Temporal and Latitudinal Occurrences of Geomagnetic Pulsations Recorded in South America by the Embrace Magnetometer Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geomagnetic Pulsations
- Pc1 (0.2–5 s): These high-frequency pulsations are typically associated with electromagnetic ion-cyclotron waves, often observed in the auroral zones. They are thought to be driven by instabilities in the plasma sheet boundary layer and are sensitive indicators of energetic particle precipitation [9,16].
- Pc2–Pc5 (5–600 s): These pulsations cover a broad frequency range and are detectable at various latitudes. Pc3 and Pc4, in particular, are often linked to waveguide modes and field line resonances within the magnetosphere, driven by solar wind pressure variations and the Kelvin–Helmholtz instability at the magnetopause [9,16].
3. Database and Methodology
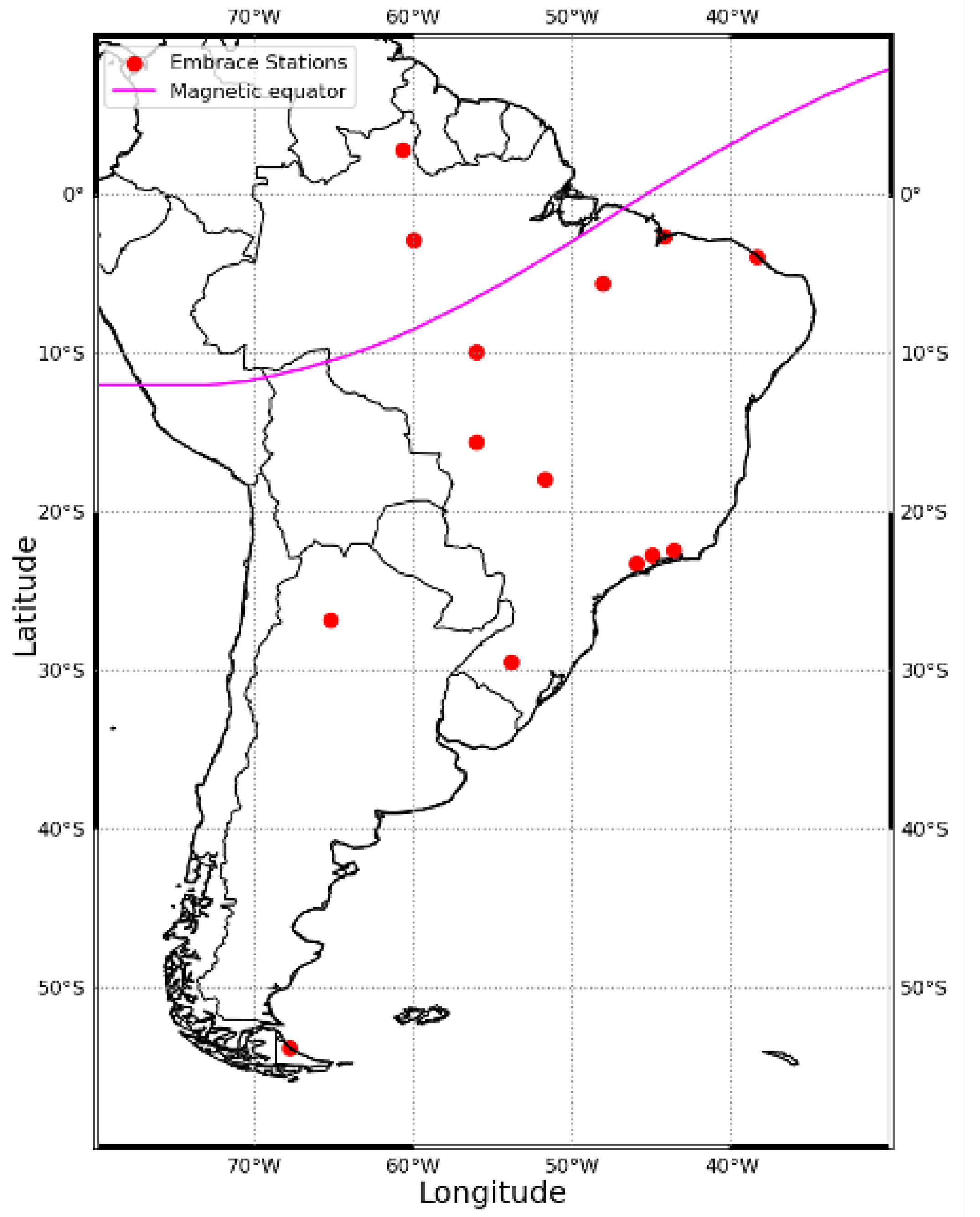
3.1. Database
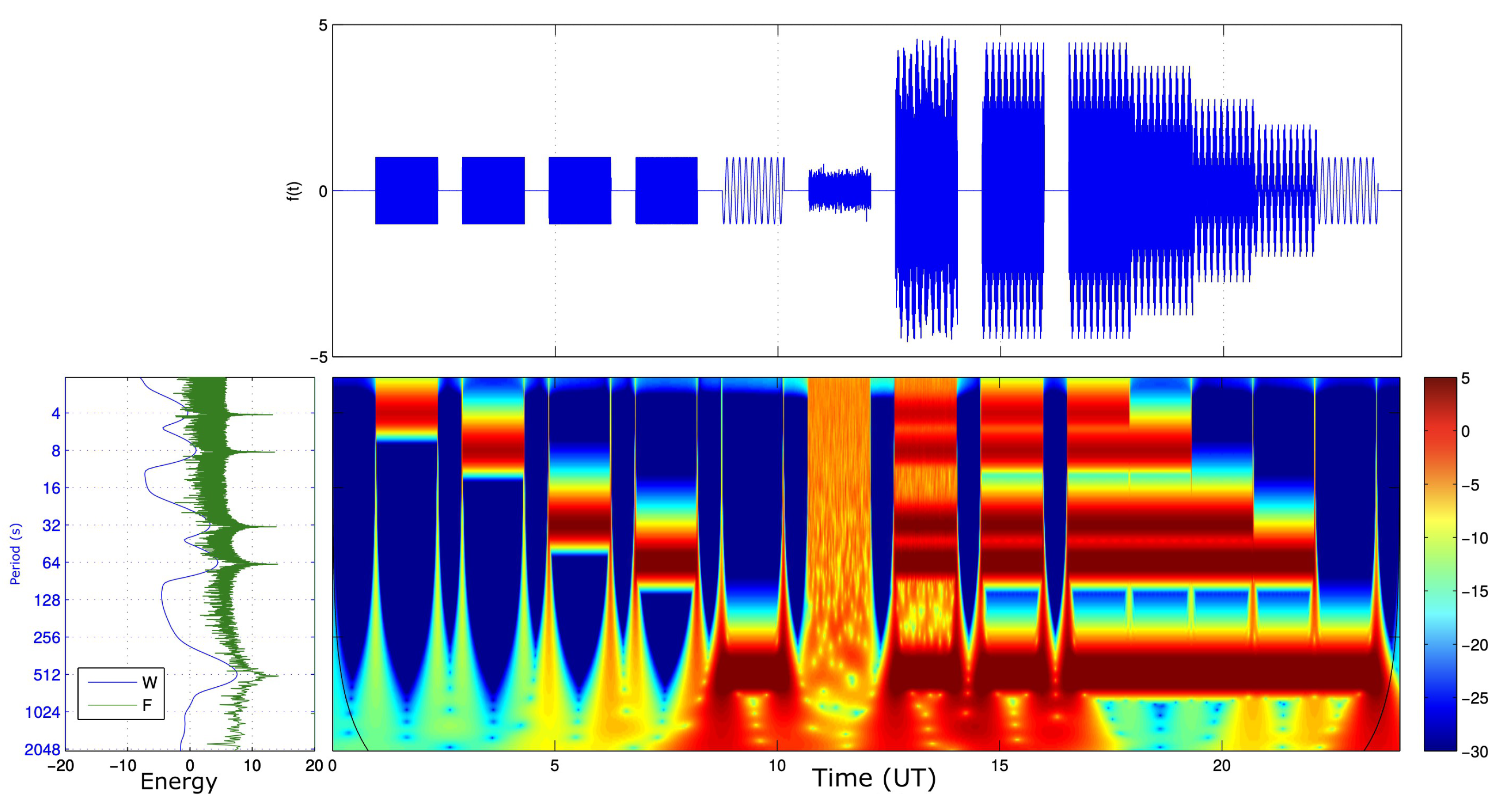
3.2. Methodology for the Signal Analysis
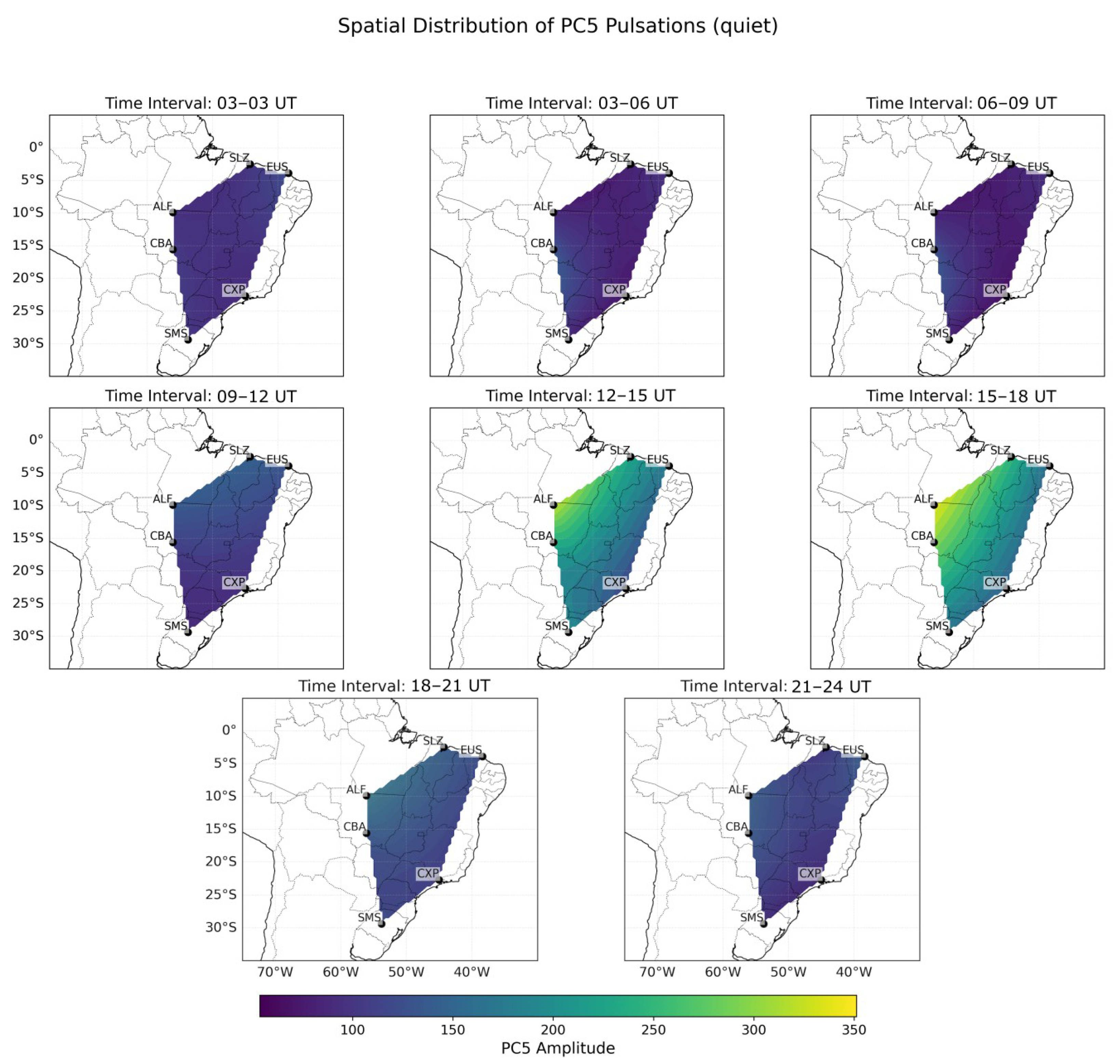
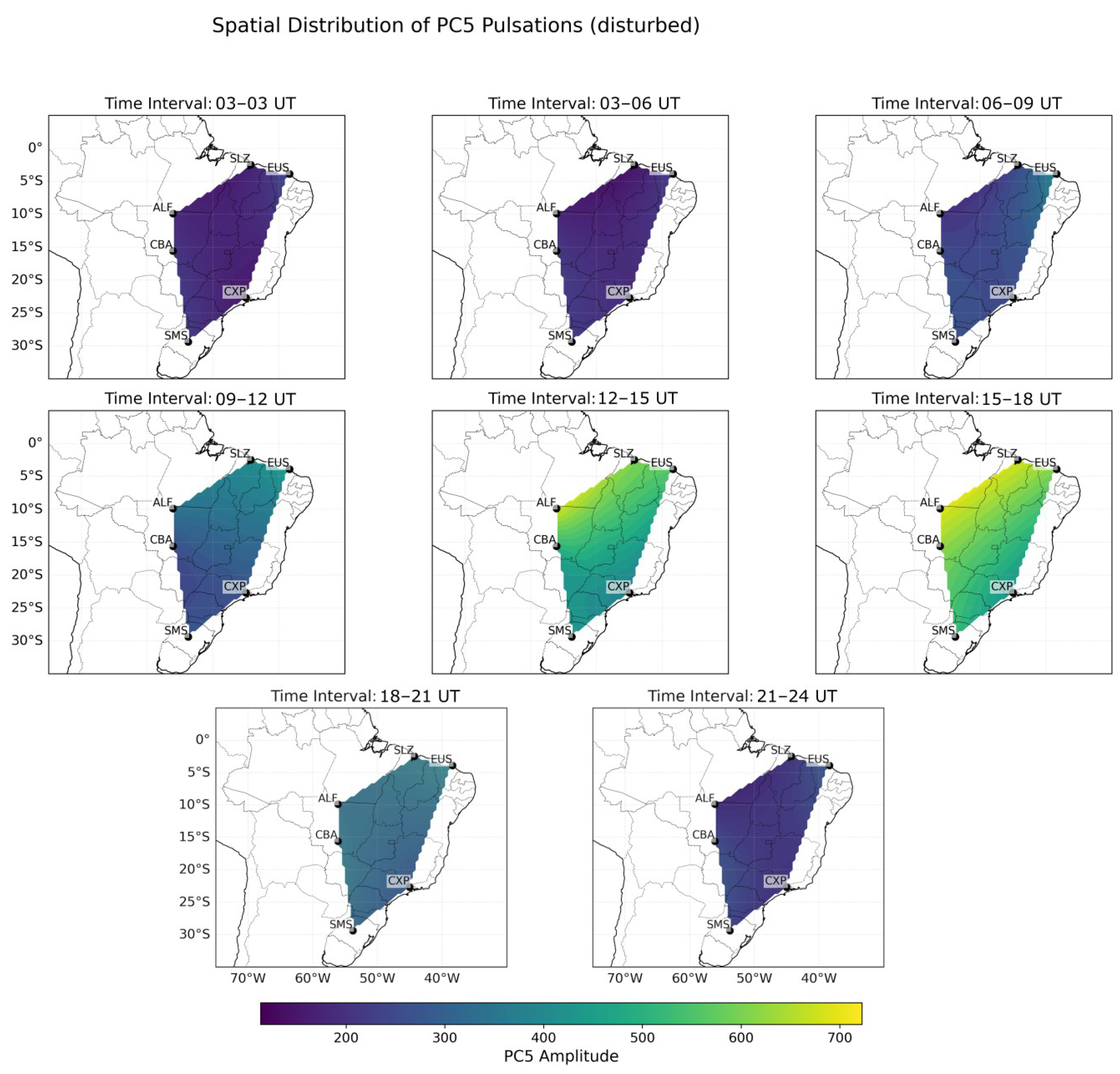
4. Results and Discussion
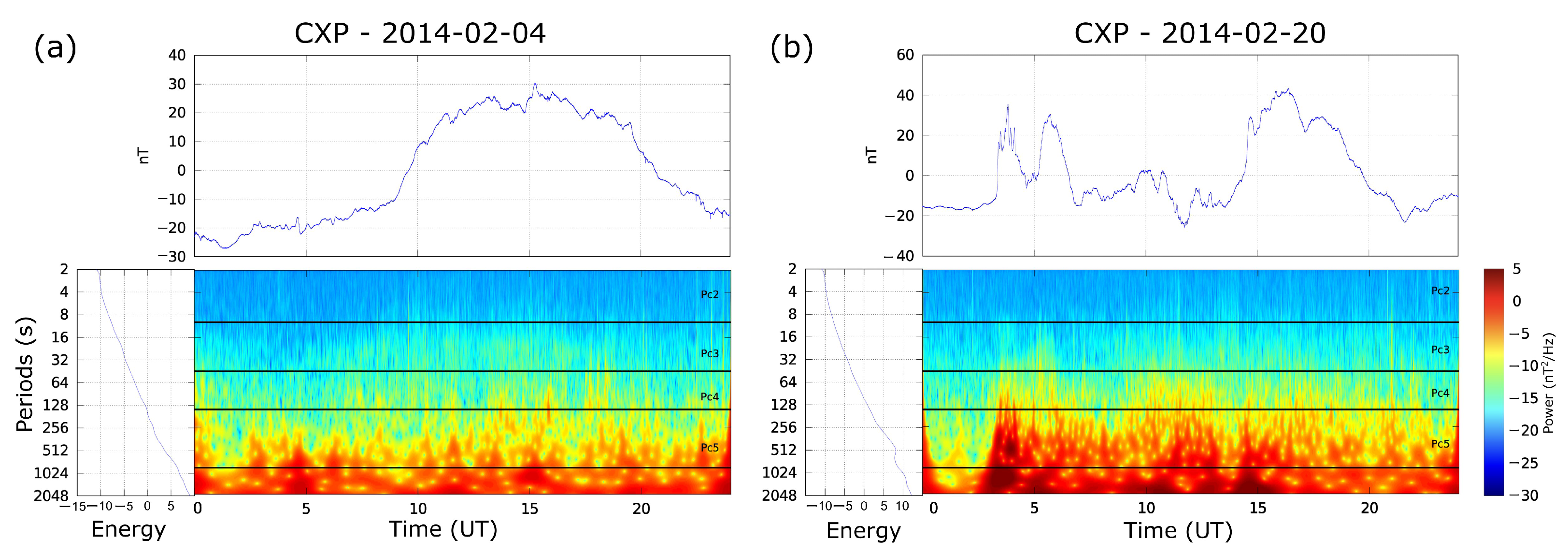
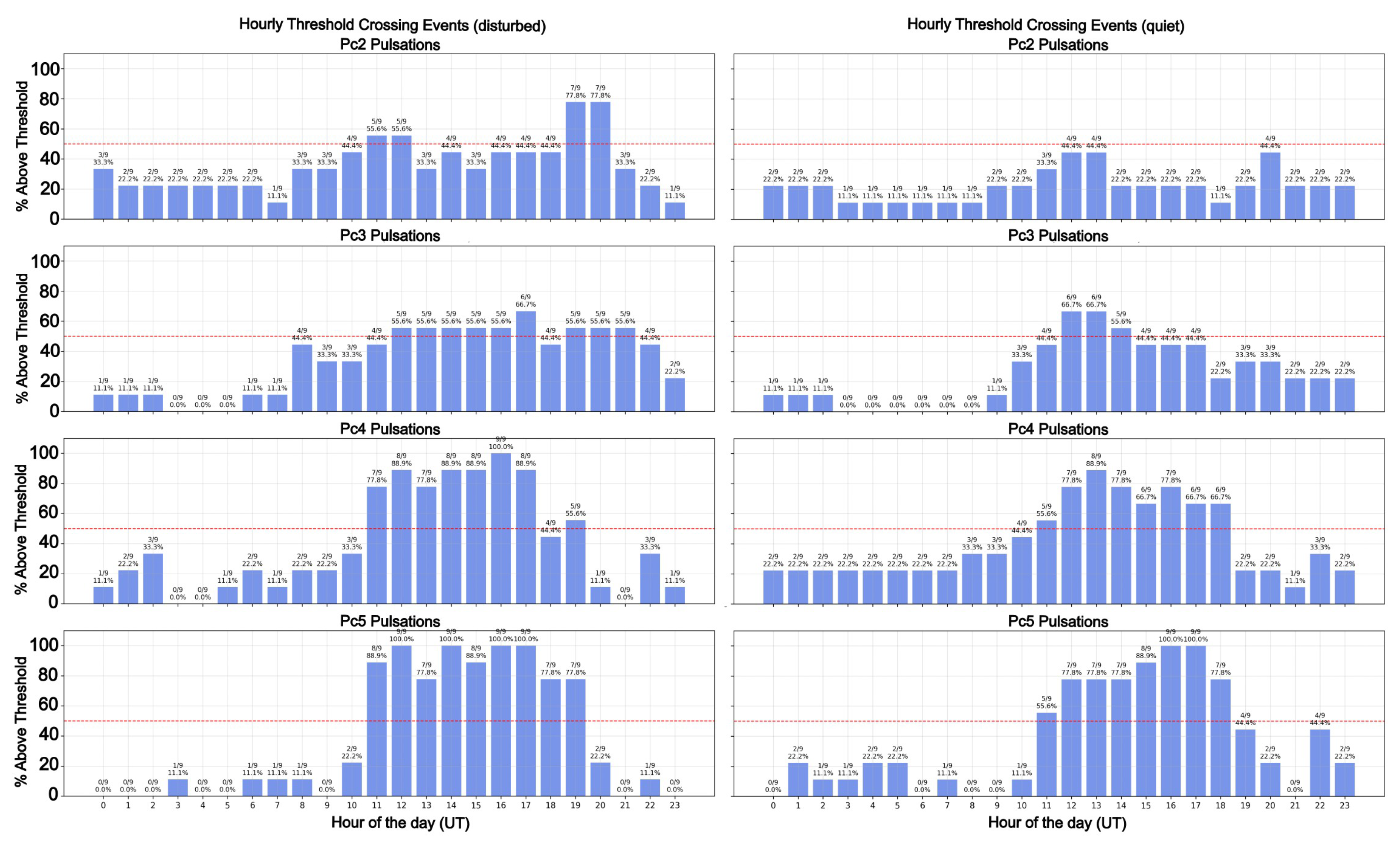
4.1. Diagnostic Analysis
4.2. Latitudinal Behavior
