Dissolved Inorganic Geogenic Phosphorus Load to a Groundwater-Fed Lake: Implications of Terrestrial Phosphorus Cycling by Groundwater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
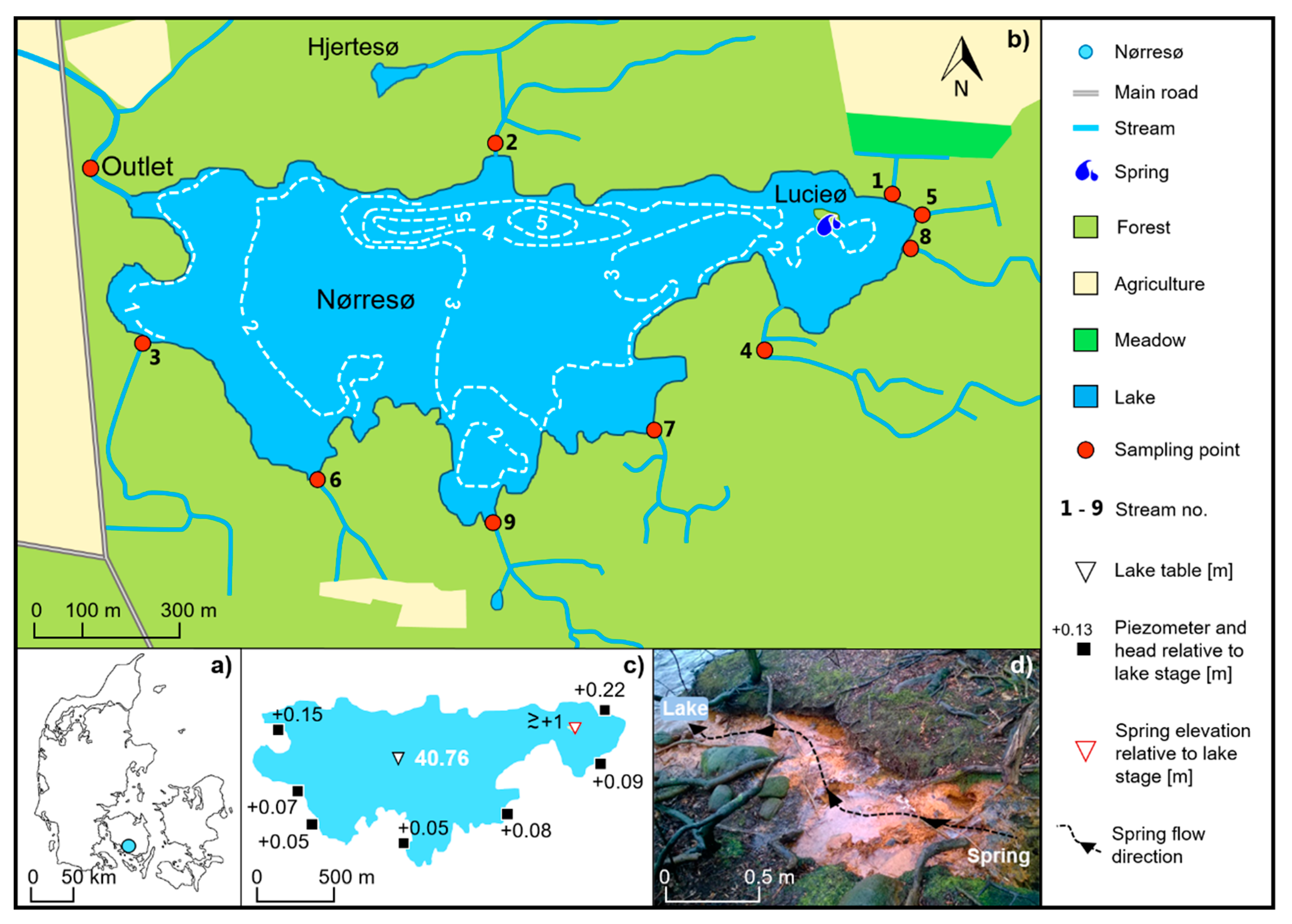
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Lithology
2.2.2. Hydraulic Heads
2.2.3. Water Budget Equation
2.2.4. Frequency of Collection of Hydrological and Hydrochemical Data
2.2.5. Outlet, Spring, and Stream Discharge
2.2.6. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.2.7. Field Measurements
2.2.8. Paleolimnological Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Lithology
3.2. Hydraulic Heads
3.3. Water Samples
3.3.1. Stable Isotopes of Water
3.3.2. Ca2+ and Alkalinity
3.3.3. Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus
3.3.4. Fe2+, O2 and NO3− Concentrations
3.3.5. Temperature
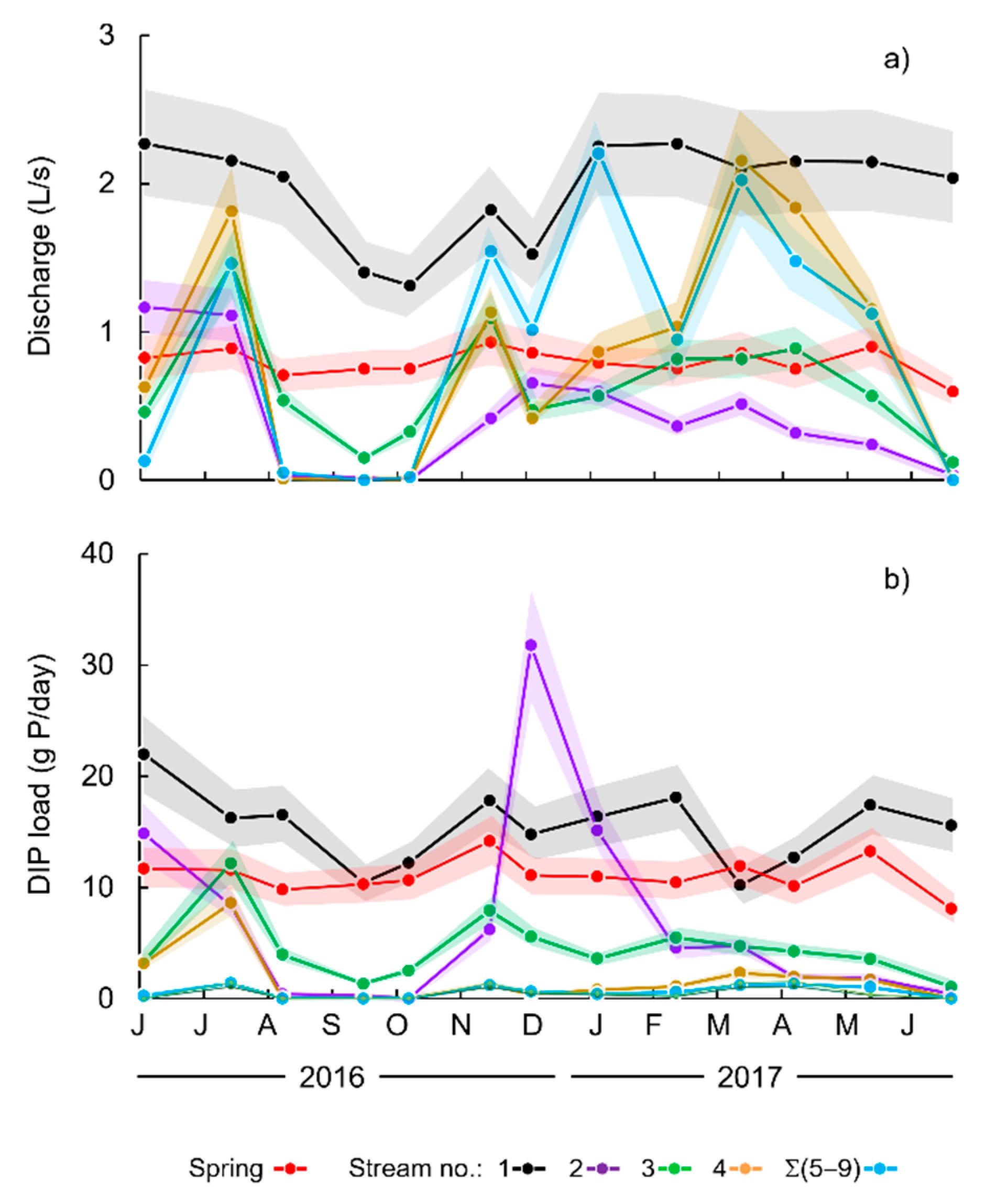
3.4. Stream and Spring Discharge and DIP Load to the Lake
3.5. Annual Water Budget and DIP Load to Nørresø
3.6. Paleolimnological Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Identifying Deep Groundwater Discharge
4.2. Identifying Discharge of Shallow Groundwater or Surface Runoff
4.3. Water Budget and External Water-Borne DIP Load to Nørresø
4.4. Origin of the Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus
4.5. Paleolimnological Indicators for P Sources to the Lake
5. Conclusions
- Phosphorus transport with groundwater over long (km) distances;
- Natural significant releases of geogenic phosphorus to groundwater;
- Groundwater-borne dissolved inorganic phosphorus can potentially be the main contributor of P to surface freshwater ecosystems. In the studied lake, Nørresø, groundwater inputs accounted for 90% of the total annual external DIP load, even though groundwater constituted only one third of water input to the lake.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E. Anthropogenic impacts on lake and stream ecosystems, and approaches to restoration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Environment for the Future We Want; Progress Press Ltd: Valletta, Malta, 2012; ISBN 9789280731774. [Google Scholar]
- EEA. Assessment of Global Megatrends—An Update. Global Megatrend 1: Diverging Global Population Trends; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014.
