SD-WACCM-X Study of Nonmigrating Tidal Responses to the 2019 Antarctic Minor SSW
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. SD-WACCM-X
2.2. SABER
3. Results
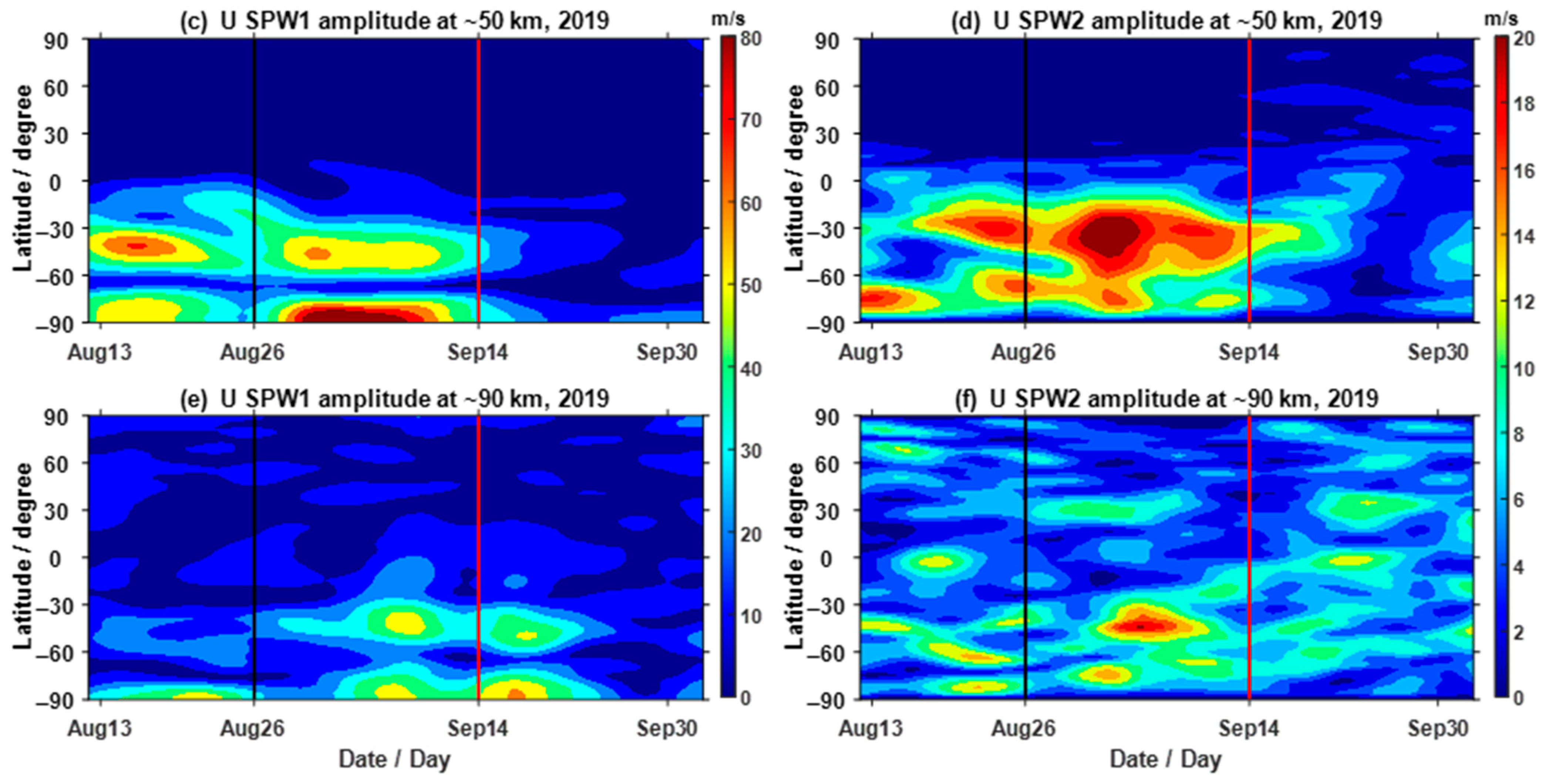
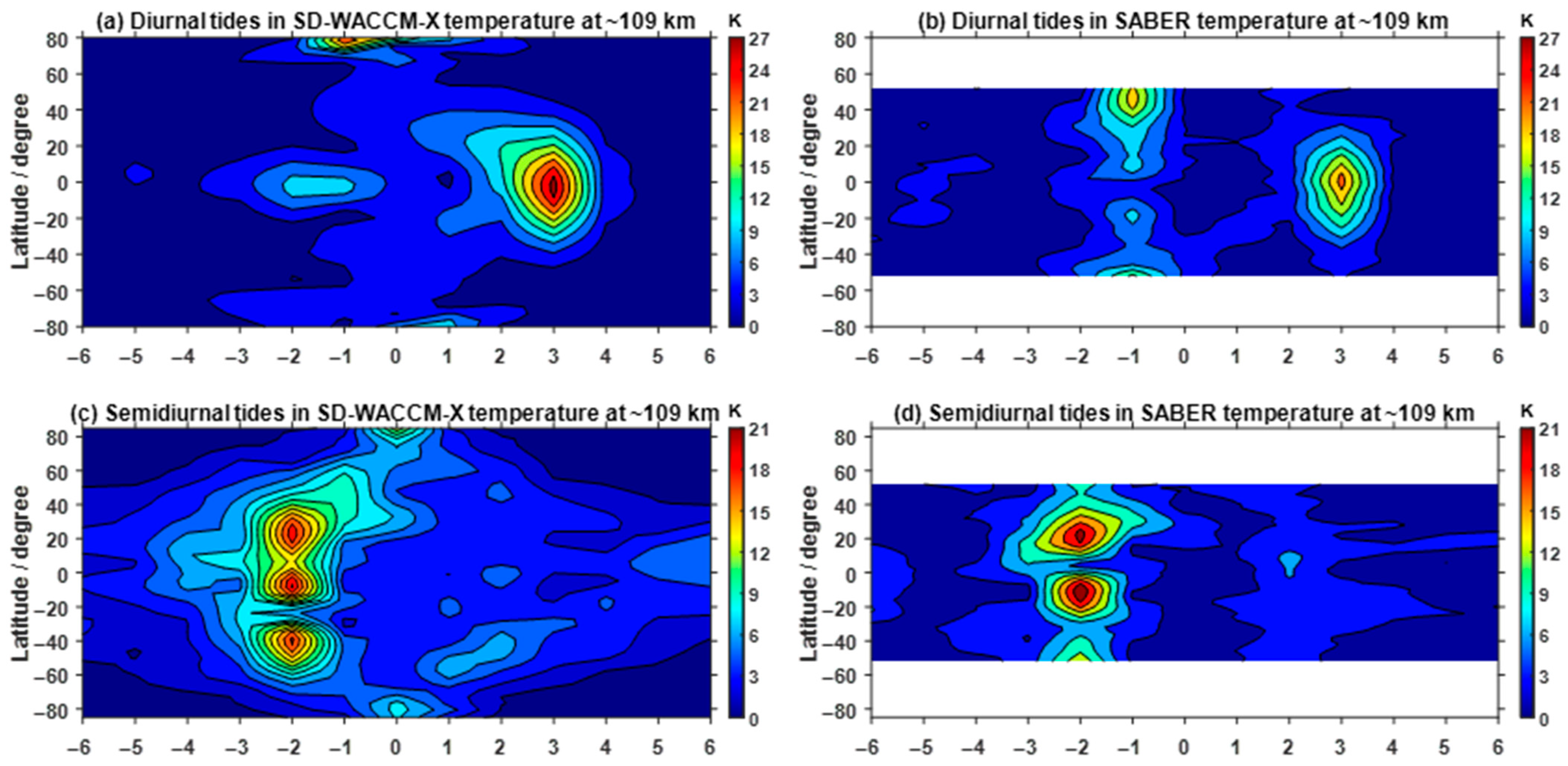
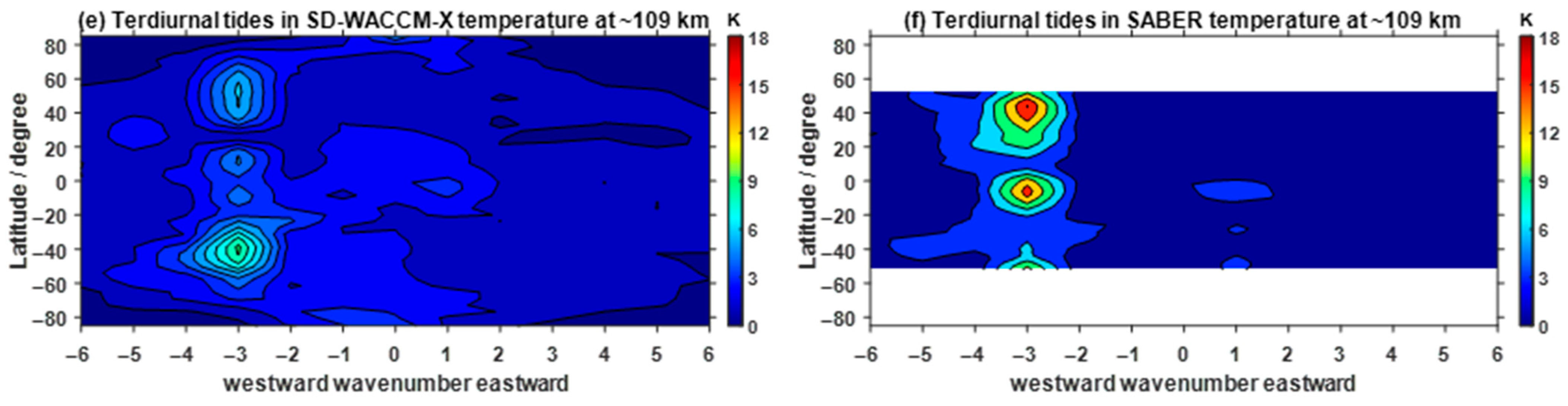
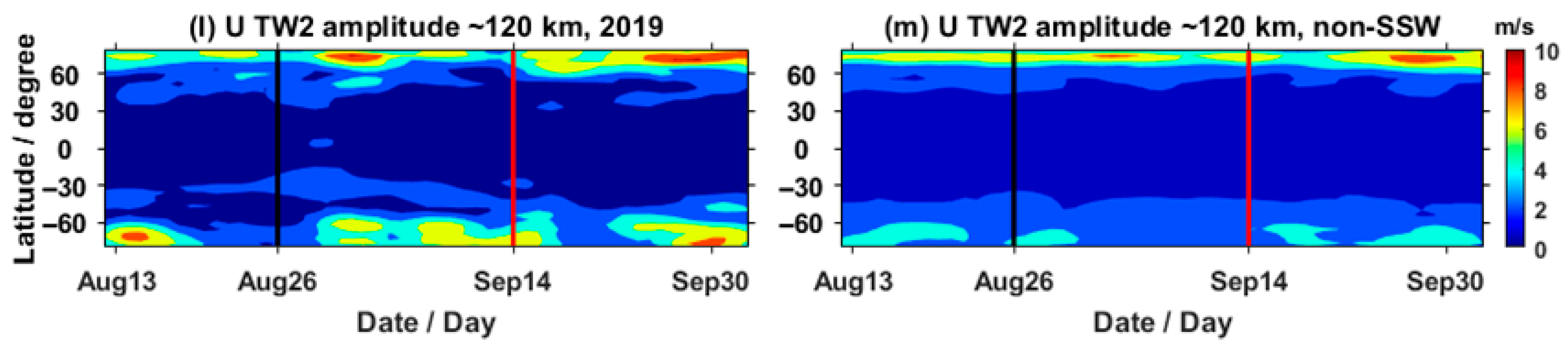
