Causes and Effects of Scale Deposition in Water Supply Pipelines in Surakarta City, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
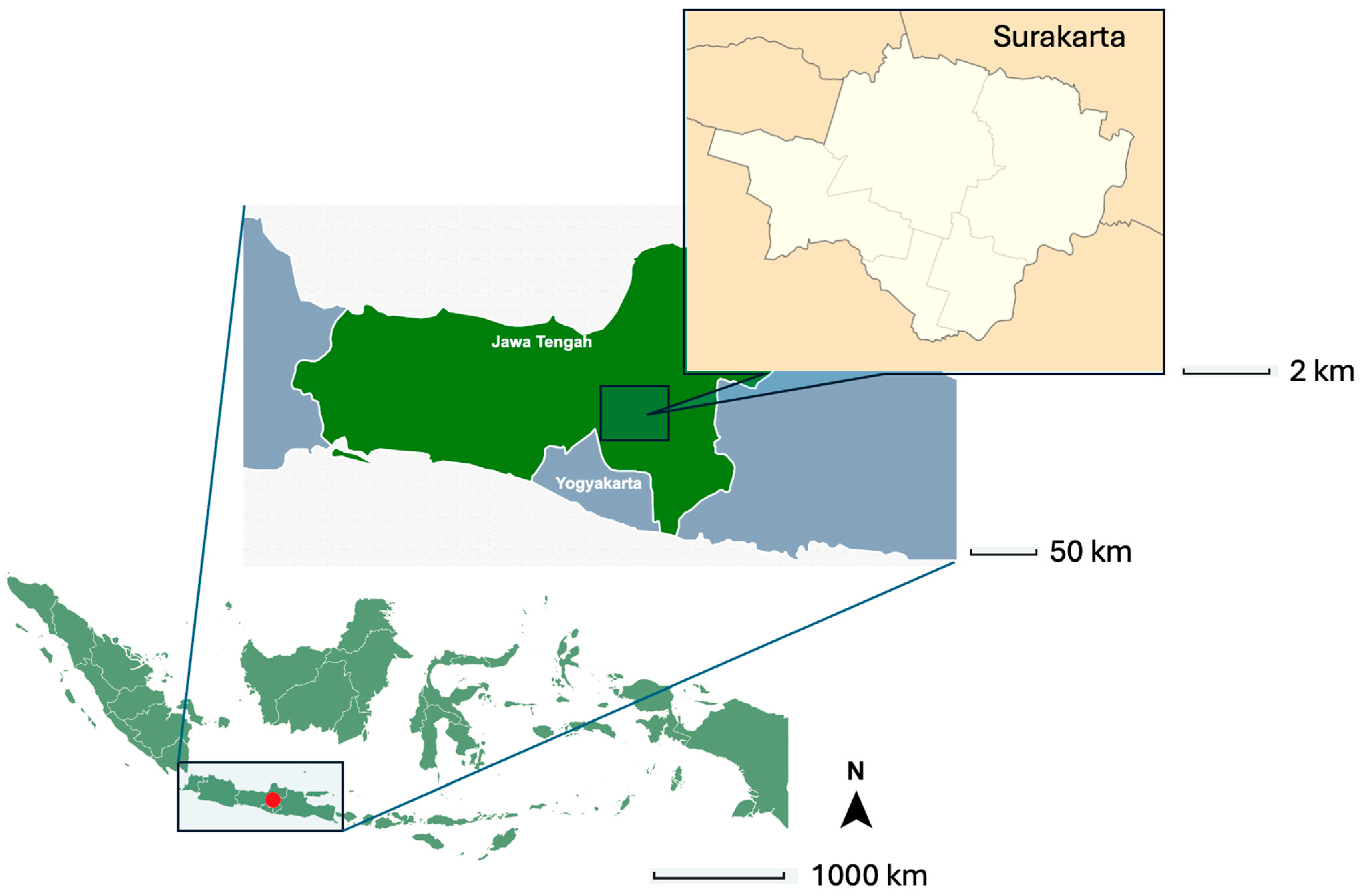
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Analyses
2.2.1. Water Sampling and Water Quality Analyses
2.2.2. Sampling and Analysis of Scale Deposits
2.2.3. Saturation Indexes
3. Results
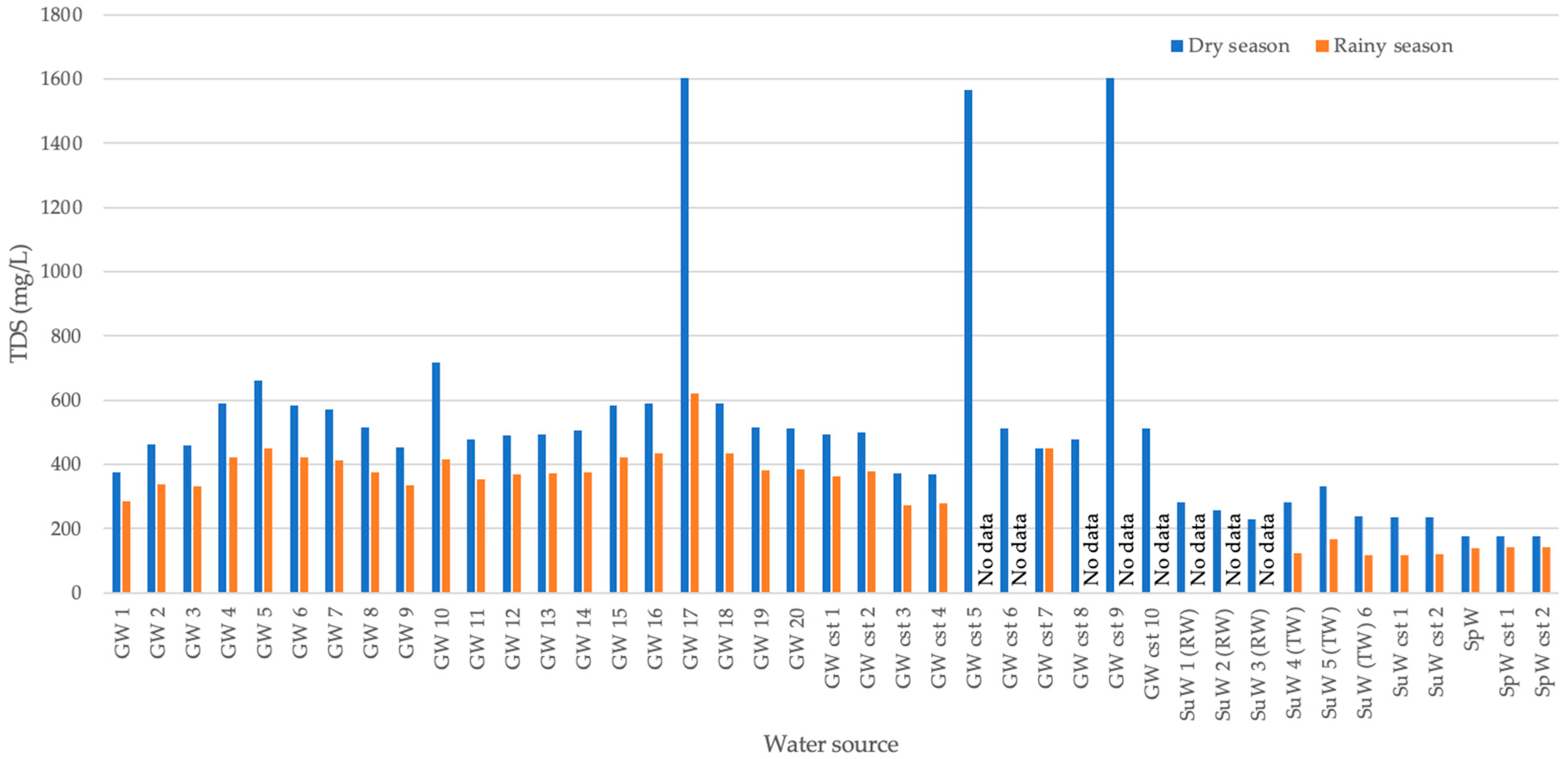
3.1. Water Quality in Source Waters and at Customer Taps
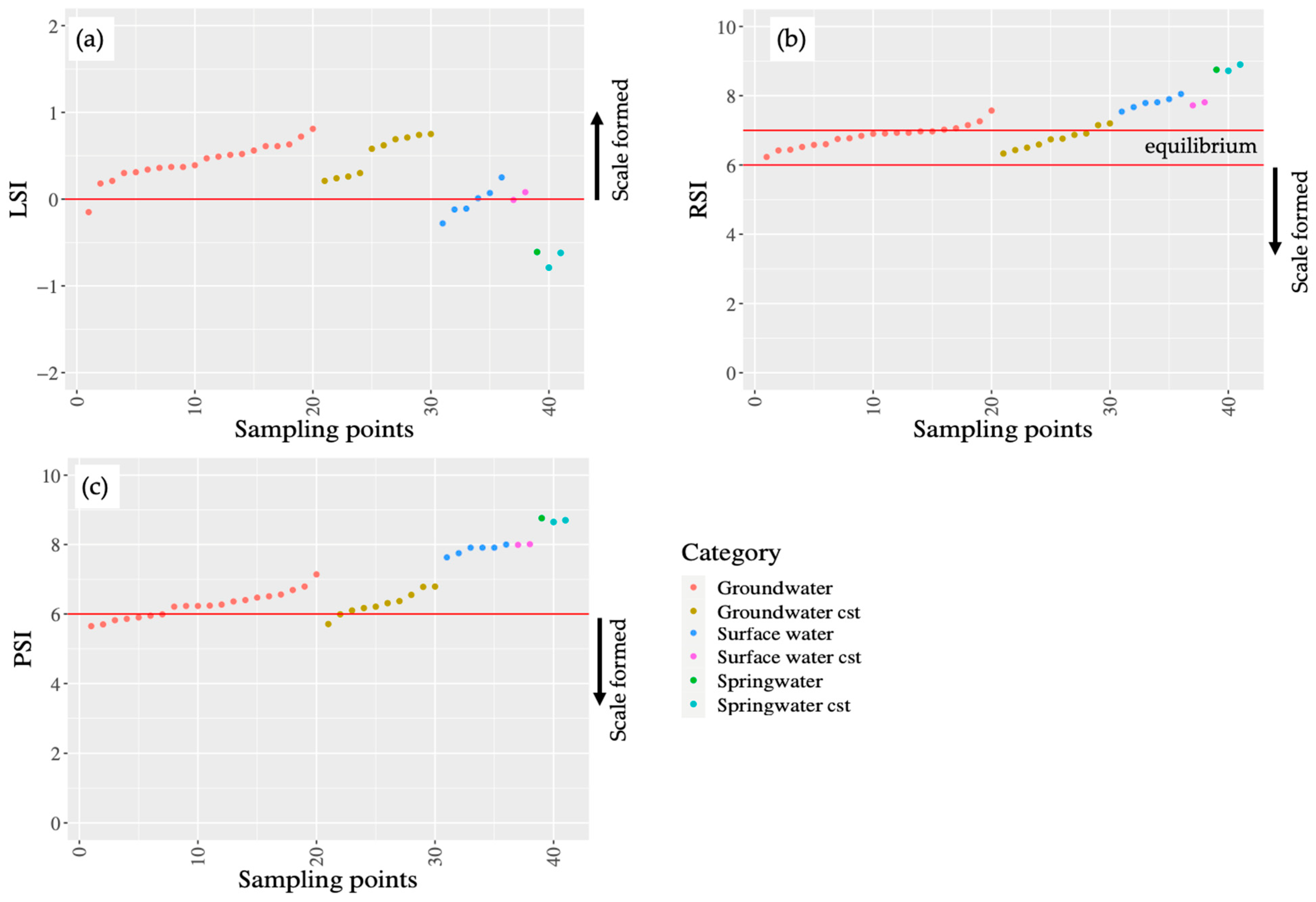
3.2. Saturation Indexes
3.3. Elemental Composition of Scale Samples
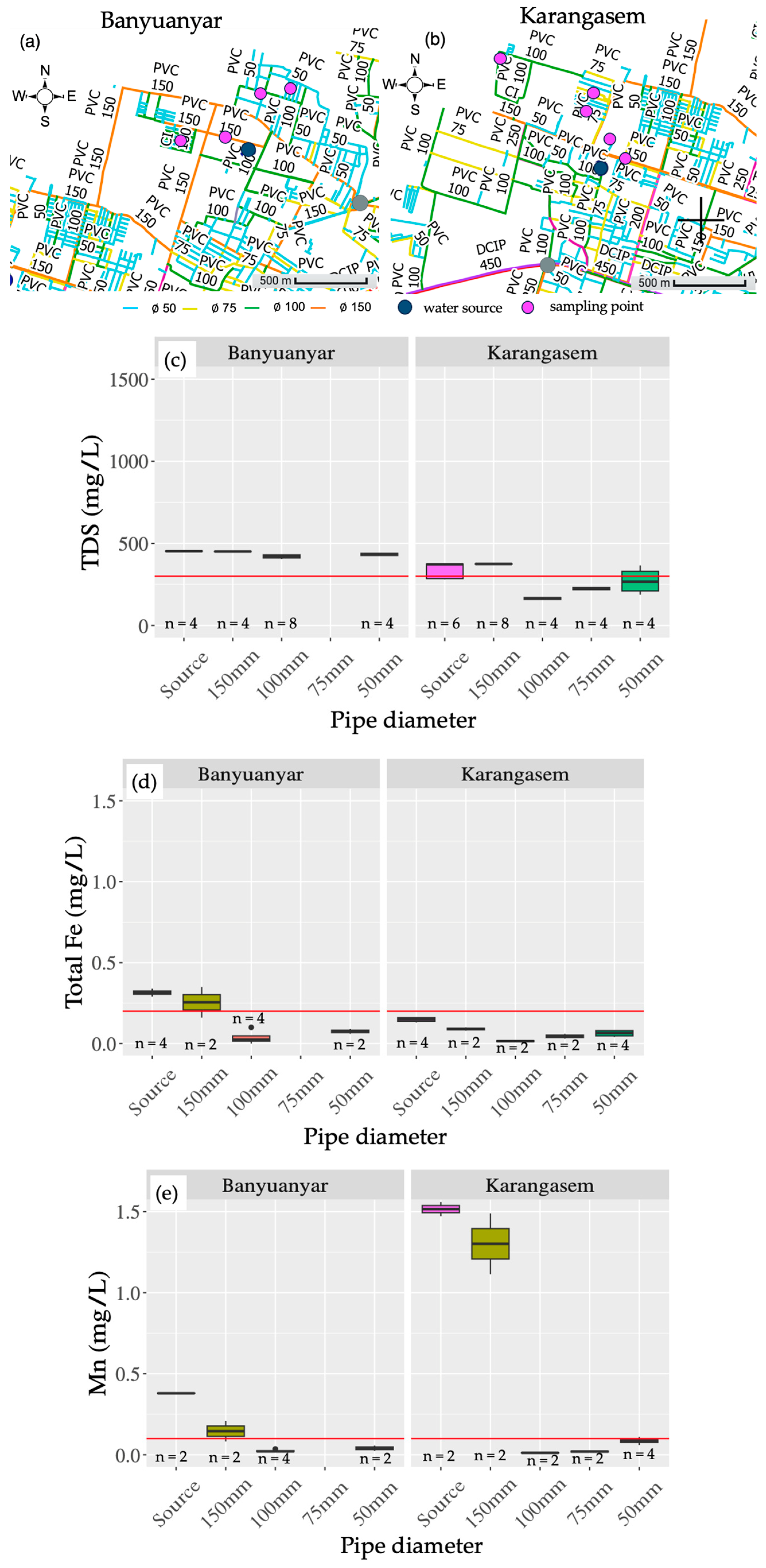
3.4. Effects of Iron and Manganese Scale in PDAM Surakarta
4. Discussion
4.1. Scale Deposition and Saturation Indexes in PDAM Surakarta
4.2. Analyses of Water Sources and Scale Deposition in the Distribution Network Using Water Quality Data
4.3. Prevention of Manganese Scale Deposition in PDAM Surakarta
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Gw | Gw cst | Spw | Spw cst | Sw | Sw cst | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | |
| Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | ||
| Cation | |||||||
| Na+ | mg/L | 110.86 25.78–350.58 | 128.29 26.85–360.28 | 15.39 | 15.43 15.42–15.44 | 29.43 20.58–50.01 | 21.55 21.52–21.58 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 48.46 13.85–75.09 | 52.92 32.53–70.60 | 20.78 | 20.75 20.73–20.78 | 37.06 35.99–38.38 | 37.29 37.25–37.32 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 16.45 7.02–29.99 | 17.31 8.68–24.01 | 10.08 | 10.13 10.13–10.14 | 8.99 8.39–10.04 | 8.56 8.56–8.57 |
| K+ | mg/L | 8.38 4.19–12.52 | 7.61 3.12–9.89 | 4.69 | 4.6 4.54–4.66 | 4.24 3.48–5.33 | 3.42 3.40–3.45 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | 0.23 ND–1.54 | 0.67 ND–1.44 | ND | 0.01 ND–0.02 | 0.36 ND–0.99 | ND |
| Anion | |||||||
| HCO3− | mg/L | 451.89 305.0–561.81 | 403.15 297.98–492.88 | 130.54 | 133.89 132.37–135.42 | 170.66 151.89–193.57 | 149.24 146.4–152.93 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 55.19 9.49–511.94 | 116.86 8.55–507.61 | 8.95 | 9.01 8.99–9.03 | 32.93 21.70–51.86 | 32.91 32.78–33.06 |
| SO42– | mg/L | 7.74 1.47–16.42 | 7.94 1.51–15.98 | 5.67 | 5.79 5.79–5.80 | 16.10 14.53–17.56 | 14.64 14.56–14.72 |
