Effects of Temperature on Growth and Grain Maturity of Spring Maize in Northeast China: A Study of Different Sowing Dates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
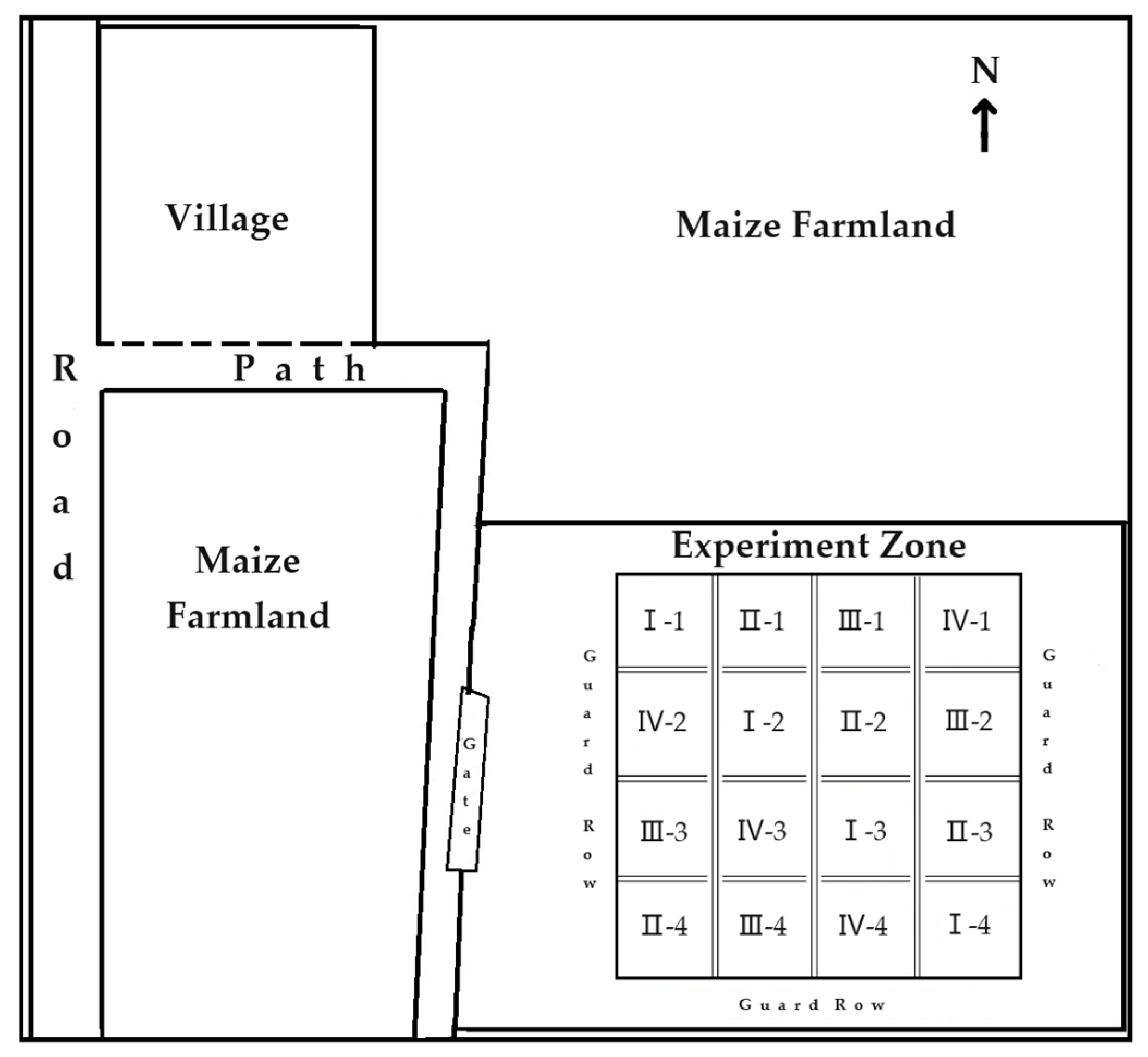
2.1. Overview of Test Area
2.2. Design of Experiments
2.3. Observation Items
2.4. Research Methods
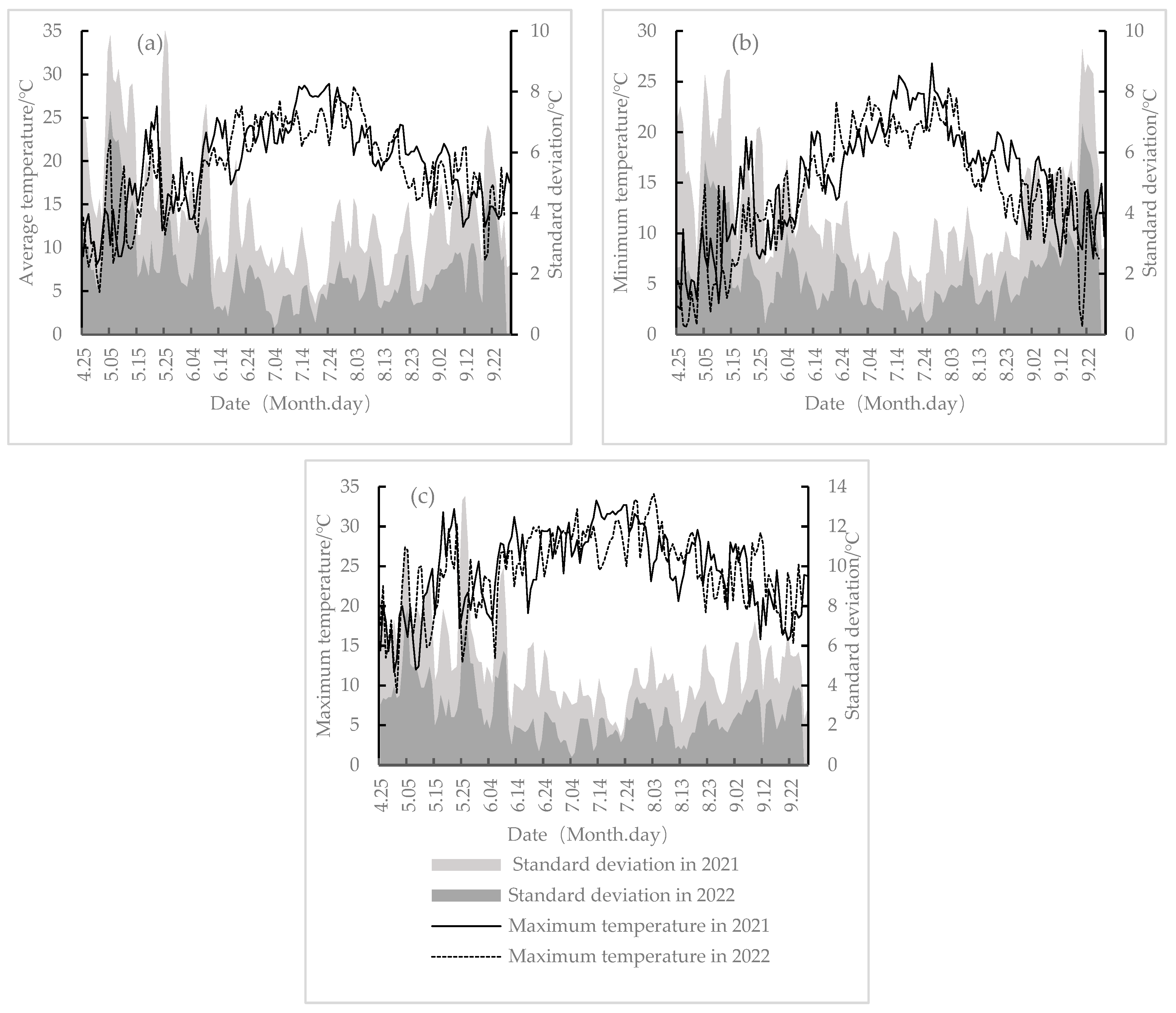
2.4.1. Expression of Statistical Dispersion of Temperature
2.4.2. Analysis Method for the Relationship between Temperature and the Growth Rate and Yield Formation of Spring Maize
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Temperature on the Growth of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
3.1.1. Growth Rate of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
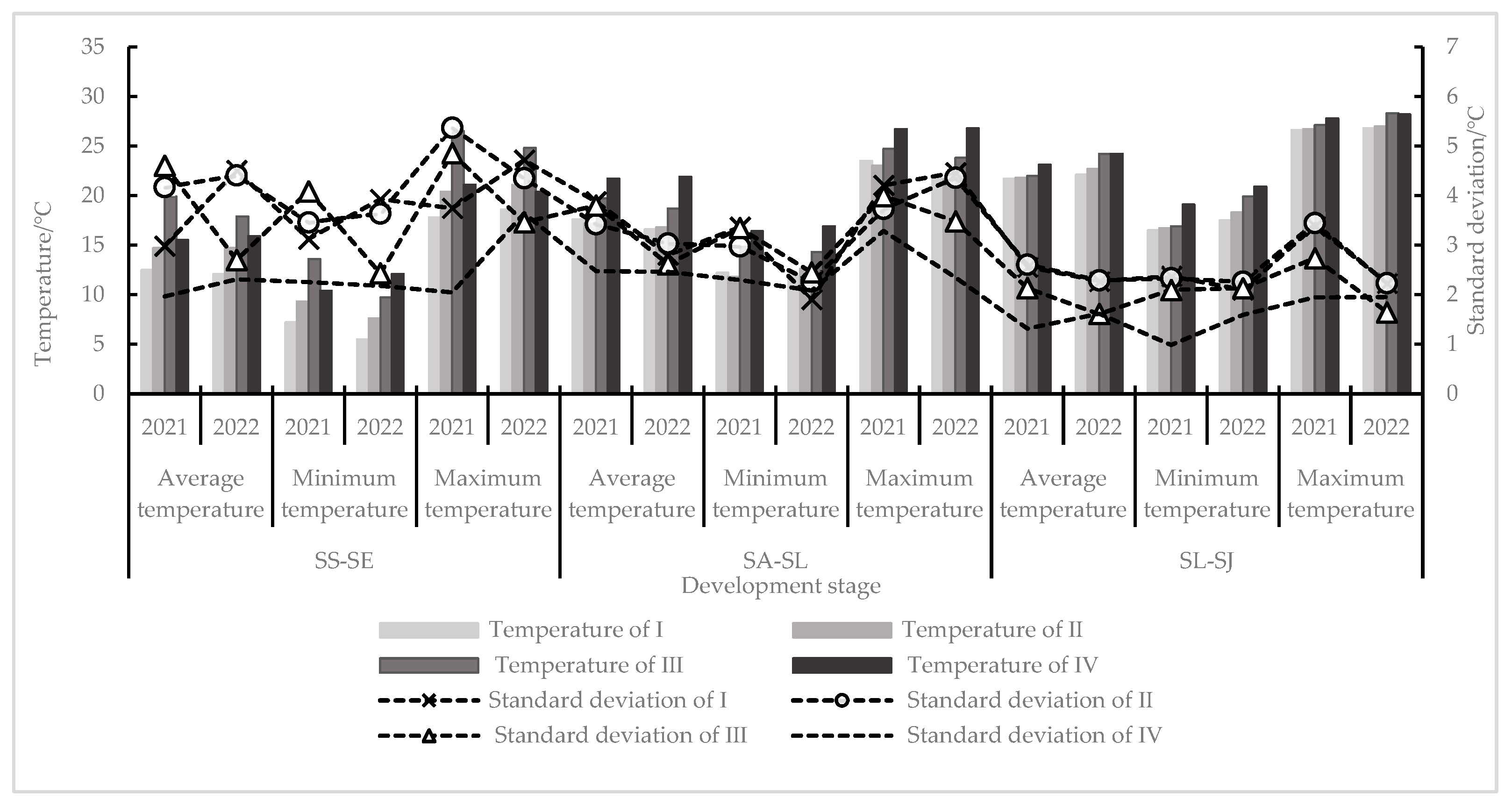
3.1.2. Thermal Condition of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
3.1.3. Effect of Temperature Change on the Development Rate of Spring Maize
3.2. Effect of Temperature on Dry Weight of Grain Kernel of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
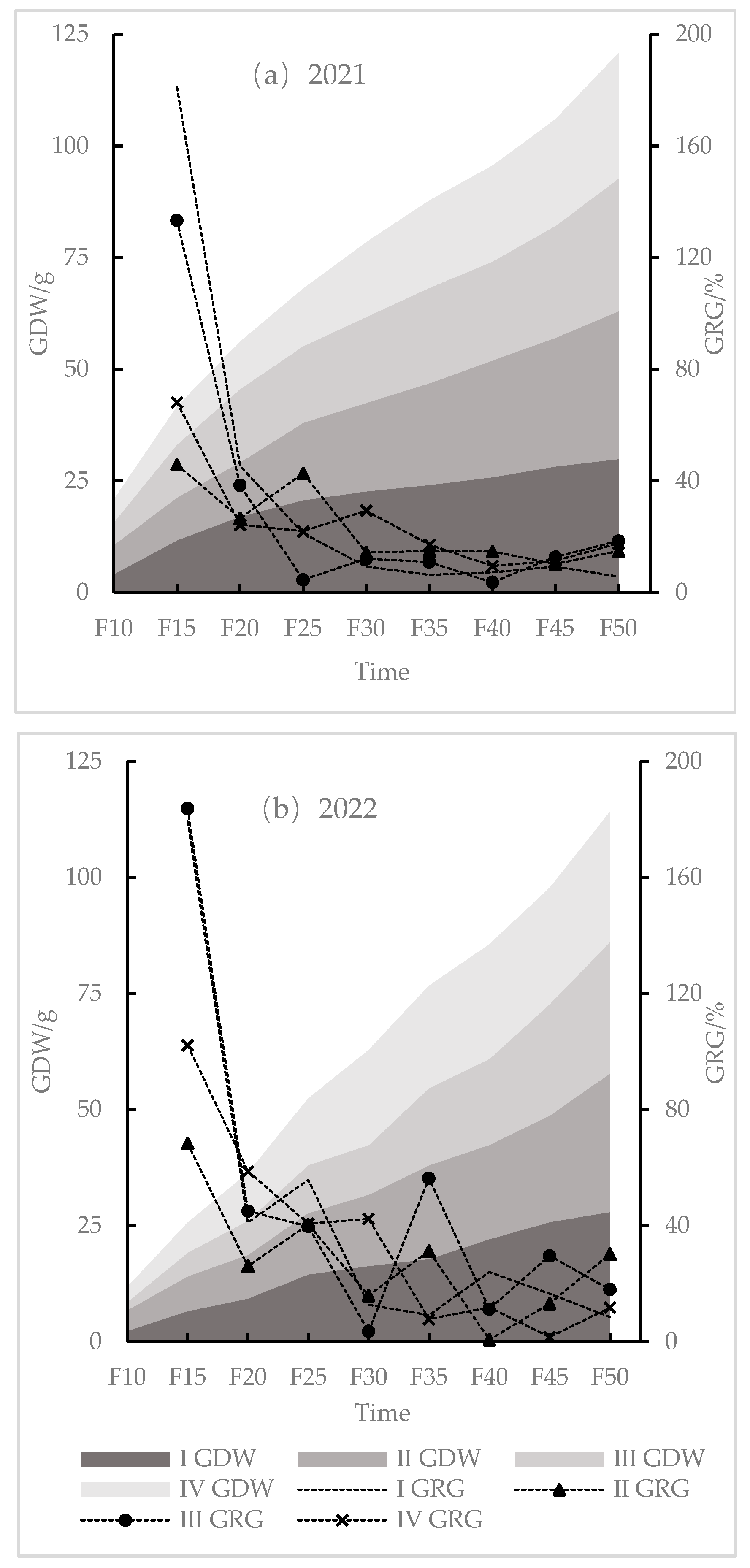
3.2.1. Changes in Dry Weight of Grain Kernel of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
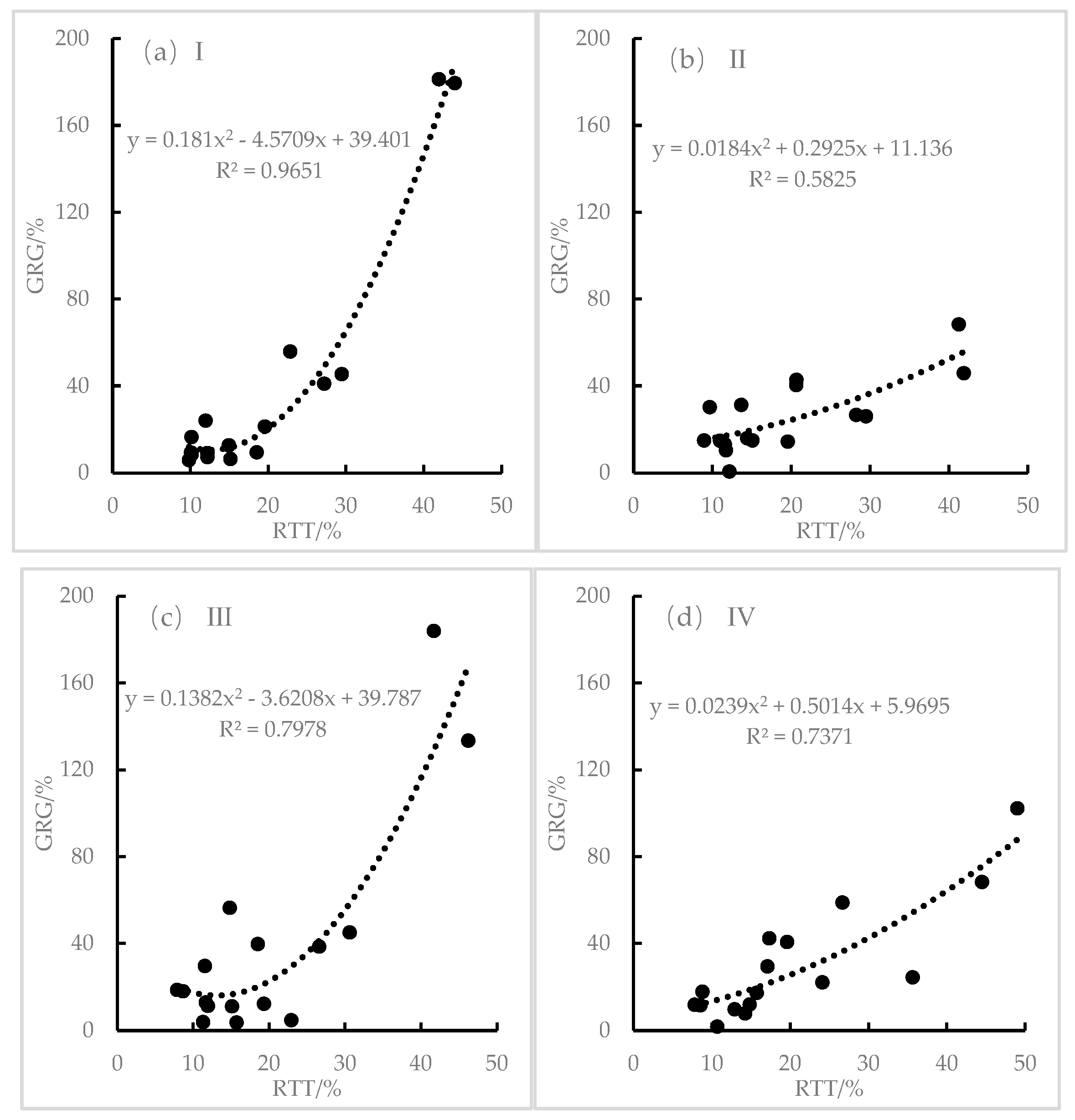
3.2.2. Effect of Accumulated Temperature on Dry Weight of Grain Kernel in Spring Maize
3.3. Effect of Temperature on Grain Moisture Content of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
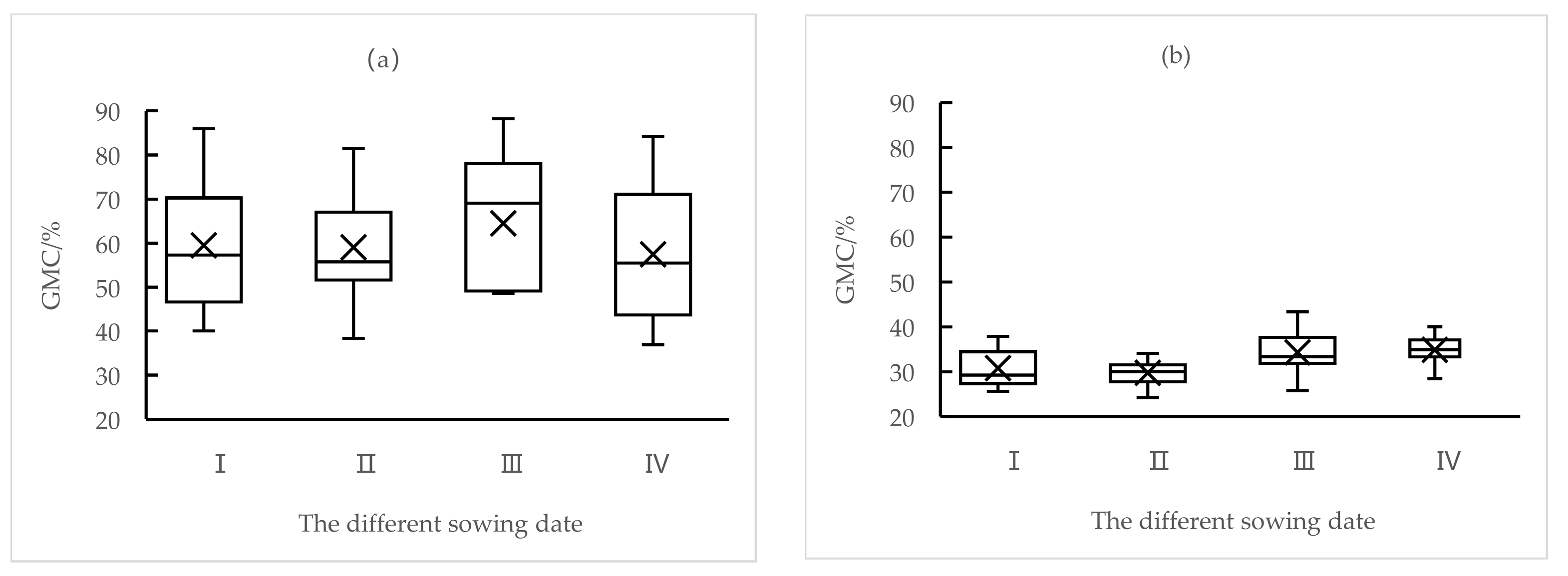
