Fugitive Emission Characteristics of Fume and Dust from Short-Process Electric Furnace Tap Hole and Optimization of Dust Hood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Weight Analysis of the Influence of Fugitive Emission Location on Workshop Environment
2.1. Selection of Comprehensive Evaluation Methods
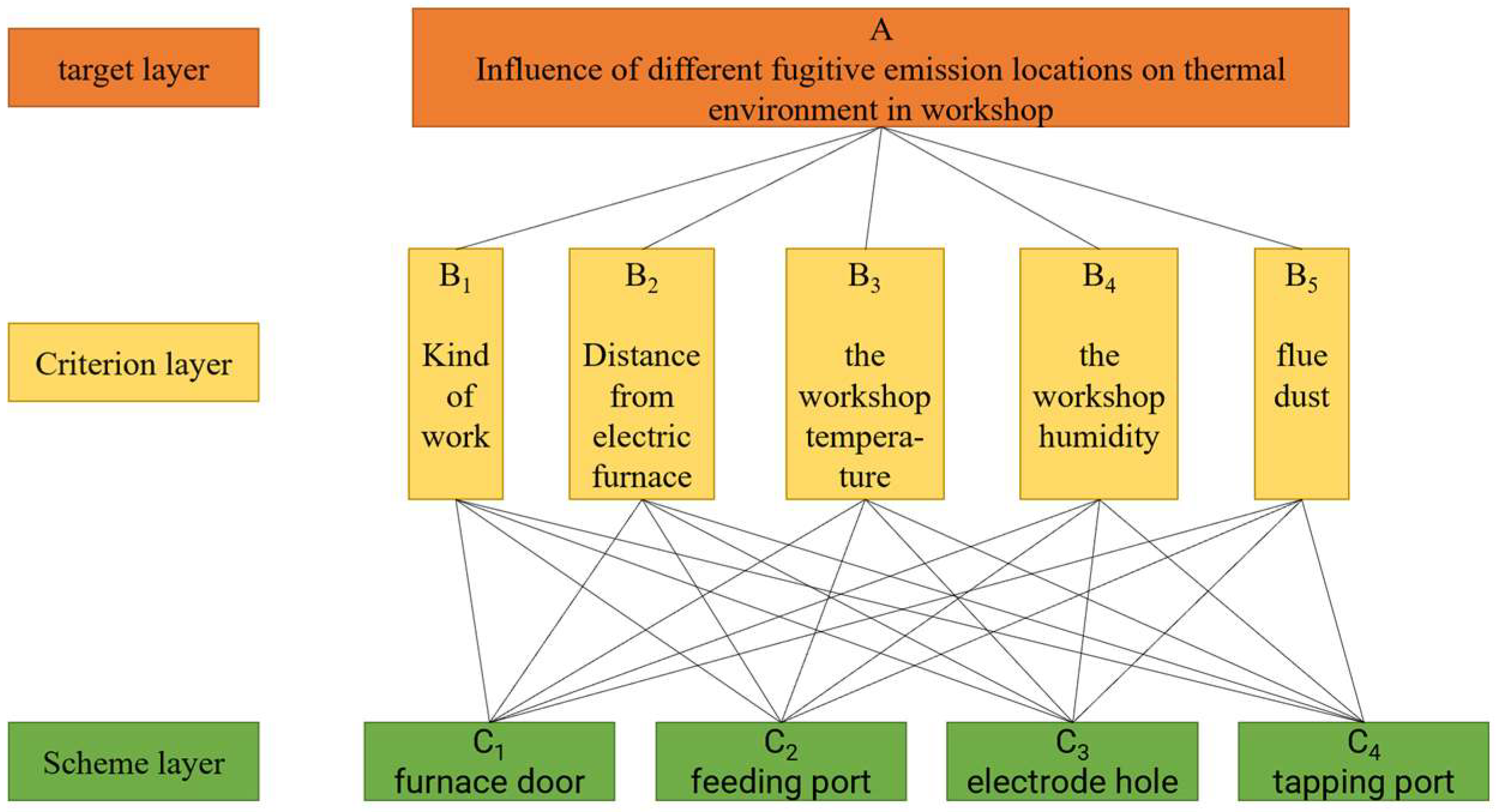
2.2. Build Analytic Hierarchy Model
2.3. Hierarchical Total Ordering and Consistency Check
3. Field Test
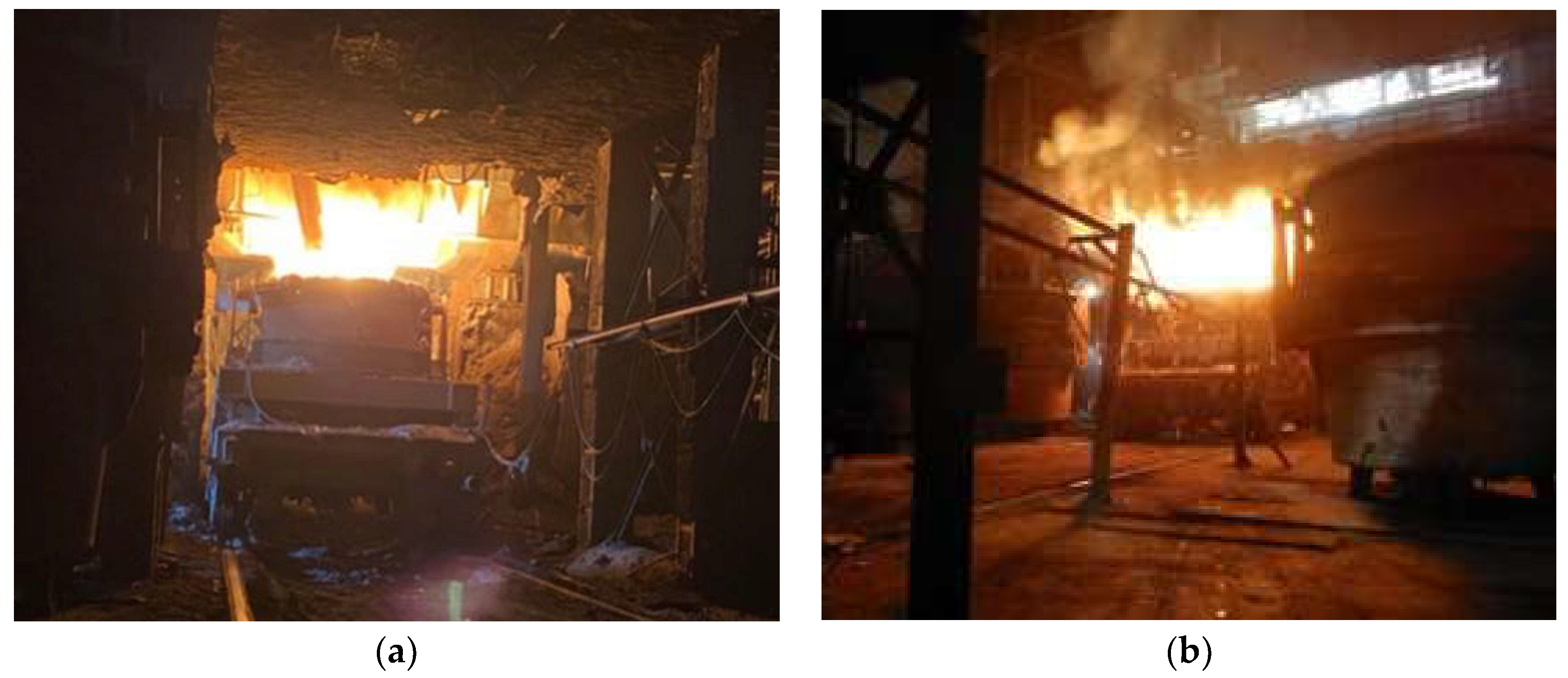
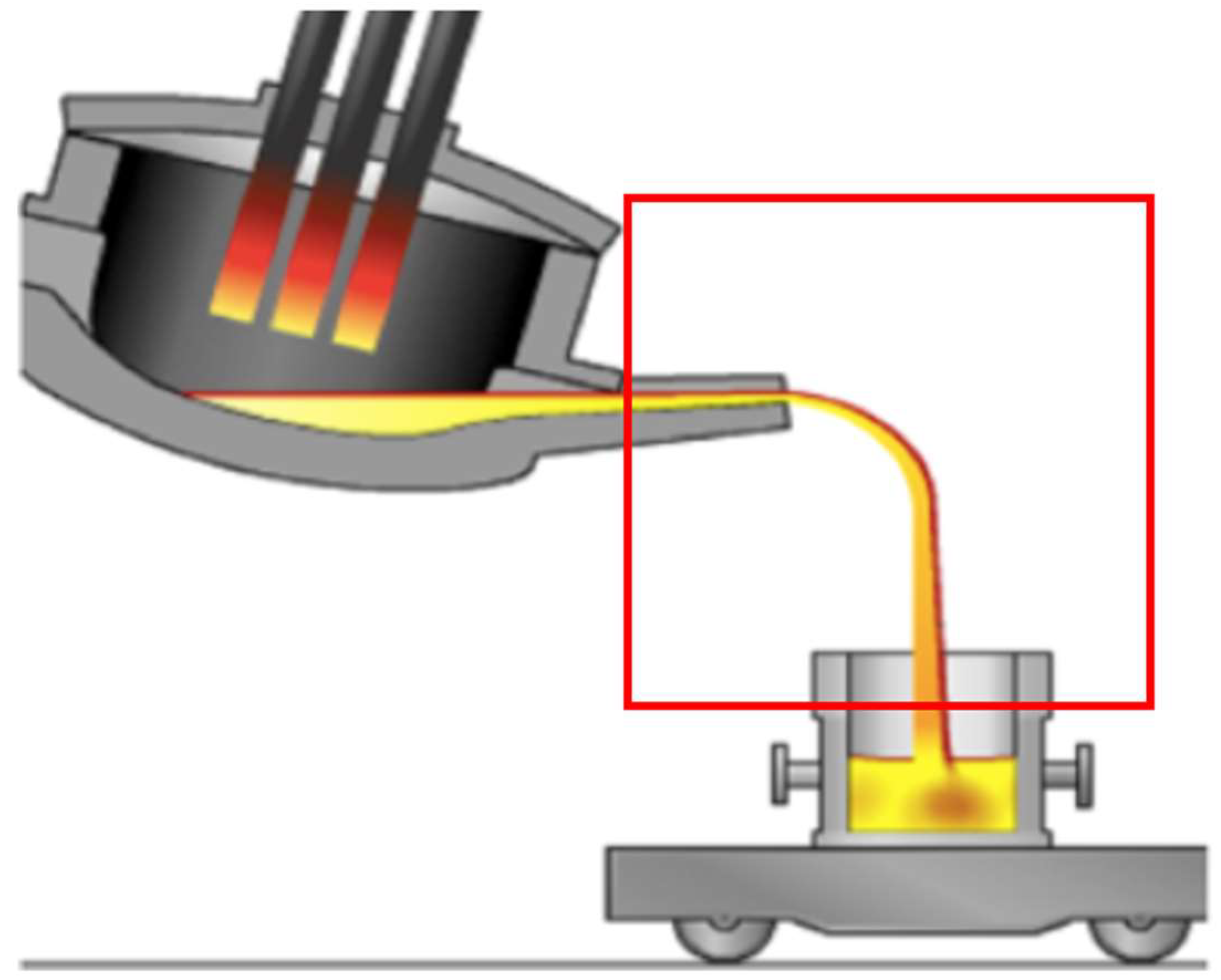
3.1. Test Workshop Status
3.2. Test Content and Method
3.3. Test Time and Test Point
3.4. Test Instrument
3.5. Analysis of Test Results
4. Model Establishment
4.1. Physical Model
4.2. Mathematical Model
- The continuity equation
- 2.