| PO43– | mg/L | 0.68 ND–2.16 | 0.31 ND–1.56 | ND | ND | 0.5 0.00– 1.51 | ND |
| NO3− | mg/L | 2.05 0.69–9.68 | 2.00 0.69–8.87 | 10.27 | 10.45 10.45–10.45 | 5.24 3.24–7.38 | 3.84 3.81–3.86 |
References
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Lin, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Review on Corrosion and Corrosion Scale Formation upon Unlined Cast Iron Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 117, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, T.L.; Little, B.J.; Barry Maynard, J. Manganese Deposition in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, Q.; Shi, B. Heavy Metal Enrichment in Drinking Water Pipe Scales and Speciation Change with Water Parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Tao, H.; Shi, B. Field Studies of Manganese Deposition and Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems: Insight into Deposit Control. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.H.; Shan, M.G.; Wu, H.X. Formation Mechanisms and Supervisory Prediction of Scaling in Water Supply Pipelines: A Review. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobadi, F.; Jeong, G.; Kang, D. Water Pipe Replacement Scheduling Based on Life Cycle Cost Assessment and Optimization Algorithm. Water 2021, 13, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, A.; Ljunggren, O.; Bergstedt, O.; Pettersson, T.J.R.; Morrison, G.M. Replacement Predictions for Drinking Water Networks through Historical Data. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, P.P.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Ruiz-Canales, A.; González-Trinidad, J.; Júnez-Ferreira, H.E.; Rodríguez, A.R.C.; Rovelo, C.O.R. Characterization of Scale Deposits in a Drinking Water Network in a Semi-Arid Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tut Haklidir, F.; Haklidir, M. Fuzzy Control of Calcium Carbonate and Silica Scales in Geothermal Systems. Geothermics 2017, 70, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, M. Factors Affecting Scale Formation in Sea Water Environments—An Experimental Approach. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2008, 31, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Su, Y.; Wu, B.; Han, G.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Shi, B. Initial Formation and Accumulation of Manganese Deposits in Drinking Water Pipes: Investigating the Role of Microbial-Mediated Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5497–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torvinen, E.; Suomalainen, S.; Lehtola, M.J.; Miettinen, I.T.; Zacheus, O.; Paulin, L.; Katila, M.-L.; Martikainen, P.J. Mycobacteria in Water and Loose Deposits of Drinking Water Distribution Systems in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, H.; Qiu, M.; Zhou, L. Control of Loose Deposits in a Simulated Drinking Water Distribution System Using Ultrafiltration. Water 2023, 15, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhang, G.; Shi, B. Spatial Variation of Loose Deposit Characteristics in a 40 Km Long Operational Drinking Water Distribution System. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafid, N.; Ben-Aazza, S.; Hadfi, A.; Ezahri, M.; Driouiche, A. Characterization of Scale Formed in Drinking Water and Hot Water Pipes in the Taliouine Downtown—Morocco. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 6, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belattar, M.; Hadfi, A.; Said, B.; Mohareb, S.; Hafid, N. Characterization of Scale Deposits Formed in Sanitary Hot Water Pipelines in the Northern Tourist Zone of Agadir City. Mediterr. J. Chem. 2018, 7, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, K.; Alia, E.; Zendah, H.; Elfil, H.; Hannachi, A. Sand Filters Scaling by Calcium Carbonate Precipitation during Groundwater Reverse Osmosis Desalination. Desalination 2018, 430, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanpour, N.; Noshadi, M.; Tavanpour, N. Scale Formation and Corrosion of Drinking Water Pipes: A Case Study of Drinking Water Distribution System of Shiraz City. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2016, 10, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, B.; Yosra, M.; Nadia, A. Effects of Magnetic Treatment on Scaling Power of Hard Waters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 171, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobersek, D.; Goricanec, D. An Experimentally Evaluated Magnetic Device’s Efficiency for Water-Scale Reduction on Electric Heaters. Energy 2014, 77, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belattar, M.; Hadfi, A.; Ben-Aazza, S.; Mohareb, S.; Karmal, I.; Hafid, N.; Driouiche, A. Kinetic Study of the Scaling Power of Sanitary Water in the Tourist Area of Agadir. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, N. Case Study of Calcium Carbonate Scale at EGS and Hot Spring Binary System. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 April 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.-Y.; Korshin, G. V Speciation of Trace Inorganic Contaminants in Corrosion Scales and Deposits Formed in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5553–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Kosaka, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Welfringer, T.; Itoh, S. Manganese Accumulation on Pipe Surface in Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System: Contributions of Physical and Chemical Pathways. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, W.H.; Wiatr, C. Manganese-Related Corrosion and Fouling in Water Systems. Analyst 2013, 20, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, T.L.; Little, B.J. Manganese. In Encyclopedia of Geochemistry: A Comprehensive Reference Source on the Chemistry of the Earth; White, W.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 864–867. ISBN 978-3-319-39312-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kousa, A.; Komulainen, H.; Hatakka, T.; Backman, B.; Hartikainen, S. Variation in Groundwater Manganese in Finland. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1193–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusydi, A.; Onodera, S.-I.; Saito, M.; Ioka, S.; Maria, R.; Ridwansyah, I.; Delinom, R. Vulnerability of Groundwater to Iron and Manganese Contamination in the Coastal Alluvial Plain of a Developing Indonesian City. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Elevated Manganese Concentrations in Shallow Groundwater of Various Aquifers in a Rapidly Urbanized Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Joode, B.V.W.; Barbeau, B.; Bouchard, M.F.; Mora, A.M.; Skytt, Å.; Córdoba, L.; Quesada, R.; Lundh, T.; Lindh, C.H.; Mergler, D. Manganese Concentrations in Drinking Water from Villages near Banana Plantations with Aerial Mancozeb Spraying in Costa Rica: Results from the Infants’ Environmental Health Study (ISA). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Ahmed, E.; Parvez, F.; Slavkovich, V.; Levy, D.; Mey, J.; van Geen, A. Manganese Exposure from Drinking Water and Children’s Classroom Behavior in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Sharma, A.; Goel, P.; Thakur, A.; Raturi, M. Groundwater Quality Assessment in the Alluvial Region of Upper Yamuna Basin, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 22, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillispie, E.C.; Austin, R.E.; Rivera, N.A.; Bolich, R.; Duckworth, O.W.; Bradley, P.; Amoozegar, A.; Hesterberg, D.; Polizzotto, M.L. Soil Weathering as an Engine for Manganese Contamination of Well Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9963–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sly, L.I.; Hodgkinson, M.C.; Arunpairojana, V. Deposition of Manganese in a Drinking Water Distribution System. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrato, J.M.; Reyes, L.P.; Alvarado, C.N.; Dietrich, A.M. Effect of PVC and Iron Materials on Mn(II) Deposition in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, T.G.; Bargar, J.R.; Sposito, G.; Tebo, B.M. Bacteriogenic Manganese Oxides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, J.; Tani, Y.; Miyata, N.; Seyama, H.; Mitsunobu, S.; Naitou, H. Concurrent Sorption of As(V) and Mn(II) during Biogenic Manganese Oxide Formation. Chem. Geol. 2012, 306–307, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center of Data and Information Technology Kinerja BUMD Air Minum (Regional Drinking Water Enterprise Performance) (In Indonesian Language). Available online: https://data.pu.go.id/visualisasi/kinerja-bumd-air-minum (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Intani, D.; Suripin; Suharyanto; Soetrisno, Y.A.A. Multi Criteria Decision Making for Integrated Assessment of Indonesian Water Company. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 2020, 12, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutrisno, E. Air Sebagai Prioritas Utama Pembangunan Di Indonesia (Water Is the Main Development Priority in Indonesia) (In Bahasa Indonesia). Available online: https://indonesia.go.id/kategori/editorial/7000/air-sebagai-prioritas-utama-pembangunan-di-indonesia?lang=1 (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Directorate of Drinking Water Kinerja BUMD Air Minum 2022 (Regional Drinking Water Enterprise Performance 2022) (In Bahasa Indonesia); Jakarta. 2023. Available online: https://www.perpamsi.or.id/publikasi/buku (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Knibbe, W.-J.; Feng, C.; Liu, W.; Medema, G.; van der Meer, W. Potential Impacts of Changing Supply-Water Quality on Drinking Water Distribution: A Review. Water Res. 2017, 116, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetiawan, T.; Nastiti, A.; Muntalif, B.S. ‘Bad’ Piped Water and Other Perceptual Drivers of Bottled Water Consumption in Indonesia. WIREs Water 2017, 4, e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics of Surakarta Municipality Kota Surakarta Dalam Angka (Surakarta Municipality in Figure) 2023 (In Bahasa Indonesia); Surakarta. 2023. Available online: https://surakartakota.bps.go.id/publication/2023/02/28/8da64ce70793fbb9886e147f/kota-surakarta-dalam-angka-2023.html (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Puslitbang Geologi Peta Geologi Lembar Surakarta—Giritontro, Jawa. Available online: https://geologi.esdm.go.id/geomap/pages/preview/peta-geologi-lembar-yogyakarta-jawa (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Patriadi, A.; Soemitro, R.A.A.; Warnana, D.D. Preliminary Assessment to Sediment Evaluation On The Estuary of Bengawan Solo River. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Problematic Soils and Ground Improvement (Soft Soils 2016), Bandung, Indonesia, 27–28 September 2016; pp. X1-1–X1-4. [Google Scholar]
- PDAM Surakarta Rencana Bisnis 2020–2024 Perumda Air Minum Kora Surakarta (Business Plan 2020–2024 of Surakarta Municipal Water Supply) (In Bahasa Indonesia); Surakarta, 2020.