3.3.1. Changes in Grain Moisture Content of Spring Maize on Different Sowing Dates
3.3.2. Effect of Accumulated Temperature on Grain Moisture Content of Spring Maize
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mir, K.A.; Park, C.; Purohit, P.; Kim, S. Comparative analysis of greenhouse gas emission inventory for Pakistan: Part II agriculture, forestry and other land use and waste. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2021, 12, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H. Sustainalbe management and action in China under the increasing risks of global climate change. Engineering 2018, 4, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.F.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhao, J.C.; Li, S.; Chu, Q.Q. Spatiotemporal variation of high temperature stress in different regions of China under climate change. Acta Agron. Sin. 2023, 49, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.X.; Li, X.F.; Zhu, H.X.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q.J.; Yan, P.; Gong, L.J.; Zhai, M.; Ji, Y.H.; Wang, P. Characteristics of combination of cold damage and drought during seedling period and its effects on maize yield in Heilongjang Province. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2020, 38, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Waldhoff, S.T.; Wing, I.S.; Edmonds, J.; Leng, G.; Zhang, X. Future climate impacts on global agricultural yields over the 21st century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.D.; Leng, P.F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Song, S.; Qiao, Y.F.; Gu, C.K.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Mulubrhan, B.; Dagne, M.; et al. Understanding agriculture production and food security in Ethiopia from the perspective of China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2018, 9, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.X.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Yan, P.; Han, J.J.; Jiang, L.Q.; Chu, Z. Characteristics of temperature and water in drought and cold damage cross-stress of maize and its yield analysis in Heilongjiang province. J. Catastrophol. 2022, 37, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.P. Advances in impacts of climate on agricultural production in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2015, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, B.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, N.; Liu, C.G.; Cao, T.H. Effect of Temperature on the Growth and Yield of Maize under Different Planting Patterns. Mol. Plant Breed. 2018, 16, 8208–8213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.C.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zhang, K.X.; Zhou, Z.W.; Che, X.J. The Effect of Temperature Changes on the Growth Rate and Yield of Different Organs of Maize in Longdong Region. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Hou, Q.; Yun, W.L. Effect of Temperature Change on Growth and Yield Structure of Maize in Hetao Irrigation District. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, S.B.; Dong, X.; Tao, H.B.; Wang, P. Effect of high temperture during flowering on pollen development and seed setting rate of maize (Zea mays L.). J. China Agric. Univ. 2020, 25, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.M.; Ren, J.Q.; Cao, T.H.; Xu, C.; Li, J.P.; Qu, S.M. Effect of low temperture during ear differentiation stage on yield components of spring maize. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2018, 29, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, S.Q.; Guo, J.P.; Zhang, T.L.; Yu, H.; Xu, L.P. Effect of airtemperature on maize growth and its yield. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.H.; Zhou, D.W.; Qin, L.J. Sowing date of corn in semiarid region of Jilin Province, Northeast China in adapting to climate change. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, N.K. Integrated nutrient management in winter maize (Zea mays L.) sown at different dates. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2011, 3, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.L.; Mao, L.X.; Zhou, G.S. Changes in global main crop yields and its meteorological risk assessment. Rransactions Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.M.; Zheng, D.F.; Du, J.D. Effects of meteorological factors on yield traits of maize (Zea mays L.) in Heilongjiang during various sowing seasons. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2016, 34, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Solaimalai, A.; Arunkumar, N.; Jeyakumar, M.; Jawahar, D. Effect of dates of sowing and integrated nutrient management practices on growth, yield attributes and yield of hybrid maize under rainfed vertisol of Tamil Nadu. Adv. Life Sci. 2016, 5, 3456–3460. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.G.; Gao, M.; Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.G. Sowing Date and Yield of Maize: Effects on Photosynthetic Characteristics. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 36, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ahammad, K.U.; Ahmed, M. Effect of seed priming on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling emergence under different sowing dates. Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2014, 39, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlapur, S.; Kulkarni, M.K.; Hegde, Y. Effect of sowing date and weather parameters on turcicum leaf blight severity and yield in maize. Indian Phytopathol. 2007, 60, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.L.; Cui, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, X. Comparison of Grain Dehydration Process and Yield Formation for Summer Maize under Different Sowing Dates in Huanghuaihai Plain. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2022, 43, 112–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Yue, Y.; Sun, X.F.; Ding, Z.S.