- The momentum conservation equation
- 3.
- The energy equation
- 4.
- The turbulence model
4.3. Boundary Conditions and Solution Settings
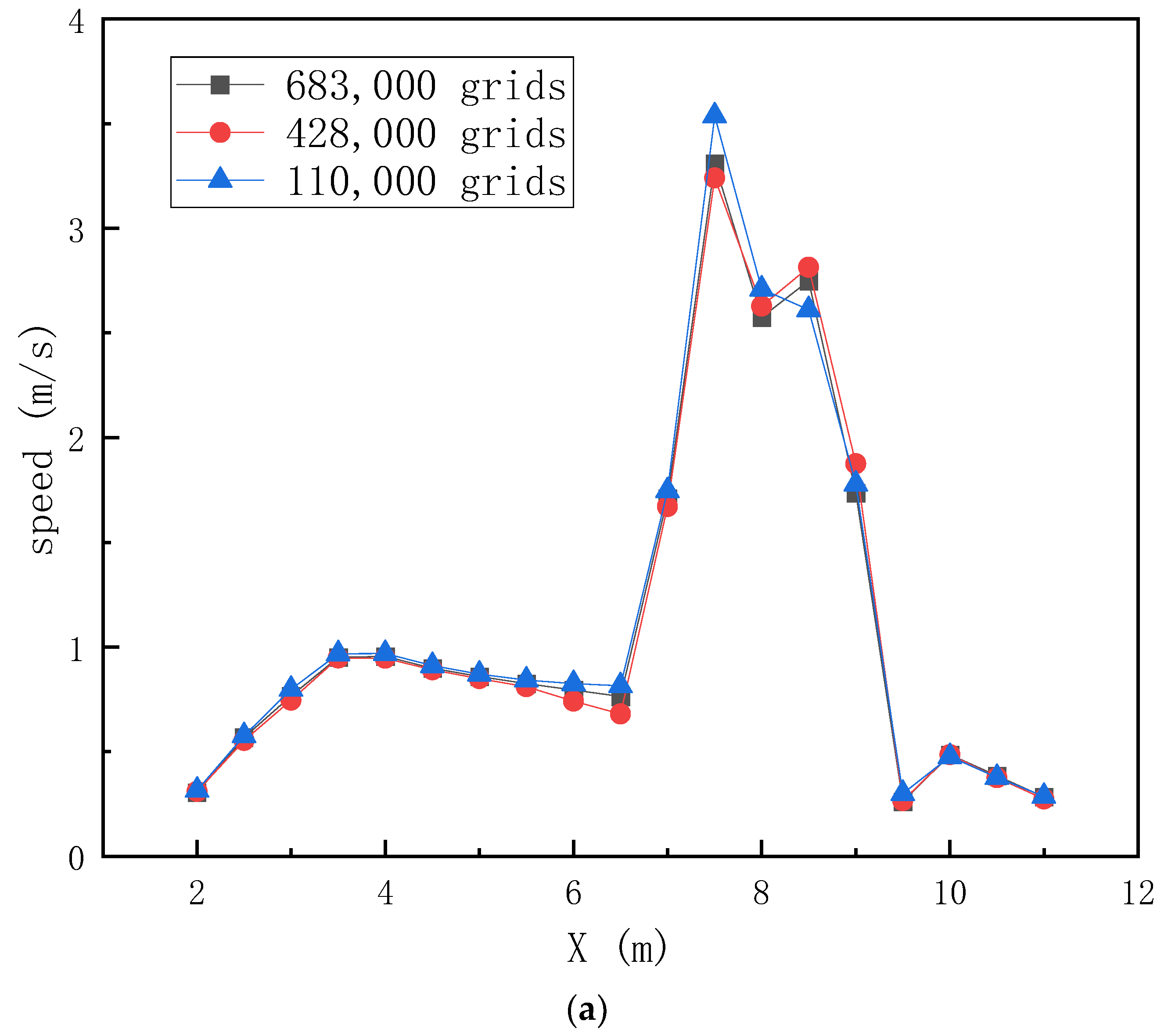
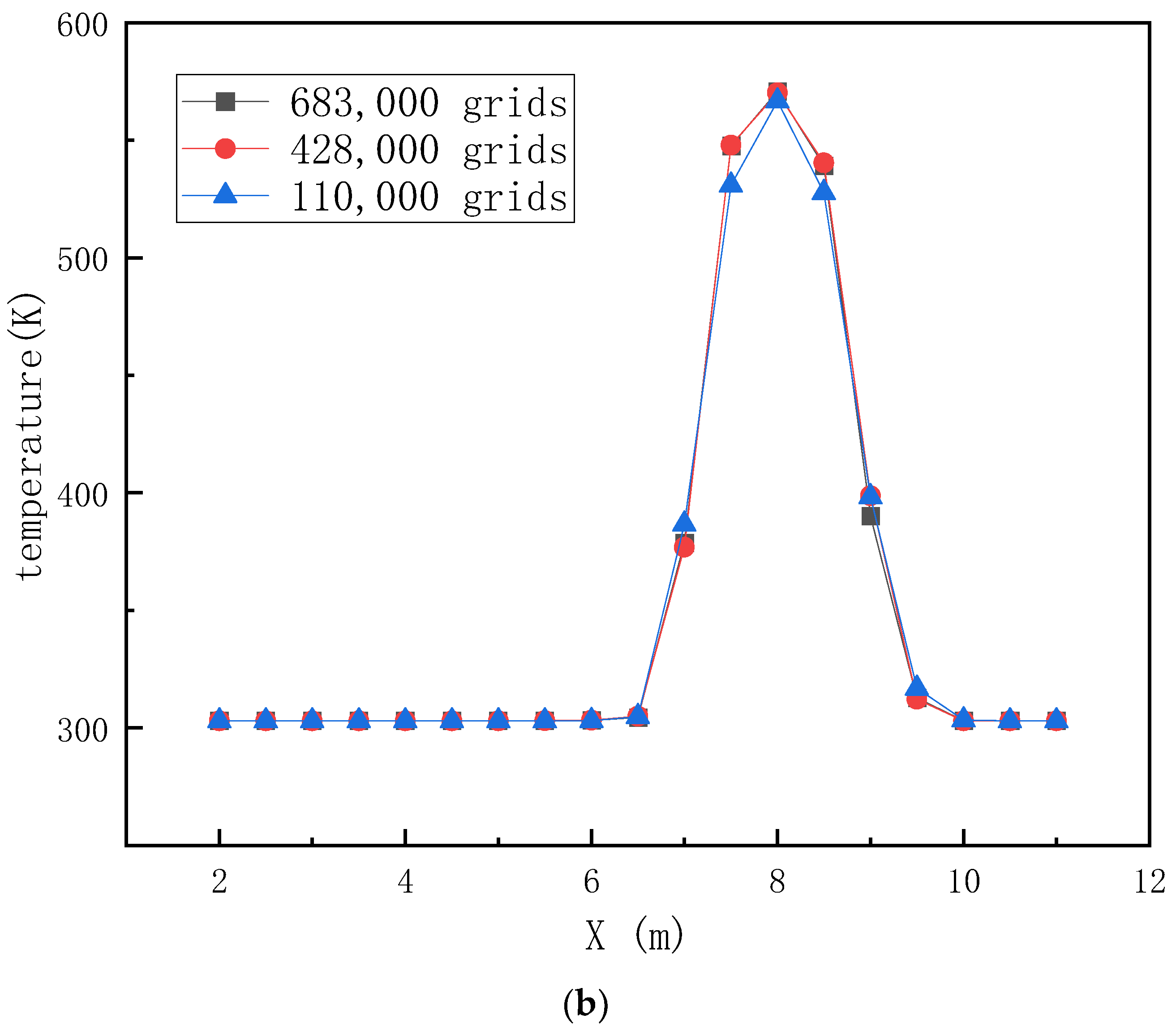
4.4. Grid Division
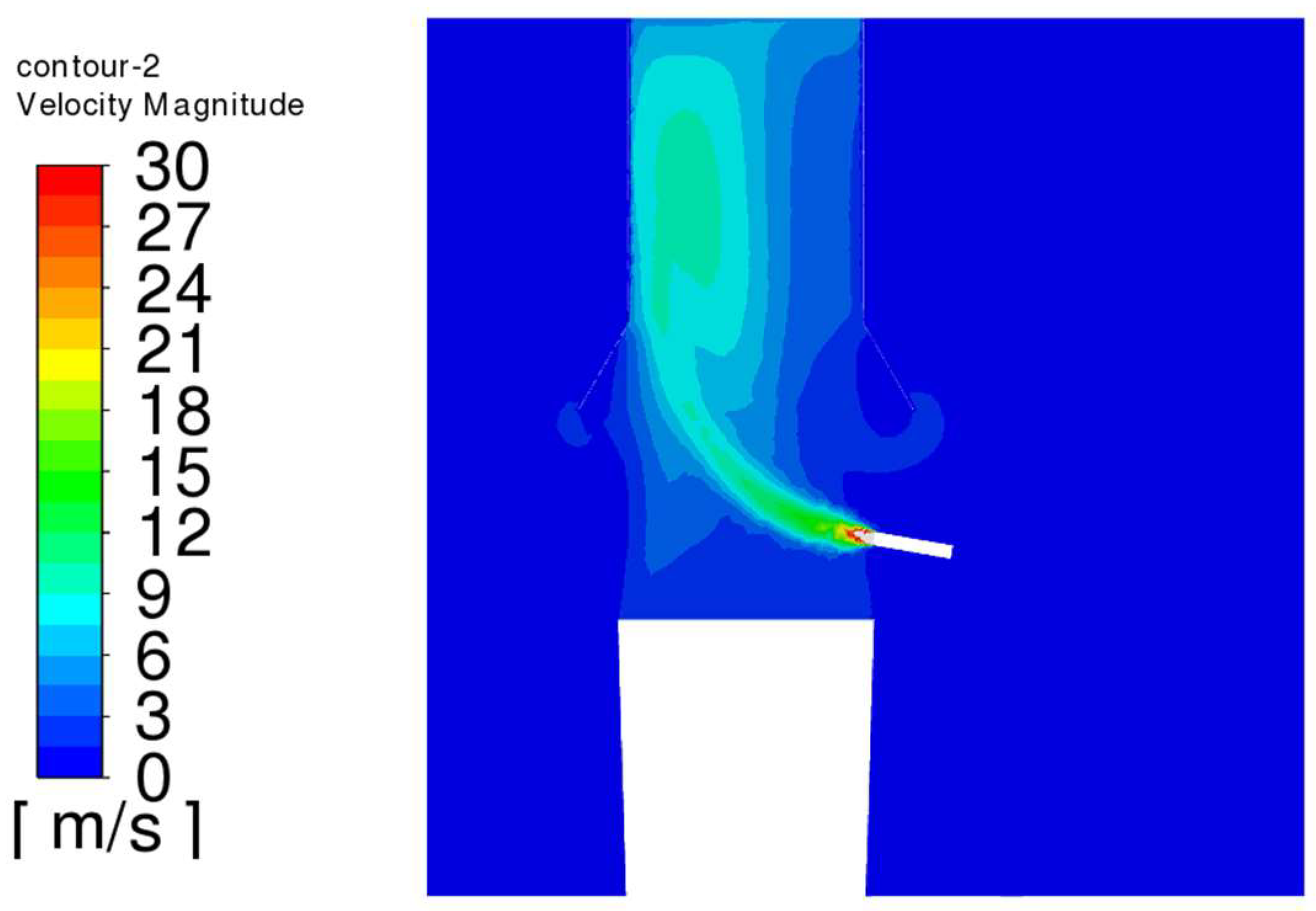
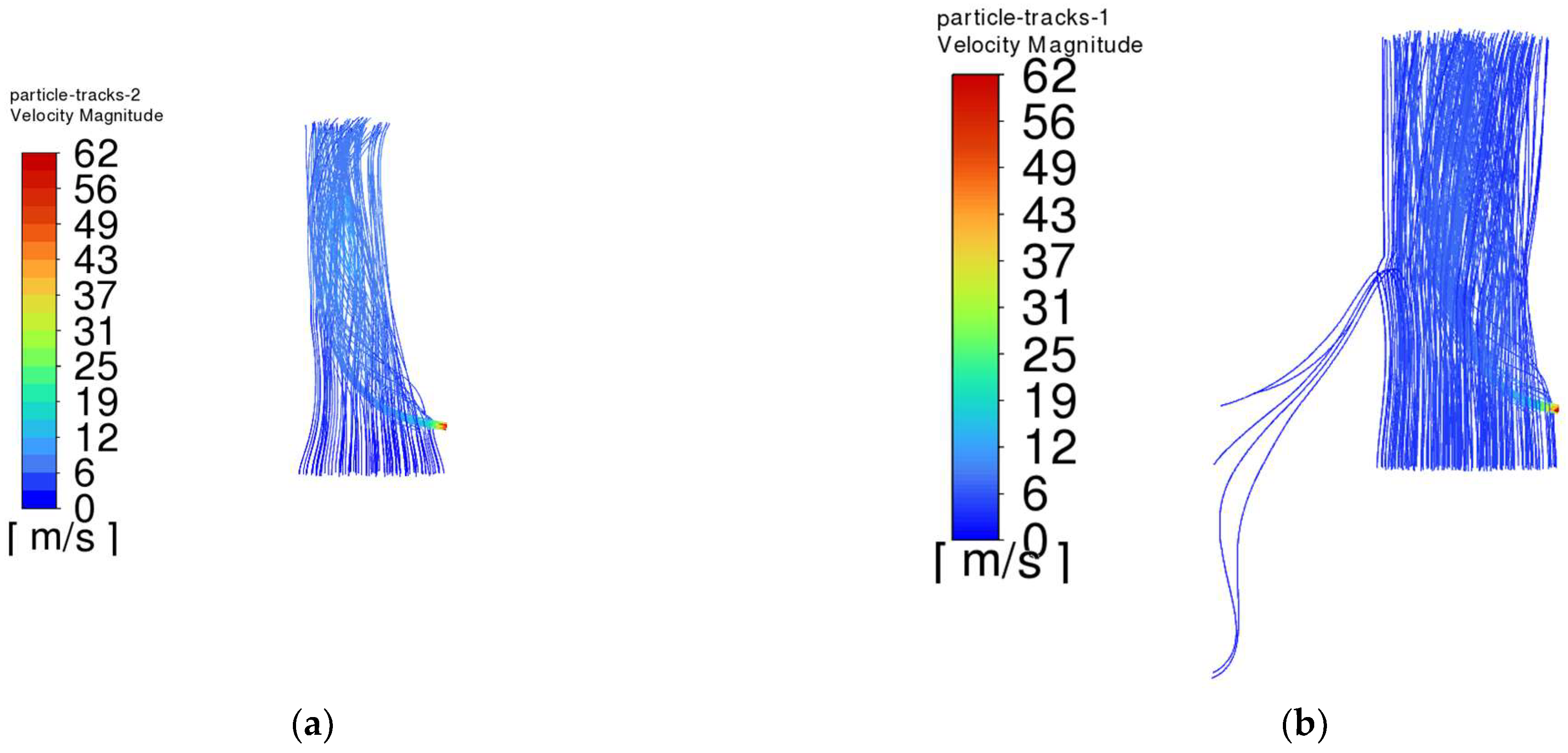
