Abstract
Agro-meteorological disasters are a significant cause of crop yield reduction. Northeast China is a major base for commodity grain production and is also highly sensitive to climate change. Early frost is one of the most significant meteorological disasters in Northeast China. The typical weather system serves as the primary meteorological cause of the occurrence of early frost. The Northeast Cold Vortex is a cyclonic system of certain intensity located in Northeast China, which has the potential to induce severe weather conditions such as extreme low temperatures and intense convection. Despite extensive research on the first occurrence of frost in Northeast China, the evolutionary characteristics under the combined influence of climate change and the Northeast Cold Vortex remain unclear. This limitation hinders the development of effective monitoring and early warning systems for early frost, as well as the formulation of disaster prevention and mitigation plans for crop production. Therefore, this study aims to objectively document the occurrence of early frost in maize crops in Northeast China from 1961 to 2021 under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex. It seeks to unveil the climatic characteristics and evolutionary patterns of early frost events in maize crops within this region, considering the impact of the Northeast Cold Vortex. Additionally, it endeavors to analyze the factors contributing to varying degrees of early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex. The results showed that the occurrence of both early frost and frost influenced by the Northeast Cold Vortex exhibited a declining trend. Furthermore, there was also a decreasing proportion of initial frost attributed to the Northeast Cold Vortex, with a decline rate of 2% per decade, indicating a diminishing dominance of initial frost caused by this weather system. The onset date for the early frost under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex progressively advanced from southeast to northwest, occurring 4 days earlier than during the period from 1961 to 1990 between 1991 and 2021. While early frost displayed an increasing spatial distribution from southeast to northwest, it is noteworthy that the majority concentration of the Northeast Cold Vortex was observed in central regions, highlighting its predominant role in causing early frost in Northeast China.
1. Introduction
Representative of ongoing global climate change and characterized by temperature rise, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) highlights that over the past decade, global surface temperatures have increased by 1.09 °C compared to the period from 1850 to 1900 [1]. The average temperature change rate in China, as a highly vulnerable region to global climate change, between 1951 and 2021, has changed by 0.26 °C per decade, which surpasses the global average by 0.11 °C per decade [2,3]. Simultaneously, climate change has also led to a heightened amplification of the risk associated with extreme weather and climate events. The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction highlights that from 2000 to 2019, meteorological disasters accounted for as much as 90% of global disaster events, thus affirming that climate change exacerbates the incidence of such calamities [4]. The agricultural sector, highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change [5], is significantly influenced by this phenomenon. The impact of climate change on the long-term average temperature is manifested in gradual global warming, while in the short term, it is reflected in changes in daily average temperature and daily maximum and minimum temperatures [6]. Compared to long-term global warming, current extreme weather and climate events have a greater impact on agricultural production [7,8]. Early frost refers to the first occurrence of frost during the transition from the warm season to the cold season within the growing season [9].
Northeast China, located in the middle and high latitudes of China and eastern Eurasia, experiences a higher rate of temperature change compared to the national average rate. Therefore, it is considered a sensitive region to climate change in China [10,11]. Northeast China accounts for 16.6% of arable land nationwide and contributes 20% of total grain output and 25% of commercial grain output, making it the largest commercial grain base in China [12,13]. Maize cultivation plays a significant role as it represents 30% of national maize output and directly impacts food security [14]. Early frost is one of the most important meteorological disasters affecting maize yield in Northeast China. Studies suggest that abnormal early frost dates can lead to a reduction in maize yield ranging from 2 to 10% [15,16], with Heilongjiang alone experiencing such reductions. In 1969, Heilongjiang suffered an early frost disaster, resulting in rural areas alone experiencing over 400 million catties reduction in yield [17]. Therefore, objectively understanding the causes and mastering spatiotemporal patterns related to early frost disasters holds great significance for prevention and mitigation efforts aimed at reducing their impact on agriculture production.
The early frost date in the United States has experienced a delay of 5 days from 1900 to 2014 in most regions, although the temporal and spatial distribution is uneven. In certain areas, this delay can even extend up to 20–40 days, while before the 1930s, the occurrence of early frost was advanced by approximately 2–3 days. However, a significant postponement was observed after 1970 [18,19,20,21]. The autumn frost dates in agricultural areas of Canada have experienced a slight delay, although not statistically significant [22,23,24,25,26]. In Europe, the occurrence of spring frost has been advancing, while autumn frost has been experiencing delays, resulting in an extended growing season [27,28,29]. In the Iberian Peninsula, the occurrence of spring frost has been advanced by 0.4–1.2 days per year, and autumn frost has been delayed by 0.4–1.0 days per year. In Romania, Slovakia, the Czech Republic, and Poland in central and eastern Europe, where frost days typically occur in late October, the frost-free period from 1990 to 2019 was longer compared to 1950–1979; however, this was primarily due to earlier final frost (spring frost), although there were slight delays in early frost that were not significant [30,31,32]. The onset of the early frost in Northern China has gradually been delayed under the influence of climate change. However, during the 1990s, there was a reversal with an earlier occurrence, followed by further delays. In particular, major maize-producing regions experienced a general delay of 8–10 days, significantly impacting grain yield per unit area [33,34]. The aforementioned studies have primarily focused on the impact of climate change on autumn frost within the context of agricultural production in various regions [35,36,37]. However, there remains a limited understanding of the weather system influencing frost occurrences, thereby impeding accurate prediction and early warning systems for early frost. Meanwhile, the Northeast Cold Vortex will induce excessive precipitation and cooling during summer and autumn, thereby posing a significant threat to the agricultural system in this region [38,39]. Previous studies on the early frost primarily focus on the spatiotemporal distribution of climate change, with limited analyses conducted on the impact of various weather systems on its occurrence. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the significant influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex, which represents a prevalent cut-off low-pressure weather system in Northeast China, and its cooling effect on initiating frost events cannot be disregarded. Therefore, this study focuses on Northeast China, a crucial grain-producing region, as the research area and examines the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of maize’s early frost occurrence under the backdrop of climate change and in response to the influence of the Northeast cold vortex weather system. This paper aims to provide technical support for enhancing the predictive capability of early frost occurrence in maize cultivation within Northeast China. Additionally, it seeks to establish a scientific foundation for adapting to and mitigating climate change impacts by implementing strategic management and technical measures that capitalize on favorable conditions while minimizing potential drawbacks, thereby ensuring sustainable agricultural development.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
The meteorological data utilized in this study were sourced from the China Meteorological Science Data Sharing Service Network (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 28 March 2024), encompassing daily minimum temperature records from 1961 to 2021 across 143 meteorological stations situated in Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, and East Four League of Inner Mongolia (the four league cities in northeastern Inner Mongolia, namely Hulunbuir, Tongliao, Chifeng, and Xingan League).