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Maize kernel weight responses to sowing date-associated variation in weather conditions. Crop J. 2017, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Ground observed climatology and trend in snow cover phenology across China with consideration of snow-free breaks. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 2867–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.X.; Zhao, H.Y.; Qu, H.H. Effect of drought and cold damage cross-stress on maize yield in Heilongjiang Province. Meteorol. Mon. 2021, 47, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- QX/T 361-2016; Specifications for Agrometeorological Observation-Maize. China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Yu, Z.F.; Ding, W.X.; Chen, M. Statistical processing and interpretation of data. In Judgment and Processing of Outliers of Normal Samples; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.Y. Modern Climate Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Techniques; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.Q.; Wang, Q.; Luo, X.L. Effect of climate change on maize (Zea mays) growth and yield based on stage sowing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.P.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, H.Y. Quantitative analysis of temperature conditions and maize growth and yield formation in spring maize region of Northeast China. J. Maz. Sci. 2022, 30, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, M. Research progress on regulation of maize growth, development and yield by sowing date under climate change. South China Agric. 2022, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- QX/T 259-2015; Drought Grade of Spring Maize in Northern China. China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Li, S.; Du, C.Y. Manual of Agrometeorological Application Service in Heilongjiang; Northeast Forestry University Press: Harbin, China, 2013; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]

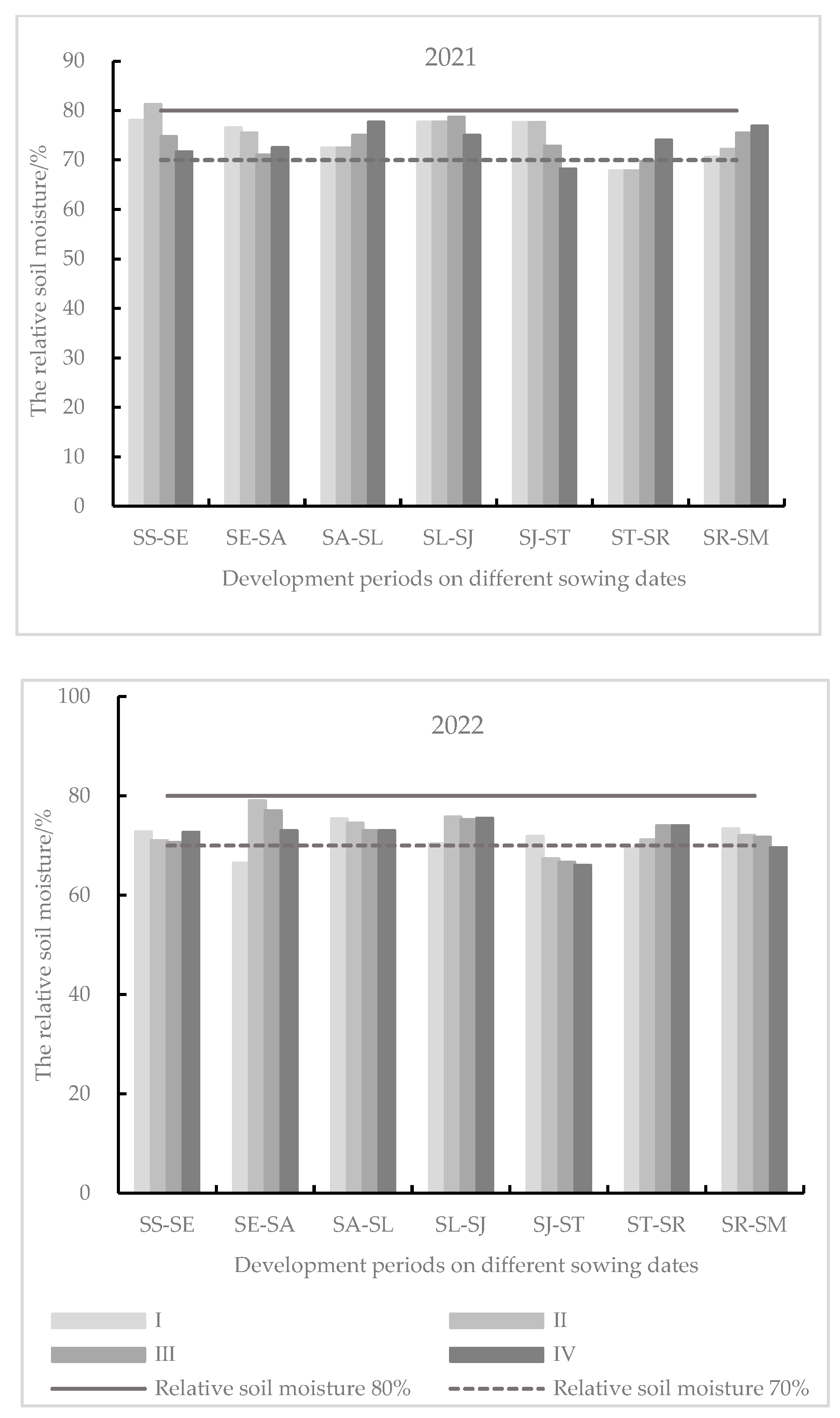
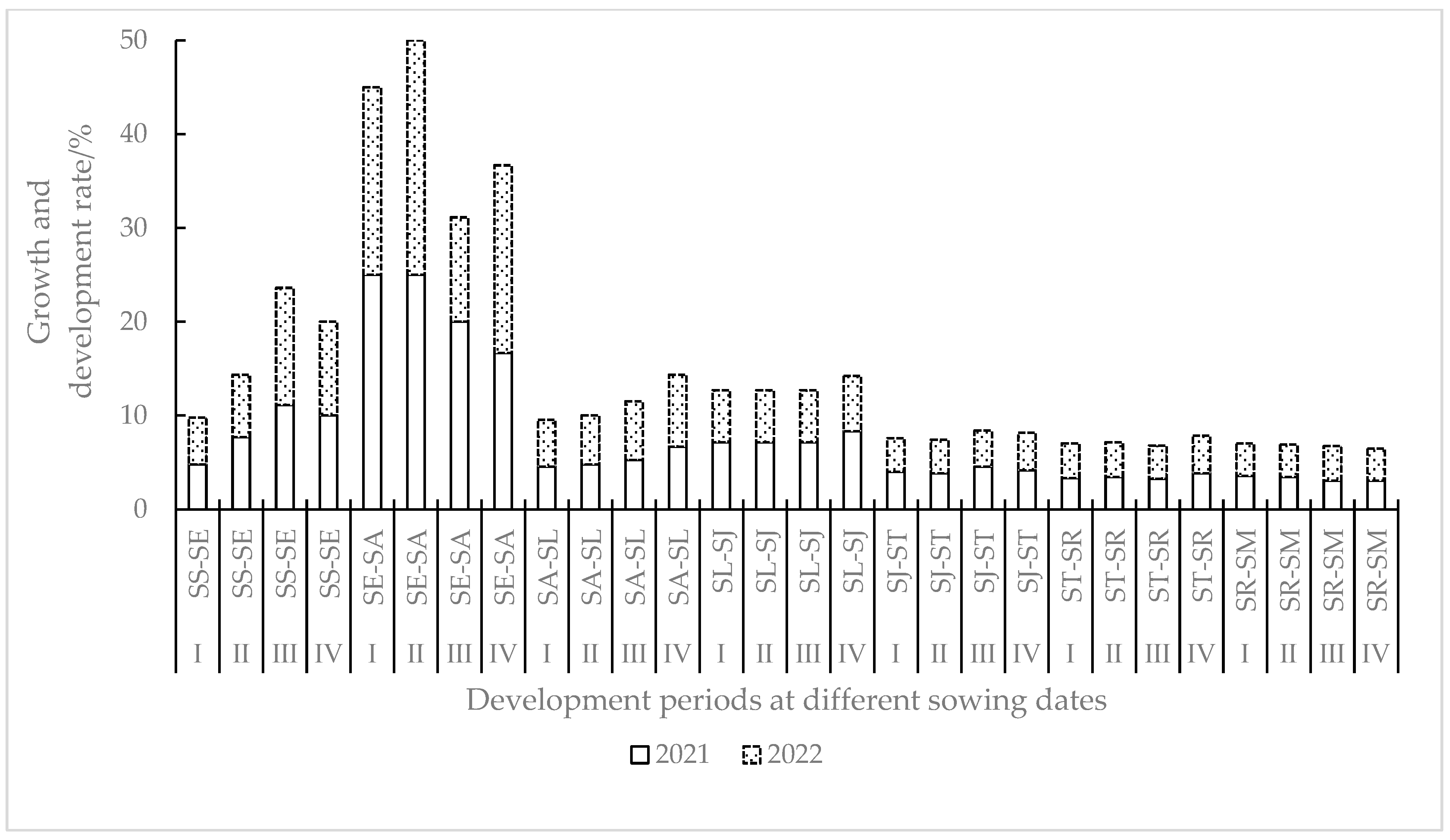
| Growth Stage | Code | Development Stage | Code | Interval Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sowing stage | SS | sowing–seedling stage | SS-SE | 17 |
| seedling stage | SE | seedling–three leaves stage | SE-SA | 7 |
| three leaves stage | SA | three leaves–seven leaves stage | SA-SL | 16 |
| seven leaves stage | SL | seven leaves–jointing stage | SL-SJ | 17 |
| jointing stage | SJ | jointing–tasseling stage | SJ-ST | 24 |
| tasseling stage | ST | tasseling–milk ripening stage | ST-SR | 28 |
| milk ripening stage | SR | milk ripening–mature stage | SR-SM | 34 |
| mature stage | SM |
| Temperature Factors | Emergence Rate | |
| Regression Equation | ||
| Average temperature | 0.886 ** 1 | |
| Average minimum temperature | 0.707 * | |
| Average maximum temperature | 0.794 * | |
| Temperature Factors | Vegetative Growth Rate | |
| Regression Equation | ||
| Average temperature | 0.790 * | |
| Average minimum temperature | 0.565 * | |
| Average maximum temperature | 0.893 ** | |
| Measuring Time | I | II |