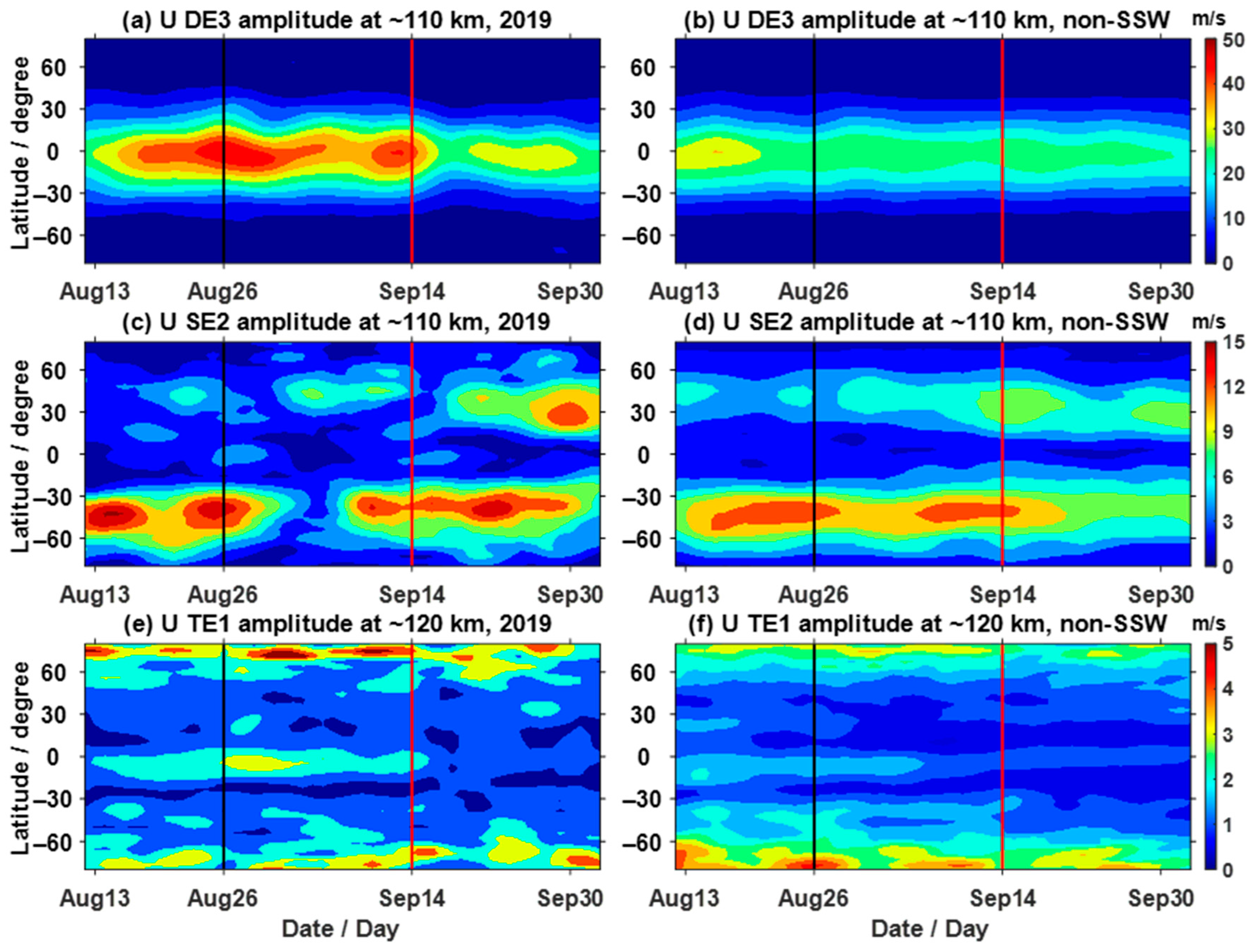
3.1. Nonmigrating Tidal Variations in the Neutral Atmosphere
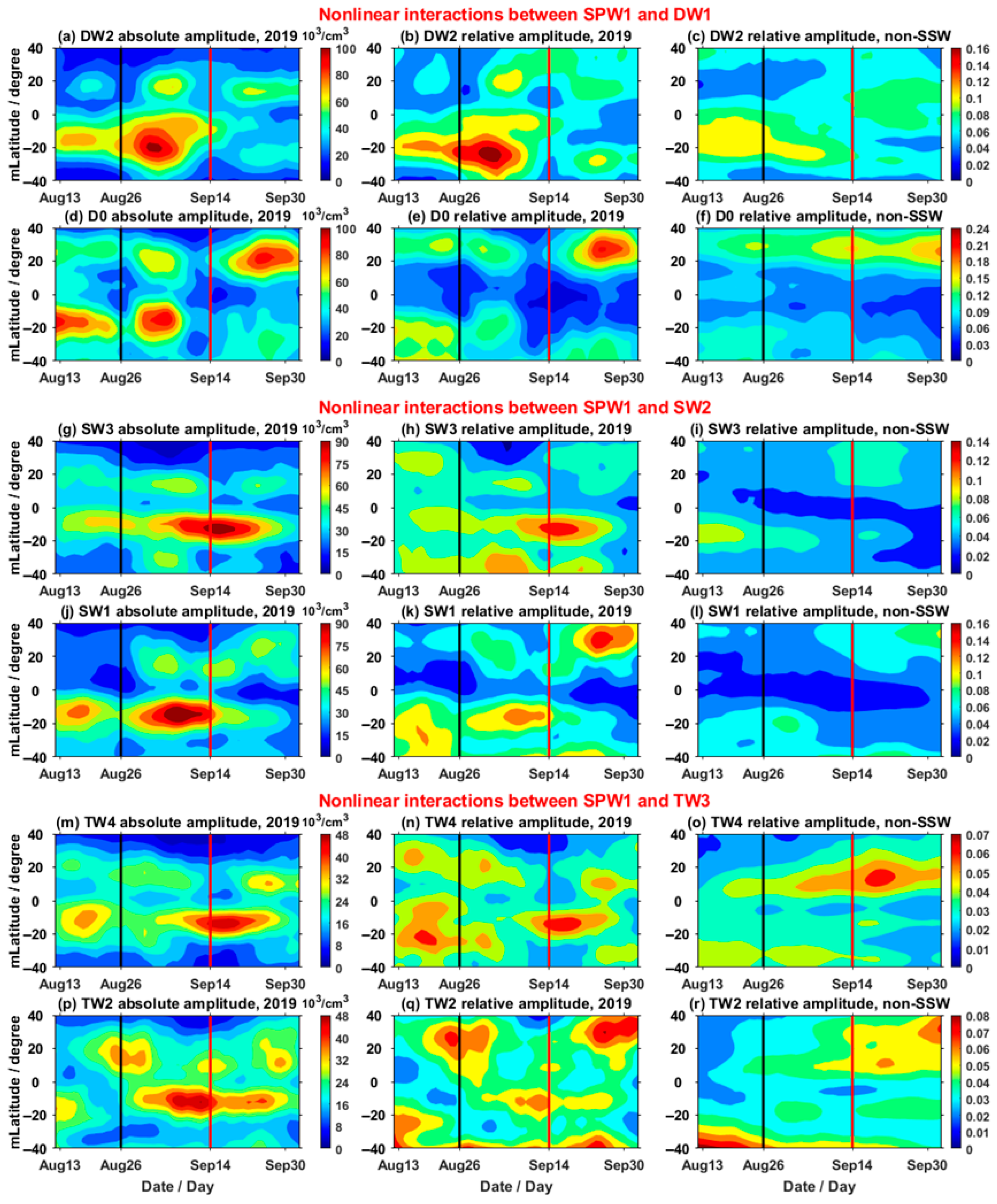