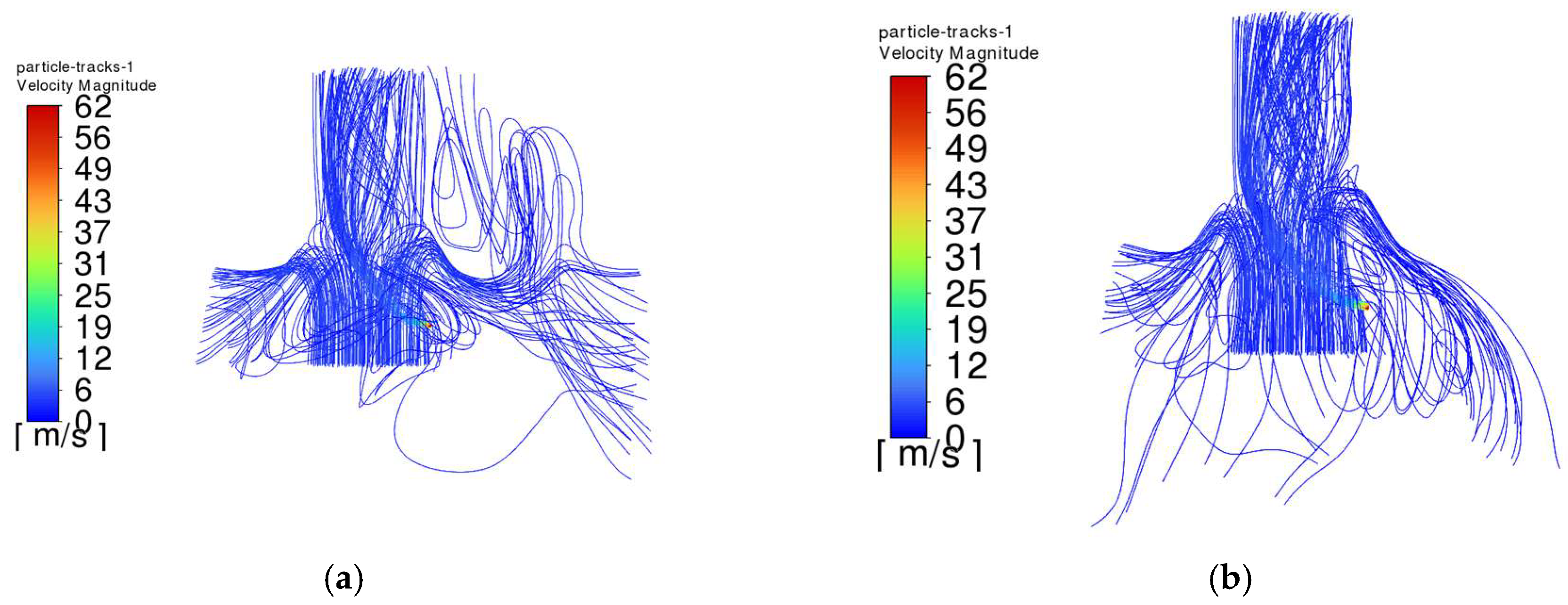
4.5. Analysis of Simulation Results
4.5.1. Influence of the Inclination Angle of the Hood of the Dust Hood on the Collection Efficiency
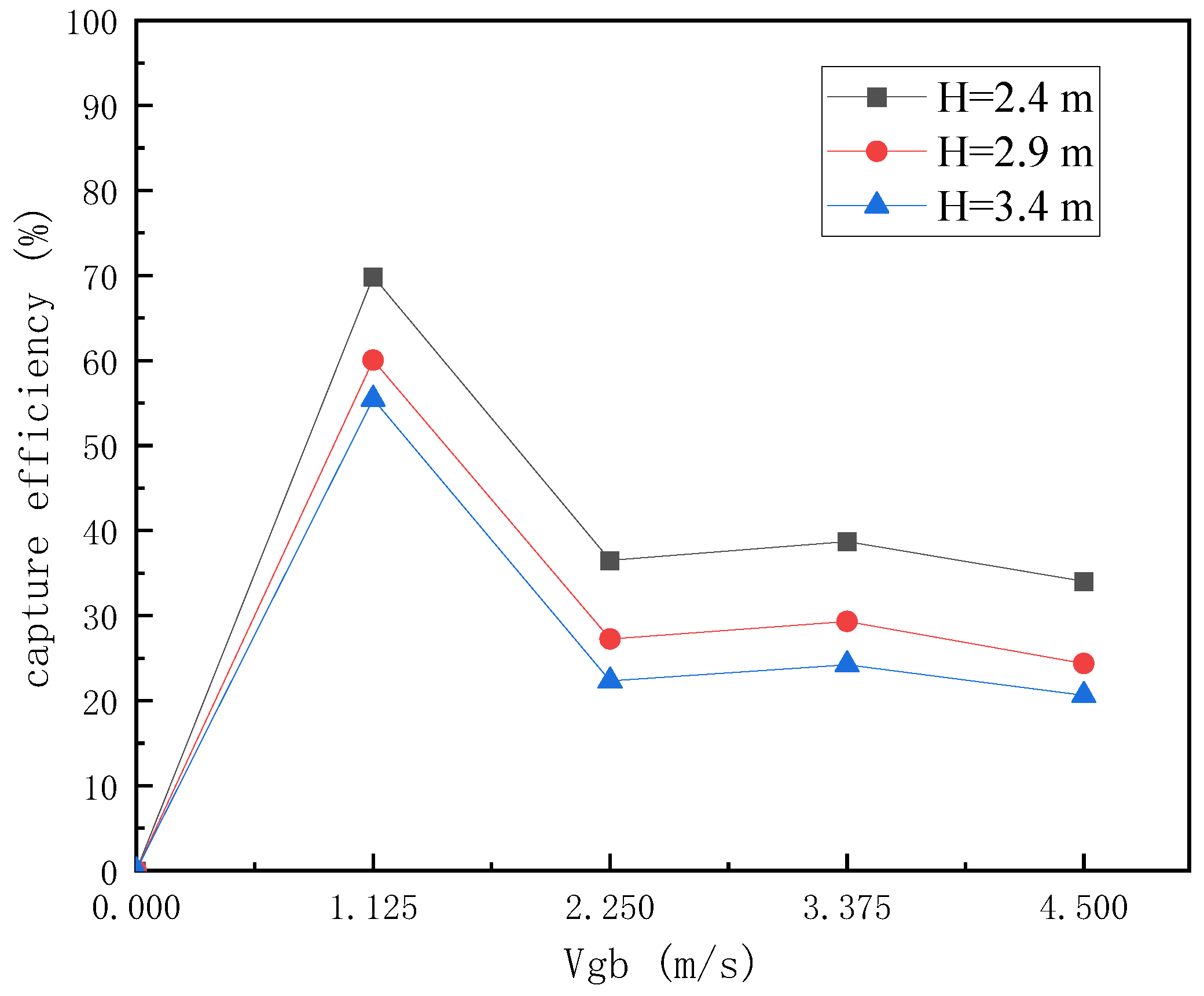
4.5.2. The Effect of Dust Hood Arrangement Height on Collection Efficiency
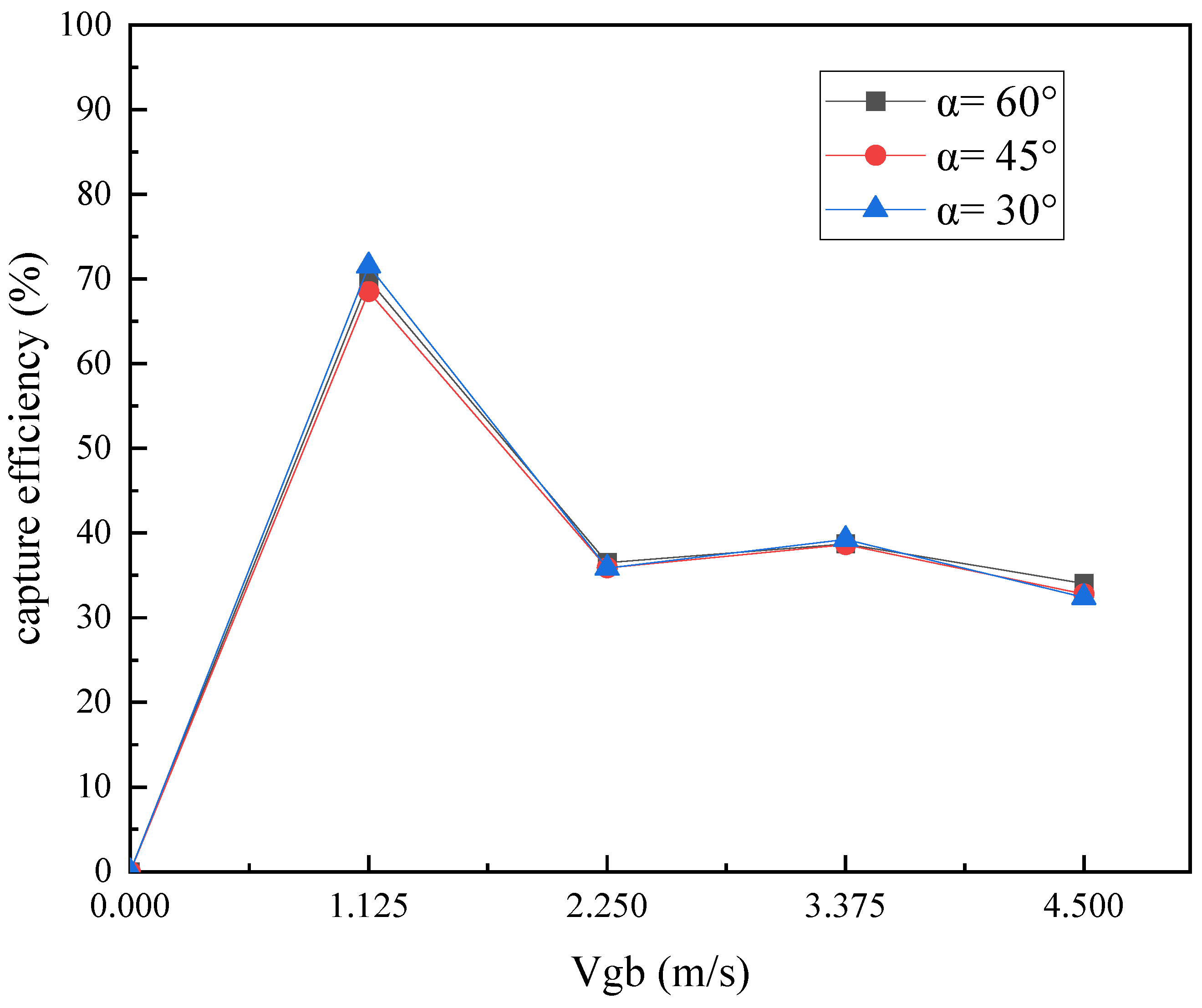
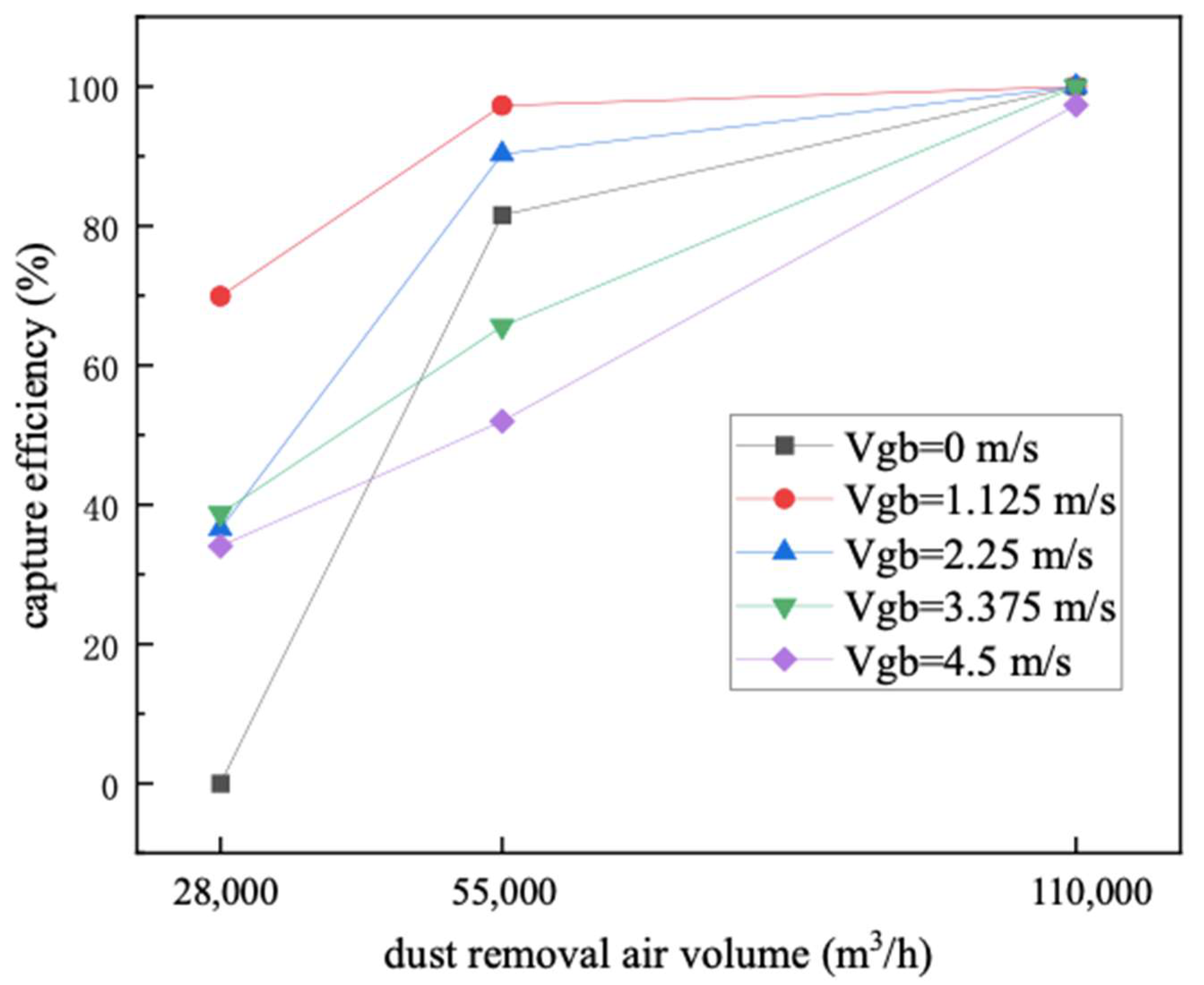