| Flowering during 10–50 days | 0.98 ** | 0.92 ** |
| After physiological maturity | 0.83 ** | 0.75 ** |
| III | IV | |
| 10–50 days after flowering | 0.92 ** | 0.95 ** |
| After physiological maturity | 0.64 ** | 0.56 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Wang, M.; Chu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Guo, L.; Ji, S.; Jiang, L.; Gong, L. Effects of Temperature on Growth and Grain Maturity of Spring Maize in Northeast China: A Study of Different Sowing Dates. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121755
Jiang L, Wang M, Chu Z, Gao Y, Guo L, Ji S, Jiang L, Gong L. Effects of Temperature on Growth and Grain Maturity of Spring Maize in Northeast China: A Study of Different Sowing Dates. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(12):1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121755
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Lixia, Ming Wang, Zheng Chu, Yonggang Gao, Lifeng Guo, Shengtai Ji, Lanqi Jiang, and Lijuan Gong. 2023. "Effects of Temperature on Growth and Grain Maturity of Spring Maize in Northeast China: A Study of Different Sowing Dates" Atmosphere 14, no. 12: 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121755
APA StyleJiang, L., Wang, M., Chu, Z., Gao, Y., Guo, L., Ji, S., Jiang, L., & Gong, L. (2023). Effects of Temperature on Growth and Grain Maturity of Spring Maize in Northeast China: A Study of Different Sowing Dates. Atmosphere, 14(12), 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121755






