Air Pollution Monitoring and Modeling: A Comparative Study of PM, NO2, and SO2 with Meteorological Correlations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Emission Sources of SO2, NO2, PM10 and PM2.5 in Poland Based on NIR Data
2.2. Ground-Based Monitoring Data
2.3. Satellite-Based Data Collection for NO2 and SO2 Using Google Earth Engine
3. Results
3.1. Long-Term NIR Data Analysis
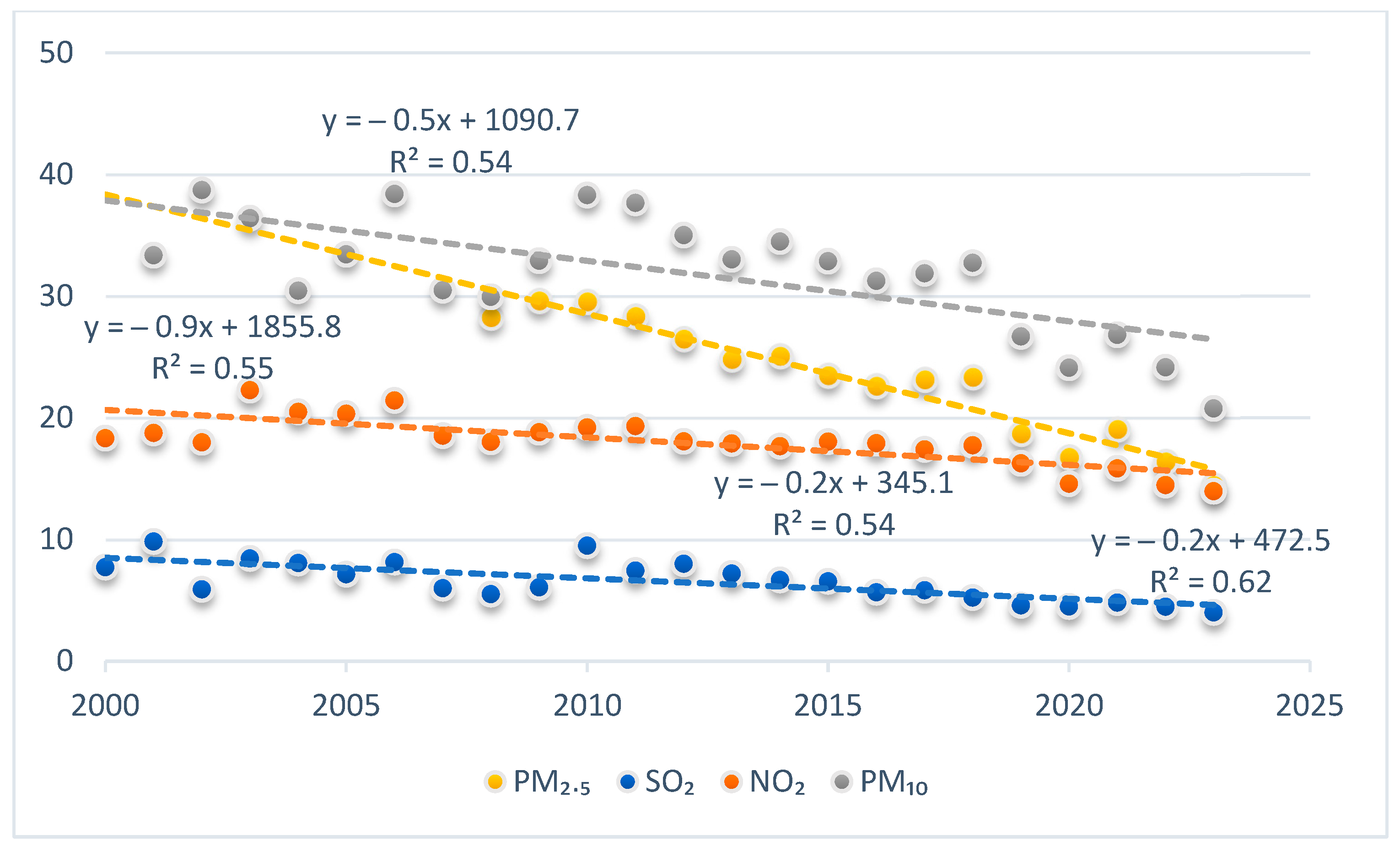
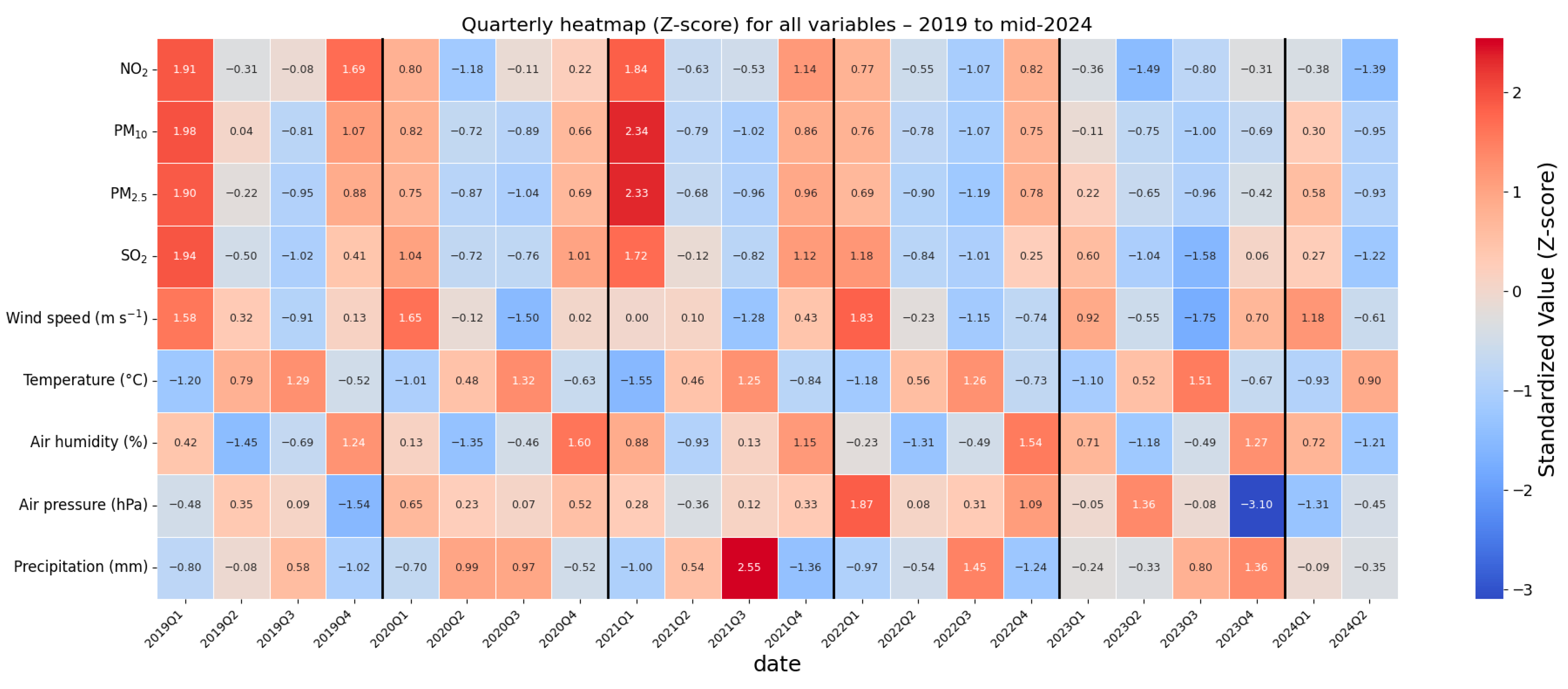
3.2. Ground-Level Concentration Trends (2000–2023)
3.3. Satellite-Derived Concentrations of NO2 and SO2 (2019–2025)
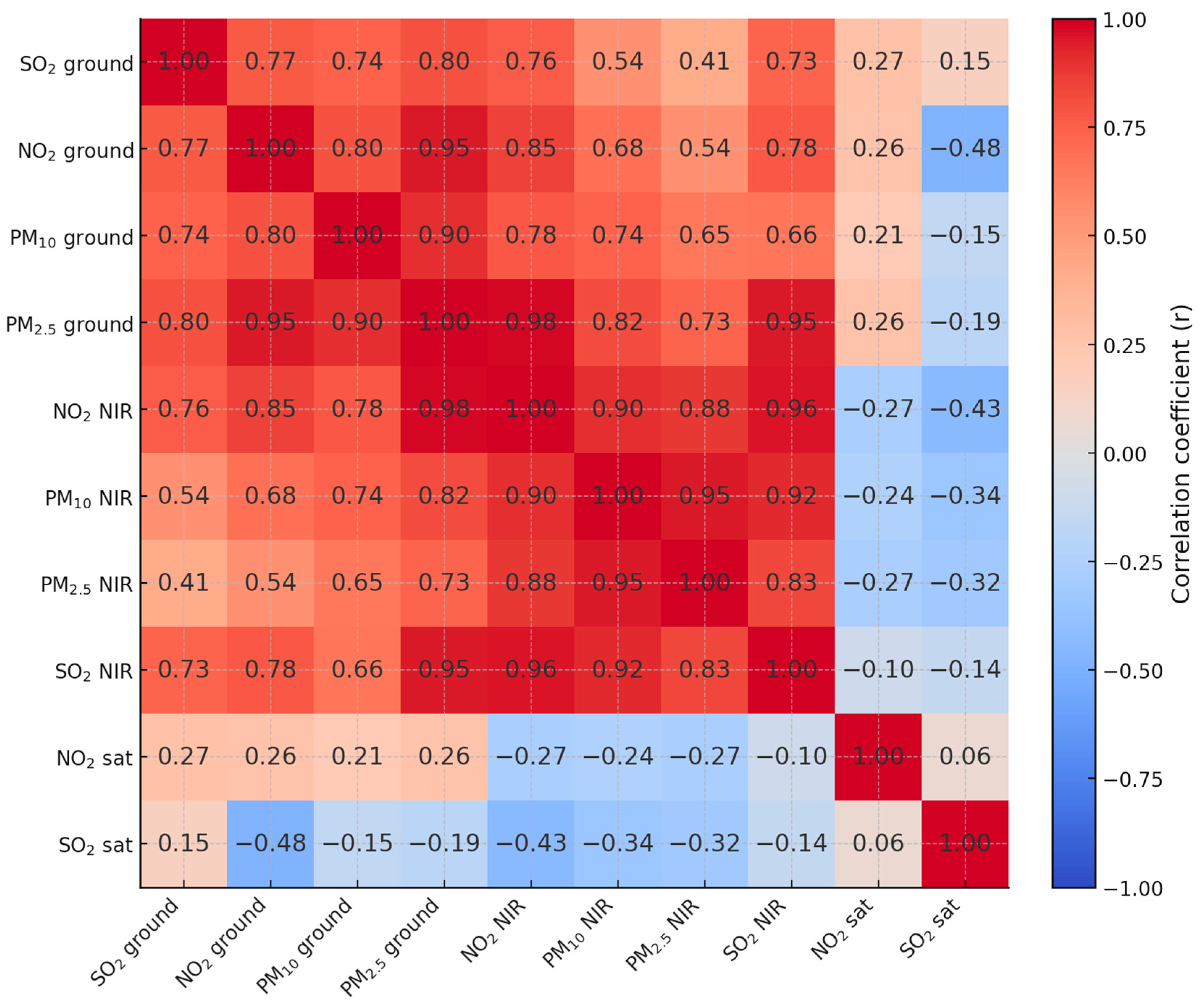
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Ground-Based, Inventory, and Satellite-Derived Pollutant Data
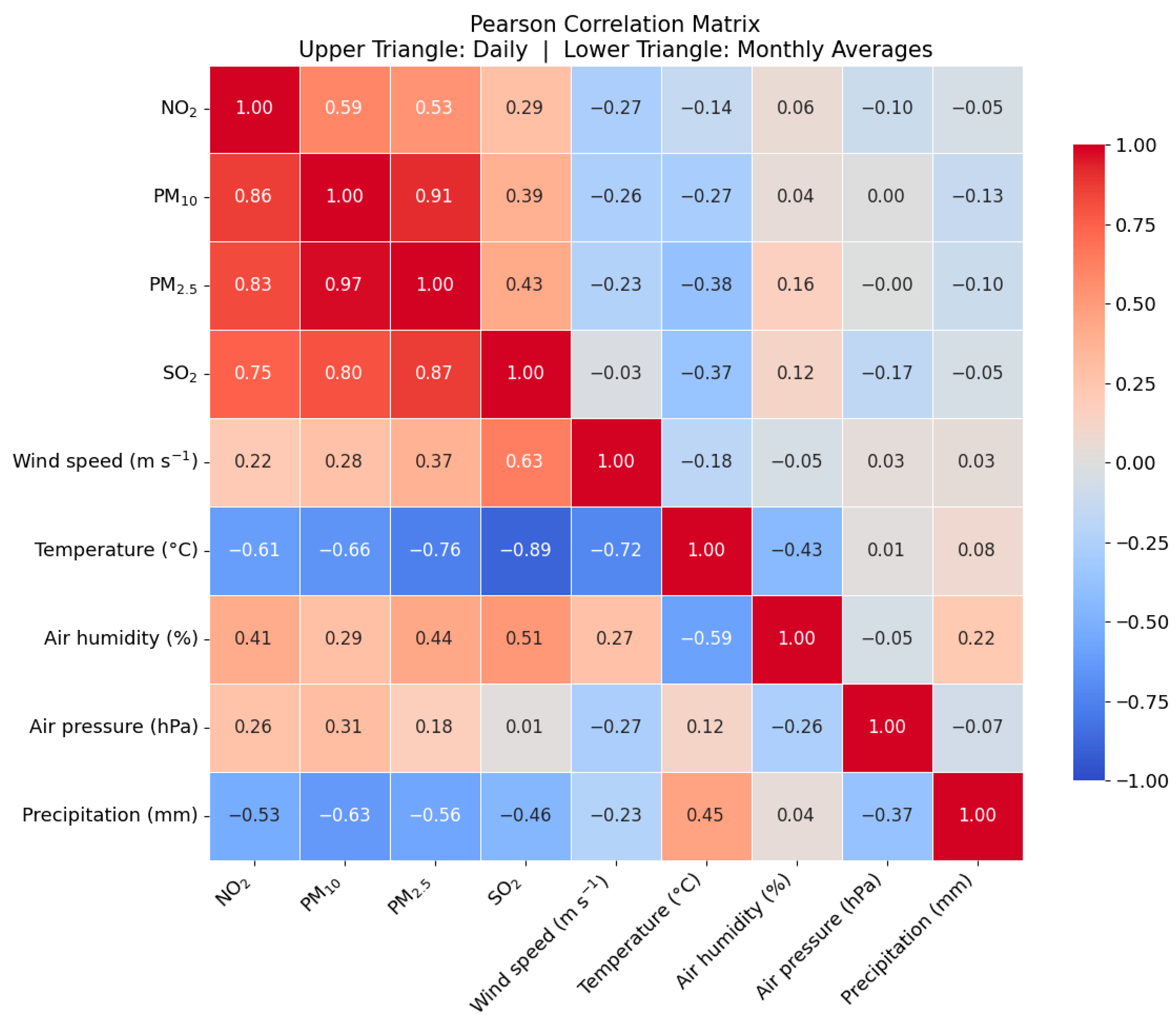
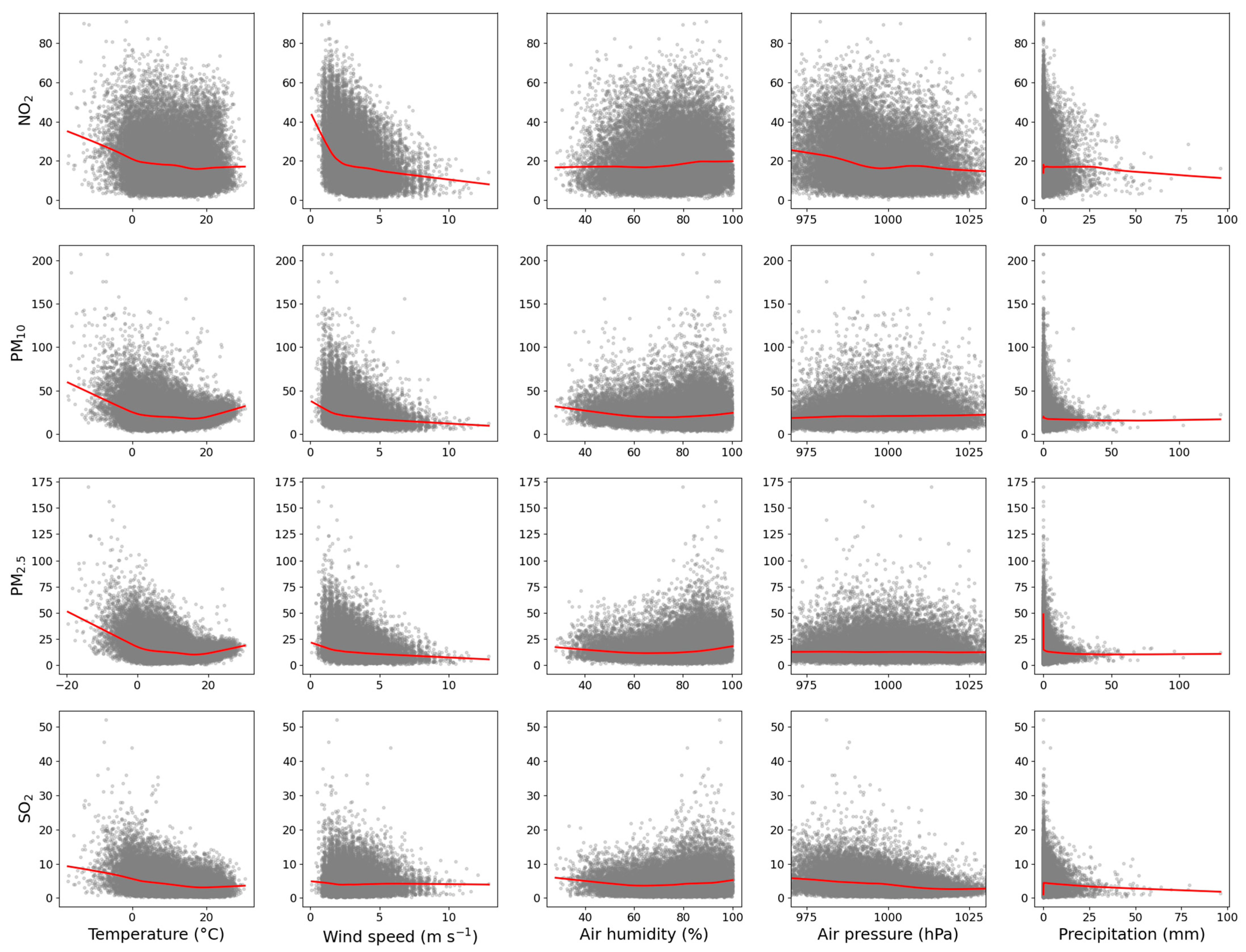
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Ground-Based Pollutant Data and Meteorological Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenger, J. Air pollution in the last 50 years—From local to global. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.S.; Gaffikin, L.; Golden, C.D.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Redford, K.H.; Ricketts, T.H.; Turner, W.R.; Osofsky, S.A. Human health impacts of ecosystem alteration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18753–18760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: A review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A. Trouble in the Air: Recent Developments under the 1979 Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution. Rev. Eur. Comp. Int. Environ. Law 2017, 26, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Yan, H. Urban Air Pollution Monitoring by Ground-Based Stations and Satellite Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 10, pp. 973–978. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniuk-Kluska, A.; Kluska, M. Transformation of the Energy Market in Poland in the Context of the European Union over the Last 20 Years. Energies 2025, 18, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrek-Gerstenkorn, Z.; Syrek-Gerstenkorn, B.; Paul, S. A Comparative Study of SOx, NOx, PM2.5 and PM10 in the UK and Poland from 1970 to 2020. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechle, M.J.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. Remote sensing of exposure to NO2: Satellite versus ground-based measurement in a large urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshi, A.R.; Pichuka, S.; Tripathi, A. Applications of Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Satellite Sensor: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 20312–20321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik-Gront, E.; Wnuk, A. Evaluating Methane Emission Estimates from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Compared to Sentinel-Derived Air–Methane Data. Sustainability 2025, 17, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data Applications: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yue, Y.; Lü, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of the factors influencing transportation and accumulation processes during a persistent pollution event in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1420–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeron, Y.; Staquet, C. Persistent inversion dynamics and wintertime PM10 air pollution in Alpine valleys. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 135, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowicz, R.; Wielgosiński, G.; Fetter, W. Dispersion of atmospheric air pollution in summer and winter season. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, G.; de Lieto Vollaro, R. Correlation between air pollution and weather data in urban areas: Assessment of the city of Rome (Italy) as spatially and temporally independent regarding pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, C.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Vega, A.; Gonzalez-Quintero, R.; Chavarro-Lobo, J.A.; Mazzetto, A.M.; Chadwick, D.R. Measured ammonia emissions from tropical and subtropical pastures: A comparison with 2006 IPCC, 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC, and EMEP/EEA (European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme and European Environmental Agency) inventory estimates. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 6706–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowska-Mieszkowska, E. UNECE Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution–40 years of action for cleaner air. Econ. Environ. 2020, 72, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Peszko, G.; Amann, M.; Awe, Y.; Kleiman, G.; Rabie, T.S. Air Pollution and Climate Change: From Co-Benefits to Coherent Policies; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Galos, K.A.; Smakowski, T.S.; Szlugaj, J. Flue-gas desulphurisation products from Polish coal-fired power-plants. Appl. Energy 2003, 75, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlugaj, J.; Galos, K. Limestone Sorbents Market for Flue Gas Desulphurisation in Coal-Fired Power Plants in the Context of the Transformation of the Power Industry—A Case of Poland. Energies 2021, 14, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, F. Comparative study on the impact of road traffic and residential natural gas heating on indoor-outdoor NO2 concentration in Chinese urban areas. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Li, S.-Q.; Xu, H.-W.; Zhuo, J.