- Hecky, R.E.; Kilham, P. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 796–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blake, R.E.; O’Neil, J.R.; Surkov, A.V. Biogeochemical cycling of phosphorus: Insights from oxygen isotope effects of phosphoenzymes. Am. J. Sci. 2005, 305, 596–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanek, V. The interactions between lake and groundwater and their ecological significance. Stygologia 1987, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kilroy, G.; Coxon, C. Temporal variability of phosphorus fractions in Irish karst springs. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, I.P.; Whelan, M.J.; Howden, N.J.K.; Bellamy, P.H.; Willby, N.J.; Rivas-Casado, M.; McConvey, P. Phosphorus in groundwater—An overlooked contributor to eutrophication? Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 5121–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, I.P.; Howden, N.J.K.; Bellamy, P.; Willby, N.; Whelan, M.J.; Rivas-Casado, M. An assessment of the risk to surface water ecosystems of groundwater P in the UK and Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiberg, L.; Pedersen, T.V.; Jensen, H.S.; Kjaergaard, C.; Hansen, H.C.B. A comparative study of phosphate sorption in lowland soils under oxic and anoxic conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, C.; Heiberg, L.; Jensen, H.S.; Hansen, H.C.B. Phosphorus mobilization in rewetted peat and sand at variable flow rate and redox regimes. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prem, M.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Wenzel, W.; Heiberg, L.; Sørensen, H.; Borggaard, O.K. High Spatial and Fast Changes of Iron Redox State and Phosphorus Solubility in a Seasonally Flooded Temperate Wetland Soil. Wetlands 2015, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, D.A.; Rea, B.A.; Sollenwerk, K.G.; Savoie, J. Geochemical and Hydrologic Controls on Phosphorus Transport in a Sewage Contaminated Sand and Gravel Aquifer Near Ashumet Pond, Cape Cod, Massachusetts; Technical Report; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1996.
- Burkart, M.R.; Simpkins, W.W.; Morrow, A.J.; Gannon, J.M. Occurrence of total dissolved phosphorus in unconsolidated aquifers and aquitards in Iowa. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 40, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, J. Extent of immobilisation of phosphate during aeration of nutrient-rich, anoxic groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.; Meinikmann, K.; Nützmann, G.; Rosenberry, D.O. Groundwater—The disregarded component in lake water and nutrient budgets. Part 2: Effects of groundwater on nutrients. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2922–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinikmann, K.; Lewandowski, J.; Hupfer, M. Phosphorus in groundwater discharge—A potential source for lake eutrophication. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidmose, J.; Nilsson, B.; Engesgaard, P.; Frandsen, M.; Karan, S.; Landkildehus, F.; Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E. Focused groundwater discharge of phosphorus to a eutrophic seepage lake (Lake Væng, Denmark): Implications for lake ecological state and restoration. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak, J.; Müller, S.; Nilsson, B.; Postma, D.; Czekaj, J.; Sebok1, E.; Jessen, S.; Karan, S.; Stenvig Jensen, C.; Edelvang, K.; et al. Groundwater flow and heterogeneous discharge into a seepage lake: Combined use of physical methods and hydrochemical tracers. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9109–9130. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, R.D.; Shaw, J.F.H.; Fricker, H.; Prepas, E.E. An integrated approach to quantify groundwater transport of phosphorus to Narrow Lake, Alberta. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenoyer, G.; Anderson, M.P. Groundwater’s dynamic role in regulating acidity and chemistry in a precipitatuon-dominated lake. J. Hydrol. 1989, 109, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilas, C.P.; Borggaard, O.K.; Hansen, H.C.B. Potential iron and phosphate mobilization during flooding of soil material. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 1998, 106, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. The Phosphorus Cycle. In Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 242–250. ISBN 9780127447605. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, N.J. Naturally eutrophic lakes: Reality, myth or myopia? Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 137–138. [Google Scholar]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Internal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes. Hydrobiologia 1999, 408–409, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, W.A. Geochemical cycling of phosphorous in rivers. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyn’s County. Nørresø 1989–1993, Lake Monitoring in Fyn’s County; Technical Report No. 1; Fyn’s County: Odense, Denmark, May 1994; 70p. [Google Scholar]