4.5.3. Effect of Dust Removal Air Volume on Capture Efficiency
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The comprehensive weights of the four fugitive emission positions of the furnace door, feeding port, electrode hole and tapping port of the electric furnace are 0.102, 0.285, 0.114 and 0.498, respectively. Among them, the positions of the feeding port and the steel outlet account for a relatively large weight, and the sum of the two weights can reach 0.783.
- (2)
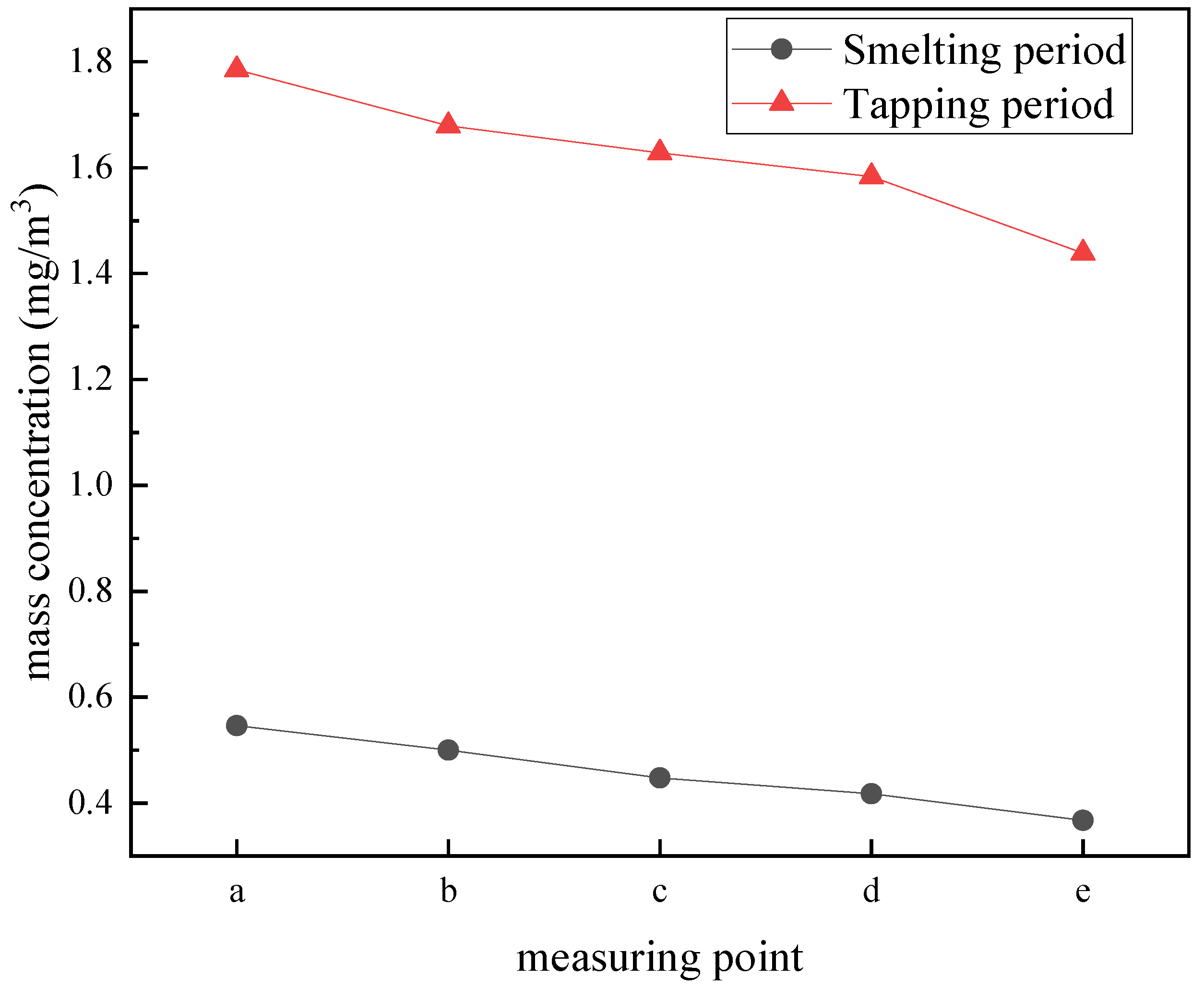
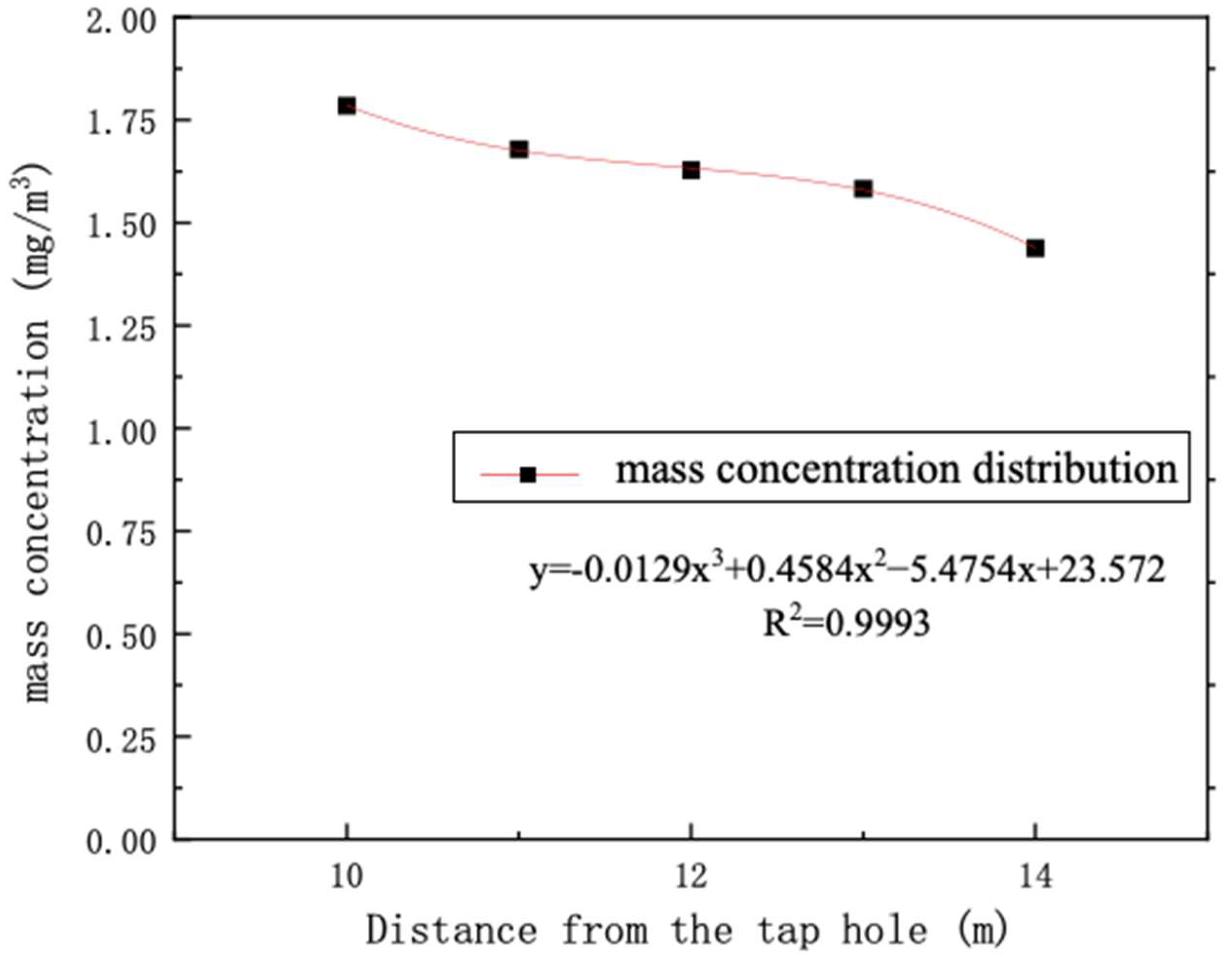
- During the tapping period, the mass concentration of dust at each measuring point increased