- Gholizadeh, A.; Mokhtari, M.; Naimi, N.; Shiravand, B.; Ehrampoush, M.; Miri, M.; Ebrahimi, A. Assessment of Corrosion and Scaling Potential in Groundwater Resources; a Case Study of Yazd-Ardakan Plain, Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 5, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baroudi, H.; Ouazzani, C.; Moustaghfir, A.; Er-ramly, A.; El Baroudi, Y.; Dami, A.; Balouch, L. Assessing the Corrosion and Scaling Potential of Drinking Water in Morocco Using Water Stability Indices. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health Ministry of Health Decree Number 2 Regarding Regulations on Implementing Government Regulation Number 66 of 2014 Concerning Environmental Health; Indonesia. 2023. Available online: https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Details/245563/permenkes-no-2-tahun-2023 (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- World Health Organization. Hardness in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/70168/WHO_HSE_WSH_10.01_10_Rev1_eng.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Mulato. After Being Shut Down Twice Due to Waste Exposure, the Semanggi Water Treatment Plant (IPA Semanggi) Has Been Reoperated. (In Bahasa Indonesia). Radio Republik Indonesia. 2024. Available online: https://www.rri.co.id/daerah/707415/sempat-2-kali-off-terpapar-limbah-ipa-semanggi-dioperasikan-kembali (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Zhang, S.; Tian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shan, J.; Liu, R. Manganese Release from Corrosion Products of Cast Iron Pipes in Drinking Water Distribution Systems: Effect of Water Temperature, PH, Alkalinity, SO42− Concentration and Disinfectants. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Fadzil, F.; Eva, H.; Nazaruddin, D.; Shah, Z. Significance of Silica Analysis in Groundwater Studies of Domestic Shallow Wells in Parts of Jeli District, Kelantan, Malaysia. In Water Resources in Arid Areas: The Way Forward; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 103–114. ISBN 978-3-319-51856-5. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Lead in Drinking Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/lead-background-feb17.pdf?sfvrsn=fc50727b_4 (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Levallois, P.; Barn, P.; Valcke, M.; Gauvin, D.; Kosatsky, T. Public Health Consequences of Lead in Drinking Water. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Fu, C. Manganese-Oxidizing Microbes and Biogenic Manganese Oxides: Characterization, Mn(II) Oxidation Mechanism and Environmental Relevance. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y.; Wu, B.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Shi, B. Manganese and Iron Oxides on Pipe Surface Promote Dissolved Aluminum Accumulation in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wei, L.; Yu, T.; Shen, H.; Zhao, W.; Chu, X. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) on Layered Pipe Scales and the Effects of Disinfectants in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.J. Chapter 30—Scaling Indices: Types and Applications. In Mineral Scales and Deposits; Amjad, Z., Demadis, K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 721–735. ISBN 978-0-444-63228-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ozair, G. An Overview of Calcium Carbonate Saturation Indices as a Criterion to Protect Desalinated Water Transmission Lines from Deterioration. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2012, 11, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi, A.; Naimi, I.; Zinoubi, R.; Elfil, H. A New Index for Scaling Assessment. In Proceedings of the IDA World Congress, Gran Canaria, Spain, 21–26 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tobiason, J.E.; Bazilio, A.; Goodwill, J.; Mai, X.; Nguyen, C. Manganese Removal from Drinking Water Sources. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Usage | Pipe Type | Diameter (mm) | Length (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission | PVC | 200 | 14.50 |
| PVC | 250 | 5.25 | |
| AC | 300 | 12.17 | |
| CI | 450 | 29.42 | |
| CI | 500 | 16.25 | |
| DCI | 600 | 20.49 | |
| Sub-total | 98.08 | ||
| Distribution | PVC | 40 | 0.07 |
| PVC | 50 | 283.60 | |
| PVC | 75 | 107.82 | |
| CI | 80 | 33.29 | |
| PVC | 100 | 188.53 | |
| CI | 125 | 20.70 | |
| PVC | 150 | 90.15 | |
| Sub-total | 724.16 | ||
| Total | 822.24 | ||
| Parameter | Unit | Method/Analytical Device | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | MP-6 Portable Meter; Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA | |
| TDS | mg/L | ||
| EC | µS/cm | ||
| Temperature | °C | ||
| Hardness | mg/L | Calmagite colorimetric method | DR900 Multiparameter Portable Colorimeter; Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA |
| Total iron | mg/L | FerroVer® Method | |
| Ferrous iron | mg/L | 1,10-Phenanthroline method | |
| Total chlorine | mg/L | USEPA DPT method | |
| Manganese | mg/L | PAN method (LR Mn) | |
| Silica | mg/L | Heteropoly blue method | |
| Alkalinity | mg/L as CaCO3 | Digital titration | Digital Titration Kit; Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA |
| Dissolved oxygen (DO) | % | DO Meter DO-30N; Kasahara Chemical Instruments Corp., Saitama, Japan | |
| Ion concentration | mg/L | 861 Advanced Compact IC; Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland | |
| Index | Equation | Index Value | Water Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSI | LSI = pH − pHs If pH ≤ 9.3, use pHs = A + B − log[Ca2+] − log[alk] Else (pH > 9.3), use pHs = (9.3 + A + B) − (C + D) A B = −1.12[log(°C + 273)] + 34.55 C = log[Ca2+ + CaCO3] − 0.4 D = log[alk as CaCO3] | LSI > 0 LSI = 0 LSI < 0 | CaCO3 scale likely to be formed CaCO3 in equilibrium CaCO3 tends to be dissolved |
| RSI | RSI = 2(pHs) – pH | RSI < 6 6 < RSI < 7 RSI > 7 | CaCO3 scale likely to be formed CaCO3 in equilibrium CaCO3 tends to be dissolved, corrosive |
| PSI | PSI = 2(pHs) − pHeq pHeq = 1.465log[alk] + 4.54 | PSI < 6 PSI > 6 PSI > 8 | CaCO3 scale likely to be formed CaCO3 tends to be dissolved, corrosive Significantly corrosive |
| Parameter | Gw | Gw cst | Spw | Spw cst | Sw | Sw cst | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Ave. | Ave. | Ave. | Ave. | Ave. | Ave. | |
| Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | Min–Max | ||
| pH | - | 7.45 7.0–8.07 | 7.38 7.31–7.50 | 7.19 7.15–7.26 | 7.14 7.10–7.18 | 7.13 6.93–7.23 | 7.39 7.36–7.42 |
| Temp. | °C | 28.25 24.70–29.30 | 28.51 27.30–29.47 | 28.51 27.30–29.47 | 26.93 26.80–27.10 | 26.90 26.40–27.53 | 29.01 29.00–29.03 |
| EC | µS/cm | 806.3 567.7–2241.0 | 658.9 571.9–2240.0 | 276.2 275.5–276.7 | 276.3 276–277.1 | 416.7 340.8–542.1 | 379.8 374.6–384.7 |
| Total Cl2 | mg/L | 0.08 NA–0.50 | 0.02 NA–0.12 | 0.14 0.11–0.16 | 0.12 0.08–0.12 | 0.57 0.08–1.41 | 0.15 0.14–0.16 |
| Alkalinity | mg/L | 375.2 226.7–533.3 | 297.0 250.7–382.0 | 103.0 102.0–104.0 | 115.0 113.7–116.3 | 87.9 73.3–102.7 | 82.3 80.0–85.3 |
| Silica | mg/L | 66.0 44.0–84.0 | 68.0 52.0–90.0 | 74.0 74.0–74.0 | 73.0 72.0–74.0 | 27.0 18.0–44.0 | 18.5 18.0–19.0 |
| Ferrous iron | mg/L | 0.03 BDL–0.32 | 0.01 BDL–0.03 | 0.04 BDL–0.09 | 0.02 BDL–0.02 | 0.03 BDL–0.11 | 0.01 BDL–0.03 |
| DO | mg/L | 1.76 0.50–2.70 | 2.34 0.80–3.70 | 3.12 2.80–3.50 | 3.10 2.60–3.60 | 2.50 0.40–4.00 | 3.50 2.90–4.60 |
| Sample | Composition (%wt.) | Water Source | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Fe | Al | Si | Ca | Zn | Others | ||
| 1 | 55.24 | 15.51 | 13.62 | 8.17 | 2.98 | 2.44 | 2.04 | Gw |
| 2 | 52.46 | 7.04 | 16.69 | 14.72 | 6.41 | 1.74 | 0.95 | Gw |
| 3 | 50.15 | 9.54 | 12.49 | 17.52 | 6.57 | 1.45 | 2.27 | Gw |
| 4 | 59.15 | 11.00 | 6.66 | 13.06 | 6.35 | 0.98 | 2.80 | Gw |
| 5 | 64.57 | 4.31 | 11.18 | 10.20 | 7.66 | 1.33 | 0.75 | Gw |
| 6 | 80.82 | 4.92 | ND | 0.77 | 7.83 | 0.06 | 5.59 | Gw |
| 7a | 3.29 | 63.82 | 3.10 | 19.25 | 5.36 | ND | 5.18 | Gw |
| 7b | 11.21 | 58.66 | 1.79 | 17.25 | 4.68 | 0.05 | 6.37 | Gw |
| 8 | 31.22 | 45.60 | 4.88 | 12.09 | 3.53 | 0.19 | 2.50 | Gw + Sw |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, S.; Kazama, S.; Sawangjang, B.; Takizawa, S. Causes and Effects of Scale Deposition in Water Supply Pipelines in Surakarta City, Indonesia. Water 2024, 16, 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162275
Amin S, Kazama S, Sawangjang B, Takizawa S. Causes and Effects of Scale Deposition in Water Supply Pipelines in Surakarta City, Indonesia. Water. 2024; 16(16):2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162275
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Saiful, Shinobu Kazama, Benyapa Sawangjang, and Satoshi Takizawa. 2024. "Causes and Effects of Scale Deposition in Water Supply Pipelines in Surakarta City, Indonesia" Water 16, no. 16: 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162275
APA StyleAmin, S., Kazama, S., Sawangjang, B., & Takizawa, S. (2024). Causes and Effects of Scale Deposition in Water Supply Pipelines in Surakarta City, Indonesia. Water, 16(16), 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162275