The data pertaining to the growth period of maize were acquired from 52 agro-meteorological observation stations within the study area, primarily comprising the duration of each growth stage spanning from sowing to maturity. In order to ensure data comprehensiveness throughout the growth period, we specifically selected an agro-meteorological observation station with over three decades worth of observational records as our research site.
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Determine the Northeast Cold Vortex
The Northeast Cold Vortex process is defined as a cyclonic circulation system on a 500 hPa upper air chart, characterized by at least one closed contour and a distinct cold trough or cold center coordination over the northeast region (35–60° N, 105–145° E) persisting for three or more consecutive days. The application of ERA5 (fifth generation ECMWF atmospheric reanalysis of the global climate) facilitated the objective identification of Northeast Cold Vortex events spanning from 1961 to 2021, culminating in the confirmation of 1959 instances of the Northeast Cold Vortex.
2.2.2. Determine the Early Frost Grade of Maize
To conduct a detailed analysis of the impact of early frost on maize, this study will focus on evaluating the severity of early frost disasters in terms of maize damage. Due to limited ground temperature data coverage and a short observation period, we adopted the national meteorological industry standard QX/T88-2008 “Crop Frost Damage Grade” [40] as the method for identifying the occurrence time and severity level of early frost on maize in Northeast China, based on daily minimum temperatures. Typically, maize in Northeast China becomes close to maturity before experiencing its early frost. Therefore, we consider using the classification method based on the milk maturity stage as the standard for categorizing different grades of early frost damage in maize across Northeast China, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Early frost grade of maize in Northeast China (Unit: °C).
2.2.3. Identification of the Early Frost Influenced by the Northeast Cold Vortex
Via the aforementioned methodology, we identified the dates of occurrence for both the Northeast Cold Vortex and maize early frost. We assert that if the date of early frost occurrence falls within the period of the Northeast Cold Vortex event, it signifies the impact of the Northeast Cold Vortex on the onset of maize early frost disaster. Conversely, if the date of early frost occurrence does not align with the period of the Northeast Cold Vortex event, it suggests that the maize early frost disaster has not been influenced by the Northeast Cold Vortex.
2.2.4. Determine the Growth Period
The average maturity date of maize across all sites in each province was calculated as the province’s average growing period. Subsequently, the identification of the occurrence date and severity of the early frost was conducted based on meteorological data from each site. This approach was necessitated by the disparate spatiotemporal resolutions between maize growth period data and meteorological data. However, there is a significant disparity between the northern and southern regions within the East Four League of Inner Mongolia, which renders it inadequate to capture complete information regarding maize growth using a single growth period. Therefore, considering the location of each station, we aggregated the growth period information from neighboring provinces through averaging before conducting an analysis based on this comprehensive dataset.
2.2.5. Proportion of Early Frost Sites Occurred
Based on the proportion of early frost disasters in 143 meteorological sites in Northeast China every year, the influence degree of the early frost disasters in Northeast China every year was analyzed. The ratio of early frost stations to the total number of assessed stations (IOC) was utilized as an indicator for quantifying the extent of early frost in a given year [41] The higher the proportion of site occurrence in the current year, the greater the degree of impact; conversely, a lower proportion results in a smaller impact. The analysis of the interannual change in proportion allows for the identification of trends in initial frost disasters, given the extensive number of sites and long research time series.
2.2.6. Data Visualization
To clearly elucidate the spatiotemporal characteristics of the early frost in maize under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex, this study used Excel 2019 and ArcGIS 10.3 software for data visualization. Initially, the daily meteorological data and maize development stage data from 1961 to 2021 were preprocessed and statistically analyzed in Excel 2019. Using Excel’s charting capabilities, line charts depicting the frequency and severity distribution of cold damage were generated. These charts facilitate a straightforward understanding of the temporal evolution of early frost occurrences in maize under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex.
To further analyze the spatial distribution characteristics of the early frost in maize impacted by the Northeast Cold Vortex, the Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) interpolation method in ArcGIS was utilized to interpolate the frequency and severity of the Northeast Cold Vortex induced cold damage. IDW interpolation method has played a pivotal role across multiple interdisciplinary domains [42,43,44,45]. IDW interpolation, which allocates weights inversely proportional to the distance, emphasizes the influence of nearby observation points on the interpolation results, thereby effectively reflecting local variation characteristics. The parameters of IDW interpolation are adjustable, allowing the selection of appropriate search radii and power parameters according to actual conditions, thus optimizing the accuracy of the interpolation results. IDW interpolation is capable of effectively handling meteorological data with sparse distribution characteristics and is suitable for analyzing the spatial heterogeneity of cold damage within a region.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Maize Early Frost in Northeast China
3.1.1. Early Frost Distribution from 1961 to 2021
The regions with a high incidence of early frost are primarily concentrated in Heilongjiang and northern Inner Mongolia, where the annual frequency of frost occurrence is 14%. The highest region experiences almost 100% occurrence, while other areas have frequencies above 15% (Figure 1). Among them, light frost occurs in the largest area and has a higher frequency, with the highest occurrence primarily concentrated in Hulunbuir, the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains, and Changbai Mountain. In the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains, heavy frost occurs more frequently than medium frost. In the Changbai Mountain area, there is a more pronounced occurrence of medium frost.