by 1.17 mg/m3 on average, and the concentration of unorganized emission dust near the outlet was 23.57 mg/m3. The paroxysmal unorganized emission dust generated during the tapping period would be scattered in the workshop.
- (3)
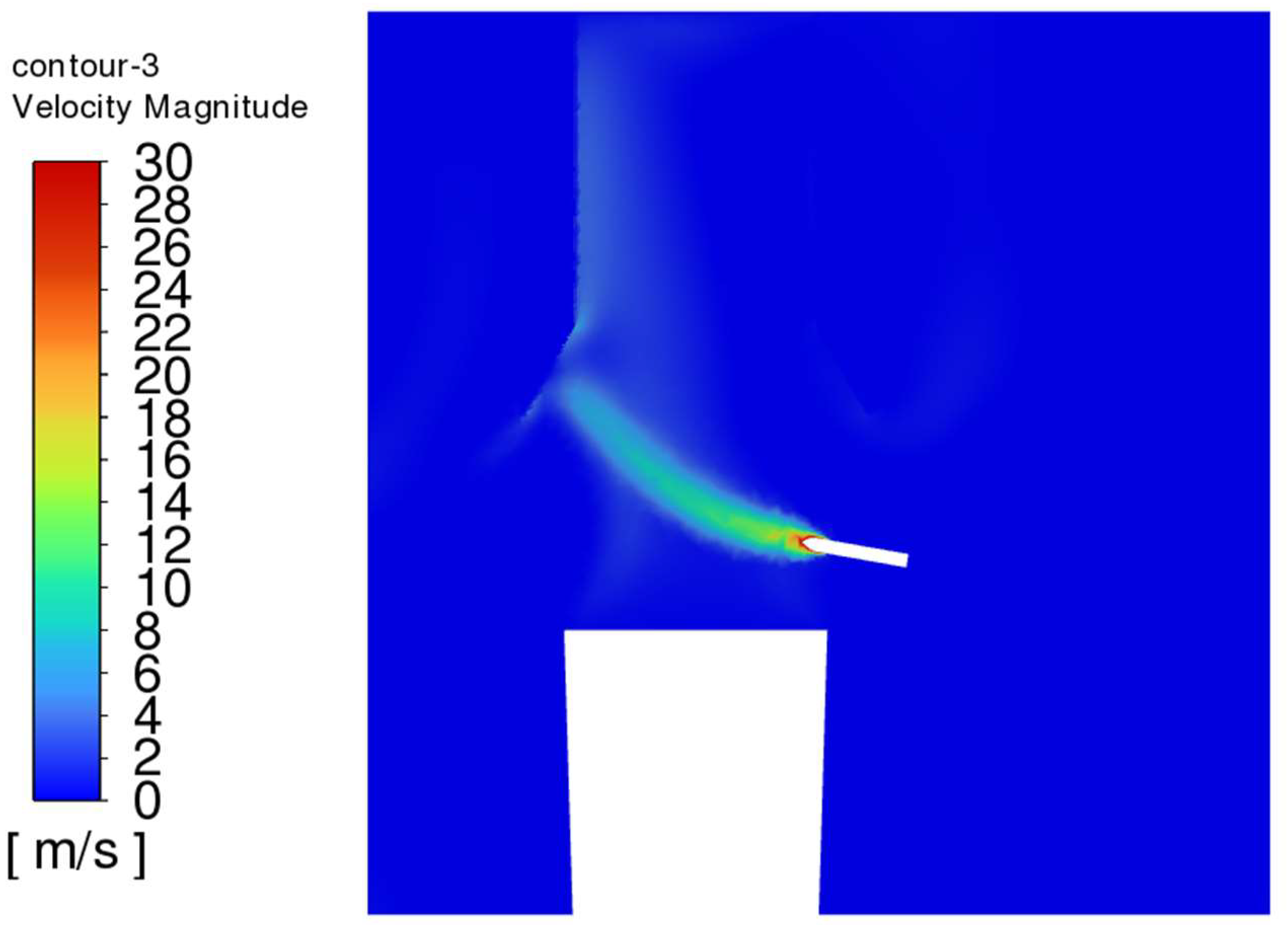
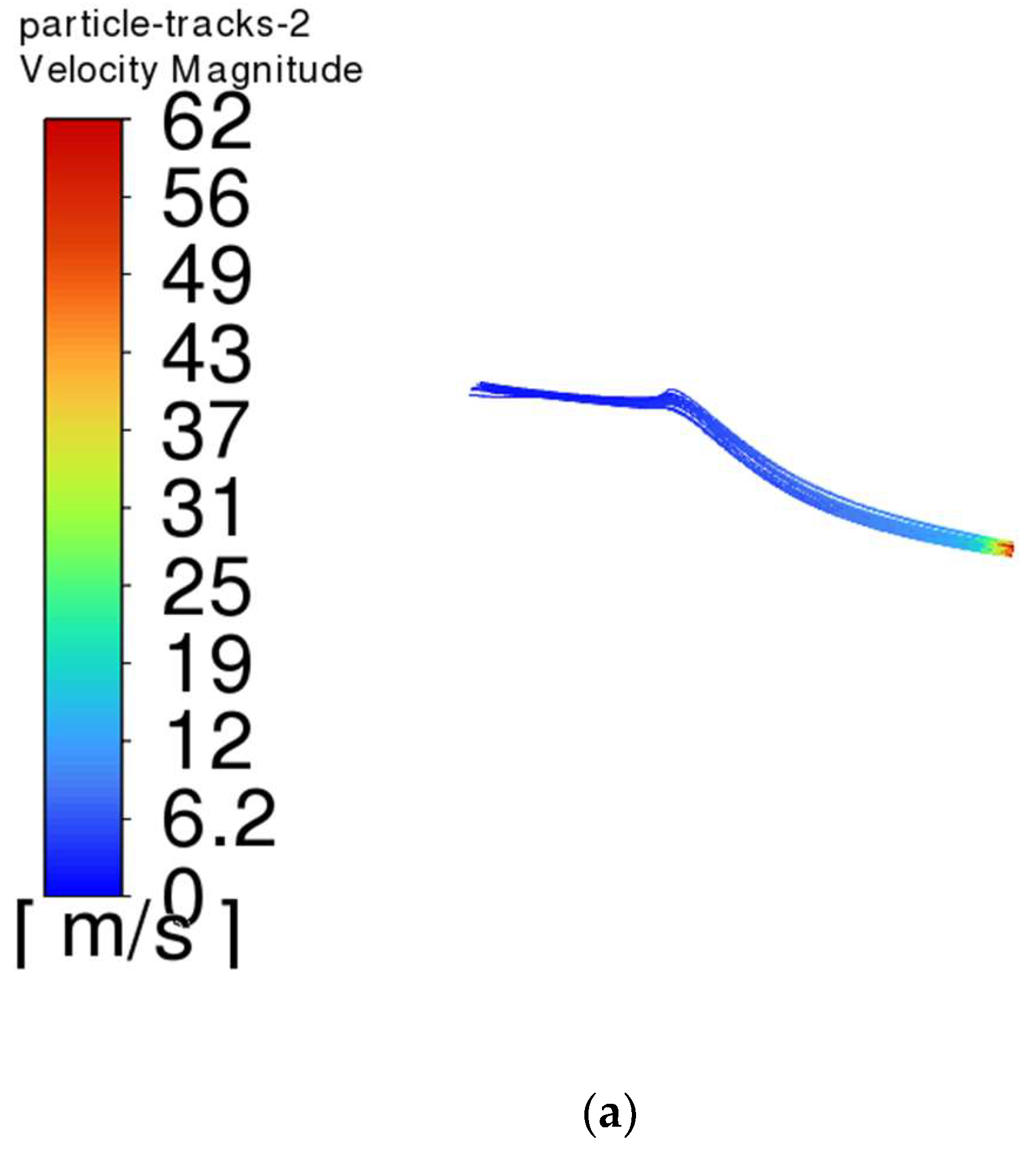
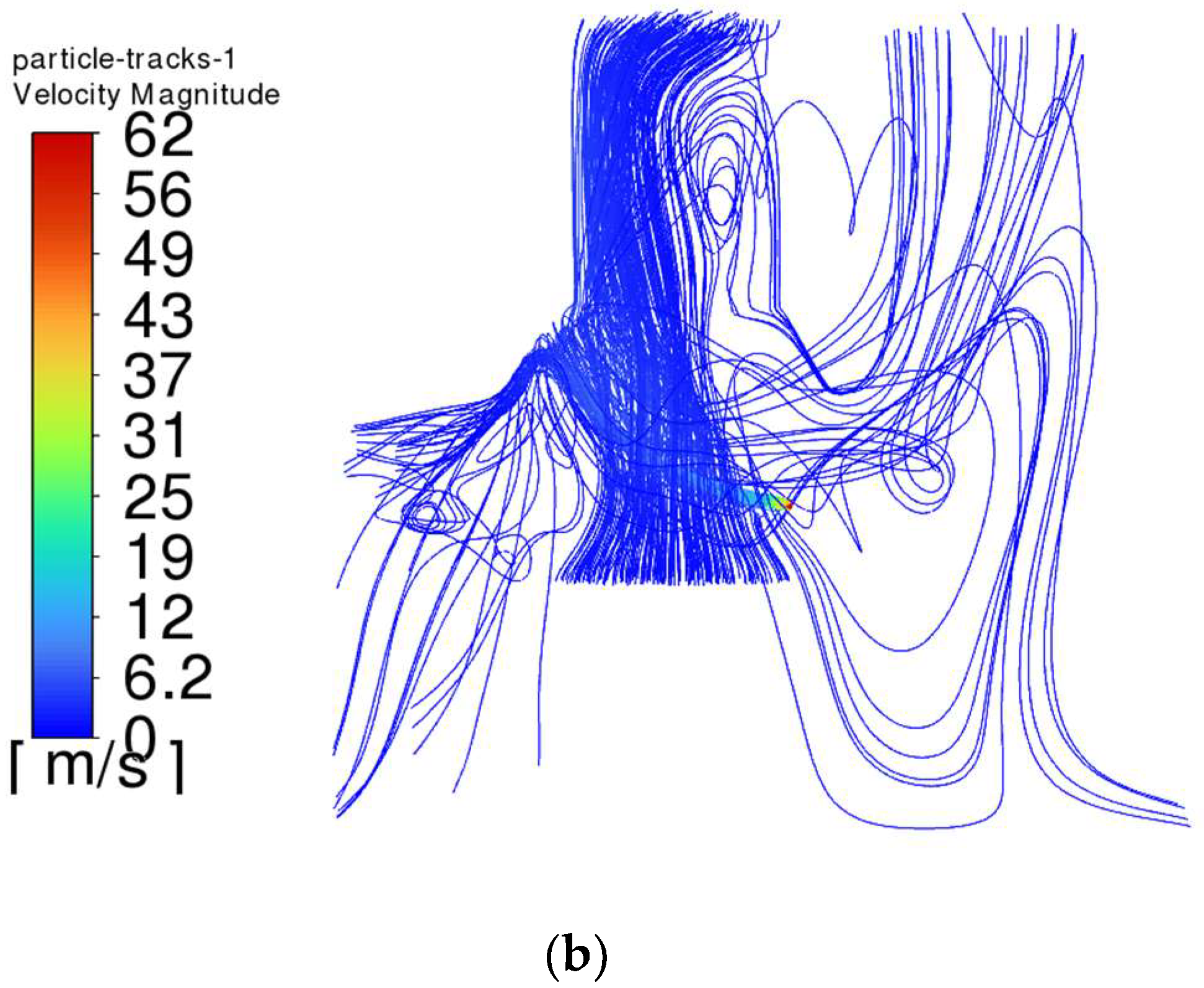