- Odgaard, B.; Møller, P.F.; Wolin, J.A.; Rasmussen, P.; Anderson, N.J. Brahetrolleborg Nørresø. Palæolimnologisk Undersøgelse og Oplandsanalyse; Company Report (48); Denmark’s Geological Surveys: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1995; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Høy, T. Danmarks Søer—Søerne i Fyns Amt; Strandbergs Forlag: Charlottenlund, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Moorleghem, V.C.; De Schutter, N.; Smolders, E.; Merckx, R. The bioavailability of colloidal and dissolved organic phosphorus to the alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata in relation to analytical phosphorus measurements. Hydrobiologia 2013, 709, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbeth, C.S.; Jessen, S.; Bennike, O.; Kidmose, J.; Reitzel, K. Role of Groundwater-Borne Geogenic Phosphorus for the Internal P Release in Shallow Lakes. Water 2019, 11, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS). Danish National Borehole Achieve (Jupiter). 2018. Available online: www.geus.dk (accessed on 21 September 2018).
- Jørgensen, F.; Sandersen, P.B.E.; Auken, E. Imaging buried Quaternary valleys using the transient electromagnetic method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberry, D.O.; LaBaugh, J.W. Field Techniques for Estimating Water Fluxes Between Surface Water and Ground Water Techniques and Methods; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008.
- Fitts, C.R. Groundwater Science, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780123847058. [Google Scholar]
- Det Nationale Overvågningsprogram for Vandmiljø og Natur (NOVANA). Available online: http://novana.dmi.dk/ (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Skogerboe, G.V.; Bennett, R.S.; Walker, W.R. Selection and Installation of Cutthroat Flumes for Measuring Irrigation and Drainage Water; Technical Bulletin 120; Colorado State University: Denver, CO, USA, December 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Skogerboe, G.V.; Bennett, R.S.; Walker, W.R. Generalized Discharge Relations for Cutthroat Flumes. J. Irrig. Drain. Divis. 1972, 98, 569–583. [Google Scholar]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine—A New Spectrophotometric Reagent for Iron. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Beck, J.W.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Buck, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curves 0–50,000 Years cal BP. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battarbee, R.W.; Jones, V.J.; Flower, R.J.; Cameron, N.G.; Bennion, H.; Carvalho, L.; Juggins, S. Diatoms. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments. Terrestrial, Algal, and Siliceous Indicators; Smol, J.P., Birks, H.J.P., Last, W.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 3, pp. 155–202. ISBN 9780306476686. [Google Scholar]
- Faegri, K.; Iversen, J. Textbook of Pollen Analysis, 3rd ed.; Munksgaard: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, S.; Stumpp, C.; Sørensen, J.H.; Jessen, S. Spatiotemporal variation of stable isotopic composition in precipitation: Post-condensational effects in a humid area. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3146–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirkel, D.G.; Van Beek, C.G.E.M.; Witte, J.P.M.; Van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. Sulphate reduction and calcite precipitation in relation to internal eutrophication of groundwater fed alkaline fens. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Mark Jensen, M.; Jakobsen, R.; Thamdrup, B.; Joest Andersen, T.; Kovacs, A.; Bruun Hansen, H.C. Vivianite formation and its role in phosphorus retention in Lake Ørn, Denmark. Chem. Geol. 2015, 409, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellermann, T.; Bossi, R.; Christensen, J.; Løfstrøm, P.; Monies, C.; Grundahl, L.; Geels, C. Atmosfærisk Deposition 2014; Technical Report 163; Department of Environmental Sciences (DCE): Aarhus, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 9781439833544. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis: Boca Raton, FL, USA; New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 1566702496. [Google Scholar]