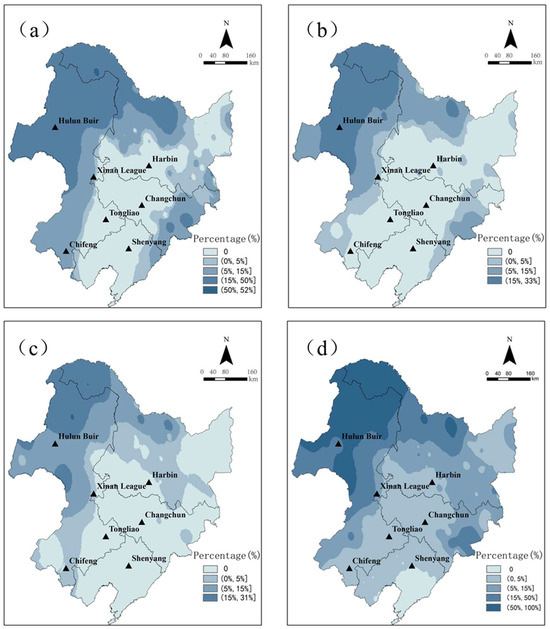
Figure 1.
Frequency of early frost year in Northeast China from 1961 to 2021. ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost. The frequency of early frost is calculated by dividing the total number of early frost occurring from 1961 to 2021 by the number of years in that period).
3.1.2. Distribution of Early Frost Daily Sequence from 1961 to 2021
The average date of the early frost is day 261 (day of year, DOY), with an overall spatial distribution showing earlier occurrences in the western regions, later occurrences in the eastern regions, and the latest occurrence at 290 days in the west (Figure 2).
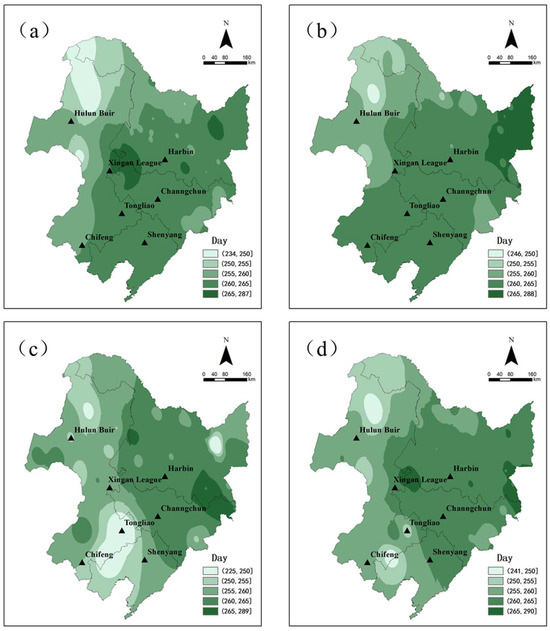
Figure 2.
Early frost occurred in Northeast China from 1961 to 2021. ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
Cold damage occurred earlier in Hulunbuir and the northern part of Heilongjiang Province, and it took place before the 265th day. The average frost date for mild and moderate cold damage in the Chifeng and Tongliao regions is typically between 255 and 265 days, whereas the average frost date for severe cold damage occurs at approximately day 250. The occurrence of light frost in Xingan League was delayed, while the medium and heavy frost arrived more than 10 days earlier than the light frost.
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Early Frost under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex
3.2.1. Distribution of Early Frost under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex from 1961 to 2021
The spatial distribution of early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex can effectively demonstrate the impact of cold vortices on the occurrence of early frost. The greater the proportion, the stronger the influence exerted by the Northeast Cold Vortex on local initial frost. In most areas of central and Sanjiang Plain, the early occurrence of frost is predominantly attributed to cold vortices, reaching up to 100% (Figure 3). Conversely, the southern parts experience minimal impact from these weather systems, while light and medium frost areas exhibit similar patterns, with significant influence observed in the central and eastern parts. Apart from heavy frost occurring in central and eastern regions, the western Hulunbuir area also faces substantial effects from the Northeast Cold Vortex.
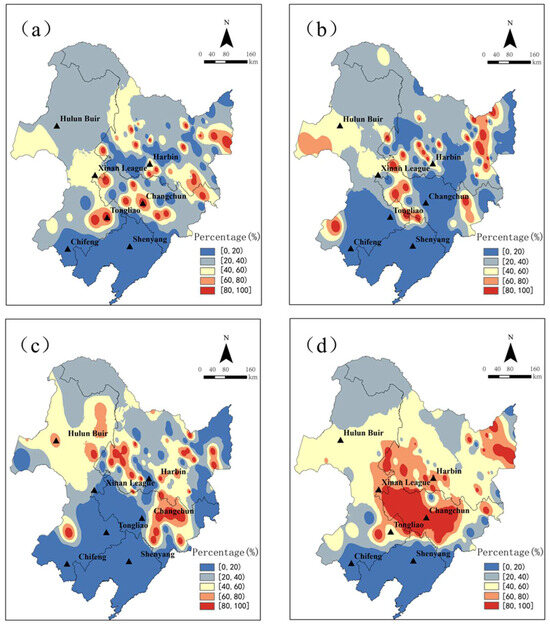
Figure 3.
Proportion of early frost occurrence caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex from 1961 to 2021 ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
3.2.2. Distribution of Early Frost Daily Sequence under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex from 1961 to 2021
The Northeast Cold Vortex gradually altered the overall daily sequence of early frost occurrence from northwest to southeast (Figure 4), while the distribution of early frost in different grades exhibited variations. The average occurrence of early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex is on the 261st day (15 September), while in the Tuli River of Inner Mongolia, it occurs on the 239th day (26 August). In most places, early frost typically appears on the 260th day (16 September), whereas in some areas, it occurs on the 265th day. The earliest occurrence of frost took place in northern Inner Mongolia and northern Greater Khingan Mountains, with an average date for medium and heavy frost occurring around the 261st day, although medium frost was delayed further east.
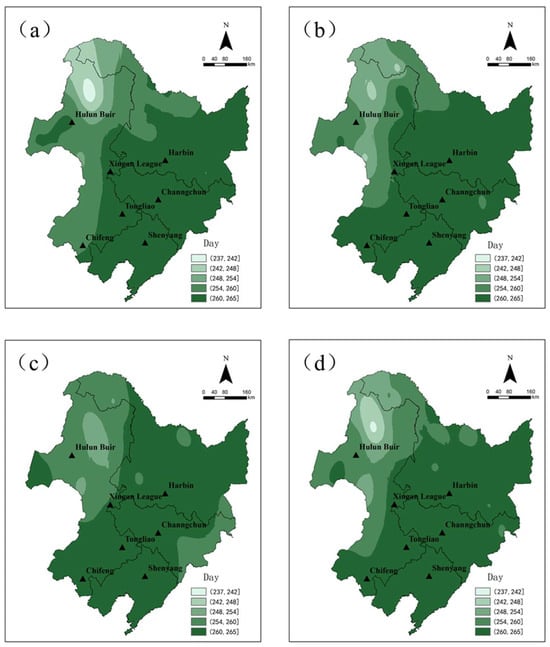
Figure 4.