-K.; Song, Q. Studies on formation and control of combustion particulate matter in China: A review. Energy 2009, 34, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, M.Y.; Makarov, M.M.; Aslamov, I.A.; Tyurnev, I.N.; Molozhnikova, Y.V. Application of Modern Low-Cost Sensors for Monitoring of Particle Matter in Temperate Latitudes: An Example from the Southern Baikal Region. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, M.Y.; Molozhnikova, Y.V.; Obolkin, V.A.; Potemkin, V.L.; Lutskin, E.S.; Khodzher, T.V. Features of Temporal Variability of the Concentrations of Gaseous Trace Pollutants in the Air of the Urban and Rural Areas in the Southern Baikal Region (East Siberia, Russia). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tan, Y.; Ren, X.; Peng, K.; Yang, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ren, Y.; et al. Deviations of Boundary Layer Height and Meteorological Parameters Between Ground-Based Remote Sensing and ERA5 over the Complex Terrain of the Mongolian Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowiecki, P.; Chciałowski, A.; Dąbrowiecka, A.; Badyda, A. Ambient Air Pollution and Risk of Admission Due to Asthma in the Three Largest Urban Agglomerations in Poland: A Time-Stratified, Case-Crossover Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzano, C.; Di Stefano, F.; Conti, V.; Graziani, E.; Petroianni, A. Air pollution ultrafine particles: Toxicity beyond the lung. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 14, 809–821. [Google Scholar]
- Kozłowski, R.; Szwed, M.; Kozłowska, A.; Przybylska, J.; Mach, T. Quality Management System in Air Quality Measurements for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velastegui-Montoya, A.; Montalván-Burbano, N.; Carrión-Mero, P.; Rivera-Torres, H.; Sadeck, L.; Adami, M. Google Earth Engine: A global analysis and future trends. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, A.; Bell, W.; Brocca, L.; Bulgin, C.E.; Burdanowitz, J.; Calbet, X.; Donner, R.V.; Ghent, D.; Gruber, A.; Kaminski, T. Validation practices for satellite-based Earth observation data across communities. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 779–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kholy, O. The World Environment 1972–1992: Two Decades of Challenge; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gingerich, D.B.; Grol, E.; Mauter, M.S. Fundamental challenges and engineering opportunities in flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment at coal fired power plants. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautsar, F.R. The European Union’s Euro 1 to Euro 6 Programme. J. Soc. Political Sci. 2024, 5, 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, J.; Godden, L.; Keenan, R.J. Climate change law in an era of multi-level governance. Transnatl. Environ. Law 2012, 1, 245–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, S.; Shimadera, H.; Wang, X.; Bressi, M.; de Miranda, R.M.; Jiang, J. Status and characteristics of ambient PM2.5 pollution in global megacities. Environ. Int. 2016, 89, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthaus, S.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Collaud Coen, M.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Costa, M.J.; Cimini, D.; O’Connor, E.J.; Hervo, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Jiménez-Portaz, M. Atmospheric boundary layer height from ground-based remote sensing: A review of capabilities and limitations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareba, M.; Weglinska, E.; Danek, T. Air pollution seasons in urban moderate climate areas through big data analytics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, O.E. Comparative analysis of meteorological parameters and their relationship with NO2, PM10, PM2.5 and O3 concentrations at selected urban air quality monitoring stations in Krakow, Paris, and Milan. Discov. Environ. 