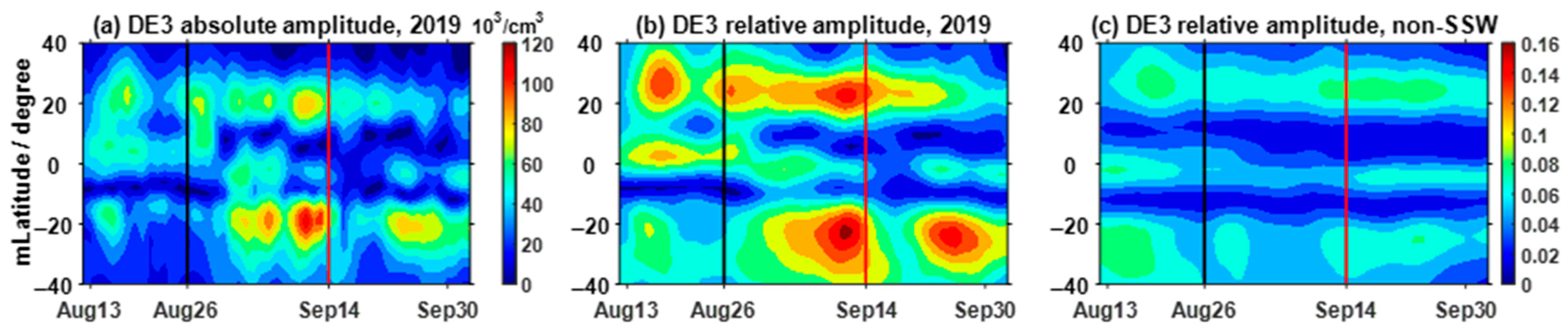
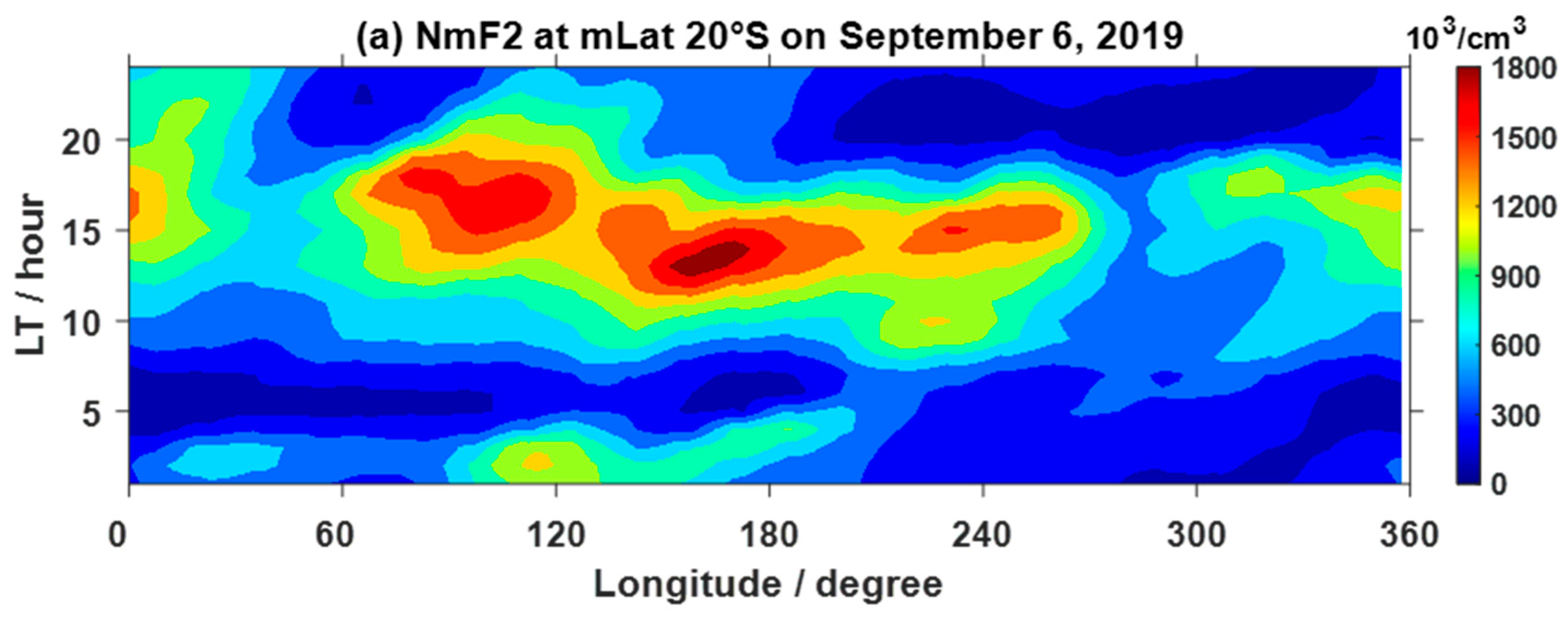
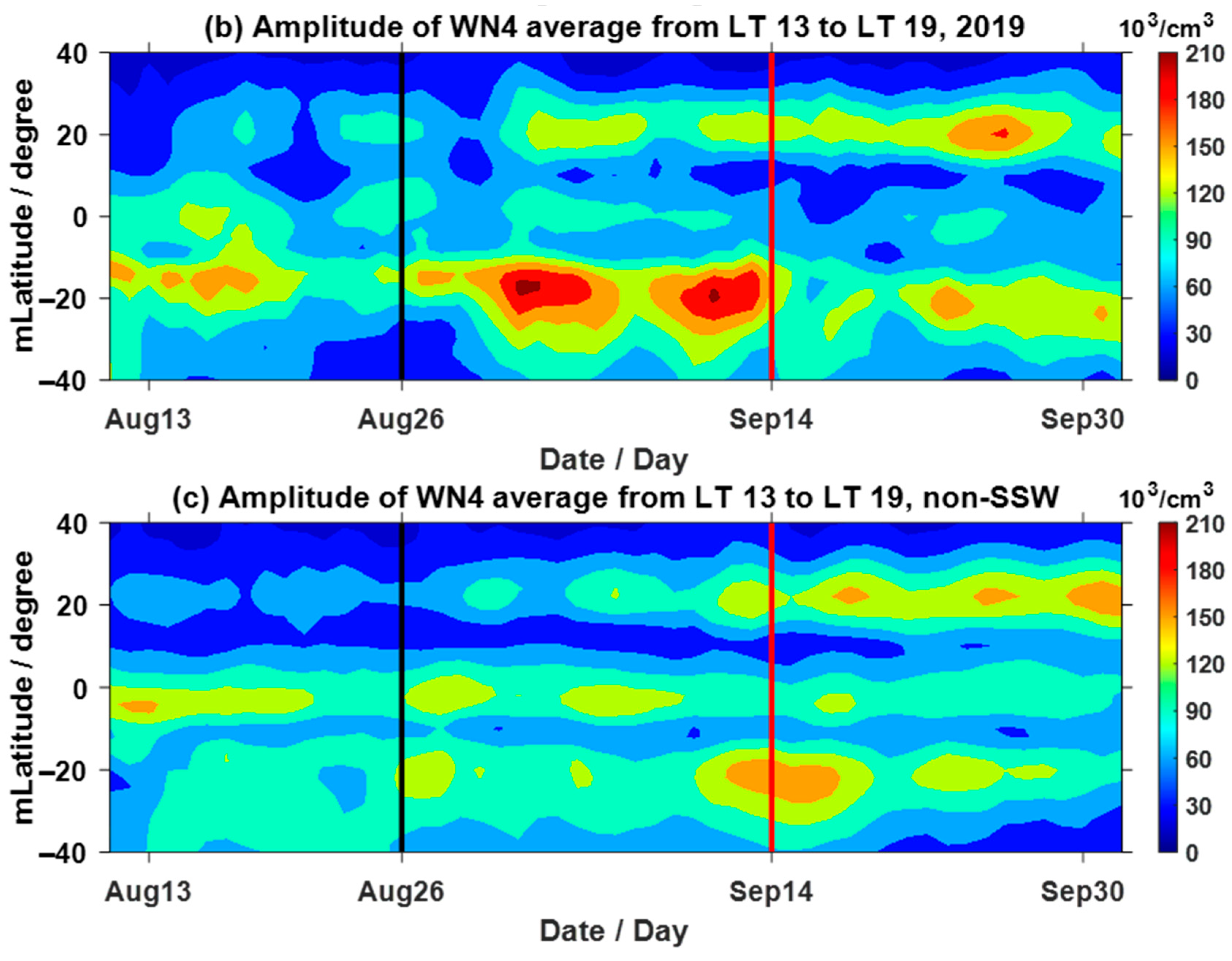
3.2. Nonmigrating Tidal Effects on the Ionosphere
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- This SSW was dominated by a strong SPW1 activity, and a weak increase in SPW2 also occurred during this SSW.