Daily sequence of early frost caused by Northeast China cold vortex in Northeast China from 1961 to 2021 ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
3.3. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Early Frost in Northeast China
3.3.1. Distribution of Early Frost Change from 1961 to 2021 (Decades Difference)
The difference in the frequency of early frost between 1991 and 2021 and 1961 and 1990 was utilized to depict the temporal and spatial variations of early frost across different grades (Figure 5) On average, there was a 4% reduction in overall frost occurrences, with the most significant reductions observed in the eastern and western regions, while increases were noted in the central and northern regions. In the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains, all grades of frost experienced an increase exceeding 10%, including higher frequencies of frost in Changchun and Tongliao compared to the period from 1961 to 1990. Notably, reductions in frost occurrences were primarily concentrated among light frost, predominantly found within the western region.
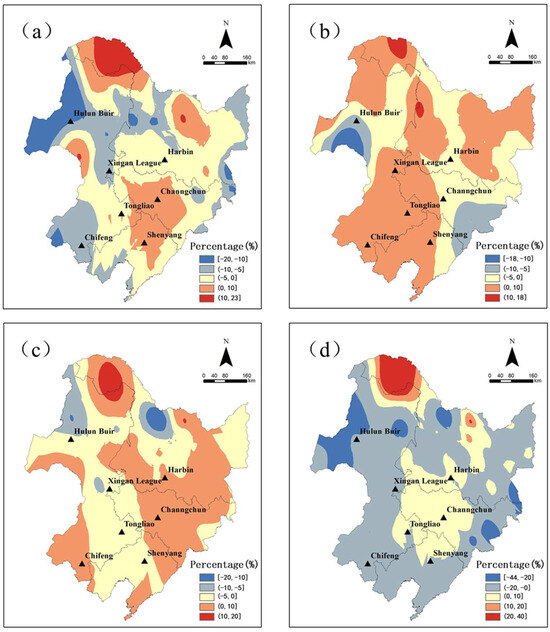
Figure 5.
The temporal and spatial variability of early frost occurrence in Northeast China from 1961 to 2021 ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
3.3.2. Variation Distribution of Early Frost Daily Sequence from 1961 to 2021 (Decades Difference)
From 1991 to the beginning of 2021, there has been an overall advancement in the frost date, with an average advance of 0.6 days for all early frost(Figure 6). This early frost is primarily concentrated in the southern and northern regions of the Greater Khingan Mountains, while a general delay is experienced in other areas. The most significant number of delayed days can be observed in the eastern and Hinggan League areas, typically ranging from 4 to 8 days. In terms of grade classification, all categories of early frost exhibit advancement in the southern region, particularly heavy frost, which demonstrates a remarkable advance of up to 8 days across most parts of this area. Conversely, the delay is more pronounced in the eastern and Hinggan League areas, with a general postponement ranging from 4 to 8 days.
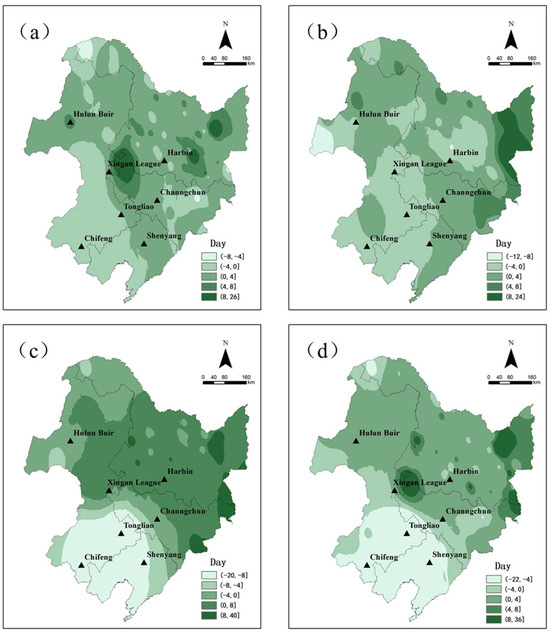
Figure 6.
The temporal and spatial variability of the daily sequence of early frost in Northeast China from 1961 to 2021 ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
3.4. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Early Frost under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex
3.4.1. Change Distribution of Early Frost Proportion under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex from 1961 to 2021
The spatiotemporal variation of the early frost caused by the cold vortex in the northeast is represented by subtracting the proportion from 1961 to 1990 from that of 1991 to 2021 (Figure 7). The overall distribution reveals an increase in the proportion of early frost caused by the Northwest Cold Vortex during the period from 1991 to 2021, while a significant decrease is observed in both central and northeast regions. Among all early frost, there was an increase in western Inner Mongolia and northern Heilongjiang, with a maximum increase of approximately 10%. Areas experiencing increased proportions of light frost and heavy frost were concentrated mainly in Hulunbuir, Inner Mongolia, with respective maximum increases of about 40–50%. Except for western Inner Mongolia, Changbai Mountain, and some sporadic areas, there was a decrease in medium frost proportions across other regions.
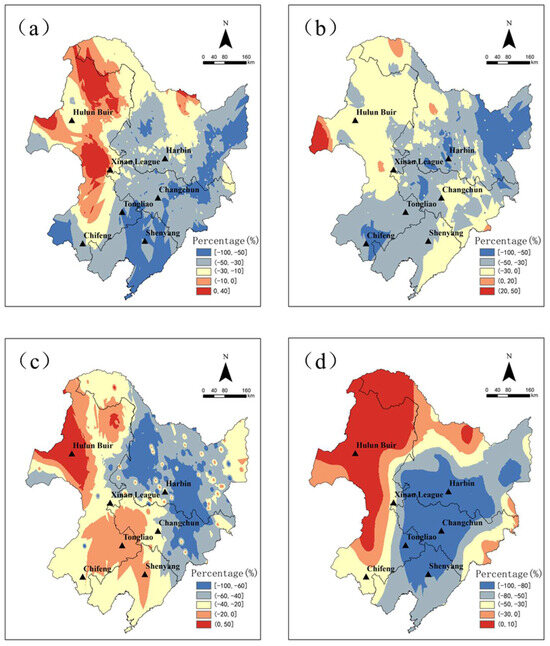
Figure 7.