2024, 2, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, B.; Serat, S.; Arifoglu, Y.D.; Ozdemir, S. Seasonal Analysis and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Air Pollutants in Relation to Meteorological Parameters: A Case Study from Sakarya, Türkiye. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Ke, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; et al. Spatial–Temporal Variations of Air Pollutants and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors During 2014 to 2022 in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, M.L.; Alonso, A.M.; Peña, D. Modelling time series with multiple seasonalities: An application to hourly NO2 pollution levels. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2025, 39, 2063–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Sun, S. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Air Pollutants in Zaozhuang China from 2018 to 2022. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J. Exploring the relationship between air pollution and meteorological conditions in China under environmental governance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamurugan, R.; Kumaravel, B.; Palanivelraja, S.; Chockalingam, M. Influence of temperature, relative humidity and seasonal variability on ambient air quality in a coastal urban area. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 2013, 264046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zou, B.; Wang, J.; Gu, X. Dominant variables of global air pollution-climate interaction: Geographic insight. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kumar, P.; Choudhary, M.P.; Mathur, A.K. Integrated geospatial and statistical analysis of urban air pollutants (PM10, SO2 and NO2) and their relationships with land surface temperature over a semi-arid environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, S.R.; Fattah, M.A.; Kafy, A.A.; Alsulamy, S.; Almulhim, A.I.; Shohan, A.A.A.; Khedher, K.M. Decoding seasonal variability of air pollutants with climate factors: A geostatistical approach using multimodal regression models for informed climate change mitigation. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, A.; Roy Chowdhury, I. Investigating the association between air pollutants’ concentration and meteorological parameters in a rapidly growing urban center of West Bengal, India: A statistical modeling-based approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 2877–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Wan, H.; Shen, S.; Guo, X. A Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Air Quality Prediction Based on the Time–Frequency Domain Relationship. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, H.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Nadda, A.K. Development of Equations to Predict the Concentration of Air Pollutants Indicators in Yazd City, Iran. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 34, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gond, A.K.; Jamal, A.; Verma, T. Developing a machine learning model using satellite data to predict the Air Quality Index (AQI) over Korba Coalfield, Chhattisgarh (India). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
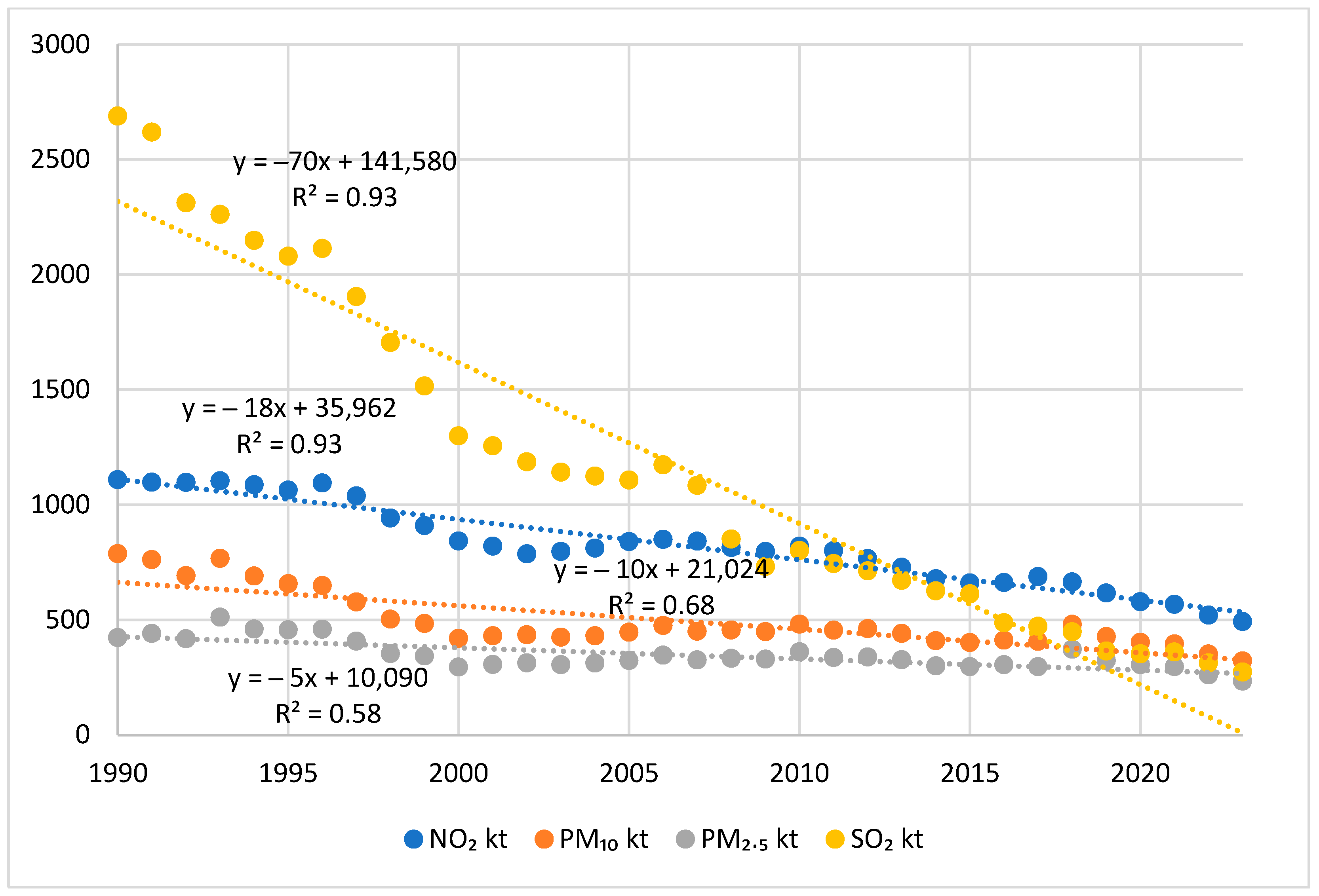



| Pollutant | Main Sources | Shares in 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| SO2 | Power plants, residential heating, heavy industry (especially metallurgy), refineries |  |
| NO2 | Road transport, power generation, industrial combustion, and household heating |  |
| PM10 | Residential heating, industrial processes, road transport (including road dust), construction |  |
| PM2.5 | Residential heating, transport, metallurgy, agriculture (secondary particles), waste burning |  |