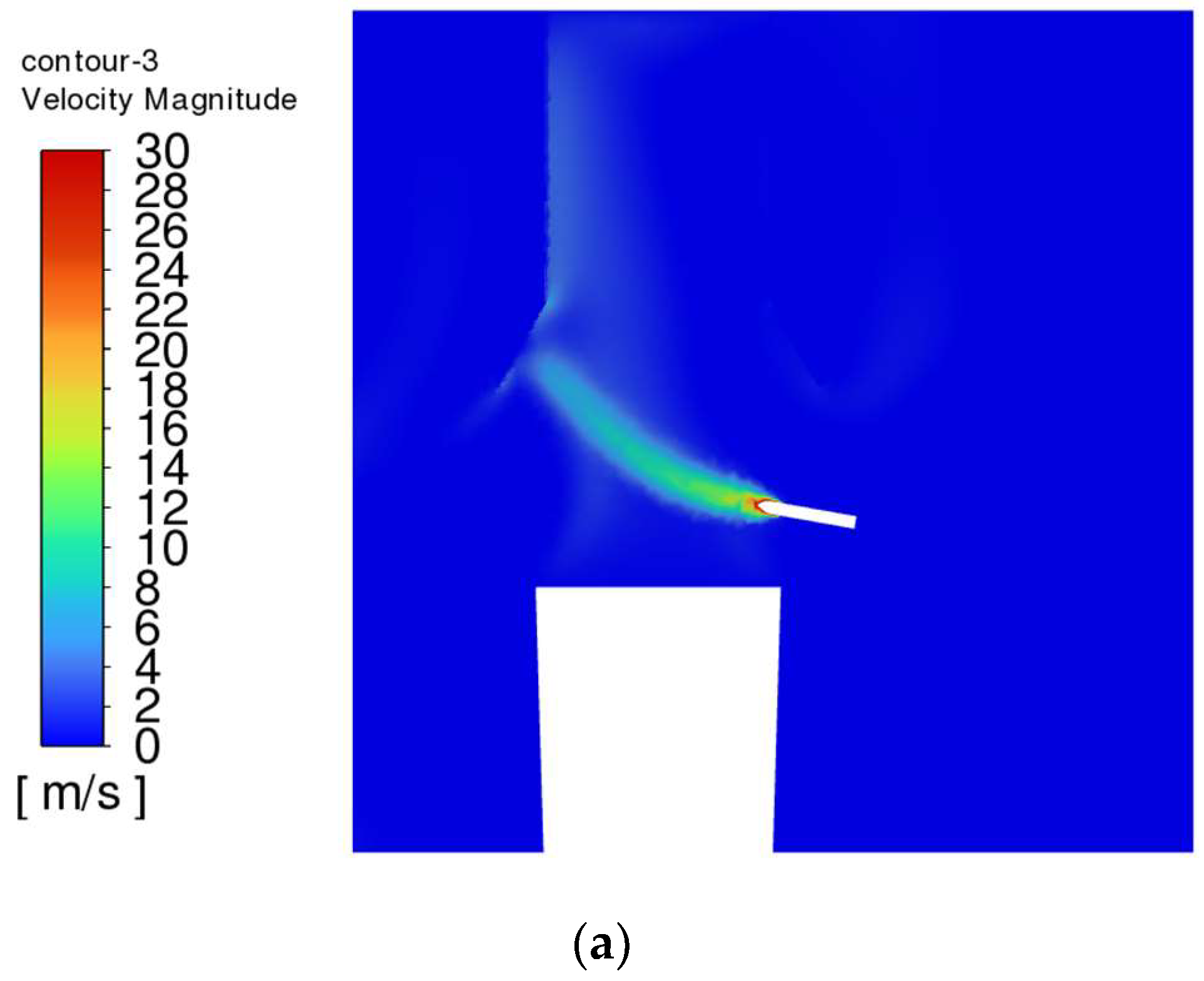
- The trajectory of the jet dust at the exit of the steel is bent upward due to the movement of the plume dust, and the jet dust with Vgb = 0 rushes out of the control range of the dust collector quickly. The greater the Vgb value, the greater the upward curvature of the jet soot.