- Cucarella, V.; Renman, G. Phosphorus sorption capacity of filter materials used for on-site wastewater treatment determined in batch experiments—A comparative study. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battarbee, R.W.; Juggins, S.; Gasse, F.; Anderson, N.J.; Bennion, H.; Cameron, N.G.; Ryves, D.B.; Pailles, C.; Chalie, F.; Telford, R. European Diatom Database (EDDI): An Information System for Palaeoenvironmental Reconstruction; Environmental Change Research Centre (ECRC) Report 81; University College London: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McGowan, S.; Britton, G.; Haworth, E.; Moss, B. Ancient blue-green blooms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilinc, S.; Moss, B. Whitemere, a lake that defies some conventions about nutrients. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Booth, E.G.; Kucharik, C.J.; Lathrop, R.C. Extreme daily loads: Role in annual phosphorus input to a north temperate lake. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 77, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.S. Paleolimnology: The History and Evolution of Lake Systems; Oxford University Press: New york, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kuneš, P.; Odgaard, B.V.; Gaillard, M.J. Soil phosphorus as a control of productivity and openness in temperate interglacial forest ecosystems. J. Biogeogr. 2011, 38, 2150–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupryjanowicz, M.; Fiłoc, M.; Czerniawska, D. Occurrence of slender naiad (Najas flexilis (Willd.) Rostk. & W. L. E. Schmidt) during the Eemian Interglacial—An example of a palaeolake from the Hieronimowo site, NE Poland. Quat. Int. 2018, 467, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kenney, W.F.; Brenner, M.; Curtis, J.H.; Arnold, T.E.; Schelske, C.L. A holocene sediment record of phosphorus accumulation in shallow Lake Harris, Florida (USA) offers new perspectives on recent cultural eutrophication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgaard, B.V. The Holocene vegetation history in northern West Jutland, Denmark. Opera Bot. 1994, 123, 1–171. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, S.A.; Perry, R.H.; Saros, J.E.; Jacobson, G.L.; Fernandez, I.J.; Kopáček, J.; Wilson, T.A.; SanClements, M.D. The controls on phosphorus availability in a Boreal lake ecosystem since deglaciation. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 46, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nisbeth, C.S.; Kidmose, J.; Weckström, K.; Reitzel, K.; Odgaard, B.V.; Bennike, O.; Thorling, L.; McGowan, S.; Schomacker, A.; Kristensen, D.L.J.; et al. Dissolved Inorganic Geogenic Phosphorus Load to a Groundwater-Fed Lake: Implications of Terrestrial Phosphorus Cycling by Groundwater. Water 2019, 11, 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112213
Nisbeth CS, Kidmose J, Weckström K, Reitzel K, Odgaard BV, Bennike O, Thorling L, McGowan S, Schomacker A, Kristensen DLJ, et al. Dissolved Inorganic Geogenic Phosphorus Load to a Groundwater-Fed Lake: Implications of Terrestrial Phosphorus Cycling by Groundwater. Water. 2019; 11(11):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112213
Chicago/Turabian StyleNisbeth, Catharina Simone, Jacob Kidmose, Kaarina Weckström, Kasper Reitzel, Bent Vad Odgaard, Ole Bennike, Lærke Thorling, Suzanne McGowan, Anders Schomacker, David Lajer Juul Kristensen, and et al. 2019. "Dissolved Inorganic Geogenic Phosphorus Load to a Groundwater-Fed Lake: Implications of Terrestrial Phosphorus Cycling by Groundwater" Water 11, no. 11: 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112213
APA StyleNisbeth, C. S., Kidmose, J., Weckström, K., Reitzel, K., Odgaard, B. V., Bennike, O., Thorling, L., McGowan, S., Schomacker, A., Kristensen, D. L. J., & Jessen, S. (2019). Dissolved Inorganic Geogenic Phosphorus Load to a Groundwater-Fed Lake: Implications of Terrestrial Phosphorus Cycling by Groundwater. Water, 11(11), 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112213