Comparison of the proportion of early frost occurrence caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex during 1961–1990 and 1991–2021 ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
3.4.2. Variation Distribution of Early Frost Daily Sequence under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex from 1961 to 2021
The chronological variation of the early frost occurrence day sequence was calculated by the average day sequence from 1991 to 2021 minus the average day sequence from 1961 to 1990. Compared with 1961–1990, the early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex in 1991–2021 is about 4 days earlier overall, but the spatial distribution difference is significant, in which the occurrence date in northwestern Inner Mongolia, northern Heilongjiang, and Changbai Mountains is delayed, while the occurrence date in central and southern Inner Mongolia is significantly advanced by up to 7–10 days (Figure 8). Light frost overall occurs 3 days in in areas concentrated in the northern region. Medium frost and heavy frost occur about 6 days in advance, with heavy frost also observed to the north of the obvious advance; additionally, the Changbai Mountain area has also demonstrated an advance.
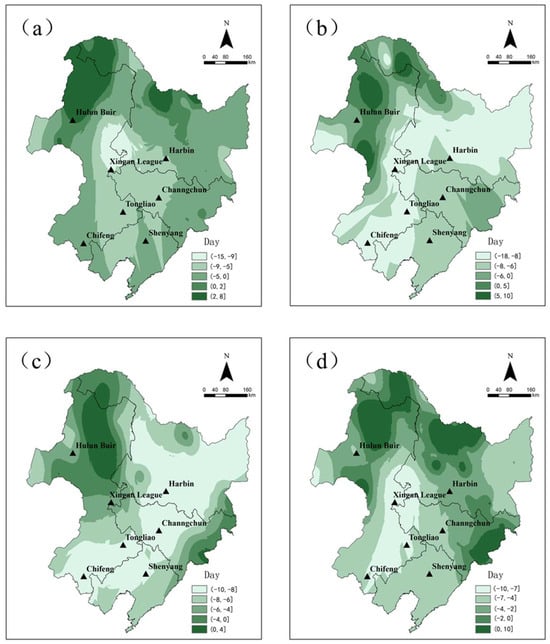
Figure 8.
Comparison of the daily sequence of early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex during 1961–1990 and 1991–2021 ((a–d) are, respectively, light frost, medium frost, heavy frost, and total frost).
3.5. Evolutionary Characteristics of Early Frost Occurrence in Northeast China
The changing trend of frost in Northeast China over the past 60 years can be analyzed by examining the proportion of frost disaster stations among all meteorological stations annually. Overall, there has been a decreasing trend in frost occurrences; however, the reduction rates vary significantly across different grades. Medium frost experienced the fastest reduction rate, while light and heavy frost showed similar reduction rates (Figure 9 and Figure 10). In certain years, early frost accounted for a large proportion, with as high as 77% observed in 1977. It can be postulated that maize in most parts of Northeast China is affected by the occurrence of early frost.
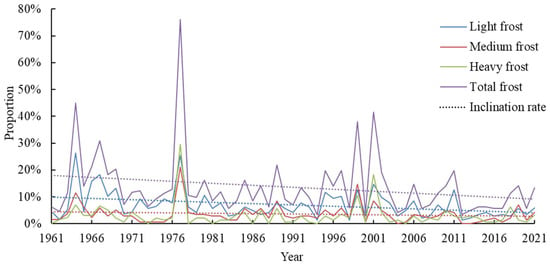
Figure 9.
Proportion of the early frost station occurrence in Northeast China.
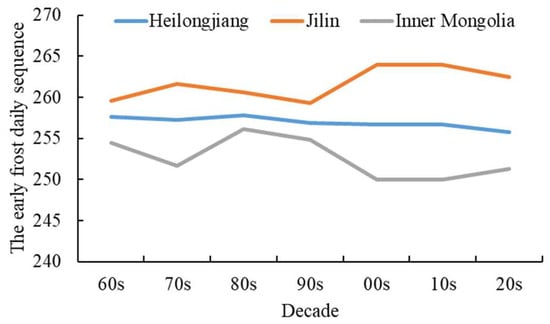
Figure 10.
Variation of the early frost daily sequence in Northeast China.
The first occurrence of frost in East Four League of Inner Mongolia consistently marks the earliest onset across all periods, while it is observed at its latest in Jilin Province. In Heilongjiang Province, the timing remains relatively stable, with a range of 256–257 days. In both Jilin and Inner Mongolia, frost typically appears within 259–264 days at the beginning of each decade. Notably, during the early 1990s and late 2000s, there was an earlier appearance of frost compared to other years. Within East Four League of Inner Mongolia, variations ranged from 251 to 256 days, with the first occurrence appearing in the 2000s and reaching its latest point in the 1980s.
3.6. Evolutionary Characteristics of Early Frost Occurrence under the Influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex
The impact of the Northeast Cold Vortex on frost damage also exhibited a declining trend, with the reduction rate being higher for all grades compared to total frost. Notably, light frost experienced the most rapid reduction rate, while heavy frost showed the slowest decline. In 1977, early frost influenced by cold vortex accounted for 61% of all stations, indicating a significant role played by cold vortex weather in Northeast China’s early frost that year. Similarly, in 1999 and 2001, early frost had a higher proportion (38% and 41%, respectively), but their association with the Northeast Cold Vortex was minimal (0% and 6%, respectively), suggesting less influence from the Northeast Cold Vortex during these two years. As depicted in the figure provided, there is an evident decrease over time in the extent of frost damage caused by early frost associated with the Northeast Cold Vortex. The temporal changes in the proportion of early frost disasters attributed to the Northeast Cold Vortex among all frost disasters within each year can be observed (Figure 11 and Figure 12). Under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex, early frost across all grades exhibits a downward trend; medium frost experiences the fastest reduction rate, while light frost shows slower decline rates. The annual occurrence of early frost disasters induced by the Northeast Cold Vortex at all stations demonstrates a general decreasing pattern (Figure 12), where medium frost has the highest reduction rate, and light frost displays relatively slower declines.