| Mean | Median | Min. | Max. | Q1 | Q3 | SD | CV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2 (μg/m3) | 19.7 | 16.5 | 0.1 | 91.0 | 10.4 | 26.1 | 12.3 | 62.4 |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | 23.7 | 19.8 | 1.6 | 207.2 | 14.2 | 28.7 | 14.8 | 62.4 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 15.1 | 12.1 | 0.0 | 170.4 | 8.2 | 18.2 | 10.8 | 71.7 |
| SO2 (μg/m3) | 4.5 | 3.6 | 0.2 | 52.2 | 2.1 | 5.9 | 3.4 | 77.1 |
| Wind speed (m/s) | 3.0 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 12.9 | 2.0 | 3.8 | 1.4 | 45.5 |
| Temperature (C) | 9.9 | 9.6 | −19.6 | 30.3 | 3.8 | 16.5 | 7.8 | 78.7 |
| Air humidity (%) | 76.0 | 77.6 | 28.0 | 100.3 | 66.9 | 86.6 | 13.5 | 17.8 |
| Air pressure (hPa) | 997.7 | 997.3 | 954.7 | 1045.3 | 988.7 | 1006.4 | 12.7 | 1.3 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 130.4 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 4.3 | 266.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wójcik-Gront, E.; Gozdowski, D. Air Pollution Monitoring and Modeling: A Comparative Study of PM, NO2, and SO2 with Meteorological Correlations. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101199
Wójcik-Gront E, Gozdowski D. Air Pollution Monitoring and Modeling: A Comparative Study of PM, NO2, and SO2 with Meteorological Correlations. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101199
Chicago/Turabian StyleWójcik-Gront, Elżbieta, and Dariusz Gozdowski. 2025. "Air Pollution Monitoring and Modeling: A Comparative Study of PM, NO2, and SO2 with Meteorological Correlations" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101199
APA StyleWójcik-Gront, E., & Gozdowski, D. (2025). Air Pollution Monitoring and Modeling: A Comparative Study of PM, NO2, and SO2 with Meteorological Correlations. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101199