- (4)
- According to the actual layout structure in the workshop, a dust removal system with a heat-receiving dust-collecting cover is added above the ladle position to control the unorganized emission of smoke at the steel outlet. The size of the dust-collecting cover is 3.8 m long and 3.5 m wide. The optimal structural parameters of the dust-collecting cover are as follows: the inclination angle of the cover is 60°, and the layout height is 2.4 m; the optimal dust removal air volume is 110,000 m3/h.
6. Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Geng, X.; Hao, S. Long-term scenario forecast of production routes, energy consumption and emissions for Chinese steel industry. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2014, 36, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, X. Status and trend of China EAF steelmaking development. Iron Steel 2017, 52, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Yue, Q. Forecast of steel demand and the availability of depreciated steel scrap in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 109, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, A.; De Santis, M.; Cirilli, F.; Barbanera, M. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of biochar combustion in a simulated ironmaking electric arc furnace. Fuel 2022, 328, 125267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kandpal, T.C. Iron and steel manufacturing technologies in India: Estimation of CO2 emission. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 21, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangming, L.; Lei, L.; Qiming, X. Development and application of electric furnace flue gas dust removal and waste heat recovery system. Technol. Wind. 2009, 19, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, H.; Jiang, R.W. Analysis of gas diffusion process of furnace smoke and optimization of dust collecting hood. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahery, S.; Visuri, V.-V.; Wasbø, S.O.; Hammervold, A.; Hyttinen, N.; Schlautmann, M. Thermophysical model for online optimization and control of the electric arc furnace. Metals 2021, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W. Shape optimization of the exhaust hood in machining workshops by a discrete adjoint method. Build. Environ. 2023, 244, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, A.; Ge, C. Reduced-scale experimental investigation on flow field characteristics of exhaust hood of double helix lifting transportation equipment in an industrial plant. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 43, 102798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Study on Flow Field Characteristics and Contaminant Capture Effect of Vortex Side Suction Exhaust Hood; Xian University of Architecture and Technology: Xian, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.; Marzal, F.; Minana, A.; Doval, M. Influence of exhaust hood geometry on the capture efficiency of lateral exhaust and push–pull ventilation systems in surface treatment tanks. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2010, 27, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T. Effect of steelmaking dust characteristics on suitable recycling process determining: Ferrochrome converter (CRC) and electric arc furnace (EAF) dusts. Powder Technol. 2017, 308, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, F.; Zhuang, J. Simulation study on diffusion and collection characteristics of high temperature smoke and dust in blast furnace cast house. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonthoux, F. Factors Affecting the Capture Efficiency of a Fume Extraction Torch for Gas Metal Arc Welding. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2016, 60, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, K.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y. Study on limit flow ratio method for a lateral exhaust hood above high-temperature buoyant jets. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Xie, M.; Cao, C.; Lv, L.; Zeng, L. Experimental and numerical study of the effect of perimeter jet enhancement on the capture velocity of a rectangular exhaust hood. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torano, J.; Torano, S.; Menendez, M.; Gent, M. Auxiliary ventilation in mining roadways driven with roadheaders: Validated CFD modelling of dust behaviour. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2011, 26, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroussi, A.; Simmons, K.; Pickering, S.J. Particulate deposition on candle filters. Fuel 2001, 80, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Analysis on the understanding and application of the balanced score method by financial personnel. Mod. Bus. 2021, 7, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirehn, L.; Danielsson, A.; Nesset, T.S. Assessment of composite index methods for agricultural vulnerability to climate change. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, C.; Cao, X.; Hsu, Y. The Sustainability Evaluation of Masks Based on the Integrated Rank Sum Ratio and Entropy Weight Method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Gou, L.; Ren, J.; Hou, Y.; Ye, Y. A study on the evaluation of environmental factors based on TOPSIS method to construct ecological reserves. Environ. Resour. Ecol. J. 2022, 6, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkeh, N.S.; Abdulhussein, S.M.; Mohammed, M.A. Implementation of the decision making along with analytic hierarchy process (AHP) approaches in the assessment of the petroleum products cost based on the statical model. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2022, 4, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Panyue, Z.; Jiaqiang, E.; Dandan, H.; Changlin, F. Effects of inlet velocity and structure parameters on the performance of a rotary diesel particulate filter for truck diesel engine based on fuzzy grey relational analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Meng, Q.; Gong, A.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Q. Summer outdoor thermal comfort assessment in city squares—A case study of cold dry winter, hot summer climate zone. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnath, R.A.; Thyla, P.; Harishsharran, A. Machining parameter selection in milling epoxy granite composites based on AHP. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 42, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukozkan, G.; Havle, C.A.; Feyzioglu, O. A new digital service quality model and its strategic analysis in aviation industry using interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2020, 86, 101817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, H.; Feng, G.; Yan, S.; Guo, G.; Du, Y.; Wu, S. The research of PM/PM2.5 test method for ultra-low emission. Boil. Technol. 2018, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, J.; Tan, H.; Zhou, J. Research on influencing factors of asphalt fume release based on quality method. For. Eng. 2022, 38, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Z.; Zheng, S.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Fang, X.; Guo, G.; Zhang, J. Study on the determination of particulate matter in coal—Fired power plants. Clean Coal Technol. 2019, 25, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Study on Sampling Method of Low Concentration Particulate Matter in Coal-Fired Power Plant; Xinjiang Normal University: Ürümqi, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GBZ/T192.1-2007; Determination of Airborne Dust in Workplace Part 1: Total Dust Concentration. People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Xiong, H.; Peng, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, J. Study on multi-pollution sources of harmful gas control with integrated exhaust hood. J. Univ. South China (Sci. Technol.) 2019, 33, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Nielsen, P.V.; Jensen, R.L.; Yang, X. Performance of constant exhaust ventilation for removal of transient high-temperature contaminated airflows and ventilation-performance comparison between two local exhaust hoods. Energy Build. 2017, 154, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, G.; Zhou, J.; Fan, X. Application of third-time dedusting technology for converter. Shanxi Metall. 2018, 41, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Yi, B.; Huang, X. Mathematical models and numerical simulation of concentration distribution of dust flowing in limited space. China Saf. Sci. J. 2007, 10, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; You, H.; Shang, W.; Sun, F.; Yue, S.; Sun, J. CFD model coupled with particles force analysis and its application in ultrafiltration membrane fouling. Environ. Eng. 2021, 39, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ban, J. Discussion on numerical simulation modeling and mesh generation for a boiler in power plant. Energy Eng. 2009, 4, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Evaluation Method | Advantage | Shortcoming | Suitable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scoring method | Simple and practical, no need to find another comparison standard | The original data have a certain loss | Evaluation questions do not have a clear frame of reference |
| Comprehensive index method | Fully reflect the gap between the evaluation units | There is no clear value range for a single evaluation value, and it is easy to exaggerate the influence of a certain evaluation index on the total evaluation value. | There is little difference between the evaluated objects, and the fluctuation range of the individual index of each evaluation index is not much different |
| Rank sum ratio method | Targeted and easy to operate | Metric transformations change the original information | Medical field, statistical forecasting, etc. |
| Topsis method | No restrictions on data distribution and sample size | It is easy to cause reverse order problems due to the addition of new solutions | Comprehensive evaluation of enterprise scale and social benefits |
| Analytic hierarchy process method | Strong reliability and small error | Generally, no more than 9 evaluation objects | Environmental issues, military fields, resource allocation |
| Fuzzy analysis method | Solve the disadvantage of “unique solution”, and can obtain solutions to multi-level problems according to different possibilities | Cannot solve the problem of information duplication caused by the association between evaluation indicators | Portfolio investment, bank loan project identification |
| C | Kind of Work | Distance from Electric Furnace | Workshop Temperature | Workshop Humidity | Flue Dust |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furnace door | 0.099 | 0.90 | 0.084 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Feeding port | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.24 |
| Electrode hole | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Tapping port | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Luan, S.; Li, X. Fugitive Emission Characteristics of Fume and Dust from Short-Process Electric Furnace Tap Hole and Optimization of Dust Hood. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121829
Wu Y, Luan S, Li X. Fugitive Emission Characteristics of Fume and Dust from Short-Process Electric Furnace Tap Hole and Optimization of Dust Hood. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(12):1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121829
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yanpeng, Shanshan Luan, and Xiaoyu Li. 2023. "Fugitive Emission Characteristics of Fume and Dust from Short-Process Electric Furnace Tap Hole and Optimization of Dust Hood" Atmosphere 14, no. 12: 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121829
APA StyleWu, Y., Luan, S., & Li, X. (2023). Fugitive Emission Characteristics of Fume and Dust from Short-Process Electric Furnace Tap Hole and Optimization of Dust Hood. Atmosphere, 14(12), 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121829