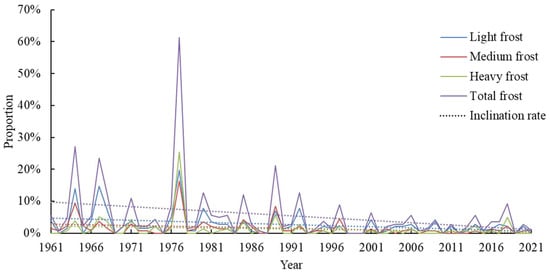
Figure 11.
The proportion of the early frost stations caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex.
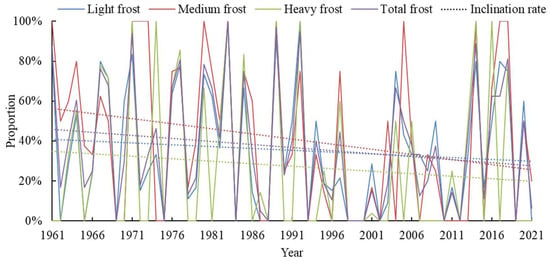
Figure 12.
The proportion of the early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex to total early frost occurrence in Northeast China.
The early frost disaster occurred at an earlier stage of growth in the East Four League of Inner Mongolia, followed by Heilongjiang Province. In Jilin Province, the early frost disaster occurred later, while Liaoning Province did not experience any early frost disasters (Figure 13). The changing trend of the early frost date differs among these three provinces. The East Four League of Inner Mongolia initially witnessed a delay in the early frost date, which was then followed by an advancement. Before the 2010s, Heilongjiang Province experienced an advancing trend in early frost, which later shifted towards a delayed trend. On the other hand, Jilin Province exhibited a fluctuating pattern. During years with early frost disasters, Heilongjiang Province had the earliest occurrence, with an average daily sequence of 259 days, and East Four League of Inner Mongolia had the latest occurrence with 265 days.
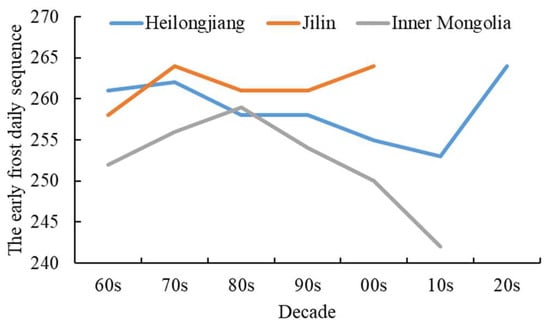
Figure 13.
The variation of the early frost daily sequence was caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex.
4. Discussion
As a significant meteorological phenomenon in Northeast China, the Northeast Cold Vortex exerts a profound influence on the weather and climate conditions of this region. The persistent presence of the cold vortex leads to severe weather events in Northeast China [46,47], posing a threat to sustainable food security in this area. While previous studies have primarily focused on investigating its impact on precipitation and summer cooling, it is important to acknowledge that simplistic weather and climate analyses have inherent limitations when it comes to guiding agricultural practices [48,49,50,51,52]. By examining the climatic characteristics associated with early frost disasters in maize cultivation under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex, this study effectively expands our understanding of how this meteorological system affects maize production. Consequently, these findings not only broaden our research scope regarding the Northeast Cold Vortex but also provide practical guidance for agricultural activities.
The findings of this study align with previous research regarding the characteristics of frost disasters concerning climate change. In terms of the frequency distribution of early frost disasters across different grades, it is observed that light frost occurrences are the most frequent, while heavy frost incidents are the least common. This conclusion is consistent with earlier studies [53,54]. However, the occurrence date of the early frost and the early frost influenced by the Northeast Cold Vortex in this study exhibited an earlier trend, diverging from findings observed in regions such as America and Europe. In light of climate change, the northeastern region of China has experienced a warming trend. However, this phenomenon has also contributed to anomalies in extreme weather events like the Northeast Cold Vortex. Consequently, these factors may ultimately result in earlier occurrences of initial frost disasters, but the occurrence of earlier.
The declining trend of early frost in Northeast China is attributed to climate and weather changes, particularly the influence of global warming. However, the impact of climate change on frost disasters is multifaceted, exhibiting strong temporal and spatial characteristics while being influenced by agricultural production activities. In the Huang-Huai region of China, temperature fluctuations resulting from global warming and frequent occurrences of extremely low temperatures have led to severe cold damage in crops [55]. In Chifeng City, despite a prolonged frost-free period, early frost intensified due to abnormal climatic conditions, resulting in significant losses in grain output [56]. Furthermore, rising temperatures have reduced crop cold resistance and necessitated the adoption of longer growth period varieties, thereby increasing the vulnerability to frost disasters in agriculture.
The innovative finding of this study is that the early frost gradually decreases under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex. However, in contrast, the Northeast Cold Vortex exhibits an increasing trend in autumn. This phenomenon is closely associated with climate change characterized by rising temperatures. Although the Northeast Cold Vortex can generate cooling weather conditions, the higher temperature prior to cooling will mitigate the risk of maize being affected by the initial frost disaster. Numerous scholars have confirmed a significant increase in temperature in Northeast China. Another discovery from this study reveals that the impact of the Northeast Cold Vortex on early frost primarily concentrates on the central region and has minimal effect on lower temperatures in the Greater Khingan Mountains to the north and higher temperatures in Liaoning to the south. While rising temperatures reduce initial frost disasters and promotes maize yield formation, adverse effects may still arise due to heavy rain and strong convective weather brought about by the Northeast Cold Vortex [57,58].
The present study examines the relationship between the impact of the Northeast Cold Vortex and the climatic characteristics of early frost disasters in maize. However, a comprehensive elucidation of the influence mechanism and internal correlation among different types of cold vortexes and disasters is lacking. Additionally, further research is needed to explore the exogenous weather system associated with cold vortex. In addition, this study examined the spatiotemporal variation pattern of the early frost disaster in the entire northeast region by conducting spatial interpolation on data collected from 143 meteorological stations. It is worth noting that addressing the potential uncertainty and error associated with spatial interpolation in relation to the early frost disaster is also a crucial aspect for future research endeavors.