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, J.A. Geomagnetism; Number v. 4 in Geomagnetism; Academic Press: London, UK, 1991; p. 806. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, E.N. Dynamics of the Interplanetary Gas and Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 1958, 128, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, M.G.; Russell, C.T. Introduction to Space Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, M.G. Planetary magnetospheres. In Handbook of Solar-Terrestrial Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.K. The Solar-Terrestrial Environment: An Introduction to Geospace–the Science of the Terrestrial Upper Atmosphere, Ionosphere, and Magnetosphere; Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Schunk, R.W.; Nagy, A.F. Ionospheres, 2nd ed.; Cambrigde University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; Volume 82, p. 628. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, R.E.; Gonzalez, W.D. Magnetospheric balance of solar wind dynamic pressure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2991–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, R.T.; McFadden, P.L.; McElhinny, M.W. The Magnetic Field of the Earth, ilustrada ed.; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; p. 531. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T. Geomagnetic pulsations. Space Sci. Rev. 1969, 10, 319–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere; International Geophysics; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McPherron, R.L. Magnetic pulsations: Their sources and relation to solar wind and geomagnetic activity. Surv. Geophys. 2005, 26, 545–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, W.J. Magnetospheric ULF Waves: A Tutorial With a Historical Perspective. In Solar Wind Sources of Magnetospheric Ultra-Low-Frequency Waves; Engebretson, M.J., Takahashi, K., Scholer, M., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.a.; Kato, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Troitskaya, V.a. Classification of geomagnetic micropulsations. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumjohann, W.; Treumann, R.A. Basic Space Plasma Physics; World Scientific: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Glaßmeier, K.H. Geomagnetic pulsations. In Encyclopedia of Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, J.A.; Jacobs, J. The Morphology of Geomagnetic Micropulsations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Ripka, P. Review of fluxgate sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1992, 33, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denardini, C.; Chen, S.; Resende, L.C.A.; Moro, J.; Bilibio, A.; Fagundes, P.R.; Gende, M.A.; Cabrera, M.A.; Bolzan, M.; Padilha, A.L.; et al. The embrace magnetometer network for South America: Network description and its qualification. Radio Sci. 2018, 53, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.N.; Sugiura, M. Auroral electrojet activity index AE and its universal time variations. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, M. Hourly Values of Equatorial Dst for the IGY; Technical Report; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1963.
- Bartels, J. The geomagnetic measures for the time-variations of solar corpuscular radiation, described for use in correlation studies in other geophysical fields. Ann. Intern. Geophys. 1957, 4, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Matzka, J.; Stolle, C.; Yamazaki, Y.; Bronkalla, O.; Morschhauser, A. The geomagnetic Kp index and derived indices of geomagnetic activity. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2020SW002641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; Volume 61, p. 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, M.O.; Mendes, O.; da Costa, A.M. On wavelet techniques in atmospheric sciences. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, J.E.; Domingues, M.O.; Pagamisse, A.; Mendes, O. Introdução ao Mundo das Wavelets, Notas em Matemática Aplicada; SBMAC: Sao Carlos, Brazil, 2012; Volume 62, 144p. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, S.D.; Kelly, B.G.; O’Brien, J.J. An Introduction to Wavelet Analysis in Oceanography and Meteorology: With Application to the Dispersion of Yanai Waves. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2858–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Weng, H. Climate signal detection using wavelet transform: How to make a time series sing. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, C.K. An Introduction to Wavelets; Wavelet Analysis and Its Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, H.; Lau, K.M. Wavelets, Period Doubling, and Time-Frequency Localization with Application to Organization of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 2523–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farge, M. Wavelet Transforms and Their Applications To Turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1992, 24, 395–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Wavelet analysis for geophysical applications. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, O.; Domingues, M.O.; Mendes da Costa, A.; Clúa de Gonzalez, A.L.; Oliveira Domingues, M.; Mendes da Costa, A.; Clúa de Gonzalez, A.L. Wavelet analysis applied to magnetograms: Singularity detections related to geomagnetic storms. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, D.B.; Walden, A.T. Wavelet Methods for Time Series Analysis; Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nosé, M.; Iyemori, T.; Takeda, M.; Kamei, T.; Milling, D.; Orr, D.; Singer, H.; Worthington, E.; Sumitomo, N. Automated detection of Pi 2 pulsations using wavelet analysis: 1. Method and an application for substorm monitoring. Earth Planets Space 1998, 50, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H. Numerical Recipes, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; 1235p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckheit, J.B.; Donoho, D.L. Wavelab and Reproducible Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Heyns, M.J.; Lotz, S.I.; Gaunt, C.T. Geomagnetic Pulsations Driving Geomagnetically Induced Currents. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2020SW002557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanandrea, A.; Da Costa, J.; Dutra, S.; Trivedi, N.B.; Kitamura, T.; Yumoto, K.; Tachihara, H.; Shinohara, M.; Saotome, O. Pc3-4 geomagnetic pulsations at very low latitude in Brazil. Planet. Space Sci. 2004, 52, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, D.; Webb, D. Statistical studies of geomagnetic pulsations with periods between 10 and 70 sec and their relationship to the plasmapause region. Planet. Space Sci. 1975, 23, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, K.V.; Padilha, A.L.; Alves, L.R. Effects of ionospheric conductivity and ground conductance on geomagnetically induced currents during