- Nonlinear interactions between SPW1 and migrating tides have also been triggered during this SSW event, which have significant influences on the corresponding nonmigrating tides. Also, these diurnal and semidiurnal nonmigrating tides, generated and influenced by the nonlinear interactions, show simultaneous enhancements in the neutral atmosphere and ionosphere.
- The DE3, SE2 and TE1 have significant concurrent increases in the neutral atmosphere and ionosphere, and the amplitudes of the ionospheric longitudinal WN4 structure also show simultaneous increases. This indicates that the ionospheric longitudinal WN4 structure was influenced by these three nonmigrating tides during this SSW, and the influence of DE3 was the strongest.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, D.G.; Holton, J.R.; Leovy, C.B. Middle Atmosphere Dynamics; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1987; pp. xi, 489. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, A.H.; Seidel, D.J.; Hardiman, S.C.; Butchart, N.; Birner, T.; Match, A. Defining Sudden Stratospheric Warmings. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.H.; Sjoberg, J.P.; Seidel, D.J.; Rosenlof, K.H. A sudden stratospheric warming compendium. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, T. A Dynamical Model of the Stratospheric Sudden Warming. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, H.; Jenne, R.L.; Labitzke, K. Zonal harmonic standing waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 4463–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Matthias, V.; Miyoshi, Y.; Stolle, C.; Siddiqui, T.; Kervalishvili, G.; Laštovička, J.; Kozubek, M.; Ward, W.; Themens, D.R.; et al. September 2019 Antarctic Sudden Stratospheric Warming: Quasi-6-Day Wave Burst and Ionospheric Effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Teng, C.K.M.; Li, N.; Jia, M.; Li, G.; Xie, H.; Ding, Z.; Dou, X. Multivariate Analysis on the Ionospheric Responses to Planetary Waves During the 2019 Antarctic SSW Event. J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.; Collins, R.L. Stratospheric sudden warming effects on winds and temperature in the middle atmosphere at middle and low latitudes: A study using WACCM. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 32, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, L.P.; Chau, J.L.; Liu, H.L.; Coster, A.J. Unexpected connections between the stratosphere and ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Miyoshi, Y.; Miyahara, S.; Jin, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Shinagawa, H. Thermal and dynamical changes of the zonal mean state of the thermosphere during the 2009 SSW: GAIA simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 6784–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller-Rowell, T.; Akmaev, R.; Wu, F.; Fedrizzi, M.; Viereck, R.A.; Wang, H.J. Did the January 2009 sudden stratospheric warming cool or warm the thermosphere? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L18104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Ayarzaguena, B.; Birner, T.; Butchart, N.; Butler, A.H.; Charlton-Perez, A.J.; Domeisen, D.I.V.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Garny, H.; Gerber, E.P.; et al. Sudden Stratospheric Warmings. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, e2020RG000708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.M. Tidal and Planetary Waves. In The Upper Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere: A Review of Experiment and Theory; Geophysical Monograph Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 67–87. [Google Scholar]
- Lindzen, R.S.; Chapman, S.J. Atmospheric tides. Space Sci. Rev. 1969, 10, 3–188. [Google Scholar]
- Goncharenko, L.P.; Coster, A.J.; Chau, J.L.; Valladares, C.E. Impact of sudden stratospheric warmings on equatorial ionization anomaly. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A00g07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedatella, N.M.; Liu, H.L. The influence of atmospheric tide and planetary wave variability during sudden stratosphere warmings on the low latitude ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 5333–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, A.S. Variations in Ionospheric Peak Electron Density During Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in the Arctic Region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Roble, R.G. A study of a self-generated stratospheric sudden warming and its mesospheric-lower thermospheric impacts using the coupled TIME-GCM/CCM3. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Wang, W.; Richmond, A.D.; Roble, R.G. Ionospheric variability due to planetary waves and tides for solar minimum conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A00g01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, S.; Sathishkumar, S.; Gurubaran, S. Variabilities of mesospheric tides and equatorial electrojet strength during major stratospheric warming events. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 4125–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedatella, N.M.; Richmond, A.D.; Maute, A.; Liu, H.L. Impact of semidiurnal tidal variability during SSWs on the mean state of the ionosphere and thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 8077–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.A.; Schreiner, W.S.; Lei, J.H.; Rocken, C.; Hunt, D.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wan, W.X. Global ionospheric response observed by COSMIC satellites during the January 2009 stratospheric sudden warming event. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A00g09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedatella, N.M.; Forbes, J.M. Evidence for stratosphere sudden warming-ionosphere coupling due to vertically propagating tides. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller-Rowell, T.; Wu, F.; Akmaev, R.; Fang, T.W.; Araujo-Pradere, E. A whole atmosphere model simulation of the impact of a sudden stratospheric warming on thermosphere dynamics and electrodynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A00g08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Miyoshi, Y.; Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P.; Fujiwara, H.; Shinagawa, H. Response of migrating tides to the stratospheric sudden warming in 2009 and their effects on the ionosphere studied by a whole atmosphere-ionosphere model GAIA with COSMIC and TIMED/SABER observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Ratnam, M.V.; Rao, S.V.B. Effect of Southern Hemisphere Sudden Stratospheric Warmings on Antarctica Mesospheric Tides: First Observational Study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guharay, A.; Batista, P.P. On the variability of tides during a major stratospheric sudden warming in September 2002 at Southern hemispheric extra-tropical latitude. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.K.M.; Gu, S.Y.; Qin, Y.; Dou, X.; Li, N.; Tang, L. Unexpected Decrease in TW3 Amplitude During Antarctic Sudden Stratospheric Warming Events as Revealed by SD-WACCM-X. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA029050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, W.; Hwang, J.; Kumar, K.N.; Kim, Y.H. Unusual Changes in the Antarctic Middle Atmosphere During the 2019 Warming in the Southern Hemisphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Roble, R.G. Dynamical coupling of the stratosphere and mesosphere in the 2002 Southern Hemisphere major stratospheric sudden warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, L.P.; Harvey, V.L.; Greer, K.R.; Zhang, S.R.; Coster, A.J. Longitudinally Dependent Low-Latitude Ionospheric Disturbances Linked to the Antarctic Sudden Stratospheric Warming of September 2019. J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Janches, D.; Ma, J.; Lieberman, R.S.; Stober, G.; Moffat-Griffin, T.; Mitchell, N.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.; Murphy, D.J. Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere Winds and Tidal Variations During the 2019 Antarctic Sudden Stratospheric Warming. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2021JA030177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chau, J.L.; Forbes, J.M.; Thorsen, D.; Li, G.; Siddiqui, T.A.; Yamazaki, Y.; Hocking, W.K. Quasi-10-Day Wave and Semidiurnal Tide Nonlinear Interactions During the Southern Hemispheric SSW 2019 Observed in the Northern Hemispheric Mesosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL091453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Miyoshi, Y. Ionospheric Signatures of Secondary Waves from Quasi-6-Day Wave and Tide Interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lei, J.; Huang, F.; Yi, W.; Chen, J.; Xue, X.; Gu, S.; Luan, X.; Zhong, J.; Liu, F.; et al. Responses of the Ionosphere and Neutral Winds in the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere in the Asian-Australian Sector to the 2019 Southern Hemisphere Sudden Stratospheric Warming. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpasuvan, V.; Richter, J.H.; Orsolini, Y.J.; Stordal, F.; Kvissel, O.K. The roles of planetary and gravity waves during a major stratospheric sudden warming as characterized in WACCM. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 78–79, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Gu, S.Y.; Teng, C.K.M.; Dou, X.K.; Yu, Y.; Li, N. Comprehensive Study of the Climatology of the Quasi-6-Day Wave in the MLT Region Based on Aura/MLS Observations and SD-WACCM-X Simulations. J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys. 2020, 126, e2020JA028454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, F.; Liu, H.L.; Ma, J.; Garcia, R.R. The lower thermosphere during the northern hemisphere winter of 2009: A modeling study using high-altitude data assimilation products in WACCM-X. J. Geophys. Res.Atmos. 2013, 118, 8954–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.E.; Sassi, F.; Mannucci, A.J. SAMI3/SD-WACCM-X simulations of ionospheric variability during northern winter 2009. Space Weather. Int. J. Res. Appl. 2015, 13, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, F.; Siskind, D.E.; Tate, J.L.; Liu, H.L.; Randall, C.E. Simulations of the Boreal Winter Upper Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere with Meteorological Specifications in SD-WACCM-X. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3791–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Foster, B.T.; Hagan, M.E.; McInerney, J.M.; Maute, A.; Qian, L.; Richmond, A.D.; Roble, R.G.; Solomon, S.C.; Garcia, R.R.; et al. Thermosphere extension of the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model. J. Geophys. Res. Space 2010, 115, A12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Bardeen, C.G.; Foster, B.T.; Lauritzen, P.H.; Liu, J.; Lu, G.; Marsh, D.R.; Maute, A.; McInerney, J.M.; Pedatella, N.M.; et al. Development and Validation of the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model with Thermosphere and Ionosphere Extension (WACCM-X 2.0). J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D.R. Chemical–Dynamical Coupling in the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere. In Aeronomy of the Earth's Atmosphere and Ionosphere; Abdu, M.A., Pancheva, D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P.; Hall, C.; Meek, C.; Tsutsumi, M.; Pedatella, N.; Nozawa, S. Climatology of the main (24-h and 12-h) tides observed by meteor radars at Svalbard and Tromsø: Comparison with the models CMAM-DAS and WACCM-X. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 207, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Limpasuvan, V.; Orsolini, Y.J.; Espy, P.J.; Hibbins, R.E. Climatological Westward-Propagating Semidiurnal Tides and Their Composite Response to Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in SuperDARN and SD-WACCM-X. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD032895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.L.; Hays, P.B.; Skinner, W.R. A Least-Squares Method for Spectral-Analysis of Space-Time Series. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P.; Andonov, B.; Mitchell, N.J.; Forbes, J.M. Planetary waves observed by TIMED/SABER in coupling the stratosphere–mesosphere–lower thermosphere during the winter of 2003/2004: Part 1—Comparison with the UKMO temperature results. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2009, 71, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, H.; Vial, F. On Tidal Variability Induced by Nonlinear-Interaction with Planetary-Waves. J. Geophys. Res. Space 1991, 96, 14169–14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K. Observation of Wave-Wave Interactions in the Stratosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 2484–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Yamazaki, Y. Excitation Mechanism of Ionospheric 6-Day Oscillation During the 2019 September Sudden Stratospheric Warming Event. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, S. Variabilities of Low-Latitude Migrating and Nonmigrating Tides in GPS-TEC and TIMED-SABER Temperature During the Sudden Stratospheric Warming Event of 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Space 2017, 122, 10748–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P.; Andonov, B. Nonmigrating tidal activity related to the sudden stratospheric warming in the Arctic winter of 2003/2004. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maute, A.; Hagan, M.E.; Richmond, A.D.; Roble, R.G. TIME-GCM study of the ionospheric equatorial vertical drift changes during the 2006 stratospheric sudden warming. J. Geophys. Res. Space 2014, 119, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.M.; Russell, J.; Miyahara, S.; Zhang, X.; Palo, S.; Mlynczak, M.; Mertens, C.J.; Hagan, M.E. Troposphere-thermosphere tidal coupling as measured by the SABER instrument on TIMED during July-September 2002. J. Geophys. Res. Space 2006, 111, A10s06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lieberman, R.S.; Harvey, V.L.; Pedatella, N.M.; Oberheide, J.; Hibbins, R.E.; Espy, P.J.; Janches, D. Tidal Variations in the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere Before, During, and After the 2009 Sudden Stratospheric Warming. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Smith, A.K.; Liu, M.H.; Liu, X.; Gao, H.; Jiang, G.Y.; Yuan, W. Evidence for nonmigrating tides produced by the interaction between tides and stationary planetary waves in the stratosphere and lower mesosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, R.S.; Riggin, D.M.; Ortland, D.A.; Oberheide, J.; Siskind, D.E. Global observations and modeling of nonmigrating diurnal tides generated by tide-planetary wave interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 11419–11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.J.; Du, J.; Zhu, X.W. Statistics on Nonmigrating Diurnal Tides Generated by Tide-Planetary Wave Interaction and Their Relationship to Sudden Stratospheric Warming. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Palo, S.E.; Liu, H.L. Short-term variation of the s1 nonmigrating semidiurnal tide during the 2002 stratospheric sudden warming. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D03109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Ren, Z.; Ding, F.; Xiong, J.; Liu, L.; Ning, B.; Zhao, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, M.L. A simulation study for the couplings between DE3 tide and longitudinal WN4 structure in the thermosphere and ionosphere. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2012, 90–91, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedatella, N.M.; Hagan, M.E.; Maute, A. The comparative importance of DE3, SE2, and SPW4 on the generation of wave-number-4 longitude structures in the low-latitude ionosphere during September equinox. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L19108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onohara, A.N.; Batista, I.S.; Batista, P.P. Wavenumber-4 structures observed in the low-latitude ionosphere during low and high solar activity periods using FORMOSAT/COSMIC observations. Ann. Geophys. 2018, 36, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wan, W.X.; Cao, J.B.; Ren, Z.P. Wavenumber-4 spectral component extracted from TIMED/SABER observations. Earth Planet. Phys. 2020, 4, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Jin, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Shinagawa, H.; Liu, H.X. Wave-4 structure of the neutral density in the thermosphere and its relation to atmospheric tides. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 90–91, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, C.-K.-M.; Fan, Z.; Cheng, W.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J. SD-WACCM-X Study of Nonmigrating Tidal Responses to the 2019 Antarctic Minor SSW. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070848
Teng C-K-M, Fan Z, Cheng W, Qin Y, Yang Z, Sun J. SD-WACCM-X Study of Nonmigrating Tidal Responses to the 2019 Antarctic Minor SSW. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070848
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Chen-Ke-Min, Zhiqiang Fan, Wei Cheng, Yusong Qin, Zhenlin Yang, and Jingzhe Sun. 2025. "SD-WACCM-X Study of Nonmigrating Tidal Responses to the 2019 Antarctic Minor SSW" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070848
APA StyleTeng, C.-K.-M., Fan, Z., Cheng, W., Qin, Y., Yang, Z., & Sun, J. (2025). SD-WACCM-X Study of Nonmigrating Tidal Responses to the 2019 Antarctic Minor SSW. Atmosphere, 16(7), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070848





