspectral imagery from UAVs. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 159, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legleiter, C.J.; Fosness, R.L. Defining the limits of spectrally based bathymetric mapping on a large river. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Seo, I.W.; Noh, H.; Kim, B. Hyperspectral retrievals of suspended sediment using cluster-based machine learning regression in shallow waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, D.; Seo, I.W.; You, H. Estimation of shallow stream bathymetry under varying suspended sediment concentrations and compositions using hyperspectral imagery. Geomorphology 2023, 433, 108722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Noh, H.; Seo, I.W.; Park, Y.S. Effects of spectral variability due to sediment and bottom characteristics on remote sensing for suspended sediment in shallow rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leathers, R.A.; Downes, T.V.; Priest, R.G. Scene-based nonuniformity corrections for optical and SWIR pushbroom sensors. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 5136–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, D.; Seo, I.W.; Kim, J.S.; Nelson, J.M. UAV-based measurements of spatio-temporal concentration distributions of fluorescent tracers in open channel flows. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 127, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Steinmetz, F.; Navarro, G. Evaluation of the first year of operational Sentinel-2A data for retrieval of suspended solids in medium-to high-turbidity waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; De Carvalho, L.A.S.; Jorge, D.S.F.; Lobo, F.D.L.; Novo, E.M.L.D.M. Assessment of atmospheric correction methods for Sentinel-2 MSI images applied to Amazon floodplain lakes. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legleiter, C.J.; Mobley, C.D.; Overstreet, B.T. A framework for modeling connections between hydraulics, water surface roughness, and surface reflectance in open channel flows. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1715–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, B.T.; Legleiter, C.J. Removing sun glint from optical remote sensing images of shallow rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinet, S.; Martinez, J.M.; Ouillon, S.; Lartiges, B.; Villar, R.E. Variability of apparent and inherent optical properties of sediment-laden waters in large river basins–lessons from in situ measurements and bio-optical modeling. Opt. Express 2017, 25, A283–A310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing to assess spatial distribution of water quality characteristics in large rivers: The Mississippi River and its tributaries in Minnesota. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, W.; Calzado, V.S.; Trees, C.; Stamnes, S.; Fournier, G.; McKee, D.; Stamnes, K. Inferring inherent optical properties and water constituent profiles from apparent optical properties. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A987–A1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Liew, S.C.; Wong, E.; Lee, Z. Modeling the remote-sensing reflectance of highly turbid waters. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 2671–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legleiter, C.J.; Roberts, D.A. A forward image model for passive optical remote sensing of river bathymetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1025–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. SMART-SDB: Sample-specific multiple band ratio technique for satellite-derived bathymetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.R.; Harmel, T.; Martinez, J.M.; Filizola Junior, N.P. Spatiotemporal dynamics of suspended sediments in the Negro River, Amazon Basin, from in situ and Sentinel-2 remote sensing data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Baek, D.; Seo, I.W.; Shin, J. Retrieving shallow stream bathymetry from UAV-assisted RGB imagery using a geospatial regression method. Geomorphology 2019, 341, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Y.; He, X.Y.; Wang, D.Z. Experimental study on the effects of sediment size and porosity on contaminant adsorption/desorption and interfacial diffusion characteristics. J. Hydrodyn. 2013, 25, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondzell, S.M.; Gooseff, M.N. Geomorphic controls on hyporheic exchange across scales: Watersheds to particles. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Marani, M.; Albertson, J.D.; Silvestri, S. Hyperspectral and multispectral retrieval of suspended sediment in shallow coastal waters using semi-analytical and empirical methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Gwon, Y.; Kim, D.; Seo, I.W.; You, H. Unsupervised Classification of Riverbed Types for Bathymetry Mapping in Shallow Rivers Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Case | Sediment Type | Bottom Type | Mean Depth (m) | Sediment Density (mg/m3) | d50 (µm) | Injected Mass (kg) | Injected Volume (L) | Data Acquisition Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | QS | Sand | 0.59 | 2.36 | 165 | 60 | 127 | 28 April 2021 |
| Case 2 | Vegetation | 0.55 | 2.36 | 165 | 60 | 128 | 27 April 2021 | |
| Case 3 | YL | Sand | 0.59 | 1.23 | 16.3 | 40 | 127 | 28 April 2021 |
| Case 4 | Vegetation | 0.55 | 1.23 | 16.3 | 40 | 127 | 27 April 2021 |
| Sediment Type | Clay (d < 4 µm) | Silt (4 < d < 62 µm) | Sand (62 µm < d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| QS | 0.35 | 3.43 | 96.2 |
| YL | 18.9 | 80.6 | 0.44 |
| Case | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 356 | 228 | 314 | 437 |
| SSC (ppm) | 26.67 ± 20.76 | 19.97 ± 8.12 | 65.34 ± 67.90 | 45.19 ± 38.22 |
| Reflectance range | 0.01–0.24 | 0.01–0.32 | 0.01–0.33 | 0.04–0.15 |
| Type of Dataset | Spectral Range | Number of Bands Used | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multispectral bands (MSI data) | Landsat-9 | Band 1–Band 8 (430–880 nm) | 6 |
| Sentinel-2 | Band 1–Band 9 (432–955 nm) | 9 | |
| Hyperspectral bands (HSI data) | - | 400–1000 nm | 150 |
| Dataset | Sediment Particle Type | Bed Type | R2 | Optimal Bands | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperspectral (HSI data) | QS | Sand | 0.82 | 527 nm/743 nm | 17.0 |
| YL | 0.80 | 607 nm/619 nm | 37.9 | ||
| QS | Vegetated | 0.35 | 467 nm/607 nm | 45.9 | |
| YL | 0.39 | 567 nm/803 nm | 84.5 | ||
| Landsat-9 (MSI data) | QS | Sand | 0.79 | Band 3 (560 nm)/Band 5 (865 nm) | 18.7 |
| YL | 0.77 | Band 3 (560 nm)/Band 8 (590 nm) | 38.8 | ||
| QS | Vegetated | 0.29 | Band 2 (480 nm)/Band 8 (590 nm) | 51.2 | |
| YL | 0.34 | Band 2 (480 nm)/Band 5 (865 nm) | 93.6 | ||
| Sentinel-2 (MSI data) | QS | Sand | 0.81 | Band 2 (492.4 nm)/Band 6 (740.5 nm) | 16.0 |
| YL | 0.78 | Band 3 (559.8 nm)/Band 5 (704.1 nm) | 40.3 | ||
| QS | Vegetated | 0.26 | Band 1(442.7 nm)/Band 4 (664.6 nm) | 52.7 | |
| YL | 0.38 | Band 3 (559.8 nm)/Band 8 (832.8 nm) | 84.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.H.; Kwon, S.; Seo, I.W.; Kim, J.S. Comparison between Hyperspectral and Multispectral Retrievals of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Rivers. Water 2024, 16, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091275
Jung SH, Kwon S, Seo IW, Kim JS. Comparison between Hyperspectral and Multispectral Retrievals of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Rivers. Water. 2024; 16(9):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091275
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Sung Hyun, Siyoon Kwon, Il Won Seo, and Jun Song Kim. 2024. "Comparison between Hyperspectral and Multispectral Retrievals of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Rivers" Water 16, no. 9: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091275
APA StyleJung, S. H., Kwon, S., Seo, I. W., & Kim, J. S. (2024). Comparison between Hyperspectral and Multispectral Retrievals of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Rivers. Water, 16(9), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091275