geomagnetic storms: Case studies at low-latitude and equatorial regions. Space Weather 2019, 17, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, A.; Bernabeu, E.; Thomson, A.; Viljanen, A.; Pirjola, R.; Boteler, D.; Eichner, J.; Cilliers, P.; Welling, D.; Savani, N.; et al. Geomagnetically induced currents: Science, engineering, and applications readiness. Space Weather 2017, 15, 828–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engebretson, M.J.; Simms, L.E.; Pilipenko, V.A.; Bouayed, L.; Moldwin, M.B.; Weygand, J.M.; Hartinger, M.D.; Xu, Z.; Clauer, C.R.; Coyle, S.; et al. Geomagnetic disturbances that cause GICs: Investigating their interhemispheric conjugacy and control by IMF orientation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2022JA030580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.; Liu, G.; Yizengaw, E.; Wu, C.C.; Zheng, Y.; Vines, S.; Buzulukova, N. Responses of field-aligned currents and equatorial electrojet to sudden decrease of solar wind dynamic pressure during the March 2023 geomagnetic storm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D. Ionosphere-magnetosphere coupling and field-aligned currents. Rev. Bras. Ensino Física 2014, 36, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | Period (s) | Frequency (mHz) | Wavelet Details | Wavelet Periods (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pc2 | 5–10 | 100–200 | d14–d15 | 3.03–6.25 |
| Pc3 | 10–45 | 22.2–100 | d13–d14 | 6.25–48.07 |
| Pc4 | 45–150 | 6.6–22.2 | d11 | 48.07–192.3 |
| Pc5 | 150–600 | 1.6–6.6 | d9–d10 | 96.15–769.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchezi, J.P.; Mendes, O.; Denardini, C.M. Temporal and Latitudinal Occurrences of Geomagnetic Pulsations Recorded in South America by the Embrace Magnetometer Network. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060742
Marchezi JP, Mendes O, Denardini CM. Temporal and Latitudinal Occurrences of Geomagnetic Pulsations Recorded in South America by the Embrace Magnetometer Network. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(6):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060742
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchezi, Jose Paulo, Odim Mendes, and Clezio Marcos Denardini. 2025. "Temporal and Latitudinal Occurrences of Geomagnetic Pulsations Recorded in South America by the Embrace Magnetometer Network" Atmosphere 16, no. 6: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060742
APA StyleMarchezi, J. P., Mendes, O., & Denardini, C. M. (2025). Temporal and Latitudinal Occurrences of Geomagnetic Pulsations Recorded in South America by the Embrace Magnetometer Network. Atmosphere, 16(6), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060742