5. Conclusions
Under the context of climate change, the spatial distribution of early frost in Northeast China exhibits a northward bias with reduced occurrence in the southern regions. The high-frequency areas are concentrated in the mountainous regions with higher elevations, where light frost displays the highest frequency and widest coverage. Heavy frost primarily occurs in the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains. An overall decrease was noted in total frost occurrences from 1991 to 2021; however, central China, northern Greater Khingan Mountains, and certain areas of Sanjiang Plain experienced an increase, particularly notable in northern regions where all grades exhibited an increase.
During the period from 1961 to 2021, the onset date of the early frost gradually advanced from west to east across Northeast China. Hulunbuir and Chifeng were identified as locations with concentrated early frost for each grade category, typically occurring before 250 days (4 September). The latest occurrences were mainly observed in the Xingan League and western regions of Sanjiang Plain, where a total early frost could occur after 265 days (19 September).
The spatial distribution of frost indicates that early frost in the central and Sanjiang plain regions is primarily attributed to the Northeast Cold Vortex, while the southern region is largely unaffected by these meteorological phenomena. Light and medium frost predominantly impacts the central and eastern regions, with heavy frost occurring outside these areas, particularly with significant consequences observed in Hulunbuir. From 1991 to 2021, compared to the period between 1961 and 1990, there was an increase in initial frost occurrences caused by the Northwest Cold Vortex. The areas experiencing increased light and heavy frost are concentrated near Hulunbuir. Overall, under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex, there has been a decreasing trend in early frost occurrences across all regions studied, with light frost exhibiting the most rapid decline.
Under the influence of the Northeast Cold Vortex, the timing of the early frost occurrence gradually shifted from northwest to southeast. The average date for the onset of the early frost was 261 days (15 September), with light frost occurring earliest, and both medium and heavy frost averaging around 261 days. The onset of the early frost caused by the Northeast Cold Vortex has advanced by approximately 4 days from 1991 to 2021, while the occurrence of light frost has advanced by 3 days. Medium and heavy frost advanced by about 6 days. In East Four League of Inner Mongolia, on average, the initial occurrence of frost took place on day 265, representing a delayed event compared to other regions, whereas Heilongjiang region initially experienced an early onset before transitioning to a later occurrence after the 2010s. Overall, there has been a decreasing trend in early frost across all severity levels; while light frost has consistently been more frequent than others throughout history, medium and heavy frost surpassed light ones during the decades of the 1970s and 1980s. In recent years, East Four League of Inner Mongolia and Jilin Province have not experienced any disasters since the 2000s and 2010s.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D. and Z.C.; Methodology, J.D. and Z.C.; resources, Q.W.; data curation, Y.J. and J.L.; visualization, L.J. and J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.D. and Z.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2022YFD2300201); the China Meteorological Administration Northeast Cold Vortex Research Business Capability Enhancement Research Team, 2022; and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (No. LH2021D020). The main funders of the study were Jiang Lixia, the Heilongjiang Province Institute of Meteorological Science; Duan Juqi, National Climate Center; Chu Zheng, the Heilongjiang Province Institute of Meteorological Science.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to that high precision meteorological data are not suitable for public disclosure.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, D.L.; Maisa, R.; Bjorn, H.S. The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC; Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.H. The physical science basis. Contribution of working group to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Comput. Geom. 2013, 18, 616–617. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.H. Effects of Climate and Frost Change on Vegetation Greening Rate in the Greater Khingan Mountains. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters CRED. The Human Cost of Weather Related Disasters 1995–2015; The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.T.; Huang, C.F.; Chen, X.; Li, N. Comprehensive assessment of climate change-crop yield-economic impact in seven sub-regions of China. Clim. Chang. 2021, 17, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.J.; Zhao, J.; Cui, W.Q.; Li, M.Y.; Li, E.; Gong, X.Y.; Yang, X.G. Effects of changing normal and extreme climate states on maize meteorological yield in Northeast China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2023, 56, 1859–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.L.; Yin, S.Y.; Liu, H.H. Analysis of agrometeorological disasters facing extreme climate events in Hebei, Shandong, and Henan provinces. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tao, F.; Liu, X. Spatial pattern and decadal change of agro-meteorological disasters in the main wheat production area of China during 1991–2009. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W. Climate change characteristics and circulation anomaly causes of the first frost date in Ningxia based on ground temperature. Arid Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.X.; Liu, J. Long-term trends of aridity index and its sensitivity to climate factors in Northeast China: 1971–2008. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, A.Q.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, Y.X. Estimation of Climate Comfort in Eastern China in the Context of Climate Change. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2019, 55, 887–898. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, Q.Q. Cultivated Land Resources and Grain Production Potential in the Three Northeast Provinces. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 48, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.E.; Liu, Z.J.; Yang, W.R.; Zhu, G.X.; Shi, D.Y.; Yang, X.G. Climate Suitable Zones for Mechanical Kernel Harvesting of Middle-late Maturing Spring Maize in Northeast China under Future Climate Scenarios. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2023, 44, 649–663. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.C.; Liang, H.B.; Wei, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, X.J.; Li, F.; Wei, N.; Zhang, S.P.; Yuan, H.; Liu, S.F.; et al. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Crop Yields and Exploring Adaptation Strategies in Northeast China. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Parsons, D.; Mao, X.M. Exploring limiting factors for maize growth in Northeast China and potential coping strategies. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 41, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.R.; Yu, H.M.; Yao, J.Y.; Liu, H.N.; Sun, S. Frost hazard risk assessment of rice in Heilongjiang Province. J. Catastrophol. 2012, 27, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.S.; Liu, Y.S. Weather, Climate and Agriculture in Sanjiang Plain; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kukal, M.S.; Irmak, S.U.S. Agro-Climate in 20th Century: Growing Degree Days, First and Last Frost, Growing Season Length, and Impacts on Crop Yields. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, K.E.; Easterling, D.R.; Hubbard, K.; Redmond, K. Temporal variations in frost-free season in the United States: 1895–2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Q. Changes in agro-meteorological indicators in the contiguous United States: 1951–2000. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 78, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R. Recent changes in frost days and the frost-free season in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyader, J.; Baron, V.S.; Beauchemin, K.A. Effect of Harvesting Maize after Frost in Alberta (Canada) on Whole-Plant Yield, Nutritive Value, and Kernel Properties. Agronomy 2021, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, D.J.; McGinn, S.M.; Beauchemin, K.A. Climate change impacts on maize heat units for the Canadian Prairie provinces. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutforth, H.; O’Brien, E.G.; Tuchelt, J.; Rickwood, R. Long-term changes in the frost-free season on the Canadian prairies. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 84, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynard, T.B.; Tanner, J.W.; Duncan, W.G. Duration of the grain filling period and its relation to grain yield in maize, Zea mays L. Crop Sci. 1971, 11, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyader, J.; Baron, V.S.; Beauchemin, K.A. Maize forage yield and quality for silage in short growing season areas of the Canadian prairies. Agronomy 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, A.M.G.K.; Konnen, G.P. Trends in indices of daily temperature and precipitation extremes in Europe, 1946–1999. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3665–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.M.; Szyga-Pluta, K.; Bednorz, E. Occurrence and synoptic background of strong and very strong frost in spring and autumn in Central Europe. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wypych, A.; Ustrnul, Z.; Sulikowska, A.; Chmielewski, F.M.; Bochenek, B. Spatial and temporal variability of the frost-free season in Central Europe and its circulation background. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3340–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martin, A.; Paniagua, L.L.; Moral, F.J.; Rebollo, F.J.; Rozas, M.A. Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Frost Regime in the Iberian Peninsula in the Context of Climate Change (1975–2018). Sustainability 2021, 13, 8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervenkov, H.; Slavov, K. Inter-annual variability and trends of the frost-free season characteristics over Central and Southeast Europe in 1950–2019. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2022, 23, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidzgorska-Lencewicz, J.; Makosza, A.; Kozminski, C.; Michalska, B. Potential Risk of Frost in the Growing Season in Poland. Agriculture 2024, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Henderson, M.; Xu, M. Spatiotemporal change in China’s frost days and frost-free season, 1955–2000. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.F.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhao, J.C.; Li, S.; Chu, Q.Q. Spatiotemporal variation of high-temperature stress in different regions of China under climate change. Acta Agron. Sin. 2023, 49, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Liu, B.C.; Lei, T.J.; Yang, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Bai, W.; Han, R.; Bai, H.Q.; Chang, N.J. Monitoring and Mapping Winter Wheat Spring Frost Damage with MODIS Data and Statistical Data. Plants 2023, 12, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.L.; Yang, X.G.; Sun, S.; Gao, J.Q.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.T.; Liu, T. A spatiotemporal analysis of extreme agrometeorological events during selected growth stages of maize (Zea mays L.) from 1960 to 2017 in Northeast China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 143, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Guo, E.L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, R. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Meteorological Factors and Delayed Chilling Damage in Eastern Jilin Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhao, T.L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.X. Fine Resolution Simulation of a Cold Vortex in Northeast China by Using a Meso-Scale Meteorological Model. Int. Conf. Math. Model. Simul. Technol. Appl. 2017, 215, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, L.J.; Cui, X.P. Statistical Characteristics of the Northeast China Cold Vortex and Its Impact on Precipitation Distribution from 2000 to 2019. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 47, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.D.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, X.Q. QX/T 88-2008 Grade of Crop Frost Damage; Meteorological Industry Standard of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, R.P.; Yu, W.Y.; Feng, R.; Wu, J.W.; Zhang, Y.S. Construction and application of Rice Sterile-type Cold Damage Indexincold area: A case study of Liaoning Province. Prog. Geogr. 2017, 36, 438–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ljaz, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ljaz, N.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ljaz, A. Novel application of Google earth engine interpolation algorithm for the development of geotechnical soil maps: A case study of mega-district. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 18196–18216. [Google Scholar]
- Ljaz, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ljaz, N.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ljaz, A. Spatial mapping of geotechnical soil properties at multiple depths in Sialkot region, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 787. [Google Scholar]
- Ljaz, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ljaz, N.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ljaz, A.; Junaid, M.F. Geospatial modeling of heterogeneous geotechnical data using conventional and enhanced conception of modified Shepard method-based IDW algorithms: Application and appraisal. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 428. [Google Scholar]
- Ljaz, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ljaz, N.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ljaz, A. Development and optimization of geotechnical soil maps using various geostatistical and spatial interpolation techniques: A comprehensive study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Tao, S.Y.; Zhang, S.L. A study of excessively heavy rainfall in the Songhuajiang-Nenjiang River valley in 1998. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 25, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.X.; Sun, J.H. Study on cut-off low-pressure systems with floods over Northeast Asia. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2007, 96, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.X.; Lu, R.Y.; Wang, D.H. Seasonal climatology of cut-off lows and associated precipitation patterns over Northeast China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2010, 106, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Wen, M.; He, J.H.; Zhang, R.H. Characteristics of the northeast cold vortex at intraseasonal and timescale and its impact. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 959–973. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.W.; Bueh, C. Different types of cold vortex circulations over Northeast China and their weather impacts. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2015, 143, 845–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Yuan, D.Y.; Li, S.F. A case study on a severe convection weather process caused by northeast cold vortex. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2014, 30, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Su, A.F.; Liang, J.P.; Cui, L.M.; Liu, C. Warning characteristic and trigger mechanism of a local strong hailstorm in northern Henan Province. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2012, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, P.; Wang, L.L. The climate risk zones of frost damage to soybean in Northeast China. In Proceedings of the 6th Shenyang Rain and Snow Freezing (Frost) Disaster Forum; Chinese Meteorological Society: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, F.; Wen, Y.Q.; Shi, C.X.; Wu, J.; Shang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Meng, J.Y. Evolution of the Frost Hazards Based on Gridded Meteorological Data across China in 1961–2018. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 761–774. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Q.H.; Cai, R.S.; Guo, H.X. The climatic variations of temperature extremes in the Eastern of China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.G.; Hu, G.J.; Su, R.N.; Li, C.; Han, G.R. The climate anomaly under the background of climate warming caused the aggravation of early frost disaster in Chifeng City. Inn. Mong. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2017, 22, 68–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.H.; Zhi, R.; Shen, Q.; Yang, J.; Feng, G.L. Prediction of the distribution of the 2012 summer rainfall in China and analysis of the cause for Anomaly. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 38, 237–250. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Hu, L.; He, J.H.; Lou, X.F. Comparison of two rainstorm processes in Zhejiang province caused by northeast cold vortex. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2011, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).